Does Head Orientation Influence 3D Facial Imaging? A Study on Accuracy and Precision of Stereophotogrammetric Acquisition
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Polishape Technology
2.2. Object and Data Acquisition
- 8 median: Glabella (Gb), Nasion (N), Pronasale (Prn), Subnasale (Sn), Labiale superius (Ls), Labiale inferius (Li), Sublabiale (Sl), and Pogonion (Pg);
- 7 bilateral: Frontotemporalis (Ft r/l), Zygion (Zy r/l), Tragion (Tr r/l), Gonion (Gn r/l), Cheek (Ch r/l), Cheilion (Chel r/l), and Orbitale inferius (Or inf r/l).
- 4 median: Chel(r)-Chel(l), N-Prn, Sn-Pg, and N-Pg;
- 5 bilateral: Glab-Ch(r), Glab-Ch(l), Glab-Ft(r), Glab-Ft(l), Zy(l)-Tr(l), Zy(r)-Tr(r), Ch(r)-Tr(r), Ch(l)-Tr(l), Ch(r)-Gn(r), and Ch(l)-Gn(l).
2.3. Data Processing and Operational Definitions
2.4. Data Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Intra-Operator Error
3.2. Inter-Operator Error
3.3. Acquisition Error
3.4. Reproducibility Error
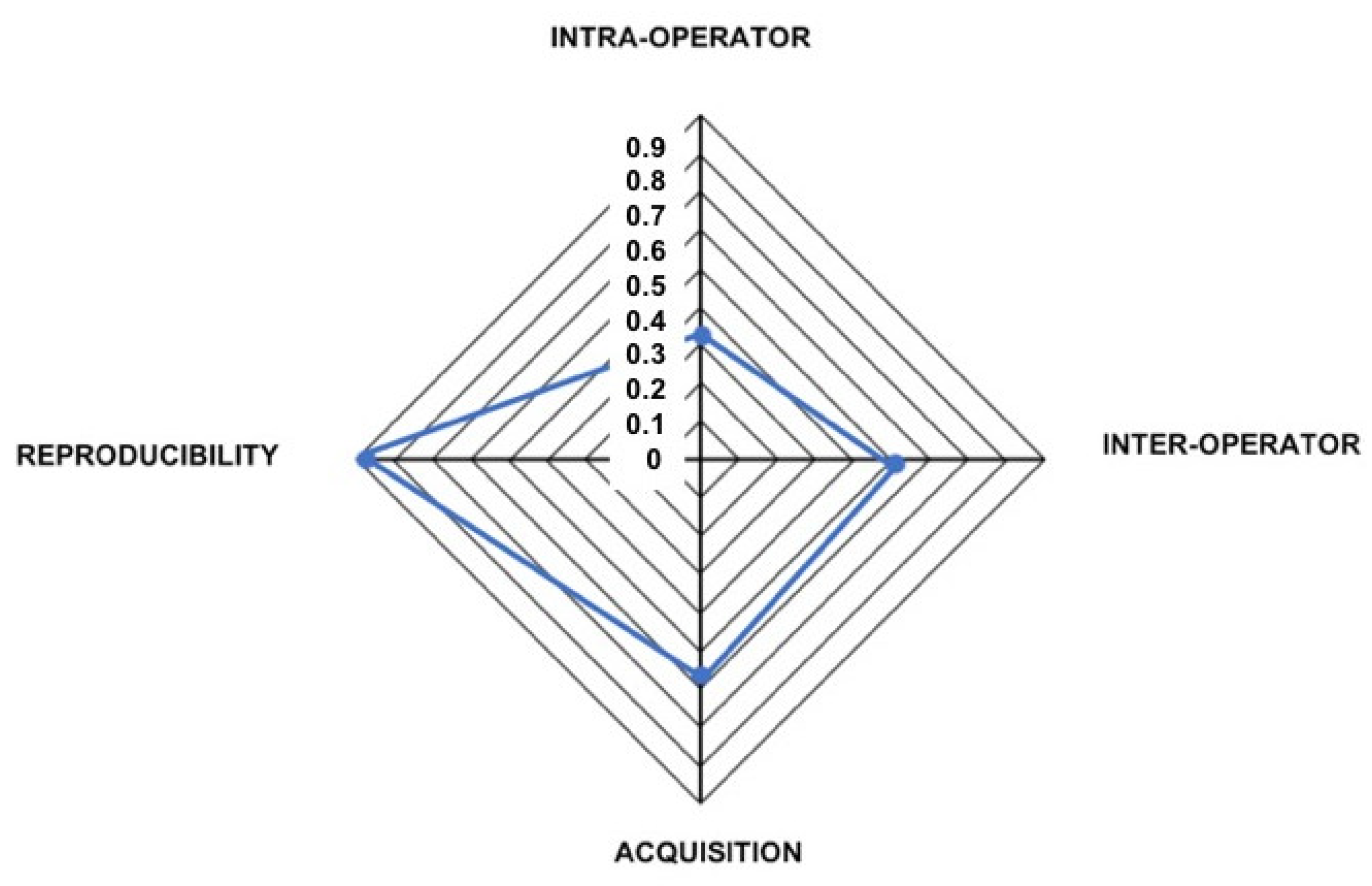
3.5. Error Analysis and Rotations Equivalence
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Strengths and Limitations
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sforza, C.; De Menezes, M.; Ferrario, V.F. Soft and Hard Tissue Facial Anthropometry in Three Dimensions: What’s New. J. Anthropol. Sci. 2013, 91, 159–184. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Smeets, D.; Claes, P.; Vandermeulen, D.; Clement, J.G. Objective 3D face recognition: Evolution, approaches and challenges. Forensic Sci. Int. 2010, 201, 125–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blaszczyk, M.; Jabbar, R.; Szmyd, B.; Radek, M. 3D Printing of Rapid, Low-Cost and Patient-Specific Models of Brain Vasculature for Use in Preoperative Planning in Clipping of Intracranial Aneurysms. J. Clin. Med. 2021, 10, 1201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cassi, D.; Battistoni, G.; Magnifico, M.; Di Blasio, C.; Pedrazzi, G.; Di Blasio, A. Three-dimensional evaluation of facial asymmetry in patients with hemifacial microsomia using stereophotogrammetry. J. Cranio-Maxillofac. Surg. 2019, 47, 179–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Blasio, A.; Di Blasio, C.; Pedrazzi, G.; Cassi, D.; Magnifico, M.; Manfredi, E.; Gandolfini, M. Combined Photographic and Ultraso-nographic Measurement of the ANB Angle: A Pilot Study. Oral Radiol. 2017, 33, 212–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hallac, R.R.; Feng, J.; Kane, A.A.; Seaward, J.R. Dynamic facial asymmetry in patients with repaired cleft lip using 4D imaging (video stereophotogrammetry). J. Cranio-Maxillofac. Surg. 2017, 45, 8–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lauren, M.; McIntyre, F. A New 4-Dimensional Imaging System for Jaw Tracking. Int. J. Comput. Dent. 2014, 17, 75–82. [Google Scholar]
- Lauren, M.; McIntyre, F. 4D Clinical Imaging for Dynamic CAD. Int. J. Dent. 2013, 2013, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Metzger, T.E.; Kula, K.S.; Eckert, G.J.; Ghoneima, A.A. Orthodontic soft-tissue parameters: A comparison of cone-beam computed tomography and the 3dMD imaging system. Am. J. Orthod. Dentofac. Orthop. 2013, 144, 672–681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plooij, J.M.; Maal, T.J.; Haers, P.; Borstlap, W.A.; Kuijpers-Jagtman, A.M.; Bergè, S.J. Digital Three-Dimensional Image Fusion Processes for Planning and Evaluating Orthodontics and Orthognathic Surgery. A Systematic Review. Int. J. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. 2011, 40, 341–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kau, C.H.; Richmond, S.; Incrapera, A.; English, J.; Xia, J.J. Three-dimensional surface acquisition systems for the study of facial morphology and their application to maxillofacial surgery. Int. J. Med Robot. Comput. Assist. Surg. 2007, 3, 97–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weinberg, S.M.; Scott, N.M.; Neiswanger, K.; Brandon, C.A.; Marazita, M.L. Digital Three-Dimensional Photogrammetry: Evaluation of Anthropometric Precision and Accuracy Using a Genex 3D Camera System. Cleft Palate-Craniofac. J. 2004, 41, 507–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luebbers, H.-T.; Messmer, P.; Obwegeser, J.A.; Zwahlen, R.A.; Kikinis, R.; Graetz, K.W.; Matthews, F. Comparison of different registration methods for surgical navigation in cranio-maxillofacial surgery. J. Cranio-Maxillofac. Surg. 2008, 36, 109–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Marmulla, R.; Mühling, J.; Eggers, G.; Hassfeld, S. Markerless patient registration. A new technique for image-guided surgery of the lateral base of the skull. HNO 2005, 53, 148–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jamovi Project, Version 0.9, Computer Software. 2018. Available online: https://www.jamovi.org (accessed on 15 February 2021).
- Abramson, J.H. WINPEPI updated: Computer programs for epidemiologists, and their teaching potential. Epidemiol. Perspect. Innov. 2011, 8, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lung, K.R.; Gorko, M.A.; Llewelyn, J.; Wiggins, N. Statistical Method for the Determination of Equivalence of Automated Test Procedures. J. Autom. Method Manag. 2003, 25, 123–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ialongo, C. The logic of equivalence testing and its use in laboratory medicine. Biochem. Medica 2017, 27, 5–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baysal, A.; Sahan, A.; Ozturk, M.; Uysal, T. Reproducibility and Reliability of Three-Dimensional Soft Tissue Landmark Iden-tification Using Three-Dimensional Stereophotogrammetry. Angle Orthod. 2016, 86, 1004–1009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cassi, D.; De Biase, C.; Tonni, I.; Gandolfini, M.; Di Blasio, A.; Piancino, M. Natural position of the head: Review of two-dimensional and three-dimensional methods of recording. Br. J. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. 2016, 54, 233–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cooke, M.S.; Orth, D. Five-year reproducibility of natural head posture: A longitudinal study. Am. J. Orthod. Dentofac. Orthop. 1990, 97, 489–494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferrario, V.; Sforza, C.; Germano, D.; Dallorca, L.; Miani, A. Head Posture and Cephalometric Analyses: An Integrated Pho-tographic/Radiographic Technique. Am. J. Orthod. Dentofac. Orthop. 1994, 106, 257–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, L.; Cooke, M.S. Fifteen-year reproducibility of natural head posture: A longitudinal study. Am. J. Orthod. Dentofac. Orthop. 1999, 116, 82–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magnifico, M.; Cassi, D.; Gandolfini, M.; Toffoli, A.; Zecca, P.; Di Blasio, A. Orthodontics and Moebius Syndrome: An Ob-servational Study. Minerva Stomatol. 2018, 67, 165–171. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Bister, D.; Edler, R.J.; Tom, B.D.M.; Prevost, A.T. Natural head posture—Considerations of reproducibility. Eur. J. Orthod. 2002, 24, 457–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hughes, G.N.; Gateño, J.; English, J.D.; Teichgraeber, J.F.; Xia, J.J. There is variability in our perception of the standard head orientation. Int. J. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. 2017, 46, 1512–1516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lübbers, H.-T.; Medinger, L.; Kruse, A.; Grätz, K.W.; Matthews, F. Precision and Accuracy of the 3dMD Photogrammetric System in Craniomaxillofacial Application. J. Craniofac. Surg. 2010, 21, 763–767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Aldridge, K.; Boyadjiev, S.A.; Capone, G.T.; DeLeon, V.B.; Richtsmeier, J.T. Precision and error of three-dimensional phenotypic measures acquired from 3dMD photogrammetric images. Am. J. Med. Genet. Part A 2005, 138A, 247–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ayoub, A.; Garrahy, A.; Hood, C.; White, J.; Bock, M.; Siebert, J.P.; Spencer, R.; Ray, A. Validation of a Vision-Based, Three-Dimensional Facial Imaging System. Cleft Palate-Craniofac. J. 2003, 40, 523–529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

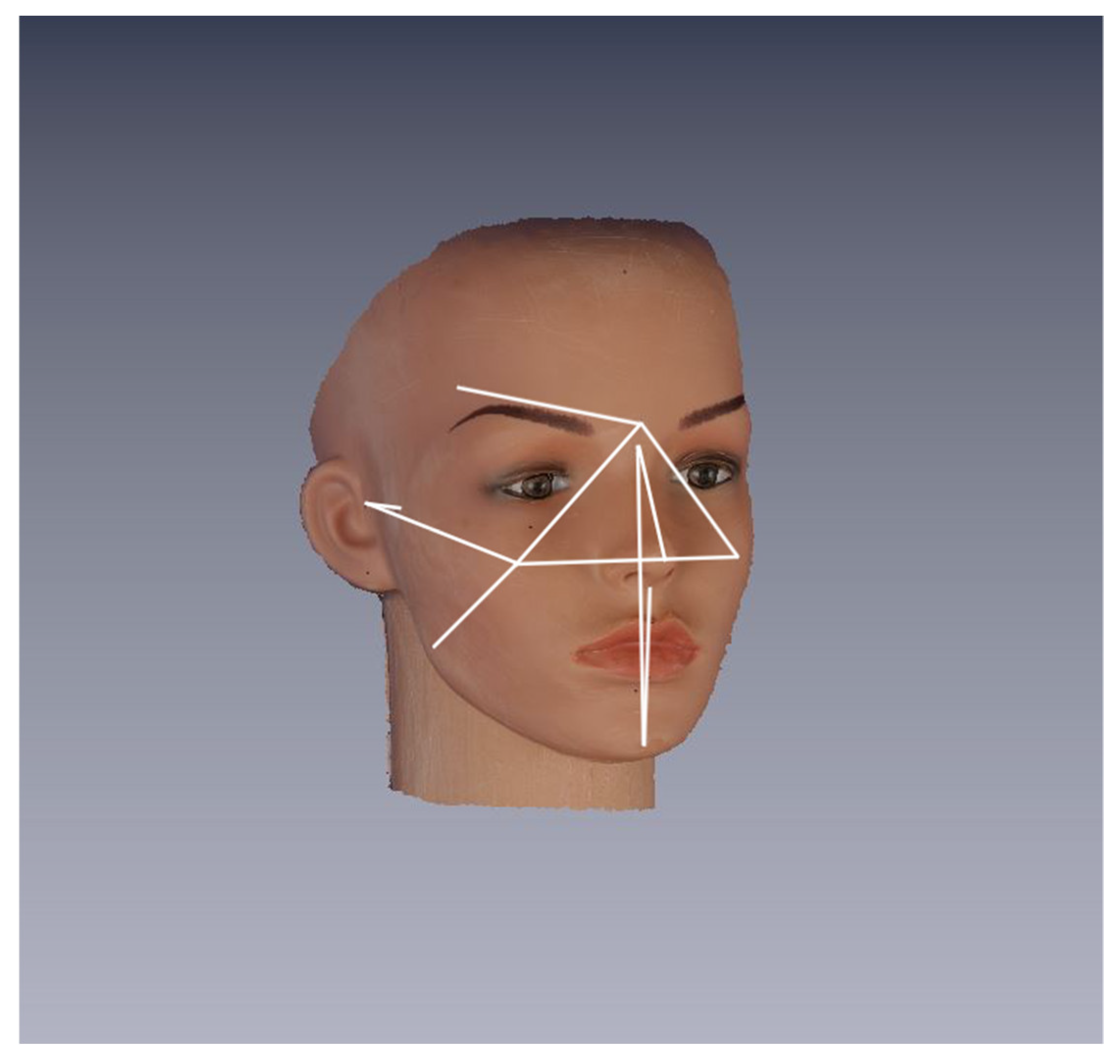
| Head Position | Rotation | Number of Captures |
|---|---|---|
| REFERENCE POSITION | None | 10 |
| YAW | 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 8, 12, and 16 degrees (right) 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 8, 12, and 16 degrees (left) | 16 |
| ROLL | 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 8, 12, and 16 degrees (right) 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 8, 12, and 16 degrees (left) | 16 |
| PITCH | 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 7, 9, and 11 degrees (upward) 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 7, 9, and 11 degrees (downward) | 16 |
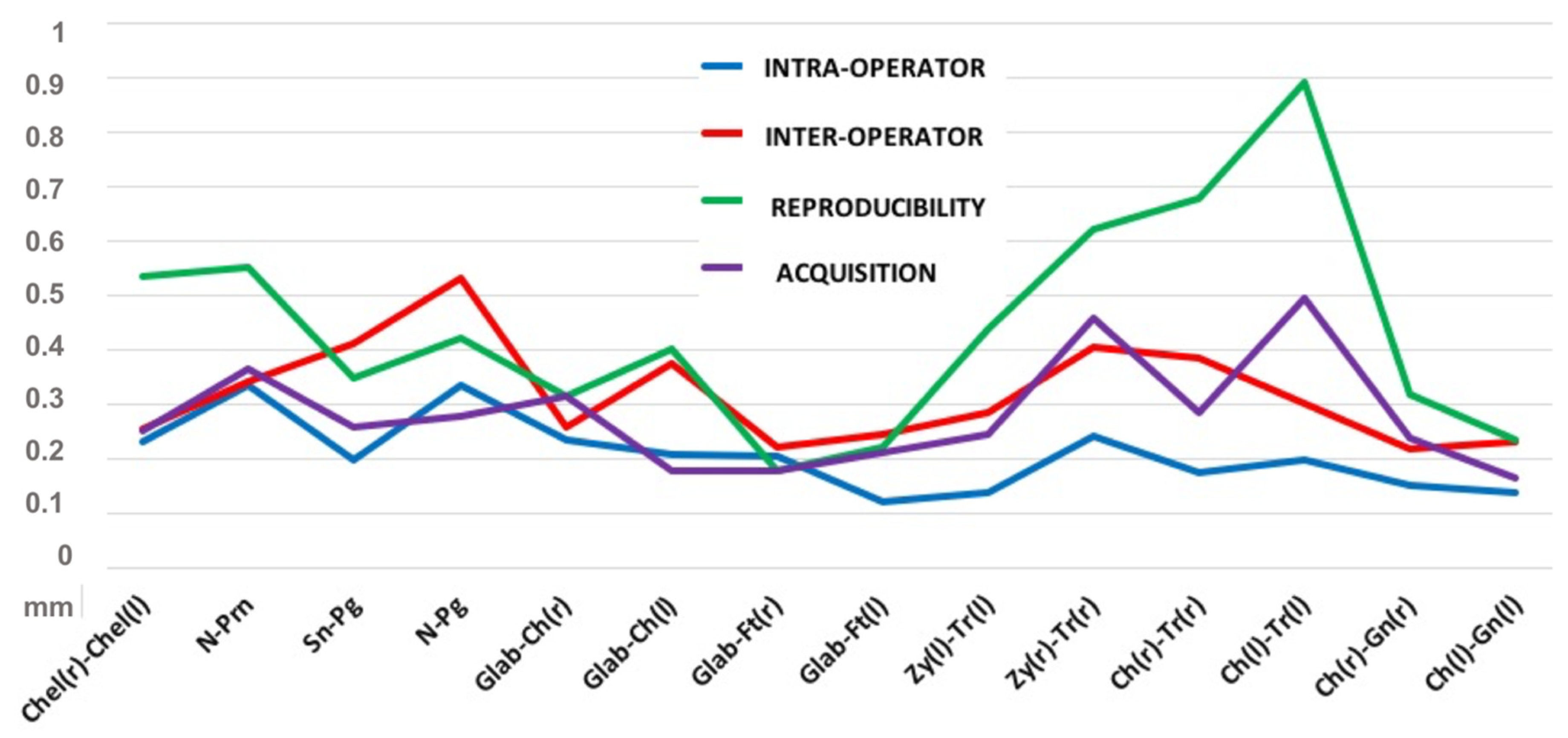
| Measurements | Error Indices | Intra-Operator (mm) | Inter-Operator (mm) | Acquisition (mm) | Reproducibility (mm) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Chel(r)-Chel(l) | maximum error | 0.231 | 0.257 | 0.253 | 0.535 |
| standard error | 0.042 | 0.052 | 0.084 | 0.106 | |
| standard deviation | 0.133 | 0.165 | 0.187 | 0.334 | |
| coefficient of variation | 0.243 | 0.301 | 0.340 | 0.610 | |
| N-Prn | maximum error | 0.334 | 0.343 | 0.365 | 0.551 |
| standard error | 0.059 | 0.084 | 0.131 | 0.098 | |
| standard deviation | 0.188 | 0.265 | 0.293 | 0.310 | |
| coefficient of variation | 0.437 | 0.620 | 0.688 | 0.728 | |
| Sn-Pg | maximum error | 0.200 | 0.411 | 0.259 | 0.349 |
| standard error | 0.039 | 0.072 | 0.097 | 0.069 | |
| standard deviation | 0.124 | 0.227 | 0.216 | 0.218 | |
| coefficient of variation | 0.219 | 0.400 | 0.381 | 0.384 | |
| N-Pg | maximum error | 0.336 | 0.532 | 0.280 | 0.423 |
| standard error | 0.081 | 0.111 | 0.105 | 0.087 | |
| standard deviation | 0.257 | 0.351 | 0.236 | 0.275 | |
| coefficient of variation | 0.244 | 0.333 | 0.224 | 0.261 | |
| Glab-Ch(r) | maximum error | 0.236 | 0.258 | 0.314 | 0.314 |
| standard error | 0.043 | 0.054 | 0.102 | 0.060 | |
| standard deviation | 0.135 | 0.170 | 0.229 | 0.189 | |
| coefficient of variation | 0.200 | 0.251 | 0.338 | 0.279 | |
| Glab-Ch(l) | maximum error | 0.210 | 0.374 | 0.179 | 0.401 |
| standard error | 0.040 | 0.074 | 0.078 | 0.080 | |
| standard deviation | 0.125 | 0.234 | 0.174 | 0.252 | |
| coefficient of variation | 0.184 | 0.343 | 0.256 | 0.370 | |
| Glab-Ft(r) | maximum error | 0.205 | 0.223 | 0.179 | 0.179 |
| standard error | 0.034 | 0.046 | 0.066 | 0.032 | |
| standard deviation | 0.107 | 0.147 | 0.148 | 0.102 | |
| coefficient of variation | 0.163 | 0.224 | 0.225 | 0.155 | |
| Glab-Ft(l) | maximum error | 0.123 | 0.246 | 0.214 | 0.221 |
| standard error | 0.023 | 0.048 | 0.082 | 0.051 | |
| standard deviation | 0.071 | 0.153 | 0.183 | 0.160 | |
| coefficient of variation | 0.109 | 0.234 | 0.280 | 0.245 | |
| Zy(l)-Tr(l) | maximum error | 0.138 | 0.286 | 0.246 | 0.437 |
| standard error | 0.030 | 0.062 | 0.084 | 0.082 | |
| standard deviation | 0.096 | 0.197 | 0.188 | 0.259 | |
| coefficient of variation | 0.109 | 0.673 | 0.643 | 0.891 | |
| Zy(r)-Tr(r) | maximum error | 0.242 | 0.405 | 0.460 | 0.620 |
| standard error | 0.047 | 0.082 | 0.177 | 0.131 | |
| standard deviation | 0.149 | 0.258 | 0.396 | 0.413 | |
| coefficient of variation | 0.330 | 0.836 | 1.283 | 1.333 | |
| Ch(r)-Tr(r) | maximum error | 0.176 | 0.386 | 0.286 | 0.670 |
| standard error | 0.035 | 0.068 | 0.110 | 0.128 | |
| standard deviation | 0.112 | 0.217 | 0.247 | 0.404 | |
| coefficient of variation | 0.486 | 0.262 | 0.299 | 0.488 | |
| Ch(l)-Tr(l) | maximum error | 0.198 | 0.303 | 0.496 | 0.890 |
| standard error | 0.036 | 0.053 | 0.162 | 0.164 | |
| standard deviation | 0.114 | 0.167 | 0.363 | 0.520 | |
| coefficient of variation | 0.136 | 0.203 | 0.440 | 0.632 | |
| Ch(r)-Gn(r) | maximum error | 0.153 | 0.220 | 0.239 | 0.326 |
| standard error | 0.029 | 0.040 | 0.104 | 0.069 | |
| standard deviation | 0.092 | 0.127 | 0.232 | 0.220 | |
| coefficient of variation | 0.139 | 0.236 | 0.447 | 0.423 | |
| Ch(l)-Gn(l) | maximum error | 0.139 | 0.231 | 0.165 | 0.236 |
| standard error | 0.031 | 0.049 | 0.054 | 0.047 | |
| standard deviation | 0.097 | 0.154 | 0.121 | 0.147 | |
| coefficient of variation | 0.187 | 0.296 | 0.224 | 0.273 |
| Measurements | Yaw | Roll | Pitch | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mean Difference (95% CI) | TOST p-Value | Mean Difference (95% CI) | TOST p-Value | Mean Difference (95% CI) | TOST p-Value | |
| Chel(r)-Chel(l) | 54.691 (52.519; 55.917) | <0.001 | 54.882 (53.158; 55.398) | <0.001 | 54.873 (53.144; 55.412) | <0.001 |
| N-Prn | 42.605 (40.107; 44.661) | <0.001 | 42.820 (39.941; 44.423) | 0.032 | 42.755 (40.309; 44.055) | 0.002 |
| Sn-Pg | 56.868 (55.449; 57.703) | <0.001 | 56.783 (55.504; 57.496) | <0.001 | 56.739 (55.543; 57.425) | <0.001 |
| N-Pg | 105.308 (104.394; 105.758) | <0.001 | 105.187 (103.996; 105.605) | <0.001 | 105.162 (104.187; 105.444) | <0.001 |
| Glab-Ch(r) | 67.644 (67.144; 67.802) | <0.001 | 67.704 (66.289; 68.172) | <0.001 | 67.693 (66.041; 68.029) | <0.001 |
| Glab-Ch(l) | 68.312 (66.555; 69.131) | 0.006 | 68.062 (66.490; 68.688) | <0.001 | 68.074 (66.866; 68.663) | <0.001 |
| Glab-Ft(r) | 65.653 (65.747; 65.747) | <0.001 | 65.689 (64.768; 65.998) | <0.001 | 65.677 (64.851; 66.031) | <0.001 |
| Glab-Ft(l) | 65.601 (64.714; 66.012) | 0.006 | 65.325 (63.514; 66.086) | <0.001 | 65.346 (63.750; 66.035) | <0.001 |
| Zy(l)-Tr(l) | 28.972 (26.219; 31.047) | <0.001 | 28.888 (25.126; 31.632) | <0.001 | 28.761 (22.139; 33.940) | <0.001 |
| Zy(r)-Tr(r) | 30.965 (26.7521; 34.341) | 0.004 | 30.813 (25.609; 33.925) | <0.001 | 30.814 (26.951; 33.827) | <0.001 |
| Ch(r)-Tr(r) | 82.730 (80.600; 83.858) | 0.033 | 82.578 (80.944; 83.062) | <0.001 | 82.439 (81.390; 83.014) | <0.001 |
| Ch(l)-Tr(l) | 82.154 (78.962; 83.156) | <0.001 | 82.169 (80.345; 82.736) | <0.001 | 82.026 (79.201; 82.602) | <0.001 |
| Ch(r)-Gn(r) | 53.961 (52.814; 54.712) | <0.001 | 54.012 (51.262; 54.785) | 0.002 | 54.032 (53.084; 54.522) | <0.001 |
| Ch(l)-Gn(l) | 51.923 (50.621; 52.891) | <0.001 | 51.937 (50.835; 52.511) | <0.001 | 51.953 (50.788; 52.558) | <0.001 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Battistoni, G.; Cassi, D.; Magnifico, M.; Pedrazzi, G.; Di Blasio, M.; Vaienti, B.; Di Blasio, A. Does Head Orientation Influence 3D Facial Imaging? A Study on Accuracy and Precision of Stereophotogrammetric Acquisition. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 4276. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph18084276
Battistoni G, Cassi D, Magnifico M, Pedrazzi G, Di Blasio M, Vaienti B, Di Blasio A. Does Head Orientation Influence 3D Facial Imaging? A Study on Accuracy and Precision of Stereophotogrammetric Acquisition. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health. 2021; 18(8):4276. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph18084276
Chicago/Turabian StyleBattistoni, Giuditta, Diana Cassi, Marisabel Magnifico, Giuseppe Pedrazzi, Marco Di Blasio, Benedetta Vaienti, and Alberto Di Blasio. 2021. "Does Head Orientation Influence 3D Facial Imaging? A Study on Accuracy and Precision of Stereophotogrammetric Acquisition" International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health 18, no. 8: 4276. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph18084276
APA StyleBattistoni, G., Cassi, D., Magnifico, M., Pedrazzi, G., Di Blasio, M., Vaienti, B., & Di Blasio, A. (2021). Does Head Orientation Influence 3D Facial Imaging? A Study on Accuracy and Precision of Stereophotogrammetric Acquisition. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 18(8), 4276. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph18084276






