Review of the Upright Balance Assessment Based on the Force Plate
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Balance Control
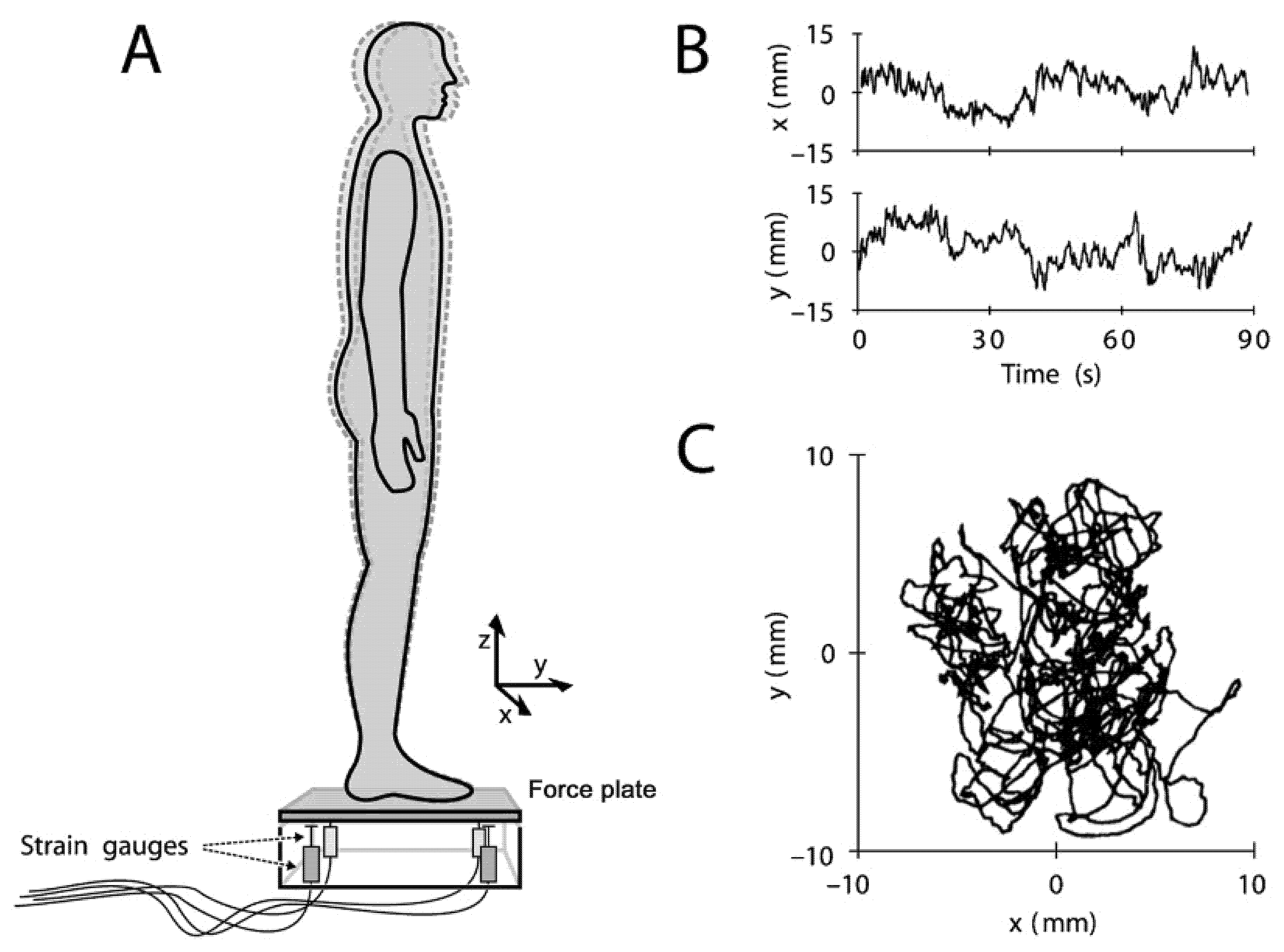
3. Center of Pressure (COP) and Center of Gravity (COG)
4. Standardization of Experimental Conditions for Balance Assessment
5. Common Parameters in Balance Measurement Based on the Force Plate
6. Discussion
7. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kemlin, C.; Verite, F.; Marchand-Pauvert, V.; Pradat, P.F.; Pradat-Diehl, P.; Giron, A.; Bachta, W. Closed-loop control of the centre of pressure in post-stroke patients with balance impairments. IEEE Trans. Neural Syst. Rehabil. Eng. 2019, 27, 265–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Martelli, D.; Vashista, V.; Micera, S.; Agrawal, S.K. Direction-dependent adaptation of dynamic gait stability following waist-pull perturbations. Trans. Neural Syst. Rehabil. Eng. 2016, 24, 1304–1313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montesinos, L.; Castaldo, R.; Pecchia, L. Wearable inertial sensors for fall risk assessment and prediction in older adults: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Trans. Neural Syst. Rehabil. Eng. 2018, 26, 573–582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nouredanesh, M.; Gordt, K.; Schwenk, M.; Tung, J. Automated detection of multidirectional compensatory balance reactions: A step towards tracking naturally occurring near falls. Trans. Neural Syst. Rehabil. Eng. 2020, 28, 478–487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- World Health Organization. Global Report on Falls Prevention in Older Age; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Peel, N.M. Epidemiology of falls in older age. Can. J. Aging Rev. Can. Vieil. 2011, 30, 7–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohtsu, H.; Yoshida, S.; Minamisawa, T.; Katagiri, N.; Yamaguchi, T.; Takahashi, T.; Yomogida, S.I.; Kanzaki, H. Does the balance strategy during walking in elderly persons show an association with fall risk assessment? J. Biomech. 2020, 103, 109657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rubenstein, L.Z.; Josephson, K.R. The epidemiology of falls and syncope. Clin. Geriatr. Med. 2002, 18, 141–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sibley, K.M.; Beauchamp, M.K.; Van Ooteghem, K.; Straus, S.E.; Jaglal, S.B. Using the systems framework for postural control to analyze the components of balance evaluated in standardized balance measures: A scoping review. Arch. Phys. Med. Rehabil. 2015, 96, 122–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tinetti, M.E.; Kumar, C. The Patient Who Falls. JAMA 2010, 303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, P.; Huang, S.; Feng, Y.; Chen, J.; Wang, Q.; Guo, Y.; Yuan, Q.; Yao, D.; Ma, D. Assessment of Balance Control Subsystems by Artificial Intelligence. IEEE Trans. Neural Syst. Rehabil. Eng. 2020, 28, 658–668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schut, I.M.; Pasma, J.H.; Veij Mestdagh, J.C.; Kooij, H.V.; Schouten, A.C. Effect of Amplitude and Number of Repetitions of the Perturbation on System Identification of Human Balance Control During Stance. IEEE Trans. Neural Syst. Rehabil. Eng. 2019, 27, 2336–2343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schneiders, A.; Gregory, K.; Karas, S.; Mundermann, A. Effect of foot position on balance ability in single-leg stance with and without visual feedback. J. Biomech. 2016, 49, 1969–1972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Montesinos, L.; Castaldo, R.; Cappuccio, F.P.; Pecchia, L. Day-to-day variations in sleep quality affect standing balance in healthy adults. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 17504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Browne, J.E.; O’Hare, N.J. Review of the Different Methods for Assessing Standing Balance. Physiotherapy 2001, 87, 489–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pizzigalli, L.; Micheletti Cremasco, M.; Mulasso, A.; Rainoldi, A. The contribution of postural balance analysis in older adult fallers: A narrative review. J. Bodyw. Mov. Ther. 2016, 20, 409–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garcia-Soidan, J.L.; Leiros-Rodriguez, R.; Romo-Perez, V.; Garcia-Lineira, J. Accelerometric Assessment of Postural Balance in Children: A Systematic Review. Diagnostics 2020, 11, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duarte, M.; Freitas, S. Revision of posturography based on force plate for balance evaluation. Rev. Bras. Fisioter. 2010, 14, 183–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kingma, H.; Gauchard, G.C.; de Waele, C.; van Nechel, C.; Bisdorff, A.; Yelnik, A.; Magnusson, M.; Perrin, P.P. Stocktaking on the development of posturography for clinical use. J. Vestib. Res. 2011, 21, 117–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horak, F.B. Postural orientation and equilibrium: What do we need to know about neural control of balance to prevent falls? Age Ageing 2006, 35, 7–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Gary, P.; Jacobson, N.T.S. Balance Function Assessment and Management; Plural Publishing: San Diego, CA, USA, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Horak, F.B.; Wrisley, D.M.; Frank, J. The Balance Evaluation Systems Test (BESTest) to differentiate balance deficits. Phys. Ther. 2009, 89, 484–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Winter, D. Human balance and posture control during standing and walking. Gait Posture 1995, 3, 193–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lafond, D.; Duarte, M.; Prince, F. Comparison of three methods to estimate the center of mass during balance assessment. J. Biomech. 2004, 37, 1421–1426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patti, A.; Bianco, A.; Sahin, N.; Sekulic, D.; Paoli, A.; Iovane, A.; Messina, G.; Gagey, P.M.; Palma, A. Postural control and balance in a cohort of healthy people living in Europe An observational study. Medicine 2018, 97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borrelli, J.; Komisar, V.; Novak, A.C.; Maki, B.E.; King, E.C. Extending the center of pressure to incorporate handhold forces: Derivation and sample application. J. Biomech. 2020, 104, 109727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klimiec, E.; Jasiewicz, B.; Piekarski, J.; Zaraska, K.; Guzdek, P.; Kołaszczyński, G. Measuring of foot plantar pressure—Possible applications in quantitative analysis of human body mobility. Meas. Sci. Technol. 2017, 28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prieto, T.E.; Myklebust, J.B.; Myklebust, B.M. Characterization and modeling of postural steadiness in the elderly: A review. IEEE Trans. Rehabil. Eng. 1993, 1, 26–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, M.G.; Moreira, P.V.S.; Rocha, H.M. Development of a low cost force platform for biomechanical parameters analysis. Res. Biomed. Eng. 2017, 33, 259–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Richmond, S.B.; Dames, K.D.; Goble, D.J.; Fling, B.W. Leveling the playing field: Evaluation of a portable instrument for quantifying balance performance. J. Biomech. 2018, 75, 102–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bastiaan, R.; Bloema, J.E.; Visser, H.J.; Allum, J. Posturography; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Zulkifli, S.S.; Loh, W.P. A state-of-the-art review of foot pressure. Foot Ankle Surg. 2020, 26, 25–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Winter, D.A. Biomechanics and Motor Control of Human Movement; John and Wiley: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Paillard, T.; Noé, F. Techniques and Methods for Testing the Postural Function in Healthy and Pathological Subjects. BioMed. Res. Int. 2015, 2015, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Dewan, B.M.; Roger James, C.; Kumar, N.A.; Sawyer, S.F. Kinematic Validation of Postural Sway Measured by Biodex Biosway (Force Plate) and SWAY Balance (Accelerometer) Technology. BioMed. Res. Int. 2019, 2019, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hof, A.L. Comparison of three methods to estimate the center of mass during balance assessment. J. Biomech. 2005, 38, 2134–2135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mansfield, A.; Inness, E.L. Force Plate Assessment of Quiet Standing Balance Control: Perspectives on Clinical Application within Stroke Rehabilitation. Rehabil. Process Outcome 2015, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Matjacic, Z.; Sok, D.; Jakovljevic, M.; Cikajlo, I. Organization of functional postural responses following perturbations in multiple directions in elderly fallers standing quietly. Int. J. Rehabil. Res. 2013, 36, 68–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ku, P.X.; Abu Osman, N.A.; Yusof, A.; Wan Abas, W.A. The effect on human balance of standing with toe-extension. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e41539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weaver, T.B.; Glinka, M.N.; Laing, A.C. Stooping, crouching, and standing-Characterizing balance control strategies across postures. J. Biomech. 2017, 53, 90–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wieslaw Blaszczyk, J.; Fredyk, A.; Mikolaj Blaszczyk, P. Transition from double-leg to single-leg stance in the assessment of postural stability. J. Biomech. 2020, 110, 109982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dingenen, B.; Staes, F.F.; Janssens, L. A new method to analyze postural stability during a transition task from double-leg stance to single-leg stance. J. Biomech. 2013, 46, 2213–2219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cappa, F.P.A.P. A 3-DOF Parallel Robot with Spherical Motion for the Rehabilitation and Evaluation of Balance Performance. IEEE Trans. Neural Syst. Rehabil. Eng. 2011, 19, 157–166. [Google Scholar]
- Chiba, R.; Takakusaki, K.; Ota, J.; Yozu, A.; Haga, N. Human upright posture control models based on multisensory inputs; in fast and slow dynamics. Neurosci. Res. 2016, 104, 96–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Winter, D.A.; Patla, A.E.; Ishac, M.; Gage, W.H. Motor mechanisms of balance during quiet standing. J. Electromyogr. Kinesiol. 2003, 13, 49–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rougier, P.R. Relative contribution of the pressure variations under the feet and body weight distribution over both legs in the control of upright stance. J. Biomech. 2007, 40, 2477–2482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eysel-Gosepath, K.; McCrum, C.; Epro, G.; Brueggemann, G.-P.; Karamanidis, K. Visual and proprioceptive contributions to postural control of upright stance in unilateral vestibulopathy. Somatosens. Motor Res. 2016, 33, 72–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scoppa, F.; Capra, R.; Gallamini, M.; Shiffer, R. Clinical stabilometry standardization Basic definitions-Acquisition interval-Sampling frequency. Gait Posture 2013, 37, 290–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duarte, M.; Harvey, W.; Zatsiorsky, V. Stabilographic analysis of unconstrained standing. Ergonomics 2000, 43, 1824–1839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freitas, S.; Wieczorek, S.A.; Marchetti, P.H.; Duarte, M. Age-related changes in human postural control of prolonged standing. Gait Posture 2005, 22, 322–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lafond, D.; Champagne, A.; Descarreaux, M.; Dubois, J.D.; Prado, J.M.; Duarte, M. Postural control during prolonged standing in persons with chronic low back pain. Gait Posture 2009, 29, 421–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fujimoto, M.; Bair, W.-N.; Rogers, M.W. Center of pressure control for balance maintenance during lateral waist-pull perturbations in older adults. J. Biomech. 2015, 48, 963–968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Chang, C.-J.; Chern, J.-S.; Yang, T.-F.; Yang, S.-W. Age-Related Changes in Postural Re-Balanced Ability during a Continuous and Unexpected Perturbation Integrated with Virtual Reality Scenes. Biomed. Eng. Appl. Basis Commun. 2016, 28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiari, L.; Rocchi, L.; Cappello, A. Stabilometric parameters are affected by anthropometry and foot placement. Clin. Biomech. 2002, 17, 666–677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rocchi, L.; Chiari, L.; Mancini, M.; Carlson-Kuhta, P.; Gross, A.; Horak, F.B. Step initiation in Parkinson’s disease: Influence of initial stance conditions. Neurosci. Lett. 2006, 406, 128–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Palmisano, C.; Todisco, M.; Marotta, G.; Volkmann, J.; Pacchetti, C.; Frigo, C.A.; Pezzoli, G.; Isaias, I.U. Gait initiation in progressive supranuclear palsy: Brain metabolic correlates. Neuroimage Clin. 2020, 28, 102408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, C.J.; Yang, T.F.; Yang, S.W.; Chern, J.S. Cortical Modulation of Motor Control Biofeedback among the Elderly with High Fall Risk during a Posture Perturbation Task with Augmented Reality. Front Aging Neurosci. 2016, 8, 80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kharboutly, H.; Ma, J.; Benali, A.; Thoumie, P.; Pasqui, V.; Bouzit, M. Design of Multiple Axis Robotic Platform for Postural Stability Analysis. IEEE Trans. Neural Syst. Rehabil. Eng. 2015, 23, 93–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Engelhart, D.; Schouten, A.C.; Aarts, R.G.; van der Kooij, H. Assessment of Multi-Joint Coordination and Adaptation in Standing Balance: A Novel Device and System Identification Technique. IEEE Trans. Neural Syst. Rehabil. Eng. 2015, 23, 973–982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hur, P.; Pan, Y.T.; DeBuys, C. Free Energy Principle in Human Postural Control System: Skin Stretch Feedback Reduces the Entropy. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 16870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sozzi, S.; Crisafulli, O.; Schieppati, M. Haptic Cues for Balance: Use of a Cane Provides Immediate Body Stabilization. Front. Neurosci. 2017, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.-G.; Kim, J.-H.; Do, K.-S.; Yim, J. Effect of light touch on body sway during a stable posture with blocked visual information. Phys. Ther. Rehabil. Sci. 2016, 5, 138–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Prado, J.M.; Stoffregen, T.A.; Duarte, M. Postural Sway during Dual Tasks in Young and Elderly Adults. Gerontology 2007, 53, 274–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blaszczyk, J.W. The use of force-plate posturography in the assessment of postural instability. Gait Posture 2016, 44, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blaszczyk, J.W.; Beck, M.; Szczepanska, J.; Sadowska, D.; Bacik, B.; Juras, G.; Slomka, K.J. Directional Measures of Postural Sway as Predictors of Balance Instability and Accidental Falls. J. Hum. Kinet. 2016, 52, 75–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Roerdink, M.; De Haart, M.; Daffertshofer, A.; Donker, S.F.; Geurts, A.C.; Beek, P.J. Dynamical structure of center-of-pressure trajectories in patients recovering from stroke. Exp. Brain Res. 2006, 174, 256–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Baltich, J.; von Tscharner, V.; Zandiyeh, P.; Nigg, B.M. Quantification and reliability of center of pressure movement during balance tasks of varying difficulty. Gait Posture 2014, 40, 327–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prieto, T.E.; Myklebust, J.B.; Hoffmann, R.G.; Lovett, E.G.; Myklebust, B.M. Measures of postural steadiness: Differences between healthy young and elderly adults. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 1996, 43, 956–966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Valle, M.S.; Casabona, A.; Fiumara, A.; Castiglione, D.; Sorge, G.; Cioni, M. Quantitative analysis of upright standing in adults with late-onset Pompe disease. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 37040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Masani, K.; Vette, A.H.; Abe, M.O.; Nakazawa, K. Center of pressure velocity reflects body acceleration rather than body velocity during quiet standing. Gait Posture 2014, 39, 946–952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mansfield, A.; Wong, J.S.; McIlroy, W.E.; Biasin, L.; Brunton, K.; Bayley, M.; Inness, E.L. Do measures of reactive balance control predict falls in people with stroke returning to the community? Physiotherapy 2015, 101, 373–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rougier, P.R.; Genthon, N. Dynamical assessment of weight-bearing asymmetry during upright quiet stance in humans. Gait Posture 2009, 29, 437–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Richman, J.S.; Moorman, J.R. Physiological time-series analysis using approximate entropy and sample entropy. American journal of physiology. Heart Circ. Physiol. 2000, 278, H2039–H2049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hunt, C.M.; Widener, G.; Allen, D.D. Variability in Postural Control with and without Balance-Based Torso-Weighting in People with Multiple Sclerosis and Healthy Controls. Phys. Ther. 2014, 94, 1489–1498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Huisinga, J.M.; Yentes, J.M.; Filipi, M.L.; Stergiou, N. Postural control strategy during standing is altered in patients with multiple sclerosis. Neurosci. Lett. 2012, 524, 124–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mani, H.; Hsiao, S.F.; Konishi, T.; Izumi, T.; Tsuda, A.; Hasegawa, N.; Takeda, K.; Colley, N.; Asaka, T. Adaptation of postural control while standing on a narrow unfixed base of support. Int. J. Rehabil. Res. 2016, 39, 92–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kovacikova, Z.; Zemkova, E.; Neumannova, K.; Jelen, M.; Jelen, K.; Janura, M. The role of lateral preference of lower limbs in a postural stabilization task. Neuroendocrinol. Lett. 2015, 36, 91–95. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Freyler, K.; Gollhofer, A.; Colin, R.; Bruederlin, U.; Ritzmann, R. Reactive Balance Control in Response to Perturbation in Unilateral Stance: Interaction Effects of Direction, Displacement and Velocity on Compensatory Neuromuscular and Kinematic Responses. PLoS ONE 2015, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rinaldin, C.D.P.; Avila de Oliveira, J.; Coelho, D.B.; Scheeren, E.M.; Teixeira, L.A. Instantaneous interjoint rescaling and adaptation to balance perturbation under muscular fatigue. Eur. J. Neurosci. 2020, 51, 1478–1490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neptune, R.; Vistamehr, A. Dynamic Balance during Human Movement: Measurement and Control Mechanisms. J. Biomech. Eng. 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Negahban, H.; Mazaheri, M.; Kingma, I.; van Dieen, J.H. A systematic review of postural control during single-leg stance in patients with untreated anterior cruciate ligament injury. Knee Surg. Sports Traumatol. Arthrosc. 2014, 22, 1491–1504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- dos Santos, M.J.; Gorges, A.L.; Rios, J.L. Individuals with chronic ankle instability exhibit decreased postural sway while kicking in a single-leg stance. Gait Posture 2014, 40, 231–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berg, K.O.; Wood-Dauphinee, S.L.; Williams, J.I.; Maki, B. Measuring balance in the elderly: Validation of an instrument. Can. J. Public Health 1992, 83 (Suppl. S2), S7–S11. [Google Scholar]
- Tinetti, M.E. Performance-oriented assessment of mobility problems in elderly patients. J. Am. Geriatr. Soc. 1986, 34, 119–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shumway-Cook, A.; Baldwin, M.; Polissar, N.L.; Gruber, W. Predicting the probability for falls in community-dwelling older adults. Phys. Ther. 1997, 77, 812–819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Korner-Bitensky, N.; Wood-Dauphinee, S.; Teasell, R.; Desrosiers, J.; Malouin, F.; Thomas, A.; Harrison, M.; Hanley, J.; Kaizer, F.; Kehayia, E.; et al. Best versus actual practices in stroke rehabilitation: Results of the Canadian national survey. Stroke 2006, 37, 631. [Google Scholar]
- Dibble, L.E.; Lange, M. Predicting falls in individuals with Parkinson disease: A reconsideration of clinical balance measures. J. Neurol. Phys. Ther. 2006, 30, 60–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cattaneo, D.; Regola, A.; Meotti, M. Validity of six balance disorders scales in persons with multiple sclerosis. Disabil. Rehabil. 2006, 28, 789–795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Whitney, S.L.; Hudak, M.T.; Marchetti, G.F. The dynamic gait index relates to self-reported fall history in individuals with vestibular dysfunction. J. Vestib. Res. Equilib. Orientat. 2000, 10, 99–105. [Google Scholar]
- Harro, C.C.; Garascia, C. Reliability and Validity of Computerized Force Platform Measures of Balance Function in Healthy Older Adults. J. Geriatr. Phys. Ther. 2019, 42, E57–E66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Visser, J.E.; Carpenter, M.G.; van der Kooij, H.; Bloem, B.R. The clinical utility of posturography. Clin. Neurophysiol. 2008, 119, 2424–2436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levy, S.S.; Thralls, K.J.; Kviatkovsky, S.A. Validity and Reliability of a Portable Balance Tracking System, BTrackS, in Older Adults. J. Geriatr. Phys. Ther. 2018, 41, 102–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cretual, A. Which biomechanical models are currently used in standing posture analysis? Neurophysiol. Clin. Clin. Neurophysiol. 2015, 45, 285–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mansfield, A.; Danells, C.J.; Inness, E.; Mochizuki, G.; McIlroy, W.E. Between-limb synchronization for control of standing balance in individuals with stroke. Clin. Biomech. 2011, 26, 312–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Venkadesan, M.; Yawar, A.; Eng, C.M.; Dias, M.A.; Singh, D.K.; Tommasini, S.M.; Haims, A.H.; Bandi, M.M.; Mandre, S. Stiffness of the human foot and evolution of the transverse arch. Nature 2020, 579, 97–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Salathe, E.P.; Arangio, G.A. A biomechanical model of the foot: The role of muscles, tendons, and ligaments. J. Biomech. Eng. 2002, 124, 281–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McIlroy, W.E.; Maki, B.E. Preferred placement of the feet during quiet stance: Development of a standardized foot placement for balance testing. Clin. Biomech. 1997, 12, 66–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leal-Junior, A.G.; Díaz, C.R.; Marques, C.; Pontes, M.J.; Frizera, A. 3D-printed POF insole: Development and applications of a low-cost, highly customizable device for plantar pressure and ground reaction forces monitoring. Opt. Laser Technol. 2019, 116, 256–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaudhry, H.; Bukiet, B.; Ji, Z.; Findley, T. Measurement of balance in computer posturography: Comparison of methods—A brief review. J. Bodyw. Mov. Ther. 2011, 15, 82–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Blaszczyk, J.W. Sway ratio-A new measure for quantifying postural stability. Acta Neurobiol. Exp. 2008, 68, 51–57. [Google Scholar]
- Blaszczyk, J.W.; Orawiec, R. Assessment of postural control in patients with Parkinson’s disease: Sway ratio analysis. Hum. Mov. Sci. 2011, 30, 396–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Piirtola, M.; Era, P. Force platform measurements as predictors of falls among older people—A review. Gerontology 2006, 52, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chen, B.; Liu, P.; Xiao, F.; Liu, Z.; Wang, Y. Review of the Upright Balance Assessment Based on the Force Plate. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 2696. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph18052696
Chen B, Liu P, Xiao F, Liu Z, Wang Y. Review of the Upright Balance Assessment Based on the Force Plate. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health. 2021; 18(5):2696. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph18052696
Chicago/Turabian StyleChen, Baoliang, Peng Liu, Feiyun Xiao, Zhengshi Liu, and Yong Wang. 2021. "Review of the Upright Balance Assessment Based on the Force Plate" International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health 18, no. 5: 2696. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph18052696
APA StyleChen, B., Liu, P., Xiao, F., Liu, Z., & Wang, Y. (2021). Review of the Upright Balance Assessment Based on the Force Plate. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 18(5), 2696. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph18052696





