Exposure to PM2.5 and Obesity Prevalence in the Greater Mexico City Area
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Population
2.2. PM2.5 Exposure Assessment
2.3. Anthropometric Assessment
2.4. Covariates
2.5. Statistical Analysis
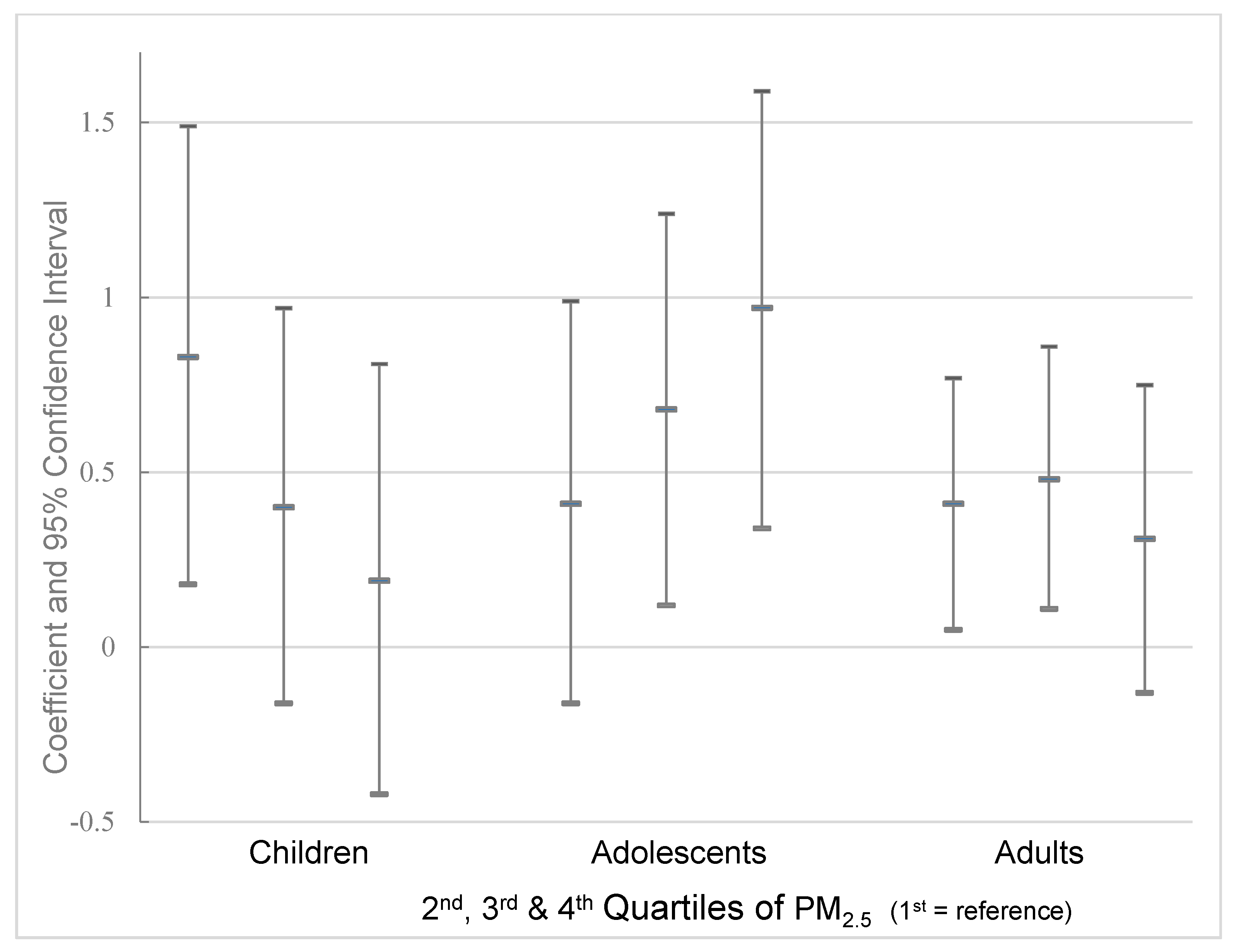
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Di Cesare, M.; Bentham, J.; Stevens, G.A.; Zhou, B.; Danaei, G.; Lu, Y.; Bixby, H.; Cowan, M.J.; Riley, L.M.; Hajifathalian, K.; et al. Trends in adult body-mass index in 200 countries from 1975 to 2014: A pooled analysis of 1698 population-based measurement studies with 19.2 million participants. Lancet 2016, 387, 1377–1396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ameye, H.; Swinnen, J. Obesity, income and gender: The changing global relationship. Glob. Food Sec. 2019, 23, 267–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Instituto Nacional de Salud Publica; Instituto Nacional de Estadistica y Geografia; Secreteria de Salud. Encuesta Nacional de Salud y Nutrición 2018 Presentación de Resultados; ENSANUT: Cuernavaca, Mexico, 2019.
- Secretaria de Medio Ambiente CDMX. 5o Informe de Gobierno; Gobierno del Distrito Federal: Ciudad de México, México, 2017.
- Shamah-Levi, T.; Cuevas-Nasu, L.; Dommarco-Rivera, J.; Hernandez-Avila, M. Encuesta nacional de salud y nutrición de medio camino 2016 (ENSANUT MC 2016). Inst. Nac. Salud Pública 2016, 2016, 151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- An, R.; Ji, M.; Yan, H.; Guan, C. Impact of ambient air pollution on obesity: A systematic review. Int. J. Obes. 2018, 42, 1112–1126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gon, Y. Toll-like receptors and airway inflammation. Allergol. Int. 2008, 57, 33–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Xu, M.X.; Ge, C.X.; Qin, Y.T.; Gu, T.T.; Lou, D.S.; Li, Q.; Hu, L.F.; Feng, J.; Huang, P.; Tan, J. Prolonged PM2.5 exposure elevates risk of oxidative stress-driven nonalcoholic fatty liver disease by triggering increase of dyslipidemia. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2019, 130, 542–556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, X.; Yavar, Z.; Verdin, M.; Ying, Z.; Mihai, G.; Kampfrath, T.; Wang, A.; Zhong, M.; Lippmann, M.; Chen, L.-C.; et al. Effect of early particulate air pollution exposure on obesity in mice: Role of p47phox. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2010, 30, 2518–2527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zordao, O.P.; Claro, L.W.; Saldiva, P.; Donato, J.; Veras, M.; Prada, P.O. Air pollution exposure during pregnancy and lactation induces obesity and glucose intolerance in the offspring. Diabetes 2018, 67, 223-OR. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bolton, J.L.; Smith, S.H.; Huff, N.C.; Gilmour, M.I.; Foster, W.M.; Auten, R.L.; Bilbo, S.D. Prenatal air pollution exposure induces neuroinflammation and predisposes offspring to weight gain in adulthood in a sex-specific manner. FASEB J. 2012, 26, 4743–4754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seo, M.Y.; Kim, S.H.; Park, M.J. Air pollution and childhood obesity. Korean J. Pediatr. 2020, 63, 382–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fioravanti, S.; Cesaroni, G.; Badaloni, C.; Michelozzi, P.; Forastiere, F.; Porta, D. Traffic-related air pollution and childhood obesity in an Italian birth cohort. Environ. Res. 2018, 160, 479–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fleisch, A.F.; Luttmann-Gibson, H.; Perng, W.; Rifas-Shiman, S.L.; Coull, B.A.; Kloog, I.; Koutrakis, P.; Schwartz, J.D.; Zanobetti, A.; Mantzoros, C.S.; et al. Prenatal and early life exposure to traffic pollution and cardiometabolic health in childhood. Pediatr. Obes. 2017, 12, 48–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fossati, S.; Valvi, D.; Martinez, D.; Cirach, M.; Estarlich, M.; Fernández-Somoano, A.; Guxens, M.; Iñiguez, C.; Irizar, A.; Lertxundi, A.; et al. Prenatal air pollution exposure and growth and cardio-metabolic risk in preschoolers. Environ. Int. 2020, 138, 105619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chiu, Y.H.; Hsu, H.H.; Wilson, A.; Coull, B.A.; Pendo, M.P.; Baccarelli, A.; Kloog, I.; Schwartz, J.; Wright, R.O.; Taveras, E.M.; et al. Prenatal particulate air pollution exposure and body composition in urban preschool children: Examining sensitive windows and sex-specific associations. Environ. Res. 2017, 158, 798–805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, Y.; Zhang, J.; Li, Z.; Gow, A.; Chung, K.F.; Hu, M.; Sun, Z.; Zeng, L.; Zhu, T.; Jia, G.; et al. Chronic exposure to air pollution particles increases the risk of obesity and metabolic syndrome: Findings from a natural experiment in Beijing. FASEB J. 2016, 30, 2115–2122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Bont, J.; Casas, M.; Barrera-Gómez, J.; Cirach, M.; Rivas, I.; Valvi, D.; Álvarez, M.; Dadvand, P.; Sunyer, J.; Vrijheid, M. Ambient air pollution and overweight and obesity in school-aged children in Barcelona, Spain. Environ. Int. 2019, 125, 58–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, G.H.; Qian, Z.; Liu, M.M.; Wang, D.; Ren, W.H.; Flick, L.H.; Fu, J.; Wang, J.; Chen, W.; Simckes, M.; et al. Ambient air pollution and the prevalence of obesity in Chinese children: The seven northeastern cities study. Obesity 2014, 22, 795–800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, X.; Zhao, H.; Chow, W.; Bixby, M.; Durand, C.; Markham, C.; Zhang, K. Population-based study of traffic-related air pollution and obesity in Mexican Americans. Obesity 2020, 28, 412–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bloemsma, L.D.; Wijga, A.H.; Klompmaker, J.O.; Janssen, N.A.H.; Smit, H.A.; Koppelman, G.H.; Brunekreef, B.; Lebret, E.; Hoek, G.; Gehring, U. The associations of air pollution, traffic noise and green space with overweight throughout childhood: The PIAMA birth cohort study. Environ. Res. 2019, 169, 348–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, N.; Wang, L.; Zhang, M.; Nazroo, J. Air quality and obesity at older ages in China: The role of duration, severity and pollutants. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0226279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Vrijheid, M.; Fossati, S.; Maitre, L.; Márquez, S.; Roumeliotaki, T.; Agier, L.; Andrusaityte, S.; Cadiou, S.; Casas, M.; de Castro, M.; et al. Early-life environmental exposures and childhood obesity: An exposome-wide approach. Environ. Health Perspect. 2020, 128, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Z.; Herting, M.M.; Chatzi, L.; Belcher, B.R.; Alderete, T.L.; McConnell, R.; Gilliland, F.D. Regional and traffic-related air pollutants are associated with higher consumption of fast food and trans fat among adolescents. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2019, 109, 99–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jerrett, M.; McConnell, R.; Chang, C.C.R.; Wolch, J.; Reynolds, K.; Lurmann, F.; Gilliland, F.; Berhane, K. Automobile traffic around the home and attained body mass index: A longitudinal cohort study of children aged 10–18 years. Prev. Med. (Baltim). 2010, 50, S50–S58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Yu, W.; Sulistyoningrum, D.C.; Gasevic, D.; Xu, R.; Julia, M.; Murni, I.K.; Chen, Z.; Lu, P.; Guo, Y.; Li, S. Long-term exposure to PM2.5 and fasting plasma glucose in non-diabetic adolescents in Yogyakarta, Indonesia. Environ. Pollut. 2020, 257, 113423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, W.; Dorans, K.S.; Wilker, E.H.; Rice, M.B.; Schwartz, J.; Coull, B.A.; Koutrakis, P.; Gold, D.R.; Fox, C.S.; Mittleman, M.A. Residential proximity to major roadways, fine particulate matter, and adiposity: The framingham heart study. Obesity 2016, 24, 2593–2599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Jerrett, M.; McConnell, R.; Wolch, J.; Chang, R.; Lam, C.; Dunton, G.; Gilliland, F.; Lurmann, F.; Islam, T.; Berhane, K. Traffic-related air pollution and obesity formation in children: A longitudinal, multilevel analysis. Environ. Health 2014, 13, 49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Calderón-Garcidueñas, L.; Franco-Lira, M.; D’Angiulli, A.; Rodríguez-Díaz, J.; Blaurock-Busch, E.; Busch, Y.; Chao, C.; Thompson, C.; Mukherjee, P.S.; Torres-Jardón, R.; et al. Mexico City normal weight children exposed to high concentrations of ambient PM2.5 show high blood leptin and endothelin-1, vitamin D deficiency, and food reward hormone dysregulation versus low pollution controls. Relevance for obesity and Alzheimer dise. Environ. Res. 2015, 140, 579–592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Neill, M.S.; Veves, A.; Sarnat, J.A.; Zanobetti, A.; Gold, D.R.; Economides, P.A.; Horton, E.S.; Schwartz, J. Air pollution and inflammation in type 2 diabetes: A mechanism for susceptibility. Occup. Environ. Med. 2007, 64, 373–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mao, G.; Nachman, R.M.; Sun, Q.; Zhang, X.; Koehler, K.; Chen, Z.; Hong, X.; Wang, G.; Caruso, D.; Zong, G.; et al. Individual and joint effects of early-life ambient PM2.5 exposure and maternal prepregnancy obesity on childhood overweight or obesity. Environ. Health Perspect. 2017, 125, 067005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barquera, S.; Campos-Nonato, I.; Hernández-Barrera, L.; Pedroza, A.; Rivera-Dommarco, J.A. Prevalencia de obesidad en adultos mexicanos, 2000. Salud Publica Mex. 2013, 55, S151–S160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Just, A.C.; Wright, R.O.; Schwartz, J.; Coull, B.A.; Baccarelli, A.A.; Tellez-Rojo, M.M.; Moody, E.; Wang, Y.; Lyapustin, A.; Kloog, I. Using High-resolution satellite aerosol optical depth to estimate daily PM2.5 geographical distribution in Mexico City. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2015, 49, 8576–8584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Gutiérrez, J.P. Household socioeconomic classification in the National Health and Nutrition Survey. Salud Publica Mex. 2013, 55, 341–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.S.; Chen, Z.; Alderete, T.L.; Toledo-Corral, C.; Lurmann, F.; Berhane, K.; Gilliland, F.D. Associations of air pollution, obesity and cardiometabolic health in young adults: The Meta-AIR study. Environ. Int. 2019, 133, 105180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fleisch, A.F.; Rifas-Shiman, S.L.; Koutrakis, P.; Schwartz, J.D.; Kloog, I.; Melly, S.; Coull, B.A.; Zanobetti, A.; Gillman, M.W.; Gold, D.R.; et al. Prenatal exposure to traffic pollution: Associations with reduced fetal growth and rapid infant weight gain. Epidemiology 2015, 26, 43–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mazidi, M.; Speakman, J.R. Ambient particulate air pollution (PM2.5) is associated with the ratio of type 2 Diabetes to obesity. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Weichenthal, S.; Hoppin, J.A.; Reeves, F. Obesity and the cardiovascular health effects of fine particulate air pollution. Obesity 2014, 22, 1580–1589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Koman, P.D.; Mancuso, P. Ozone exposure, cardiopulmonary health, and obesity: A substantive review. Chem. Res. Toxicol. 2017, 30, 1384–1395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lim, H.J.; Xue, H.; Wang, Y. Global trends in obesity. In Handbook of Eating and Drinking; Springer International Publishing: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2020; pp. 1217–1235. [Google Scholar]
- Vazquez, C.E.; Cubbin, C. Socioeconomic status and childhood obesity: A review of literature from the past decade to inform intervention research. Curr. Obes. Rep. 2020, 9, 562–570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, C.; Xu, R.; Gao, C.X.; Yu, W.; Zhang, Y.; Han, K.; Yu, P.; Guo, Y.; Li, S. Socioeconomic disparity in the association between long-term exposure to PM2.5 and mortality in 2640 Chinese counties. Environ. Int. 2021, 146, 106241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hajat, A.; Diez-Roux, A.V.; Adar, S.D.; Auchincloss, A.H.; Lovasi, G.S.; O’Neill, M.S.; Sheppard, L.; Kaufman, J.D. Air pollution and individual and neighborhood socioeconomic status: Evidence from the multi-ethnic study of atherosclerosis (MESA). Environ. Health Perspect. 2013, 121, 1325–1333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Villeneuve, P.J.; Goldberg, M.S.; Burnett, R.T.; Van Donkelaar, A.; Chen, H.; Martin, R.V. Associations between cigarette smoking, obesity, sociodemographic characteristics and remote-sensing-derived estimates of ambient PM2.5: Results from a Canadian population-based survey. Occup. Environ. Med. 2011, 68, 920–927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sun, Q.; Yue, P.; Deiuliis, J.A.; Lumeng, C.N.; Kampfrath, T.; Mikolaj, M.B.; Cai, Y.; Ostrowski, M.C.; Lu, B.; Parthasarathy, S.; et al. Ambient Air pollution exaggerates adipose inflammation and insulin resistance in a mouse model of diet-induced obesity. Circulation 2009, 119, 538–546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Xu, Y.; Wang, W.; Chen, M.; Zhou, J.; Huang, X.; Tao, S.; Pan, B.; Li, Z.; Xie, X.; Li, W.; et al. Developmental programming of obesity by maternal exposure to concentrated ambient PM2.5 is maternally transmitted into the third generation in a mouse model. Part. Fibre Toxicol. 2019, 16, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, M.; Liang, S.; Zhou, H.; Xu, Y.; Qin, X.; Hu, Z.; Wang, X.; Qiu, L.; Wang, W.; Zhang, Y.; et al. Prenatal and postnatal mothering by diesel exhaust PM2.5-exposed dams differentially program mouse energy metabolism. Part. Fibre Toxicol. 2017, 14, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kenny, P.J. Reward mechanisms in obesity: New insights and future directions. Neuron 2011, 69, 664–679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- López-Olmedo, N.; Popkin, B.M.; Taillie, L.S. Association between socioeconomic status and diet quality in Mexican men and women: A cross-sectional study. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0224385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kloog, I.; Koutrakis, P.; Coull, B.A.; Lee, H.J.; Schwartz, J. Assessing temporally and spatially resolved PM2.5 exposures for epidemiological studies using satellite aerosol optical depth measurements. Atmos. Environ. 2011, 45, 6267–6275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bennette, C.; Vickers, A. Against quantiles: Categorization of continuous variables in epidemiologic research, and its discontents. BMC Med. Res. Methodol. 2012, 12, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]

| Ensanut 2006 | Ensanut 2012 | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Variable | Children (0–9 Years) | Adolescents (10–19 Years) | Adults (≥20 Years) | Children (0–9 Years) | Adolescents (10–19 Years) | Adults (≥20 Years) |
| Sample size (n) | 1005 | 1082 | 2281 | 1233 | 986 | 2302 |
| Sample representativeness (N) | 31,00,923 | 3,565,877 | 12,695,627 | 3,552,214 | 3,636,732 | 13,760,947 |
| Sex | ||||||
| Male (%) | 50.3 | 55.3 | 44.9 | 51 | 49.1 | 45.9 |
| Female (%) | 49.7 | 44.7 | 55.1 | 49 | 50.9 | 54.1 |
| Age mean (years) a | 4.7 ± 2.9 | 14.4 ± 2.9 | 42.9 ± 16.4 | 4.6 ± 2.7 | 14.3 ± 2.9 | 44.9 ± 16.3 |
| SES b | −0.16 ± 0.05 | −0.03 ± 0.06 | −0.16 ± 0.06 | 0.05 ± 0.10 | 0.03 ± 0.082 | −0.12 ± 0.05 |
| BMI | ||||||
| Normal (%) | 58.45% | 58.01% | 27.81% | 59.02% | 56.48% | 26.12% |
| Overweight (%) | 20.05% | 25.18% | 41.45% | 17.42% | 22.98% | 37.34% |
| Obesity (%) | 21.49% | 16.81% | 30.73% | 23.55% | 20.53% | 35.94% |
| Average past year PM2.5 (µg/m3) | 25.9 (2.4) | 24.8 (1.5) | ||||
| ENSANUT 2006 | Children | Adolescents | Adults | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| n = 618 | n = 801 | n = 1559 | ||||
| n = 2,529,289 | n = 3,548,352 | n = 12,541,729 | ||||
| OR | 95% CI | OR | 95% CI | OR | 95% CI | |
| Logistic model * | ||||||
| Obesity | 1.19 | (0.47, 3.08) | 3.53 | (1.45, 8.58) | 1.01 | (0.59, 1.73) |
| Logistic model stratified by sex ** | ||||||
| Male | 0.57 | (0.17, 1.95) | 4.19 | (1.24, 14.19) | 1.09 | (0.40, 2.91) |
| Female | 2.7 | (0.71, 10.21) | 2.64 | (0.74, 9.44) | 0.94 | (0.49, 1.79) |
| p interaction | 0.07 | 0.53 | 0.82 | |||
| Multinomial model (RRR) * | ||||||
| Overweight | 1.57 | (0.54, 4.56) | 1.36 | (0.68, 2.73) | 0.82 | (0.41, 1.62) |
| Obesity | 1.43 | (0.53, 3.84) | 3.89 | (1.51, 10.03) | 0.89 | (0.43, 1.85) |
| ENSANUT 2012 | Children | Adolescents | Adults | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| n = 752 | n = 718 | n = 1538 | ||||
| n = 2,769,354 | n = 3,245,296 | n = 11,415,512 | ||||
| OR | 95% CI | OR | 95% CI | OR | 95% CI | |
| Logistic model * | ||||||
| Obesity | 1.98 | (0.92, 4.22) | 3.79 | (1.40, 10.24) | 2.73 | (0.97, 7.71) |
| Logistic models stratified by sex ** | ||||||
| Male | 2.29 | (0.69, 7.55) | 2.61 | (0.41, 16.73) | 2.56 | (0.59, 11.20) |
| Female | 1.29 | (0.79, 2.10) | 7.83 | (0.96, 64.12) | 2.88 | (0.83, 10.04) |
| p interaction | 0.44 | 0.44 | 0.85 | |||
| Multinomial model (RRR) * | ||||||
| Overweight | 0.84 | (0.02, 42.96) | 2.34 | (0.83, 6.65) | 0.39 | (0.13, 1.18) |
| Obesity | 1.69 | (0.63, 4.59) | 4.82 | (2.16, 10.76) | 1.54 | (0.46, 5.14) |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tamayo-Ortiz, M.; Téllez-Rojo, M.M.; Rothenberg, S.J.; Gutiérrez-Avila, I.; Just, A.C.; Kloog, I.; Texcalac-Sangrador, J.L.; Romero-Martinez, M.; Bautista-Arredondo, L.F.; Schwartz, J.; et al. Exposure to PM2.5 and Obesity Prevalence in the Greater Mexico City Area. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 2301. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph18052301
Tamayo-Ortiz M, Téllez-Rojo MM, Rothenberg SJ, Gutiérrez-Avila I, Just AC, Kloog I, Texcalac-Sangrador JL, Romero-Martinez M, Bautista-Arredondo LF, Schwartz J, et al. Exposure to PM2.5 and Obesity Prevalence in the Greater Mexico City Area. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health. 2021; 18(5):2301. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph18052301
Chicago/Turabian StyleTamayo-Ortiz, Marcela, Martha María Téllez-Rojo, Stephen J. Rothenberg, Ivan Gutiérrez-Avila, Allan Carpenter Just, Itai Kloog, José Luis Texcalac-Sangrador, Martin Romero-Martinez, Luis F. Bautista-Arredondo, Joel Schwartz, and et al. 2021. "Exposure to PM2.5 and Obesity Prevalence in the Greater Mexico City Area" International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health 18, no. 5: 2301. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph18052301
APA StyleTamayo-Ortiz, M., Téllez-Rojo, M. M., Rothenberg, S. J., Gutiérrez-Avila, I., Just, A. C., Kloog, I., Texcalac-Sangrador, J. L., Romero-Martinez, M., Bautista-Arredondo, L. F., Schwartz, J., Wright, R. O., & Riojas-Rodriguez, H. (2021). Exposure to PM2.5 and Obesity Prevalence in the Greater Mexico City Area. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 18(5), 2301. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph18052301









