Study on Factors of People’s Wearing Masks Based on Two Online Surveys: Cross-Sectional Evidence from China
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Data Resource
2.2. Methods and Design
3. Results
3.1. Demographic Characteristics of Samples
3.2. Behaviors of Masks-Wearing in Different Population
3.3. Results of Logistic Regression Analysis
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
6. Theoretical and Practical Implications
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Mrcs, S.L.; Mrcs, T.L.M.Y.; Frcp, E.Y.K.T.; Frcpa, K.S.C.F.; Frcs, E.W.H.T.; Frcs, K.K.W.L.F. Study of Conjunctival Carriage of SARS-CoV2 using Serial Sampling: Risk factors and Protective factors. Can. J. Ophthalmol. 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madas, B.G.; Füri, P.; Farkas, R.; Nagy, A.; Horváth, A. Deposition distribution of the new coronavirus (SARS-CoV-2) in the human airways upon exposure to cough-generated droplets and aerosol particles. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 22430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okello, G. Findings of a Cross-Sectional Survey on Knowledge, Attitudes, and Practices about COVID-19 in Uganda: Implications for Public Health Prevention and Control Measures. Biomed Res. Int. 2020, 2020, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maclntyre, C.R.; Cauchemez, S.; Dwyer, D.E.; Seale, H.; Cheung, P.; Browne, G.; Fasher, M.; Wood, J.; Gao, Z.H.; Booy, R.; et al. Face Mask Use and Control of Respiratory Virus Transmission in Households. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2009, 15, 233–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verma, S.; Dhanak, M.; Frankenfield, J. Visualizing the effectiveness of face masks in obstructing respiratory jets. Phys. Fluids 2020, 32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, V.C.C.; Wong, S.C.; Chuang, V.W.M.; So, S.Y.C.; Chen, J.H.K.; Sridhar, S.; To, K.K.W.; Chan, J.F.W.; Hung, I.F.N.; Ho, P.L.; et al. The role of community-wide wearing of face mask for control of coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) epidemic due to SARS-CoV-2. J. Infect. 2020, 81, 107–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leffler, C.T.; Ing, E.; Lykins, J.D.; Hogan, M.C.; McKeown, C.A.; Grzybowski, A. Association of Country-wide Coronavirus Mortality with Demographics, Testing, Lockdowns, and Public Wearing of Masks. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 2020, 103, 2400–2411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choudhury, A.; Singh, M.; Khurana, D.K.; Mustafi, S.M.; Ganapathy, U.; Kumar, A.; Sharma, S. Physiological Effects of N95 FFP and PPE in Healthcare Workers in COVID Intensive Care Unit: A Prospective Cohort Study. Indian J. Crit. Care Med. 2020, 24, 1169–1173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farronato, M.; Boccalari, E.; Del Rosso, E.; Lanteri, V.; Mulder, R.; Maspero, C. A Scoping Review of Respirator Literature and a Survey among Dental Professionals. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 5968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- C, H.M. The relations between age, face mask perceptions and face mask wearing. J. Public Health 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haischer, M.H.; Beilfuss, R.; Hart, M.R.; Opielinski, L.; Wrucke, D.; Zirgaitis, G.; Uhrich, T.D.; Hunter, S.K. Who is wearing a mask? Gender-, age-, and location-related differences during the COVID-19 pandemic. PLoS ONE 2020, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iglesias, R.L.B.; Alonso, A.H.I. Quarantined democracies: Policy responses to the COVID-19 and the future of democracy. Rev. Esp. Sociol. 2020, 29, 703–714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taghrir, M.H.; Akbarialiabad, H.; Marzaleh, M.A. Efficacy of Mass Quarantine as Leverage of Health System Governance during COVID-19 Outbreak: A Mini Policy Review. Arch. Iran. Med. 2020, 23, 265–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Damiani, G.; Gironi, L.C.; Grada, A.; Kridin, K.; Finelli, R.; Buja, A.; Bragazzi, N.L.; Pigatto, P.D.M.; Savoia, P. COVID-19 related masks increase severity of both acne (maskne) and rosacea (mask rosacea): Multi-center, real-life, telemedical, and observational prospective study. Dermatol. Ther. 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, X.; Song, B.; Wu, A.N.S.; Mo, P.K.H.; Di, J.L.; Wang, Q.; Lau, J.T.F.; Wang, L.H. Social, Cognitive, and eHealth Mechanisms of COVID-19-Related Lockdown and Mandatory Quarantine That Potentially Affect the Mental Health of Pregnant Women in China: Cross-Sectional Survey Study. J. Med. Internet Res. 2021, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nie, J.; Duan, X.L.; Wang, B.B.; Zhao, X.G.; Huang, N. Survey of Environmental Exposure-Related Wearing Masks Behavior Patterns in Chinese Adults. Journal of Environment and Health; Ministry of Health Director: Tianjin, China, 2015.
- Xu, C.J.; Jin, J.F.; Song, J.P.; Yang, Y.; Yao, M.Q.; Zhang, Y.P.; Zhao, R.Y.; Chen, Z.M. Application of re fined management in prevention and control of the coronavirus disease 2019 epidemic in non-isol.ated areas of a general hospital. Int. J. Nurs. Sci. 2020, 7, 143–147. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Howard, M.C. Gender, face mask perceptions, and face mask wearing: Are men being dangerous during the COVID-19 pandemic? Pers. Indiv. Differ. 2021, 170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Callaghan, T.; Lueck, J.A.; Trujillo, K.L.; Ferdinand, A.O. Rural and urban differences in COVID-19 prevention behaviors. J. Rural Health 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.Y.; Ran, L.; Liu, Q.; Hu, Q.K.; Du, X.Y.; Tan, X.D. Hand Hygiene, Mask-Wearing Behaviors and Its Associated Factors during the COVID-19 Epidemic: A Cross-Sectional Study among Primary School Students in Wuhan, China. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 2893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Konig, A.; Dressler, A. A mixed-methods analysis of mobility behavior changes in the COVID-19 era in a rural case study. Eur. Transp. Res. Rev. 2021, 13, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Javid, B.W.M. Covid-19: Should the public wear face masks? BMJ NJMJ 2020, 369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Tamura, E.; Kishimoto, K.; Fukushima, N. Patients’ reaction to pharmacists wearing a mask during their consultations. Yakugaku Zasshi J. Pharm. Soc. Jpn. 2013, 133, 737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lazzarino, A.I.; Steptoe, A.; Hamer, M.; Michie, S. Covid-19: Important potential side effects of wearing face masks that we should bear in mind. BMJ-Brit. Med. J. 2020, 369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toomey, E.C.; Conway, Y.; Burton, C.; Smith, S.; Smalle, M.; Chan, X.H.S.; Adisesh, A.; Tanveer, S.; Ross, L.; Thomson, I.; et al. Extended use or reuse of single-use surgical masks and filtering face-piece respirators during the coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) pandemic: A rapid systematic review. Infect. Control Hosp. Epidemiol. 2021, 42, 75–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ishida, R.; Matsumoto, Y.; Onguchi, T.; Kaido, M.; Iwamuro, K.; Kobayashi, J.; Takano, Y.; Shimazaki, J.; Goto, E.; Dogru, M.; et al. Tear film with “Orgahexa EyeMasks” in patients with meibomian gland dysfunction. Optom. Vis. Sci. 2008, 85, 684–691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kitamura, R. The effects of added transportation capacity on travel: A review of theoretical and empirical results. Transportation 2009, 36, 745–762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wolfel, R.; Corman, V.M.; Guggemos, W.; Seilmaier, M.; Zange, S.; Muller, M.A.; Niemeyer, D.; Jones, T.C.; Vollmar, P.; Rothe, C.; et al. Virological assessment of hospitalized patients with COVID-2019 (vol 581, pg 465, 2020). Nature 2020, 588, E35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Variable | Variable Assignment/Range | Total (N = 6761) | Survey 1 (n = 3104) | Survey 2 (n = 3657) | χ2 | p |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sex | 11.169 | <0.001 | ||||
| “Male = 1” | 2218 (32.8) | 954 (30.7) | 1264 (34.6) | |||
| “Female = 2” | 4543 (67.2) | 2150 (69.3) | 2393 (65.4) | |||
| Age | 52.800 | <0.001 | ||||
| 19–29 | 1822 (26.9) | 814 (26.2) | 1008 (27.6) | |||
| 30–39 | 2040 (30.2) | 1044 (33.6) | 996 (27.2) | |||
| 40–49 | 1823 (27.0) | 834 (26.9) | 989 (27.0) | |||
| 50–59 | 936 (13.8) | 369 (11.9) | 567 (15.5) | |||
| ≥60 | 140 (2.1) | 43 (1.4) | 97 (2.7) | |||
| Area | 0.027 | 0.869 | ||||
| “Urban = 1” | 5349 (79.1) | 2453 (79.0) | 2896 (79.2) | |||
| “Rural = 2” | 1412 (22.3) | 651 (21.0) | 761 (20.8) | |||
| Current residence | 360.001 | <0.001 | ||||
| “Wuhan, Hubei = 1” | 1912 (28.3) | 619 (12.3) | 1293 (35.4) | |||
| “Other cities in Hubei = 2” | 850 (12.6) | 267 (5.1) | 583 (15.9) | |||
| “Other provinces and cities = 3” | 3999 (59.1) | 2218 (82.7) | 1781 (48.7) | |||
| Education | 54.189 | <0.001 | ||||
| “Middle school or below = 1” | 274 (4.1) | 149 (5.5) | 125 (4.3) | |||
| “High school = 2” | 882 (13) | 453 (13.9) | 429 (11.8) | |||
| “College = 3” | 4371 (64.7) | 2035 (66.4) | 2336 (64.9) | |||
| “Master degree and above = 4” | 1234 (18.3) | 467 (14.2) | 767 (19.1) | |||
| Marital status | 0.298 | 0.585 | ||||
| “Single = 1” | 2112 (31.2) | 980 (31.6) | 1132 (31.0) | |||
| “Married = 2” | 2404 (68.8) | 2124 (68.4) | 2525 (69.0) | |||
| Monthly income (Yuan) | 31.061 | <0.001 | ||||
| <2000 | 1042 (15.4) | 397 (12.8) | 645 (17.6) | |||
| 2000–5000 | 2171 (32.1) | 1034 (33.3) | 1137 (31.1) | |||
| 5001–10,000 | 1967 (29.1) | 939 (30.3) | 1028 (28.1) | |||
| 10,001–15,000 | 815 (12.1) | 381 (12.3) | 434 (11.9) | |||
| >15,000 | 766 (11.3) | 353 (11.4) | 413 (11.3) | |||
| Living alone | 9.440 | 0.002 | ||||
| “No = 1” | 4934 (73) | 1343 (98.5) | 2364 (96.5) | |||
| Yes = 1” | 1827 (27) | 20 (1.5) | 86 (3.5) | |||
| Whether there is a job or not | 47.418 | <0.001 | ||||
| “No = 1” | 1277 (18.9) | 537 (17.3) | 740 (82.7) | |||
| “Yes = 1” | 5484 (81.1) | 2567 (20.2) | 2917 (79.8) | |||
| Living alone | 80.504 | <0.001 | ||||
| No | “No = 1” | 6500 (96.1) | 3055 (98.4) | 3445 (94.2) | ||
| Yes | “Yes = 1” | 261 (3.9) | 49 (1.6) | 212 (5.8) | ||
| Whether there is a job or not | 1013.286 | <0.001 | ||||
| No | “No = 1” | 4934 (73.0) | 1686 (54.3) | 3248 (88.8) | ||
| Yes | “Yes = 1” | 1827 (27.0) | 1418 (45.7) | 409 (11.2) | ||
| Confirmed infected in personal network | 21.771 | <0.001 | ||||
| No | “No = 1” | 5586 (82.6) | 2637 (85.0) | 2949 (80.6) | ||
| Yes | “Yes = 1” | 1175 (17.4) | 467 (15.0) | 708 (19.4) |
| Wave | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Variable | Category | No | Yes | χ2/t | p |
| Gender | 2.836 | 0.092 | |||
| Male | 3.70% | 96.30% | |||
| Female | 3.00% | 97.00% | |||
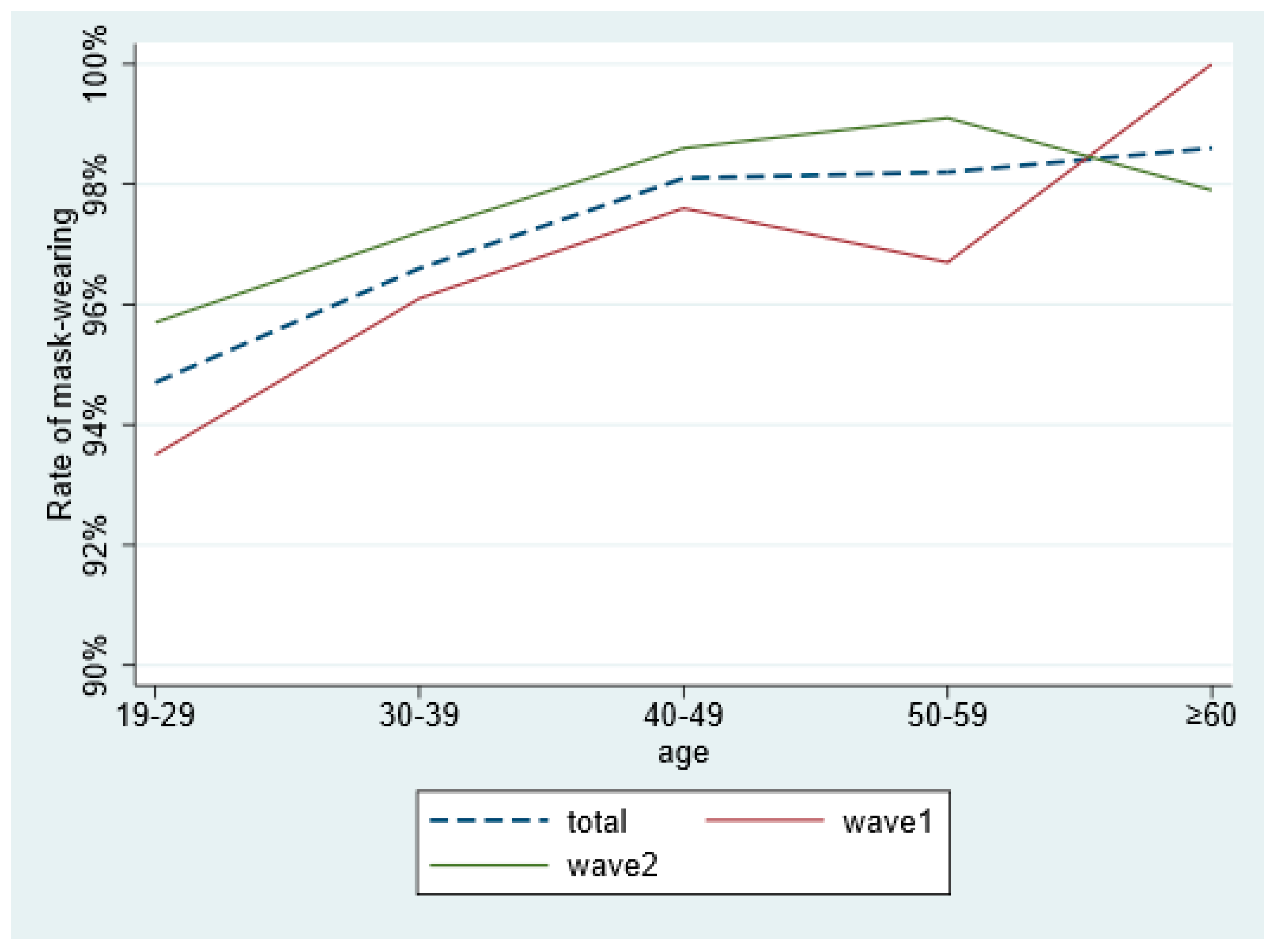
| Age | 42.761 | <0.001 | |||
| 19–29 | 5.30% | 94.70% | |||
| 30–39 | 3.40% | 96.60% | |||
| 40–49 | 1.90% | 98.10% | |||
| 50–59 | 1.80% | 98.20% | |||
| ≥60 | 1.40% | 98.60% | |||
| Current residence | |||||
| Wuhan, Hubei | 2.60% | 97.40% | 5.061 | 0.080 | |
| Other cities in Hubei | 4.10% | 95.90% | |||
| Other provinces and cities | 3.40% | 96.60% | |||
| Area | 115.572 | <0.001 | |||
| Urban | 2.00% | 98.00% | |||
| Rural | 7.70% | 92.30% | |||
| Education | 11.311 | 0.023 | |||
| Middle school or below | 6.60% | 93.40% | |||
| High school | 2.60% | 97.40% | |||
| College | 3.20% | 96.80% | |||
| Master degree and above | 3.00% | 97.00% | |||
| Marital status | 15.665 | <0.001 | |||
| Not married | 5.20% | 94.80% | |||
| Married | 2.30% | 97.70% | |||
| Job status | 67.836 | <0.001 | |||
| No | 6.90% | 93.1% | |||
| Yes | 2.40% | 97.6% | |||
| Living alone | 0.745 | 0.388 | |||
| No | 3.30% | 96.70% | |||
| Yes | 2.30% | 97.70% | |||
| Monthly income (RMB) | 82.700 | <0.001 | |||
| <2000 | 7.70% | 92.30% | |||
| 2000–5000 | 2.80% | 97.20% | |||
| 5001–10,000 | 2.10% | 97.90% | |||
| 10,001–15,000 | 3.10% | 96.90% | |||
| >15,000 | 1.6% | 98.4% | |||
| Quarantine | 16.362 | <0.001 | |||
| No | 2.70% | 97.30% | |||
| Yes | 4.70% | 95.30% | |||
| Confirmed infected in personal network | 0.275 | 0.600 | |||
| No | 3.30% | 96.70% | |||
| Yes | 3.00% | 97.00% | |||
| Wave 1 (n = 3104) | Wave 2 (n = 3657) | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Category | Model 1 | Model 2 | Model 3 | Model 4 | Model 5 | Model 6 | |
| Gender | Female | 1.544 * | 1.376 | 1.396 | 1.239 | 1.191 | 1.186 |
| Age | 19–29 | ||||||
| 30–39 | 0.724 | 0.596 | 0.604 | 0.752 | 0.670 | 0.660 | |
| 40–49 | 1.217 | 0.878 | 0.861 | 1.528 | 1.430 | 1.398 | |
| 50–59 | 1.076 | 0.668 | 0.672 | 2.929 | 2.508 | 2.455 | |
| ≥60 | 1.492 | 1.282 | 1.219 | ||||
| Education | Middle school or below | ||||||
| High school | 3.804 * | 2.707 * | 2.744 | 0.541 | 0.547 | 0.527 | |
| College | 2.75 * | 1.498 | 1.447 | 0.822 | 0.625 | 0.589 | |
| Master degree and above | 4.424 * | 1.923 | 1.940 | 0.573 | 0.41 | 0.384 | |
| Marital status | Married | 1.967 * | 1.704 * | 1.724 | 0.784 | 0.879 | 0.858 |
| Job status | Have a job | 1.749 | 1.733 | 1.670 | 2.001 | 2.307 * | 2.306 * |
| Monthly income (RMB) | <2000 | ||||||
| 2000–5000 | 1.508 | 1.15 | 1.156 | 2.348 * | 2.149 | 2.178 * | |
| 5001–10,000 | 1.852 | 1.32 | 1.364 | 3.085 * | 2.437 | 2.518 * | |
| 10,001–15,000 | 1.181 | 0.837 | 0.843 | 1.914 | 1.404 | 1.468 | |
| >15,000 | 2.395 | 1.696 | 1.808 | 3.504* | 2.154 | 2.216 | |
| Current residence | Wuhan, Hubei | ||||||
| Other cities in Hubei | 0.822 | 0.814 | 0.709 | 0.705 | |||
| Other provinces and cities | 0.755 | 0.698 | 1.842 * | 1.840 * | |||
| Area | Rural | 0.262 * | 0.262 * | 0.573 * | 0.568 * | ||
| Quarantine | Yes | 0.629 * | 0.617 | ||||
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, L.; Zhu, S.; Yao, H.; Li, M.; Si, G.; Tan, X. Study on Factors of People’s Wearing Masks Based on Two Online Surveys: Cross-Sectional Evidence from China. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 3447. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph18073447
Zhang L, Zhu S, Yao H, Li M, Si G, Tan X. Study on Factors of People’s Wearing Masks Based on Two Online Surveys: Cross-Sectional Evidence from China. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health. 2021; 18(7):3447. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph18073447
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Ling, Sirong Zhu, Hui Yao, Mengying Li, Guanglin Si, and Xiaodong Tan. 2021. "Study on Factors of People’s Wearing Masks Based on Two Online Surveys: Cross-Sectional Evidence from China" International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health 18, no. 7: 3447. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph18073447
APA StyleZhang, L., Zhu, S., Yao, H., Li, M., Si, G., & Tan, X. (2021). Study on Factors of People’s Wearing Masks Based on Two Online Surveys: Cross-Sectional Evidence from China. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 18(7), 3447. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph18073447






