Quadratus Lumborum and Transversus Abdominis Plane Blocks and Their Impact on Acute and Chronic Pain in Patients after Cesarean Section: A Randomized Controlled Study
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Design
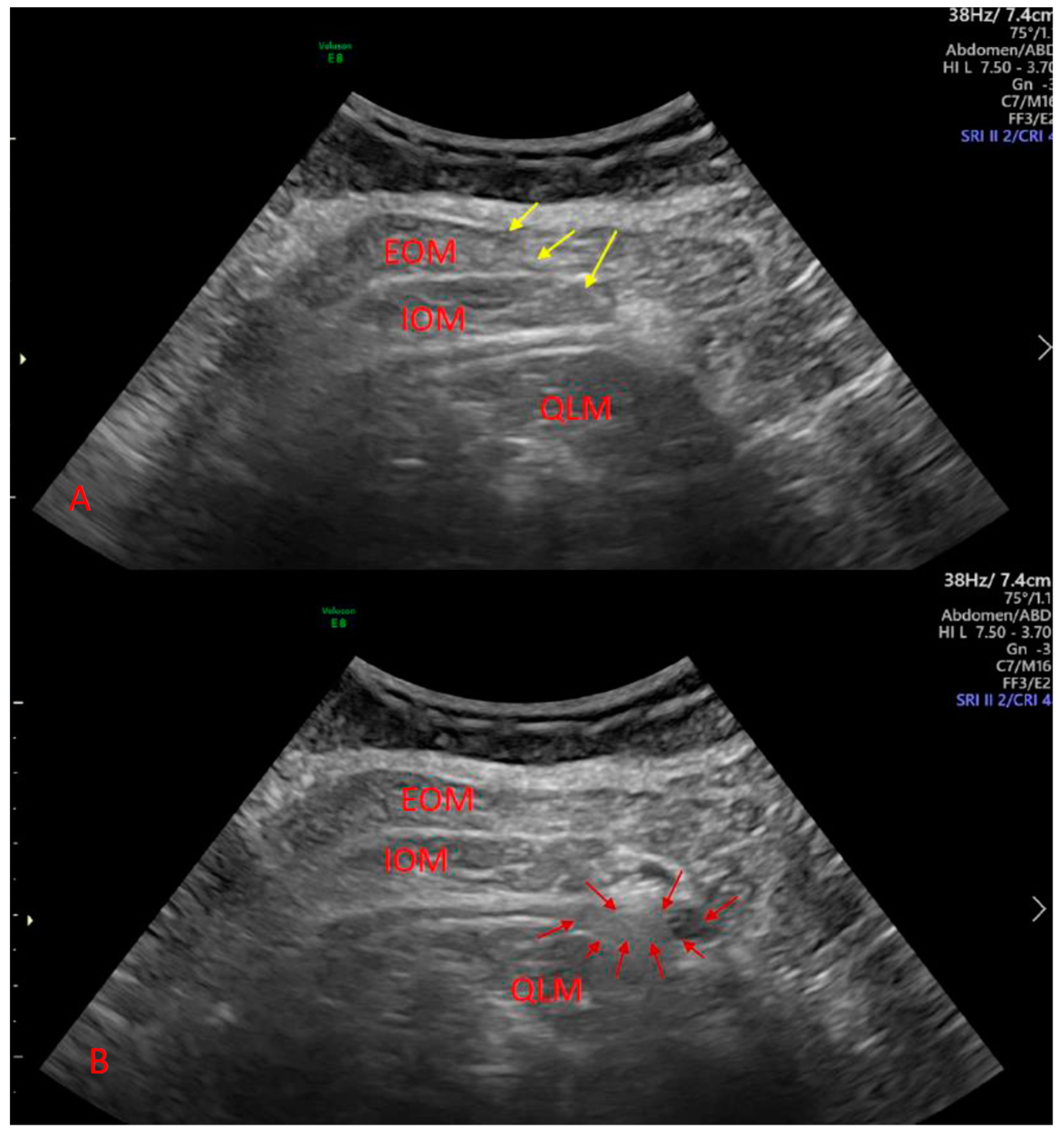
2.2. Procedure
2.3. Pain Management
2.4. Outcomes
2.5. Statistical Analysis and Sample Size Calculation
3. Results
3.1. Acute Pain
3.2. Chronic Pain
3.3. Chronic Pain Predictors
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Betrán, A.; Ye, J.; Moller, A.; Zhang, J.; Gülmezoglu, A.; Torloni, M. The increasing trend in Caesarean section rates: Global, regional and national estimates: 1990–2014. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0148343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rollins, M.; Lucero, J. Overview of anesthetic considerations for Cesarean delivery. Br. Med. Bull. 2012, 101, 105–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Borys, M.; Zyzak, K.; Hanych, A.; Domagała, M.; Gałkin, P.; Gałaszkiewicz, K.; Kłaput, A.; Wróblewski, K.; Miękina, J.; Onichimowski, D.; et al. Survey of postoperative pain control in different types of hospitals: A multicenter observational study. BMC Anesthesiol. 2018, 18, 83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eisenach, J.; Pan, P.; Smiley, R.; Lavand’homme, P.; Landau, R.; Houle, T. Severity of acute pain after childbirth, but not type of delivery, predicts persistent pain and postpartum depression. Pain 2008, 140, 87–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Evans, S.; Keenan, T.; Shipton, E. Psychosocial adjustment and physical health of children living with maternal chronic pain. J. Paediatr. Child Health 2007, 43, 262–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chin, K.; McDonnell, J.; Carvalho, B.; Sharkey, A.; Pawa, A.; Gadsden, J. Essentials of our current understanding: Abdominal wall blocks. Reg. Anesth. Pain Med. 2019, 42, 133–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mitchell, K.; Smith, C.; Mechling, C.; Wessel, C.; Orebaugh, S.; Lim, G. A review of peripheral nerve blocks for cesarean delivery analgesia. Reg. Anesth. Pain Med. 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abdallah, F.; Halpern, S.; Margarido, C. Transversus abdominis plane block for postoperative analgesia after Caesarean delivery performed under spinal anaesthesia? A systematic review and meta-analysis. Br. J. Anaesth. 2012, 109, 679–687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Champaneria, R.; Shah, L.; Wilson, M.; Daniels, J. Clinical effectiveness of transversus abdominis plane (TAP) blocks for pain relief after caesarean section: A meta-analysis. Int. J. Obstet. Anesth. 2016, 28, 45–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blanco, R.; Ansari, T.; Girgis, E. Quadratus lumborum block for postoperative pain after caesarean section: A randomised controlled trial. Eur. J. Anaesthesiol. 2015, 32, 812–818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mieszkowski, M.; Mayzner-Zawadzka, E.; Tuyakov, B.; Mieszkowska, M.; Żukowski, M.; Waśniewski, T.; Onichimowski, D. Evaluation of the effectiveness of the Quadratus Lumborum Block type I using ropivacaine in postoperative analgesia after a cesarean section: A controlled clinical study. Ginekol. Pol. 2018, 89, 89–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Irwin, R.; Stanescu, S.; Buzaianu, C.; Rademan, M.; Roddy, J.; Gormley, C.; Tan, T. Quadratus lumborum block for analgesia after caesarean section: A randomised controlled trial. Anaesthesia 2020, 75, 89–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Krohg, A.; Ullensvang, K.; Rosseland, L.; Langesæter, E.; Sauter, A. The analgesic effect of ultrasound-guided quadratus lumborum block after cesarean delivery: A randomized clinical trial. Anesth. Analg. 2018, 126, 559–565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hansen, C.; Dam, M.; Steingrimsdottir, G.; Laier, G.; Lebech, M.; Poulsen, T.; Chan, V.; Wolmarans, M.; Bendtsen, T.; Børglum, J. Ultrasound-guided transmuscular quadratus lumborum block for elective cesarean section significantly reduces postoperative opioid consumption and prolongs time to first opioid request: A double-blind randomized trial [published online first, 2019 Jul 14). Reg. Anesth. Pain Med. 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blanco, R.; Ansari, T.; Ria, W.; Shetty, N. Quadratus lumborum block versus transversus abdominis plane block for postoperative pain after cesarean delivery: A randomized controlled trial. Reg. Anesth. Pain Med. 2016, 41, 757–762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bouhassira, D.; Attal, N.; Fermanian, J.; Alchaar, H.; Gautron, M.; Masquelier, E.; Rostaing, S.; Lanteri-Minet, M.; Collin, E.; Grisart, J.; et al. Development and validation of the Neuropathic Pain Symptom Inventory. Pain 2004, 108, 248–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Borys, M.; Potręć-Studzińska, B.; Wiech, M.; Piwowarczyk, P.; Sysiak-Sławecka, J.; Rypulak, E.; Gęca, T.; Kwaśniewska, A.; Czuczwar, M. Transversus abdominis plane block and quadratus lumborum block did not reduce the incidence or severity of chronic postsurgical pain following cesarean section: A prospective, observational study. Anaesthesiol. Intensive Ther. 2019, 51, 257–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schug, S.; Lavand’homme, P.; Barke, A.; Korwisi, B.; Rief, W.; Treede, R. IASP Taskforce for the Classification of Chronic Pain. The IASP classification of chronic pain for ICD-11: Chronic postsurgical or posttraumatic pain. Pain 2019, 160, 45–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- El-Boghdadly, K.; Desai, N.; Halpern, S.; Blake, L.; Odor, P.M.; Bampoe, S.; Carvalho, B.; Sultan, P. Quadratus lumborum block vs. transversus abdominis plane block for caesarean delivery: A systematic review and network meta-analysis. Anaesthesia 2021, 76, 393–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kairaluoma, P.; Bachmann, M.; Rosenberg, P.; Pere, P. Preincisional paravertebral block reduces the prevalence of chronic pain after breast surgery. Anesth. Analg. 2006, 103, 703–708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, Y.; Wang, X.; Lai, R.; Huang, W.; Xu, M. Correlation of acute pain treatment to occurrence of chronic pain in tumor patients after thoracotomy. Aizheng 2008, 27, 206–209. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Borys, M.; Hanych, A.; Czuczwar, M. Paravertebral block versus preemptive ketamine effect on pain intensity after posterolateral thoracotomies: A randomized controlled trial. J. Clin. Med. 2020, 9, 793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shahin, A.; Osman, A. Intraperitoneal lidocaine instillation and postcesarean pain after parietal peritoneal closure: A randomized double-blind placebo-controlled trial. Clin. J. Pain 2010, 26, 121–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tena, B.; Gomar, C.; Rios, J. Perioperative epidural or intravenous ketamine does not improve the effectiveness of thoracic epidural analgesia for acute and chronic pain after thoracotomy. Clin. J. Pain 2014, 30, 490–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mendola, C.; Cammarota, G.; Netto, R.; Cecci, G.; Pisterna, A.; Ferrante, D.; Casadio, C.; Della Corte, F. S+ -ketamine for control of perioperative pain and prevention of post thoracotomy pain syndrome: A randomized, double-blind study. Minerva Anestesiol. 2012, 78, 757–766. [Google Scholar]
- Saxena, A.; Chilkoti, G.; Chopra, A.; Banerjee, B.; Sharma, T. Chronic persistent post-surgical pain following staging laparotomy for carcinoma of ovary and its relationship to signal transduction genes. Korean J. Pain 2016, 29, 239–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yazici Yilmaz, F.; Aydogan Mathyk, B.; Yildiz, S.; Yenigul, N.; Saglam, C. Postoperative pain and neuropathy after caesarean operation featuring blunt or sharp opening of the fascia: A randomised, parallel group, double-blind study. J. Obstet. Gynaecol. 2018, 38, 933–939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niklasson, B.; Georgsson Öhman, S.; Segerdahl, M.; Blanck, A. Risk factors for persistent pain and its influence on maternal wellbeing after cesarean section. Acta Obstet. Gynecol. Scand. 2015, 94, 622–628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, L.; Wei, C.; Xiao, F.; Chang, X.; Zhang, Y. Incidence and risk factors for chronic pain after elective caesarean delivery under spinal anaesthesia in a Chinese cohort: A prospective study. Int. J. Obstet. Anesth. 2018, 34, 21–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McKeen, D.; George, R.; Boyd, C.; Allen, M.; Pink, A. Transversus abdominis plane block does not improve early or late pain outcomes after Cesarean delivery: A randomized controlled trial. Can. J. Anaesth. 2014, 61, 631–640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Groups (N) | QLB (N = 35) | CON (N = 33) | TAPB (N = 34) | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Age (years) | 30.7 ± 4.0 | 32.5 ± 5.7 | 31.4 ± 5.9 | 0.37 |
| Height (cm) | 168.3 ± 7.1 | 165.7 ± 6.4 | 169.4 ± 7.6 | 0.10 |
| Weight (kg) | 79.6 ± 13.8 | 80.2 ± 9.5 | 76.4 ± 11.0 | 0.36 |
| Subsequent cesarean section | 20 (57.1) | 14 (42.4) | 10 (29.4) | 0.35 |
| Failure to progress | 6 (17.1) | 3 (9.1) | 6 (17.6) | 0.65 |
| Nonreassuring fetal heart rate tracing | 1 (2.9) | 4 (12.1) | 3 (8.8) | 0.53 |
| Fetal macrosomia | 2 (5.7) | 6 (18.2) | 1 (2.9) | 0.14 |
| Psychological | 2 (5.7) | 0 (0) | 8 (23.5) | <0.01 |
| Fetal malpresentation | 2 (5.7) | 5 (15.2) | 2 (5.9) | 0.50 |
| Other | 2 (5.7) | 1 (3.0) | 4 (11.8) | 0.50 |
| Group (N) | QLB (N = 35) | CON (N = 33) | TAPB (N = 34) | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| VAS 2 | 1 (0–2) a | 3 (2–4) | 2 (0–3) | <0.001 |
| VAS 4 | 2 (0–4) | 3 (3–4) | 3 (1–4) | 0.2 |
| VAS 8 | 2 (0–3) b | 3 (2–4) | 3 (2–5) | 0.027 |
| VAS 12 | 2 (1–4) | 4 (2–5) | 3 (2–4.6) | 0.18 |
| VAS 24 | 2 (0–4) | 2.5 (1–5) | 3 (1–4) | 0.15 |
| Group (N) | QLB (N = 35) | CON (N = 33) | TAPB (N = 34) | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| VAS 2 | 2 (0–3) a | 3 (3–5) | 2 (1–3) b | <0.001 |
| VAS 4 | 4 (3–5) | 4 (4–5) | 3 (2–5) | 0.048 |
| VAS 8 | 4 (2–5) | 4 (4–5) | 4 (3–5) | 0.17 |
| VAS 12 | 4 (2–5) a | 5 (4–6) | 4 (3–5.4) | 0.013 |
| VAS 24 | 4 (2–5.25) a | 5 (4–6) | 4 (3.15–5.25) b | <0.01 |
| Time of Evaluation | QLB | CON | TAPB | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Month 1 | 0 (0–4) a | 12 (0–22) | 3.5 (0–9.5) | <0.01 |
| Month 3 | 0 (0–6) | 2 (0–23) | 3.5 (0–7) | 0.21 |
| Month 6 | 0 (0–6) a | 4.25 (0–13) | 0 (0–8) | 0.039 |
| Time of Evaluation | QLB | CON | TAPB | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Month 1 | 14/31 | 23/31 | 17/28 | 0.034 |
| Month 3 | 15/31 | 19/31 | 18/30 | 0.56 |
| Month 6 | 10/31 | 16/28 | 13/29 | 0.158 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Borys, M.; Zamaro, A.; Horeczy, B.; Gęszka, E.; Janiak, M.; Węgrzyn, P.; Czuczwar, M.; Piwowarczyk, P. Quadratus Lumborum and Transversus Abdominis Plane Blocks and Their Impact on Acute and Chronic Pain in Patients after Cesarean Section: A Randomized Controlled Study. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 3500. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph18073500
Borys M, Zamaro A, Horeczy B, Gęszka E, Janiak M, Węgrzyn P, Czuczwar M, Piwowarczyk P. Quadratus Lumborum and Transversus Abdominis Plane Blocks and Their Impact on Acute and Chronic Pain in Patients after Cesarean Section: A Randomized Controlled Study. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health. 2021; 18(7):3500. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph18073500
Chicago/Turabian StyleBorys, Michał, Aleksandra Zamaro, Beata Horeczy, Ewa Gęszka, Marek Janiak, Piotr Węgrzyn, Mirosław Czuczwar, and Paweł Piwowarczyk. 2021. "Quadratus Lumborum and Transversus Abdominis Plane Blocks and Their Impact on Acute and Chronic Pain in Patients after Cesarean Section: A Randomized Controlled Study" International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health 18, no. 7: 3500. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph18073500
APA StyleBorys, M., Zamaro, A., Horeczy, B., Gęszka, E., Janiak, M., Węgrzyn, P., Czuczwar, M., & Piwowarczyk, P. (2021). Quadratus Lumborum and Transversus Abdominis Plane Blocks and Their Impact on Acute and Chronic Pain in Patients after Cesarean Section: A Randomized Controlled Study. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 18(7), 3500. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph18073500







