Association of Lumbar Paraspinal Muscle Morphometry with Degenerative Spondylolisthesis
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methods
2.1. Subjects
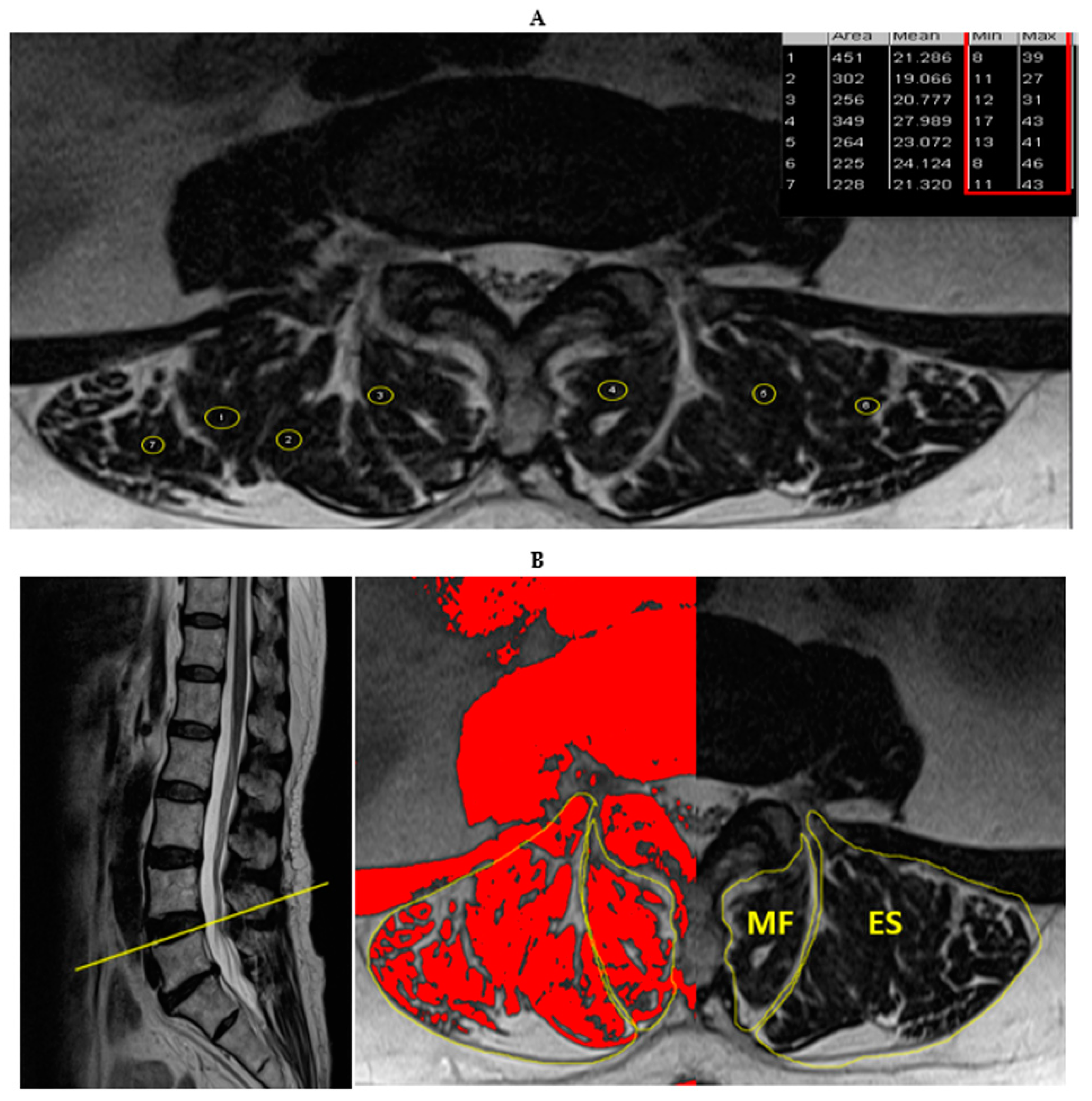
2.2. Measurements and Procedures
2.3. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Characteristics of Participants
3.2. MRI Findings
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Farfan, H. The pathological anatomy of degenerative spondylolisthesis. A cadaver study. Spine 1980, 5, 412–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morgan, F.P.; King, T. Primary instability of lumbar vertebrae as a common cause of low back pain. J. Bone Joint Surgery 1957, 39, 6–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalichman, L.; Hunter, D.J. Diagnosis and conservative management of degenerative lumbar spondylolisthesis. Eur Spine J 2008, 17, 327–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jacobsen, S.; Sonne-Holm, S.; Rovsing, H.; Monrad, H.; Gebuhr, P. Degenerative lumbar spondylolisthesis: An epidemiological perspective: The Copenhagen Osteoarthritis Study. Spine 2007, 32, 120–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fitzgerald, J.; Newman, P. Degenerative spondylolisthesis. J. Bone Joint Surgery 1976, 58, 184–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, H.J.; Lim, W.H.; Park, J.-W.; Kwon, B.S.; Ryu, K.H.; Lee, J.H.; Park, Y.G. The relationship between cross sectional area and strength of back muscles in patients with chronic low back pain. Ann. Rehabil. Med. 2012, 36, 173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kader, D.; Wardlaw, D.; Smith, F. Correlation between the MRI changes in the lumbar multifidus muscles and leg pain. Clin. Radiol. 2000, 55, 145–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cooper, R.G.; Forbes, W.S.; Jayson, M.I.V. Radiographic Demonstration of Paraspinal Muscle Wasting in Patients with Chronic Low-Back-Pain. Brit. J. Rheumatol. 1992, 31, 389–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Danneels, L.A.; Vanderstraeten, G.G.; Cambier, D.C.; Witrouw, E.E.; De Cuyper, H.J. CT imaging of trunk muscles in chronic low back pain patients and healthy control subjects. Eur. Spine J. 2000, 9, 266–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hides, J.; Stokes, M.; Saide, M.; Jull, G.; Cooper, D. Evidence of lumbar multifidus muscle wasting ipsilateral to symptoms in patients with acute/subacute low back pain. Spine 1994, 19, 165–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hides, J.A.; Richardson, C.A.; Jull, G.A. Multifidus muscle recovery is not automatic after resolution of acute, first-episode low back pain. Spine 1996, 21, 2763–2769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simmonds, A.M.; Rampersaud, Y.R.; Dvorak, M.F.; Dea, N.; Melnyk, A.D.; Fisher, C.G. Defining the inherent stability of degenerative spondylolisthesis: A systematic review. J. Neurosurg. Spine 2015, 23, 178–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pfirrmann, C.W.A.; Metzdorf, A.; Zanetti, M.; Hodler, J.; Boos, N. Magnetic resonance classification of lumbar intervertebral disc degeneration. Spine 2001, 26, 1873–1878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fujiwara, A.; Tamai, K.; Yamato, M.; An, H.S.; Yoshida, H.; Saotome, K.; Kurihashi, A. The relationship between facet joint osteoarthritis and disc degeneration of the lumbar spine: An MRI study. Eur. Spine J. 1999, 8, 396–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Inoue, H.; Ohmori, K.; Miyasaka, K.; Hosoe, H. Radiographic evaluation of the lumbosacral disc height. Skelet. Radiol. 1999, 28, 638–643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fortin, M.; Battié, M.C. Quantitative paraspinal muscle measurements: Inter-software reliability and agreement using OsiriX and ImageJ. Phys. Therapy 2012, 92, 853–864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ranson, C.A.; Burnett, A.F.; Kerslake, R.; Batt, M.E.; O’Sullivan, P.B. An investigation into the use of MR imaging to determine the functional cross sectional area of lumbar paraspinal muscles. Eur. Spine J. 2006, 15, 764–773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, G.; Karki, S.B.; Xu, S.; Hu, Z.; Chen, J.; Zhou, Z.; Fan, S. Quantitative MRI and X-ray analysis of disc degeneration and paraspinal muscle changes in degenerative spondylolisthesis. J. Back Musculoskelet 2015, 28, 277–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thakar, S.; Sivaraju, L.; Aryan, S.; Mohan, D.; Kiran, N.A.S.; Hegde, A.S. Lumbar paraspinal muscle morphometry and its correlations with demographic and radiological factors in adult isthmic spondylolisthesis: A retrospective review of 120 surgically managed cases. J. Neurosurg. Spine 2016, 24, 679–685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, M.Y.; Park, Y.; Ha, J.W.; Zhang, H.Y.; Lee, S.H.; Hong, T.H.; Lee, S.H. Paraspinal Lean Muscle Mass Measurement Using Spine MRI as a Predictor of Adjacent Segment Disease After Lumbar Fusion: A Propensity Score-Matched Case-Control Analysis. AJR Am. J. Roentgenol. 2019, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teichtahl, A.J.; Urquhart, D.M.; Wang, Y.; Wluka, A.E.; Wijethilake, P.; O’Sullivan, R.; Cicuttini, F.M. Fat infiltration of paraspinal muscles is associated with low back pain, disability, and structural abnormalities in community-based adults. Spine J. 2015, 15, 1593–1601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kalichman, L.; Carmeli, E.; Been, E. The Association between Imaging Parameters of the Paraspinal Muscles, Spinal Degeneration, and Low Back Pain. Biomed. Res. Int. 2017, 2017, 2562957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kalichman, L.; Hodges, P.; Li, L.; Guermazi, A.; Hunter, D.J. Changes in paraspinal muscles and their association with low back pain and spinal degeneration: CT study. Eur. Spine J. 2010, 19, 1136–1144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freeman, M.D.; Woodham, M.A.; Woodham, A.W. The role of the lumbar multifidus in chronic low back pain: A review. PM&R 2010, 2, 142–146. [Google Scholar]

| Sex | Patients with Spondylolisthesis (n = 30) | Patients without Spondylolisthesis (n = 32) | p |
|---|---|---|---|
| Age (years) | 74.1 ± 5.6 | 74.5 ± 5.4 | 0.727 |
| Height (cm) | 150.6 ± 6.4 | 151.7 ± 6.3 | 0.511 |
| Weight (kg) | 56.8 ± 7.1 | 57.3 ± 11.0 | 0.861 |
| BMI (kg/m2) | 25.0 ± 2.6 | 24.8 ± 4.1 | 0.801 |
| L4-L5 disc height (mm) | 9.4 ± 2.7 | 9.47 ± 2.8 | 0.949 |
| Radiologic Features | Number of Patients (%) |
|---|---|
| Level of listhesis | |
| L3-4 | 2 (6.7%) |
| L4-5 | 19 (63.34%) |
| L5-S1 | 9 (30.0%) |
| Listhesis grade | |
| grade 1 | 29 (96.6%) |
| grade 2 | 1 (3.3%) |
| grade 3 | 0 |
| grade 4 | 0 |
| Patients with Spondylolisthesis (n = 30) | Patients without Spondylolisthesis (n = 32) | p | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Disc degeneration grade | |||
| 1 | 0 | 0 | |
| 2 | 0 | 0 | |
| 3 | 2 | 1 | 0.92 |
| 4 | 14 | 16 | |
| 5 | 14 | 15 | |
| L4/L5 facet arthropathy grade | |||
| 0 | 0 | 0 | |
| 1 | 0 | 3 | |
| 2 | 11 | 16 | 0.07 |
| 3 | 19 | 13 |
| Muscle Group | Patients with Spondylolisthesis (n = 30) | Patients without Spondylolisthesis (n = 32) | p |
|---|---|---|---|
| Multifidus muscle group | |||
| Total CSA (mm2) | 553.80 ± 136.59 | 556.25 ± 157.27 | 0.948 |
| FCSA (mm2) | 244.63 ± 101.39 | 298.15 ± 88.48 | 0.030 |
| Ratio of FCSA to total CSA (%) | 43.67 ± 13.33 | 55.34 ± 13.31 | 0.001 |
| CSA/VB (rCSA) | 0.473 ± 0.395 | 0.365 ± 0.156 | 0.162 |
| FCSA/VB (rFCSA) | 0.202 ± 0.203 | 0.199 ± 0.097 | 0.940 |
| SMI(mm2/m2) | |||
| of Total CSA | 244.09 ± 60.56 | 242.26 ± 68.94 | 0.912 |
| of FCSA | 107.44 ± 43.91 | 129.79 ± 39.11 | 0.038 |
| Erector spinae muscle group | |||
| Total CSA (mm2) | 1511.05 ± 273.26 | 1384.7 ± 281.06 | 0.078 |
| FCSA (mm2) | 783.33 ± 225.09 | 666.22 ± 182.28 | 0.028 |
| Ratio of FCSA to total CSA (%) | 51.69 ± 11.79 | 48.57 ± 10.94 | 0.283 |
| CSA/VB (rCSA) | 1.225 ± 0.975 | 0.879 ± 0.261 | 0.058 |
| FCSA/VB (rFCSA) | 0.643 ± 0.586 | 0.432 ± 0.180 | 0.057 |
| SMI(mm2/m2) | |||
| of Total CSA | 667.11 ± 124.70 | 604.71 ± 128.65 | 0.057 |
| of FCSA | 343.95 ± 94.06 | 288.78 ± 72.23 | 0.012 |
| MF CSA/ES CSA | 0.37 ± 0.98 | 0.45 ± 0.23 | 0.062 |
| MF FCSA/ES FCSA | 0.33 ± 0.15 | 0.45 ± 0.12 | 0.000 |
| Significance | Odd Ratio | 95% CI for Odd Ratio | AUC Area | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Lower | Upper | ||||
| MF FCSA/ES FCSA | 0.006 | 0.001 | 0 | 0.115 | 0.796 |
| SMI MF FCSA | 0.015 | 0.974 | 0.954 | 0.995 | 0.827 |
| SMI ES FCSA | 0.002 | 1.017 | 1.006 | 1.027 | |
| MF FCSA/total CSA (%) | 0.002 | 0.898 | 0.839 | 0.961 | 0.841 |
| ES FCSA/total CSA (%) | 0.016 | 1.092 | 1.107 | 1.174 | |
| MF FCSA (mm2) | 0.005 | 0.985 | 0.975 | 0.996 | 0.817 |
| ES FCSA (mm2) | 0.004 | 1.007 | 1.002 | 1.012 | |
| MF FCSA/VB (rFCSA) | 0.882 | 1.297 | 0.042 | 39.89 | 0.758 |
| ES FCSA/VB (rFCSA) | 0.022 | 71.798 | 1.835 | 2809.979 | |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lee, E.T.; Lee, S.A.; Soh, Y.; Yoo, M.C.; Lee, J.H.; Chon, J. Association of Lumbar Paraspinal Muscle Morphometry with Degenerative Spondylolisthesis. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 4037. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph18084037
Lee ET, Lee SA, Soh Y, Yoo MC, Lee JH, Chon J. Association of Lumbar Paraspinal Muscle Morphometry with Degenerative Spondylolisthesis. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health. 2021; 18(8):4037. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph18084037
Chicago/Turabian StyleLee, Eun Taek, Seung Ah Lee, Yunsoo Soh, Myung Chul Yoo, Jun Ho Lee, and Jinmann Chon. 2021. "Association of Lumbar Paraspinal Muscle Morphometry with Degenerative Spondylolisthesis" International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health 18, no. 8: 4037. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph18084037
APA StyleLee, E. T., Lee, S. A., Soh, Y., Yoo, M. C., Lee, J. H., & Chon, J. (2021). Association of Lumbar Paraspinal Muscle Morphometry with Degenerative Spondylolisthesis. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 18(8), 4037. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph18084037






