Association between Ambient Air Pollution and MRI-Defined Brain Infarcts in Health Examinations in China
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Methods
2.1. Study Design and Study Population
2.2. Exposure to Air Pollution
2.3. Outcome Assessment
2.4. Covariates
3. Data Analysis
4. Results
5. Discussion
6. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| ANOVA | analysis of variance |
| BMI | body mass index |
| BI | brain infarcts |
| CI | confidence interval |
| CO | carbon monoxide |
| GBD | Global Burden of Diseases |
| GDP | gross domestic product |
| MRI | magnetic resonance imaging |
| NO2 | nitrogen dioxide |
| OR | odds ratio |
| PM | particulate matter |
| SD | standard deviation |
References
- GBD 2016 Stroke Collaborators. Global, regional, and national burden of stroke, 1990–2016: A systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2016. Lancet Neurol. 2019, 18, 439–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- GBD 2017 Causes of Death Collaborators. Global, regional, and national age-sex-specific mortality for 282 causes of death in 195 countries and territories, 1980–2017: A systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2017. Lancet 2018, 392, 1736–1788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liu, L.; Wang, D.; Wong, K.S.; Wang, Y. Stroke and stroke care in China: Huge burden, significant workload, and a national priority. Stroke 2011, 42, 3651–3654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feigin, V.L.; Krishnamurthi, R.V.; Parmar, P.; Norrving, B.; Mensah, G.A.; Bennett, D.A.; Barker-Clool, S.; Moran, A.E.; Sacco, R.L.; Truelsen, T.; et al. Update on the Global Burden of Ischemic and Hemorrhagic Stroke in 1990–2013: The GBD 2013 Study. Neuroepidemiology 2015, 45, 161–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Longstreth, W.T., Jr. Brain vascular disease overt and covert. Stroke 2005, 36, 2062–2063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Fanning, J.P.; Wong, A.A.; Fraser, J.F. The epidemiology of silent brain infarction: A systematic review of population-based cohorts. BMC Med. 2014, 12, 119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chauhan, G.; Adams, H.H.; Satizabal, C.L.; Bis, J.C.; Teumer, A.; Sargurupremraj, M.; Hofer, E.; Trompet, S.; Hilal, S.; Smith, A.V.; et al. Genetic and lifestyle risk factors for MRI-defined brain infarcts in a population-based setting. Neurology 2019, 92, e486–e503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Debette, S.; Beiser, A.; DeCarli, C.; Au, R.; Himali, J.J.; Kelly-Hayes, M.; Romero, J.R.; Kase, C.S.; Wolf, P.A.; Seshadri, S. Association of MRI markers of vascular brain injury with incident stroke, mild cognitive impairment, dementia, and mortality: The Framingham Offspring Study. Stroke 2010, 41, 600–606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Vermeer, S.E.; Prins, N.D.; den Heijer, T.; Hofman, A.; Koudstaal, P.J.; Breteler, M.M. Silent brain infarcts and the risk of dementia and cognitive decline. N. Engl. J. Med. 2003, 348, 1215–1222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gupta, A.; Giambrone, A.E.; Gialdini, G.; Finn, C.; Delgado, D.; Gutierrez, J.; Wright, C.; Beiser, A.S.; Seshadri, S.; Pandya, A.; et al. Silent brain infarction and risk of future stroke: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Stroke 2016, 47, 719–725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Feigin, V.L.; Roth, G.A.; Naghavi, M.; Parmar, P.; Krishnamurthi, R.; Chugh, S.; Mensah, G.A.; Norrving, B.; Shiue, I.; Ng, M.; et al. Global burden of stroke and risk factors in 188 countries, during 1990–2013: A systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2013. Lancet Neurol. 2016, 15, 913–924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- GBD 2019 Risk Factors Collaborators. Global burden of 87 risk factors in 204 countries and territories, 1990–2019: A systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2019. Lancet 2020, 396, 1223–1249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Russ, T.C.; Reis, S.; van Tongeren, M. Air pollution and brain health: Defining the research agenda. Curr. Opin. Psychiatry 2019, 32, 97–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Boda, E.; Rigamonti, A.E.; Bollati, V. Understanding the effects of air pollution on neurogenesis and gliogenesis in the growing and adult brain. Curr. Opin. Pharmacol. 2020, 50, 61–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biscetti, F.; Giovannini, S.; Straface, G.; Bertucci, F.; Angelini, F.; Porreca, C.; Landolfi, R. Flex A: RANK/RANKL/OPG pathway: Genetic association with history of ischemic stroke in Italian population. Eur. Rev. Med. Pharmacol. Sci. 2016, 20, 4574–4580. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Power, M.C.; Lamichhane, A.P.; Liao, D.; Xu, X.; Jack, C.R.; Gottesman, R.F.; Mosley, T.; Stewart, J.D.; Yanosky, J.D.; Whitsel, E.A. The association of long-term exposure to particulate matter air pollution with brain MRI findings: The ARIC Study. Environ. Health Perspect 2018, 126, 027009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kulick, E.R.; Wellenius, G.A.; Kaufman, J.D.; DeRosa, J.T.; Kinney, P.L.; Cheung, Y.K.; Wright, C.B.; Sacco, R.L.; Elkind, M.S. Long-term exposure to ambient air pollution and subclinical cerebrovascular disease in the Northern Manhattan Study. Stroke 2017, 48, 1966–1968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wilker, E.H.; Preis, S.R.; Beiser, A.S.; Wolf, P.A.; Au, R.; Kloog, I.; Li, W.; Schwartz, J.; Koutrakis, P.; DeCarli, C.; et al. Long-term exposure to fine particulate matter, residential proximity to major roads and measures of brain structure. Stroke 2015, 46, 1161–1166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Tian, Y.; Liu, H.; Wu, Y.; Si, Y.; Song, J.; Cao, Y.; Li, M.; Wu, Y.; Wang, X.; Chen, L.; et al. Association between ambient fine particulate pollution and hospital admissions for cause specific cardiovascular disease: Time series study in 184 major Chinese cities. BMJ 2019, 367, l6572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chen, R.; Yin, P.; Meng, X.; Liu, C.; Wang, L.; Xu, X.; Ross, J.A.; Tse, L.A.; Zhao, Z.; Kan, H.; et al. Fine particulate air pollution and daily mortality. A nationwide analysis in 272 Chinese cities. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2017, 196, 73–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vernooij, M.; Ikram, M.; Tanghe, H.; Vincent, A.; Hofman, A.; Krestin, G.; Niessen, W.; Breteler, M.; Van Der Lugt, A. Incidental findings on brain MRI in the general population. N. Engl. J. Med. 2007, 357, 1821–1828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Luo, X.; Xu, S.; Liu, W.; Ding, F.; Zhang, X.; Wang, L.; Liu, J.; Hu, J.; Wang, W. Trends in smoking prevalence and implication for chronic diseases in China: Serial national cross-sectional surveys from 2003 to 2013. Lancet Respir. Med. 2019, 7, 35–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teo, B.W.; Zhang, L.; Guh, J.-Y.; Tang, S.C.; Jha, V.; Kang, D.-H.; Tanchanco, R.; Hooi, L.S.; Praditpornsilpa, K.; Kong, X.; et al. Glomerular filtration rates in Asians. Adv. Chronic Kidney Dis. 2018, 25, 41–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Shah, A.S.V.; Lee, K.K.; McAllister, D.A.; Hunter, A.; Nair, H.; Whiteley, W.; Langrish, J.P.; Newby, D.E.; Mills, N.L. Short term exposure to air pollution and stroke: Systematic review and meta-analysis. BMJ 2015, 350, h1295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- De Prado Bert, P.; Mercader, E.M.H.; Pujol, J.; Sunyer, J.; Mortamais, M. The effects of air pollution on the brain: A review of studies interfacing environmental epidemiology and neuroimaging. Curr. Environ. Health Rep. 2018, 5, 351–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Nußbaum, R.; Lucht, S.; Jockwitz, C.; Moebus, S.; Engel, M.; Jöckel, K.-H.; Caspers, S.; Hoffmann, B. Associations of air pollution and noise with local brain structure in a cohort of older adults. Environ. Health Perspect. 2020, 128, 67012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.C.; Wang, X.; Wellenius, G.A.; Serre, M.L.; Driscoll, I.; Casanova, R.; McArdle, J.J.; Manson, J.E.; Chui, H.C.; Espeland, M.A. Ambient air pollution and neurotoxicity on brain structure: Evidence from women’s health initiative memory study. Ann. Neurol. 2015, 78, 466–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Casanova, R.; Wang, X.; Reyes, J.; Akita, Y.; Serre, M.L.; Vizuete, W.; Chui, H.C.; Driscoll, I.; Resnick, S.M.; Espeland, M.A.; et al. A voxel-based morphometry study reveals local brain structural alterations associated with ambient fine particles in older women. Front Hum. Neurosci. 2016, 10, 495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lucking, A.J.; Lundback, M.; Mills, N.L.; Faratian, D.; Barath, S.L.; Pourazar, J.; Cassee, F.R.; Donaldson, K.; Boon, N.A.; Badimon, J.J.; et al. Diesel exhaust inhalation increases thrombus formation in man. Eur. Heart J. 2008, 29, 3043–3051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Franchini, M.; Mannucci, P.M. Thrombogenicity and cardiovascular effects of ambient air pollution. Blood 2011, 118, 2405–2412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Tian, Y.; Xu, Y.; Huang, Z.; Huang, C.; Hu, Y.; Zhang, J. Association between ambient air pollution and hospitalization for ischemic and hemorrhagic stroke in China: A multicity case-crossover study. Environ. Pollut. 2017, 230, 234–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Eeden, S.F.; Tan, W.C.; Suwa, T.; Mukae, H.; Terashima, T.; Fujii, T.; Qui, D.; Vincent, R.; Hogg, J.C. Cytokines involved in the systemic inflammatory response induced by exposure to particulate matter air pollutants (PM(10)). Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2001, 164, 826–830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Block, M.L.; Calderón-Garcidueñas, L. Air pollution: Mechanisms of neuroinflammation and CNS disease. Trends Neurosci. 2009, 32, 506–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hoshi, T.; Kitagawa, K.; Yamagami, H.; Furukado, S.; Hougaku, H.; Hori, M. Relations of serum high-sensitivity C-reactive protein and interleukin-6 levels with silent brain infarction. Stroke 2005, 36, 768–772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Brook, R.D.; Sun, Z.; Brook, J.R.; Zhao, X.; Ruan, Y.; Yan, J.; Mukherjee, B.; Rao, X.; Duan, F.; Sun, L.; et al. Extreme air pollution conditions adversely affect blood pressure and insulin resistance: The Air Pollution and Cardiometabolic Disease (AIRCMD-China) study. Hypertension 2016, 67, 77–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaufman, J.D.; Adar, S.D.; Barr, R.G.; Budoff, M.; Burke, G.L.; Curl, C.L.; Daviglus, M.L.; Roux, A.V.D.; Gassett, A.J.; Jacobos, D.R., Jr.; et al. Association between air pollution and coronary artery calcification within six metropolitan areas in the USA (the Multi-Ethnic Study of Atherosclerosis and Air Pollution): A longitudinal cohort study. Lancet 2016, 388, 696–704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Alexeeff, S.E.; Coull, B.A.; Gryparis, A.; Suh, H.; Sparrow, D.; Vokonas, P.S.; Schwartz, J. Medium-term exposure to traffic-related air pollution and markers of inflammation and endothelial function. Environ. Health Perspect. 2011, 119, 481–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosano, C.; Naydeck, B.; Kuller, L.H.; Longstreth, W.T., Jr.; Newman, A.B. Coronary artery calcium: Associations with brain magnetic resonance imaging abnormalities and cognitive status. J. Am. Geriatr. Soc. 2005, 53, 609–615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tuttolomondo, A.; Daidone, M.; Pinto, A. Endothelial dysfunction and inflammation in ischemic stroke pathogenesis. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2020, 26, 4209–4219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
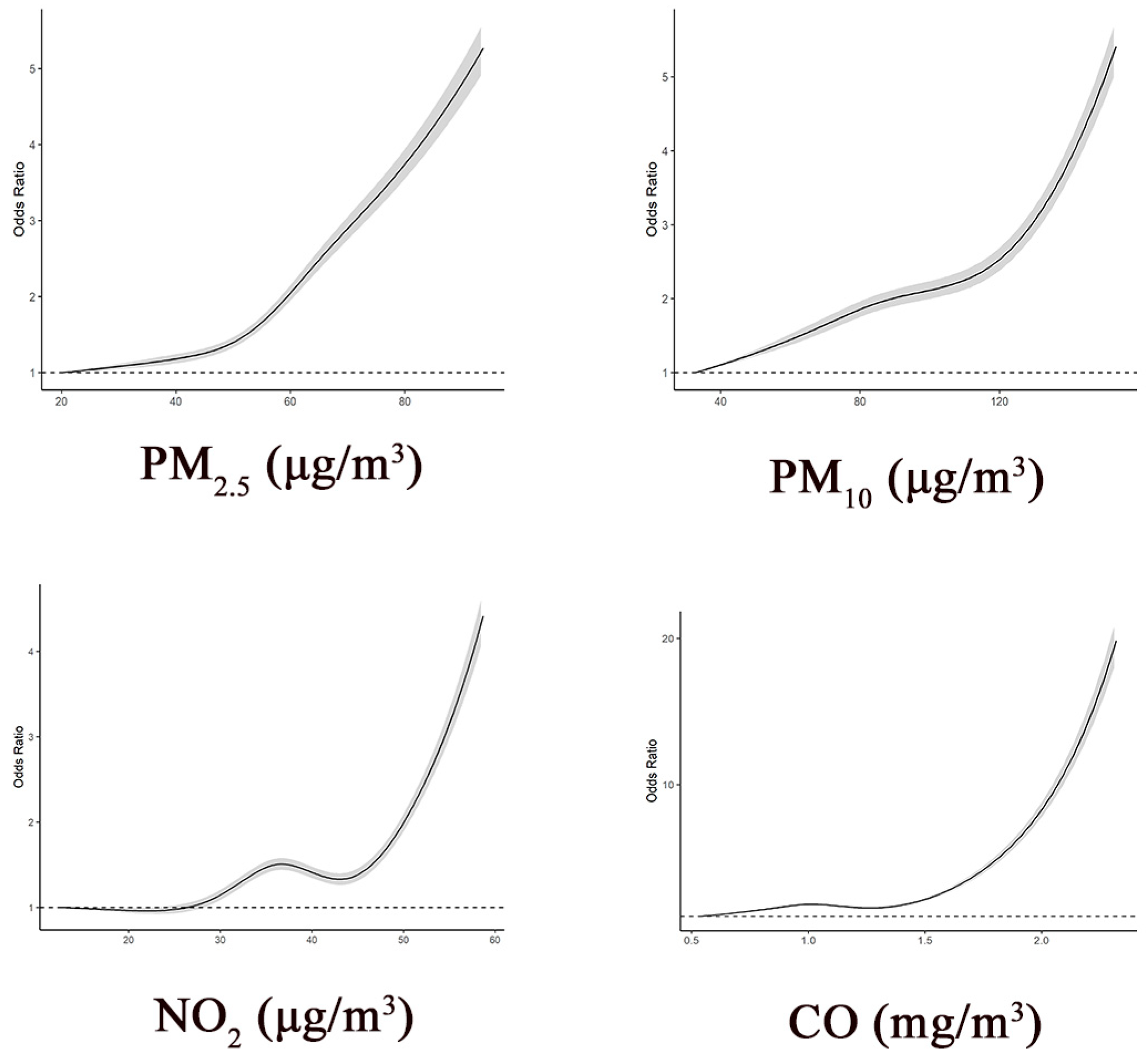
| Characteristics | Total | Participants without Brain Infarcts | Participants with Brain Infarcts |
|---|---|---|---|
| N | 1,400,503 | 1,304,832 | 95,671 |
| Age, year, mean ± SD | 46.4 ± 12.4 | 45.5 ± 12.0 | 58.8 ± 10.4 |
| Age group (years) | |||
| <30 | 131,424 (9.4) | 130,843 (10.0) | 581 (0.6) |
| 30–39 | 308,302 (22.0) | 305,401 (23.4) | 2901 (3.0) |
| 40–49 | 373,217 (26.6) | 361,220 (27.7) | 11,997 (12.5) |
| 50–59 | 372,543 (26.6) | 338,641 (26.0) | 33,902 (35.4) |
| 60–69 | 171,891 (12.3) | 138,997 (10.7) | 32,894 (34.4) |
| ≥70 | 43,126 (3.1) | 29,730 (2.3) | 13,396 (14.0) |
| Sex | |||
| Female | 692,226 (49.4) | 650,169 (49.8) | 42,057 (44.0) |
| Male | 708,277 (50.6) | 654,663 (50.2) | 53,614 (56.0) |
| BMI (kg/m2) | |||
| <18.5 | 36,842 (2.6) | 35,675 (2.7) | 1167 (1.2) |
| 18.5–23.9 | 550,388 (39.3) | 520,618 (39.9) | 29,770 (31.1) |
| 24.0–27.9 | 495,164 (35.4) | 454,421 (34.8) | 40,743 (42.6) |
| ≥28.0 | 194,292 (13.9) | 176,768 (13.5) | 17,524 (18.3) |
| Hypertension | |||
| No | 963,201 (68.8) | 924,303 (70.8) | 38,898 (40.7) |
| Yes | 368,445 (26.3) | 315,745 (24.2) | 52,700 (55.1) |
| Diabetes | |||
| No | 1,249,889 (89.2) | 1,171,788 (89.8) | 78,101 (81.6) |
| Yes | 98,689 (7.0) | 84,018 (6.4) | 14,671 (15.3) |
| Dyslipidemia | |||
| No | 838,263 (59.9) | 786,412 (60.3) | 51,851 (54.2) |
| Yes | 514,413 (36.7) | 473,239 (36.3) | 41,174 (43.0) |
| Atrial fibrillation | |||
| No | 1,315,385 (93.9) | 1,225,927 (94.0) | 89,458 (93.5) |
| Yes | 2696 (0.2) | 1995 (0.2) | 701 (0.7) |
| Fatty liver disease | |||
| No | 809,925 (57.8) | 762,058 (58.4) | 47,867 (50.0) |
| Yes | 533,952 (38.1) | 489,412 (37.5) | 44,540 (46.6) |
| Renal disease | |||
| No | 1,277,281 (91.2) | 1,190,110 (91.2) | 87,171 (91.1) |
| Yes | 23,024 (1.6) | 19,966 (1.5) | 3058 (3.2) |
| Mean ± SD | Range | PM2.5 (μg/m3) | PM10 (μg/m3) | NO2 (μg/m3) | CO (mg/m3) | Temp (°C) | RH (%) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PM2.5 (μg/m3) | 51.12 ± 15.61 | 20.20–93.70 | 1.00 | 0.92 | 0.74 | 0.68 | −0.43 | −0.49 |
| PM10 (μg/m3) | 88.93 ± 30.08 | 32.70–153.40 | - | 1.00 | 0.74 | 0.76 | −0.59 | −0.65 |
| NO2 (μg/m3) | 35.98 ± 10.07 | 12.60–58.70 | - | - | 1.00 | 0.59 | −0.32 | −0.50 |
| CO (mg/m3) | 1.07 ± 0.29 | 0.54–2.32 | - | - | - | 1.00 | −0.52 | −0.64 |
| Temp (°C) | 15.81 ± 4.44 | 2.96–24.66 | - | - | - | - | 1.00 | 0.74 |
| RH (%) | 69.10 ± 9.77 | 39.68–87.22 | - | - | - | - | - | 1.00 |
| Case/N | Model 1 OR (95% CI) | Model 2 OR (95% CI) | Model 3 OR (95% CI) | Model 4 OR (95% CI) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PM2.5 (μg/m3) | |||||
| Tertile 1 | 20,150/467,596 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 |
| Tertile 2 | 29,973/458,733 | 1.55 (1.52–1.58) | 1.52 (1.49–1.55) | 1.54 (1.52–1.57) | 1.37 (1.35–1.40) |
| Tertile 3 | 45,548/474,174 | 2.36 (2.32–2.40) | 2.24 (2.20–2.28) | 2.20 (2.16–2.24) | 2.00 (1.96–2.03) |
| p-trend | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | |
| Per SD increase | 1.50 (1.49–1.51) | 1.48 (1.47–1.49) | 1.46 (1.45–1.47) | 1.42 (1.40–1.43) | |
| PM10 (μg/m3) | |||||
| Tertile 1 | 21,474/473,040 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 |
| Tertile 2 | 30,779/465,562 | 1.49 (1.46–1.52) | 1.37 (1.34–1.40) | 1.35 (1.32–1.38) | 1.22 (1.20–1.25) |
| Tertile 3 | 43,418/461,901 | 2.18 (2.15–2.22) | 2.02 (1.98–2.05) | 1.96 (1.92–1.99) | 1.68 (1.65–1.71) |
| p-trend | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | |
| Per SD increase | 1.45 (1.44–1.46) | 1.42 (1.41–1.43) | 1.41 (1.40–1.42) | 1.35 (1.34–1.36) | |
| NO2 (μg/m3) | |||||
| Tertile 1 | 24,936/477,987 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 |
| Tertile 2 | 35,786/461,923 | 1.53 (1.50–1.55) | 1.52 (1.50–1.55) | 1.64 (1.61–1.67) | 1.50 (1.48–1.53) |
| Tertile 3 | 34,949/460,593 | 1.49 (1.47–1.52) | 1.52 (1.49–1.54) | 1.73 (1.70–1.77) | 1.58 (1.55–1.61) |
| p-trend | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | |
| Per SD increase | 1.24 (1.23–1.25) | 1.26 (1.25–1.26) | 1.35 (1.34–1.36) | 1.28 (1.27–1.29) | |
| CO (μg/m3) | |||||
| Tertile 1 | 21,278/466,523 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 |
| Tertile 2 | 34,397/469,207 | 1.66 (1.63–1.69) | 1.70 (1.67–1.73) | 1.72 (1.69–1.76) | 1.57 (1.54–1.60) |
| Tertile 3 | 39,996/464,773 | 1.97 (1.94–2.00) | 1.90 (1.86–1.93) | 1.84 (1.81–1.88) | 1.57 (1.54–1.60) |
| p-trend | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | |
| Per SD increase | 1.37 (1.36–1.38) | 1.37 (1.36–1.38) | 1.35 (1.34–1.36) | 1.30 (1.29–1.31) |
| PM2.5 | PM10 | NO2 | CO | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Age, years | ||||
| <65 | 1.38 (1.37–1.39) | 1.33 (1.31–1.34) | 1.26 (1.25–1.27) | 1.28 (1.27–1.29) |
| ≥65 | 1.52 (1.49–1.54) | 1.41 (1.39–1.44) | 1.34 (1.32–1.37) | 1.33 (1.31–1.35) |
| p-interaction | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 |
| Sex | ||||
| Male | 1.43 (1.41–1.44) | 1.36 (1.35–1.38) | 1.28 (1.26–1.29) | 1.31 (1.30–1.32) |
| Female | 1.40 (1.39–1.42) | 1.34 (1.32–1.35) | 1.29 (1.27–1.30) | 1.28 (1.27–1.30) |
| p-interaction | 0.02 | 0.13 | 0.13 | 0.03 |
| Model 1 OR (95% CI) | Model 2 OR (95% CI) | Model 3 OR (95% CI) | |
|---|---|---|---|
| PM2.5 (μg/m3) | |||
| Tertile 1 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 |
| Tertile 2 | 1.42 (1.39–1.45) | 1.39 (1.36–1.42) | 1.45 (1.42–1.48) |
| Tertile 3 | 1.87 (1.83–1.91) | 1.94 (1.90–1.98) | 1.98 (1.94–2.02) |
| p-trend | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 |
| Per SD increase | 1.39 (1.38–1.41) | 1.40 (1.38–1.41) | 1.40 (1.39–1.41) |
| PM10 (μg/m3) | |||
| Tertile 1 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 |
| Tertile 2 | 1.23 (1.20–1.25) | 1.26 (1.23–1.28) | 1.26 (1.24–1.29) |
| Tertile 3 | 1.49 (1.46–1.53) | 1.66 (1.62–1.69) | 1.73 (1.70–1.77) |
| p-trend | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 |
| Per SD increase | 1.34 (1.33–1.36) | 1.33 (1.32–1.34) | 1.35 (1.34–1.36) |
| NO2 (μg/m3) | |||
| Tertile 1 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 |
| Tertile 2 | 1.39 (1.37–1.42) | 1.46 (1.44–1.49) | 1.58 (1.55–1.61) |
| Tertile 3 | 1.42 (1.39–1.45) | 1.53 (1.50–1.56) | 1.62 (1.59–1.66) |
| p-trend | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 |
| Per SD increment | 1.22 (1.21–1.23) | 1.26 (1.25–1.27) | 1.29 (1.28–1.30) |
| CO (μg/m3) | |||
| Tertile 1 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 |
| Tertile 2 | 1.51 (1.48–1.54) | 1.62 (1.59–1.66) | 1.63 (1.60–1.66) |
| Tertile 3 | 1.29 (1.26–1.32) | 1.57 (1.54–1.60) | 1.61 (1.57–1.64) |
| p-trend | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 |
| Per SD increase | 1.27 (1.26–1.28) | 1.30 (1.29–1.31) | 1.29 (1.28–1.30) |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wu, J.; Ning, Y.; Gao, Y.; Shan, R.; Wang, B.; Lv, J.; Li, L. Association between Ambient Air Pollution and MRI-Defined Brain Infarcts in Health Examinations in China. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 4325. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph18084325
Wu J, Ning Y, Gao Y, Shan R, Wang B, Lv J, Li L. Association between Ambient Air Pollution and MRI-Defined Brain Infarcts in Health Examinations in China. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health. 2021; 18(8):4325. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph18084325
Chicago/Turabian StyleWu, Jing, Yi Ning, Yongxiang Gao, Ruiqi Shan, Bo Wang, Jun Lv, and Liming Li. 2021. "Association between Ambient Air Pollution and MRI-Defined Brain Infarcts in Health Examinations in China" International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health 18, no. 8: 4325. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph18084325
APA StyleWu, J., Ning, Y., Gao, Y., Shan, R., Wang, B., Lv, J., & Li, L. (2021). Association between Ambient Air Pollution and MRI-Defined Brain Infarcts in Health Examinations in China. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 18(8), 4325. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph18084325






