Nephrogenic Systemic Fibrosis as a Complication after Gadolinium-Containing Contrast Agents: A Rapid Review
Abstract
1. Introduction
1.1. Contrast Agents Used for Magnetic Resonance Imaging
1.2. Aim
2. Methods
2.1. Study Design
2.2. Definition of a Rapid Review
2.3. Search Strategy
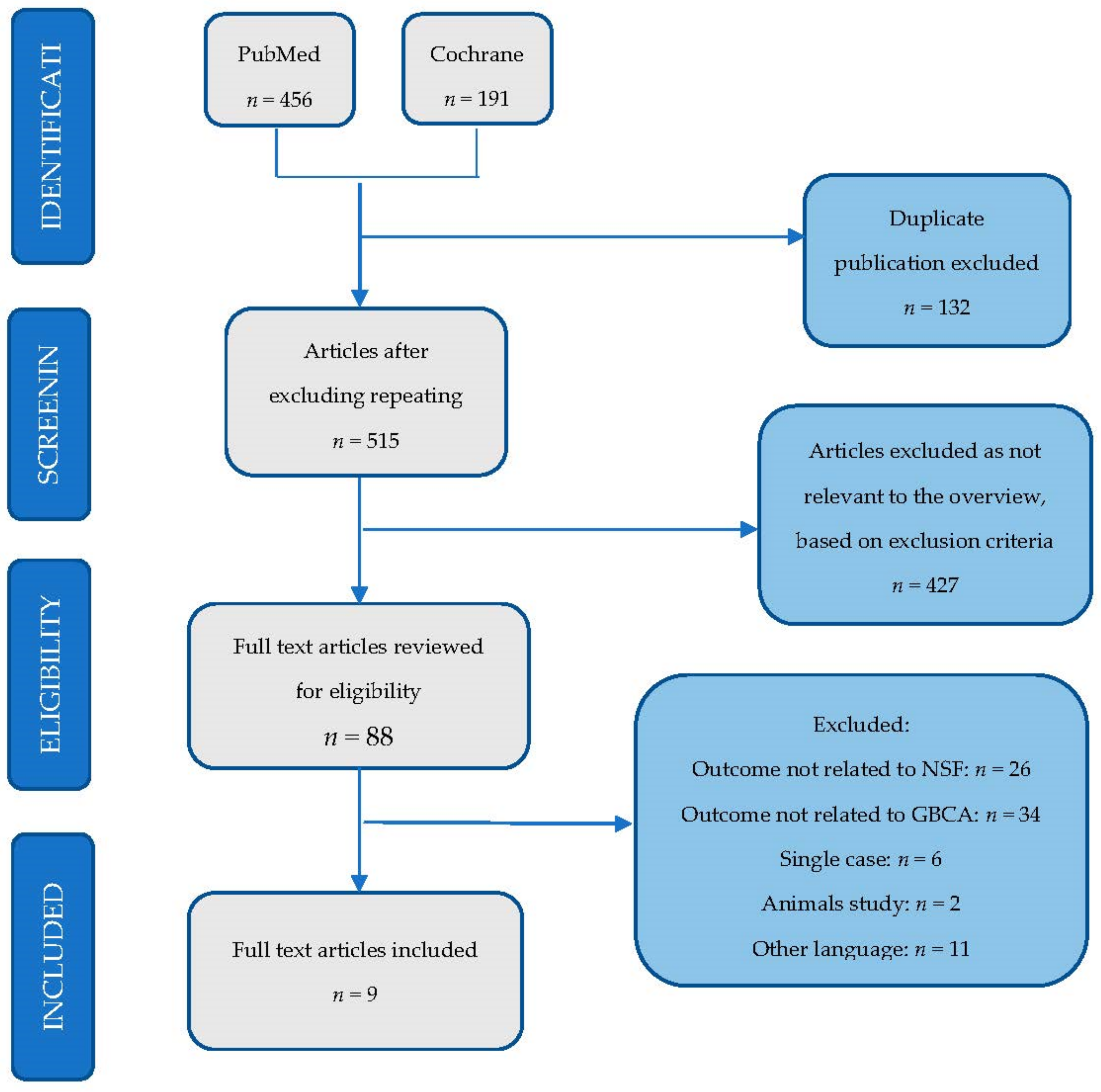
2.4. Study Selection
2.5. Screening Process
2.6. Data Extraction
3. Results
3.1. Demographic and Social Data
3.2. Dialysis
3.3. Contrast Agents, Duration of NSF Symptoms
3.4. Other Potential Risk Factors of NSF
4. Discussion
5. A Limitation of the Systematic Review
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Cowper, S.E.; Robin, H.S.; Steinberg, S.M.; Su, L.D.; Gupta, S.; LeBoit, P.E. Scleromyxoedema-like cutaneous diseases in renal-dialysis patients. Lancet 2000, 356, 1000–1001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhave, G.; Lewis, J.B.; Chang, S.S. Association of gadolinium based magnetic resonance imaging contrast agents and nephrogenic systemic fibrosis. J. Urol. 2008, 180, 830–835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deo, A.; Fogel, M.; Cowper, S. Nephrogenic Sysyemic Fibrosis: A Population Study Examining the Relationship of Disease Development to Gadolinium Exposure. Clin. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2007, 2, 264–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nainani, N.; Panesar, M. Nephrogenic Systemic Fibrosis. Am. J. Nephrol. 2009, 29, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grobner, T. Gadolinium—A specific trigger for the development of nephrogenic fibrosing dermopathy and nephrogenic systemic fibrosis? Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 2006, 21, 1104–1108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shah, A.H.; Olivero, J.J. Gadolinium-Induced Nephrogenic Systemic Fibrosis. Methodist DeBakey Cardiovasc. J. 2017, 3, 172–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tood, D.; Kagan, A.; Chibnik, L.; Kay, J. Cutaneous Changes of Nephrogenic Systemic Fibrosis. Predictor of Early Mortality and Association with Gadolinium Exposure. Arthritis Rheum. 2007, 56, 3433–3441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marckmann, P.; Skov, L.; Rossen, K.; Heal, G.J.; Thomsen, H.S. Case-control study of gadodiamide-related nephrogenic systemic fibrosis. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 2007, 22, 3174–3178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- High, W.A.; Ayers, R.A.; Chandler, J.; Zito, G.; Cowper, S.E. Gadolinium is detectable within the tissue of patients with nephrogenic systemic fibrosis. J. Am. Acad. Dermatol. 2007, 56, 21–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuo, P.H.; Kanal, E.; Abu-Alfa, A.K.; Cowper, S.E. Gadolinium-based MR contrast agents and nephrogenic systemic fibrosis. Radiology 2007, 242, 647–649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boyd, A.S.; Zic, J.A.; Abraham, J.L. Gadolinium deposition in nephrogenic fibrosing dermopathy. J. Am. Acad. Dermatol. 2007, 56, 27–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saitoh, T.; Hayasaka, K.; Tanaka, Y.; Kuno, T.; Nagura, Y. Dialyzability of gadodiamide in hemodialysis patients. Radiat. Med. 2006, 24, 445–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomsen, H.S.; Marckmann, P.; Logager, B. Nephrogenic systemic fibrosis (NSF): A late adverse reaction to some of the gadolinium based contrast agents. Cancer Imaging 2007, 7, 130–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Caravan, P.; Ellison, J.J.; McMurry, T.J.; Lauffer, R.B. Gadolinium (III) chelates as MRI contrast agents: Structure, dynamics, and applications. Chem. Rev. 1999, 99, 2293–2352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmitt-Willich, H. Stability of linear and macrocyclic gadolinium based contrast agents. Br. J. Radiol. 2007, 80, 581–582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Broome, D.R.; Girgius, M.; Baron, P.; Cottrel, A.; Kjellin, I.; Kirk, G. Gadodiamide-associated nephrogenic systemic fibrosis; Why radiologists ahould be concered. Am. J. Roentgenol. 2007, 188, 586–592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- FDA Drug Safety Communication: New Warnings for Using Gadolinium-Based Contrast Agents in Patients with Kidney Dysfunction. Available online: https://www.fda.gov/drugs/drug-safety-and-availability/fda-drug-safety-communication-new-warnings-using-gadolinium-based-contrast-agents-patients-kidney (accessed on 15 December 2020).
- Gadolinium-Containing Contrast Agents. Available online: https://www.ema.europa.eu/en/documents/referral/gadolinium-article-31-referral-emas-final-opinion-confirms-restrictions-use-linear-gadolinium-agents_en.pdf (accessed on 30 December 2020).
- Weinreb, J.C.; Rodby, R.A.; Jerry Yee, J.; Wang, C.L.; Fine, D.; McDonald, R.J.; Perazella, M.A.; Dillman, J.R.; Davenport, M.S. Use of Intravenous Gadolinium-Based Contrast Media in Patients with Kidney Disease: Consensus Statements from the American College of Radiology and the National Kidney Foundation. Kidney Med. 2021, 3, 142–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rapid Review Protocol. Available online: https://guides.library.vcu.edu/rapidreview#s-lg-box-4862777 (accessed on 25 January 2021).
- Stang, A. Critical evaluation of the Newcastle-Ottawa scale for the assessment of the quality of nonrandomized studies in meta-analyses. Eur. J. Epidemiol. 2010, 25, 603–605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marcmann, P.; Skov, L.; Rossen, K.; Dupont, A.; Damholt, M.B.; Heaf, A.G.; Thomsen, H.S. Nephrogenic Systemic Fibrosis: Suspected Causative Role of Gadodiamide Used for Contrast-Enhanced Magnetic Resonance Imaging. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2006, 17, 2359–2362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Golding, L.P.; Provenzale, J.M. Nephrogenic Systrmic Fibrosis: Possible Association with a Predisposing Infection. Am. J. Roentgenol. 2008, 190, 1069–1075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perez-Rodriguez, J.; Lai, S.; Ehst, B.D.; Fine, D.M.; Bluemke, D.A. Incidence, Associations, and Effect of Risk Factor Assessment-Raport of 33 Cases. Radiology 2009, 250, 371–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elmholdt, T.; Olesen, A.; Jørgensen, B.; Kvist, S.; Skov, L.; Thomsen, H.; Marckmann, P.; Pedersen, M. Nephrogenic Systemic Fibrosis in Benmark-A Nationwiden Investition. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e82037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Becker, S.; Walter, S.; Witzke, O.; Wilde, B.; Hillen, U.; Napieralski, D.; Kreuter, A.; Altmeyer, P.; Schieren, G.; Daul, A.; et al. The German registry for nephrogenic systemic fibrosis: Finding from 23 patients. Clin. Nephrol. 2010, 73, 426–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Othersen, J.B.; Maize, J.C.; Woolson, R.F.; Budisavljevic, M.N. Nephrogenic systemic fibrosis after exposure to gadolinium in patients with renal failure. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 2007, 22, 3179–3185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shea, B.J.; Reeves, B.C.; Wells, G.; Thuku, M.; Hamel, C.; Moran, J.; Moher, D.; Tugwell, P.; Welch, V.; Kristjansson, E.; et al. AMSTAR 2: A critical appraisal tool for systematic reviews that include randomised or non-randomised studies of healthcare interventions, or both. BMJ 2017, 358, j4008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rudnick, M.R.; Wahba, I.M.; Leonberg-Yoo, A.K.; Miskulin, D.; Litt, H.I. Risks and Options with Gadolinium-Based Contrast Agents in Patients with CKD: A Review. Am. J. Kidney Dis. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weigle, J.P.; Broome, B.R. Nephrogenic systemic fibrosis: Chronic imaging findings and review of the medical literature. Skelet. Radiol. 2008, 37, 457–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dharnidharka, V.R.; Wesson, S.K.; Fennell, R.S. Gadolinium and nephrogenic fibrosing dermopathy in pediatric patients. Pediatr. Nephrol. 2006, 22, 1395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swaminathan, S.; Ahmed, I.; McCarthy, J.T.; Albright, R.C.; Pittelkow, M.R.; Caplice, N.M.; Griffin, M.D.; Ne Leung, N. Nephrogenic fibrosing dermopathy and high-dose erythropoietin therapy. Ann. Intern. Med. 2006, 145, 234–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Idee, J.M.; Port, M.; Raynal, I.; Schaefer, M.; Greneur, S.L.; Corot, C. Clinical and biological consequences of transmetallation induced by contrast agents for magnetic resonance imaging: A review. Fundam. Clin. Pharmacol. 2006, 20, 563–576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ACR Committee on Drugs and Contrast Media. ACR Manual on Contrast Media, Version 10.3 June 2018. Available online: https://www.acr.org/-/media/ACR/Files/Clinical-Resources/Contrast_Media.pdf (accessed on 29 January 2021).
- FDA Adverse Events Reporting System (FAERS) Public Dashboard. Nephrogenic Systemic Fibrosis. Available online: https://fis.fda.gov (accessed on 7 March 2021).
- Schieren, G.; Tokmak, F.; Lefringhausen, L.; van Bracht, M.; Perings, C.; Willers, R.; Günsel, A.; Kemper, F.; Wiesmüller, G.A.; Rump, L.C. C-reactive protein levels and clinical sumptoms following gadolinium administratio in hemodialysis patients. Am. J. Kidney Dis 2008, 51, 976–986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kitajima, K.; Maeda, T.; Watanabe, S.; Ueno, Y.; Sugimura, K. Recent topics related to nephrogenic systemic fibrosis associated with gadolinium-based contrast agents. Int. J. Urol. 2012, 19, 806–811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Attari, H.; Cao, Y.; Elmholdt, T.R.; Zhao, Y.; Prince, M.R. A Systematic Review of 639 Patients with Biopsy-confirmed Nephrogenic Systemic Fibrosis. Radiology 2019, 292, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woolen, S.A.; Shankar, P.R.; Gagnier, J.J.; MacEachern, M.P.; Singer, L.; Davenport, M.S. Risk of Nephrogenic Systemic Fibrosis in Patients with Stage 4 or 5 Chronic Kidney Disease Receiving a Group II Gadolinium-Based Contrast Agent: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis. JAMA Intern. Med. 2020, 180, 223–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Trade Name | Generic Name | Chemical Structure | Charge | Elimination Way | Risk of NSF * | ACR Classification of GBCA ** |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Omniscan ® | Gadodiamide | Linear | Nonionic | Kidney | High | Group I |
| OptiMARK ® | Gadoversetamide | Linear | Nonionic | Kidney | High | Group I |
| Magnevist ® | Gadopentetate dimeglumine | Linear | Ionic | Kidney | High | Group I |
| MultiHance ® | Gadobenate dimeglumine | Linear | Ionic | 97% Kidney 3% Bile | Medium | Group II |
| Primovist ® | Gadoxetate disodium | Linear | Ionic | 50% Kidney 50% Bile | Medium | Group III |
| Dotarem ® | Gadoterate meglumine | Cyclic | Ionic | Kidney | Low | Group II |
| ProHance ® | Gadoteridol | Cyclic | Nonionic | Kidney | Low | Group II |
| Gadovist ® | Gadobutrol | Cyclic | Nonionic | Kidney | Low | Group II |
| Databases Used | PubMed 1 | Cochrane Library 1 | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Strategies Used | Indexed Search Terms | Free Text Words | Combination of Free Text Words and Indexed Terms | Indexed Search Terms | Free Text Words | Combination of Free Text Words and Indexed Terms |
| Participant/Patient 2 | “Renal failure” (MeSH) | Renal failure | Renal failure | MeSH descriptor: (renal failure) | Renal failure | MeSH descriptor: (renal failure) * Renal failure |
| Intervention 3 | “Gadolinium” (MeSH) | Contrast medium, *MRI | Gadolinium Contrast medium, MRI | MeSH descriptor: (gadolinium) | Contrast medium, MRI | MeSH descriptor: (gadolinium) Contrast medium, * MRI |
| Comparison 4 | “nephrogenic systemic fibrosis” (MeSH) | NSF | Nephrogenic systemic fibrosis *NSF | MeSH descriptor: (nephrogenic systemic fibrosis) | NSF | MeSH descriptor: (nephrogenic systemic fibrosis) NSF |
| Number of Systematic Review Retrieved | 3 | 36 | 39 | 1 | 21 | 26 |
| Articles Chosen after Title Screening | 2 | 12 | 15 | 1 | 3 | 6 |
| Articles Chosen after Abstract Screening | 1 | 3 | 6 | 1 | 2 | 3 |
| First Author, Year | Study Design | Selection | Comparability | Exposure/Outcome | Total Scores |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Deo A. et al., 2007 [3] | Retrospective cohort study | *** | * | *** | 7 |
| Grobner T et al., 2006 [5] | Observational cohort study | *** | ** | ** | 7 |
| Marckmann P. et al., 2006 [8] | Retrospective cohort study | *** | * | *** | 7 |
| Marckmann P. et al., 2007 [22] | Case–control studies | *** | ** | *** | 8 |
| Golding L.P. et al., 2007 [23] | Observational cohort study | *** | ** | ** | 7 |
| Perez-Rodrigue J. et al., 2009 [24] | Retrospective cohort study | ** | * | *** | 6 |
| Elmholdt T. et al., 2013 [25] | Retrospective cohort study | *** | ** | ** | 7 |
| Becker S. et al., 2010 [26] | Retrospective cohort study | *** | ** | ** | 7 |
| Othersen J. et al., 2007 [27] | Observational cohort study | *** | * | *** | 7 |
| Deo A. et al., 2007 [3] | Grobner T et al., 2006 [5] | Marckmann P. et al., 2006 [8] | Marckmann P. et al., 2007 [22] | Golding LP. et al., 2007 [23] | Perez-Rodrigue J. et al., 2009 [24] | Elmholdt T. et al., 2013 [25] | Becker S., et al., 2010 [26] | Othersen J. et al., 2007 [27] | Total, N (%) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| (1) Question and Inclusion | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | 9(100%) |
| (2) Protocol | No | No | No | No | No | No | No | No | No | 0(0%) |
| (3) Study Design | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | 9(100%) |
| (4) Comprehensive Search | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | 9(100%) |
| (5) Study Selection | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | 9(100%) |
| (6) Data Extraction | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | 9(100%) |
| (7) Excluded Studies Justification | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | 9(100%) |
| (8) Included Studies Details | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | 9(100%) |
| (9) Risk of Bias (RoB) | No | No | No | No | No | No | No | No | No | 0(0%) |
| (10) Funding Sources | No | No | No | No | No | No | No | No | No | 0(0%) |
| (11) Statistical Methods | Yes | No | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | No | No | Yes | 6(67%) |
| (12) RoB on Meta-Analysis | No | No | No | No | Yes | No | No | No | No | 1(11%) |
| (13) RoB in Individual Studies | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | 9(100%) |
| (14) Explanation for Heterogeneity | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | 9(100%) |
| (15) Publication Bias | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | 9(100%) |
| (16) Conflict of Interest | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | 9(100%) |
| First Author, Year | Number of NSF Cases | Average Age | Treatment of Kidney Disease | Contrast Agent | Amount of Contrast Agent | Time of Occurrence of NSF Symptoms from Exposure (Days) | Other Potential Factors |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Deo A. et al., 2007 [3] | 3 | 60 | 3, dialysis | Omniscan Magnevist | 20–125 mL | 60 | - |
| Grobner T et al., 2006 [5] | 5 | 57 | 5, dialysis | Magnevist | 16.3–20.7 mmol/L | 14–28 | Metabolic acidosis |
| Marckmann P. et al., 2006 [8] | 13 | 50 | 8, dialysis 5, no dialysis | Omniscan | 9–25 mmol/L | 2–75 | - |
| Marckmann P. et al., 2007 [22] | 19 | 52 | 7, dialysis 7, no dialysis | Omniscan | 0.18–0.50 mmol/kg | No data | Higher doses of erythropoietin; higher serum concentrations of ionized calcium and phosphate |
| Golding LP. et al., 2007 [23] | 7 | 56 | 6, dialysis 1, no dialysis | Omniscan | 0.10–0.32 mmol/kg | 2–150 | Infection |
| Perez-Rodrigue J. et al., 2009 [24] | 33 | 49 | 25, dialysis 8, no dialysis | Omniscan Magnevist | 12–80 mL | 14–112 | - |
| Elmholdt T. et al., 2013 [25] | 65 | 53 | 44, dialysis 16, no dialysis 5, no data | Omniscan Magnevist Dotarem Gadovist Multihance | 31.5 mL | No data | - |
| Becker S. et al., 2010 [26] | 23 | 61 | 21, dialysis 2, dialysis | Omniscan Magnevist Gadovist | No data | 1 days–3 years | Infection |
| Othersen J. et al., 2007 [27] | 5 | No data | 5, dialysis | Omniscan Magnevist Multihance | 7.5–10 mmol | 60–90 | - |
| First Author, Year | Country | Gender | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Females | Males | No Description | ||
| Deo A. et al., 2007 [3] | USA | 1 | 2 | - |
| Grobner T. et al., 2006 [5] | Austria | 3 | 2 | - |
| Marckmann P. et al., 2006 [8] | Denmark | 8 | 5 | - |
| Marckmann P. et al., 2007 [22] | Denmark | 10 | 9 | - |
| Golding L.P. et al., 2007 [23] | USA | - | - | 7 |
| Perez-Rodrigue J. et al., 2009 [24] | USA | 13 | 20 | - |
| Elmholdt T. et al., 2013 [25] | Denmark | 28 | 37 | - |
| Becker S. et al., 2010 [26] | Germany | 11 | 12 | - |
| Othersen J. et al., 2007 [27] | USA | - | - | 5 |
| Total | 74 | 87 | 12 | |
| 173 | ||||
| First Author, Year | Number of NSF Cases | Type of Dialysis | Conservative Treatment | Not Recorded | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Hemodialysis | Peritoneal Dialysis | Not Described | ||||
| Deo A. et al., 2007 [3] | 3 | - | - | 3 | 0 | - |
| Grobner T. et al., 2006 [5] | 5 | 5 | 0 | - | 0 | - |
| Marckmann P. et al., 2006 [8] | 13 | 7 | 1 | - | 5 | - |
| Marckmann P. et.al., 2007 [22] | 19 | 9 | 3 | - | 7 | - |
| Golding L.P. et.al., 2007 [23] | 7 | 6 | 0 | - | 1 | - |
| Perez-Rodrigue J. et al., 2009 [24] | 33 | 20 | 5 | - | 8 | - |
| Elmholdt T. et al., 2013 [25] | 65 | - | - | 44 | 16 | 5 |
| Becker S. et al., 2010 [26] | 23 | 21 | 1 | - | 1 | - |
| Othersen J. et al., 2007 [27] | 5 | 3 | 2 | - | 0 | - |
| Total | 71 | 12 | 47 | 38 | 5 | |
| 173 | ||||||
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lange, S.; Mędrzycka-Dąbrowska, W.; Zorena, K.; Dąbrowski, S.; Ślęzak, D.; Malecka-Dubiela, A.; Rutkowski, P. Nephrogenic Systemic Fibrosis as a Complication after Gadolinium-Containing Contrast Agents: A Rapid Review. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 3000. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph18063000
Lange S, Mędrzycka-Dąbrowska W, Zorena K, Dąbrowski S, Ślęzak D, Malecka-Dubiela A, Rutkowski P. Nephrogenic Systemic Fibrosis as a Complication after Gadolinium-Containing Contrast Agents: A Rapid Review. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health. 2021; 18(6):3000. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph18063000
Chicago/Turabian StyleLange, Sandra, Wioletta Mędrzycka-Dąbrowska, Katarzyna Zorena, Sebastian Dąbrowski, Daniel Ślęzak, Anna Malecka-Dubiela, and Przemysław Rutkowski. 2021. "Nephrogenic Systemic Fibrosis as a Complication after Gadolinium-Containing Contrast Agents: A Rapid Review" International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health 18, no. 6: 3000. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph18063000
APA StyleLange, S., Mędrzycka-Dąbrowska, W., Zorena, K., Dąbrowski, S., Ślęzak, D., Malecka-Dubiela, A., & Rutkowski, P. (2021). Nephrogenic Systemic Fibrosis as a Complication after Gadolinium-Containing Contrast Agents: A Rapid Review. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 18(6), 3000. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph18063000









