Students’ Perceptions of Instructional Rubrics in Neurological Physical Therapy and Their Effects on Students’ Engagement and Course Satisfaction
Abstract
1. Introduction
1.1. Assessment Rubrics in University Studies
1.2. Research on Rubrics in PT Studies
1.3. Process of Development and Use of Neurological PT Rubrics
1.4. Objectives and Hypotheses
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Design and Procedure
2.2. Measures
2.3. Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Previous Analyses. Factorial Structure of the PVURE
3.2. Rating of the Validity/Reliability and Usefulness of the Rubrics
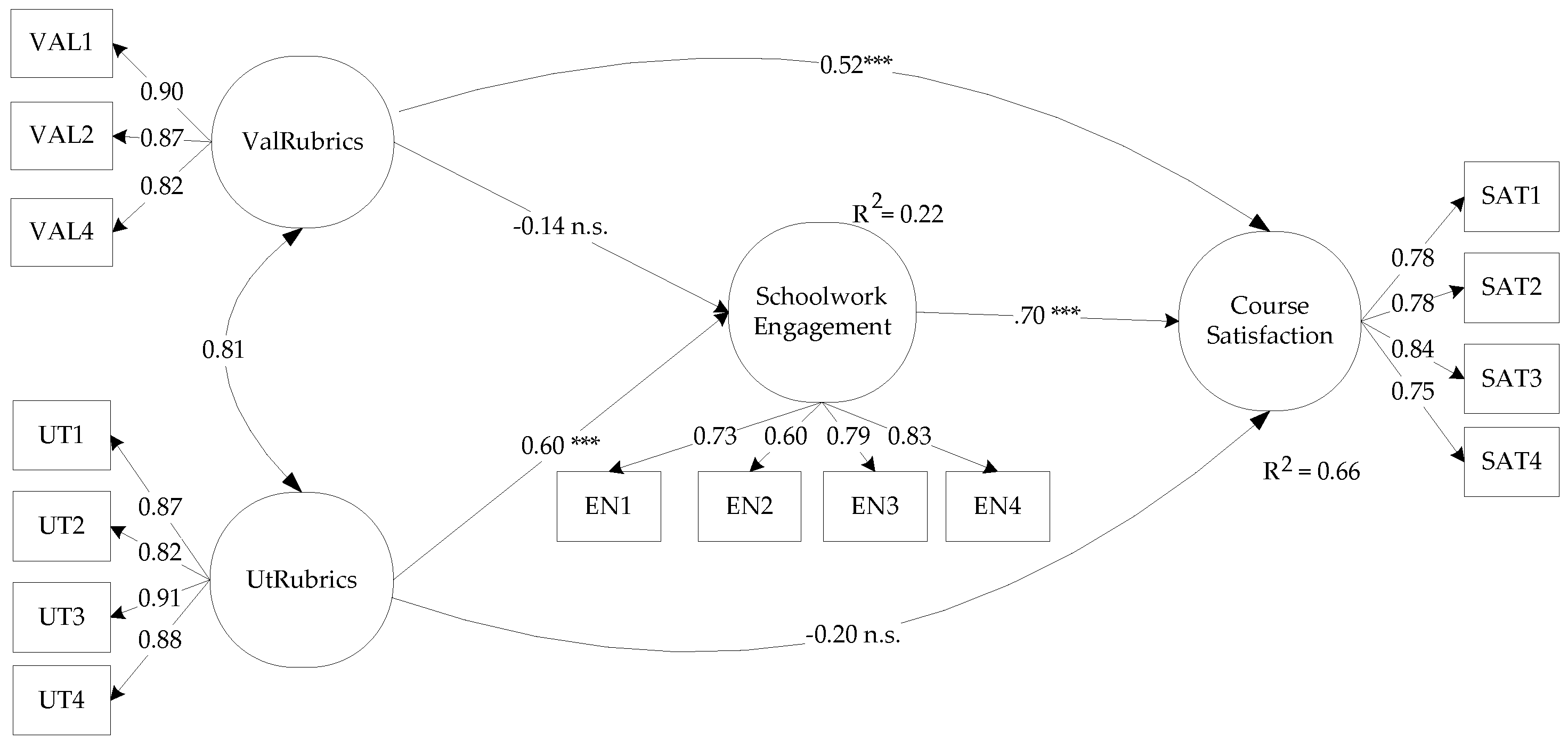
3.3. Relationships between the Perception of the Rubrics and the Educational Outcomes
3.4. Difficulties in Learning the Maneuvers and Improvements in the Rubrics
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Khalid, M.T.; Sarwar, M.F.; Sarwar, M.H.; Sarwar, M. Current role of physiotherapy in response to changing healthcare needs of the society. Int. J. Inf. Educ. 2015, 1, 6. [Google Scholar]
- Khan, F.; Amatya, B.; Galea, M.P.; Gonzenbach, R.; Kesselring, J. Neurorehabilitation: Applied neuroplasticity. J. Neurol. 2017, 264, 603–615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nahum, M.; Lee, H.; Merzenich, M.M. Principles of neuroplasticity-based rehabilitation. In Progress in Brain Research; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2013; Volume 207, pp. 141–171. ISBN 978-0-444-63327-9. [Google Scholar]
- Li, P.; Legault, J.; Litcofsky, K.A. Neuroplasticity as a function of second language learning: Anatomical changes in the human brain. Cortex 2014, 58, 301–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- WCPT. Physical Therapist Professional Entry Level Education Guideline; World Confederation for Physical: London, UK, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Lekkas, P.; Larsen, T.; Kumar, S.; Grimmer, K.; Nyland, L.; Chipchase, L.; Jull, G.; Buttrum, P.; Carr, L.; Finch, J. No model of clinical education for physiotherapy students is superior to another: A systematic review. Aust. J. Physiother. 2007, 53, 19–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delany, C.; Bragge, P. A study of physiotherapy students’ and clinical educators’ perceptions of learning and teaching. Med. Teach. 2009, 31, e402–e411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rossettini, G.; Rondoni, A.; Palese, A.; Cecchetto, S.; Vicentini, M.; Bettale, F.; Furri, L.; Testa, M. Effective teaching of manual skills to physiotherapy students: A randomised clinical trial. Med. Educ. 2017, 51, 826–838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sole, G.; Rose, A.; Bennett, T.; Jaques, K.; Rippon, Z.; van der Meer, J. A student experience of peer assisted study sessions in physiotherapy. J. Peer Learn. 2012, 5, 42–51. [Google Scholar]
- Sharma, V.; Kaur, J. Effect of core strengthening with pelvic proprioceptive neuromuscular facilitation on trunk, balance, gait, and function in chronic stroke. J. Exerc. Rehabil. 2017, 13, 200–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Michielsen, M.; Vaughan-Graham, J.; Holland, A.; Magri, A.; Suzuki, M. The bobath concept—A model to illustrate clinical practice. Disabil. Rehabil. 2019, 41, 2080–2092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Connors, K.A.; Galea, M.P.; Said, C.M.; Remedios, L.J. Feldenkrais Method balance classes are based on principles of motor learning and postural control retraining: A qualitative research study. Physiotherapy 2010, 96, 324–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nordin, N.A.M.; Ishak, N.A.; Azmi, N.A.; Chui, C.S.; Hassan, F.H. Does neurophobia exist among rehabilitation sciences students? A survey at Universiti Kebangsaan Malaysia. J. Sains Kesihat. Malays. Malays. J. Health Sci. 2018, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panadero, E.; Andrade, H.; Brookhart, S. Fusing self-regulated learning and formative assessment: A roadmap of where we are, how we got here, and where we are going. Aust. Educ. Res. 2018, 45, 13–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leader, D.; Clinton, M. Students Perceptions of the effectiveness of rubrics. J. Bus. Educ. Leadersh. 2018, 8, 86–103. [Google Scholar]
- Brookhart, S.M. How to Create and Use Rubrics for Formative Assessment and Grading; ASCD: Alexandria, VA, USA, 2013; ISBN 978-1-4166-1552-1. [Google Scholar]
- Jonsson, A.; Svingby, G. The use of scoring rubrics: Reliability, validity and educational consequences. Educ. Res. Rev. 2007, 2, 130–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reddy, Y.M.; Andrade, H. A review of rubric use in higher education. Assess. Eval. High. Educ. 2010, 35, 435–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panadero, E.; Jonsson, A. The use of scoring rubrics for formative assessment purposes revisited: A review. Educ. Res. Rev. 2013, 9, 129–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brookhart, S.M.; Chen, F. The quality and effectiveness of descriptive rubrics. Educ. Rev. 2015, 67, 343–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reddy, M.Y. Design and development of rubrics to improve assessment outcomes: A pilot study in a master’s level business program in India. Qual. Assur. Educ. 2011, 19, 84–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chong, D.Y.K.; Tam, B.; Yau, S.Y.; Wong, A.Y.L. Learning to prescribe and instruct exercise in physiotherapy education through authentic continuous assessment and rubrics. BMC Med. Educ. 2020, 20, 258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bearman, M.; Ajjawi, R. Can a rubric do more than be transparent? Invitation as a new metaphor for assessment criteria. Stud. High. Educ. 2021, 46, 359–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hafner, J.; Hafner, P. Quantitative analysis of the rubric as an assessment tool: An empirical study of student peer–group rating. Int. J. Sci. Educ. 2003, 25, 1509–1528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panadero, E.; Alonso-Tapia, J.; Reche, E. Rubrics vs. self-assessment scripts effect on self-regulation, performance and self-efficacy in pre-service teachers. Stud. Educ. Eval. 2013, 39, 125–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schreiber, J.; Gagnon, K.; Kendall, E.; Fiss, L.A.; Rapport, M.J.; Wynarczuk, K.D. Development of a grading rubric to assess learning in pediatric physical therapy education. Pediatr. Phys. Ther. 2020, 32, 70–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moni, R.W.; Beswick, E.; Moni, K.B. Using student feedback to construct an assessment rubric for a concept map in physiology. Adv. Physiol. Educ. 2005, 29, 197–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stellmack, M.A.; Konheim-Kalkstein, Y.L.; Manor, J.E.; Massey, A.R.; Schmitz, J.A.P. An assessment of reliability and validity of a rubric for grading APA-style introductions. Teach. Psychol. 2009, 36, 102–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andrade, H.L.; Du, Y.; Mycek, K. Rubric-referenced self-assessment and middle school students’ writing. Assess. Educ. Princ. Policy Pr. 2010, 17, 199–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magin, D.; Helmore, P. Peer and teacher assessments of oral presentation skills: How reliable are they? Stud. High. Educ. 2001, 26, 287–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wollenschläger, M.; Hattie, J.; Machts, N.; Möller, J.; Harms, U. What makes rubrics effective in teacher-feedback? Transparency of learning goals is not enough. Contemp. Educ. Psychol. 2016, 44–45, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panadero, E.; Jonsson, A.; Strijbos, J.-W. Scaffolding self-regulated learning through self-assessment and peer assessment: Guidelines for classroom implementation. The Enabling Power of Assessment. In Assessment for Learning: Meeting the Challenge of Implementation; Laveault, D., Allal, L., Eds.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2016; pp. 311–326. ISBN 978-3-319-39211-0. [Google Scholar]
- Andrade, H.; Du, Y. Student perspectives on rubric-referenced assessment. Pract. Assess. Res. Eval. 2005, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, Z.; Ho, S. Good and bad practices in rubrics: The perspectives of students and educators. Assess. Eval. High. Educ. 2019, 44, 533–545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W. Using rubrics in student self-assessment: Student perceptions in the english as a foreign language writing context. Assess. Eval. High. Educ. 2017, 42, 1280–1292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kite, J.; Phongsavan, P. Evaluating standards-based assessment rubrics in a postgraduate public health subject. Assess. Eval. High. Educ. 2017, 42, 837–849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atkinson, D.; Lim, S. Improving assessment processes in higher education: Student and teacher perceptions of the effectiveness of a rubric embedded in a LMS. Aust. J. Educ. Technol. 2013, 29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bolton, F. Rubrics and adult learners: Andragogy and assessment. Assess. Update 2006, 18, 5–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gezie, A.; Khaja, K.; Chang, V.N.; Adamek, M.E.; Johnsen, M.B. Rubrics as a tool for learning and assessment: What do baccalaureate students think? J. Teach. Soc. Work 2012, 32, 421–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Lindsey, P. Understanding variations between student and teacher application of rubrics. Assess. Writ. 2015, 26, 67–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tierney, R.; Simon, M. What’s still wrong with rubrics: Focusing on the consistency of performance criteria across scale levels. Pract. Assess. Res. Eval. 2019, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, K.H. A conceptual model of assessing teaching performance and intellectual development of teacher candidates: A pilot study in the US. Teach. High. Educ. 2006, 11, 175–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bharuthram, S. Lecturers’ perceptions: The value of assessment rubrics for informing teaching practice and curriculum review and development. Afr. Educ. Rev. 2015, 12, 415–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boateng, B.A.; Bass, L.D.; Blaszak, R.T.; Farrar, H.C. The development of a competency-based assessment rubric to measure resident milestones. J. Grad. Med. Educ. 2009, 1, 45–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- González-Chordá, V.M.; Mena-Tudela, D.; Salas-Medina, P.; Cervera-Gasch, A.; Orts-Cortés, I.; Maciá-Soler, L. Assessment of bachelor’s theses in a nursing degree with a rubrics system: Development and validation study. Nurse Educ. Today 2016, 37, 103–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allen, D.; Tanner, K. Rubrics: Tools for making learning goals and evaluation criteria explicit for both teachers and learners. CBE Life Sci. Educ. 2006, 5, 197–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blommel, M.L.; Abate, M.A. A rubric to assess critical literature evaluation skills. Am. J. Pharm. Educ. 2007, 71, 63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Nicholson, P.; Gillis, S.; Dunning, A.M.T. The use of scoring rubrics to determine clinical performance in the operating suite. Nurse Educ. Today 2009, 29, 73–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haack, S.; Fornoff, A.; Caligiuri, F.; Dy-Boarman, E.; Bottenberg, M.; Mobley-Bukstein, W.; Bryant, G.; Bryant, A. comparison of electronic versus paper rubrics to assess patient counseling experiences in a skills-based lab course. Curr. Pharm. Teach. Learn. 2017, 9, 1117–1122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stevens, D.D.; Levi, A.J. Introduction to Rubrics: An Assessment Tool to Save Grading Time, Convey Effective Feedback, and Promote Student Learning; Stylus Publishing, LLC: Sterling, VA, USA, 2013; ISBN 978-1-57922-590-2. [Google Scholar]
- Roach, K.E.; Frost, J.S.; Francis, N.J.; Giles, S.; Nordrum, J.T.; Delitto, A. Validation of the revised physical therapist clinical performance instrument (PT CPI): Version 2006. Phys. Ther. 2012, 92, 416–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fitzgerald, L.M.; Delitto, A.; Irrgang, J.J. Validation of the clinical internship evaluation tool. Phys. Ther. 2007, 87, 844–860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dogan, C.; Yosmaoglu, H. The effect of the analytical rubrics on the objectivity in physiotherapy practical examination. Türkiye Klin. Spor Bilim. Derg. 2015, 7, 9–15. [Google Scholar]
- Yeung, E.; Kulasagarem, K.; Woods, N.; Dubrowski, A.; Hodges, B.; Carnahan, H. Validity of a new assessment rubric for a short-answer test of clinical reasoning. BMC Med. Educ. 2016, 16, 192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Torres-Narváez, M.-R.; Vargas-Pinilla, O.-C.; Rodríguez-Grande, E.-I. Validity and reproducibility of a tool for assessing clinical competencies in physical therapy students. BMC Med. Educ. 2018, 18, 280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turbow, D.J.; Evener, J. Norming a VALUE rubric to assess graduate information literacy skills. J. Med. Libr. Assoc. JMLA 2016, 104, 209–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Turbow, D.J.; Werner, T.P.; Lowe, E.; Vu, H.Q. Norming a written communication rubric in a graduate health science course. J. Allied Health 2016, 45, 37E–42E. [Google Scholar]
- Boruff, J.T.; Harrison, P. Assessment of knowledge and skills in information literacy instruction for rehabilitation sciences students: A scoping review. J. Med. Libr. Assoc. JMLA 2018, 106, 15–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thomas, A.; Saroyan, A.; Lajoie, S.P. Creation of an evidence-based practice reference model in falls prevention: Findings from occupational therapy. Disabil. Rehabil. 2012, 34, 311–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Furze, J.; Gale, J.R.; Black, L.; Cochran, T.M.; Jensen, G.M. Clinical reasoning: Development of a grading rubric for student assessment. J. Phys. Ther. Educ. 2015, 29, 34–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gamel, C.; van Andel, S.G.; de Haan, W.I.; Hafsteinsdóttir, T.B. Development and testing of an analytic rubric for a master’s course systematic review of the literature: A cross-sectional study. Educ. Health 2018, 31, 72–79. [Google Scholar]
- Martiañez, N.L.; Rubio, M.; Terrón, M.J.; Gallego, T. Diseño de una rúbrica para evaluar las competencias del prácticum del grado en fisioterapia. percepción de su utilidad por los estudiantes. Fisioterapia 2015, 37, 83–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Del Rossi, L.; Kientz, M.; Padden, M.; McGinnis, P.; Pawlowska, M. A novel approach to pediatric education using interprofessional collaboration. J. Phys. Ther. Educ. 2017, 31, 119–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tappan, R.S.; Hedman, L.D.; López-Rosado, R.; Roth, H.R. Checklist-style rubric development for practical examination of clinical skills in entry-level physical therapist education. J. Allied Health 2020, 49, 202–211. [Google Scholar]
- Jonsson, A. Rubrics as a way of providing transparency in assessment. Assess. Eval. High. Educ. 2014, 39, 840–852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fraile, J.; Panadero, E.; Pardo, R. Co-creating rubrics: The effects on self-regulated learning, self-efficacy and performance of establishing assessment criteria with students. Stud. Educ. Eval. 2017, 53, 69–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, Z.; Brown, G.T.L. A cyclical self-assessment process: Towards a model of how students engage in self-assessment. Assess. Eval. High. Educ. 2017, 42, 1247–1262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Green, H.J.; Hood, M.; Neumann, D.L. Predictors of student satisfaction with university psychology courses: A review. Psychol. Learn. Teach. 2015, 14, 131–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lombard, B.J.J. Revisiting the value of rubrics for student engagement in assessment and feedback in the South African University classroom. J. Transdiscipl. Res. S. Afr. 2011, 7, 367–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Denson, N.; Loveday, T.; Dalton, H. Student evaluation of courses: What predicts satisfaction? High. Educ. Res. Dev. 2010, 29, 339–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holmes, N. Engaging with assessment: Increasing student engagement through continuous assessment. Act. Learn. High. Educ. 2018, 19, 23–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gutiérrez, M.; Tomás, J.-M.; Romero, I.; Barrica, J.-M. Perceived social support, school engagement and satisfaction with school. Rev. Psicodidáct. Engl. Ed. 2017, 22, 111–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomás, J.M.; Gutiérrez, M.; Alberola, S.; Georgieva, S. Psychometric properties of two major approaches to measure school engagement in university students. Curr. Psychol. 2020, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fredricks, J.A.; Blumenfeld, P.C.; Paris, A.H. School engagement: Potential of the concept, state of the evidence. Rev. Educ. Res. 2004, 74, 59–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lam, S.; Jimerson, S.; Wong, B.P.H.; Kikas, E.; Shin, H.; Veiga, F.H.; Hatzichristou, C.; Polychroni, F.; Cefai, C.; Negovan, V.; et al. Understanding and measuring student engagement in school: The results of an international study from 12 countries. Sch. Psychol. Q. 2014, 29, 213–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reeve, J. How students create motivationally supportive learning environments for themselves: The concept of agentic engagement. J. Educ. Psychol. 2013, 105, 579–595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Veiga, F.H. Assessing student engagement in school: Development and validation of a four-dimensional scale. Procedia Soc. Behav. Sci. 2016, 217, 813–819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schaufeli, W.; Bakker, A. UWES–Utrecht Work Engagement Scale: Test Manual; Department of Psichology, Utrecht University: Utrecht, The Netherlands, 2003; (unpublished). [Google Scholar]
- Salmela-Aro, K.; Upadaya, K. The schoolwork engagement inventory. Eur. J. Psychol. Assess. 2012, 28, 60–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García-Ros, R.; Pérez-González, F.; Tomás, J.M.; Fernández, I. The schoolwork engagement inventory: Factorial structure, measurement invariance by gender and educational level, and convergent validity in secondary education (12–18 Years). J. Psychoeduc. Assess. 2018, 36, 588–603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García-Ros, R. Analysis and validation of a rubric to assess oral presentation skills in university contexts. Electron. J. Res. Educ. Psychol. 2011, 9, 1043–1063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schnettler, B.; Orellana, L.; Sepúlveda, J.; Miranda, H.; Grunert, K.; Lobos, G.; Hueche, C. Psychometric properties of the multidimensional students’ life satisfaction scale in a sample of Chilean University students. Suma Psicol. 2017, 24, 97–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huebner, E.S. Preliminary development and validation of a multidimensional life satisfaction scale for children. Psychol. Assess. 1994, 6, 149–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zullig, K.J.; Huebner, E.S.; Gilman, R.; Patton, J.M.; Murray, K.A. Validation of the brief multidimensional students’ life satisfaction scale among college students. Am. J. Health Behav. 2005, 29, 206–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bentler, P.M. EQS 6 Structural Equations Program Manual; Multivariate Software, Inc.: Encino, CA, USA, 1995; p. 422. [Google Scholar]
- Satorra, A.; Bentler, P.M. A scaled difference chi-square test statistic for moment structure analysis. Psychometrika 2001, 66, 507–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bentler, P.M. Comparative fit indexes in structural models. Psychol. Bull. 1990, 107, 238–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, L.; Bentler, P.M. Cutoff criteria for fit indexes in covariance structure analysis: Conventional criteria versus new alternatives. Struct. Equ. Model. Multidiscip. J. 1999, 6, 1–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marsh, H.W.; Hau, K.-T. Assessing goodness of fit. J. Exp. Educ. 1996, 64, 364–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Little, T.D.; Rhemtulla, M.; Gibson, K.; Schoemann, A.M. Why the items versus parcels controversy needn’t be one. Psychol. Methods 2013, 18, 285–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Astin, A.W. What Matters in College; Jossey-Bass: San Francisco, CA, USA, 1993. [Google Scholar]
- Kuh, G.D. The National Survey of Student Engagement: Conceptual Framework and Overview of Psychometric Properties. Ph.D. Thesis, Indiana University, Bloomington, IN, USA, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Tinto, V. Completing College: Rethinking Institutional Action; University of Chicago Press: Chicago, IL, USA, 2012; ISBN 978-0-226-80452-1. [Google Scholar]
- Reynolds-Keefer, L. Rubric-referenced assessment in teacher preparation: An opportunity to learn by using. Pract. Assess. Res. Eval. 2010, 15, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walvoord, B.E.; Anderson, V.J. Effective Grading: A Tool for Learning and Assessment in College; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2011; ISBN 978-1-118-04554-1. [Google Scholar]
- Mostafa, A.A.-M. The impact of electronic assessment-driven instruction on preservice efl teachers’ quality teaching. Int. J. Appl. Educ. Stud. 2011, 10, 18–35. [Google Scholar]
- Korobova, N.; Starobin, S.S. A comparative study of student engagement, satisfaction, and academic success among international and american students. J. Int. Stud. 2015, 5, 14. [Google Scholar]
- Kuh, G.D.; Kinzie, J.; Schuh, J.H.; Whitt, E.J. Assessing Conditions to Enhance Educational Effectiveness: The Inventory for Student Engagement and Success; Jossey-Bass: San Francisco, CA, USA, 2005; ISBN 978-0-7879-8220-1. [Google Scholar]
- Ojeda, L.; Flores, L.Y.; Navarro, R.L. Social cognitive predictors of mexican american college students’ academic and life satisfaction. J. Couns. Psychol. 2011, 58, 61–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gray, J.A.; DiLoreto, M. The effects of student engagement, student satisfaction, and perceived learning in online learning environments. Int. J. Educ. Leadersh. Prep. 2016, 11, n1. [Google Scholar]
- Letcher, D.W.; Neves, J.S. Determinants of undergraduate business student satisfaction. Res. High. Educ. J. 2010, 6, 1–26. [Google Scholar]
- Dempsey, M.S.; PytlikZillig, L.M.; Bruning, R.H. Helping preservice teachers learn to assess writing: Practice and feedback in a web-based environment. Assess. Writ. 2009, 14, 38–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zimmerman, B.J. Attaining Self-Regulation: A Social Cognitive Perspective. In Handbook of Self-Regulation; Boekaerts, M., Pintrich, P.R., Zeidner, M., Eds.; Academic Press: San Diego, CA, USA, 2000; pp. 13–35. ISBN 978-0-12-109890-2. [Google Scholar]
- Malouff, J.M.; Hall, L.; Schutte, N.S.; Rooke, S.E. Use of motivational teaching techniques and psychology student satisfaction. Psychol. Learn. Teach. 2010, 9, 39–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Picón Jácome, É. La rúbrica y la justicia en la evaluación. Ikala 2013, 18, 79–94. [Google Scholar]
- Lent, R.W.; Singley, D.; Sheu, H.-B.; Schmidt, J.A.; Schmidt, L.C. Relation of social-cognitive factors to academic satisfaction in engineering students. J. Career Assess. 2007, 15, 87–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Upcraft, M.; Gardner, J.; Barefoot, B. Challenging and Supporting the First-Year Student; Jossey-Bass: San Francisco, CA, USA, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Yorke, M.; Longden, B. The First-Year Experience in Higher Education in the UK; Higher Education Academy: New York, NY, USA, 2008. [Google Scholar]
| I Think the Rubric … | Mean | SD | Min | Max | Sk | Ku |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1. Integrates the most important elements to consider in the maneuvers | 4.32 | 0.85 | 1 | 5 | −1.7 | 3.5 |
| 2. Makes it possible to evaluate the important competencies in this subject | 4.20 | 0.88 | 1 | 5 | −1.3 | 2.1 |
| 3. Integrates criteria that will be useful to me in my future professional career | 3.76 | 1.11 | 1 | 5 | −0.8 | 0.1 |
| 4. Is a reliable tool (makes it possible to measure the quality of the execution) | 4.12 | 0.94 | 1 | 5 | −1.2 | 1.6 |
| 5. Clearly highlights and differentiates the levels considered in each criterion | 4.07 | 0.90 | 1 | 5 | −1.2 | 1.9 |
| 6. Fosters a fair comparison of the different students on the practical assessment test | 4.09 | 0.99 | 1 | 5 | −1.1 | 0.9 |
| 7. Helps to understand the criteria involved in adequate performance | 4.26 | 0.85 | 1 | 5 | −1.4 | 2.7 |
| Total | 4.12 | 0.78 | 1 | 5 | −1.5 | 3.2 |
| I Think the Rubric is Useful for | Mean | SD | Min | Max | Sk | Ku |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1. Clarifying how we have to perform each maneuver | 4.22 | 0.90 | 1 | 5 | −1.1 | 0.9 |
| 2. Planning the study/practice of the maneuvers | 4.14 | 0.92 | 1 | 5 | −0.8 | 0.1 |
| 3. Reviewing what is learned in order to make adjustments | 4.17 | 0.90 | 1 | 5 | −0.9 | 0.5 |
| 4. Realistically rating the execution of the maneuvers | 4.17 | 0.92 | 1 | 5 | −1.2 | 1.7 |
| 5. Guiding the study/practice of the maneuvers | 4.28 | 0.93 | 1 | 5 | −1.4 | 2.1 |
| 6. Discussing and determining what to improve in their execution | 4.08 | 0.95 | 1 | 5 | −1.1 | 1.1 |
| 7. Being able to perform the maneuvers with greater quality | 4.21 | 0.94 | 1 | 5 | −1.1 | 1.0 |
| 8. Facilitating the study/practice of the maneuvers | 4.21 | 0.89 | 1 | 5 | −1.2 | 1.4 |
| 9. Knowing more about the criteria that will be used to assess us | 4.49 | 0.78 | 1 | 5 | −1.7 | 3.1 |
| 10. Reducing my anxiety in the process of learning the maneuvers | 3.35 | 1.28 | 1 | 5 | −0.3 | −0.9 |
| Total | 4.13 | 0.77 | 1 | 5 | −1.2 | 1.8 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
García-Ros, R.; Ruescas-Nicolau, M.-A.; Cezón-Serrano, N.; Carrasco, J.J.; Pérez-Alenda, S.; Sastre-Arbona, C.; San Martín-Valenzuela, C.; Flor-Rufino, C.; Sánchez-Sánchez, M.L. Students’ Perceptions of Instructional Rubrics in Neurological Physical Therapy and Their Effects on Students’ Engagement and Course Satisfaction. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 4957. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph18094957
García-Ros R, Ruescas-Nicolau M-A, Cezón-Serrano N, Carrasco JJ, Pérez-Alenda S, Sastre-Arbona C, San Martín-Valenzuela C, Flor-Rufino C, Sánchez-Sánchez ML. Students’ Perceptions of Instructional Rubrics in Neurological Physical Therapy and Their Effects on Students’ Engagement and Course Satisfaction. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health. 2021; 18(9):4957. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph18094957
Chicago/Turabian StyleGarcía-Ros, Rafael, Maria-Arantzazu Ruescas-Nicolau, Natalia Cezón-Serrano, Juan J. Carrasco, Sofía Pérez-Alenda, Clara Sastre-Arbona, Constanza San Martín-Valenzuela, Cristina Flor-Rufino, and Maria Luz Sánchez-Sánchez. 2021. "Students’ Perceptions of Instructional Rubrics in Neurological Physical Therapy and Their Effects on Students’ Engagement and Course Satisfaction" International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health 18, no. 9: 4957. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph18094957
APA StyleGarcía-Ros, R., Ruescas-Nicolau, M.-A., Cezón-Serrano, N., Carrasco, J. J., Pérez-Alenda, S., Sastre-Arbona, C., San Martín-Valenzuela, C., Flor-Rufino, C., & Sánchez-Sánchez, M. L. (2021). Students’ Perceptions of Instructional Rubrics in Neurological Physical Therapy and Their Effects on Students’ Engagement and Course Satisfaction. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 18(9), 4957. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph18094957











