The Impacts of Illegal Toxic Waste Dumping on Children’s Health: A Review and Case Study from Pasir Gudang, Malaysia
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methods
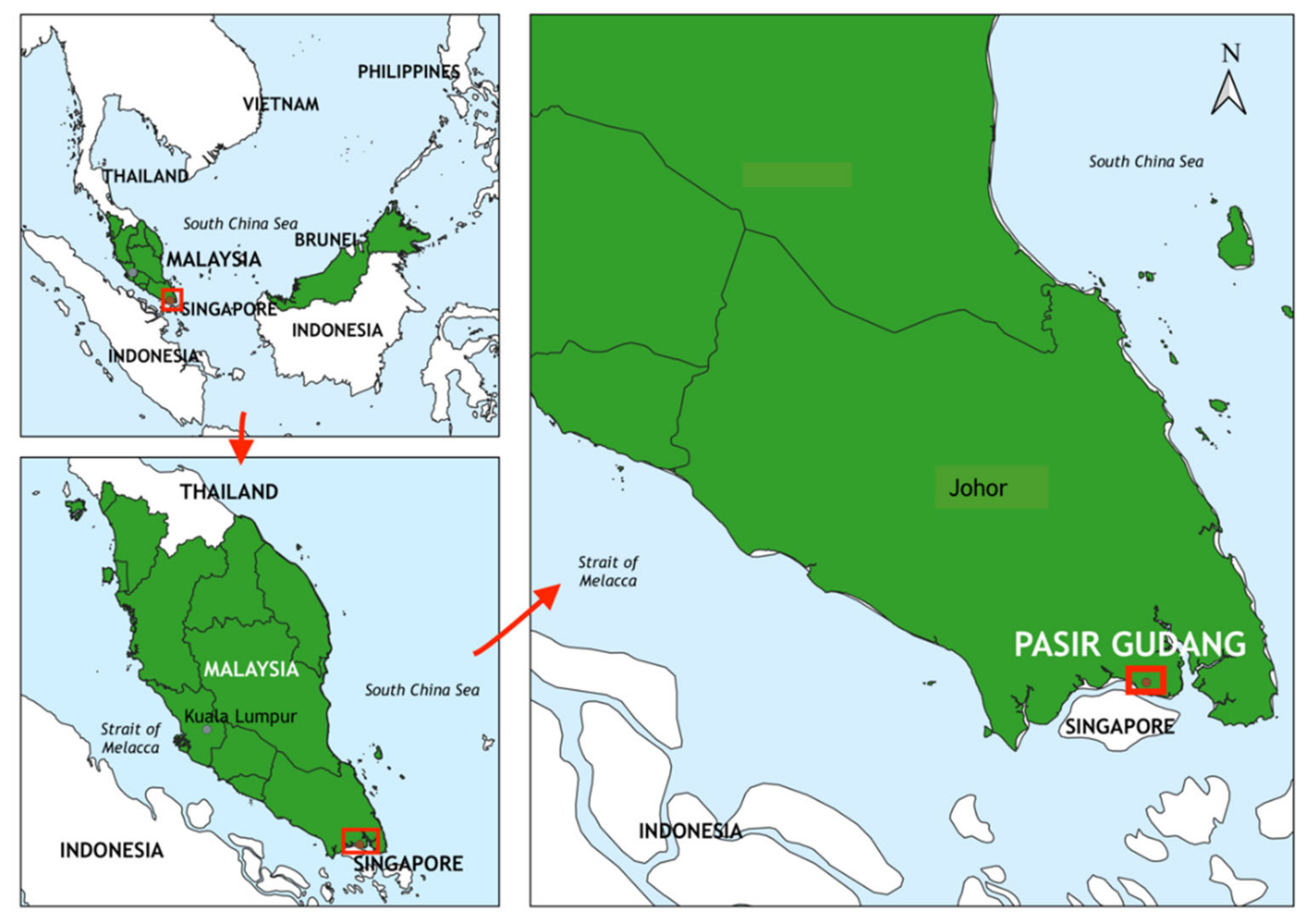
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Data Source
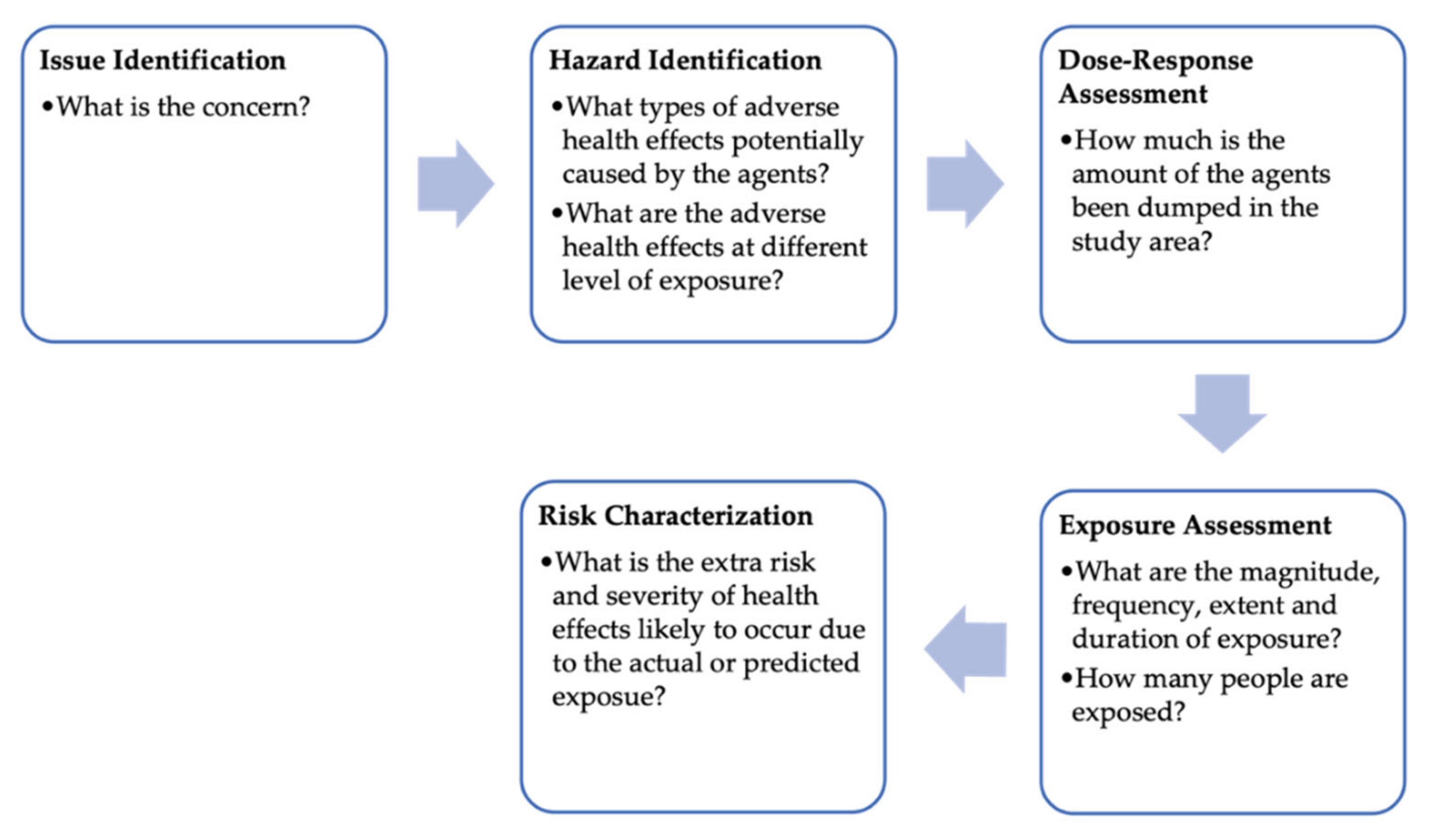
2.3. Health Risk Assessment
- exposed population
- exposure pathways
- source of exposure
- time of exposure
- number of people affected
2.4. Wireless Information System for Emergency Responders (WISER) Protective Distance and Hybrid Single-Particle Lagrangian Integrated Trajectory (HYSPLIT) Backward Trajectory
3. Results
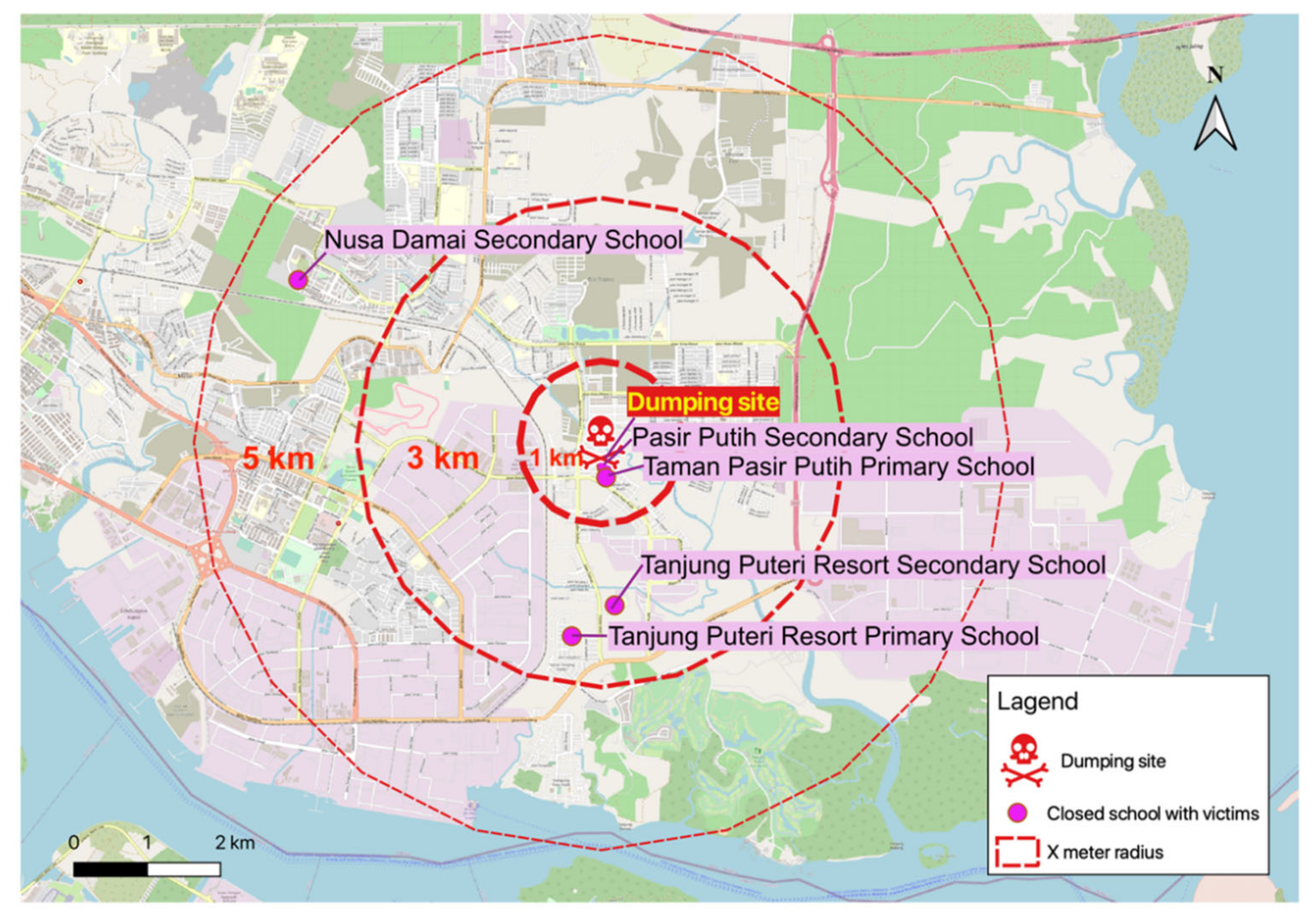
3.1. Case Study
3.1.1. First Wave
3.1.2. Second Wave
3.1.3. Response and Mitigation
3.2. Health Risk Assessment Results
3.2.1. Issue Identification
3.2.2. Hazard Identification and Dose–Response Assessment
3.2.3. Environmental Exposure
3.2.4. Risk Characterization
3.2.5. Environmental Fate
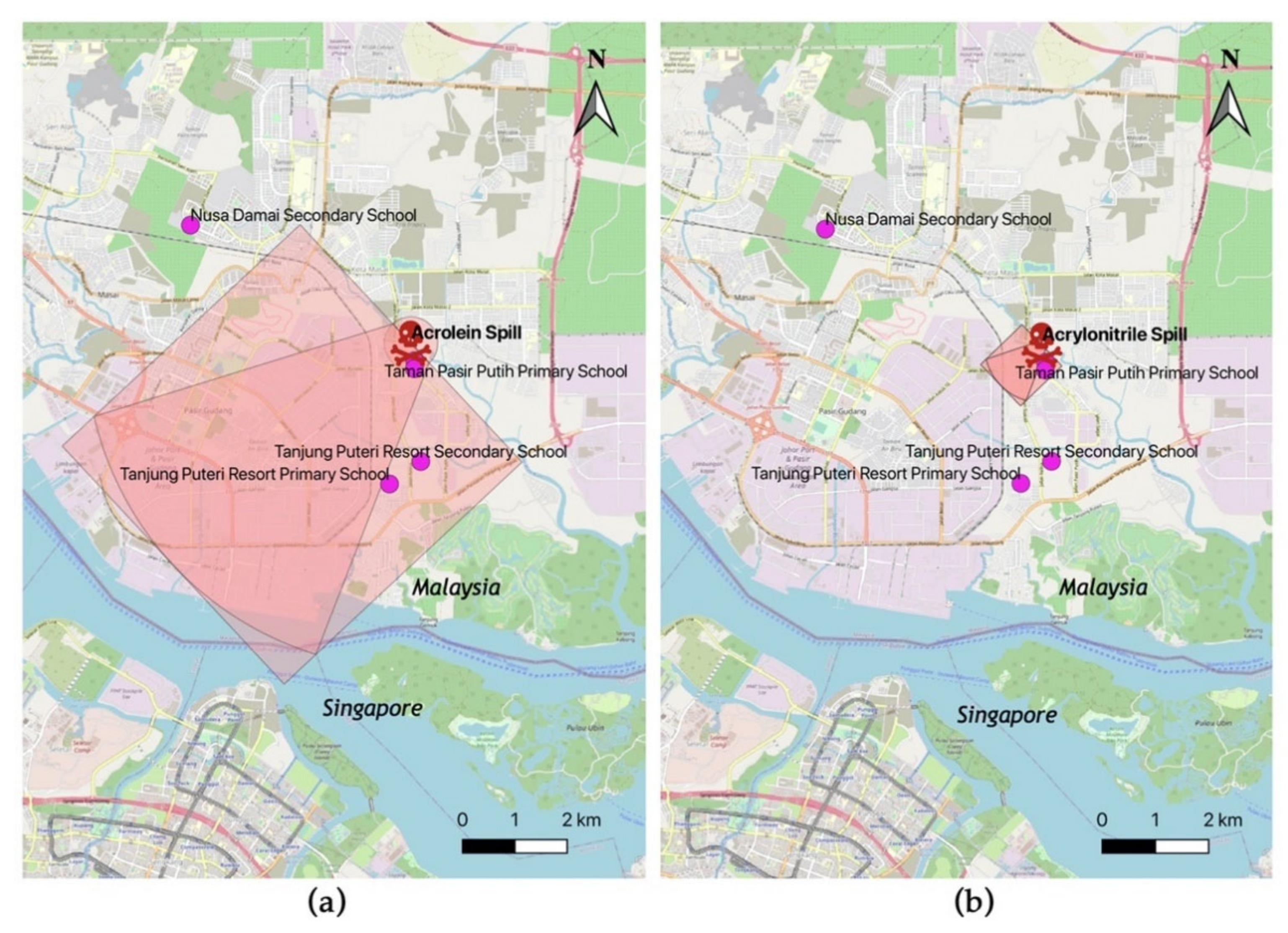
3.3. WISER Protective Distance and Backward Wind Trajectories
4. Discussion
4.1. Respiratory Diseases
4.2. Cancer
4.3. Mental Health
4.4. Limitations
4.5. Policy Implication
4.6. Recommendations for Future Work
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Duan, H.; Huang, Q.; Wang, Q.; Zhou, B.; Li, J. Hazardous waste generation and management in China: A review. J. Hazard. Mater. 2008, 158, 221–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haq, I.; Chakrabarti, S.P. Hazardous waste management in developing countries (India): A case study. Int. J. Environ. Stud. 1997, 53, 215–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferronato, N.; Torretta, V. Waste Mismanagement in Developing Countries: A Review of Global Issues. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2019, 16, 1060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Fadel, M.; Zeinati, M.; El-Jisr, K.; Jamali, D. Industrial-waste management in developing countries: The case of Lebanon. J. Environ. Manag. 2001, 61, 281–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anandalingam, G.; Westfall, M. Hazardous Waste Generation and Disposal: Options for Developing Countries. Nat. Resour. Forum 1987, 11, 37–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Begum, R.A.; Siwar, C.; Pereira, J.J.; Jaafar, A.H. Implementation of waste management and minimisation in the construction industry of Malaysia. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2007, 51, 190–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ziraba, A.K.; Haregu, T.N.; Mberu, B. A review and framework for understanding the potential impact of poor solid waste management on health in developing countries. Arch. Public Health 2016, 74, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nnorom, I.; Osibanjo, O. Overview of electronic waste (e-waste) management practices and legislations, and their poor applications in the developing countries. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2008, 52, 843–858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fazzo, L.; Minichilli, F.; Santoro, M.; Ceccarini, A.; Della Seta, M.; Bianchi, F.; Comba, P.; Martuzzi, M. Hazardous waste and health impact: A systematic review of the scientific literature. Environ. Health 2017, 16, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karthikeyan, L.; Suresh, V.M.; Krishnan, V.; Tudor, T.; Varshini, V. The Management of Hazardous Solid Waste in India: An Overview. Environments 2018, 5, 103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Xu, J.; Li, B. Analysis of Development of Hazardous Waste Disposal Technology in China. In Proceedings of the IOP Conference Series: Earth and Environmental Science; IOP Publishing: Bristol, UK, 2018; Volume 178, p. 012027. [Google Scholar]
- Ikau, R.; Joseph, C.; Tawie, R. Factors Influencing Waste Generation in the Construction Industry in Malaysia. Procedia-Soc. Behav. Sci. 2016, 234, 11–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sari, N.M.; Bin Mokhtar, M. Hazardous Waste Management in Malaysia: The Needs of Environmental Forensic. In From Sources to Solution; Springer International Publishing: Berlin, Germnay, 2013; pp. 61–66. [Google Scholar]
- Ishak, M.B. The Law of Industrial Waste Management in Malaysia. Available online: https://www.witpress.com/elibrary/wit-transactions-on-ecology-and-the-environment/56/1098 (accessed on 16 February 2021).
- Federal Subsidiary Legislation. Environmental Quality (Scheduled Wastes) Regulations 2005, PU(A) 294/2005. In Environmental Quality Act 1974(Act 127); International Law Book Services: Petaling Jaya, Malaysia, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Noor Artika, H.; Yusof, M.Z.; Nor Faiza, M.T. An Overview of Scheduled Wastes Management in Malaysia. J. Wastes Biomass-Manag. 2019, 1, 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alam, K. Scheduled Waste Management. Available online: https://www.cenviro.com/core-business/scheduled-waste-management/kualiti-alam-sdn-bhd/ (accessed on 17 February 2021).
- Rashid, Z.A.; Alias, A.B.; Aris, M.J.; El Harbawi, M.; Rahman, N.A.; Som, A.M. Hazardous waste management: Current status and future strategies in Malaysia. Int. J. Environ. Eng. 2010, 2, 139–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zainun, N.Y.; Rahman, I.A.; Rothman, R.A. Mapping of Construction Waste Illegal Dumping Using Geographical Information System (GIS). In Proceedings of the IOP Conference Series: Materials Science and Engineering; IOP Publishing: Bristol, UK, 2016; Volume 160, p. 012049. [Google Scholar]
- Khoo, N.K.; Hussin, H.; Abdullah, N. Occupational Safety and Health (O.S.H) Towards Green Environment Practices at Malaysia Small and Medium Manufacturing Sector; Science Publishing Corporation: Ras Al-Khaimah, United Arab Emirates, 2019; Volume 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johor Firm Used Fake Papers to Import Sludge. Available online: https://www.thestar.com.my/news/nation/2004/06/09/johor-firm-used-fake-papers-to-import-sludge (accessed on 12 April 2020).
- Tan, M.; Sim, L.L. 300 Tonnes of Toxic Waste Emitting Ammonia Fumes. Available online: https://www.thestar.com.my/news/nation/2006/01/12/300-tonnes-of-toxic-waste-emitting-ammonia-fumes (accessed on 12 April 2020).
- Haidar, R.T.; Ibrahim, M.F.; Mohd Aris, N.; Selvaraji, L.; Rusli, N. The Use of “WISER” Smartphone Application in Aiding a Chemical Disaster Management: Sungai Kim Kim Experience. Available online: http://www.e-mjm.org/2019/v74s2/pst-191-192.pdf (accessed on 29 January 2021).
- Salvaraji, L.; Toha, H.R.; Mohd Aris, N.; Ayob, Q.A.; Nordin, A.; Abdul Latif, N.; Rosli, L.; Mahjom, M.; Kassim, N.; Che Mat Din, S.N.A.; et al. Application of Occupational Health Surveillance Program among Responder’s during Chemical Incident at Pasir Gudang, Johor. Available online: http://mymedr.afpm.org.my/publications/84161 (accessed on 29 January 2021).
- Chinnayah, T.; Abdul Aziz, S.; Che Mat Din, S.N.; Mahdan, N.B.; Rosli, N.; Ibrahim, M.F.; Khida, N.; Othman, N.E.; Harun, R.; Ahmad, S. Largest Acute Chemical Incident in Malaysia, March 2019: Opportunity to Assess the Preparedness and Re-sponse Capacity. Available online: http://www.e-mjm.org/2019/v74s2/fp-39-40.pdf (accessed on 25 November 2020).
- Yap, C.K.; Peng, S.H.T.; Leow, C.S. Contamination in Pasir Gudang Area, Peninsular Malaysia: What can we learn from Kim Kim River chemical waste contamination? J. Humanit. Educ. Dev. 2019, 1, 82–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arnold, S.M.; Angerer, J.; Boogaard, P.J.; Hughes, M.F.; O’Lone, R.B.; Robison, S.H.; Schnatter, A.R. The use of biomonitoring data in exposure and human health risk assessment: Benzene case study. Crit. Rev. Toxicol. 2013, 43, 119–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Black, J.C.; Welday, J.N.; Buckley, B.; Ferguson, A.; Gurian, P.L.; Mena, K.D.; Yang, I.; McCandlish, E.; Solo-Gabriele, H.M. Risk Assessment for Children Exposed to Beach Sands Impacted by Oil Spill Chemicals. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2016, 13, 853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morakinyo, O.M.; Mokgobu, M.I.; Mukhola, M.S.; Engelbrecht, J.C. Health risk assessment of exposure to ambient concentrations of benzene, toluene and xylene in Pretoria West, South Africa. Afr. J. Sci. Technol. Innov. Dev. 2017, 9, 489–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wood, M.H.; Fabbri, L. Challenges and opportunities for assessing global progress in reducing chemical accident risks. Prog. Disaster Sci. 2019, 4, 100044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwab, K. The Global Competitiveness Report 2019. Available online: http://www3.weforum.org/docs/WEF_TheGlobalCompetitivenessReport2019.pdf (accessed on 10 April 2020).
- Jain, A.; Borongan, G.; Kashyap, P.; Thawn, N.S.; Honda, S.; Memon, M. Summary Report: Waste Management in ASEAN Countries. Available online: https://www.unep.org/resources/report/waste-management-asean-countries-summary-report (accessed on 10 April 2020).
- Aja, O.C.; Al-Kayiem, H.H.; Zewge, M.G.; Joo, M.G.Z.A.M.S. Overview of Hazardous Waste Management Status in Malaysia. In Management of Hazardous Wastes; IntechOpen: London, UK, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Abdullah, J.; Ahmad, Z.; Shah, R.N.H.R.A.; Anor, N. Port City Development and Quality of Life in Pasir Gudang Port, Johor, Malaysia. Procedia -Soc. Behav. Sci. 2012, 35, 556–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MPPG. Official Portal of Pasir Gudang Municipal Council (MPPG). Available online: http://www.mppg.gov.my/en (accessed on 11 April 2020).
- Teh, B.T.; Ho, C.S.; Matsuoka, Y.; Chau, L.W.; Gomi, K. Determinant factors of industrial symbiosis: Greening Pasir Gudang industrial park. In Proceedings of the IOP Conference Series: Earth and Environmental Science; IOP Publishing: Bristol, UK, 2014; Volume 18, p. 12162. [Google Scholar]
- Emran, N.; Zaki, B. Impact of Service Quality of Land Transportation on Customer Satisfaction at Johor Port Logistics. J. Public Value Adm. Insights 2018, 1, 7–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarmldi, M.R.; Hussain, M.A.; Ramli, W.; Daud, W. Overview Petrochemical Based Industries in Malaysia. ASEAN J. Chem. Eng. 2001, 1, 7–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koh, H.-L.; Lim, P.-E.; Midun, Z. Management and control of pollution in Inner Johore Strait. Environ. Monit. Assess. 1991, 19, 349–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Keshavarzifard, M.; Zakaria, M.P.; Keshavarzifard, S.; Sharifi, R. Distributions, Composition Patterns, Sources and Potential Toxicity of Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons (PAHs) Pollution in Surface Sediments from the Kim Kim River and Segget River, Peninsula Malaysia. Available online: http://www.pertanika.upm.edu.my/ (accessed on 11 April 2020).
- Alkhadher, S.A.A.; Zakaria, M.P.; Yusoff, F.M.; Kannan, N.; Suratman, S.; Magam, S.M.; Masood, N.; Keshavarzifard, M.; Vaezzadeh, V.; Sani, M.S.A. Distribution and sources of linear alkyl benzenes (LABs) in surface sediments from Johor Bahru Coast and the Kim Kim River, Malaysia. Environ. Forensics 2016, 17, 36–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- US EPA. Conducting a Human Health Risk Assessment. Available online: https://www.epa.gov/risk/conducting-human-health-risk-assessment (accessed on 24 January 2021).
- U.S. National Library of Medicine. WISER Home. Available online: https://wiser.nlm.nih.gov/ (accessed on 30 January 2021).
- Tuah, I. SK Pasir Putih, SMK Pasir Putih Dibuka Esok. Available online: https://www.bharian.com.my/berita/wilayah/2019/03/539387/sk-pasir-putih-smk-pasir-putih-dibuka-esok (accessed on 11 April 2020).
- Treated for Chemical Poisoning after Illegal Waste Dumping in Johor’s Pasir Gudang. Available online: https://www.channelnewsasia.com/news/asia/28-treated-for-chemical-poisoning-in-pasir-gudang-johor-11321062 (accessed on 11 April 2020).
- Moses, L.T.; Zurairi, A. Six Questions About: Pasir Gudang Chemical Dumping. Available online: https://www.malaymail.com/news/malaysia/2019/03/14/six-questions-about-pasir-gudang-chemical-dumping/1732536 (accessed on 30 November 2020).
- Pasir Gudang Chemical Poisoning: 111 Schools Shut, Suspect to be Charged on Thursday. Available online: https://www.channelnewsasia.com/news/asia/pasir-gudang-chemical-poisoning-34-schools-shut-suspect-charged-11340242 (accessed on 12 April 2020).
- MOE. Kenyataan Media: Semua Sekolah Di Daerah Pasir Gudang Diarah Tutup Serta Merta. Available online: https://www.moe.gov.my/en/pemberitahuan/media-statement/kenyataan-media-semua-sekolah-di-daerah-pasir-gudang-diarah-tutup-serta-merta (accessed on 30 November 2020).
- Pasir Gudang Chemical Pollution: Malaysia Police Arrest 9 Suspects. Available online: https://www.channelnewsasia.com/news/asia/pasir-gudang-chemical-pollution-nine-people-nabbed-11355476 (accessed on 16 November 2020).
- Shah, M.F. 43 Tonnes of Chemical Waste Collected on Day Dumping was Reported. Available online: https://www.thestar.com.my/news/nation/2019/03/14/2-43-tonnes-of-chemical-waste-collected-on-day-dumping-was-reported/ (accessed on 11 April 2020).
- Update on Chronology of Chemical Pollution in Sungai Kim Kim, Pasir Gudang. Available online: https://www.theborneopost.com/2019/03/15/update-on-chronology-of-chemical-pollution-in-sungai-kim-kim-pasir-gudang/ (accessed on 11 April 2020).
- Hammim, R. Suspect in Chemical Dumping Case to be Charged Tomorrow. Available online: https://www.nst.com.my/news/nation/2019/03/468817/suspect-chemical-dumping-case-be-charged-tomorrow (accessed on 12 April 2020).
- Chung, C. Experts Warn of Serious Long-Term Health Effects. Available online: https://www.thestar.com.my/news/nation/2019/03/15/experts-warn-of-serious-longterm-health-effects/ (accessed on 11 April 2020).
- Cleaning Up Toxic River Sungai Kim Kim in Pasir Gudang to Cost S$2.16 Million. Available online: https://www.straitstimes.com/asia/se-asia/cleaning-up-toxic-river-sungai-kim-kim-in-pasir-gudang-to-cost-s216-million (accessed on 12 April 2020).
- Mokhtar, N.H. Pakar UTM Dilantik Ketua JK Saintifik bagi Kes Pencemaran Sungai Kim Kim. Available online: https://news.utm.my/ms/2019/03/pakar-utm-dilantik-ketua-jk-saintifik-bagi-kes-pencemaran-sungai-kim-kim/ (accessed on 23 November 2020).
- Yeo Unruffled by ‘Ugly Politics’ over Pollution in Pasir Gudang. Available online: https://www.thestar.com.my/news/nation/2019/07/04/yeo-unruffled-by-ugly-politics-over-pollution-in--pasir-gudang (accessed on 23 November 2020).
- Johor Royal Couple Expresses Gratitude to Sungai Kim Kim Security and Medical Personnel. Available online: https://www.malaymail.com/news/malaysia/2019/03/16/johor-royal-couple-expresses-gratitude-to-sungai-kim-kim-security-and-medic/1733419 (accessed on 23 November 2020).
- Pasir Gudang Chemical Spill: Johor Sultan Wants Authorities to Check on Pollution in Two Other Rivers. Available online: https://www.straitstimes.com/asia/se-asia/pasir-gudang-chemical-spill-johor-sultan-wants-authorities-to-check-on-pollution-in-two (accessed on 23 November 2020).
- Post, B. Govt Mulls New Law to Make Polluters Pay for Clean-Ups, Damage. Available online: https://www.theborneopost.com/2019/03/22/govt-mulls-new-law-to-make-polluters-pay-for-clean-ups-damage-2/ (accessed on 12 April 2020).
- Jalaludin, J. Respon Pelan Pencegahan isu Pembuangan sisa Toksik Sungai Kim-Kim. Available online: https://www.upm.edu.my/artikel/respon_pelan_pencegahan_isu_pembuangan_sisa_toksik_sungai_kim_kim-53373?L=en (accessed on 23 November 2020).
- 15 Types of Chemicals Found in Air Samples from Areas Near Johor’s Polluted Sungai Kim Kim. Available online: https://www.straitstimes.com/asia/se-asia/15-types-of-chemicals-found-in-air-samples-from-areas-near-polluted-sungai-kim-kim-in (accessed on 30 November 2020).
- Alias, N. Pasir Gudang Residents Lament Lack of Information on Chemical Poisoning, Vow to Sue. Available online: https://www.channelnewsasia.com/news/asia/pasir-gudang-residents-chemical-poisoning-lack-information-11347502 (accessed on 30 November 2020).
- IARC. IARC Monographs on the Evaluation of Carcinogenic Risks to Humans: Re-Evaluation of Some Organic Chemicals, Hydrazine and Hydrogen Peroxide. Available online: https://hero.epa.gov/hero/index.cfm/reference/details/reference_id/2817762 (accessed on 26 November 2020).
- National Academies. Acute Exposure Guideline Levels for Selected Airborne Chemicals. Available online: http://www.nap.edu/catalog/12770.html (accessed on 26 November 2020).
- Au, W.W. Susceptibility of children to environmental toxic substances. Int. J. Hyg. Environ. Health 2002, 205, 501–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sly, P.D.; Flack, F. Susceptibility of Children to Environmental Pollutants. Ann. New York Acad. Sci. 2008, 1140, 163–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peek, L. Children and Disasters: Understanding Vulnerability, Developing Capacities, and Promoting Resilience—An Introduction. Youth Environ. 2008, 18, 1–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calderón-Garcidueñas, L.; Leray, E.; Heydarpour, P.; Torres-Jardón, R.; Reis, J. Air pollution, a rising environmental risk factor for cognition, neuroinflammation and neurodegeneration: The clinical impact on children and beyond. Rev. Neurol. 2016, 172, 69–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goldizen, F.C.; Sly, P.D.; Knibbs, L.D. Respiratory effects of air pollution on children. Pediatr. Pulmonol. 2016, 51, 94–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zagatti, E.; Russo, M.; Pietrogrande, M.C. On-Site Monitoring Indoor Air Quality in Schools: A Real-World Investigation to Engage High School Science Students. J. Chem. Educ. 2020, 97, 4069–4072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malmqvist, E.; Liew, Z.; Källén, K.; Rignell-Hydbom, A.; Rittner, R.; Rylander, L.; Ritz, B. Fetal growth and air pollution—A study on ultrasound and birth measures. Environ. Res. 2017, 152, 73–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ATSD. ATSDR—Medical Management Guidelines (MMGs): Acrylonitrile. Available online: https://www.atsdr.cdc.gov/mmg/mmg.asp?id=443&tid=78 (accessed on 25 November 2020).
- ATSD. ATSDR—Medical Management Guidelines (MMGs): Acrolein. Available online: https://www.atsdr.cdc.gov/mmg/mmg.asp?id=552&tid=102 (accessed on 25 November 2020).
- US EPA. Toxicological Review of Acrolein (CAS No. 107-02-8). Available online: https://cfpub.epa.gov/ncea/iris/iris_documents/documents/toxreviews/0364tr.pdf (accessed on 26 November 2020).
- ATSDR. ACRYLONITRILE CAS # 107-13-1. Available online: http://www.atsdr.cdc.gov/toxfaq.html (accessed on 26 November 2020).
- Lewis-Bevan, W.; Gaston, R.D.; Tyrrell, J.; Stork, W.D.; Salmon, G.L. Formyl cyanide: A stable species. Experimental and theoretical studies. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1992, 114, 1933–1938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joseph, B.; Bhatt, B.C.; Koh, T.Y.; Chen, S. Sea breeze simulation over the Malay Peninsula in an intermonsoon period. J. Geophys. Res. Space Phys. 2008, 113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Idavain, J.; Julge, K.; Rebane, T.; Lang, A.; Orru, H. Respiratory symptoms, asthma and levels of fractional exhaled nitric oxide in schoolchildren in the industrial areas of Estonia. Sci. Total. Environ. 2019, 650, 65–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cipolla, M.; Bruzzone, M.; Stagnaro, E.; Ceppi, M.; Izzotti, A.; Culotta, C.; Piccardo, M.T. Health Issues of Primary School Students Residing in Proximity of an Oil Terminal with Environmental Exposure to Volatile Organic Compounds. BioMed Res. Int. 2016, 2016, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- D’Andrea, M.A.; Reddy, G.K. Health Risks Associated with Benzene Exposure in Children: A Systematic Review. Glob. Pediatr. Health 2018, 5, 2333794x18789275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pan, X.; Wu, X.; Yan, D.; Peng, C.; Rao, C.; Yan, H. Acrylamide-induced oxidative stress and inflammatory response are alleviated by N-acetylcysteine in PC12 cells: Involvement of the crosstalk between Nrf2 and NF-κB pathways regulated by MAPKs. Toxicol. Lett. 2018, 288, 55–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yilmaz, B.O.; Yildizbayrak, N.; Aydin, Y.; Erkan, M. Evidence of acrylamide- and glycidamide-induced oxidative stress and apoptosis in Leydig and Sertoli cells. Hum. Exp. Toxicol. 2017, 36, 1225–1235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Snow, S.J.; McGee, M.A.; Henriquez, A.; Richards, J.E.; Schladweiler, M.C.; Ledbetter, A.D.; Kodavanti, U.P. Respiratory Effects and Systemic Stress Response Following Acute Acrolein Inhalation in Rats. Toxicol. Sci. 2017, 158, 454–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiong, R.; Wu, Q.; Muskhelishvili, L.; Davis, K.; Shemansky, J.M.; Bryant, M.; Rosenfeldt, H.; Healy, S.M.; Cao, X. Evaluating Mode of Action of Acrolein Toxicity in an In Vitro Human Airway Tissue Model. Toxicol. Sci. 2018, 166, 451–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santus, P.; Corsico, A.; Solidoro, P.; Braido, F.; Di Marco, F.; Scichilone, N. Oxidative Stress and Respiratory System: Pharmacological and Clinical Reappraisal of N-Acetylcysteine. COPD: J. Chronic Obstr. Pulm. Dis. 2014, 11, 705–717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Broughton, E. The Bhopal disaster and its aftermath: A review. Environ. Health 2005, 4, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ipe, M. Bhopal Gas Tragedy: Lessons for corporate social responsibility. Soc. Responsib. J. 2005, 1, 122–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Negre, E. Crisis management and distrust: Study of an industrial accident in France. In Proceedings of the 54th Hawaii International Conference on System Sciences, Maui, HI, USA, 5–8 January 2021; p. 2235. [Google Scholar]
- Dakkoune, A.; Vernières-Hassimi, L.; Leveneur, S.; Lefebvre, D.; Estel, L. Analysis of thermal runaway events in French chemical industry. J. Loss Prev. Process. Ind. 2019, 62, 103938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakizadeh, M. Spatiotemporal variations and characterization of the chronic cancer risk associated with benzene exposure. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2019, 182, 109387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raaschou-Nielsen, O.; Hvidtfeldt, U.A.; Roswall, N.; Hertel, O.; Poulsen, A.H.; Sørensen, M. Ambient benzene at the residence and risk for subtypes of childhood leukemia, lymphoma and CNS tumor. Int. J. Cancer 2018, 143, 1367–1373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montero-Montoya, R.; López-Vargas, R.; Arellano-Aguilar, O. Volatile Organic Compounds in Air: Sources, Distribution, Exposure and Associated Illnesses in Children. Ann. Glob. Health 2018, 84, 225–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Charnsil, C.; Narkpongphun, A.; Chailangkarn, K. Post-traumatic stress disorder and related factors in students whose school burned down: Cohort study. Asian J. Psychiatry 2020, 51, 102004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carty, J.; O’Donnell, M.L.; Creamer, M. Delayed-onset PTSD: A prospective study of injury survivors. J. Affect. Disord. 2006, 90, 257–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Noh, M.F.; Malek, R. Pakar Belum Temui Bukti Sisa Toksik Bawah Tanah. Available online: https://www.bharian.com.my/berita/nasional/2019/07/581336/eksklusif-pakar-belum-temui-bukti-sisa-toksik-bawah-tanah (accessed on 20 November 2020).
- Zulkifli, S.Z.; Ismail, A.; Mohamat-Yusuff, F.; Arai, T.; Miyazaki, N. Johor Strait as a Hotspot for Trace Elements Contamination in Peninsular Malaysia. Bull. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2010, 84, 568–573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yap, C.K.; Ismail, A.; Tan, S.G. The Impact of Anthropogenic Activities on Heavy Metal (Cd, Cu, Ph and Zn) Pollution: Comparison of the Metal Levels in the Green-Lipped Mussel Perna viridis (Linnaeus) and in the Sediment from a High Activity Site at Kg. Pasir Puteh and a Relatively Low A. Available online: http://psasir.upm.edu.my/id/eprint/3583/ (accessed on 12 April 2020).
- Yap, C.K.; Ismail, A.; Edward, F.B.; Tan, S.G.; Siraj, S.S. Use of different soft tissues ofPerna viridis as biomonitors of bioavailability and contamination by heavy metals (Cd, Cu, Fe, Pb, Ni, and Zn) in a semi-enclosed intertidal water, the Johore Straits. Toxicol. Environ. Chem. 2006, 88, 683–695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yap, C.K.; Edward, F.B.; Tan, S.G. Heavy Metal Concentrations (Cu, Pb, Ni and Zn) in the Surface Sediments from a Semi-Enclosed Intertidal Water, the Johore Straits: Monitoring Data for Future Reference. J. Sustain. Sci. Manag. 2010, 5, 44–57. [Google Scholar]
- Maadin, F.S.; Abdul Rahman, M.; Abdul Zawawi, M.; Azman, S.; Oladokun, S. Copper and Zinc Accumalation in Sediment at Straits of Johor. Malays. J. Civ. Eng. 2016, 314–322. [Google Scholar]
- The Commissiner of Law Revision, M. Laws of Malaysia Environmental Quality Act 1974. Available online: https://www.doe.gov.my/portalv1/wp-content/uploads/2015/01/Environmental_Quality_Act_1974_-_ACT_127.pdf (accessed on 10 April 2020).


| Chemical | Exposure Route | Symptoms | Lowest Level for Nonlethal Irreversible Damage at 10 to 30 min Airborne Exposure Level | Cancer Risk (IARC) | Inhalation Unit Risk for Cancer |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Benzene | Inhalation, skin absorption, ingestion, skin, and/or eye contact | Irritation eyes, skin, and nose; respiratory difficulty; dizziness; headache; nausea; staggered gait; anorexia; lassitude (weakness and exhaustion); dermatitis; bone marrow depression | 1100–2000 ppm | Carcinogenic to humans. May cause leukemia | 2.2 × 10−6 per µg/m3 |
| Acrylonitrile | Inhalation, skin absorption, ingestion, skin and/or eye contact | Irritation eyes, skin; asphyxia; headache; sneezing; nausea; vomiting; lassitude (weakness, exhaustion); dizziness; skin vesiculation; scaling dermatitis | 3.2–8.6 ppm | Possibly carcinogenic to humans. Increase risk of brain tumor, lung and bowel cancer | 6.8 × 10−5 per µg/m3 |
| Acrolein | Inhalation, ingestion, skin and/or eye contact | Irritation eyes, skin, and mucous membrane; decreased pulmonary function; delayed pulmonary edema; chronic respiratory disease | 0.18–0.44 ppm | The agent is not classifiable as to its carcinogenicity to humans | - |
| Hydrogen Chloride | Inhalation, ingestion, skin and/or eye contact | Irritation nose, throat, and eye; cough; choking; dermatitis; skin burns; contact with refrigerated liquid may cause frostbite | 43–100 ppm | The agent is not classifiable as to its carcinogenicity to humans | - |
| Methane | Inhalation, ingestion, skin and/or eye contact | Breathing difficulties (i.e., suffocation and increased breathing rate); nausea and vomiting; loss of consciousness; weakness; headaches and dizziness; loss of coordination | NA | The agent is probably not carcinogenic to humans | - |
| Toluene | Inhalation, ingestion, skin and/or eye contact | Headaches; dizziness; loss of consciousness; loss of coordination; sleepiness | 760–1400 ppm | Not classifiable as to carcinogenicity to humans | - |
| Xylene | Inhalation, ingestion, skin and/or eye contact | Irritation of eyes and throat; headaches; dizziness; sleepiness; trembling; lack of coordination | 1300–2500 ppm | Not classifiable as to carcinogenicity to humans | - |
| Ethylbenzene | Inhalation, ingestion, skin and/or eye contact | Irritation of the eyes and/or throat; chest constriction; dizziness | 1600–2900 ppm | Possibly carcinogenic to humans | NA |
| d-limonene | Inhalation, ingestion, skin and/or eye contact | Breathing difficulties; skin irritation | NA | Not classifiable as to carcinogenicity to humans | - |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ibrahim, M.F.; Hod, R.; Toha, H.R.; Mohammed Nawi, A.; Idris, I.B.; Mohd Yusoff, H.; Sahani, M. The Impacts of Illegal Toxic Waste Dumping on Children’s Health: A Review and Case Study from Pasir Gudang, Malaysia. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 2221. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph18052221
Ibrahim MF, Hod R, Toha HR, Mohammed Nawi A, Idris IB, Mohd Yusoff H, Sahani M. The Impacts of Illegal Toxic Waste Dumping on Children’s Health: A Review and Case Study from Pasir Gudang, Malaysia. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health. 2021; 18(5):2221. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph18052221
Chicago/Turabian StyleIbrahim, Mohd Faiz, Rozita Hod, Haidar Rizal Toha, Azmawati Mohammed Nawi, Idayu Badilla Idris, Hanizah Mohd Yusoff, and Mazrura Sahani. 2021. "The Impacts of Illegal Toxic Waste Dumping on Children’s Health: A Review and Case Study from Pasir Gudang, Malaysia" International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health 18, no. 5: 2221. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph18052221
APA StyleIbrahim, M. F., Hod, R., Toha, H. R., Mohammed Nawi, A., Idris, I. B., Mohd Yusoff, H., & Sahani, M. (2021). The Impacts of Illegal Toxic Waste Dumping on Children’s Health: A Review and Case Study from Pasir Gudang, Malaysia. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 18(5), 2221. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph18052221






