Abstract
This study aimed to highlight the relationship between moderate-to-vigorous physical activity (MVPA) as assessed by accelerometer devices and the Physical Activity Questionnaire for Children (PAQ-C) to estimate the convergent validity of the questionnaire. A systematic review and a meta-analysis were applied by collecting pertinent studies (PubMed, Web of Science, PsycINFO, and SCOPUS) from 1997 until November 2020. The relationship between PAQ-C and MVPA scores was estimated considering correlation coefficients such as the effect size. Fisher’s transformation was used to convert each correlation coefficient into an approximately normal distribution. The pooled correlations between PAQ-C and MVPA scores were measured by r values after converting the Fisher’s z values back into correlation coefficients for presentation. A total of 13 studies were included in the meta-analysis, and a random effects model was adopted. The pooled correlation between PAQ-C and MVPA scores was significant but with a moderate effect size (r = 0.34 [0.29, 0.39], Z = 15.00, p < 0.001). No heterogeneity among the studies was observed (I2 < 25%). In conclusion, the results highlighted a moderate relationship (around 0.30–0.40) between PAQ-C and accelerometer measurements. These results suggested to concurrently administer both tools to reach a more comprehensive description of children’s PA, in terms of quality and quantity.
1. Introduction
International guidelines recommend that children should accumulate at least 60 min of daily moderate-to-vigorous physical activity (MVPA) including sports and leisure activities [1]. Reaching these recommendations is associated with positive health outcomes, such as the reduction of overweight and obesity [1,2] and risk for chronic diseases and cancer in adulthood [3,4,5], and improvement of psychological well-being (e.g., reduction of depression and stress) [6], cognitive function and academic outcomes [1], and quality of life in general [7]. On the contrary, a low level of physical activity (PA) and the increase of sedentary behavior (e.g., screen time) are associated with both short- and long-term negative health consequences [1,8,9]. Despite the benefits of PA, two-thirds of children do not meet the international recommendations [10] and spend a large part of their waking time in sedentary activities [11,12,13]. Public health actions are necessary to counter this trend [1,11,12]. For this purpose, one of the global targets of the World Health Organization for the next years to prevent non-communicable diseases is to reduce the prevalence of insufficient PA by 15% [12,14]. Thus, an accurate assessment of childhood PA behavior is fundamental to accurately identify the effectiveness and the progression of healthcare interventions [15,16].
Data collection to assess and measure PA behavior can involve subjective and self-report (e.g., diaries/logs, questionnaires, or interviews) procedures, as well as objective and direct instruments including motion sensors (e.g., accelerometers, pedometers, and heart rate monitors), physiological marker (e.g., biomarkers), and calorimetry (e.g., direct and indirect) [15,17]. Among self-report instruments, PA questionnaires (PAQ) are practical to administer, relatively inexpensive, acceptable, and allow an insight into the PA of a large-scale population [18]. Nevertheless, PAQ can present some limitations. Socioeconomic and sociodemographic factors and measurement bias including misinterpretation or deliberate changes (e.g., social desirability) and difficulty to recall activities may affect the final score [18,19]. In particular, it is common that children have difficulties in understanding questions and accurately recalling activities [20], leading to an overestimate or underestimate of the overall PA level [15,21]. An alternative approach to a self-reported measure is the objective monitoring of PA using wearable devices, such as accelerometers. Accelerometer technology allows the measurement of accelerations produced by movement and may be considered an effective and feasible instrument to measure PA levels. Nevertheless, even though accelerometer technology objectively estimates the frequency, duration, and intensity of PA, it is time and cost intensive and difficult to administer to a large-scale population [15,17]. Moreover, due to physical constraints, some specific activities (e.g., swimming or bicycle activities) may be difficult to assess [22].
Among the numerous PAQs for children (see [22] for a complete review), none emerges as the best in terms of psychometric characteristics, but the Physical Activity Questionnaire for Older Children (PAQ-C) is one of the most promising [18]. The PAQ-C has been widely used in research and field settings (e.g., school context) to discern general levels of PA over the last seven days in children aged 8–14 years [23], even if it should not be used to assess PA in the summer or holiday periods [24]. The PAQ-C assesses activities related to common sports, leisure activities, games, and physical education classes [18,23]. It consists of ten items, nine of which are used to calculate summary activity scores with a score ranging from 1 to 5 for each item, where a higher score indicates higher levels of activity [23]. Interestingly, the first item is an activity checklist of common activities aimed to aid children to recall with memory cues. The PAQ-C demonstrated acceptable psychometric properties [18,23] with an acceptable-to-good internal consistency, test–retest reliability, and sensitivity to detect gender differences [23,25,26,27,28]. The PAQ-C demonstrated convergence with athletic competence, enjoyment perception, body mass index, cardiorespiratory, and cardiovascular fitness [16,25,26,27,29]. Nevertheless, while some studies showed a moderate correlation with accelerometer scores, and in particular with MVPA [16,20,26,27,28,30,31,32], others reported a low or no correlation [23,33,34,35,36].
The PAQ-C is used in different countries and cultural contexts for research purposes (e.g., Italy [16], Greece [28], Netherlands [29], China [30]). Thus, it is necessary to better understand the convergent validity (e.g., the extent to which different measurement tools measure the same construct) [37] of the questionnaire and synthesize the concurrent evidence in children’s populations. Although previous systematic reviews discussed evidences about the convergent validity of PAQ versus accelerometers data reporting low-to-moderate correlation in children [18,22,38], no study specifically focused on the PAQ-C. Therefore, the purpose of this study was to systematically summarize the evidence on the relationship between MVPA measured with an accelerometer device and PAQ-C data. Specifically, we focus our research on MVPA because it is the reference value recommended by the general PA guidelines [1,11]. A systematic review in this field will help to provide a better understanding of the validity of PAQ-C to investigate PA patterns and behaviors in children. In addition, this study will be able to provide evidence-based recommendations for guiding population health programs aiming to promote active living and healthy lifestyles among children.
2. Materials and Methods
Four electronic databases including PubMed, Web of Science (WOS), PsycINFO (APAPsycNET), and SCOPUS were considered to search pertinent papers by using search strategies, which were similar and adaptable to each database. Search was performed using the strings (“acceleromet*” OR “motion senso*”) AND (“physical activity questionnair*” OR “PAQ-C”) AND (“child*” OR “young”). The research included the published articles from January 1997 to November 2020. We started from January 1997 because PAQ-C was developed in that period. In addition, references of included articles were screened to identify potential eligible studies.
2.1. Eligibility Criteria
The following inclusion criteria were adopted: (1) all participants in the studies were children with an age range 8–14 years; (2) all participants did not present any mental, psychological, physical, or motor disorders; (3) PA was measured objectively using accelerometers and subjectively using the PAQ-C; (4) articles written in English language. No restriction in relation to uniaxial and triaxial devices was performed. Authors were contacted if a study failed to report data about the correlation between accelerometry (i.e., MVPA data) and PAQ-C. Only original, peer-reviewed studies that used the PAQ-C and an accelerometer score were included. If a study presented longitudinal assessment (e.g., physical exercise intervention), we considered only baseline measurements. Other sources (e.g., reviews, meta-analyses, abstracts, opinion articles, books, statements, letters, editorials, comment, and non-peer-reviewed journal articles) were excluded.
2.2. Article Selection
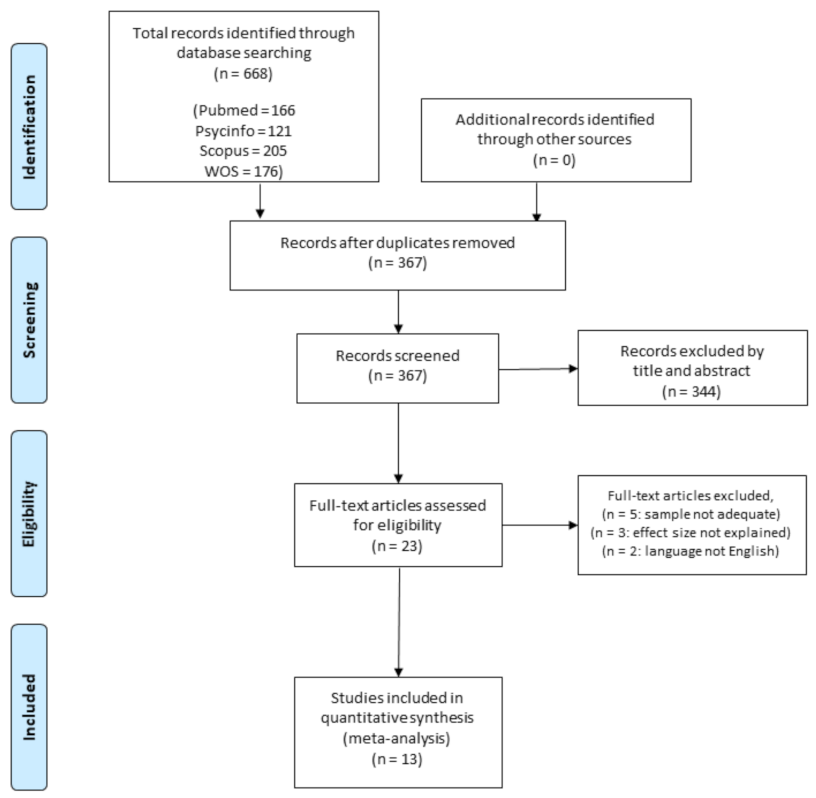
All potential studies were imported into Zotero (www.zotero.org, accessed on 21 February 2021), and duplicates were removed. A summary of the study screening protocol and selection has been provided in Figure 1. The selection process was conducted by two authors (D.M. and S.C.), who independently screened the title and/or the abstract of the selected studies to identify studies that potentially met the inclusion criteria. Then, the full texts of the potentially suitable studies were examined by the same authors for eligibility. Disagreements were resolved through discussion with a third author (P.R.B.), who finally decided in case of conflicting results. If any information useful for the data collection was missed, the corresponding author of the manuscript was contacted. If no response was provided or data were not available, the study was excluded from the analysis.
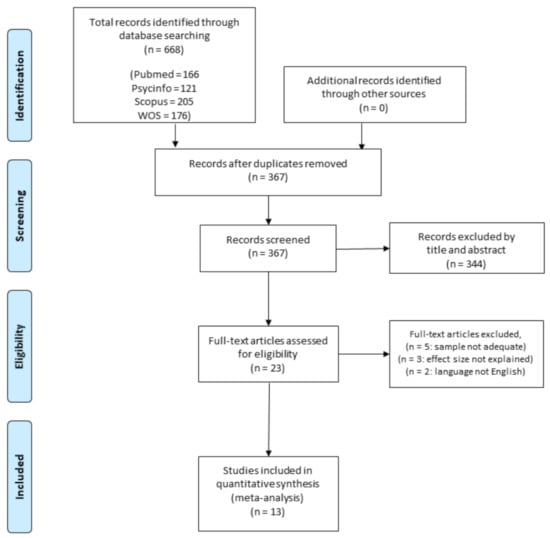
Figure 1.
Flow diagram for screening and selection of studies.
2.3. Study Quality Assessment
An adapted version of the Strengthening the Reporting of Observational Studies in Epidemiology checklist (STROBE) [39] was used to assess the quality of the study reporting. The checklist included 20 items grouped into five categories: Abstract (#1 items), Introduction (#2–#3 items), Methods (#4–#11 items), Results (#12–#15 items), and Discussion (#16–#19 items). The assessment of the quality of each item was scored as 1 (i.e., present) or 0 (i.e., not present). The total resultant score (i.e., sum of each item) was considered according to the following level: “low quality” (0–9 points), “medium quality” (10–15 points), and “high quality” (16–19 points). Two independent authors (D.M. and S.C.) completed the study quality assessment. Disagreements were resolved by discussion between assessors.
2.4. Meta-Analyses
A Microsoft Excel® (Microsoft Corp., Redmond, WA, USA) spreadsheet was compiled with the following information: study information (i.e., lead author, location, and year of publication); study population characteristics (i.e., sample size, age, and gender); accelerometer information (i.e., placement position, number of days per week and weekend, epoch length, algorithm used to investigate PA intensity, and outcome); principal outcomes (i.e., PAQ-C and MVPA scores) and correlation analysis (i.e., Pearson correlation coefficient or Spearman’s rho). The data were extracted from any section of the manuscript.
The relationship between PAQ-C and MVPA scores was estimated considering the effect size based on the correlation coefficients. Data reported as Spearman’s rho were converted into Pearson correlation coefficient using the formula ), where r is the Pearson’s correlation coefficient and rs the Spearman’s rho [40]. Fisher’s transformation was used to convert each correlation coefficient into an approximately normal distribution. The pooled correlations between PAQ-C and MVPA scores were measured by r values after converting the Fisher’s z values back into correlation coefficients for presentation. Heterogeneity (i.e., the percentage of the total variability in an effect size between studies) was evaluated using the I2 index. The level of heterogeneity represented by the I2 index was interpreted as low (25% to ≤50%), moderate (50% to ≤75%), and large (>75%) [41]. A random-effects model was adopted. Publication bias was assessed by visual inspection of the funnel plot and Begg’s and Egger’s tests. All statistical analyses were conducted using the packages “meta” and “metacor” [42] of R (version 4.0.0; R Core Team, Foundation for Statistical Computing, Vienna, Austria). The inverse variance weighting approach was used for pooling [43]. According to Cohen’s guidelines, pooled correlations were interpreted as low (<0.30), moderate (0.31–0.49), and large (≥0.50) [44]. A p-value <0.05 was considered statistically significant.
3. Results
3.1. Studies Systematically Identified
Figure 1 summarizes the systematic search and study selection process.
The initial database search yielded 668 articles. After the removal of the duplicates (N = 301), articles were screened for titles and abstracts, and 23 full-text articles were selected. Five studies were removed because they also included children older than the reference population of the questionnaire, two studies were removed because they were not written in English, and three as they did not report correlation data and the authors did not respond to our request. Overall, 13 studies met the inclusion and reporting criteria.
3.2. Study Description
Table 1 summarizes the characteristics of the identified studies according to the following items: general information, sample characteristics, accelerometer information, principal outcomes, and correlation scores between PAQ-C and MVPA scores.

Table 1.
Summary of the studies included in the meta-analysis (alphabetical order).
Ten studies were published in the last eight years [16,28,30,31,33,34,35,36,45,46], whereas three studies were published between 1997 and 2011 [27,32,47]. The studies were conducted in Europe [16,28,32,33,34,45], Asia [30,31,35], North America [27,46], North Africa [36], and Oceania [47]. Twelve studies included both male and female participants, whereas one examined girls only [45]. One study [27] did not report data about gender. Sample sizes across studies ranged from 20 to 365; eight studies had sample size ≥100 [28,30,31,32,34,35,45,46]. To objectively investigate PA, 11 studies used ActiGraph [16,28,30,31,32,33,34,35,36,46,47], one the Caltrac [27], and one the Cosmed Liferecorder device [45]. In particular, eight studies adopted triaxial accelerometers [16,28,30,31,33,34,35,36], and five uniaxial accelerometers [27,32,45,46,47].
In all 13 studies included in the meta-analysis, accelerometer devices were worn on the waist. Nevertheless, seven of them placed accelerometers on the right side through an elastic belt [16,31,32,33,34,36,47], whereas the other six studies did not specify on which side the accelerometers were worn [27,28,30,35,45,46]. The accelerometers were worn for seven consecutive days in nine studies [16,27,28,30,31,33,34,35,46], and for five days [32] and four days [47] in one study, respectively. One study [36] did not specify the total days but only four days as the minimum unit of time, whereas another one [45] did not report the days of wearing. The majority of the studies (N = 10) reported an epoch of 15 s or less [16,28,30,31,32,33,34,35,36,45], one of 30 s [46], and the other two did not report the data [27,47].
3.3. Study Quality
According to selected criteria, seven studies out of thirteen (54%) were considered “high quality” and six (46%) were considered “medium quality”, while none was considered “low quality”. Criteria commonly absent in reporting were related to defining potential confounders, using adequate power calculations to ensure the study size, and reporting statistical estimate(s) and precision (e.g., 95% CI). Additional information about quality scores is presented in Table 2.

Table 2.
The Strengthening the Reporting of Observational Studies in Epidemiology checklist (STROBE) scores and summary of studies’ quality.
3.4. Meta-Analyses
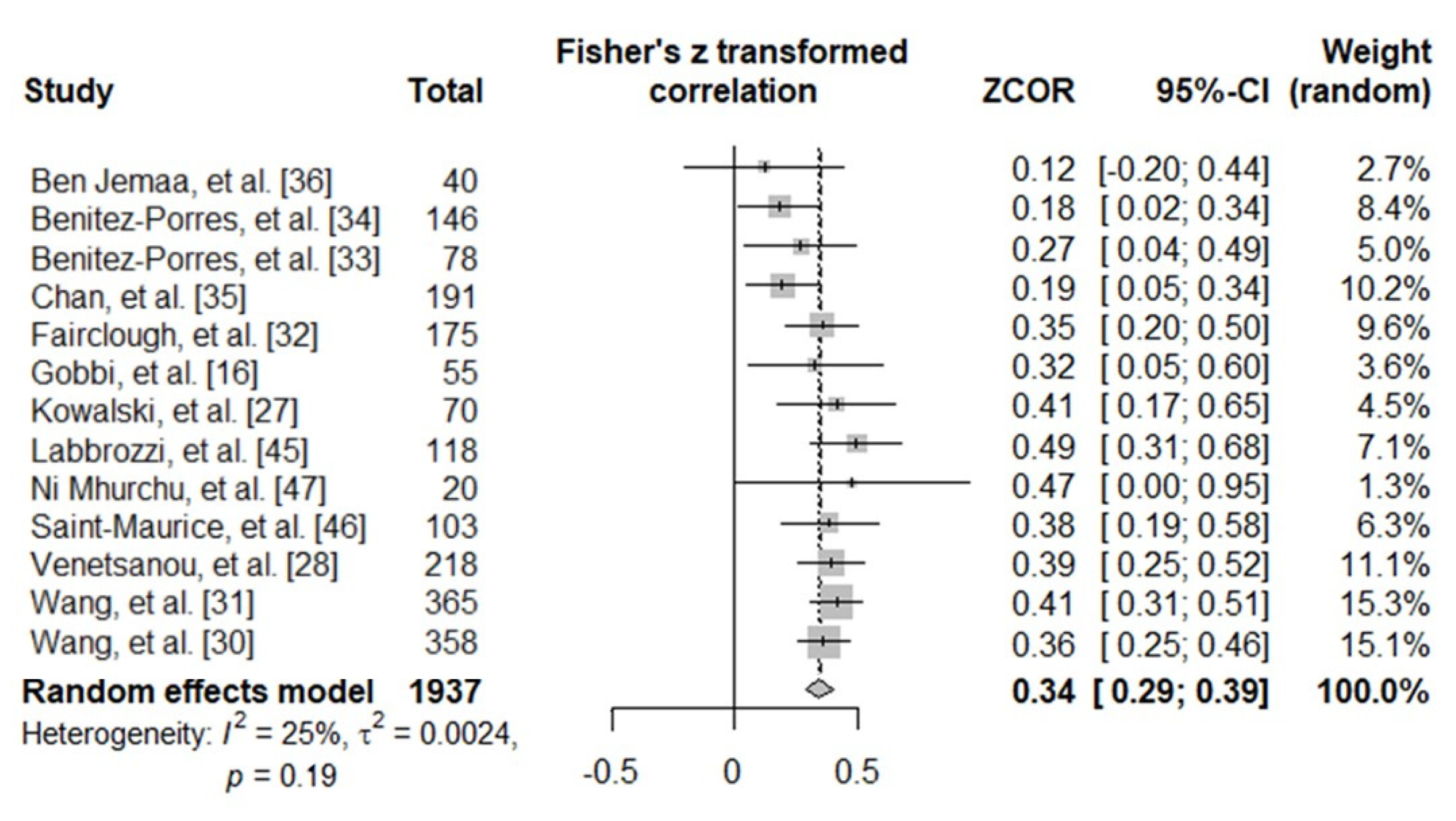
A total of 13 studies were included in the meta-analysis. A random-effects model was adopted. The pooled correlation between PAQ-C and MVPA scores was significant but moderate (r = 0.34, 95% CI [0.29, 0.39], Z = 12.16, p < 0.001) and was homogeneous (I2 = 24.7%; τ2 = 0.0024, p = 0.194). Forest plot results are presented in Figure 2.
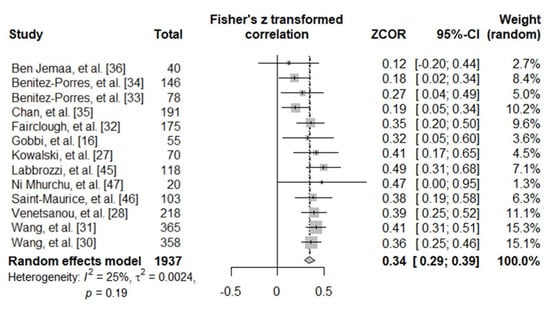
Figure 2.
Forest plot showing the relative and pooled correlations between PAQ-C and MVPA scores of the included studies.
4. Discussion
This systematic review aimed to summarize existing evidence on the convergent validity of the PAQ-C to investigate absolute PA pattern and behavior in children aged 8–14 years. For this purpose, we investigated the aggregated effect size between PAQ-C and accelerometer scores considering 13 publications. The present work is novel because there are only few reviews discussing self-reported questionaries versus objective PA in children [18,22,38], and it focused on a specific questionnaire (i.e., PAQ-C). The PAQ-C is growing in popularity in different sociocultural contexts. Thus, it is necessary to understand whether the PAQ-C may correctly monitor absolute PA in children and accurately assess the effectiveness and changes of interventions designed to increase activity levels, examine relationships between PA and health, and inform public health policy [38]. This aspect is particularly challenging because it may influence healthy lifestyles during adulthood and older age.
A review on the qualitative attributes and measurement properties of PAQ suggested that a correlation coefficient of 0.5 or higher should be acceptable for the validity of PA [48]. The present study disclosed significant moderate pooled correlations of 0.34 [0.29, 0.39] (see Figure 2) with a low degree of heterogeneity among the considered studies (I2 = 24.7%, τ2 = 0.002, p = 0.194). Additionally, our results were quite consistent: none of the selected studies reached the standard of 0.5 in correlation result (range: 0.119–0.456). These data indicate a moderate convergent validity of PAQ-C, although lower than the acceptable standard [48], when compared with the accelerometer. This result suggests a difference in the ability of PAQ-C and accelerometers to measure the same construct (i.e., PA). Thus, it is possible to argue that when investigating absolute PA with PAQ-C, the risk of bias may be large, corroborating the idea of substantial discrepancies between indirect and direct methods to assess PA in pediatric populations [38]. In other words, the wide correlation variability reported in the considered studies indicates that no clear picture can be drawn regarding the PA levels when using PAQ-C.
Our results are in line with previous reviews on children and youth [18,22,38], adult [15,17,37,49], and older population [17] that reported a large variability in correlation results between direct and indirect methods. In an extensive systematic review on the topic in adult population (age ≥ 18 years), Prince at al. [15] found a low-to-moderate correlation (−0.71 to 0.96) between PAQs and accelerometer measures pointing out that the agreement between the two methods was remarkably low. Similarly, Lee et al. [49] reported a greater variability in correlations (from −0.18 to 0.76) between vigorous or moderate activities assessed by means of the International Physical Activity Questionnaire-Short Form and accelerometer measures, as well as an overestimation in PA by 36% to 173% using self-report questionnaires. Again, with a meta-analytic approach similar to that herein presented, Kim et al. [37] examined the convergent validity of the International Physical Activity Questionnaire with an accelerometer and reported an average effect size of 0.21 [0.17, 0.26] with moderate PA. Similar comparisons were conducted in children and youth (5–17 years old). Chinapaw et al. [18] reviewed 61 PAQs for children and adolescents and reported heterogeneity in the results, with correlations between PAQ and accelerometers ranging from very low to high. These data were confirmed in a recent update study that reported lower acceptable validity, partly due to the low methodological quality of the studies [22].
In our analysis, we did not find heterogeneity among the studies (see I2 and τ2 values), despite the methodological differences of studies included in the meta-analysis. Different types of accelerometers (i.e., uniaxial and triaxial), settings of recorded data (e.g., epoch length or number of days recorded), and data analysis algorithms, such as non-wear-time definition and cutoff point to identify PA intensities (e.g., light, moderate, and vigorous PA), were identified in the selected studies. About two thirds of the studies (i.e., 61.5%) used triaxial rather than uniaxial accelerometers, which are considered more accurate than the latter. Nevertheless, it should be pointed out that all the studies using triaxial accelerometers calculated cutoff PA intensity level through Everson criteria [50], which are based only on the acceleration in the vertical plane. Additionally, we observed a wide variability in epoch lengths setting (ranging from 1 to 30 s). It is well known that the epoch length may affect the estimation of the PA bouts under free-living conditions especially in children [51], and this estimation decreases as epoch length increases [52]. Even if shorter epochs (e.g., 5 s or less) are potentially more sensitive to detect MVPA than longer ones, it seems not to weaken the correlation between PAQ-C and accelerometers. Similarly, while eight studies [16,28,30,31,33,34,35,36] used the international recommend cut-point for children [50,53] to determine the time spent on different PA intensity levels (i.e., range 0–100 counts/min for sedentary behavior, range 101–2295 counts/min for light, range 2296–4011 counts/min for moderate, and ≥4012 counts/min for vigorous PA) five studies [27,32,45,46,47] chose different cut-points. Moreover, while the PAQ-C recalls the PA behavior in the last seven days, 3 out of 13 studies [32,36,45,47] failed to collect the same timeframe due to limiting the accelerometer wearing or considering less than seven days sufficient in the data analysis. Again, not all the studies reported that the self-report and directly assessed PA levels were measured concurrently [30,31,35] leading to an increase of bias. Most of the studies (9 out of 13) [16,27,28,30,31,33,34,35,46] reported requiring that subjects wear the device at least for seven days, but higher variability range in correlation score was reported among these studies (range 0.170–0.390).
All these methodological differences among studies seems not to weaken the correlation between PAQ-C and accelerometers. On the contrary, we were not able to investigate the effect of wearing placement because all included studies placed the accelerometer on the waist. As previously discussed, accelerometers could not measure certain kinds of activities, and the wearing position could amplify this lack. For example, Troiano et al. [54] argued that wearing accelerometers on the wrist could improve wear compliance and allow the measurement of movement during sleep, while Rosemberger et al. [55] claimed that the hip is better for estimating activity energy expenditure and identify activity intensity thresholds. Probably, the appropriate wear location is dependent on specific objectives and will be outlined in the study protocol. For this reason, the effect of wearing placement on correlation between PAQ-C and accelerometers should be taken into account in future studies on the topic.
As a reasonable gold standard for measuring PA does not exist [18], in our study we focused on accelerometers as an objective criterion for measuring PA. Nevertheless, caution is needed when interpreting the findings herein. Indeed, we believe that the results from our study may not be generalized as the overall convergent validity of PAQ-C. Commonly, accelerometer devices are the most used tools to objectively evaluate levels of physical behavior. It allows to directly evaluate the frequency, duration, and intensity of movement and is considered a useful device for estimating energy expenditure [56] in different real contexts. Nevertheless, accelerometer technology did not allow the quantification of some types of activities, such as cycling- and water-based activities or upper body movements, when it is worn on the waist and is not able to discriminate between qualitatively different activities [45,57,58]. On the contrary, the PAQ-C investigates a broad range of leisure and sport activities, which can lead to a larger description of the weekly PA in terms of activity types, time frame during daily and weekly routine, and self-perception of physical activity involvement. Furthermore, differences between PAQ-C score and accelerometers MVPA could be interpreted as the children’s difficulty in judging and feeling their own physical engagement. According to the above findings, our results suggested that PAQ-C and accelerometers may be considered two different tools to investigate PA. In other words, it is possible to suggest that the PAQ-C may be used to investigate children’s PA behaviors (i.e., type and schedule of PA) rather than absolute PA. Concurrently using the two instruments might provide both a qualitative and quantitative evaluation of PA that could permit better exploration of the relation between self-perceived and actual PA in children, to make, for example, corrections to planned activities or to dedicate time to the improvement of self-perception ability. Thus, with the aim of an accurate and effective assessment of PA, it is possible to suggest the use of both instruments to have a deeper overview of PA behavior and level, especially in the first step of the assessment and design of PA interventions [33]. In light of our results, it could be possible to propose the use of the PAQ-C to take information about the type and weekly distribution of physical activities and, thus, provide a global measure of children’s PA, while accelerometers could provide more information about the quantification of the PA.
Some limitations should be finally pointed out. In this systematic review, we focused on the convergent validity of the PAQ-C, but we did not consider measurement properties such as reliability, validity, criterion validity, and measurement error. We considered only correlation coefficients that are not able to detect the agreement and the absolute difference between objective and self-report measures. We focused only on MVPA and not on total PA. It is possible that the correlation between objective and subjective measures of total PA may be larger, due to the lower specificity of the total PA to the use of different cutoffs. Moreover, comparing the PAQ-C score with total PA could overcome difficulties in the perception of physical intensity of children. Additionally, we are not able to investigate gender-related differences in convergent validity. This might be interesting considering the difference in self-perception of PA between males and females [59], even if differences in the considered samples seem not to modify our conclusion, as low heterogeneity shows. Finally, we only focused on English articles disregarding relevant studies published in other languages.
5. Conclusions
To our knowledge, the present study is the first comprehensive attempt to synthesize the scientific evidence on the convergent validity of PAQ-C using meta-analysis. Together the results of this study heightened the moderate convergent validity of PAQ-C with accelerometer measurements. Currently, the drawing of any definitive conclusion concerning the convergent validity of PAQ-C in comparison with the accelerometers is not possible. This suggests that the PAQ-C may be valid for identifying children’ PA behavior rather than for absolute PA. Both subjective and objective assessments of PA have limits and advantages. Considering the different nature of both measurements, it is suggested that, for a more comprehensible and deeper PA overview, a combination of PAQ-C and accelerometer devices appears the most promising. Finally, caution should be exerted when comparing studies using PAQ-C and accelerometers.
As practical applications, caution is needed in the choice of instruments to investigate PA in children. PAQ-C and accelerometers seem to measure different aspects of the same construct. While the first one may provide a qualification of PA (e.g., time frame, weekly routine, and self-perception) the second one may provide information about movement quantification (e.g., intensity, frequency, and duration). In addition, the use of both instruments may provide a deeper overview of PA behavior and level, especially in the first step of the assessment and planning of appropriate PA intervention in children. Finally, the use of both instruments allows for a better understanding of the association between actual and perceived physical activity in children.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, P.R.B. and D.M.; formal analysis, P.R.B.; writing—original draft preparation, P.R.B., C.L. and D.M.; writing—review and editing, D.M., S.C., C.L., A.R. and P.R.B.; supervision, P.R.B., C.L. and A.R. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was supported by the project “ACTLIFE: IS ACTIVE LIFESTYLE ENOUGH FOR HEALTH AND WELLBEING?—PRIN—Bando 2017.
Institutional Review Board Statement
The study was conducted according to the guidelines of the Declaration of Helsinki and approved by the Bioethics Committee of the University of Torino (Turin, Italy; #134691; date of approval: 9 March 2020).
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- World Health Organization WHO. Guidelines on Physical Activity and Sedentary Behaviour: Web Annex Evidence Profiles. Available online: https://apps.who.int/iris/bitstream/handle/10665/336656/9789240015128-eng.pdf (accessed on 28 November 2020).
- Hong, I.; Coker-Bolt, P.; Anderson, K.R.; Lee, D.; Velozo, C.A. Relationship Between Physical Activity and Overweight and Obesity in Children: Findings from the 2012 National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey National Youth Fitness Survey. Am. J. Occup. Ther. 2016, 70, 70051800601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pedersen, B.K.; Saltin, B. Exercise as medicine—Evidence for prescribing exercise as therapy in 26 different chronic diseases. Scand. J. Med. Sci. Sports 2015, 25 (Suppl. S3), 1–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rush, E.; Simmons, D. Physical Activity in Children: Prevention of Obesity and Type 2 Diabetes. Pediatr. Fitness 2014, 60, 113–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheikholeslami, S.; Ghanbarian, A.; Azizi, F. The Impact of Physical Activity on Non-Communicable Diseases: Findings from 20 Years of the Tehran Lipid and Glucose Study. Int. J. Endocrinol. Metab. 2018, 16 (Suppl. 4), e84740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodriguez-Ayllon, M.; Cadenas-Sánchez, C.; Estévez-López, F.; Muñoz, N.E.; Mora-Gonzalez, J.; Migueles, J.H.; Molina-García, P.; Henriksson, H.; Mena-Molina, A.; Martínez-Vizcaíno, V.; et al. Role of Physical Activity and Sedentary Behavior in the Mental Health of Preschoolers, Children and Adolescents: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Sports Med. 2019, 49, 1383–1410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marker, A.M.; Steele, R.G.; Noser, A.E. Physical activity and health-related quality of life in children and adolescents: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Health Psychol. 2018, 37, 893–903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pälve, K.S.; Pahkala, K.; Magnussen, C.G.; Koivistoinen, T.; Juonala, M.; Kähönen, M.; Lehtimäki, T.; Rönnemaa, T.; Viikari, J.S.A.; Raitakari, O.T. Association of Physical Activity in Childhood and Early Adulthood with Carotid Artery Elasticity 21 Years Later: The Cardiovascular Risk in Young Finns Study. J. Am. Heart Assoc. 2014, 3, e000594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magnussen, C.G.; Koskinen, J.; Chen, W.; Thomson, R.; Schmidt, M.D.; Srinivasan, S.R.; Kivimäki, M.; Mattsson, N.; Kähönen, M.; Laitinen, T. Pediatric Metabolic Syndrome Predicts Adulthood Metabolic Syndrome, Subclinical Atherosclerosis and Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus but is no Better than Body Mass Index Alone: The Bogalusa Heart Study and the Cardiovascular Risk in Young Finns Study. Circulation 2010, 122, 1604–1611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Steene-Johannessen, J.; Hansen, B.H.; Dalene, K.E.; Kolle, E.; Northstone, K.; Møller, N.C.; Grøntved, A.; Wedderkopp, N.; Kriemler, S.; Page, A.S.; et al. Variations in accelerometry measured physical activity and sedentary time across Europe—Harmonized analyses of 47,497 children and adolescents. Int. J. Behav. Nutr. Phys. Act. 2020, 17, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- World Health Organization WHO. Europe Publications-Physical Activity Strategy for the WHO European Region 2016–2025. Available online: https://www.euro.who.int/en/publications/abstracts/physical-activity-strategy-for-the-who-european-region-2016–2025 (accessed on 6 November 2020).
- World Health Organization Global Action Plan on Physical Activity 2018–2030: More Active People for a Healthier World. Available online: http://www.who.int/ncds/prevention/physical-activity/gappa/action-plan (accessed on 29 November 2020).
- Colley, R.C.; Garriguet, D.; Adamo, K.B.; Carson, V.; Janssen, I.; Timmons, B.W.; Tremblay, M.S. Physical activity and sedentary behavior during the early years in Canada: A cross-sectional study. Int. J. Behav. Nutr. Phys. Act. 2013, 10, 54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ding, D.; Mutrie, N.; Bauman, A.; Pratt, M.; Hallal, P.R.C.; Powell, K.E. Physical activity guidelines 2020: Comprehensive and inclusive recommendations to activate populations. Lancet 2020, 396, 1780–1782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prince, S.A.; Adamo, K.B.; Hamel, M.E.; Hardt, J.; Gorber, S.C.; Tremblay, M. A comparison of direct versus self-report measures for assessing physical activity in adults: A systematic review. Int. J. Behav. Nutr. Phys. Act. 2008, 5, 1–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gobbi, E.; Elliot, C.; Varnier, M.; Carraro, A. Psychometric Properties of the Physical Activity Questionnaire for Older Children in Italy: Testing the Validity among a General and Clinical Pediatric Population. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0156354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skender, S.; Ose, J.; Chang-Claude, J.; Paskow, M.; Brühmann, B.; Siegel, E.M.; Steindorf, K.; Ulrich, C.M. Accelerometry and physical activity questionnaires—A systematic review. BMC Public Health 2016, 16, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chinapaw, M.J.; Mokkink, L.B.; Van Poppel, M.N.M.; Van Mechelen, W.; Terwee, C.B.; Chinapaw, M.J.M. Physical Activity Questionnaires for Youth. Sports Med. 2010, 40, 539–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sabia, S.; Van Hees, V.T.; Shipley, M.J.; Trenell, M.I.; Hagger-Johnson, G.; Elbaz, A.; Kivimaki, M.; Singh-Manoux, A. Association Between Questionnaire and Accelerometer-Assessed Physical Activity: The Role of Sociodemographic Factors. Am. J. Epidemiol. 2014, 179, 781–790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Janz, K.; Lutuchy, E.; Wenthe, P.; Levy, S. Measuring Activity in Children and Adolescents using Self-Report: PAQ-C and PAQ-A. Med. Sci. Sports Exerc. 2008, 40, 767–772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Helmerhorst, H.J.F.; Brage, S.; Warren, J.; Besson, H.; Ekelund, U. A systematic review of reliability and objective criterion-related validity of physical activity questionnaires. Int. J. Behav. Nutr. Phys. Act. 2012, 9, 103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hidding, L.M.; Chinapaw, M.J.M.; Van Poppel, M.N.M.; Mokkink, L.B.; Altenburg, T.M. An Updated Systematic Review of Childhood Physical Activity Questionnaires. Sports Med. 2018, 48, 2797–2842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crocker, P.R.E.; Bailey, D.A.; Faulkner, R.A.; Kowalski, K.C.; McGrath, R. Measuring general levels of physical activity: Preliminary evidence for the Physical Activity Questionnaire for Older Children. Med. Sci. Sports Exerc. 1997, 29, 1344–1349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kowalski, K.; Crocker, P.; Donen, R.; Honours, B. The Physical Activity Questionnaire for Older Children (PAQ-C) and Adolescents (PAQ-A) Manual; College of Kinesiology, University of Saskatchewan: Saskatoon, SK, Canada, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Thomas, E.L.; Upton, D. Psychometric properties of the physical activity questionnaire for older children (PAQ-C) in the UK. Psychol. Sport Exerc. 2014, 15, 280–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Voss, C.; Harris, K.C. Physical activity evaluation in children with congenital heart disease. Heart 2017, 103, 1408–1412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kowalski, K.C.; Crocker, P.R.; Faulkner, R.A. Validation of the Physical Activity Questionnaire for Older Children. Pediatr. Exerc. Sci. 1997, 9, 174–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Venetsanou, F.; Emmanouilidou, K.; Soutos, K.; Sotiriou, S.A.; Bastida, L.; Moya, A.; Kambas, A. Towards a Functional Approach to the Assessment of Daily Life Physical Activity in Children: Are the PAQ-C and Fitbit Flex-2 Technically Adequate? Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 8503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bervoets, L.; Van Noten, C.; Van Roosbroeck, S.; Hansen, D.; Van Hoorenbeeck, K.; Verheyen, E.; Van Hal, G.; Vankerckhoven, V. Reliability and Validity of the Dutch Physical Activity Questionnaires for Children (PAQ-C) and Adolescents (PAQ-A). Arch. Public Health 2014, 72, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.J.; Baranowski, T.; Lau, W.P.; Chen, T.A.; Pitkethly, A.J. Validation of the Physical Activity Questionnaire for Older Children (PAQ-C) among Chinese Children. Biomed. Environ. Sci. 2016, 29, 177–186. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.-J.; Baranowski, T.; Lau, P.W.C.; Chen, T.-A.; Zhang, S.-G. Psychological Correlates of Self-Reported and Objectively Measured Physical Activity among Chinese Children—Psychological Correlates of PA. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2016, 13, 1006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fairclough, S.J.; Boddy, L.M.; Ridgers, N.D.; Stratton, G.; Cumming, S. Biological maturity and primary school children’s physical activity: Influence of different physical activity assessment instruments. Eur. J. Sport Sci. 2011, 11, 241–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benítez-Porres, J.; López-Fernández, I.; Raya, J.F.; Carnero, S.Á.; Alvero-Cruz, J.R.; Carnero, E. Álvarez Reliability and Validity of the PAQ-C Questionnaire to Assess Physical Activity in Children. J. Sch. Health 2016, 86, 677–685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benítez-Porres, J.; Alvero-Cruz, J.R.; Sardinha, L.B.; López-Fernández, I.; Carnero, E.A. Cut-off Values for Classifying Active Children and Adolescents using the Physical Activity Questionnaire: PAQ-C and PAQ-A. Nutr. Hosp. 2016, 33, 1036–1044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, C.H.S.; Ha, A.S.C.; Ng, J.Y.Y.; Lubans, D.R. Associations between fundamental movement skill competence, physical activity and psycho-social determinants in Hong Kong Chinese children. J. Sports Sci. 2018, 37, 229–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ben Jemaa, H.; Mankaï, A.; Mahjoub, F.; Kortobi, B.; Khlifi, S.; Draoui, J.; Minaoui, R.; Karmous, I.; Ben Hmad, H.; Ben Slama, F.; et al. Physical Activity Level Assessed by Accelerometer and PAQ-C in Tunisian Children. Ann. Nutr. Metab. 2018, 73, 234–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, Y.; Park, I.; Kang, M. Convergent validity of the International Physical Activity Questionnaire (IPAQ): Meta-analysis. Public Health Nutr. 2012, 16, 440–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adamo, K.B.; Prince, S.A.; Tricco, A.C.; Connor-Gorber, S.; Tremblay, M. A comparison of indirect versus direct measures for assessing physical activity in the pediatric population: A systematic review. Pediatr. Obes. 2009, 4, 2–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vandenbroucke, J.P.; Von Elm, E.; Altman, D.G.; Gøtzsche, P.C.; Mulrow, C.D.; Pocock, S.J.; Poole, C.; Schlesselman, J.J.; Egger, M.; Initiative, F.T.S. Strengthening the Reporting of Observational Studies in Epidemiology (STROBE): Explanation and Elaboration. PLoS Med. 2007, 4, e297–e835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rupinski, M.T.; Dunlap, W.P. Approximating Pearson Product-Moment Correlations from Kendall’s Tau and Spearman’s Rho. Educ. Psychol. Meas. 1996, 56, 419–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Higgins, J.P.T.; Thompson, S.G.; Deeks, J.J.; Altman, D.G. Measuring inconsistency in meta-analyses. BMJ 2003, 327, 557–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balduzzi, S.; Rücker, G.; Schwarzer, G. How to perform a meta-analysis with R: A practical tutorial. Évid. Based Ment. Health 2019, 22, 153–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borenstein, M.; Hedges, L.V.; Higgins, J.P.T.; Rothstein, H.R. Introduction to Meta-Analysis; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2009; p. 452. [Google Scholar]
- Cohen, J. A power primer. Tutor. Quant. Methods Psychol. 2007, 3, 79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Labbrozzi, D.; Bucci, I.; Bortoli, L.; Bertollo, M.; Doria, C.; Robazza, C. Age-Related Differences in Actual and Perceived Levels of Physical Activity in Adolescent Girls. Percept. Mot. Ski. 2012, 114, 723–734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saint-Maurice, P.F.; Welk, G.J.; Beyler, N.K.; Bartee, R.T.A.; Heelan, K. Calibration of self-report tools for physical activity research: The Physical Activity Questionnaire (PAQ). BMC Public Health 2014, 14, 461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ni Mhurchu, C.; Maddison, R.; Jiang, Y.; Jull, A.; Prapavessis, H.; Rodgers, A. Couch potatoes to jumping beans: A pilot study of the effect of active video games on physical activity in children. Int. J. Behav. Nutr. Phys. Act. 2008, 5, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Terwee, C.B.; Mokkink, L.B.; Van Poppel, M.N.; Chinapaw, M.J.; Van Mechelen, W.; De Vet, H.C. Qualitative Attributes and Measurement Properties of Physical Activity Questionnaires. Sports Med. 2010, 40, 525–537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, P.H.; Macfarlane, D.J.; Lam, T.H.; Stewart, S.M. Validity of the international physical activity questionnaire short form (IPAQ-SF): A systematic review. Int. J. Behav. Nutr. Phys. Act. 2011, 8, 115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Evenson, K.R.; Catellier, D.J.; Gill, K.; Ondrak, K.S.; McMurray, R.G. Calibration of two objective measures of physical activity for children. J. Sports Sci. 2008, 26, 1557–1565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aibar, A.E.; Bois, J.; Zaragoza, J.; Generelo, E.A.; Julián, J.; Paillard, T. Do epoch lengths affect adolescent’s compliance with physical activity guidelines? J. Sports Med. Phys. Fit. 2014, 54, 326–334. [Google Scholar]
- Banda, J.A.; Haydel, K.F.; Davila, T.; Desai, M.; Bryson, S.; Haskell, W.L.; Matheson, D.; Robinson, T.N. Effects of Varying Epoch Lengths, Wear Time Algorithms, and Activity Cut-Points on Estimates of Child Sedentary Behavior and Physical Activity from Accelerometer Data. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0150534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trost, S.G.; Loprinzi, P.D.; Moore, R.; Pfeiffer, K.A. Comparison of Accelerometer Cut Points for Predicting Activity Intensity in Youth. Med. Sci. Sports Exerc. 2011, 43, 1360–1368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Troiano, R.P.; McClain, J.J.; Brychta, R.J.; Chen, K.Y. Evolution of accelerometer methods for physical activity research. Br. J. Sports Med. 2014, 48, 1019–1023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosenberger, M.E.; Haskell, W.L.; Albinali, F.; Mota, S.; Nawyn, J.; Intille, S. Estimating Activity and Sedentary Behavior from an Accelerometer on the Hip or Wrist. Med. Sci. Sports Exerc. 2013, 45, 964–975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García-Prieto, J.C.; Martinez-Vizcaino, V.; García-Hermoso, A.; Sánchez-López, M.; Arias-Palencia, N.; Fonseca, J.F.O.; Mora-Rodriguez, R. Energy Expenditure in Playground Games in Primary School Children Measured by Accelerometer and Heart Rate Monitors. Int. J. Sport Nutr. Exerc. Metab. 2017, 27, 467–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Terrier, P.; Aminian, K.; Schutz, Y. Can accelerometry accurately predict the energy cost of uphill/downhill walking? Ergonomics 2001, 44, 48–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ayabe, M.; Kumahara, H.; Morimura, K.; Tanaka, H. Epoch length and the physical activity bout analysis: An accelerometry research issue. BMC Res. Notes 2013, 6, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Crocker, P.R.; Eklund, R.C.; Kowalski, K.C. Children’s physical activity and physical self-perceptions. J. Sports Sci. 2000, 18, 383–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).