Risk of Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis and Exposure to Particulate Matter from Vehicular Traffic: A Case-Control Study
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Methods
2.1. Study Population
2.2. Exposure Assessment
2.3. Statistical Analysis
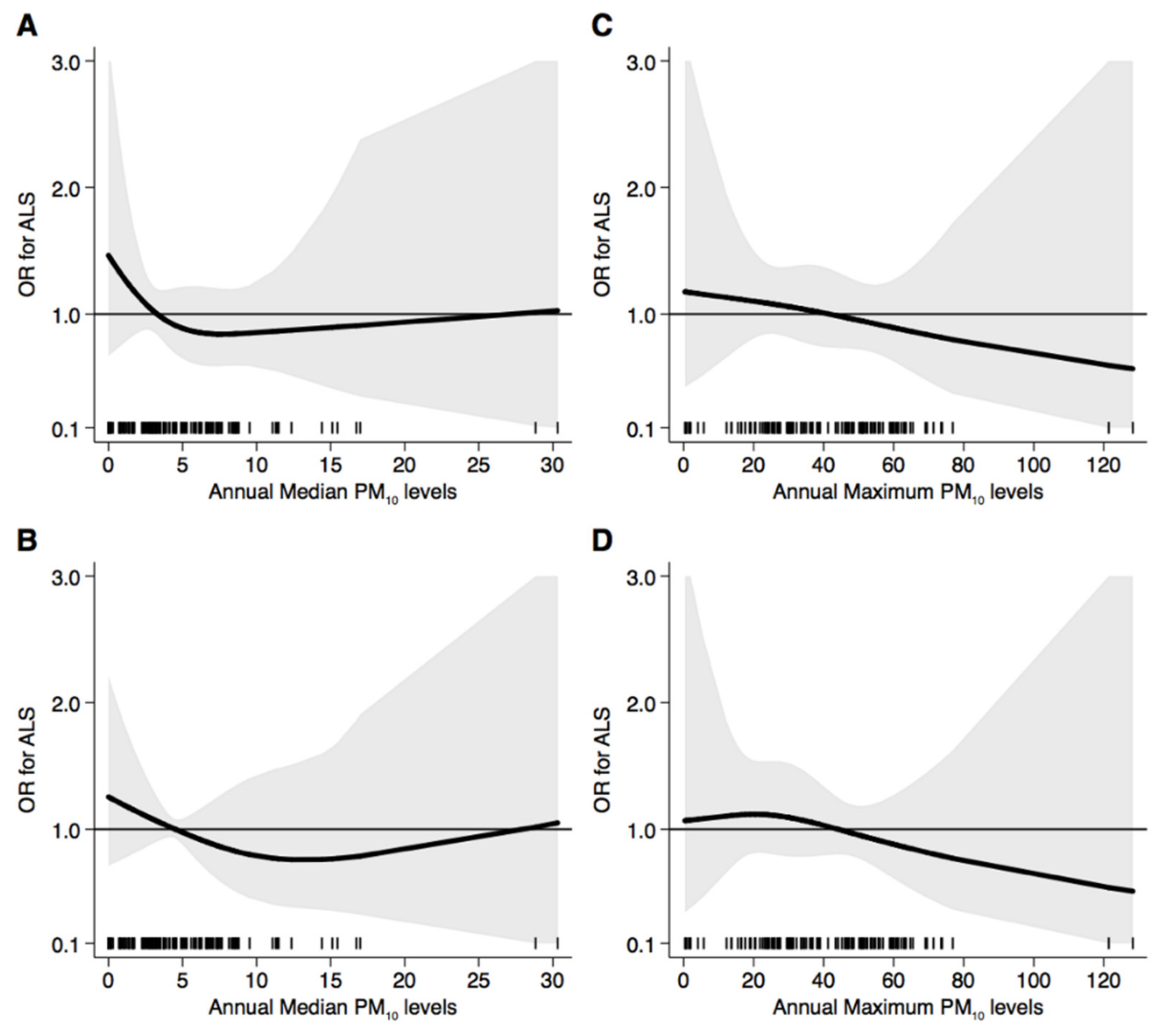
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hardiman, O.; Al-Chalabi, A.; Chiò, A.; Corr, E.M.; Logroscino, G.; Robberecht, W.; Shaw, P.J.; Simmons, Z.; van den Berg, L.H. Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Nat. Rev. Dis. Primers 2017, 3, 17071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Longinetti, E.; Fang, F. Epidemiology of amyotrophic lateral sclerosis: An update of recent literature. Curr. Opin. Neurol. 2019, 32, 771–776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tesauro, M.; Consonni, M.; Filippini, T.; Mazzini, L.; Pisano, F.; Chiò, A.; Esposito, A.; Vinceti, M. Incidence of amyotrophic lateral sclerosis in the province of Novara, Italy, and possible role of environmental pollution. Amyotroph. Lateral Scler. Frontotemporal Degener. 2017, 18, 284–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hardiman, O.; Al-Chalabi, A.; Brayne, C.; Beghi, E.; van den Berg, L.H.; Chiò, A.; Martin, S.; Logroscino, G.; Rooney, J. The changing picture of amyotrophic lateral sclerosis: Lessons from European registers. J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatry 2017, 88, 557–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mandrioli, J.; Biguzzi, S.; Guidi, C.; Venturini, E.; Sette, E.; Terlizzi, E.; Ravasio, A.; Casmiro, M.; Salvi, F.; Liguori, R.; et al. Epidemiology of amyotrophic lateral sclerosis in Emilia Romagna Region (Italy): A population based study. Amyotroph. Lateral Scler. Frontotemporal Degener. 2014, 15, 262–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dardiotis, E.; Siokas, V.; Sokratous, M.; Tsouris, Z.; Michalopoulou, A.; Andravizou, A.; Dastamani, M.; Ralli, S.; Vinceti, M.; Tsatsakis, A.; et al. Genetic polymorphisms in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis: Evidence for implication in detoxification pathways of environmental toxicants. Environ. Int. 2018, 116, 122–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Violi, F.; Solovyev, N.; Vinceti, M.; Mandrioli, J.; Lucio, M.; Michalke, B. The study of levels from redox-active elements in cerebrospinal fluid of amyotrophic lateral sclerosis patients carrying disease-related gene mutations shows potential copper dyshomeostasis. Metallomics 2020, 12, 668–681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maraldi, T.; Beretti, F.; Anselmi, L.; Franchin, C.; Arrigoni, G.; Braglia, L.; Mandrioli, J.; Vinceti, M.; Marmiroli, S. Influence of selenium on the emergence of neuro tubule defects in a neuron-like cell line and its implications for amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Neurotoxicology 2019, 75, 209–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Filippini, T.; Fiore, M.; Tesauro, M.; Malagoli, C.; Consonni, M.; Violi, F.; Arcolin, E.; Iacuzio, L.; Oliveri Conti, G.; Cristaldi, A.; et al. Clinical and lifestyle factors and risk of amyotrophic lateral sclerosis: A population-based case-control study. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Seals, R.M.; Kioumourtzoglou, M.A.; Hansen, J.; Gredal, O.; Weisskopf, M.G. Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis and the military: A population-based study in the Danish registries. Epidemiology 2016, 27, 188–193. [Google Scholar]
- Ingre, C.; Roos, P.M.; Piehl, F.; Kamel, F.; Fang, F. Risk factors for amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Clin. Epidemiol. 2015, 7, 181–193. [Google Scholar] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Vinceti, M.; Filippini, T.; Violi, F.; Rothman, K.J.; Costanzini, S.; Malagoli, C.; Wise, L.A.; Odone, A.; Signorelli, C.; Iacuzio, L.; et al. Pesticide exposure assessed through agricultural crop proximity and risk of amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Environ. Health 2017, 16, 91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fiore, M.; Parisio, R.; Filippini, T.; Mantione, V.; Platania, A.; Odone, A.; Signorelli, C.; Pietrini, V.; Mandrioli, J.; Teggi, S.; et al. Living near waterbodies as a proxy of cyanobacteria exposure and risk of amyotrophic lateral sclerosis: A population based case-control study. Environ. Res. 2020, 186, 109530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tesauro, M.; Bruschi, M.; Filippini, T.; D’Alfonso, S.; Mazzini, L.; Corrado, L.; Consonni, M.; Vinceti, M.; Fusi, P.; Urani, C. Metal(loid)s role in the pathogenesis of amyotrophic lateral sclerosis: Environmental, epidemiological, and genetic data. Environ. Res. 2021, 192, 110292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bozzoni, V.; Pansarasa, O.; Diamanti, L.; Nosari, G.; Cereda, C.; Ceroni, M. Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis and environmental factors. Funct. Neurol. 2016, 31, 7–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gunnarsson, L.G.; Bodin, L. Occupational exposures and neurodegenerative diseases-A systematic literature review and meta-analyses. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2019, 16, 337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Vinceti, M.; Filippini, T.; Malagoli, C.; Violi, F.; Mandrioli, J.; Consonni, D.; Rothman, K.J.; Wise, L.A. Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis incidence following exposure to inorganic selenium in drinking water: A long-term follow-up. Environ. Res. 2019, 179, 108742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vinceti, M.; Malagoli, C.; Fabbi, S.; Kheifets, L.; Violi, F.; Poli, M.; Caldara, S.; Sesti, D.; Violanti, S.; Zanichelli, P.; et al. Magnetic fields exposure from high-voltage power lines and risk of amyotrophic lateral sclerosis in two Italian populations. Amyotroph. Lateral Scler. Frontotemporal Degener. 2017, 18, 583–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marcilio, I.; Gouveia, N.; Pereira Filho, M.L.; Kheifets, L. Adult mortality from leukemia, brain cancer, amyotrophic lateral sclerosis and magnetic fields from power lines: A case-control study in Brazil. Rev. Bras. Epidemiol. 2011, 14, 580–588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gams, M.D.; Touré, K.; Sow, A.D.; Nyassinde, J.; Mapoure, N.Y.; Ndiaye, M.; Diop, G.A. Environmental and occupational risk factors of amyotrophic lateral sclerosis in Senegal. Afr. J. Neurol. Sci. 2018, 37, 32–37. [Google Scholar]
- Seltenrich, N. Another potential risk factor for ALS: Exposure to traffic-related air pollutants. Environ. Health Perspect. 2018, 126, 024004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Malek, A.M.; Barchowsky, A.; Bowser, R.; Heiman-Patterson, T.; Lacomis, D.; Rana, S.; Ada, Y.; Talbott, E.O. Exposure to hazardous air pollutants and the risk of amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Environ. Pollut. 2015, 197, 181–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seelen, M.; Toro Campos, R.A.; Veldink, J.H.; Visser, A.E.; Hoek, G.; Brunekreef, B.; van der Kooi, A.J.; de Visser, M.; Raaphorst, J.; van den Berg, L.H.; et al. Long-term air pollution exposure and amyotrophic lateral sclerosis in Netherlands: A population-based case-control study. Environ. Health Perspect. 2017, 125, 097023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Povedano, M.; Saez, M.; Martinez-Matos, J.A.; Barcelo, M.A. Spatial assessment of the association between long-term exposure to environmental factors and the occurrence of amyotrophic lateral sclerosis in Catalonia, Spain: A population-based nested case-control study. Neuroepidemiology 2018, 51, 33–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- EEA. Air Quality in Europe 2019; European Environment Agency Report No 10/2019; European Environment Agency: Copenhagen, Denmark, 2019; Available online: https://www.eea.europa.eu/publications/air-quality-in-europe-2019 (accessed on 6 January 2021).
- Vinceti, M.; Solovyev, N.; Mandrioli, J.; Crespi, C.M.; Bonvicini, F.; Arcolin, E.; Georgoulopoulou, E.; Michalke, B. Cerebrospinal fluid of newly diagnosed amyotrophic lateral sclerosis patients exhibits abnormal levels of selenium species including elevated selenite. Neurotoxicology 2013, 38, 25–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Vinceti, M.; Violi, F.; Tzatzarakis, M.; Mandrioli, J.; Malagoli, C.; Hatch, E.E.; Fini, N.; Fasano, A.; Rakitskii, V.N.; Kalantzi, O.I.; et al. Pesticides, polychlorinated biphenyls and polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in cerebrospinal fluid of amyotrophic lateral sclerosis patients: A case-control study. Environ. Res. 2017, 155, 261–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brooks, B.R.; Miller, R.G.; Swash, M.; Munsat, T.L.; World Federation of Neurology Research Group on Motor Neuron Diseases. El Escorial revisited: Revised criteria for the diagnosis of amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Amyotroph. Lateral Scler. Other Motor Neuron Disord. 2000, 1, 293–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Filippini, T.; Michalke, B.; Malagoli, C.; Grill, P.; Bottecchi, I.; Malavolti, M.; Vescovi, L.; Sieri, S.; Krogh, V.; Cherubini, A.; et al. Determinants of serum cadmium levels in a Northern Italy community: A cross-sectional study. Environ. Res. 2016, 150, 219–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vinceti, M.; Malagoli, C.; Malavolti, M.; Cherubini, A.; Maffeis, G.; Rodolfi, R.; Heck, J.E.; Astolfi, G.; Calzolari, E.; Nicolini, F. Does maternal exposure to benzene and PM10 during pregnancy increase the risk of congenital anomalies? A population-based case-control study. Sci. Total. Environ. 2016, 541, 444–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Modena Municipality, Statistical Yearbook 2015; Statistical Department of Modena Municipality: Modena, Italy, 2016; Available online: https://www.comune.modena.it/servizio-statistica/pubblicazioni/annuari (accessed on 6 January 2021).
- Benson, P.E. CALINE4-A dispersion model for predicting air pollution concentration near roadways; Department of Transportation, Ed.; Division of New Technology and Research: Sacramento, CA, USA, 1989. [Google Scholar]
- ISTAT. Data from the Italian National Institute of Statistic. 2020. Available online: https://www.istat.it/it/popolazione-e-famiglie (accessed on 6 January 2021).
- Vinceti, M.; Rothman, K.J.; Crespi, C.M.; Sterni, A.; Cherubini, A.; Guerra, L.; Maffeis, G.; Ferretti, E.; Fabbi, S.; Teggi, S.; et al. Leukemia risk in children exposed to benzene and PM10 from vehicular traffic: A case-control study in an Italian population. Eur. J. Epidemiol. 2012, 27, 781–790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Drufuca, A.; Battaiotto, S.; Bengo, I.; Rossi, D.; Torriani, L. Variante generale al Piano Territoriale di Coordinamento Provinciale. In Procedura di Simulazione Della Mobilità Delle Persone; Polinomia: Milano, Italy, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- WHO. WHO Air Quality Guidelines for Particulate Matter, Ozone, Nitrogen Dioxide and Sulfur Dioxide—Global Update 2005—Summary of Risk Assessment; WHO Press: Geneva, Switzerland, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Vinceti, M.; Chiari, A.; Eichmuller, M.; Rothman, K.J.; Filippini, T.; Malagoli, C.; Weuve, J.; Tondelli, M.; Zamboni, G.; Nichelli, P.F.; et al. A selenium species in cerebrospinal fluid predicts conversion to Alzheimer’s dementia in persons with mild cognitive impairment. Alzheimers Res. Ther. 2017, 9, 100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Costanzini, S.; Teggi, S.; Bigi, A.; Ghermandi, G.; Filippini, T.; Malagoli, C.; Nannini, R.; Vinceti, M. Atmospheric dispersion odelling and spatial analysis to evaluate population exposure to pesticides from farming processes. Atmosphere 2018, 9, 38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Teggi, S.; Costanzini, S.; Ghermandi, G.; Malagoli, C.; Vinceti, M. A GIS-based atmospheric dispersion model for pollutants emitted by complex source areas. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 610–611, 175–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- EEA. The European Environment State and Outlook 2020; European Environment Agency: Copenhagen, Denmark, 2020; Available online: https://www.eea.europa.eu/publications/soer-2020 (accessed on 6 January 2021).
- Emilia-Romagna Region. Piano Aria Integrato Regionale (PAIR 2020); DGR 949/2013; Giunta della Regione Emilia-Romagna: Bologna, Italy, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Filippini, T.; Hatch, E.E.; Rothman, K.J.; Heck, J.E.; Park, A.S.; Crippa, A.; Orsini, N.; Vinceti, M. Association between outdoor air pollution and childhood leukemia: A systematic review and dose-response meta-analysis. Environ. Health Perspect. 2019, 127, 46002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Filippini, T.; Rothman, K.J.; Cocchio, S.; Narne, E.; Mantoan, D.; Saia, M.; Goffi, A.; Ferrari, F.; Maffeis, G.; Orsini, N.; et al. Associations between mortality from COVID-19 in two Italian regions and outdoor air pollution as assessed through tropospheric nitrogen dioxide. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 761, 143355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marchini, T.; Zirlik, A.; Wolf, D. Pathogenic role of air pollution particulate matter in cardiometabolic disease: Evidence from mice and humans. Antioxid. Redox Signal. 2020, 33, 263–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- White, A.J.; Keller, J.P.; Zhao, S.; Carroll, R.; Kaufman, J.D.; Sandler, D.P. Air pollution, clustering of particulate matter components, and breast cancer in the Sister Study: A U.S.-wide cohort. Environ. Health Perspect. 2019, 127, 107002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasslof, H.; Molnar, P.; Andersson, E.M.; Spanne, M.; Gustafsson, S.; Stroh, E.; Engstrom, G.; Stockfelt, L. Long-term exposure to air pollution and atherosclerosis in the carotid arteries in the Malmo diet and cancer cohort. Environ. Res. 2020, 191, 110095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ranft, U.; Schikowski, T.; Sugiri, D.; Krutmann, J.; Kramer, U. Long-term exposure to traffic-related particulate matter impairs cognitive function in the elderly. Environ. Res. 2009, 109, 1004–1011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ritz, B.; Lee, P.C.; Hansen, J.; Lassen, C.F.; Ketzel, M.; Sorensen, M.; Raaschou-Nielsen, O. Traffic-related air pollution and Parkinson’s disease in Denmark: A case-control study. Environ. Health Perspect. 2016, 124, 351–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Noorimotlagh, Z.; Azizi, M.; Pan, H.F.; Mami, S.; Mirzaee, S.A. Association between air pollution and multiple sclerosis: A systematic review. Environ. Res. 2020, 110386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paul, K.C.; Haan, M.; Yu, Y.; Inoue, K.; Mayeda, E.R.; Dang, K.; Wu, J.; Jerrett, M.; Ritz, B. Traffic-related air pollution and Incident dementia: Direct and indirect pathways through metabolic dysfunction. J. Alzheimers Dis. 2020, 76, 1477–1491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Visser, A.E.; D’Ovidio, F.; Peters, S.; Vermeulen, R.C.; Beghi, E.; Chio, A.; Veldink, J.H.; Logroscino, G.; Hardiman, O.; van den Berg, L.H.; et al. Multicentre, population-based, case-control study of particulates, combustion products and amyotrophic lateral sclerosis risk. J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatry 2019, 90, 854–860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, R.M.; Schulte, P.A.; Bowman, J.D.; Walker, J.T.; Bondy, S.C.; Yost, M.G.; Touchstone, J.A.; Dosemeci, M. Potential occupational risks for neurodegenerative diseases. Am. J. Ind. Med. 2005, 48, 63–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pamphlett, R.; Rikard-Bell, A. Different occupations associated with amyotrophic lateral sclerosis: Is diesel exhaust the link? PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e80993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Weisskopf, M.G.; McCullough, M.L.; Morozova, N.; Calle, E.E.; Thun, M.J.; Ascherio, A. Prospective study of occupation and amyotrophic lateral sclerosis mortality. Am. J. Epidemiol. 2005, 162, 1146–1152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lucchini, R.G.; Dorman, D.C.; Elder, A.; Veronesi, B. Neurological impacts from inhalation of pollutants and the nose-brain connection. Neurotoxicology 2012, 33, 838–841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gerlofs-Nijland, M.E.; van Berlo, D.; Cassee, F.R.; Schins, R.P.; Wang, K.; Campbell, A. Effect of prolonged exposure to diesel engine exhaust on proinflammatory markers in different regions of the rat brain. Part. Fibre Toxicol. 2010, 7, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bai, K.J.; Chuang, K.J.; Chen, C.L.; Jhan, M.K.; Hsiao, T.C.; Cheng, T.J.; Chang, L.T.; Chang, T.Y.; Chuang, H.C. Microglial activation and inflammation caused by traffic-related particulate matter. Chem. Biol. Interact. 2019, 311, 108762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costa, L.G.; Cole, T.B.; Coburn, J.; Chang, Y.C.; Dao, K.; Roque, P.J. Neurotoxicity of traffic-related air pollution. Neurotoxicology 2017, 59, 133–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rodriguez, M.J.; Mahy, N. Neuron-microglia interactions in motor neuron degeneration. The inflammatory hypothesis in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis revisited. Curr. Med. Chem. 2016, 23, 4753–4772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ejaz, S.; Anwar, K.; Ashraf, M. MRI and neuropathological validations of the involvement of air pollutants in cortical selective neuronal loss. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. Int. 2014, 21, 3351–3362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vinceti, M.; Filippini, T.; Mandrioli, J.; Violi, F.; Bargellini, A.; Weuve, J.; Fini, N.; Grill, P.; Michalke, B. Lead, cadmium and mercury in cerebrospinal fluid and risk of amyotrophic lateral sclerosis: A case-control study. J. Trace. Elem. Med. Biol. 2017, 43, 121–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Filippini, T.; Tesauro, M.; Fiore, M.; Malagoli, C.; Consonni, M.; Violi, F.; Iacuzio, L.; Arcolin, E.; Oliveri Conti, G.; Cristaldi, A.; et al. Environmental and occupational risk factors of amyotrophic lateral sclerosis: A population-based case-control study. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 2882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Vinceti, M.; Guidetti, D.; Bergomi, M.; Caselgrandi, E.; Vivoli, R.; Olmi, M.; Rinaldi, L.; Rovesti, S.; Solime, F. Lead, cadmium, and selenium in the blood of patients with sporadic amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Ital. J. Neurol. Sci. 1997, 18, 87–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meng, E.; Mao, Y.; Yao, Q.; Han, X.; Li, X.; Zhang, K.; Jin, W. Population-based study of environmental/occupational lead exposure and amyotrophic lateral sclerosis: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Neurol. Sci. 2020, 41, 35–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Farace, C.; Fenu, G.; Lintas, S.; Oggiano, R.; Pisano, A.; Sabalic, A.; Solinas, G.; Bocca, B.; Forte, G.; Madeddu, R. Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis and lead: A systematic update. Neurotoxicology 2020, 81, 80–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oggiano, R.; Pisano, A.; Sabalic, A.; Farace, C.; Fenu, G.; Lintas, S.; Forte, G.; Bocca, B.; Madeddu, R. An overview on amyotrophic lateral sclerosis and cadmium. Neurol. Sci. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, J.; Noh, Y.; Kim, S.Y.; Sohn, J.; Noh, J.; Kim, W.; Cho, S.K.; Seo, H.; Seo, G.; Lee, S.K.; et al. Long-term ambient air pollution exposures and brain imaging markers in Korean adults: The Environmental Pollution-Induced Neurological EFfects (EPINEF) Study. Environ. Health Perspect. 2020, 128, 117006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Filippini, T.; Rothman, K.J.; Goffi, A.; Ferrari, F.; Maffeis, G.; Orsini, N.; Vinceti, M. Satellite-detected tropospheric nitrogen dioxide and spread of SARS-CoV-2 infection in Northern Italy. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 739, 140278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernetti, A.; De Lauretis, R.; Iarocci, G.; Lena, F.; Marra Campanale, R.; Taurino, E. Trasporto su strada. Inventatio nazionale delle emissioni e disaggregazione provinciale; Dipartimento Stato dell’Ambiente e Metrologia Ambientale, Ed.; Istituto Superiore per la Protezione e la Ricerca Ambientale (ISPRA): Roma, Italy, 2010. Available online: https://www.isprambiente.gov.it/contentfiles/00007500/7510-trasporto-strada-concopertina-xweb.pdf/ (accessed on 6 January 2021).
- Bernetti, A.; Caputo, A.; Colaiezzi, M.; Finocchiaro, G.; Iarocci, G. Annuario dei dati ambientali 2019. 4 Traporti; Dipartimento Stato dell’Ambiente e Metrologia Ambientale, Ed.; Istituto Superiore per la Protezione e la Ricerca Ambientale (ISPRA): Roma, Italy, 2020. Available online: https://www.isprambiente.gov.it/files2020/pubblicazioni/stato-ambiente/annuario-2020/4_Trasporti_Finale_2019.pdf (accessed on 6 January 2021).

| Characteristics | Cases | Controls | All Subjects |
|---|---|---|---|
| All subjects | 52 (100) | 80 (100) | 132 (100) |
| Sex | |||
| Men | 31 (59.6) | 39 (48.7) | 70 (53.0) |
| Women | 21 (40.4) | 41 (51.3) | 62 (47.0) |
| Age 1 | 58.2 (12.6) | 52.8 (15.4) | 54.9 (14.5) |
| <65 years | 35 (67.3) | 59 (73.7) | 94 (71.2) |
| ≥65 years | 17 (32.7) | 21 (26.3) | 38 (28.8) |
| Annual median PM10 levels 1 | 5.1 (5.0) | 5.3 (4.6) | 5.2 (4.8) |
| Annual maximum PM10 levels 1 | 37.2 (22.5) | 39.4 (21.3) | 38.6 (21.7) |
| Exposure | Cases/Controls | OR a | (95% CI) | OR b | (95% CI) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Annual median PM10 levels | |||||
| <5 µg/m3 | 30/45 | 1.00 | - | 1.00 | - |
| 5–10 µg/m3 | 17/28 | 0.91 | (0.43–1.95) | 0.87 | (0.39–1.96) |
| 10–20 µg/m3 | 4/6 | 1.00 | (0.26–3.85) | 0.94 | (0.24–13.70) |
| ≥20 µg/m3 | 1/1 | 1.50 | (0.09–24.92) | 0.87 | (0.05–15.01) |
| Annual maximum PM10 levels | |||||
| <10 µg/m3 | 4/8 | 1.00 | - | 1.00 | - |
| 10–20 µg/m3 | 6/4 | 3.00 | (0.52–17.16) | 4.27 | (0.69–26.51) |
| 20–50 µg/m3 | 28/40 | 1.40 | (0.38–5.10) | 1.49 | (0.39–5.75) |
| ≥50 µg/m3 | 14/28 | 1.00 | (0.26–3.90) | 1.16 | (0.28–4.82) |
| Exposure | Cases/Controls | OR a | (95% CI) | OR b | (95% CI) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Annual median PM10 levels | |||||
| <5 µg/m3 | 22/45 | 1.00 | - | 1.00 | - |
| 5–10 µg/m3 | 16/28 | 1.17 | (0.53–2.60) | 1.02 | (0.43–2.42) |
| 10–20 µg/m3 | 4/6 | 1.36 | (0.35–5.33) | 1.35 | (0.34–5.43) |
| ≥20 µg/m3 | 1/1 | 2.05 | (0.12–34.26) | 1.16 | (0.07–20.11) |
| Annual maximum PM10 levels | |||||
| <10 µg/m3 | 3/8 | 1.00 | - | 1.00 | - |
| 10–20 µg/m3 | 2/4 | 1.33 | (0.15–11.50) | 2.19 | (0.23–20.91) |
| 20–50 µg/m3 | 24/40 | 1.60 | (0.39–6.62) | 1.64 | (0.37–7.27) |
| ≥50 µg/m3 | 14/28 | 1.33 | (0.231–5.82) | 1.53 | (0.32–7.23) |
| Exposure Categories | Median Value (µg/m3) | Cases/ Controls | OR a | (95% CI) | OR b | (95% CI) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Annual median PM10 levels | ||||||
| T1 < 3.0 µg/m3 | 1.4 | 19/26 | 1.00 | - | 1.00 | - |
| T2 ≥ 3.0–<6.6 µg/m3 | 4.2 | 17/27 | 0.86 | (0.37–2.01) | 0.66 | (0.28–1.68) |
| T3 ≥ 6.6 µg/m3 | 8.4 | 16/27 | 0.81 | (0.34–1.91) | 0.73 | (0.30–1.79) |
| Annual maximum PM10 levels | ||||||
| T1 < 30.0 µg/m3 | 20.5 | 22/26 | 1.00 | - | 1.00 | - |
| T2 ≥ 30.0–<50.4 µg/m3 | 38.3 | 16/27 | 0.70 | (0.30–1.62) | 0.73 | (0.30–1.74) |
| T3 ≥ 50.4 µg/m3 | 59.5 | 14/27 | 0.61 | (0.26–1.45) | 0.65 | (0.26–1.58) |
| Exposure | Median Value (µg/m3) | Cases/ Controls | OR a | (95% CI) | OR b | (95% CI) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Annual median PM10 levels | ||||||
| T1 < 3.0 µg/m3 | 1.4 | 12/26 | 1.00 | - | 1.00 | - |
| T2 ≥ 3.0–<6.6 µg/m3 | 4.2 | 15/27 | 1.20 | (0.47–3.05) | 0.84 | (0.31–2.29) |
| T3 ≥ 6.6 µg/m3 | 8.4 | 16/27 | 1.28 | (0.51–3.23) | 1.07 | (0.41–2.83) |
| Annual maximum PM10 levels | ||||||
| T1 < 30.0 µg/m3 | 22.2 | 14/26 | 1.00 | - | 1.00 | - |
| T2 ≥ 30.0–<50.4 µg/m3 | 38.2 | 15/27 | 1.03 | (0.42–2.55) | 1.07 | (0.41–2.79) |
| T3 ≥ 50.4 µg/m3 | 59.5 | 14/27 | 0.96 | (0.39–2.41) | 1.04 | (0.40–2.73) |
| Exposure | Cases/ Controls | OR a | (95% CI) | OR b | (95% CI) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Annual median PM10 levels | |||||
| Q1–Q3 < 7.3 µg/m3 | 38/60 | 1.00 | - | 1.00 | - |
| Q4 ≥ 7.3 µg/m3 | 14/20 | 1.11 | (0.50–2.45) | 1.13 | (0.50–2.55) |
| Annual maximum PM10 levels | |||||
| Q1–Q3 < 55.0 µg/m3 | 45/60 | 1.00 | - | 1.00 | - |
| Q4 ≥ 55.0 µg/m3 | 7/20 | 0.47 | (0.18–1.20) | 0.45 | (0.17–1.17) |
| Exposure | Cases/ Controls | OR a | (95% CI) | OR b | (95% CI) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Annual median PM10 levels | |||||
| Q1–Q3 < 7.3 µg/m3 | 29/60 | 1.00 | - | 1.00 | - |
| Q4 ≥ 7.3 µg/m3 | 14/20 | 1.45 | (0.64–3.27) | 1.51 | (0.65–3.49) |
| Annual maximum PM10 levels | |||||
| Q1–Q3 < 55.0 µg/m3 | 36/60 | 1.00 | - | 1.00 | - |
| Q4 ≥ 55.0 µg/m3 | 7/20 | 0.58 | (0.22–1.52) | 0.56 | (0.21–1.49) |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Filippini, T.; Mandrioli, J.; Malagoli, C.; Costanzini, S.; Cherubini, A.; Maffeis, G.; Vinceti, M. Risk of Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis and Exposure to Particulate Matter from Vehicular Traffic: A Case-Control Study. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 973. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph18030973
Filippini T, Mandrioli J, Malagoli C, Costanzini S, Cherubini A, Maffeis G, Vinceti M. Risk of Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis and Exposure to Particulate Matter from Vehicular Traffic: A Case-Control Study. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health. 2021; 18(3):973. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph18030973
Chicago/Turabian StyleFilippini, Tommaso, Jessica Mandrioli, Carlotta Malagoli, Sofia Costanzini, Andrea Cherubini, Giuseppe Maffeis, and Marco Vinceti. 2021. "Risk of Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis and Exposure to Particulate Matter from Vehicular Traffic: A Case-Control Study" International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health 18, no. 3: 973. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph18030973
APA StyleFilippini, T., Mandrioli, J., Malagoli, C., Costanzini, S., Cherubini, A., Maffeis, G., & Vinceti, M. (2021). Risk of Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis and Exposure to Particulate Matter from Vehicular Traffic: A Case-Control Study. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 18(3), 973. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph18030973









