Neurological Sequelae in Patients with COVID-19: A Histopathological Perspective
Abstract
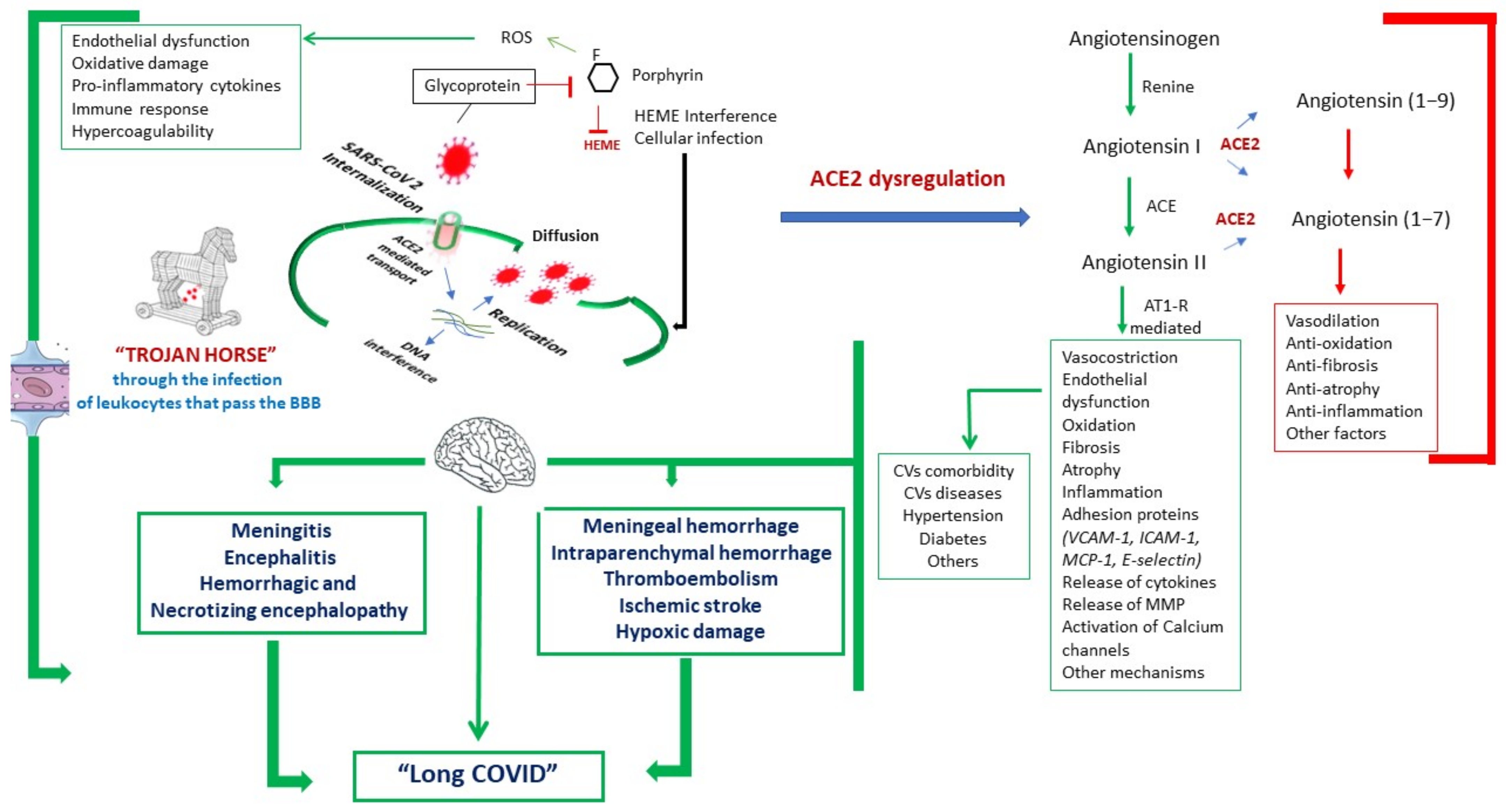
:1. Introduction
1.1. Current Neuropathogenic Hypotheses
1.2. Overview of the Main Neurological Manifestations
1.3. Autopsy, Brain Sampling, and Histopathological Assessment in COVID-19 Patients
2. Data Sources and Selection
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Main Findings
3.2. Comments and Outlooks
3.3. Limitations
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
| Study | P/CV/C | Other Organs |
|---|---|---|
| Tian et al., 2020 [80] | √ | |
| Danzi et al., 2020 [79] | √ | |
| Su et al., 2020 [81] | Kidney | |
| Peleg et al., 2020 [82] | Kidney | |
| Zhang et al., 2020 [83] | √ | |
| Yao et al., 2020 [84] | √ | Kidney, spleen, liver |
| Li et al., 2020 [85] | √ | |
| Rossi et al., 2020 [86] | Kidney | |
| Wichmann et al., 2020 [87] | √ | |
| Shanes et al., 2020 [88] | Placenta | |
| Hosier et al., 2020 [89] | Placenta | |
| Varga et al., 2020 [90] | √ | Kidney |
| Dolhnikoff et al., 2020 [91] | √ | |
| Magro et al., 2020 [92] | √ | Skin |
| Buja et al., 2020 [93] | √ | |
| Ducloyer et al., 2020 [94] | √ | |
| Lax et al., 2020 [95] | √ | |
| Suess and Hausmann 2020 [96] | √ | |
| Flikweert et al., 2020 [97] | √ | |
| Li et al., 2020 [98] | √ | |
| Sonzogni et al., 2020 [99] | √ | Liver |
| Carsana et al., 2020. [100] | √ | |
| Bradley et al., 2020 [101] | √ | Spleen |
| Schaller et al., 2020 [102] | √ | |
| Remmelink et al., 2020 [103] | √ | |
| Nunes Duarte-Neto et al., 2020 [104] | √ | |
| Prilutskiy et al., 2020 [105] | √ | |
| Xu et al., 2020 [21] | √ | |
| Konopka et al., 2020 [106] | √ | |
| Yan et al., 2020 [107] | √ | |
| Fitzek et al., 2020 [108] | √ | |
| Rev Esp Patol. 2020 [78] | √ | |
| Luo et al., 2020 [109] | √ | |
| Tian et al., 2020 [110] | √ | |
| Kuang et al., 2020 [111] | √ | |
| Pernazza et al., 2020 [112] | √ | |
| Fox et al., 2020 [113] | √ | |
| Barton et al., 2020 [114] | √ | |
| Brook et al., 2020 [115] | √ |
References
- Baig, A.M.; Khaleeq, A.; Ali, U.; Syeda, H. Evidence of the COVID-19 Virus Targeting the CNS: Tissue Distribution, Host-Virus Interaction, and Proposed Neurotropic Mechanisms. ACS Chem. Neurosci. 2020, 11, 995–998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Baig, A.M.; Sanders, E.C. Potential Neuroinvasive Pathways of SARS-CoV-2: Deciphering the Spectrum of Neurological Deficit Seen in Coronavirus Disease-2019 (COVID-19). J. Med. Virol. 2020, 92, 1845–1857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moriguchi, T.; Harii, N.; Goto, J.; Harada, D.; Sugawara, H.; Takamino, J.; Ueno, M.; Sakata, H.; Kondo, K.; Myose, N.; et al. A First Case of Meningitis/Encephalitis Associated with SARS-Coronavirus-2. Int. J. Infect. Dis. 2020, 94, 55–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bernard-Valnet, R.; Pizzarotti, B.; Anichini, A.; Demars, Y.; Russo, E.; Schmidhauser, M.; Cerutti-Sola, J.; Rossetti, A.O.; Du Pasquier, R. Two Patients with Acute Meningoencephalitis Concomitant with SARS-CoV-2 Infection. Eur. J. Neurol. 2020, 27, e43–e44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ye, M.; Ren, Y.; Lv, T. Encephalitis as a Clinical Manifestation of COVID-19. Brain. Behav. Immun. 2020, 88, 945–946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solomon, I.H.; Normandin, E.; Bhattacharyya, S.; Mukerji, S.S.; Keller, K.; Ali, A.S.; Adams, G.; Hornick, J.L.; Padera, R.F.; Sabeti, P. Neuropathological Features of Covid-19. N. Engl. J. Med. 2020, 383, 989–992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoffmann, M.; Schroeder, S.; Kleine-Weber, H.; Müller, M.A.; Drosten, C.; Pöhlmann, S. Nafamostat Mesylate Blocks Activation of SARS-CoV-2: New Treatment Option for COVID-19. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2020, 64, e00754-20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Beyerstedt, S.; Casaro, E.B.; Rangel, É.B. COVID-19: Angiotensin-Converting Enzyme 2 (ACE2) Expression and Tissue Susceptibility to SARS-CoV-2 Infection. Eur. J. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2021, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zubair, A.S.; McAlpine, L.S.; Gardin, T.; Farhadian, S.; Kuruvilla, D.E.; Spudich, S. Neuropathogenesis and Neurologic Manifestations of the Coronaviruses in the Age of Coronavirus Disease 2019: A Review. JAMA Neurol. 2020, 77, 1018–1027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Desforges, M.; Le Coupanec, A.; Brison, E.; Meessen-Pinard, M.; Talbot, P.J. Neuroinvasive and Neurotropic Human Respiratory Coronaviruses: Potential Neurovirulent Agents in Humans. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 2014, 807, 75–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gu, J.; Gong, E.; Zhang, B.; Zheng, J.; Gao, Z.; Zhong, Y.; Zou, W.; Zhan, J.; Wang, S.; Xie, Z.; et al. Multiple Organ Infection and the Pathogenesis of SARS. J. Exp. Med. 2005, 202, 415–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nicholls, J.M.; Butany, J.; Poon, L.L.M.; Chan, K.H.; Beh, S.L.; Poutanen, S.; Peiris, J.S.M.; Wong, M. Time Course and Cellular Localization of SARS-CoV Nucleoprotein and RNA in Lungs from Fatal Cases of SARS. PLoS Med. 2006, 3, e27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Spiegel, M.; Schneider, K.; Weber, F.; Weidmann, M.; Hufert, F.T. Interaction of Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome-Associated Coronavirus with Dendritic Cells. J. Gen. Virol. 2006, 87, 1953–1960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trojanowicz, B.; Ulrich, C.; Kohler, F.; Bode, V.; Seibert, E.; Fiedler, R.; Girndt, M. Monocytic Angiotensin-Converting Enzyme 2 Relates to Atherosclerosis in Patients with Chronic Kidney Disease. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. Off. Publ. Eur. Dial. Transpl. Assoc. Eur. Ren. Assoc. 2017, 32, 287–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sankowski, R.; Mader, S.; Valdés-Ferrer, S.I. Systemic Inflammation and the Brain: Novel Roles of Genetic, Molecular, and Environmental Cues as Drivers of Neurodegeneration. Front. Cell. Neurosci. 2015, 9, 28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fazzini, E.; Fleming, J.; Fahn, S. Cerebrospinal Fluid Antibodies to Coronavirus in Patients with Parkinson’s Disease. Mov. Disord. Off. J. Mov. Disord. Soc. 1992, 7, 153–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burks, J.S.; DeVald, B.L.; Jankovsky, L.D.; Gerdes, J.C. Two Coronaviruses Isolated from Central Nervous System Tissue of Two Multiple Sclerosis Patients. Science 1980, 209, 933–934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salmi, A.; Ziola, B.; Hovi, T.; Reunanen, M. Antibodies to Coronaviruses OC43 and 229E in Multiple Sclerosis Patients. Neurology 1982, 32, 292–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dessau, R.B.; Lisby, G.; Frederiksen, J.L. Coronaviruses in Spinal Fluid of Patients with Acute Monosymptomatic Optic Neuritis. Acta Neurol. Scand. 1999, 100, 88–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurtzke, J.F. Epidemiologic Evidence for Multiple Sclerosis as an Infection. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 1993, 6, 382–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Z.; Shi, L.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, J.; Huang, L.; Zhang, C.; Liu, S.; Zhao, P.; Liu, H.; Zhu, L.; et al. Pathological Findings of COVID-19 Associated with Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome. Lancet Respir. Med. 2020, 8, 420–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Payus, A.O.; Lin, C.L.S.; Noh, M.M.; Jeffree, M.S.; Ali, R.A. SARS-CoV-2 Infection of the Nervous System: A Review of the Literature on Neurological Involvement in Novel Coronavirus Disease-(COVID-19). Bosn. J. Basic Med. Sci. 2020, 20, 283–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pennisi, M.; Lanza, G.; Falzone, L.; Fisicaro, F.; Ferri, R.; Bella, R. SARS-CoV-2 and the Nervous System: From Clinical Features to Molecular Mechanisms. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 5475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Montemurro, N.; Perrini, P. Will COVID-19 Change Neurosurgical Clinical Practice? Br. J. Neurosurg. 2020, 1–2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chua, T.H.; Xu, Z.; King, N.K.K. Neurological Manifestations in COVID-19: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Brain Inj. 2020, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Carlo, D.T.; Montemurro, N.; Petrella, G.; Siciliano, G.; Ceravolo, R.; Perrini, P. Exploring the Clinical Association between Neurological Symptoms and COVID-19 Pandemic Outbreak: A Systematic Review of Current Literature. J. Neurol. 2020, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, S.; Leurent, B.; Sampson, E.L. Risk Factors for Incident Delirium among Older People in Acute Hospital Medical Units: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Age Ageing 2014, 43, 326–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Filatov, A.; Sharma, P.; Hindi, F.; Espinosa, P.S. Neurological Complications of Coronavirus Disease (COVID-19): Encephalopathy. Cureus 2020, 12, e7352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mao, L.; Jin, H.; Wang, M.; Hu, Y.; Chen, S.; He, Q.; Chang, J.; Hong, C.; Zhou, Y.; Wang, D.; et al. Neurologic Manifestations of Hospitalized Patients With Coronavirus Disease 2019 in Wuhan, China. JAMA Neurol. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Krishnan, V.; Leung, L.Y.; Caplan, L.R. A Neurologist’s Approach to Delirium: Diagnosis and Management of Toxic Metabolic Encephalopathies. Eur. J. Intern. Med. 2014, 25, 112–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poyiadji, N.; Shahin, G.; Noujaim, D.; Stone, M.; Patel, S.; Griffith, B. COVID-19-Associated Acute Hemorrhagic Necrotizing Encephalopathy: CT and MRI Features. Radiology 2020, 201187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ghosh, R.; Dubey, S.; Finsterer, J.; Chatterjee, S.; Ray, B.K. SARS-CoV-2-Associated Acute Hemorrhagic, Necrotizing Encephalitis (AHNE) Presenting with Cognitive Impairment in a 44-Year-Old Woman without Comorbidities: A Case Report. Am. J. Case Rep. 2020, 21, e925641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaya, Y.; Kara, S.; Akinci, C.; Kocaman, A.S. Transient Cortical Blindness in COVID-19 Pneumonia; a PRES-like Syndrome: Case Report. J. Neurol. Sci. 2020, 413, 116858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kakadia, B.; Ahmed, J.; Siegal, T.; Jovin, T.G.; Thon, J.M. Mild Encephalopathy with Reversible Splenium Lesion (MERS) in a Patient with COVID-19. J. Clin. Neurosci. Off. J. Neurosurg. Soc. Australas. 2020, 79, 272–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carod-Artal, F.J. Neurological Complications of Coronavirus and COVID-19. Rev. Neurol. 2020, 70, 311–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Li, M.; Wang, M.; Zhou, Y.; Chang, J.; Xian, Y.; Wang, D.; Mao, L.; Jin, H.; Hu, B. Acute Cerebrovascular Disease Following COVID-19: A Single Center, Retrospective, Observational Study. Stroke Vasc. Neurol. 2020, 5, 385–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oxley, T.J.; Mocco, J.; Majidi, S.; Kellner, C.P.; Shoirah, H.; Singh, I.P.; De Leacy, R.A.; Shigematsu, T.; Ladner, T.R.; Yaeger, K.A.; et al. Large-Vessel Stroke as a Presenting Feature of Covid-19 in the Young. N. Engl. J. Med. 2020, 382, e60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manousakis, G.; Jensen, M.B.; Chacon, M.R.; Sattin, J.A.; Levine, R.L. The Interface between Stroke and Infectious Disease: Infectious Diseases Leading to Stroke and Infections Complicating Stroke. Curr. Neurol. Neurosci. Rep. 2008, 9, 28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, Y.; Wang, H.; Shen, H.; Li, Z.; Geng, J.; Han, H.; Cai, J.; Li, X.; Kang, W.; Weng, D.; et al. The Clinical Pathology of Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome (SARS): A Report from China. J. Pathol. 2003, 200, 282–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giacomelli, A.; Pezzati, L.; Conti, F.; Bernacchia, D.; Siano, M.; Oreni, L.; Rusconi, S.; Gervasoni, C.; Ridolfo, A.L.; Rizzardini, G.; et al. Self-Reported Olfactory and Taste Disorders in SARS-CoV-2 Patients: A Cross-Sectional Study. Clin. Infect. Dis. Off. Publ. Infect. Dis. Soc. Am. 2020, 71, 889–890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Vaira, L.A.; Salzano, G.; Deiana, G.; De Riu, G. Anosmia and Ageusia: Common Findings in COVID-19 Patients. The Laryngoscope 2020, 130, 1787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lechien, J.R.; Chiesa-Estomba, C.M.; De Siati, D.R.; Horoi, M.; Le Bon, S.D.; Rodriguez, A.; Dequanter, D.; Blecic, S.; El Afia, F.; Distinguin, L.; et al. Olfactory and Gustatory Dysfunctions as a Clinical Presentation of Mild-to-Moderate Forms of the Coronavirus Disease (COVID-19): A Multicenter European Study. Eur. Arch. Oto-Rhino-Laryngol. 2020, 277, 2251–2261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hanley, B.; Lucas, S.B.; Youd, E.; Swift, B.; Osborn, M. Autopsy in Suspected COVID-19 Cases. J. Clin. Pathol. 2020, 73, 239–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Infection Prevention and Control for the Safe Management of a Dead Body in the Context of COVID-19: Interim Guidance. Available online: https://www.who.int/publications-detail-redirect/infection-prevention-and-control-for-the-safe-management-of-a-dead-body-in-the-context-of-covid-19-interim-guidance (accessed on 20 December 2020).
- CDC Collection and Submission of Postmortem Specimens from Deceased Persons with Confirmed or Suspected COVID-19. Postmortem Guidance. Available online: https://www.cdc.gov/coronavirus/2019-ncov/hcp/guidance-postmortem-specimens.html (accessed on 1 February 2021).
- Osborn, D.M. Autopsy Practice Relating to Possible Cases of COVID-19 (2019-NCov, Novel Coronavirus from China 2019/2020); The Royal College of Pathologists: London, UK, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Franca, R.A.; Ugga, L.; Guadagno, E.; Russo, D.; Del Basso De Caro, M. Neuroinvasive Potential of SARS-CoV2 with Neuroradiological and Neuropathological Findings: Is the Brain a Target or a Victim? APMIS Acta Pathol. Microbiol. Immunol. Scand. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shellhaas, R.A. Neurologists and COVID-19: A Note on Courage in a Time of Uncertainty. Neurology 2020, 94, 855–857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Montalvan, V.; Lee, J.; Bueso, T.; De Toledo, J.; Rivas, K. Neurological Manifestations of COVID-19 and Other Coronavirus Infections: A Systematic Review. Clin. Neurol. Neurosurg. 2020, 194, 105921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mansueto, G.; Niola, M.; Napoli, C. Can COVID 2019 Induce a Specific Cardiovascular Damage or It Exacerbates Pre-Existing Cardiovascular Diseases? Pathol. Res. Pract. 2020, 216, 153086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mansueto, G. COVID-19: Brief Check through the Pathologist’s Eye (Autopsy Archive). Pathol. Res. Pract. 2020, 216, 153195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Napoli, C.; Tritto, I.; Mansueto, G.; Coscioni, E.; Ambrosio, G. Immunosenescence Exacerbates the COVID-19. Arch. Gerontol. Geriatr. 2020, 90, 104174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Napoli, C.; Tritto, I.; Benincasa, G.; Mansueto, G.; Ambrosio, G. Cardiovascular Involvement during COVID-19 and Clinical Implications in Elderly Patients. A Review. Ann. Med. Surg. 2020, 57, 236–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mansueto, G.; Benincasa, G.; Capasso, E.; Graziano, V.; Russo, M.; Niola, M.; Napoli, C.; Buccelli, C. Autoptic Findings of Sudden Cardiac Death (SCD) in Patients with Arrhythmogenic Ventricular Cardiomiopathy (AVC) from Left Ventricle and Biventricular Involvement. Pathol. Res. Pract. 2020, 216, 153269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mansueto, G.; Costa, D.; Capasso, E.; Varavallo, F.; Brunitto, G.; Caserta, R.; Esposito, S.; Niola, M.; Sardu, C.; Marfella, R.; et al. The Dating of Thrombus Organization in Cases of Pulmonary Embolism: An Autopsy Study. BMC Cardiovasc. Disord. 2019, 19, 250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paternoster, M.; Capasso, E.; Di Lorenzo, P.; Mansueto, G. Fatal Exertional Rhabdomyolysis. Literature Review and Our Experience in Forensic Thanatology. Leg. Med. Tokyo Jpn. 2018, 35, 12–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Russo, C.V.; Saccà, F.; Paternoster, M.; Buonomo, A.R.; Gentile, I.; Scotto, R.; Brescia Morra, V.; Mansueto, G. Post-Mortem Diagnosis of Invasive Pulmonary Aspergillosis after Alemtuzumab Treatment for Multiple Sclerosis. Mult. Scler. Houndmills Basingstoke Engl. 2020, 26, 123–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mansueto, G.; Capasso, E.; Buccelli, C.; Niola, M. Pulmonary Eosinophilic Inflammatory Infiltration Post-Intensive Care in a Nearly Drowned Young Man with Papillary Fibroelastoma: A Rare Complication Discovered by Forensic Autopsy. Front. Med. 2018, 4, 253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Huang, C.; Wang, Y.; Li, X.; Ren, L.; Zhao, J.; Hu, Y.; Zhang, L.; Fan, G.; Xu, J.; Gu, X.; et al. Clinical Features of Patients Infected with 2019 Novel Coronavirus in Wuhan, China. Lancet Lond. Engl. 2020, 395, 497–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Vaduganathan, M.; Vardeny, O.; Michel, T.; McMurray, J.J.V.; Pfeffer, M.A.; Solomon, S.D. Renin-Angiotensin-Aldosterone System Inhibitors in Patients with Covid-19. N. Engl. J. Med. 2020, 382, 1653–1659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, A.B.; Verma, A. COVID-19 and Angiotensin-Converting Enzyme Inhibitors and Angiotensin Receptor Blockers: What Is the Evidence? JAMA 2020, 323, 1769–1770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madjid, M.; Safavi-Naeini, P.; Solomon, S.D.; Vardeny, O. Potential Effects of Coronaviruses on the Cardiovascular System: A Review. JAMA Cardiol. 2020, 5, 831–840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wenzhong, L.; Hualan, L. COVID-19:Attacks the 1-Beta Chain of Hemoglobin and Captures the Porphyrin to Inhibit Human Heme Metabolism. Am. Chem. Soc. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanberg, N.; Ashton, N.J.; Andersson, L.-M.; Yilmaz, A.; Lindh, M.; Nilsson, S.; Price, R.W.; Blennow, K.; Zetterberg, H.; Gisslén, M. Neurochemical Evidence of Astrocytic and Neuronal Injury Commonly Found in COVID-19. Neurology 2020, 95, e1754–e1759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsai, L.-K.; Hsieh, S.-T.; Chang, Y.-C. Neurological Manifestations in Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome. Acta Neurol. Taiwanica 2005, 14, 113–119. [Google Scholar]
- Román, G.C.; Spencer, P.S.; Reis, J.; Buguet, A.; Faris, M.E.A.; Katrak, S.M.; Láinez, M.; Medina, M.T.; Meshram, C.; Mizusawa, H.; et al. The Neurology of COVID-19 Revisited: A Proposal from the Environmental Neurology Specialty Group of the World Federation of Neurology to Implement International Neurological Registries. J. Neurol. Sci. 2020, 414, 116884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hung, E.C.W.; Chim, S.S.C.; Chan, P.K.S.; Tong, Y.K.; Ng, E.K.O.; Chiu, R.W.K.; Leung, C.-B.; Sung, J.J.Y.; Tam, J.S.; Lo, Y.M.D. Detection of SARS Coronavirus RNA in the Cerebrospinal Fluid of a Patient with Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome. Clin. Chem. 2003, 49, 2108–2109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Stoyanov, G.S.; Lyutfi, E.; Dzhenkov, D.L.; Petkova, L. Acute Necrotizing Encephalitis in Viral Respiratory Tract Infection: An Autopsy Case Report. Cureus 2020, 12, e8070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paniz-Mondolfi, A.; Bryce, C.; Grimes, Z.; Gordon, R.E.; Reidy, J.; Lednicky, J.; Sordillo, E.M.; Fowkes, M. Central Nervous System Involvement by Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus-2 (SARS-CoV-2). J. Med. Virol. 2020, 92, 699–702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Matschke, J.; Lütgehetmann, M.; Hagel, C.; Sperhake, J.P.; Schröder, A.S.; Edler, C.; Mushumba, H.; Fitzek, A.; Allweiss, L.; Dandri, M.; et al. Neuropathology of Patients with COVID-19 in Germany: A Post-Mortem Case Series. Lancet Neurol. 2020, 19, 919–929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Dalahmah, O.; Thakur, K.T.; Nordvig, A.S.; Prust, M.L.; Roth, W.; Lignelli, A.; Uhlemann, A.-C.; Miller, E.H.; Kunnath-Velayudhan, S.; Del Portillo, A.; et al. Neuronophagia and Microglial Nodules in a SARS-CoV-2 Patient with Cerebellar Hemorrhage. Acta Neuropathol. Commun. 2020, 8, 147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reichard, R.R.; Kashani, K.B.; Boire, N.A.; Constantopoulos, E.; Guo, Y.; Lucchinetti, C.F. Neuropathology of COVID-19: A Spectrum of Vascular and Acute Disseminated Encephalomyelitis (ADEM)-like Pathology. Acta Neuropathol. (Berl.) 2020, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bryce, C.; Grimes, Z.; Pujadas, E.; Ahuja, S.; Beasley, M.B.; Albrecht, R.; Hernandez, T.; Stock, A.; Zhao, Z.; Rasheed, M.A.; et al. Pathophysiology of SARS-CoV-2: Targeting of Endothelial Cells Renders a Complex Disease with Thrombotic Microangiopathy and Aberrant Immune Response. The Mount Sinai COVID-19 Autopsy Experience. medRxiv 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spence, J.D.; de Freitas, G.R.; Pettigrew, L.C.; Ay, H.; Liebeskind, D.S.; Kase, C.S.; Del Brutto, O.H.; Hankey, G.J.; Venketasubramanian, N. Mechanisms of Stroke in COVID-19. Cerebrovasc. Dis. Basel Switz. 2020, 49, 451–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koh, J.S.; De Silva, D.A.; Quek, A.M.L.; Chiew, H.J.; Tu, T.M.; Seet, C.Y.H.; Hoe, R.H.M.; Saini, M.; Hui, A.C.-F.; Angon, J.; et al. Neurology of COVID-19 in Singapore. J. Neurol. Sci. 2020, 418, 117118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Requena, M.; Olivé-Gadea, M.; Muchada, M.; García-Tornel, Á.; Deck, M.; Juega, J.; Boned, S.; Rodríguez-Villatoro, N.; Piñana, C.; Pagola, J.; et al. COVID-19 and Stroke: Incidence and Etiological Description in a High-Volume Center. J. Stroke Cerebrovasc. Dis. 2020, 29, 105225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abdelaziz, O.S.; Waffa, Z. Neuropathogenic Human Coronaviruses: A Review. Rev. Med. Virol. 2020, 30, e02118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- The First COVID-19 Autopsy in Spain Performed during the Early Stages of the Pandemic. Rev. Espanola Patol. 2020, 53, 182–187. [CrossRef]
- Danzi, G.B.; Loffi, M.; Galeazzi, G.; Gherbesi, E. Acute Pulmonary Embolism and COVID-19 Pneumonia: A Random Association? Eur. Heart J. 2020, 41, 1858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tian, S.; Xiong, Y.; Liu, H.; Niu, L.; Guo, J.; Liao, M.; Xiao, S.-Y. Pathological Study of the 2019 Novel Coronavirus Disease (COVID-19) through Postmortem Core Biopsies. Mod. Pathol. 2020, 33, 1007–1014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Su, H.; Yang, M.; Wan, C.; Yi, L.-X.; Tang, F.; Zhu, H.-Y.; Yi, F.; Yang, H.-C.; Fogo, A.B.; Nie, X.; et al. Renal Histopathological Analysis of 26 Postmortem Findings of Patients with COVID-19 in China. Kidney Int. 2020, 98, 219–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peleg, Y.; Kudose, S.; D’Agati, V.; Siddall, E.; Ahmad, S.; Kisselev, S.; Gharavi, A.; Canetta, P. Acute Kidney Injury Due to Collapsing Glomerulopathy Following COVID-19 Infection. Kidney Int. Rep. 2020, 5, 940–945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Zhou, P.; Wei, Y.; Yue, H.; Wang, Y.; Hu, M.; Zhang, S.; Cao, T.; Yang, C.; Li, M.; et al. Histopathologic Changes and SARS-CoV-2 Immunostaining in the Lung of a Patient With COVID-19. Ann. Intern. Med. 2020, 172, 629–632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yao, X.H.; Li, T.Y.; He, Z.C.; Ping, Y.F.; Liu, H.W.; Yu, S.C.; Mou, H.M.; Wang, L.H.; Zhang, H.R.; Fu, W.J.; et al. A pathological report of three COVID-19 cases by minimal invasive autopsies. Zhonghua Bing Li Xue Za Zhi 2020, 49, 411–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, G.; Fox, S.E.; Summa, B.; Wenk, C.; Akmatbekov, A.; Harbert, J.L.; Heide, R.S.V.; Brown, J.Q. Multiscale 3-Dimensional Pathology Findings of COVID-19 Diseased Lung Using High-Resolution Cleared Tissue Microscopy. bioRxiv 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rossi, G.M.; Delsante, M.; Pilato, F.P.; Gnetti, L.; Gabrielli, L.; Rossini, G.; Re, M.C.; Cenacchi, G.; Affanni, P.; Colucci, M.E.; et al. Kidney Biopsy Findings in a Critically Ill COVID-19 Patient With Dialysis-Dependent Acute Kidney Injury: A Case Against “SARS-CoV-2 Nephropathy. ” Kidney Int. Rep. 2020, 5, 1100–1105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wichmann, D.; Sperhake, J.-P.; Lütgehetmann, M.; Steurer, S.; Edler, C.; Heinemann, A.; Heinrich, F.; Mushumba, H.; Kniep, I.; Schröder, A.S.; et al. Autopsy Findings and Venous Thromboembolism in Patients With COVID-19. Ann. Intern. Med. 2020, 173(4). [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shanes, E.D.; Mithal, L.B.; Otero, S.; Azad, H.A.; Miller, E.S.; Goldstein, J.A. Placental Pathology in COVID-19. Am. J. Clin. Pathol. 2020, 154, 23–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hosier, H.; Farhadian, S.F.; Morotti, R.A.; Deshmukh, U.; Lu-Culligan, A.; Campbell, K.H.; Yasumoto, Y.; Vogels, C.B.; Casanovas-Massana, A.; Vijayakumar, P.; et al. SARS-CoV-2 Infection of the Placenta. J. Clin. Investig. 2020, 130, 4947–4953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Varga, Z.; Flammer, A.J.; Steiger, P.; Haberecker, M.; Andermatt, R.; Zinkernagel, A.S.; Mehra, M.R.; Schuepbach, R.A.; Ruschitzka, F.; Moch, H. Endothelial Cell Infection and Endotheliitis in COVID-19. Lancet Lond. Engl. 2020, 395, 1417–1418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dolhnikoff, M.; Duarte-Neto, A.N.; de Almeida Monteiro, R.A.; da Silva, L.F.F.; de Oliveira, E.P.; Saldiva, P.H.N.; Mauad, T.; Negri, E.M. Pathological Evidence of Pulmonary Thrombotic Phenomena in Severe COVID-19. J. Thromb. Haemost. JTH 2020, 18, 1517–1519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Magro, C.; Mulvey, J.J.; Berlin, D.; Nuovo, G.; Salvatore, S.; Harp, J.; Baxter-Stoltzfus, A.; Laurence, J. Complement Associated Microvascular Injury and Thrombosis in the Pathogenesis of Severe COVID-19 Infection: A Report of Five Cases. Transl. Res. 2020, 220, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buja, L.M.; Wolf, D.A.; Zhao, B.; Akkanti, B.; McDonald, M.; Lelenwa, L.; Reilly, N.; Ottaviani, G.; Elghetany, M.T.; Trujillo, D.O.; et al. The Emerging Spectrum of Cardiopulmonary Pathology of the Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19): Report of 3 Autopsies from Houston, Texas, and Review of Autopsy Findings from Other United States Cities. Cardiovasc. Pathol. 2020, 48, 107233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ducloyer, M.; Gaborit, B.; Toquet, C.; Castain, L.; Bal, A.; Arrigoni, P.P.; Lecomte, R.; Clement, R.; Sagan, C. Complete Post-Mortem Data in a Fatal Case of COVID-19: Clinical, Radiological and Pathological Correlations. Int. J. Legal Med. 2020, 134, 2209–2214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lax, S.F.; Skok, K.; Zechner, P.; Kessler, H.H.; Kaufmann, N.; Koelblinger, C.; Vander, K.; Bargfrieder, U.; Trauner, M. Pulmonary Arterial Thrombosis in COVID-19 With Fatal Outcome: Results From a Prospective, Single-Center, Clinicopathologic Case Series. Ann. Intern. Med. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suess, C.; Hausmann, R. Gross and Histopathological Pulmonary Findings in a COVID-19 Associated Death during Self-Isolation. Int. J. Legal Med. 2020, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Flikweert, A.W.; Grootenboers, M.J.J.H.; Yick, D.C.Y.; du Mée, A.W.F.; van der Meer, N.J.M.; Rettig, T.C.D.; Kant, M.K.M. Late Histopathologic Characteristics of Critically Ill COVID-19 Patients: Different Phenotypes without Evidence of Invasive Aspergillosis, a Case Series. J. Crit. Care 2020, 59, 149–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, S.; Jiang, L.; Li, X.; Lin, F.; Wang, Y.; Li, B.; Jiang, T.; An, W.; Liu, S.; Liu, H.; et al. Clinical and Pathological Investigation of Patients with Severe COVID-19. JCI Insight 2020, 5, e138070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sonzogni, A.; Previtali, G.; Seghezzi, M.; Grazia Alessio, M.; Gianatti, A.; Licini, L.; Morotti, D.; Zerbi, P.; Carsana, L.; Rossi, R.; et al. Liver Histopathology in Severe COVID 19 Respiratory Failure Is Suggestive of Vascular Alterations. Liver Int. 2020, 40, 2110–2116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carsana, L.; Sonzogni, A.; Nasr, A.; Rossi, R.S.; Pellegrinelli, A.; Zerbi, P.; Rech, R.; Colombo, R.; Antinori, S.; Corbellino, M.; et al. Pulmonary Post-Mortem Findings in a Series of COVID-19 Cases from Northern Italy: A Two-Centre Descriptive Study. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2020, 20, 1135–1140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bradley, B.T.; Maioli, H.; Johnston, R.; Chaudhry, I.; Fink, S.L.; Xu, H.; Najafian, B.; Deutsch, G.; Lacy, J.M.; Williams, T.; et al. Histopathology and Ultrastructural Findings of Fatal COVID-19 Infections in Washington State: A Case Series. Lancet Lond. Engl. 2020, 396, 320–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schaller, T.; Hirschbühl, K.; Burkhardt, K.; Braun, G.; Trepel, M.; Märkl, B.; Claus, R. Postmortem Examination of Patients With COVID-19. JAMA 2020, 323, 2518–2520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Remmelink, M.; De Mendonça, R.; D’Haene, N.; De Clercq, S.; Verocq, C.; Lebrun, L.; Lavis, P.; Racu, M.-L.; Trépant, A.-L.; Maris, C.; et al. Unspecific Post-Mortem Findings despite Multiorgan Viral Spread in COVID-19 Patients. Crit. Care Lond. Engl. 2020, 24, 495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duarte-Neto, A.N.; Monteiro, R.A.A.; da Silva, L.F.F.; Malheiros, D.M.A.C.; de Oliveira, E.P.; Theodoro-Filho, J.; Pinho, J.R.R.; Gomes-Gouvêa, M.S.; Salles, A.P.M.; de Oliveira, I.R.S.; et al. Pulmonary and Systemic Involvement in COVID-19 Patients Assessed with Ultrasound-Guided Minimally Invasive Autopsy. Histopathology 2020, 77, 186–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prilutskiy, A.; Kritselis, M.; Shevtsov, A.; Yambayev, I.; Vadlamudi, C.; Zhao, Q.; Kataria, Y.; Sarosiek, S.R.; Lerner, A.; Sloan, J.M.; et al. SARS-CoV-2 Infection-Associated Hemophagocytic Lymphohistiocytosis. Am. J. Clin. Pathol. 2020, 154, 466–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Konopka, K.E.; Wilson, A.; Myers, J.L. Postmortem Lung Findings in a Patient With Asthma and Coronavirus Disease 2019. Chest 2020, 158, e99–e101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, R.; Zhang, Y.; Li, Y.; Xia, L.; Guo, Y.; Zhou, Q. Structural Basis for the Recognition of SARS-CoV-2 by Full-Length Human ACE2. Science 2020, 367, 1444–1448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Fitzek, A.; Sperhake, J.; Edler, C.; Schröder, A.S.; Heinemann, A.; Heinrich, F.; Ron, A.; Mushumba, H.; Lütgehetmann, M.; Püschel, K. Evidence for Systematic Autopsies in COVID-19 Positive Deceased. Rechtsmed. Berl. Ger. 2020, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, W.-R.; Yu, H.; Gou, J.-Z.; Li, X.-X.; Sun, Y.; Li, J.-X.; He, J.-X.; Liu, L. Histopathologic Findings in the Explant Lungs of a Patient With COVID-19 Treated With Bilateral Orthotopic Lung Transplant. Transplantation 2020, 104, e329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tian, S.; Hu, W.; Niu, L.; Liu, H.; Xu, H.; Xiao, S.-Y. Pulmonary Pathology of Early-Phase 2019 Novel Coronavirus (COVID-19) Pneumonia in Two Patients With Lung Cancer. J. Thorac. Oncol. Off. Publ. Int. Assoc. Study Lung Cancer 2020, 15, 700–704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuang, D.; Xu, S.P.; Hu, Y.; Liu, C.; Duan, Y.Q.; Wang, G.P. [Pathological changes with novel coronavirus infection in lung cancer surgical specimen]. Zhonghua Bing Li Xue Za Zhi 2020, 49, 471–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pernazza, A.; Mancini, M.; Rullo, E.; Bassi, M.; De Giacomo, T.; Rocca, C.D.; d’Amati, G. Early Histologic Findings of Pulmonary SARS-CoV-2 Infection Detected in a Surgical Specimen. Virchows Arch. 2020, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fox, S.E.; Akmatbekov, A.; Harbert, J.L.; Li, G.; Brown, J.Q.; Heide, R.S.V. Pulmonary and Cardiac Pathology in African American Patients with COVID-19: An Autopsy Series from New Orleans. Lancet Respir. Med. 2020, 8, 681–686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barton, L.M.; Duval, E.J.; Stroberg, E.; Ghosh, S.; Mukhopadhyay, S. COVID-19 Autopsies, Oklahoma, USA. Am. J. Clin. Pathol. 2020, 153, 725–733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Brook, O.R.; Piper, K.G.; Mercado, N.B.; Gebre, M.S.; Barouch, D.H.; Busman-Sahay, K.; Starke, C.E.; Estes, J.D.; Martinot, A.J.; Wrijil, L.; et al. Feasibility and Safety of Ultrasound-Guided Minimally Invasive Autopsy in COVID-19 Patients. Abdom. Radiol. N. Y. 2020, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al-Sarraj, S.; Troakes, C.; Hanley, B.; Osborn, M.; Richardson, M.P.; Hotopf, M.; Bullmore, E.; Everall, I.P. Invited Review: The Spectrum of Neuropathology in COVID-19. Neuropathol. Appl. Neurobiol. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- González-Pinto, T.; Luna-Rodríguez, A.; Moreno-Estébanez, A.; Agirre-Beitia, G.; Rodríguez-Antigüedad, A.; Ruiz-Lopez, M. Emergency Room Neurology in Times of COVID-19: Malignant Ischaemic Stroke and SARS-CoV-2 Infection. Eur. J. Neurol. 2020, 27, e35–e36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, S.E.; Brealey, J.K. Visualization of Putative Coronavirus in Kidney. Kidney Int. 2020, 98, 231–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mukerji, S.S.; Solomon, I.H. What Can We Learn from Brain Autopsies in COVID-19? Neurosci. Lett. 2020, 742, 135528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parri, N.; Lenge, M.; Buonsenso, D. Coronavirus Infection in Pediatric Emergency Departments (CONFIDENCE) Research Group Children with Covid-19 in Pediatric Emergency Departments in Italy. N. Engl. J. Med. 2020, 383, 187–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsatsakis, A.; Calina, D.; Falzone, L.; Petrakis, D.; Mitrut, R.; Siokas, V.; Pennisi, M.; Lanza, G.; Libra, M.; Doukas, S.G.; et al. SARS-CoV-2 Pathophysiology and Its Clinical Implications: An Integrative Overview of the Pharmacotherapeutic Management of COVID-19. Food Chem. Toxicol. Int. J. Publ. Br. Ind. Biol. Res. Assoc. 2020, 146, 111769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carfì, A.; Bernabei, R.; Landi, F. Gemelli Against COVID-19 Post-Acute Care Study Group Persistent Symptoms in Patients After Acute COVID-19. JAMA 2020, 324, 603–605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tenforde, M.W. Symptom Duration and Risk Factors for Delayed Return to Usual Health Among Outpatients with COVID-19 in a Multistate Health Care Systems Network-United States, March–June 2020. MMWR Morb. Mortal. Wkly. Rep. 2020, 69, 993–998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mendelson, M.; Nel, J.; Blumberg, L.; Madhi, S.A.; Dryden, M.; Stevens, W.; Venter, F.W.D. Long-COVID: An Evolving Problem with an Extensive Impact. S. Afr. Med. J. 2020, 111, 10–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marshall, M. The Lasting Misery of Coronavirus Long-Haulers. Nature 2020, 585, 339–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wood, E.; Hall, K.H.; Tate, W. Role of Mitochondria, Oxidative Stress and the Response to Antioxidants in Myalgic Encephalomyelitis/Chronic Fatigue Syndrome: A Possible Approach to SARS-CoV-2 “Long-Haulers”? Chronic Dis. Transl. Med. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delgado-Roche, L.; Mesta, F. Oxidative Stress as Key Player in Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus (SARS-CoV) Infection. Arch. Med. Res. 2020, 51, 384–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mironova, G.D.; Belosludtseva, N.V.; Ananyan, M.A. Prospects for the Use of Regulators of Oxidative Stress in the Comprehensive Treatment of the Novel Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19) and Its Complications. Eur. Rev. Med. Pharmacol. Sci. 2020, 24, 8585–8591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Study [References] | n; Sex | Age (Years) | P/CV/C | RT-qPCR+ | CNS Involvement |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Stoyanov et al., 2020 [68] | 1; F | 77 | √ | √ | Acute necrotizing encephalitis |
| Al-Dalahmah et al., 2020 [71] | 1; M | 73 | √ | Neuronal damage Neuronophagy Perivascular lymphocytes Microglial reaction | |
| Paniz-Mondolfi et al., 2020 [69] | 1; M | 74 | √ | Cerebrospinal fluid negative No data about the detection of histological lesion | |
| Reichard et al., 2020 [72] | 1; M | 71 | Acute disseminated perivascular encephalomyelitis Hemorrhagic lesions Microinfarctions | ||
| Bryce et al., 2020 [73] | 67 (20 brains); 38 M | Median: 69.0 IQR: (34.0–94.0) | √ | Disseminated micro thrombosis Ischemic infarcts Hemorrhage | |
| Solomon et al., 2020 [6] | 18; 14 M | Median: 62.0 IQR: (53.0–75.0) | Acute cerebral and cerebellar hypoxia-related lesions Neuronal loss within the cerebral cortex, hippocampus, and cerebellar Purkinje cell layer Perivascular lymphocytes Focal leptomeningeal inflammation | ||
| Matschke et al., 2020 [70] | 43; 27 M | Median: 76.0 IQR: (70.0–86.0) | √ | Ischaemic lesions Astrocytosis Microglia activation Cytotoxic T lymphocytes at the brainstem, cerebellum, basal ganglia, and olfactory bulb |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Fisicaro, F.; Di Napoli, M.; Liberto, A.; Fanella, M.; Di Stasio, F.; Pennisi, M.; Bella, R.; Lanza, G.; Mansueto, G. Neurological Sequelae in Patients with COVID-19: A Histopathological Perspective. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 1415. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph18041415
Fisicaro F, Di Napoli M, Liberto A, Fanella M, Di Stasio F, Pennisi M, Bella R, Lanza G, Mansueto G. Neurological Sequelae in Patients with COVID-19: A Histopathological Perspective. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health. 2021; 18(4):1415. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph18041415
Chicago/Turabian StyleFisicaro, Francesco, Mario Di Napoli, Aldo Liberto, Martina Fanella, Flavio Di Stasio, Manuela Pennisi, Rita Bella, Giuseppe Lanza, and Gelsomina Mansueto. 2021. "Neurological Sequelae in Patients with COVID-19: A Histopathological Perspective" International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health 18, no. 4: 1415. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph18041415
APA StyleFisicaro, F., Di Napoli, M., Liberto, A., Fanella, M., Di Stasio, F., Pennisi, M., Bella, R., Lanza, G., & Mansueto, G. (2021). Neurological Sequelae in Patients with COVID-19: A Histopathological Perspective. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 18(4), 1415. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph18041415








