The Impact of Collaboration Network on Water Resource Governance Performance: Evidence from China’s Yangtze River Delta Region
Abstract
:1. Introduction
1.1. Literature Review
1.1.1. Motivation for Collaboration Network
1.1.2. Network Structure and Performance
1.1.3. Network Governance of Water Treatment
1.2. Hypotheses
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.1.1. Dependent Variable: Wastewater Treatment Performance
2.1.2. Independent Variables: Collaboration Network Structure
2.1.3. Control Variables
2.2. Method
2.2.1. Social Network Analysis
2.2.2. Empirical Model
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Freeman, L.C. Centrality in social network conceptual clarification. Soc. Netw. 1978, 1, 215–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Feiock, R.C. Rational Choice and Regional Governance. J. Urban Aff. 2007, 29, 47–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feiock, R.C. Metropolitan governance and institutional collective action. Urban Aff. Rev. 2009, 44, 356–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lubell, M.; Robins, G.; Wang, P. Policy coordination in an ecology of water management games. In Proceedings of the Political Networks Conference, Ann Arbor, MI, USA, 14–18 June 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Yi, H.-T. Network Structure and Governance Performance: What Makes a Difference? Public Adm. Rev. 2018, 78, 195–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yi, H.-T.; Suo, L.; Shen, R.; Zhang, J.; Ramaswami, A.; Feiock, R.C. Regional governance and institutional collective action for environmental sustainability. Public Adm. Rev. 2018, 78, 556–566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, J.; Suo, L.-M. Inter-city Environmental Governance Cooperation: Actions, network and Their Evolution—Analysis of Intergovernmental Agreement Data of Cities in the Yangtze River Delta. Chin. J. Adm. Manag. 2019, 9, 41–49. [Google Scholar]
- Provan, K.G.; Milward, H.B. Do Networks Really Work? A Framework for Evaluating Public-Sector Organizational Networks. Public Adm. Rev. 2001, 61, 414–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, B.; Suo, L.-M.; Ma, J. A network approach to interprovincial agreements: A study of Pan Pearl River Delta in China. State Local Gov. Rev. 2015, 47, 181–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berardo, R.; Scholz, J.T. Micro-incentives and the dynamics of policy network. In Proceedings of the American Political Science Association Annual Meeting, Washington, DC, USA, 1–4 September 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Bian, X.-H.; Zhang, C.-F. Governmental Relations and State Governance: Functions, Models and Reform Ideas. Chin. Adm. 2016, 5, 14–18. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, T.; Wen, X.-M. A Study on Regional Environmental Governance from the Perspective of Inter-governmental Relations: A Quantitative analysis of Atmospheric Governance Policies in Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei Region. Urban Dev. Res. 2017, 24, 45–53. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y.-M. Construction of Inter-city Environmental Cooperative Governance Mechanism in the Pearl River Delta. J. Guangdong Inst. Public Adm. 2011, 23, 10–17. [Google Scholar]
- Grantham, A. How network explain unintended policy implementation outcomes: The case of UK rail privatization. Public Adm. 2001, 79, 851–870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sydow, J. Network development by means of network evaluation? Explorative insights from a case in the financial services industry. Hum. Relat. 2004, 57, 201–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Assche, B.-V.S. Network stability in longitudinal data: A case study from rural Malawi. Soc. Netw. 2005, 27, 231–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mattessich, P.W.; Monsey, B.R. Collaboration: What Makes It Work. A Review of Research Literature on Factors Influencing Successful Collaboration; Amherst, H., Ed.; Wilder Foundation: St. Paul, MN, USA, 1992. [Google Scholar]
- Scholz, J.T.; Berardo, R.; Kile, B. Do network solve collective action problems? Credibility, search, and collaboration. J. Polit. 2008, 70, 393–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fischer, M. Social Network Analysis and Qualitative Comparative Analysis: Their Mutual Benefit for the Explanation of Policy Network Structures. Methodol. Innov. Online 2011, 6, 27–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ingold, K.; Balsiger, J. Sustainability principles put into practice: Case studies of network analysis in Swiss climate change adaptation. Reg. Environ. Chang. 2015, 15, 529–538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, Y.-W. Governance Network Theory and Its Applicability to Chinese Governance. Jianghai Acad. J. 2017, 2, 125–131. [Google Scholar]
- Berardo, R.; Gerlak, A.K. Conflict and cooperation along international rivers: Crafting a model of institutional effectiveness. Glob. Environ. Polit. 2012, 12, 101–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feiock, R.C.; Carr, J.B. Incentives, Entrepreneurs, and Boundary Change: A Collective Action Framework. Urban Aff. Rev. 2016, 36, 382–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mu, R.; Jia, J.-T.; Li, P. Research on the influencing factors of the effect of environmental cooperation in urban agglomeration—A qualitative comparative analysis of fuzzy sets based on 13 cases. Chin. J. Popul. Resour. Environ. 2019, 29, 12–19. [Google Scholar]
- Coleman, J.S. Social Capital in the Creation of Human Capital. Am. J. Sociol. 1988, 94, 95–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berardo, R. Bridging and Bonding capital in Two-Mode Collaboration network. Policy Stud. J. 2014, 4, 197–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, F.-Q.; Cheng, J. Evaluation and Promotion Strategy of Collaborative Development of Environmental Protection in the Yangtze River Delta. J. Environ. Prot. 2016, 44, 52–57. [Google Scholar]
- Emerson, K.; Nabatchi, T.; Balogh, S. An Integrative Framework for Collaborative Governance. J. Public Adm. Res. Theory 2012, 22, 1–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Agranoff, R. Inside Collaborative network: Ten Lessons for Public Managers. Public Adm. Rev. 2006, 66, 56–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mcguire, M. Collaborative Public Management: Assessing What We Know and How We Know It. Public Adm. Rev. 2006, 66, 33–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomson, A.M.; Perry, J.L. Collaboration Processes: Inside the Black Box. Public Adm. Rev. 2010, 66, 20–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Newman, J.; Barnes, M.; Sullivan, H.; Knops, A. Public Participation and Collaborative Governance. J. Soc. Policy 2004, 33, 203–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Vigoda, E. From Responsiveness to Collaboration: Governance, Citizens, and the Next Generation of Public Administration. Public Adm. Rev. 2002, 62, 527–540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gray, B.; Wood, D. Collaborative Alliances: Moving from practice to theory. J. Appl. Behav. Sci. 1991, 27, 3–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ansell, C.; Gash, A. Collaborative Governance in Theory and Practice. J. Public Adm. Res. Theory 2008, 18, 543–571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yang, Y.; Sun, T. Research on Cross-regional Environmental Governance and Local Government Cooperation Mechanism. Chin. J. Adm. Manag. 2009, 1, 66–69. [Google Scholar]
- Gray, B. Conditions Facilitating Interorganizational Collaboration. Hum. Relat. 1985, 38, 911–936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Youm, J.; Feiock, R.C. Interlocal collaboration and local climate protection. Local Gov. Stud. 2019, 45, 777–802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wood, D.J.; Gray, B. Toward a Comprehensive Theory of Collaboration. J. Appl. Behav. Sci. 1991, 27, 139–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, I.W.; Feiock, R.C.; Lee, Y. Competitors and Cooperators: A Micro-Level Analysis of Regional Economic Development Collaboration network. Public Adm. Rev. 2012, 72, 253–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Selin, S.; Deborah, C. Developing a collaborative model for environmental planning and management. Environ. Manag. 1995, 19, 189–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huxham, C.; Vangen, S.; Huxham, C.; Eden, C. The challenge of collaborative governance. Public Manag. Int. J. Res. Theory 2000, 2, 337–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feiock, R.C. Institutional Collective Action and Local Goverance; Working Group on Interlocal Services Cooperation; Paper 5; Wayne State University: Detroit, MI, USA, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Park, H.J.; Feiock, R.C. Institutional collective action, social capital and regional development partnership. Int. Rev. Public Adm. 2006, 11, 57–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carr, J.B.; Leroux, K.; Shrestha, M. Institutional Ties, Transaction Costs, and External Service Production. Urban Aff. Rev. 2008, 44, 403–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Germà, B.; Xavier, F.; Melania, M. Does Cooperation Reduce Service Delivery Costs? Evidence from Residential Solid Waste Services. J. Public Adm. Res. Theory 2014, 1, 85–107. [Google Scholar]
- Germà, B.; Mildred, E.W. Inter-Municipal Cooperation and Costs: Expectations and Evidence. Public Adm. 2015, 93, 52–67. [Google Scholar]
- Berardo, R.; Scholz, J.T. Self-Organizing Policy Networks: Risk, Partner Selection, and Cooperation in Estuaries. Am. J. Polit. Sci. 2010, 54, 632–649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lubell, M.; Henry, A.D.; McCoy, M. Collaborative institutions in an ecology of games. Am. J. Polit. Sci. 2010, 54, 287–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feiock, R.C.; Steinacker, A.; Park, H.J. Institutional collective action and economic development joint ventures. Public Adm. Rev. 2009, 69, 256–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feiock, R.C. The institutional collective action framework. Policy Studies J. 2013, 41, 397–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Provan, K.G.; Patrick, K. Modes of Network Governance: Structure, Management, and Effectiveness. J. Public Adm. Res. Theory 2008, 18, 229–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zakocs, R.C.; Edwards, E.M. What explains community coalition effectiveness? A review of the literature. Am. J. Prev. Med. 2006, 30, 351–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, W.-J. Exploring the Determinants of Network Effectiveness: The Case of Neighborhood Governance Networks in Beijing. J. Public Adm. Res. Theory 2016, 27, 375–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Provan, K.G.; Milward, H.B. A preliminary theory of interorganizational network effectiveness: A comparative study of four community mental health systems. Adm. Sci. Q. 1995, 40, 1–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Provan, K.G.; Sebastian, J.G. Networks Within Networks: Service Link Overlap, Organizational Cliques, and Network Effectiveness. Acad. Manag. J. 1998, 41, 453–463. [Google Scholar]
- Meier, K.J.; O’Toole, L.J. Managerial Strategies and Behavior in Networks: A Model with Evidence from U.S. Public Education. J. Public Adm. Res.Theory 2001, 3, 271–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Klijn, E.H.; Steijn, B.; Edelenbos, J. The Impact of Network Management on Outcomes in Governance Networks. Public Adm. 2010, 88, 1063–1082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ysa, T.; Sierra, V.; Esteve, M. Determinants of Network Outcomes: The Impact of Management Strategies. Public Adm. 2014, 92, 636–655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Klijn, E.H.; Sierra, V.; Ysa, T.; Berman, E.; Edelenbos, J.; Chen, D.Y. The Influence of Trust on Network Performance in Taiwan, Spain, and the Netherlands: A Cross-Country Comparison. Int. Public Manag. J. 2016, 19, 111–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meier, K.J.; O’Toole, L.J. Public Management and Educational Performance: The Impact of Managerial Networking. Public Adm. Rev. 2010, 63, 689–699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kenis, P.; Provan, K.G. Towards an Exogenous Theoty of Public Network Performance. Public Adm. 2009, 87, 440–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Turrini, A.; Cristofoli, D.; Frosini, F.; Nasi, G. Networking literature about determinants of network effectiveness. Public Adm. 2010, 88, 528–550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Owen-Smith, J.; Walter, W.P. Knowledge Networks as Channels and Conduits: The Effects of Spillovers in the Boston Biotechnology Community. Organ. Sci. 2004, 15, 5–21. [Google Scholar]
- Raab, J.; Mannak, R.S.; Cambré, B. Combining Structure, Governance, and Context: A Configurational Approach to Network Effectiveness. J. Public Adm. Res. Theory 2015, 25, 479–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Milward, H.B.; Provan, K.G. Measuring Network Structure. Public Adm. 1998, 76, 387–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laan, G.V.D.; Moes, N. Collective Decision Making in An International River Pollution Model. Nat. Resour. Modeling 2016, 29, 374–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, C.; Chen, T.; Yi, H.; Xu, X.; Chen, S.; Chen, W. Collaborative environmental governance, inter-agency cooperation and local water sustainability in China. Sustainability 2017, 9, 2305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Imperial, M.T. Using Collaboration as a Governance Strategy: Lessons From Six Watershed Management Programs. Adm. Soc. 2005, 37, 281–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bryson, J.M.; Crosby, B.C.; Stone, M.M. The Design and Implementation of Cross-Sector Collaborations: Propositions from the Literature. Public Adm. Rev. 2010, 66, 44–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lubell, M. Collaborative watershed management: A view from the grassroots. Policy Stud. J. 2004, 32, 341–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lazega, E.; Burt, R.S. Structural Holes: The Social Structure of Competition. Revue Franaise Sociol. 1995, 36, 779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bourdieu, P. The Forms of Capital. In Handbook of Theory and Research for the Sociology of Education; Richardson, J., Ed.; Greenwood Press: New York, NY, USA, 1986; pp. 241–258. [Google Scholar]
- Putnam, R.; Leonardi, R.; Naetti, R. Making Democracy Work: Civic Traditions in Modern Italy. Contemp. Sociol. 1994, 26, 306–308. [Google Scholar]
- Woolcock, M.; Naranyan, D. Social Capital: Implications for Development Theory, Research and Policy. World Bank Res. Obs. 2000, 15, 225–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Andrew, S.A. Institutional Ties, Interlocal Contractual Arrangements, and the Dynamic of Metropolitan Governance. Ph.D. Thesis, Florida State University, Tallahassee, FL, USA, 1 August 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Graddy, E.A. Influences on the Size and Scope of Networks for Social Service Delivery. J. Public Adm. Res. Theory 2006, 16, 533–552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Huxham, C. Theorizing collaboration practice. Public Manag. Rev. 2003, 5, 401–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vangen, S.; Chris, H. Nurturing Collaborative Relations Building Trust in Interorganizational Collaboration. J. Appl. Behav. Sci. 2003, 39, 5–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Berardo, R. Generalized trust in multi-organizational policy arenas: Studying its emergence from a network perspective. Polit. Res. Q. 2009, 62, 178–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berardo, R.; Lubell, M. Understanding What Shapes a Polycentric Governance System. Public Adm. Rev. 2016, 76, 738–751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suo, L.-M.; Ma, J.; Chen, B. Bilateral Cooperation and Multilateral Coordination in Regional Environmental Governance: An Analysis Based on the Pan-Pearl River Delta Agreement from 2003 to 2015. Fudan Rev. Public Adm. 2017, 1, 149–172. [Google Scholar]
- Cole, J.J.; Beierls, B.L.; Caraco, N.F.; Pace, M.L. Nitrogen Loading of Rivers as Human-Driven Process. In Humans as Components of Ecosystems: The Ecology of Subtle Huamn Effects and Populated Areas; McDonnel, M.J., Pickett, T.A., Eds.; Springer Science & Business Media: New York, NY, USA, 1993. [Google Scholar]
- Mink, S.D. Poverty Population and the Environment; World Bank Discussion Papers; World Bank: Washington, DC, USA, 1993. [Google Scholar]
- Tarr, J.; Ayres, R. Environmental Change in the Hudson River Basin and the Hudson-Raritan Estuary; Turner, B., Clark, W., Cates, R., Richards, J., Matthews, J., Meyer, W., Eds.; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 1990; pp. 623–640. [Google Scholar]
- Diekmann, A.; Franzen, A. The Wealth of Nations and Environmental Concern. Environ. Behav. 1999, 31, 540–549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Markandya, A.; Baumol, W.J.; Oates, W.E. Economics, Environmental Policy, and the Quality of Life. Econ. J. 1979, 89, 1002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grossman, G.M.; Krueger, A.B. Economic-Growth and the Environment. Q. J. Econ. 1995, 110, 353–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, P. Is there an Inverted U-shaped Relationship Between Industrial Structure Adjustment and Environmental Pollution? Explor. Econ. Probl. 2015, 12, 56–67. [Google Scholar]

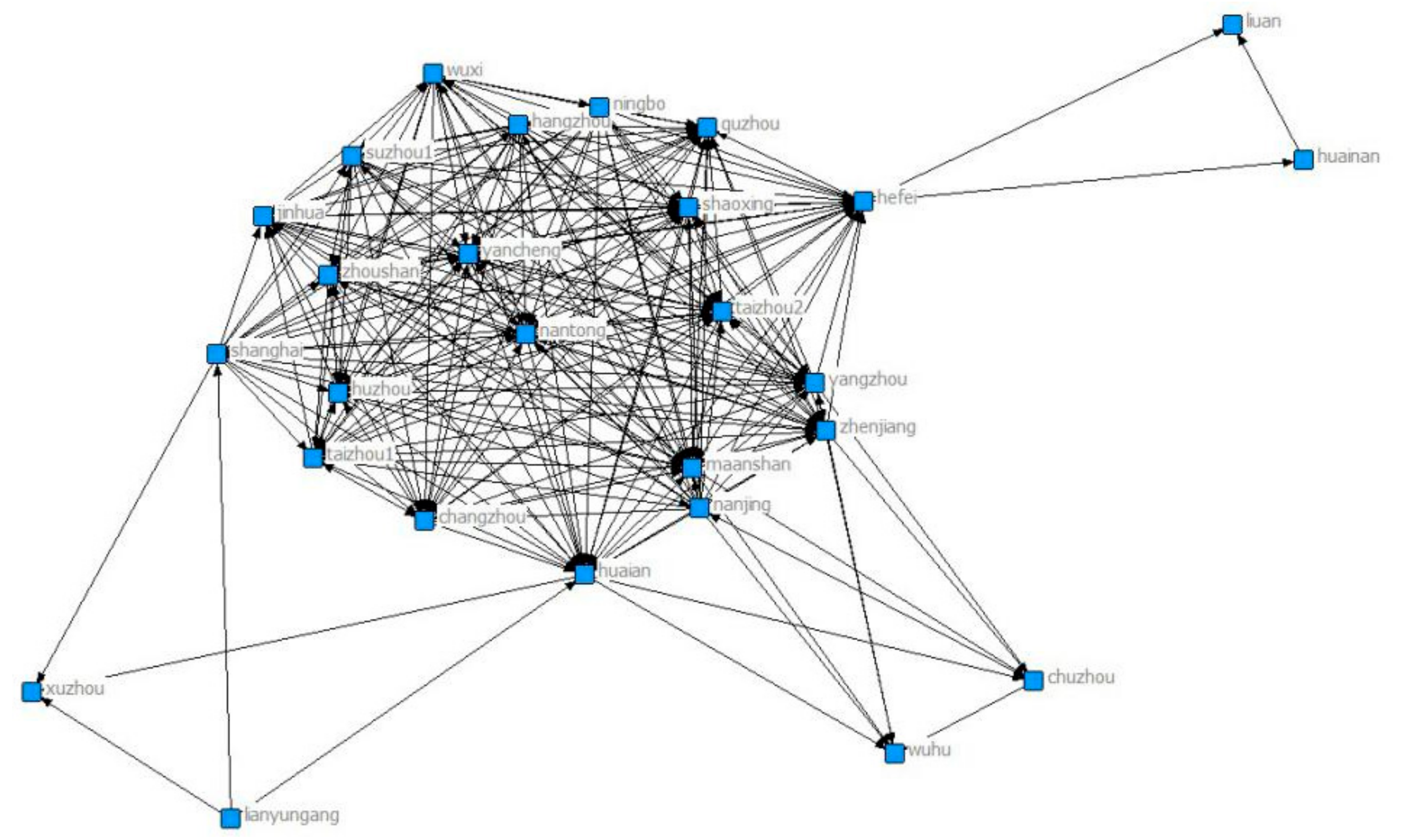
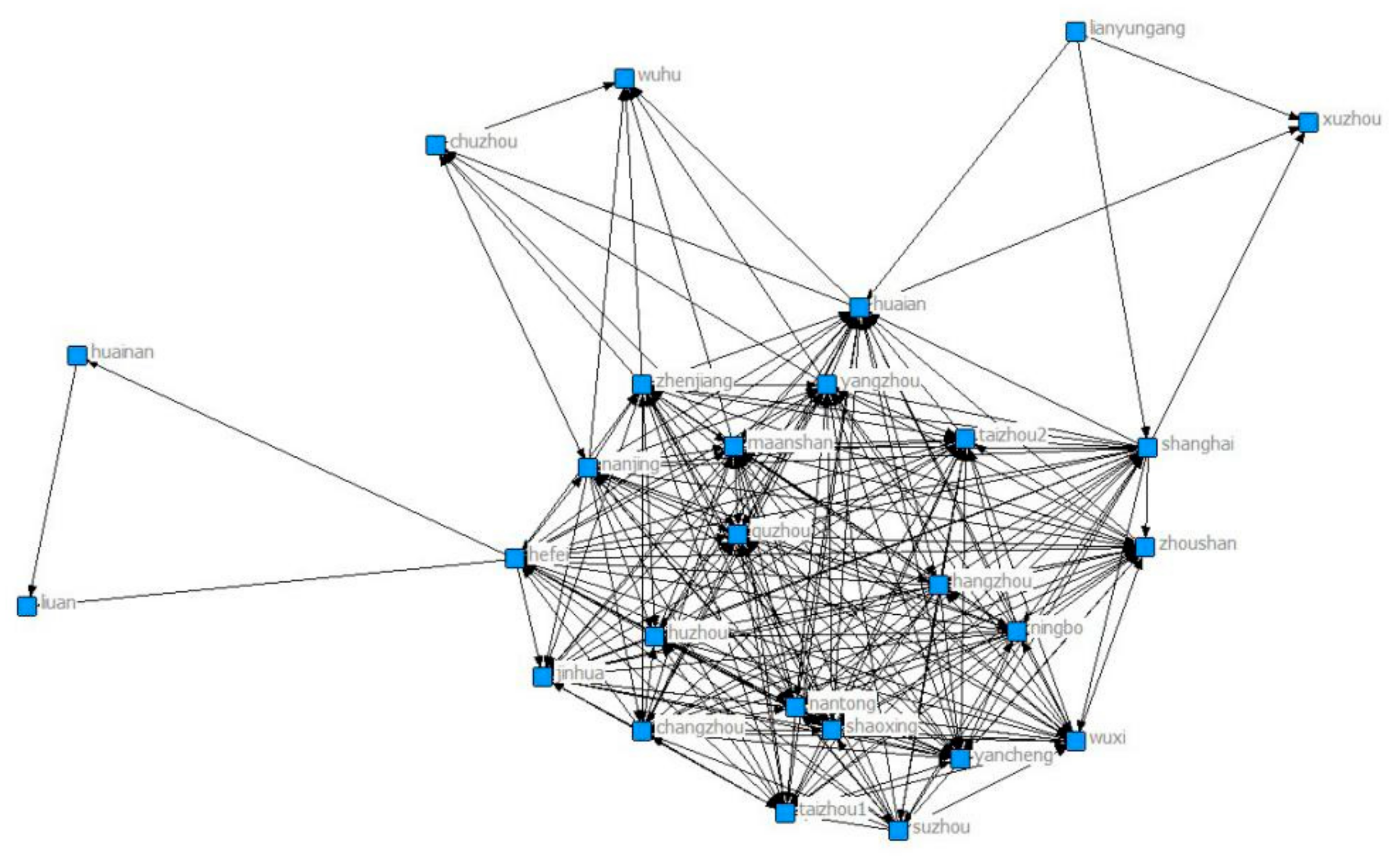


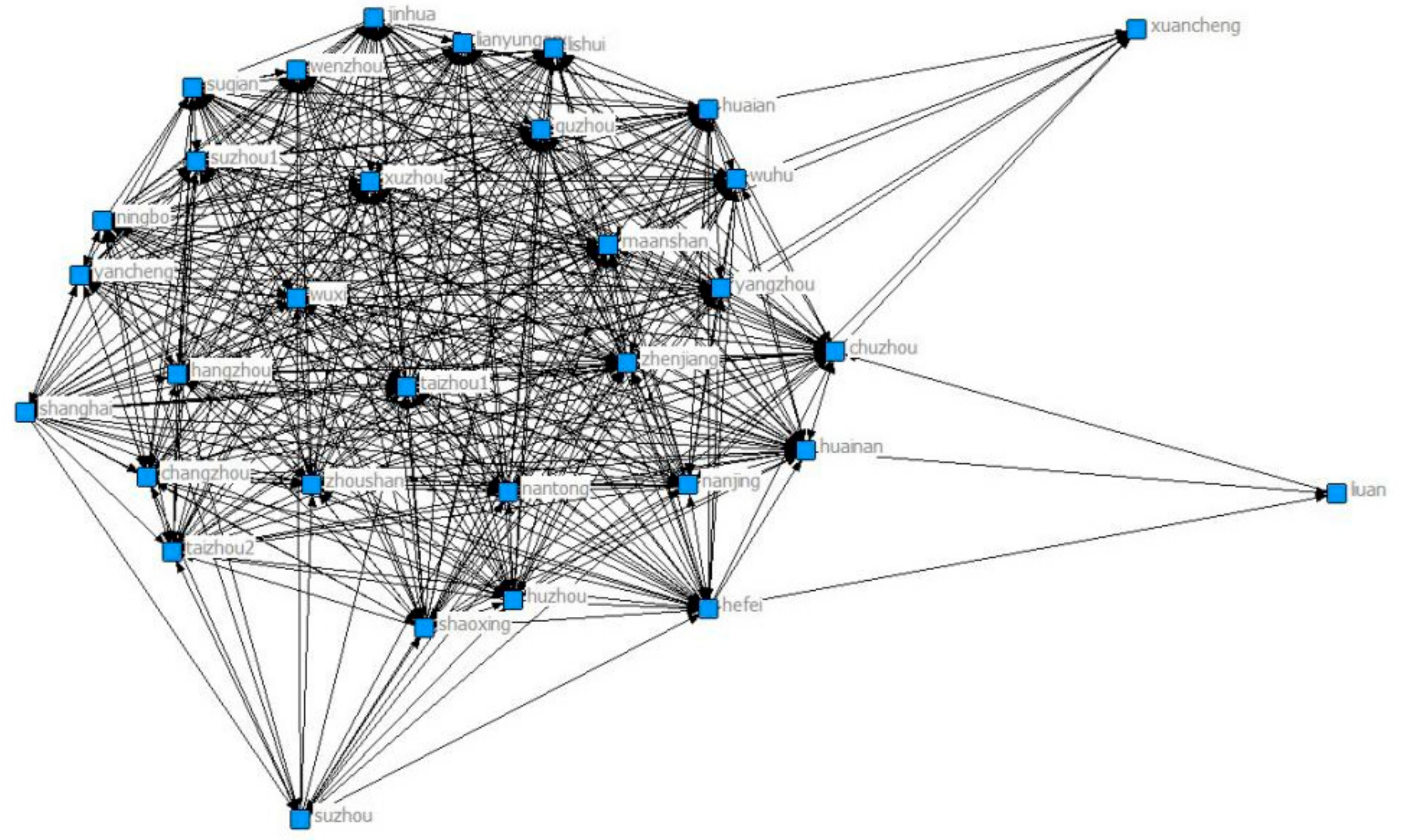

| Variables | Measures | Predicted Relationship | Data Source |
|---|---|---|---|
| Wastewater management performance (watertre) | The rate of wastewater treatment | China City Yearbook | |
| Bridging social capital (closeness) | Closeness centrality | + | Calculated by author |
| Bonding social capital (clustering) | Clustering coefficient | + | Calculated by author |
| Population (pop) | The number in the population | control | China City Yearbook |
| Population growth (popgro) | The rate of population growth | control | China City Yearbook |
| Population density (popden) | Population/administrative area | control | China City Yearbook |
| GDP (GDP) | RMB Ten thousand yuan | control | China City Yearbook |
| GDP growth (GDPgro) | The rate of GDP growth | control | China City Yearbook |
| The proportion of the primary (pri) | GDP of the primary/GDP | control | China City Yearbook |
| The proportion of the secondary (sec) | GDP of the secondary/GDP | control | China City Yearbook |
| The propotion of the tertiary (ter) | GDP of the tertiary/GDP | control | China City Yearbook |
| The number of factories (numofidu) | Count | control | China City Yearbook |
| Water resource (waterres) | City water supply amount | control | China City Yearbook |
| Variables | Obs | Mean | SD | Min | Max |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Watertre | 287 | 79.44 | 12.00 | 27.27 | 96.34 |
| Closeness | 287 | 35.40 | 25.40 | 0 | 86 |
| Clustering | 287 | 2.28 | 2.29 | 0 | 10.02 |
| GDP | 287 | 3.06 | 3.74 | 2,455,896 | 251,234,500 |
| GDP gro | 287 | 10.90 | 2.51 | 3.74 | 18.20 |
| Pop | 287 | 501.16 | 274.26 | 73.8 | 1442.97 |
| Popgro | 287 | 4.65 | 4.57 | −2.6 | 27.4 |
| Popden | 287 | 658.53 | 342.40 | 145.29 | 2275.67 |
| Pri | 287 | 9.61 | 6.91 | 0.44 | 29.7 |
| Sec | 287 | 50.62 | 7.50 | 31.81 | 74.73 |
| Ter | 287 | 39.76 | 7.49 | 23.36 | 67.76 |
| Numofidu | 287 | 3023.54 | 2945.02 | 174 | 17,906 |
| Waterres | 287 | 26,167.84 | 53,213.03 | 2172 | 399,226 |
| Variables | Model 1 | Model 2 | Model 3 | Model 4 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Closeness | 0.11 *** (0.04) | 0.09 ** (0.04) | 0.07 * (0.04) | |
| Clustering | 1.98 *** (0.33) | 1.46 *** (0.40) | 1.09 *** (0.36) | |
| GDP | 5.21 *** (8.00) | 2.48 *** (7.96) | 7.17 (8.95) | |
| Popden | −0.01 (0.02) | −0.01 (0.02) | −0.01 (0.02) | |
| Sec | 0.43 (0.22) | 0.51 ** (0.21) | −38.59 (85.71) | |
| Numofidu | 0.00 (0.00) | 0.00 (0.00) | 0.00 (0.00) | |
| GDPgro | −1.17 *** (0.31) | |||
| Pop | 0.02 (0.03) | |||
| Popgro | −0.27 (0.20) | |||
| Pri | −40.63 (85.71) | |||
| Ter | −38.86 (85.69) | |||
| Waterres | −0.00 (0.00) | |||
| Constant | 45.68 * (18.18) | 70.88 *** (1.20) | 45.01 *** (16.26) | 3972.81 (8569.33) |
| N | 287 | 287 | 287 | 287 |
| Adjusted R2 | 0.18 | 0.32 | 0.35 | 0.46 |
| Variables | Model 1 | Model 2 | Model 3 | Model 4 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Closeness | 0.11 *** (0.03) | 0.09 ** (0.04) | 0.07 * (0.04) | |
| Clustering | 1.98 *** (0.27) | 1.80 *** (0.32) | 1.09 *** (0.35) | |
| GDP | 5.21 *** (1.45) | 2.48 ** (1.06) | 7.17 (8.25) | |
| Popden | −0.01 (0.02) | −0.01 (0.01) | −0.01 (0.02) | |
| Sec | 0.43 (0.48) | 0.51 (0.44) | −38.59 (105.79) | |
| Numofidu | 0.00 * (0.00) | 0.00 (0.00) | 0.00 (0.00) | |
| GDPgro | −1.17 * (0.62) | |||
| Pop | 0.02 (0.04) | |||
| Popgro | −0.27 (0.22) | |||
| Pri | −40.63 (106.00) | |||
| Ter | −38.86 (106.04) | |||
| Waterres | −0.00 (0.00) | |||
| Constant | 45.68 (29.87) | 70.88 *** (1.06) | 45.01 * (24.80) | 3972.81 (10,597.27) |
| N | 287 | 287 | 287 | 287 |
| Adjusted R2 | 0.32 | 0.35 | 0.47 | 0.47 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yi, H.; Yang, Y.; Zhou, C. The Impact of Collaboration Network on Water Resource Governance Performance: Evidence from China’s Yangtze River Delta Region. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 2557. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph18052557
Yi H, Yang Y, Zhou C. The Impact of Collaboration Network on Water Resource Governance Performance: Evidence from China’s Yangtze River Delta Region. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health. 2021; 18(5):2557. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph18052557
Chicago/Turabian StyleYi, Hongtao, Yan Yang, and Chao Zhou. 2021. "The Impact of Collaboration Network on Water Resource Governance Performance: Evidence from China’s Yangtze River Delta Region" International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health 18, no. 5: 2557. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph18052557
APA StyleYi, H., Yang, Y., & Zhou, C. (2021). The Impact of Collaboration Network on Water Resource Governance Performance: Evidence from China’s Yangtze River Delta Region. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 18(5), 2557. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph18052557





