The Optimization Strategy of the Existing Urban Green Space Soil Monitoring System in Shanghai, China
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
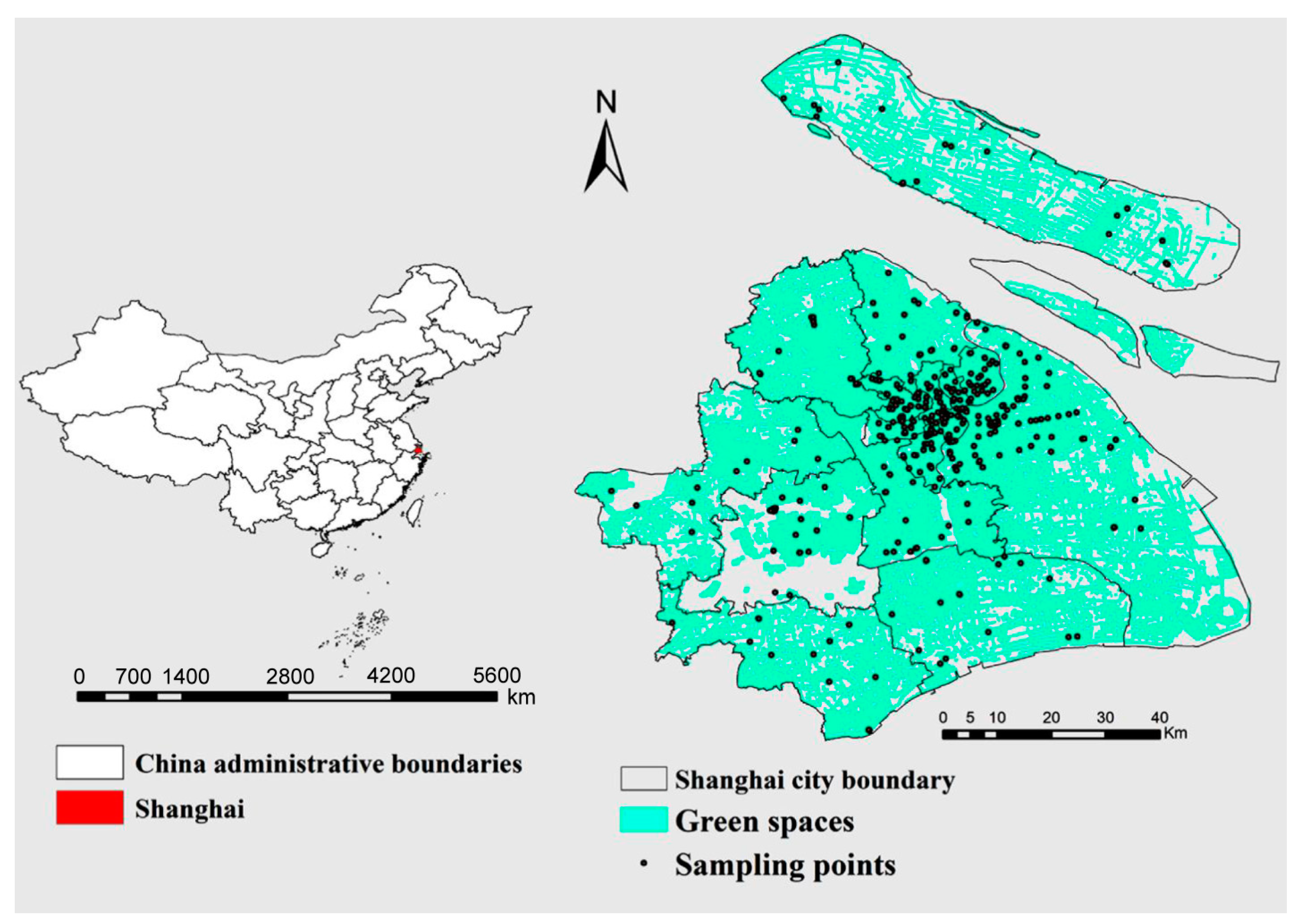
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Soil Sampling and Chemical Analysis
2.3. Geostatistical Methods
2.4. Prediction Accuracy Improvement Procedures
Perturb Initial Sampling Design by SSA and Evaluations
2.5. Statistical Analysis Software and Tools
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Mean Concentrations and Summary Statistics of Potentially Toxic Elements
3.2. Optimization Strategy and Evaluation of Existing Monitoring Points
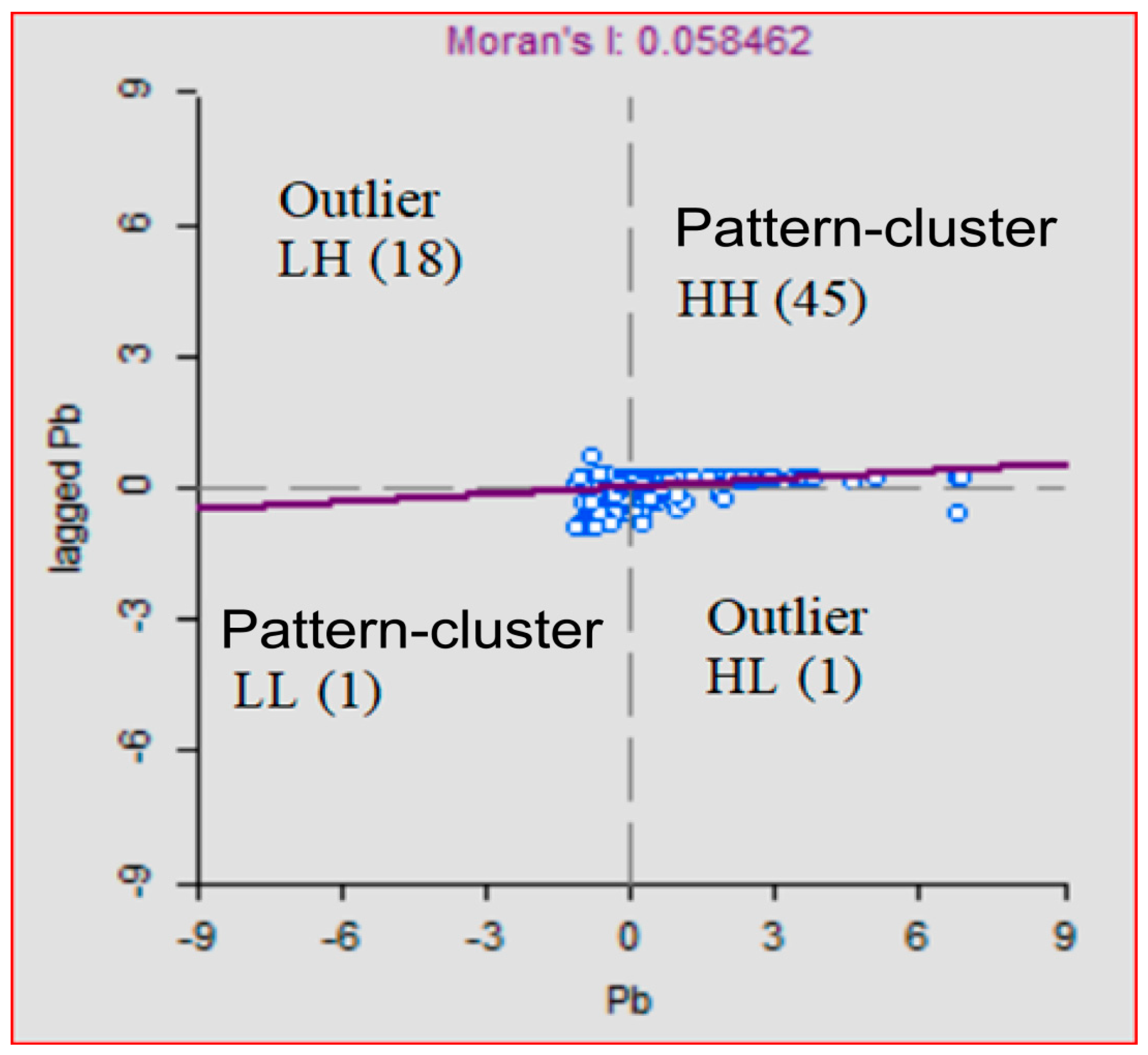
3.2.1. Spatial Patterns of Existing Monitoring Points
3.2.2. Spatial Structures and Dependency
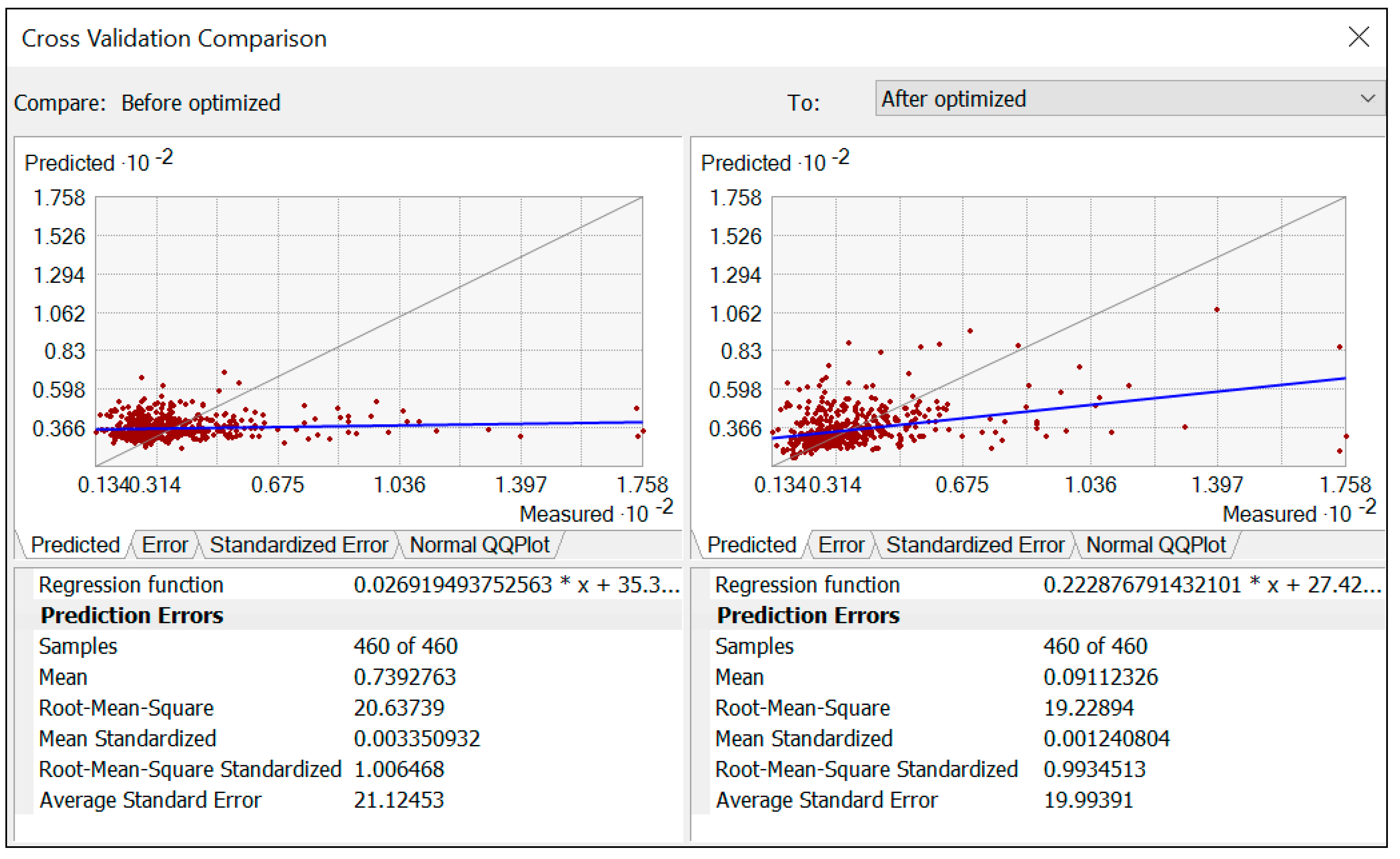
3.2.3. Prediction Accuracy Improvement by Optimization Strategy
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Reynolds, W.D.; Drury, C.F.; Yang, X.M.; Tan, C.S. Optimal soil physical quality inferred through structural regression and parameter interactions. Geoderma 2008, 146, 466–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jadoon, S.; Muhammad, S.; Hilal, Z.; Ali, M.; Khan, S.; Khattak, N.U. Spatial distribution of potentially toxic elements in urban soils of Abbottabad city, (N Pakistan): Evaluation for potential risk. Microchem. J. 2020, 153, 104489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lan, T.; Guo, S.-W.; Han, J.-W.; Yang, Y.-L.; Zhang, K.; Zhang, Q.; Yang, W.; Li, P.-F. Evaluation of physical properties of typical urban green space soils in Binhai Area, Tianjin, China. Urban For. Urban Green. 2019, 44, 126430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Purves, D. Contamination of urban garden soils with copper and boron. Nat. Cell Biol. 1966, 210, 1077–1078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilkins, C. The distribution of lead in the soils and herbage of West Pembrokeshire. Environ. Pollut. 1978, 15, 23–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, Q.-Y.; Mo, C.-H.; Li, H.-Q.; Lü, H.; Zeng, Q.-Y.; Li, Y.-W.; Wu, X.-L. Heavy metal contamination of urban soils and dusts in Guangzhou, South China. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2012, 185, 1095–1106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, S.; Shao, G.; Wang, L.; Tang, L. Spatial distribution and potential sources of five heavy metals and one metalloid in the soils of Xiamen city, China. Bull. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2019, 103, 308–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodríguez-Seijo, A.; Andrade, M.L.; Vega, F.A. Origin and spatial distribution of metals in urban soils. J. Soils Sediments 2017, 17, 1514–1526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minguillón, M.C.; Cirach, M.; Hoek, G.; Brunekreef, B.; Tsai, M.; De Hoogh, K.; Jedynska, A.; Kooter, I.M.; Nieuwenhuijsen, M.J.; Querol, X. Spatial variability of trace elements and sources for improved exposure assessment in Barcelona. Atmos. Environ. 2014, 89, 268–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dao, L.; Morrison, L.; Zhang, H.; Zhang, C. Influences of traffic on Pb, Cu and Zn concentrations in roadside soils of an urban park in Dublin, Ireland. Environ. Geochem. Health 2013, 36, 333–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C. Using multivariate analyses and GIS to identify pollutants and their spatial patterns in urban soils in Galway, Ireland. Environ. Pollut. 2006, 142, 501–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, X.; Wu, J.; Xu, J. Characterizing the risk assessment of heavy metals and sampling uncertainty analysis in paddy field by geostatistics and GIS. Environ. Pollut. 2006, 141, 257–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miao, L.; Xu, R.; Ma, Y.; Zhu, Z.; Wang, J.; Cai, R.; Chen, Y. Geochemistry and biogeochemistry of rare earth elements in a surface environment (soil and plant) in South China. Environ. Earth Sci. 2008, 56, 225–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adedeji, O.H.; Olayinka, O.O.; Tope-Ajayi, O.O. Spatial distribution and health risk assessment of soil pollution by heavy metals in Ijebu-Ode, Nigeria. J. Health Pollut. 2019, 9, 190601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farmer, J.G.; Lyon, T.D.B. Lead in glasgow street dirt and soul. Sci. Total Environ. 1977, 8, 89–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kelly, J.; Thornton, I.; Simpson, P.R. Urban geochemistry: A study of the influence of anthropogenic activity on the heavy metal content of soils in traditionally industrial and non-industrial areas of Britain. Appl. Geochem. 1996, 11, 363–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Chi-sun, P.; Pui Sum, L. Heavy metal contamination of urban soils and street dusts in Hong Kong. Appl. Geochem. 2001, 16, 1361–1368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mielke, H.W.; Gonzales, C.R.; Smith, M.K.; Mielke, P.W. Quantities and associations of lead, zinc, cadmium, manganese, chromium, nickel, vanadium, and copper in fresh Mississippi delta alluvium and New Orleans alluvial soils. Sci. Total Environ. 2000, 246, 249–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tijhuis, L.; Brattli, B.; Sæther, O.M. A geochemical survey of topsoil in the city of Oslo, Norway. Environ. Geochem. Health 2002, 24, 67–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sahoo, P.K.; Dall’Agnol, R.; Salomão, G.N.; Junior, J.D.S.F.; Da Silva, M.S.; Martins, G.C.; Filho, P.W.M.E.S.; Powell, M.A.; Maurity, C.W.; Angelica, R.S.; et al. Source and background threshold values of potentially toxic elements in soils by multivariate statistics and GIS-based mapping: A high density sampling survey in the Parauapebas basin, Brazilian Amazon. Environ. Geochem. Health 2019, 42, 255–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ciupa, T.; Suligowski, R.; Kozłowski, R. Trace metals in surface soils under different land uses in Kielce city, south-central Poland. Environ. Earth Sci. 2020, 79, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nazarpour, A.; Watts, M.J.; Madhani, A.; Elahi, S. Source, spatial distribution and pollution assessment of Pb, Zn, Cu, and Pb, Isotopes in urban soils of Ahvaz city, a semi-arid metropolis in southwest Iran. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 5349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, S.; Yang, L.; Chen, L.; Zhao, F.; Sun, L. Spatial distribution of heavy metal concentrations in peri-urban soils in eastern China. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2018, 26, 1615–1627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Balkaya, N.; Guneysu, S. Recycling and Reuse Approaches for Better Sustainability; Metzler, J.B., Ed.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2019; p. 297. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Y.; Chen, Q. Contents of heavy metals in urban parks and university campuses. IOP Conf. Ser. Earth Environ. Sci. 2018, 108, 42060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gąsiorek, M.; Kowalska, J.; Mazurek, R.; Pająk, M. Comprehensive assessment of heavy metal pollution in topsoil of historical urban park on an example of the Planty Park in Krakow (Poland). Chemosphere 2017, 179, 148–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Praveena, S.M.; Yuswir, N.S.; Aris, A.Z.; Hashim, Z. Contamination assessment and potential human health risks of heavy metals in Klang urban soils: A preliminary study. Environ. Earth Sci. 2015, 73, 8155–8165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amari, T.; Ghnaya, T.; Abdelly, C. Nickel, cadmium and lead phytotoxicity and potential of halophytic plants in heavy metal extraction. S. Afr. J. Bot. 2017, 111, 99–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiwan, S.; Ajay, K. Effects of heavy metals on soil, plants, human health and aquatic life. Int. J. Res. Chem. Environ. 2011, 1, 15–21. [Google Scholar]
- Khelifi, F.; Melki, A.; Hamed, Y.; Adamo, P.; Caporale, A.G. Environmental and human health risk assessment of potentially toxic elements in soil, sediments, and ore-processing wastes from a mining area of southwestern Tunisia. Environ. Geochem. Health 2020, 42, 4125–4139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, B.; Yang, L. A review of heavy metal contaminations in urban soils, urban road dusts and agricultural soils from China. Microchem. J. 2010, 94, 99–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manta, D.S.; Angelone, M.; Bellanca, A.; Neri, R.; Sprovieri, M. Heavy metals in urban soils: A case study from the city of Palermo (Sicily), Italy. Sci. Total Environ. 2002, 300, 229–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, S.; Duan, X.; Zhao, X.; Chen, Y.; Wang, B.; Sun, C.; Zheng, B.; Wei, F. Health risks of children’s cumulative and aggregative exposure to metals and metalloids in a typical urban environment in China. Chemosphere 2016, 147, 404–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martín, J.R.; Ramos-Miras, J.; Boluda, R.; Gil, C. Spatial relations of heavy metals in arable and greenhouse soils of a mediterranean environment region (Spain). Geoderma 2013, 200–201, 180–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caeiro, S.; Costa, M.; Ramos, T.; Fernandes, F.; Silveira, N.; Coimbra, A.; Medeiros, G.; Painho, M. Assessing heavy metal contamination in Sado Estuary sediment: An index analysis approach. Ecol. Indic. 2005, 5, 151–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong-Gui, D.; Teng-Feng, G.; Ming-Hui, L.; Xu, D. Comprehensive assessment model on heavy metal pollution in soil. Int. J. Electrochem. Sci. 2012, 7, 5286–5296. [Google Scholar]
- Kowalska, J.B.; Mazurek, R.; Gąsiorek, M.; Zaleski, T. Pollution indices as useful tools for the comprehensive evaluation of the degree of soil contamination—A review. Environ. Geochem. Health 2018, 40, 2395–2420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Liao, Y.; Li, D.; Zhang, N. Comparison of interpolation models for estimating heavy metals in soils under various spatial characteristics and sampling methods. Trans. GIS 2018, 22, 409–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brus, D.J.; Heuvelink, G.B. Optimization of sample patterns for universal kriging of environmental variables. Geoderma 2007, 138, 86–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berman, J.D.; Jin, L.; Bell, M.L.; Curriero, F.C. Developing a geostatistical simulation method to inform the quantity and placement of new monitors for a follow-up air sampling campaign. J. Expo. Sci. Environ. Epidemiol. 2019, 29, 248–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wadoux, A.M.; Marchant, B.P.; Lark, R.M. Efficient sampling for geostatistical surveys. Eur. J. Soil Sci. 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Groenigen, J.W.; Stein, A. Constrained optimization of spatial sampling using continuous simulated annealing. J. Environ. Qual. 1998, 27, 1078–1086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonçalves, M.; Jimenez-Guerrero, P.; Baldasano, J.M. Air quality management strategies in large cities: Effects of changing the vehicle fleet composition in Barcelona and Madrid Greater Areas (Spain) by introducing natural gas vehicles. In Air Pollution Modeling and Its Application XIX; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2008; pp. 54–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matte, T.D.; Ross, Z.; Kheirbek, I.; Eisl, H.; Johnson, S.E.; Gorczynski, J.; Kass, D.; Markowitz, S.; Pezeshki, G.E.; Clougherty, J. Monitoring intraurban spatial patterns of multiple combustion air pollutants in New York City: Design and implementation. J. Expo. Sci. Environ. Epidemiol. 2013, 23, 223–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shanghai Municipal Government (SMG). Shanghai Master Plan 2017–2035; Shanghai Municipal Government (SMG): Shanghai, China, 2018; pp. 1–80. Available online: https://doi.org/http://www.shanghai.gov.cn/newshanghai/xxgkfj/2035004.pdf (accessed on 20 December 2020).
- Shi, G.; Chen, Z.; Xu, S.; Zhang, J.; Wang, L.; Bi, C.; Teng, J. Potentially toxic metal contamination of urban soils and roadside dust in Shanghai, China. Environ. Pollut. 2008, 156, 251–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, Z.; Chen, R.; Meadows, M.E.; Sengupta, D.; Xu, D. Changing urban green spaces in Shanghai: Trends, drivers and policy implications. Land Use Policy 2019, 87, 104080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Environmental Protection Agency (EPA). Environmental Protection Agency (EPA), “Method 3052: Microwave Assisted Acid Digestion of Siliceous and Organically Based Matrices; Environmental Protection Agency (EPA): Washington, DC, USA, 1996; pp. 1–20.
- Zhang, C.; McGrath, D. Geostatistical and GIS analyses on soil organic carbon concentrations in grassland of southeastern Ireland from two different periods. Geoderma 2004, 119, 261–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Zhang, S. Approach of developing spatial. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Computer and Computing Technologies in Agriculture, Wuyishan, China, 18–20 August 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Campbell, J.B. Divisions-5—Soil genesis, morphology, Spatial variation of sand content and pH within single contiguousdelineations of two. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 1978, 42, 460–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goovaerts, P. Geostatistics in soil science: State-of-the-art and perspectives. Geoderma 1999, 89, 1–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haining, R.; Wise, S.; Ma, J. Exploratory spatial data analysis in a geographic information system environment. J. R. Stat. Soc. 1998, 457–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haining, R.; Wise, S. Unit 128—Exploratory spatial data analysis. J. R. Stat. Soc. 2002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anselin, L. Local indicators of spatial Association—LISA. Geogr. Anal. 1995, 27, 1–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moran, B.Y.P.A.P. Notes on Continuous Stochastic Phenomena. Biometrika 1950, 37, 17–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Haining, R.; Cao, Z. Sample surveying to estimate the mean of a heterogeneous surface: Reducing the error variance through zoning. Int. J. Geogr. Inf. Sci. 2010, 24, 523–543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barca, E.; Passarella, G.; Uricchio, V. Optimal extension of the rain gauge monitoring network of the apulian regional consortium for crop protection. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2007, 145, 375–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lark, R.M. Kriging a soil variable with a simple nonstationary variance model. J. Agric. Biol. Environ. Stat. 2009, 14, 301–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samuel-rosa, A.; Heuvelink, G.; Vasques, G.; Anjos, L. Spsann—Optimization of Sample Patterns Using Spatial Simulated Annealing. 2015. Available online: https://cran.r-project.org/web/packages/spsann/vignettes/spsann.pdf (accessed on 5 January 2021).
- Bivand, R.S.; Pebesma, E.; Gómez-Rubio, V. Applied Spatial Data Analysis with R.; Springer Science and Business Media: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Anselin, L.; Syabri, I.; Kho, Y. GeoDa: An introduction to spatial data analysis. Geogr. Anal. 2006, 38, 5–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Luo, H. The Backgrounds of Soil Environment in Shanghai; China Environmental Science Press: Beijing, China, 1992. [Google Scholar]
- CNEMC. The Backgrounds of Soil Environment in China, Beijing; Environmental Science Press of China: Beijing, China, 1990. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Chen, T.; Liu, X.; Li, X.; Zhao, K.; Zhang, J.; Xu, J.; Shi, J.; Dahlgren, R.A. Heavy metal sources identification and sampling uncertainty analysis in a field-scale vegetable soil of Hangzhou, China. Environ. Pollut. 2009, 157, 1003–1010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adimalla, N.; Chen, J.; Qian, H. Spatial characteristics of heavy metal contamination and potential human health risk assessment of urban soils: A case study from an urban region of South India. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2020, 194, 110406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Duan, X.; Wang, L. Spatial distribution and source analysis of heavy metals in soils influenced by industrial enterprise distribution: Case study in Jiangsu Province. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 710, 134953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Said, I.; Salman, S.A.E.-R.; Samy, Y.; Awad, S.A.; Melegy, A.; Hursthouse, A.S. Environmental factors controlling potentially toxic element behaviour in urban soils, El Tebbin, Egypt. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2019, 191, 267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liang, J.; Wu, H.B.; Wang, X.X. Distribution characteristics and health risk assessment of heavy metals and PAHs in the soils of green spaces in Shanghai, China. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2019, 191, 345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fang, H.L.; Dong, Y.; Gu, B.; Hao, G.J.; Lv, Z.W.; Liang, J.; Chen, L. Distribution of heavy metals and arsenic in greenbelt roadside soils of Pudong new district in Shanghai. Soil Sediment Contam. Int. J. 2009, 18, 702–714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhaoyong, Z.; Xiaodong, Y.; Simay, Z.; Mohammed, A. Health risk evaluation of heavy metals in green land soils from urban parks in Urumqi, northwest China. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2018, 25, 4459–4473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duzgoren-Aydin, N.; Wong, C.; Aydin, A.; Song, Z.; You, M.; Li, X. Heavy metal contamination and distribution in the urban environment of Guangzhou, SE China. Environ. Geochem. Health 2006, 28, 375–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Wang, H. Concentrations and chemical forms of potentially toxic metals in road-deposited sediments from different zones of Hangzhou, China. J. Environ. Sci. 2009, 21, 625–631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madrid, L.; Díaz-Barrientos, E.; Madrid, F. Distribution of heavy metal contents of urban soils in parks of Seville. Chemosphere 2002, 49, 1301–1308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morton-Bermea, O.; Hernández-Álvarez, E.; González-Hernández, G.; Romero, F.; Lozano, R.; Beramendi-Orosco, L. Assessment of heavy metal pollution in urban topsoils from the metropolitan area of Mexico City. J. Geochem. Explor. 2009, 101, 218–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Onder, S.; Dursun, S.; Gezgin, S.; Demirbas, A. Determination of heavy metal pollution in grass and soil of city centre green areas (Konya, Turkey). Pol. J. Environ. Stud. 2007, 16, 145–154. [Google Scholar]
- Linde, M.; Bengtsson, H.; Öborn, I. Concentrations and pools of heavy metals in urban soils in Stockholm, Sweden. Water Air Soil Pollut. Focus 2001, 1, 83–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rizo, O.D.; Morell, D.F.; López, J.O.A.; Muñoz, J.L.B.; Rodríguez, K.D.; Pino, N.L. Spatial distribution and contamination assessment of heavy metals in urban Topsoils from Las Tunas City, Cuba. Bull. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2013, 91, 29–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liebens, J.; Mohrherr, C.J.; Rao, K.R. Trace metal assessment in soils in a small city and its rural surroundings, Pensacola, FL, USA. Environ. Earth Sci. 2011, 65, 1781–1793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Getis, A.; Ord, J.K. The analysis of spatial association by use of distance statistics. Geogr. Anal. 2010, 24, 189–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Tang, Y.; Luo, L.; Xu, W. Outlier identification and visualization for Pb concentrations in urban soils and its implications for identification of potential contaminated land. Environ. Pollut. 2009, 157, 3083–3090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Johnston, K.; Ver Hoef, J.M.; Krivoruchko, K.; Lucas, N. Using ArcGIS Geostatistical Analyst; GIS by ESRI: California, CA, USA, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Cambardella, C.A.; Moorman, T.B.; Novak, J.M.; Parkin, T.B.; Karlen, D.L.; Turco, R.F.; Konopka, A.E. Field-scale variability of soil properties in central Iowa soils. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 1994, 58, 1501–1511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, R.; Liu, S.; Yang, Y.; Huang, W.; Han, Z.; Fu, P. Optimization of soil sampling design based on road networks—A simulated annealing/neural network algorithm. Earth Sci. 2019, 8, 335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Groenigen, J.W.; Siderius, W.; Stein, A. Constrained optimisation of soil sampling for minimisation of the kriging variance. Geoderma 1999, 87, 239–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pagliosa, L.; Justiniano, P.; Maria, S.A.M. Optimization of spatial sample configurations using hybrid genetic algorithm and simulated annealing. Chil. J. Stat. 2011, 2, 39–50. [Google Scholar]
- Gao, B.; Lu, A.; Pan, Y.; Huo, L.; Gao, Y.; Li, X.; Li, S.; Chen, Z. Additional sampling layout optimization method for environmental quality grade classifications of farmland Soil. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2017, 10, 5350–5358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szatmári, G.; Barta, K.; Pásztor, L. An application of a spatial simulated annealing sampling optimization algorithm to support digital soil mapping. Hung. Geogr. Bull. 2015, 64, 35–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wadoux, A.M.-C.; Brus, D.J.; Rico-Ramirez, M.A.; Heuvelink, G.B. Sampling design optimisation for rainfall prediction using a non-stationary geostatistical model. Adv. Water Resour. 2017, 107, 126–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pang, S.; Li, T.-X.; Wang, Y.-D.; Yu, H.-Y.; Li, X. Spatial interpolation and sample size optimization for soil copper (Cu) investigation in cropland soil at county scale using Cokriging. Agric. Sci. China 2009, 8, 1369–1377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| PTE | Mean | Median | Range Values | SD | CV (%) | Background Values of Shanghai * | Background Values of China ** |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pb | 36.96 | 31.70 | 13.41–175.8 | 20.20 | 54.66 | 25.47 | 23.50 |
| Cu | 34.41 | 30.27 | 10.09–225.4 | 19.04 | 55.32 | 28.59 | 20.70 |
| Zn | 130.3 | 113.6 | 49.15–1098 | 84.83 | 65.10 | 83.68 | 68.00 |
| Cr | 73.09 | 73.20 | 38.24–143.2 | 10.76 | 14.73 | 75.00 | 57.30 |
| Cd | 0.21 | 0.17 | 0.06–3.68 | 0.21 | 100.50 | 0.13 | 0.08 |
| Study Areas | Pb | Cu | Zn | Cr | Cd | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Parks of Seville, Spain | 161.0 | 72.00 | 210.0 | 75.00 | - | [74] |
| Mexico City, Mexico | 82.00 | 54.00 | 219.0 | - | 116.0 | [75] |
| Konya Park, Turkey | 289.4 | 427.4 | 289.8 | 14.0 | 21.0 | [76] |
| Stockholm, Sweden | 104.0 | 47.0 | 157.0 | 27.0 | 0.43 | [77] |
| Tunas City, Cuba | 42.0 | 94.0 | 199.0 | 97.0 | - | [78] |
| Pensacola, USA | 23.98 | 6.26 | 33.22 | 9.01 | 0.13 | [79] |
| Urumqi, China | 43.22 | 42.54 | 94.79 | 30.97 | 0.71 | [71] |
| Guangzhou, China | 240.0 | 176.0 | 586.0 | 78.8 | 2.41 | [72] |
| Hangzhou, China | 202.1 | 116.0 | 321.4 | 51.25 | 1.59 | [73] |
| Shanghai, China | 70.69 | 59.25 | 301.4 | 107.9 | 0.52 | [46] |
| Shanghai, China | 36.96 | 34.40 | 130.3 | 73.09 | 0.21 | This study |
| Variables | Moran’s I | Variance | Z-Score | p-Value | Distribution | Skewness | Kurtosis |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pb | 0.159968 | 0.000312 | 9.178694 | 0.000000 | Clustered | 3.31 | 14.97 |
| Cu | 0.134803 | 0.000403 | 6.824677 | 0.000000 | 5.01 | 35.06 | |
| Zn | 0.134243 | 0.00028 | 8.143643 | 0.000000 | 6.77 | 55.94 | |
| Cr | 0.196636 | 0.000428 | 9.614280 | 0.000000 | 1.43 | 8.41 | |
| Cd | 0.057502 | 0.000286 | 3.530263 | 0.000415 | 10.01 | 130.23 |
| PTE | Mean Error | RMSE | MSE | ASE | RMSSE |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pb | 0.091 | 19.22 | 0.001 | 19.99 | 0.993 |
| CU | 0.295 | 18.52 | 0.009 | 18.93 | 1.120 |
| Zn | 0.422 | 81.35 | 0.002 | 104.43 | 0.828 |
| Cr | 0.004 | 9.89 | −0.002 | 11.06 | 0.898 |
| Cd | 0.000 | 0.21 | 0.001 | 0.22 | 0.994 |
| PTE | Model | Nugget (C0) | Partial Sill (C) | Sill (C0 + C) | Range (m) | Nugget Ratio % C0/(C0 + C) | Spatial Dependency |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pb | Spherical | 0.047 | 0.133 | 0.18 | 2263.30 | 26.11 | Moderate |
| Cu | Gaussian | 0.053 | 0.128 | 0.181 | 2597.00 | 29.28 | Moderate |
| Zn | Gaussian | 0.000 | 0.141 | 0.141 | 213.98 | 0.00 | Strong |
| Cr | Spherical | 0.000 | 0.015 | 0.015 | 120.48 | 0.00 | strong |
| Cd | Exponential | 0.000 | 0.238 | 0.238 | 140.93 | 0.00 | Strong |
| Numbers of Points Perturbed | Soil Pb MKV (mg kg−1) | Improvement MKV (%) |
|---|---|---|
| 50 | 128.9 | 2.16 |
| 100 | 118.2 | 10.25 |
| 150 | 109.1 | 17.16 |
| 200 | 102.3 | 22.36 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, W.; Han, J.; Molla, A.; Zuo, S.; Ren, Y. The Optimization Strategy of the Existing Urban Green Space Soil Monitoring System in Shanghai, China. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 4820. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph18094820
Zhang W, Han J, Molla A, Zuo S, Ren Y. The Optimization Strategy of the Existing Urban Green Space Soil Monitoring System in Shanghai, China. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health. 2021; 18(9):4820. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph18094820
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Weiwei, Jigang Han, Abiot Molla, Shudi Zuo, and Yin Ren. 2021. "The Optimization Strategy of the Existing Urban Green Space Soil Monitoring System in Shanghai, China" International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health 18, no. 9: 4820. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph18094820
APA StyleZhang, W., Han, J., Molla, A., Zuo, S., & Ren, Y. (2021). The Optimization Strategy of the Existing Urban Green Space Soil Monitoring System in Shanghai, China. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 18(9), 4820. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph18094820






