Data Mining in Healthcare: Applying Strategic Intelligence Techniques to Depict 25 Years of Research Development
Abstract
:1. Introduction
- RQ1: What are the strategic themes of data mining in healthcare?
- RQ2: How is the thematic evolution structure of data mining in healthcare?
- RQ3: What are the trends and opportunities of data mining in healthcare for academics and practitioners?
2. Methodology and Dataset
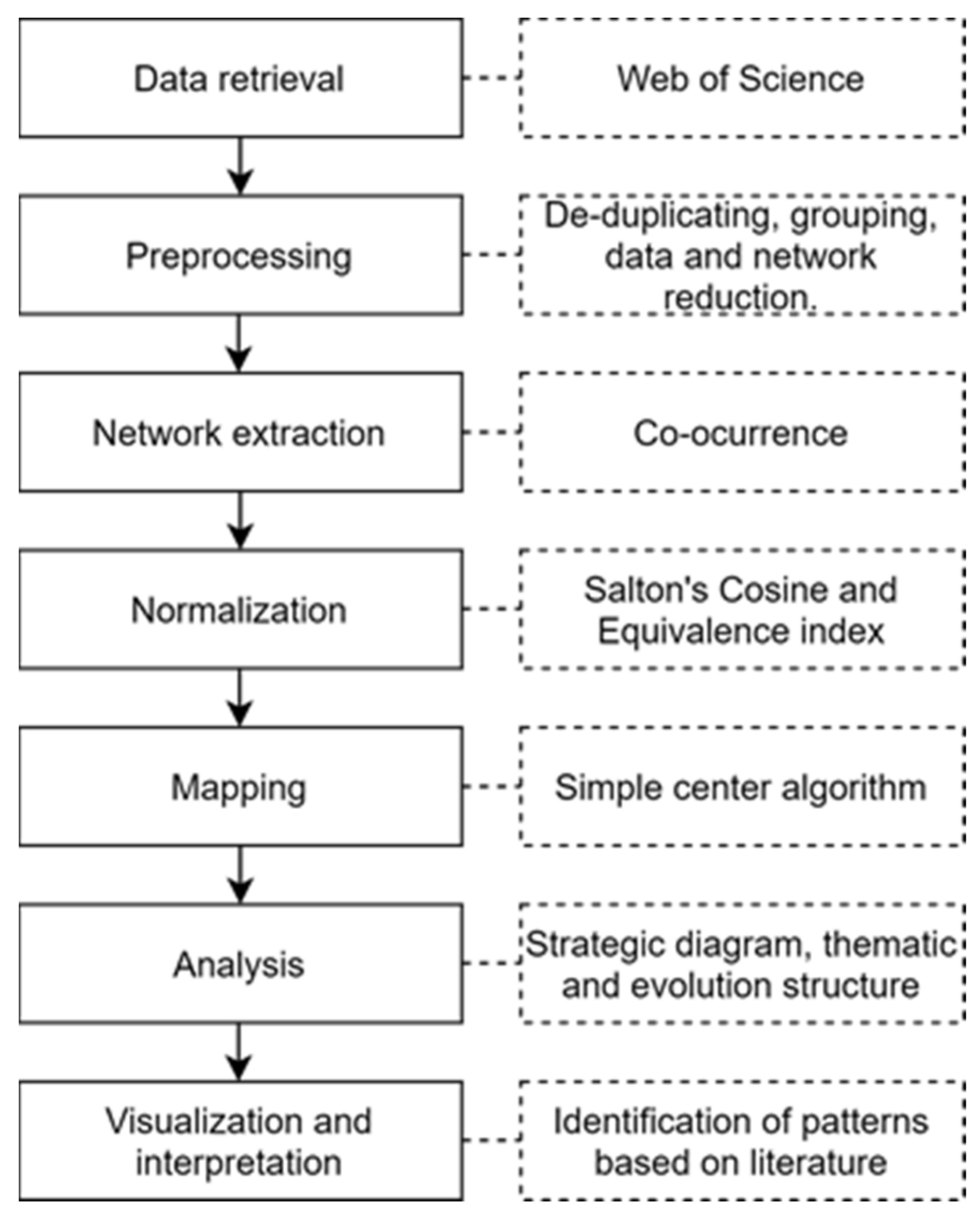
2.1. Methodology
2.1.1. Discovery of Research Themes
2.1.2. Depicting Research Themes
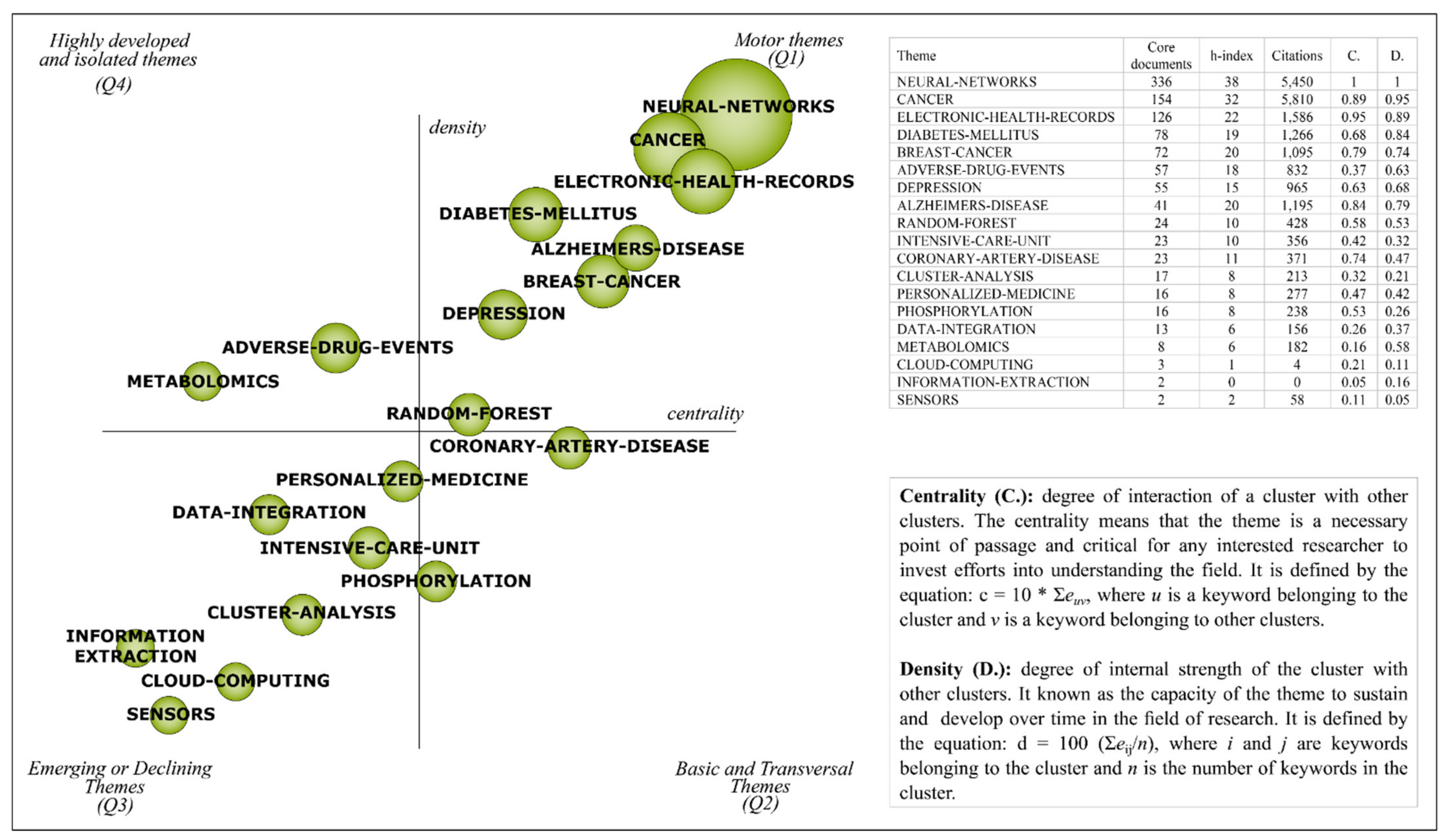
- (a)
- First quadrant—motor themes: trending themes for the field of research with high development.
- (b)
- Second quadrant—basic and transversal themes: themes that are inclined to become motor themes in the future due to their high centrality.
- (c)
- Third quadrant—emerging or declining themes: themes that require a qualitative analysis to define whether they are emerging or declining.
- (d)
- Fourth quadrant—highly developed and isolated themes: themes that are no longer trending due to a new concept or technology.
2.1.3. Thematic Network Structure and Detection of Thematic Areas
2.1.4. Performance Analysis
2.2. Dataset
3. Bibliometric Performance of Data Mining in Healthcare
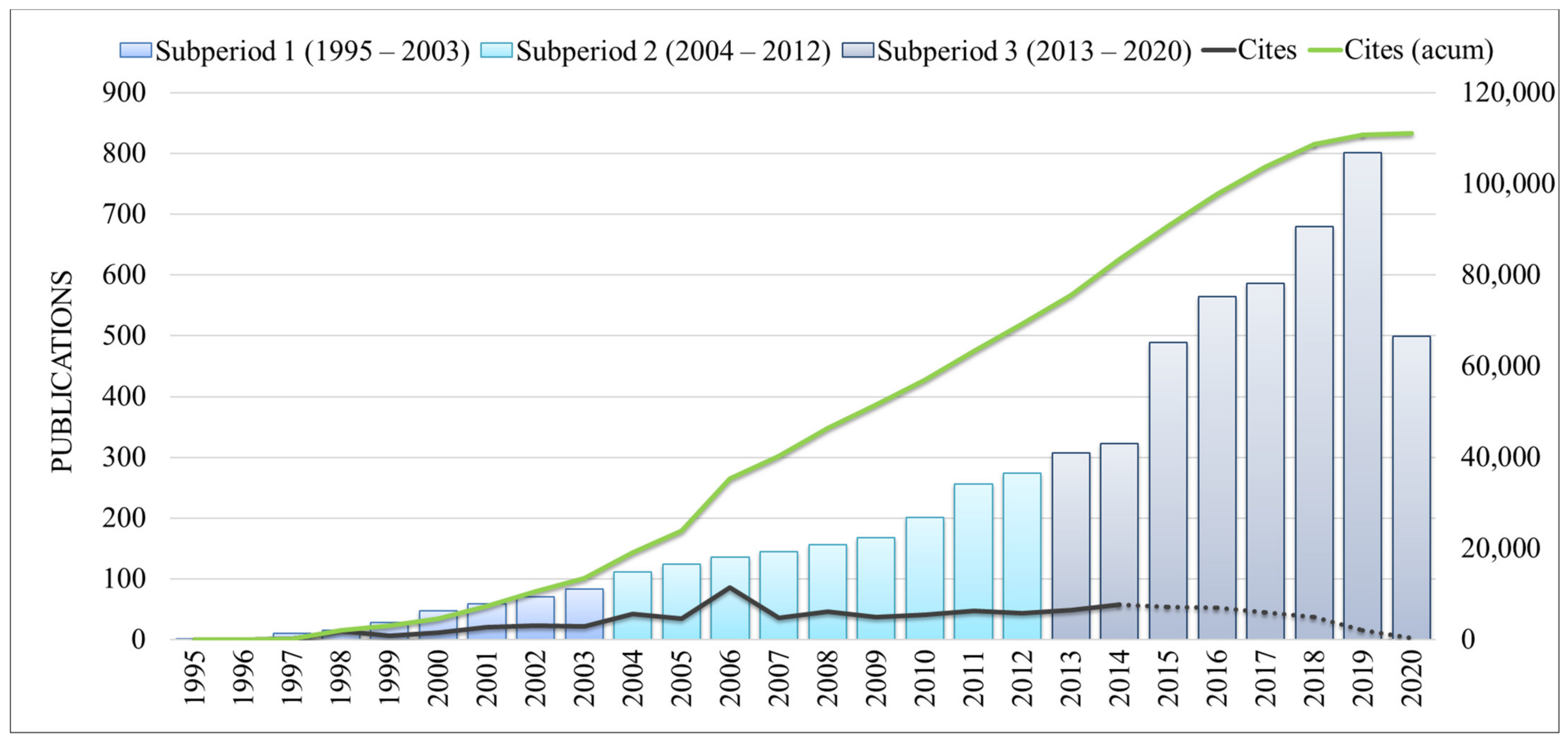
3.1. Publications and Citations Overtime
3.2. Most Productive and Cited Authors
3.3. Productivity of Scientific Journals, Universities, Countries and Most Important Research Fields
4. Science Mapping Analysis of Data Mining in Healthcare
4.1. Strategic Diagram Analysis
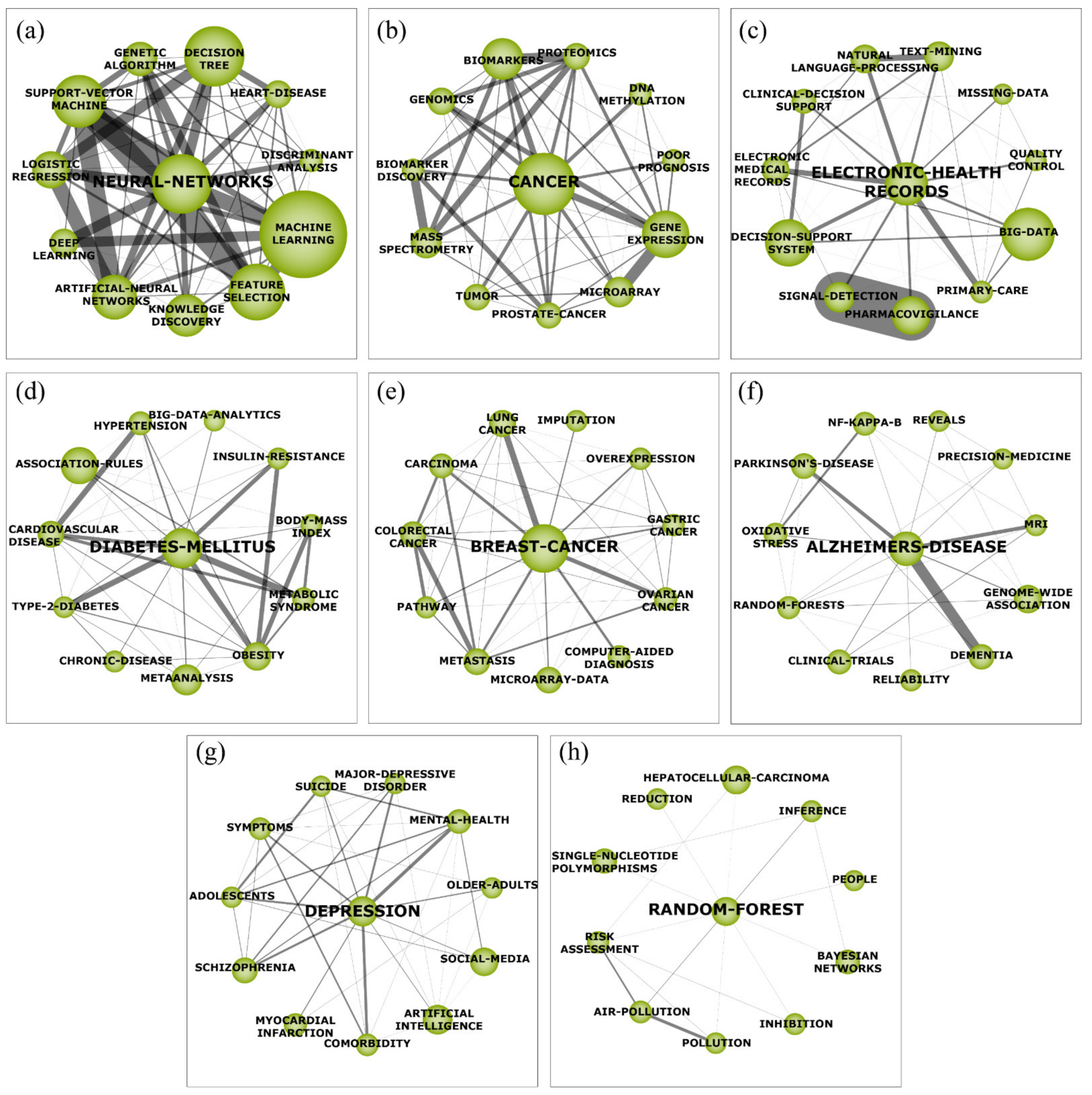
4.2. Thematic Network Structure Analysis of Motor Themes
4.2.1. Neural Network (a)
4.2.2. Cancer (b)
4.2.3. Electronic Health Records (HER—c)
4.2.4. Diabetes Mellitus (DM—d)
4.2.5. Breast Cancer (e)
4.2.6. Alzheimer’s Disease (AD—f)
4.2.7. Depression (g)
4.2.8. Random Forest (h)
4.3. Thematic Evolution Structure Analysis
4.3.1. Practices and Techniques Related to Data Mining in Healthcare
4.3.2. Health Concepts and Disease Supported by Data Mining
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Jayaraman, P.P.; Forkan, A.R.M.; Morshed, A.; Haghighi, P.D.; Kang, Y. Healthcare 4.0: A Review of Frontiers in Digital Health. In Wiley Interdisciplinary Reviews: Data Mining and Knowledge Discovery; Wiley: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2020; Volume 10, p. e1350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jothi, N.; Husain, W. Data mining in healthcare—A review. Procedia Comput. Sci. 2015, 72, 306–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ricciardi, C.; Cantoni, V.; Improta, G.; Iuppariello, L.; Latessa, I.; Cesarelli, M.; Triassi, M.; Cuocolo, A. Application of data mining in a cohort of Italian subjects undergoing myocardial perfusion imaging at an academic medical center. Comput. Methods Programs Biomed. 2020, 189, 105343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pika, A.; Wynn, M.T.; Budiono, S.; Ter Hofstede, A.H.; van der Aalst, W.M.; Reijers, H.A. Privacy-Preserving Process Mining in Healthcare. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 1612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ricciardi, C.; Amboni, M.; de Santis, C.; Improta, G.; Volpe, G.; Iuppariello, L.; Ricciardelli, G.; D’Addio, G.; Vitale, C.; Barone, P.; et al. Using gait analysis’ parameters to classify Parkinsonism: A data mining approach. Comput. Methods Programs Biomed. 2019, 180, 105033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ayyoubzadeh, S.M.; Ghazisaeedi, M.; Kalhori, S.R.N.; Hassaniazad, M.; Baniasadi, T.; Maghooli, K.; Kahnouji, K. A study of factors related to patients’ length of stay using data mining techniques in a general hospital in southern Iran. Health Inf. Sci. Syst. 2020, 8, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, C.; Xu, X.; Cai, Y.; Ge, Q.; Zeng, G.; Li, X.; Zhang, W.; Ji, C.; Yang, L. Mining the Characteristics of COVID-19 Patients in China: Analysis of Social Media Posts. J. Med. Internet Res. 2020, 22, e19087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yim, S.J.; Lui, L.M.; Lee, Y.; Rosenblat, J.D.; Ragguett, R.-M.; Park, C.; Subramaniapillai, M.; Cao, B.; Zhou, A.; Rong, C.; et al. The utility of smartphone-based, ecological momentary assessment for depressive symptoms. J. Affect. Disord. 2020, 274, 602–609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uba, M.M.; Jiadong, R.; Sohail, M.N.; Irshad, M.; Yu, K. Data mining process for predicting diabetes mellitus based model about other chronic diseases: A case study of the northwestern part of Nigeria. Healthc. Technol. Lett. 2019, 6, 98–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, S.-I.; Tseng, H.-T.; Hsieh, C.-C. Evaluating the impact of soy compounds on breast cancer using the data mining approach. Food Funct. 2020, 11, 4561–4570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rahman, A.; Honan, B.; Glanville, T.; Hough, P.; Walker, K. Using data mining to predict emergency department length of stay greater than 4 hours: Derivation and single-site validation of a decision tree algorithm. Emerg. Med. Australas. 2019, 32, 416–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, P.; Qamar, S.; Rizvi, S.Q.A. Techniques of Data Mining In Healthcare: A Review. Int. J. Comput. Appl. 2015, 120, 38–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ţăranu, I. Data mining in healthcare: Decision making and precision. Database Syst. J. 2016, 6, 33–40. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, X.; Guo, J.; Gu, D.; Yang, Y.; Yang, X.; Zhu, K. Tracking knowledge evolution, hotspots and future directions of emerging technologies in cancers research: A bibliometrics review. J. Cancer 2019, 10, 2643–2653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- dos Santos, B.S.; Steiner, M.T.A.; Fenerich, A.T.; Lima, R.H.P. Data mining and machine learning techniques applied to public health problems: A bibliometric analysis from 2009 to 2018. Comput. Ind. Eng. 2019, 138, 106120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Y.; Yu, Z.; Cheng, X.; Luo, Y.; Wen, C. A bibliometric analysis and visualization of medical data mining research. Medicine 2020, 99, e20338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Severo, P.; Furstenau, L.; Sott, M.; Cossul, D.; Bender, M.; Bragazzi, N. Thirty Years of Human Rights Study in the Web of Science Database (1990–2020). Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 2131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cobo, M.J.; López-Herrera, A.G.; Herrera-Viedma, E.; Herrera, F. SciMAT: A new science mapping analysis software tool. J. Am. Soc. Inf. Sci. Technol. 2012, 63, 1609–1630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sott, M.; Bender, M.S.; Furstenau, L.B.; Machado, L.M.; Cobo, M.J.; Bragazzi, N.L. 100 Years of Scientific Evolution of Work and Organizational Psychology: A Bibliometric Network Analysis From 1919 to 2019. Front. Psychol. 2020, 11, 559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Furstenau, L.B.; Sott, M.K.; Homrich, A.J.O.; Kipper, L.M.; Al Abri, A.A.; Cardoso, T.F.; López-Robles, J.R.; Cobo, M.J. 20 Years of Scientific Evolution of Cyber Security: A Science Mapping. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Industrial Engineering and Operations Management, Dubai, UAE, 10–12 March 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Furstenau, L.B.; Sott, M.; Kipper, L.M.; Machado, E.L.; Lopez-Robles, J.R.; Dohan, M.S.; Cobo, M.J.; Zahid, A.; Abbasi, Q.H.; Imran, M.A. Link Between Sustainability and Industry 4.0: Trends, Challenges and New Perspectives. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 140079–140096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sott, M.; Furstenau, L.B.; Kipper, L.M.; Giraldo, F.D.; Lopez-Robles, J.R.; Cobo, M.J.; Zahid, A.; Abbasi, Q.H.; Imran, M.A. Precision Techniques and Agriculture 4.0 Technologies to Promote Sustainability in the Coffee Sector: State of the Art, Challenges and Future Trends. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 149854–149867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- López-Robles, J.R.; Otegi-Olaso, J.R.; Cobo, M.J.; Bertolin-Furstenau, L.; Kremer-Sott, M.; López-Robles, L.D.; Gamboa-Rosales, N.K. The relationship between Project Management and Industry 4.0: Bibliometric Analysis of Main Research Areas through Scopus. In Proceedings of the 3rd International Conference on Research and Education in Project Management—REPM 2020, Bilbao, Spain, 20–21 February 2020; p. 56. [Google Scholar]
- Kipper, L.M.; Iepsen, S.; Forno, A.J.D.; Frozza, R.; Furstenau, L.; Agnes, J.; Cossul, D. Scientific mapping to identify competencies required by industry 4.0. Technol. Soc. 2021, 64, 101454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kipper, L.M.; Furstenau, L.B.; Hoppe, D.; Frozza, R.; Iepsen, S. Scopus scientific mapping production in industry 4.0 (2011–2018): A bibliometric analysis. Int. J. Prod. Res. 2019, 58, 1605–1627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Furstenau, L.; Rabaioli, B.; Sott, M.; Cossul, D.; Bender, M.; Farina, E.; Filho, F.; Severo, P.; Dohan, M.; Bragazzi, N. A Bibliometric Network Analysis of Coronavirus during the First Eight Months of COVID-19 in 2020. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Furstenau, L.B.; Sott, M.K.; Homrich, A.J.O.; Kipper, L.M.; Dohan, M.S.; López-Robles, J.R.; Cobo, M.J.; Tortorella, G.L. An overview of 42 years of lean production: Applying bibliometric analysis to investigate strategic themes and scientific evolution structure. Technol. Anal. Strateg. Manag. 2021, 33, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Callon, M.; Courtial, J.P.; Laville, F. Co-word analysis as a tool for describing the network of interactions between basic and technological research: The case of polymer chemsitry. Scientometrics 1991, 22, 155–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Viedma, E.H.; Robles, J.R.L.; Guallar, J.; Cobo, M.J. Global trends in coronavirus research at the time of Covid-19: A general bibliometric approach and content analysis using SciMAT. Inf. Prof. 2020, 29, 11. [Google Scholar]
- Cobo, M.J.; López-Herrera, A.G.; Herrera-Viedma, E.; Herrera, F. Science mapping software tools: Review, analysis, and cooperative study among tools. J. Am. Soc. Inf. Sci. Technol. 2011, 62, 1382–1402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cobo, M.J.; Martínez, M.Á.; Gutiérrez-Salcedo, M.; Fujita, H.; Herrera-Viedma, E. 25 years at Knowledge-based systems: A bibliometric analysis. Knowl. Based Syst. 2015, 80, 3–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- López-Robles, J.R.; Otegi-Olaso, J.R.; Gómez, I.P.; Cobo, M.J. 30 years of intelligence models in management and business: A bibliometric review. Int. J. Inf. Manag. 2019, 48, 22–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, A.L.E.; Moraes, J.A.R.; Benitez, L.B.; Kaufmann, E.A.; Furstenau, L.B. Mapeamento da produção científica acerca do uso de biocompósitos nos processos de impressões 3D. Ibero Am. J. Environ. Sci. 2020, 11, 236–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- López-Robles, J.R.; Otegi-Olaso, J.R.; Porto-Gomez, I.; Gamboa-Rosales, H.; Gamboa-Rosales, N.K. Understanding the intellectual structure and evolution of Competitive Intelligence: A bibliometric analysis from 1984 to 2017. Technol. Anal. Strateg. Manag. 2019, 32, 604–619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cobo, M.J.; López-Herrera, A.G.; Herrera-Viedma, E.; Herrera, F. An approach for detecting, quantifying, and visualizing the evolution of a research field: A practical application to the fuzzy sets theory field. J. Informetr. 2011, 5, 146–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szolovits, P. Uncertainty and decisions in medical informatics. Methods Inf. Med. 1995, 34, 111–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fawcett, T. An introduction to ROC analysis. Pattern Recognit. Lett. 2006, 27, 861–874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dohan, M.S.; Califf, C.B.; Ghosh, K.; Tan, J. Digital Transformation in Healthcare: New Value for a New Movement; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, J. Citation time window choice for research impact evaluation. Scientometrics 2013, 94, 851–872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eyal-Altman, N.; Last, M.; Rubin, E. PCM-SABRE: A platform for benchmarking and comparing outcome prediction methods in precision cancer medicine. BMC Bioinform. 2017, 18, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Urbanowicz, R.J.; Olson, R.S.; Schmitt, P.; Meeker, M.; Moore, J.H. Benchmarking relief-based feature selection methods for bioinformatics data mining. J. Biomed. Inform. 2018, 85, 168–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mansiaux, Y.; Carrat, F. Detection of independent associations in a large epidemiologic dataset: A comparison of random forests, boosted regression trees, conventional and penalized logistic regression for identifying independent factors associated with H1N1pdm influenza infections. BMC Med. Res. Methodol. 2014, 14, 99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ilic, D.; Neuberger, M.M.; Djulbegovic, M.; Dahm, P. Screening for prostate cancer. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2013, CD004720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Torrano, V.; Valcarcel-Jimenez, L.; Cortazar, A.R.; Liu, X.; Urosevic, J.; Castillo-Martin, M.; Fernández-Ruiz, S.; Morciano, G.; Caro-Maldonado, A.; Guiu, M.; et al. The metabolic co-regulator PGC1α suppresses prostate cancer metastasis. Nat. Cell Biol. 2016, 18, 645–656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Harder, N.; Athelogou, M.; Hessel, H.; Brieu, N.; Yigitsoy, M.; Zimmermann, J.; Baatz, M.; Buchner, A.; Stief, C.G.; Kirchner, T.; et al. Tissue Phenomics for prognostic biomarker discovery in low- and intermediate-risk prostate cancer. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coates, J.; Souhami, L.; El Naqa, I. Big Data Analytics for Prostate Radiotherapy. Front. Oncol. 2016, 6, 149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Trifirò, G.; Pariente, A.; Coloma, P.M.; Kors, J.A.; Polimeni, G.; Miremont-Salamé, G.; Catania, M.A.; Salvo, F.; David, A.; Moore, N.; et al. Data mining on electronic health record databases for signal detection in pharmacovigilance: Which events to monitor? Pharmacoepidemiol. Drug Saf. 2009, 18, 1176–1184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harpaz, R.; Vilar, S.; DuMouchel, W.; Salmasian, H.; Haerian, K.; Shah, N.H.; Chase, H.S.; Friedman, C. Combing signals from spontaneous reports and electronic health records for detection of adverse drug reactions. J. Am. Med. Inform. Assoc. 2013, 20, 413–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Stiglic, G.; Kocbek, P.; Fijacko, N.; Sheikh, A.; Pajnkihar, M. Challenges associated with missing data in electronic health records: A case study of a risk prediction model for diabetes using data from Slovenian primary care. Health Inform. J. 2017, 25, 951–959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Purwar, A.; Singh, S.K. Hybrid prediction model with missing value imputation for medical data. Expert Syst. Appl. 2015, 42, 5621–5631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kavakiotis, I.; Tsave, O.; Salifoglou, A.; Maglaveras, N.; Vlahavas, I.; Chouvarda, I. Machine Learning and Data Mining Methods in Diabetes Research. Comput. Struct. Biotechnol. J. 2017, 15, 104–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, N.; Shaw, J.; Karuranga, S.; Huang, Y.; Fernandes, J.D.R.; Ohlrogge, A.; Malanda, B. IDF Diabetes Atlas: Global estimates of diabetes prevalence for 2017 and projections for 2045. Diabetes Res. Clin. Pract. 2018, 138, 271–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- García-Laencina, P.J.; Abreu, P.H.; Abreu, M.H.; Afonoso, N. Missing data imputation on the 5-year survival prediction of breast cancer patients with unknown discrete values. Comput. Biol. Med. 2015, 59, 125–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oskouei, R.J.; Kor, N.M.; Maleki, S.A. Data mining and medical world: Breast cancers’ diagnosis, treatment, prognosis and challenges. Am. J. Cancer Res. 2017, 7, 610–627. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Zadeh, A.H.; Alsabi, Q.; Ramirez-Vick, J.E.; Nosoudi, N. Characterizing basal-like triple negative breast cancer using gene expression analysis: A data mining approach. Expert Syst. Appl. 2020, 148, 113253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, H.; Chen, Z.; Zheng, W.; Sun, J.; Fu, Q.; Teng, R.; Chen, J.; Xie, S.; Wang, L.; Yu, X.-F.; et al. FKBP4 is a malignant indicator in luminal A subtype of breast cancer. J. Cancer 2020, 11, 1727–1736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wu, X.; Khorshidi, H.A.; Aickelin, U.; Edib, Z.; Peate, M. Imputation techniques on missing values in breast cancer treatment and fertility data. Health Inf. Sci. Syst. 2019, 7, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nekouie, A.; Moattar, M.H. Missing value imputation for breast cancer diagnosis data using tensor factorization improved by enhanced reduced adaptive particle swarm optimization. J. King Saud Univ. Comput. Inf. Sci. 2019, 31, 287–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kassim, S.K.; Shehata, H.H.; Abou-Alhussein, M.M.; Sallam, M.M.; Amin, I.I. Laboratory validation of formal concept analysis of the methylation status of microarray-detected genes in primary breast cancer. Tumor Biol. 2017, 39, 1010428317698390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Chou, H.-L.; Yao, C.-T.; Su, S.-L.; Lee, C.-Y.; Hu, K.-Y.; Terng, H.-J.; Shih, Y.-W.; Chang, Y.-T.; Lu, Y.-F.; Chang, C.-W.; et al. Gene expression profiling of breast cancer survivability by pooled cDNA microarray analysis using logistic regression, artificial neural networks and decision trees. BMC Bioinform. 2013, 14, 100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Maind, A.; Raut, S. Identifying condition specific key genes from basal-like breast cancer gene expression data. Comput. Biol. Chem. 2019, 78, 367–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valarmathie, P.; Sivakrithika, V.; Dinakaran, K. Classification of mammogram masses using selected texture, shape and margin features with multilayer perceptron classifier. Biomed. Res. 2016, 27, S310. [Google Scholar]
- Tsutsui, S.; Bu, Y.; Ding, Y. Using Machine Reading to Understand Alzheimer’s and Related Diseases from the Literature. J. Data Inf. Sci. 2017, 2, 81–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Walker, P.R.; Smith, B.; Liu, Q.Y.; Famili, A.F.; Valdés, J.J.; Liu, Z.; Lach, B. Data mining of gene expression changes in Alzheimer brain. Artif. Intell. Med. 2004, 31, 137–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Colangelo, V.; Schurr, J.; Ball, M.J.; Pelaez, R.P.; Bazan, N.G.; Lukiw, W.J. Gene expression profiling of 12633 genes in Alzheimer hippocampal CA1: Transcription and neurotrophic factor down-regulation and up-regulation of apoptotic and pro-inflammatory signaling. J. Neurosci. Res. 2002, 70, 462–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lazli, L.; Boukadoum, M.; Mohamed, O.A. A Survey on Computer-Aided Diagnosis of Brain Disorders through MRI Based on Machine Learning and Data Mining Methodologies with an Emphasis on Alzheimer Disease Diagnosis and the Contribution of the Multimodal Fusion. Appl. Sci. 2020, 10, 1894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Plant, C.; Teipel, S.J.; Oswald, A.; Böhm, C.; Meindl, T.; Mourao-Miranda, J.; Bokde, A.W.; Hampel, H.; Ewers, M. Automated detection of brain atrophy patterns based on MRI for the prediction of Alzheimer’s disease. NeuroImage 2010, 50, 162–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zhang, M.; Schmitt-Ulms, G.; Sato, C.; Xi, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Zhou, Y.; George-Hyslop, P.S.; Rogaeva, E. Drug Repositioning for Alzheimer’s Disease Based on Systematic ‘omics’ Data Mining. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0168812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Mohammadi, M.; Al-Azab, F.; Raahemi, B.; Richards, G.; Jaworska, N.; Smith, D.; de La Salle, S.; Blier, P.; Knott, V. Data mining EEG signals in depression for their diagnostic value. BMC Med. Inform. Decis. Mak. 2015, 15, 108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kautzky, A.; Baldinger-Melich, P.; Kranz, G.S.; Vanicek, T.; Souery, D.; Montgomery, S.; Mendlewicz, J.; Zohar, J.; Serretti, A.; Lanzenberger, R.; et al. A New Prediction Model for Evaluating Treatment-Resistant Depression. J. Clin. Psychiatry 2017, 78, 215–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zimmerman, M.; Balling, C.; Chelminski, I.; Dalrymple, K. Symptom presence versus symptom intensity in understanding the severity of depression: Implications for documentation in electronic medical records. J. Affect. Disord. 2019, 256, 344–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Cao, W.; Gao, X.; Ong, H.; Ji, T. Predicting postoperative complications of head and neck squamous cell carcinoma in elderly patients using random forest algorithm model. BMC Med. Inform. Decis. Mak. 2015, 15, 44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kaur, P.; Kumar, R.; Kumar, M. A healthcare monitoring system using random forest and internet of things (IoT). Multimed. Tools Appl. 2019, 78, 19905–19916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krizhevsky, A.; Sutskever, I.; Hinton, G.E. Imagenet classification with deep convolutional neural networks. Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. 2012, 25, 1097–1105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patil, H.K.; Seshadri, R. Big Data Security and Privacy Issues in Healthcare; IEEE: New York, NY, USA, 2014; pp. 762–765. [Google Scholar]
- Rajput, A.; Li, Q.; Ahvanooey, M. A Blockchain-Based Secret-Data Sharing Framework for Personal Health Records in Emergency Condition. Healthcare 2021, 9, 206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abouelmehdi, K.; Beni-Hessane, A.; Khaloufi, H. Big healthcare data: Preserving security and privacy. J. Big Data 2018, 5, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, A.E.W.; Pollard, T.J.; Shen, L.; Lehman, L.-W.H.; Feng, M.; Ghassemi, M.; Moody, B.; Szolovits, P.; Anthony Celi, L.; Mark, R.G. MIMIC-III, a freely accessible critical care database. Sci. Data 2016, 3, 160035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Li, D. Gene expression studies with DGL global optimization for the molecular classification of cancer. Soft Comput. 2011, 15, 111–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mirnics, K.; Middleton, F.A.; Lewis, D.A.; Levitt, P. Analysis of complex brain disorders with gene expression microarrays: Schizophrenia as a disease of the synapse. Trends Neurosci. 2001, 24, 479–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romero, I.G.; Ruvinsky, I.; Gilad, Y. Comparative studies of gene expression and the evolution of gene regulation. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2012, 13, 505–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Doja, M.; Kaur, I.; Ahmad, T. Age-specific survival in prostate cancer using machine learning. Data Technol. Appl. 2020, 54, 215–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barber, L.E.; Gerke, T.; Markt, S.C.; Peisch, S.F.; Wilson, K.M.; Ahearn, T.U.; Giovannucci, E.L.; Parmigiani, G.; Mucci, L.A. Family History of Breast or Prostate Cancer and Prostate Cancer Risk. Clin. Cancer Res. 2018, 24, 5910–5917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Shivade, C.; Raghavan, P.; Fosler-Lussier, E.; Embi, P.J.; Elhadad, N.; Johnson, S.B.; Lai, A.M. A review of approaches to identifying patient phenotype cohorts using electronic health records. J. Am. Med. Inform. Assoc. 2014, 21, 221–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhugra, D.; Mastrogianni, A. Globalisation and mental disorders: Overview with relation to depression. Br. J. Psychiatry 2004, 184, 10–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]


| Study | Coverage | Focus |
|---|---|---|
| [14] | 2000–2017 | Analysis of the evolution of emerging technologies (e.g., data mining, machine learning, among others) in cancer using CiteSpace software. |
| [15] | 2009–2018 | Exploration of data mining and machine learning in public health sector. |
| [16] | 2011–2019 | Investigation of medical data mining using VOSviewer and CiteSpace software. |
| This paper | 1995–2020 | A BPNA of data mining in healthcare: performance analysis, strategic themes, thematic evolution structure, trends and future opportunities using SciMAT software. |
| Author Citation | Citations | Author Productivity | Documents |
|---|---|---|---|
| Bate, Andrew C. | 945 | Li, Chien-Feng | 36 |
| Lindquist, Marie | 943 | Acharya, U. Rajendra | 21 |
| Edwards, E.R. | 888 | Chung, Kyungyong | 21 |
| Moore, Jason H. | 711 | Chen, Gang | 19 |
| Cook, Diane, J. | 599 | Lee, Sung-Wei | 18 |
| Eppig, Janan, T. | 577 | Moore, Jason H. | 17 |
| White, Bill, C. | 541 | Cano, Maria | 17 |
| Bellazi, Riccardo | 527 | Chang, I-Wei | 16 |
| Szarfman, A. | 511 | He, Hong-Lin | 16 |
| Lambin, Philippe | 489 | Moro, Pedro L. | 16 |
| Journal | Doc. | JIF |
|---|---|---|
| PLOS One | 124 | 2.74 |
| Expert Systems with Applications | 105 | 5.89 |
| Artificial Intelligence in Medicine | 75 | 4.47 |
| Journal of Biomedical Informatics | 75 | 3.57 |
| BMC Bioinformatics | 66 | 2.13 |
| Journal of Medical Systems | 65 | 2.83 |
| IEEE Access | 65 | 3.74 |
| Computer Methods and Programs in Biomedicine | 59 | 3.63 |
| International Journal of Advanced Computer Science and Applications | 54 | 1.32 |
| Journal of The American Medical Informatics Association | 53 | 4.11 |
| University | Documents | Country | Documents |
|---|---|---|---|
| Columbia University | 62 | United States | 1973 |
| U.S. FDA Registration | 62 | China | 923 |
| Harvard University | 60 | England | 370 |
| Stanford University | 55 | India | 354 |
| Chinese Academy of Sciences | 53 | Germany | 312 |
| Chi Mei Medical Center | 47 | Italy | 297 |
| University of Pennsylvania | 45 | Taiwan | 294 |
| Kaohsiung Medical University | 44 | Australia | 282 |
| University of Toronto | 44 | Canada | 252 |
| University of Pittsburgh | 44 | Netherlands | 117 |
| WoS Subject Categories | Doc. |
|---|---|
| Computer Science Artificial Intelligence | 768 |
| Medical Informatics | 744 |
| Computer Science Information Systems | 722 |
| Computer Science Interdisciplinary Applications | 603 |
| Mathematical Computational Biology | 505 |
| Health Care Sciences Services | 419 |
| Pharmacology Pharmacy | 370 |
| Engineering Electrical Electronic | 364 |
| Computer Science Theory Methods | 357 |
| Biochemical Research Methods | 304 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kolling, M.L.; Furstenau, L.B.; Sott, M.K.; Rabaioli, B.; Ulmi, P.H.; Bragazzi, N.L.; Tedesco, L.P.C. Data Mining in Healthcare: Applying Strategic Intelligence Techniques to Depict 25 Years of Research Development. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 3099. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph18063099
Kolling ML, Furstenau LB, Sott MK, Rabaioli B, Ulmi PH, Bragazzi NL, Tedesco LPC. Data Mining in Healthcare: Applying Strategic Intelligence Techniques to Depict 25 Years of Research Development. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health. 2021; 18(6):3099. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph18063099
Chicago/Turabian StyleKolling, Maikel Luis, Leonardo B. Furstenau, Michele Kremer Sott, Bruna Rabaioli, Pedro Henrique Ulmi, Nicola Luigi Bragazzi, and Leonel Pablo Carvalho Tedesco. 2021. "Data Mining in Healthcare: Applying Strategic Intelligence Techniques to Depict 25 Years of Research Development" International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health 18, no. 6: 3099. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph18063099
APA StyleKolling, M. L., Furstenau, L. B., Sott, M. K., Rabaioli, B., Ulmi, P. H., Bragazzi, N. L., & Tedesco, L. P. C. (2021). Data Mining in Healthcare: Applying Strategic Intelligence Techniques to Depict 25 Years of Research Development. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 18(6), 3099. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph18063099








