Chemical Leaching from Tire Wear Particles with Various Treadwear Ratings
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Tire and Target Compounds
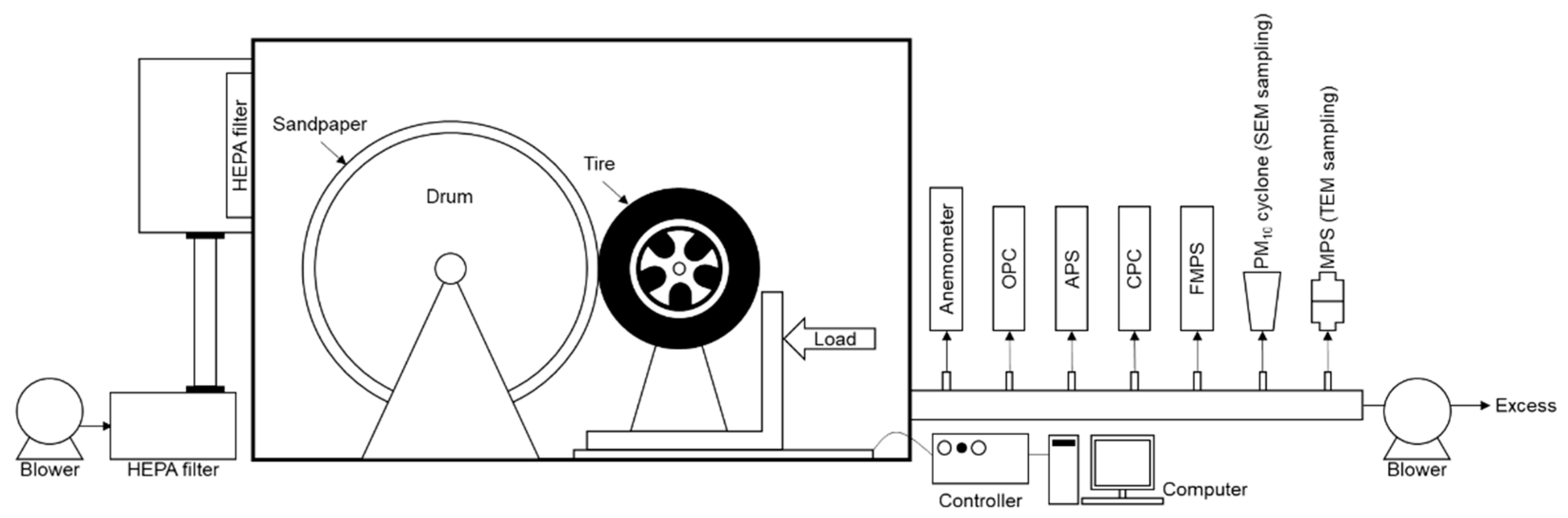
2.2. Tire Wear Particle Generator
2.3. Chemical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Scanning Electron Microscopy–Energy-Dispersive X-ray Spectrometry
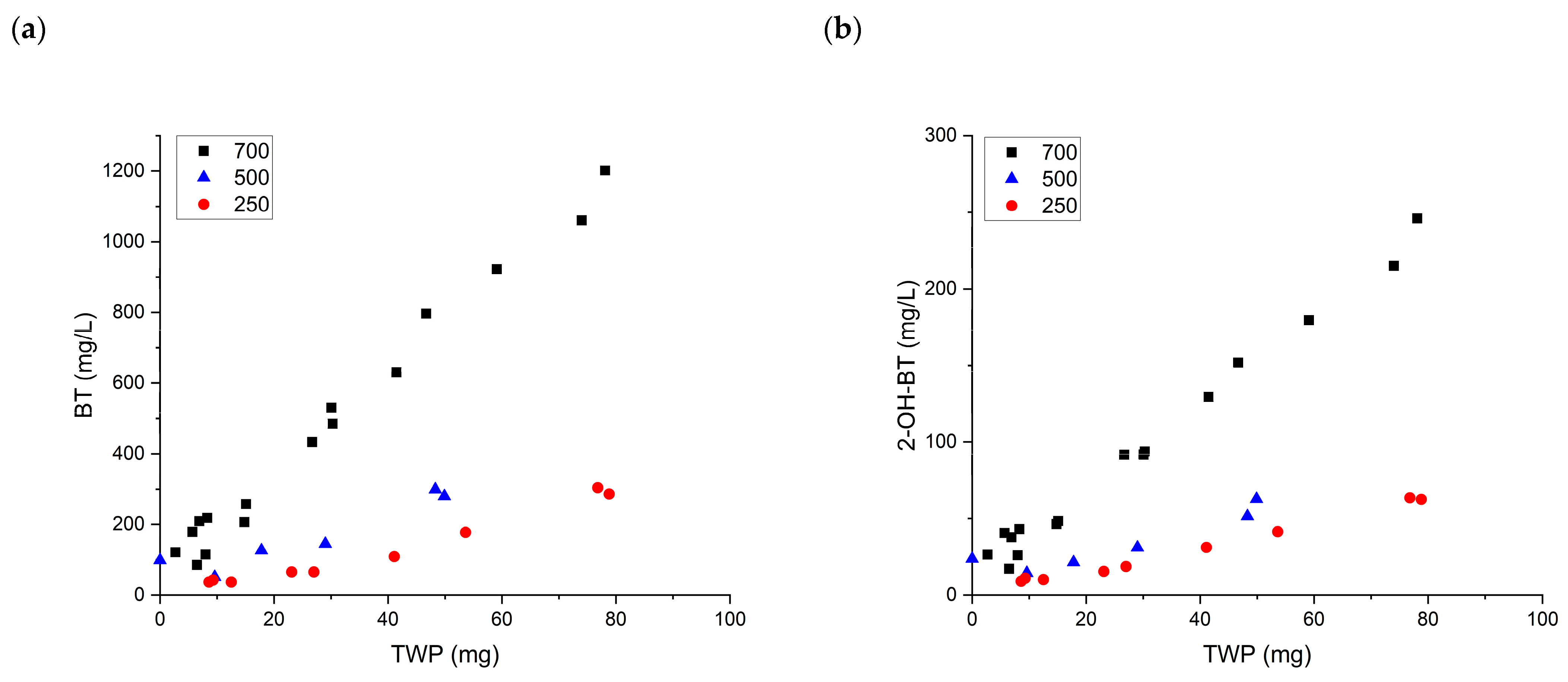
3.2. Quantitative Analysis of Chemical Leaching from TWP
3.3. Qualitative Analysis of Chemical Leaching from TWP
4. Implications of This Study
4.1. Environmental Risk of TWPs
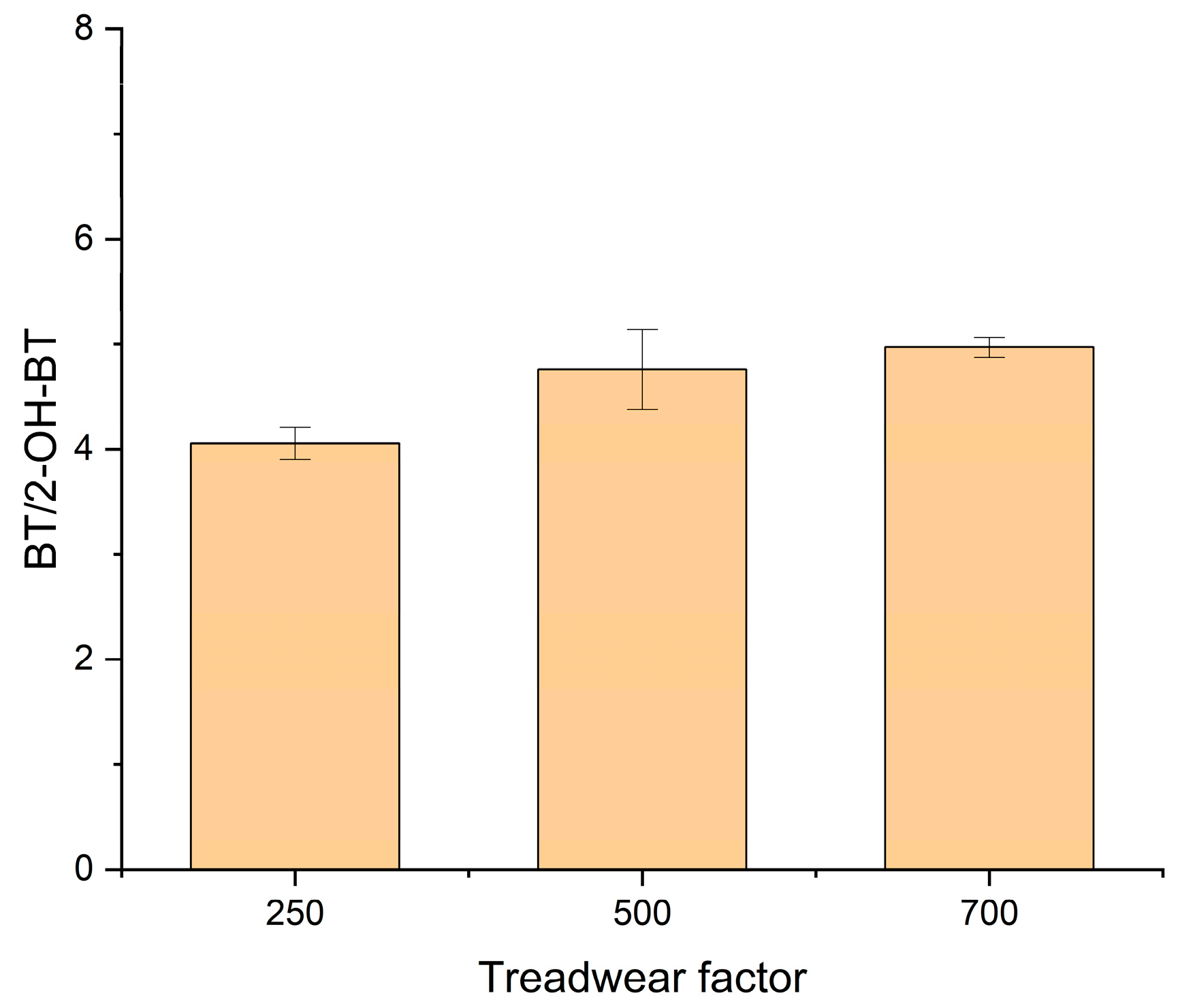
4.2. BT as a Marker Compound of TWP
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Grigoratos, T.; Martini, G. Non-Exhaust Traffic Related Emissions—Brake and Tyre Wear PM; Publications Office of the European Union: Luxembourg, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Baensch-Baltruschat, B.; Kocher, B.; Stock, F.; Reifferscheid, G. Tyre and road wear particles (TRWP)—A review of generation, properties, emissions, human health risk, ecotoxicity, and fate in the environment. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 733, 137823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eisentraut, P.; Dümichen, E.; Ruhl, A.S.; Jekel, M.; Albrecht, M.; Gehde, M.; Braun, U. Two birds with one stone—Fast and simultaneous analysis of microplastics: Microparticles derived from thermoplastics and tire wear. Environ. Sci. Technol. Lett. 2018, 5, 608–613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wik, A.; Dave, G. Occurrence and effects of tire wear particles in the environment—A critical review and an initial risk assessment. Environ. Pollut. 2009, 157, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gualtieri, M.; Rigamonti, L.; Galeotti, V.; Camatini, M. Toxicity of tire debris extracts on human lung cell line A549. Toxicol. In Vitro 2005, 19, 1001–1008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kershaw, P. Sources, Fate and Effects of Microplastics in the Marine Environment: A Global Assessment; International Maritime Organization: London, UK, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Bai, C.-L.; Liu, L.-Y.; Hu, Y.-B.; Zeng, E.Y.; Guo, Y. Microplastics: A review of analytical methods, occurrence and characteristics in food, and potential toxicities to biota. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 806, 150263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siegfried, M.; Koelmans, A.A.; Besseling, E.; Kroeze, C. Export of microplastics from land to sea. A modelling approach. Water Res. 2017, 127, 249–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rødland, E.S.; Lind, O.C.; Reid, M.J.; Heier, L.S.; Okoffo, E.D.; Rauert, C.; Thomas, K.V.; Meland, S. Occurrence of tire and road wear particles in urban and peri-urban snowbanks, and their potential environmental implications. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 824, 153785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boucher, J.; Friot, D. Primary Microplastics in the Oceans: A Global Evaluation of Sources; Sousa, J., Ed.; IUCN: Gland, Switzerland, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Tappe, M.; Null, V. Requirements for Tires from the Environmental View Point. In Proceedings of the Tire Technology Expo Conference, Hamburg, Germany, 20–22 February 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Kreider, M.L.; Panko, J.M.; McAtee, B.L.; Sweet, L.I.; Finley, B.L. Physical and chemical characterization of tire-related particles: Comparison of particles generated using different methodologies. Sci. Total Environ. 2010, 408, 652–659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wagner, S.; Hüffer, T.; Klöckner, P.; Wehrhahn, M.; Hofmann, T.; Reemtsma, T. Tire wear particles in the aquatic environment—A review on generation, analysis, occurrence, fate and effects. Water Res. 2018, 139, 83–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goonetilleke, A.; Wijesiri, B.; Bandala, E.R. Water and soil pollution implications of road traffic. In Environmental Impacts of Road Vehicles: Past, Present and Future; Harrison, R.M., Hester, R.M., Eds.; Royal Society of Chemistry: London, UK, 2017; pp. 86–106. [Google Scholar]
- Park, I.; Kim, H.; Lee, S. Characteristics of tire wear particles generated in a laboratory simulation of tire/road contact conditions. J. Aerosol Sci. 2018, 124, 30–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grigoratos, T.; Gustafsson, M.; Eriksson, O.; Martini, G. Experimental investigation of tread wear and particle emission from tyres with different treadwear marking. Atmos. Environ. 2018, 182, 200–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boulter, P.G.; Thorpe, A.J.; Harrison, R.M.; Allen, A.G. Road Vehicle Non-Exhaust Particulate Matter: Final Report on Emission Modelling; Wokingham: Berkshire, UK, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Panko, J.; McAtee, B.L.; Kreider, M.; Gustafsson, M.; Blomqvist, G.; Gudmundsson, A.; Sweet, L.; Finley, B. Physio-chemical Analysis of Airborne Tire Wear Particles. In Proceedings of the 46th Congress of the European Societies of Toxicology, Eurotox, Dresden, Germany, 13–16 September 2009; pp. 13–16. [Google Scholar]
- Reddy, C.M.; Quinn, J.G. Environmental chemistry of benzothiazoles derived from rubber. Environ. Sci. Technol. 1997, 31, 2847–2853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Zhang, X.; Wu, L.; Wang, T.; Zhao, J.; Yanjie, Z.; Men, Z.; Mao, H. Occurrence of benzothiazole and its derivates in tire wear, road dust, and roadside soil. Chemosphere 2018, 201, 310–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, G.; Lee, S. Characteristics of tire wear particles generated by a tire simulator under various driving conditions. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2018, 52, 12153–12161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kovochich, M.; Liong, M.; Parker, J.A.; Oh, S.C.; Lee, J.P.; Xi, L.; Kreider, M.L.; Unice, K.M. Chemical mapping of tire and road wear particles for single particle analysis. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 757, 144085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hildemann, L.M.; Markowski, G.R.; Cass, G.R. Chemical composition of emissions from urban sources of fine organic aerosol. Environ. Sci. Technol. 1991, 25, 744–759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- McKenzie, E.R.; Money, J.E.; Green, P.G.; Young, T.M. Metals associated with stormwater-relevant brake and tire samples. Sci. Total Environ. 2009, 407, 5855–5860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Unice, K.M.; Kreider, M.L.; Panko, J.M. Comparison of tire and road wear particle concentrations in sediment for watersheds in France, Japan, and the United States by quantitative pyrolysis GC/MS analysis. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2013, 47, 8138–8147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumata, H.; Takada, H.; Ogura, N. Determination of 2-(4-Morpholinyl)benzothiazole in environmental samples by a gas chromatograph equipped with a flame photometric detector. Anal. Chem. 1996, 68, 1976–1981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumata, H.; Yamada, J.; Masuda, K.; Takada, H.; Sato, Y.; Sakurai, T.; Fujiwara, K. Benzothiazolamines as tire-derived molecular markers: Sorptive behavior in street runoff and application to source apportioning. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2002, 36, 702–708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, F.-L.; Hussein, W.M.; Ross, B.P.; McGeary, R.P. 2-Mercaptobenzothiazole and its derivatives: Syntheses, reactions and applications. Curr. Org. Chem. 2012, 16, 1555–1580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Avagyan, R.; Sadiktsis, I.; Thorsén, G.; Östman, C.; Westerholm, R. Determination of benzothiazole and benzotriazole derivates in tire and clothing textile samples by high performance liquid chromatography–electrospray ionization tandem mass spectrometry. J. Chromatogr. A 2013, 1307, 119–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kloepfer, A.; Jekel, M.; Reemtsma, T. Occurrence, sources, and fate of benzothiazoles in municipal wastewater treatment plants. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2005, 39, 3792–3798. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- van Leeuwen, C.J.; Vermeire, T.G. Risk Assessment of Chemicals: An introduction; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2007; Volume 94. [Google Scholar]
- Kloeckner, P.; Reemtsma, T.; Eisentraut, P.; Braun, U.; Ruhl, A.S.; Wagner, S. Tire and road wear particles in road environment—Quantification and assessment of particle dynamics by Zn determination after density separation. Chemosphere 2019, 222, 714–721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Halle, L.L.; Palmqvist, A.; Kampmann, K.; Khan, F.R. Ecotoxicology of micronized tire rubber: Past, present and future considerations. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 706, 135694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Halsband, C.; Sørensen, L.; Booth, A.M.; Herzke, D. Car tire crumb rubber: Does leaching produce a toxic chemical cocktail in coastal marine systems? Front. Environ. Sci. 2020, 8, 125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pochron, S.; Nikakis, J.; Illuzzi, K.; Baatz, A.; Demirciyan, L.; Dhillon, A.; Gaylor, T.; Manganaro, A.; Maritato, N.; Moawad, M.; et al. Exposure to aged crumb rubber reduces survival time during a stress test in earthworms (Eisenia fetida). Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2018, 25, 11376–11383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, F.R.; Halle, L.L.; Palmqvist, A. Acute and long-term toxicity of micronized car tire wear particles to Hyalella azteca. Aquat. Toxicol. 2019, 213, 105216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Redondo-Hasselerharm, P.E.; de Ruijter, V.N.; Mintenig, S.M.; Verschoor, A.; Koelmans, A.A. Ingestion and chronic effects of car tire tread particles on freshwater benthic macroinvertebrates. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2018, 52, 13986–13994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wik, A.; Dave, G. Acute toxicity of leachates of tire wear material to Daphnia magna—Variability and toxic components. Chemosphere 2006, 64, 1777–1784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Domínguez, C.; Reyes-Contreras, C.; Bayona, J.M. Determination of benzothiazoles and benzotriazoles by using ionic liquid stationary phases in gas chromatography mass spectrometry. Application to their characterization in wastewaters. J. Chromatogr. A 2012, 1230, 117–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Loi, C.H.; Busetti, F.; Linge, K.L.; Joll, C.A. Development of a solid-phase extraction liquid chromatography tandem mass spectrometry method for benzotriazoles and benzothiazoles in wastewater and recycled water. J. Chromatogr. A 2013, 1299, 48–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Herrero, P.; Borrull, F.; Marcé, R.M.; Pocurull, E. A pressurised hot water extraction and liquid chromatography–high resolution mass spectrometry method to determine polar benzotriazole, benzothiazole and benzenesulfonamide derivates in sewage sludge. J. Chromatogr. A 2014, 1355, 53–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Asimakopoulos, A.G.; Ajibola, A.; Kannan, K.; Thomaidis, N.S. Occurrence and removal efficiencies of benzotriazoles and benzothiazoles in a wastewater treatment plant in Greece. Sci. Total Environ. 2013, 452–453, 163–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kiefer, K.; Du, L.; Singer, H.; Hollender, J. Identification of LC-HRMS nontarget signals in groundwater after source related prioritization. Water Res. 2021, 196, 116994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, P.; Qiu, J.; Gao, Y.; Stefan, M.I.; Li, X.-F. Nontargeted identification and predicted toxicity of new byproducts generated from UV treatment of water containing micropollutant 2-mercaptobenzothiazole. Water Res. 2021, 188, 116542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banasiak, L.; Chiaro, G.; Palermo, A.; Granello, G. Recycling of End-of-Life Tyres in Civil Engineering Applications: Environmental Implications. In Proceedings of the WasteMINZ 2019 Conference, Hamilton, New Zealand, 23–26 September 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Adachi, K.; Tainosho, Y. Characterization of heavy metal particles embedded in tire dust. Environ. Int. 2004, 30, 1009–1017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Compound | Retention Time (min) | Retention Time Window (min) | Precursor Ion (m/z) | Product Ion (m/z) | Collision Energy (V) | Radio Frequency Lens (V) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| BT | 4.90 | 2 | 136 | 65.000 | 33.56 | 66 |
| 77.054 | 26.61 | 66 | ||||
| 109.113 | 25.81 | 66 | ||||
| 2-OH-BT | 4.63 | 2 | 152 | 80.125 | 28.17 | 72 |
| 92.054 | 20.04 | 72 | ||||
| 124.113 | 20.08 | 72 |
| Chemical | CAS Number | Chemical Structure | Formula | Retention Time | m/z |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Benzothiazole-2-sulfonic acid | 941-57-1 | 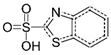 | C7H5NO3S2 | 4.78 | 215.0 |
| 2-mercaptobenzothiazole | 149-30-4 | 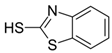 | C7H5NS2 | 8.33 | 167.0 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Jeong, Y.; Lee, S.; Woo, S.-H. Chemical Leaching from Tire Wear Particles with Various Treadwear Ratings. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 6006. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph19106006
Jeong Y, Lee S, Woo S-H. Chemical Leaching from Tire Wear Particles with Various Treadwear Ratings. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health. 2022; 19(10):6006. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph19106006
Chicago/Turabian StyleJeong, Yoonah, Seokhwan Lee, and Sang-Hee Woo. 2022. "Chemical Leaching from Tire Wear Particles with Various Treadwear Ratings" International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health 19, no. 10: 6006. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph19106006
APA StyleJeong, Y., Lee, S., & Woo, S.-H. (2022). Chemical Leaching from Tire Wear Particles with Various Treadwear Ratings. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 19(10), 6006. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph19106006






