Air Pollution Exposure and the Relative Risk of Sudden Sensorineural Hearing Loss in Taipei
Abstract
1. Introduction
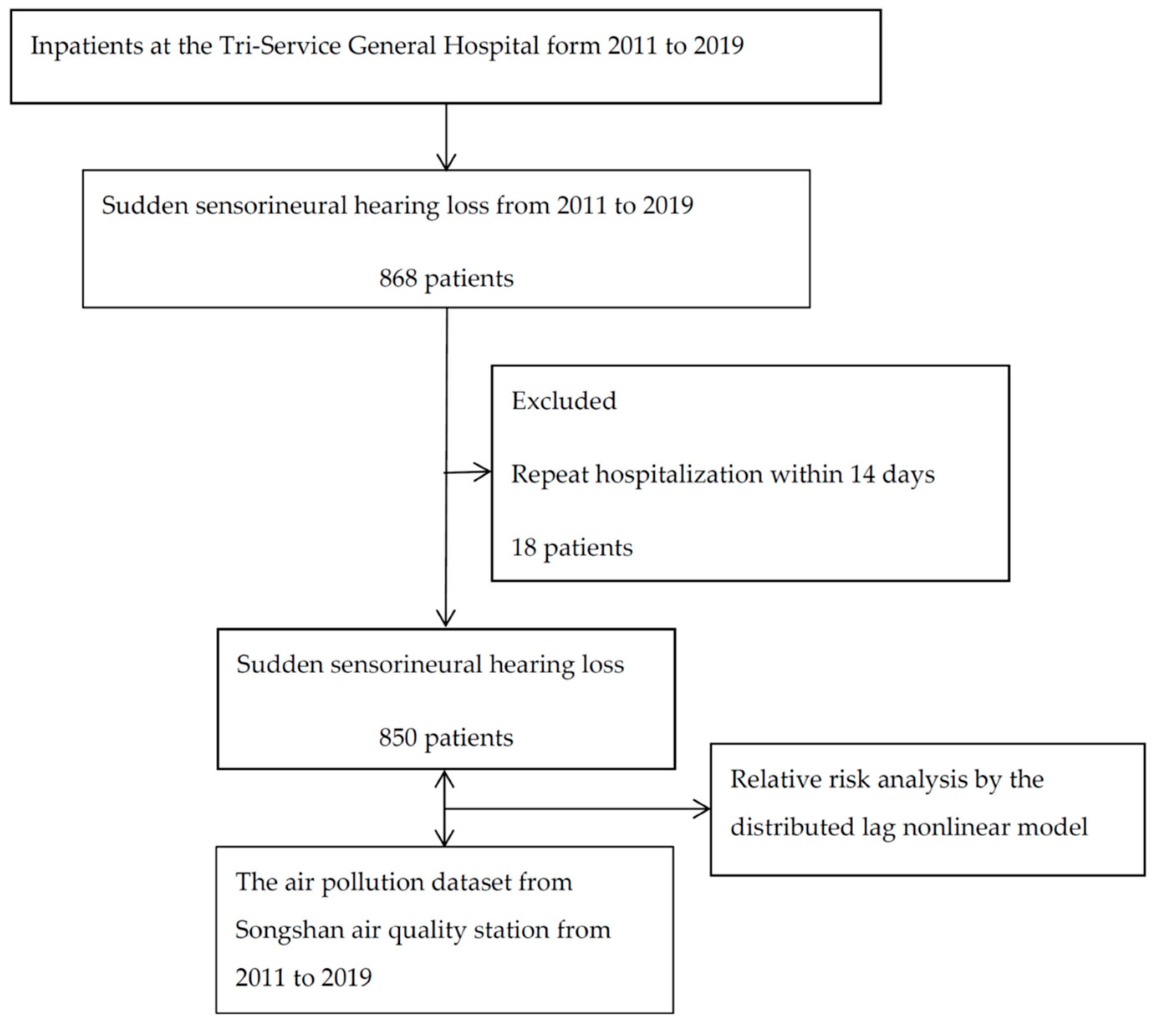
2. Materials and Methods
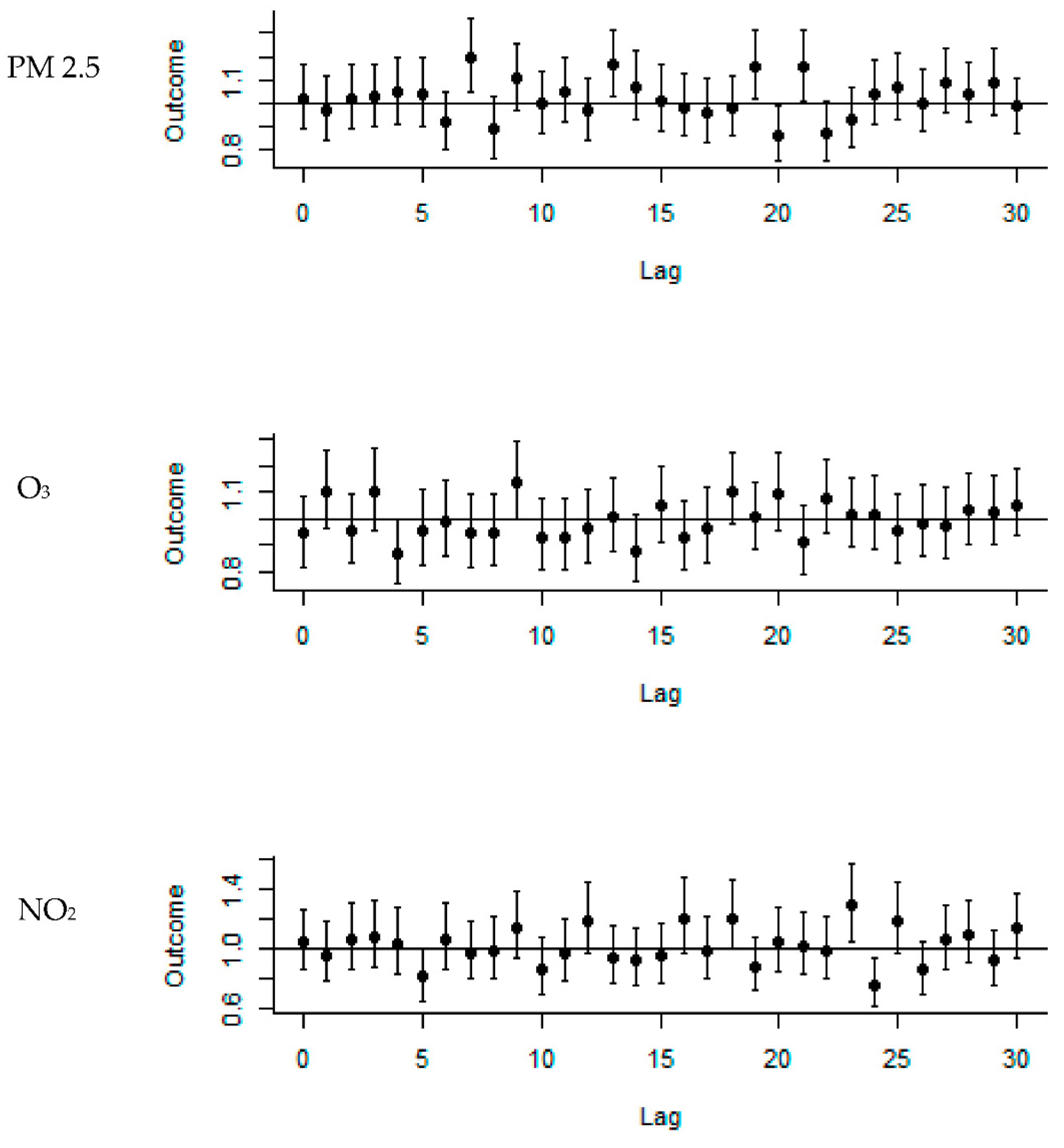
3. Results
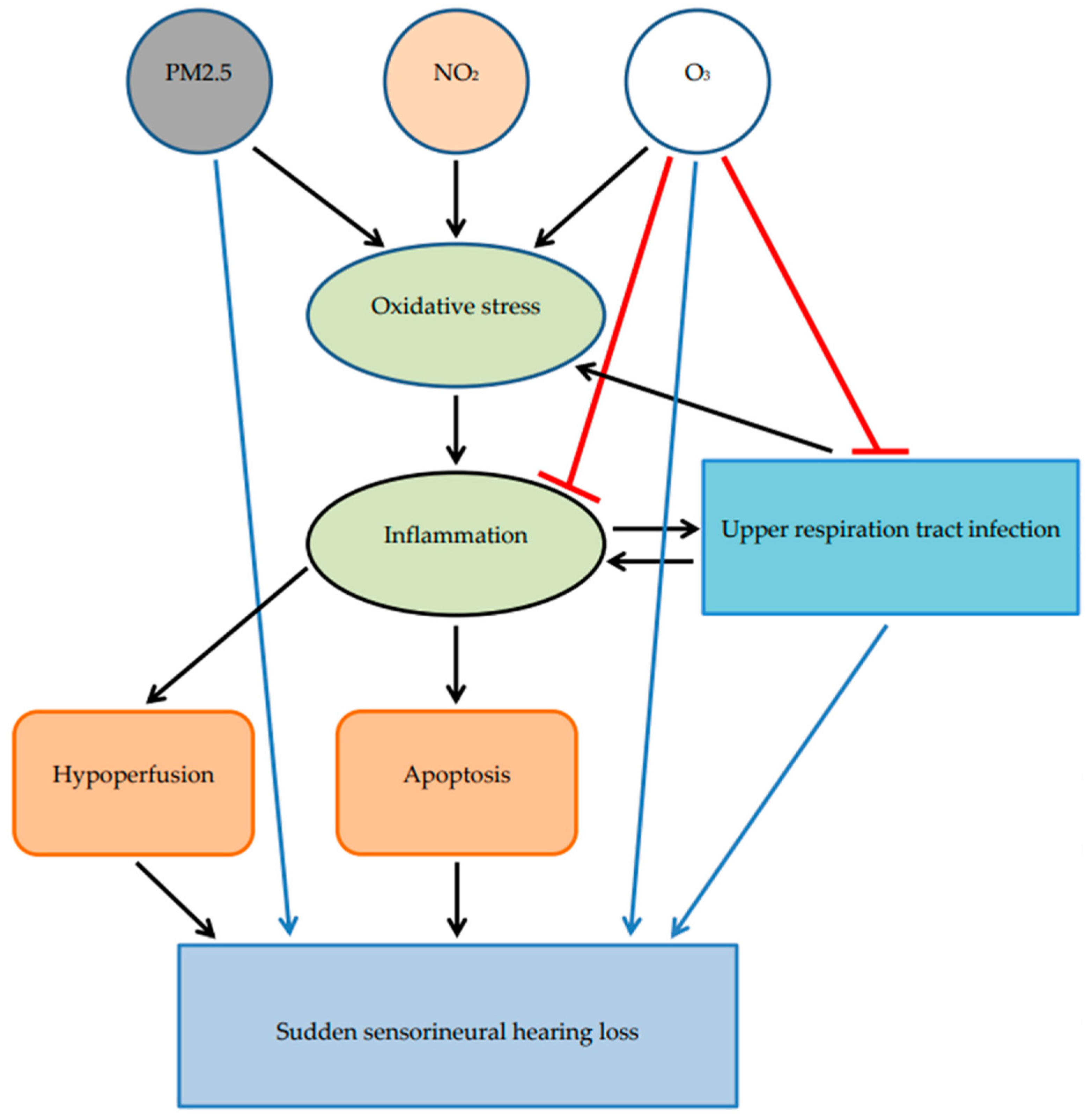
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kim, S.H.; Kim, S.-J.; Im, H.; Kim, T.-H.; Song, J.-J.; Chae, S.-W. A trend in sudden sensorineural hearing loss: Data from a population-based study. Audiol. Neurotol. 2017, 22, 311–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuhn, M.; Heman-Ackah, S.E.; Shaikh, J.A.; Roehm, P.C. Sudden sensorineural hearing loss: A review of diagnosis, treatment, and prognosis. Trends Amplif. 2011, 15, 91–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chau, J.K.; Lin, J.R.; Atashband, S.; Irvine, R.A.; Westerberg, B.D. Systematic review of the evidence for the etiology of adult sudden sensorineural hearing loss. Laryngoscope 2010, 120, 1011–1021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alexander, T.H.; Harris, J.P. Incidence of sudden sensorineural hearing loss. Otol. Neurotol. 2013, 34, 1586–1589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chandrasekhar, S.S.; Tsai Do, B.S.; Schwartz, S.R.; Bontempo, L.J.; Faucett, E.A.; Finestone, S.A.; Hollingsworth, D.B.; Kelley, D.M.; Kmucha, S.T.; Moonis, G. Clinical practice guideline: Sudden hearing loss (update). Otolaryngol. Head Neck Surg. 2019, 161 (Suppl. 1), S1–S45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Young, Y.-H. Contemporary review of the causes and differential diagnosis of sudden sensorineural hearing loss. Int. J. Audiol. 2020, 59, 243–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vidale, S.; Campana, C. Ambient air pollution and cardiovascular diseases: From bench to bedside. Eur. J. Prev. Cardiol. 2018, 25, 818–825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simkovich, S.M.; Goodman, D.; Roa, C.; Crocker, M.E.; Gianella, G.E.; Kirenga, B.J.; Wise, R.A.; Checkley, W. The health and social implications of household air pollution and respiratory diseases. NPJ Prim. Care Respir. Med. 2019, 29, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pope, I.I.I.C.A.; Coleman, N.; Pond, Z.A.; Burnett, R.T. Fine particulate air pollution and human mortality: 25+ years of cohort studies. Environ. Res. 2020, 183, 108924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.M.; Kim, M.S.; Kim, D.J.; Uhm, T.W.; Yi, S.B.; Han, J.H.; Lee, I.W. Effects of meteorological factor and air pollution on sudden sensorineural hearing loss using the health claims data in Busan, Republic of Korea. Am. J. Otolaryngol. 2019, 40, 393–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsai, S.C.-S.; Hsu, Y.-C.; Lai, J.-N.; Chou, R.-H.; Fan, H.-C.; Lin, F.C.-F.; Zhang, R.; Lin, C.-L.; Chang, K.-H. Long-term exposure to air pollution and the risk of developing sudden sensorineural hearing loss. J. Transl. Med. 2021, 19, 424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choi, H.G.; Min, C.; Kim, S.Y. Air pollution increases the risk of SSNHL: A nested case-control study using meteorological data and national sample cohort data. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 8270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taiwanese Environmental Protection Administration. The Air Pollution Data; Taiwanese Environmental Protection Administration: Taipei, Taiwan, 2020. Available online: https://airtw.epa.gov.tw/CHT/Query/His_Data.aspx (accessed on 1 April 2021).
- Gasparrini, A.; Armstrong, B.; Gasparrini, M.A. Package ‘dlnm’; London, UK, 2021; Available online: https://CRAN.R-project.org/package=dlnm (accessed on 1 April 2021).
- Taipei City Statistical Inquiry System. The Number of Motor Vehicle in Taipei; Taipei, Taiwan. 2021. Available online: https://statdb.dbas.gov.taipei/pxweb2007-tp/dialog/statfile9.asp (accessed on 1 April 2021).
- Lehner, C.; Gehwolf, R.; Tempfer, H.; Krizbai, I.; Hennig, B.; Bauer, H.-C.; Bauer, H. Oxidative stress and blood–brain barrier dysfunction under particular consideration of matrix metalloproteinases. Antioxid. Redox Signal. 2011, 15, 1305–1323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gonzalez-Gonzalez, S. The role of mitochondrial oxidative stress in hearing loss. Neurol. Disord. 2017, 1, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Capaccio, P.; Pignataro, L.; Gaini, L.M.; Sigismund, P.E.; Novembrino, C.; De Giuseppe, R.; Uva, V.; Tripodi, A.; Bamonti, F. Unbalanced oxidative status in idiopathic sudden sensorineural hearing loss. Eur. Arch. Oto-Rhino-Laryngol. 2012, 269, 449–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calderón-Garcidueñas, L.; Leray, E.; Heydarpour, P.; Torres-Jardón, R.; Reis, J. Air pollution, a rising environmental risk factor for cognition, neuroinflammation and neurodegeneration: The clinical impact on children and beyond. Rev. Neurol. 2016, 172, 69–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arpornchayanon, W.; Canis, M.; Ihler, F.; Settevendemie, C.; Strieth, S. TNF-α inhibition using etanercept prevents noise-induced hearing loss by improvement of cochlear blood flow in vivo. Int. J. Audiol. 2013, 52, 545–552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sahin, C.; Varim, C.; Karacaer, C. Investigation of neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio and red cell distribution width in sudden senseurineural hearing loss. Int. J. Adv. Med. 2019, 6, 424–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Del Zoppo, G.; Ginis, I.; Hallenbeck, J.M.; Iadecola, C.; Wang, X.; Feuerstein, G.Z. Inflammation and stroke: Putative role for cytokines, adhesion molecules and Inos in brain response to ischemia. Brain Pathol. 2000, 10, 95–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, J.-H.; Song, S.-H.; Guo, M.; Zhou, J.; Liu, F.; Peng, L.; Fu, Z.-R. Long-term exposure to PM2.5 lowers influenza virus resistance via down-regulating pulmonary macrophage Kdm6a and mediates histones modification in IL-6 and IFN-β promoter regions. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2017, 493, 1122–1128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nenna, R.; Evangelisti, M.; Frassanito, A.; Scagnolari, C.; Pierangeli, A.; Antonelli, G.; Nicolai, A.; Arima, S.; Moretti, C.; Papoff, P. Respiratory syncytial virus bronchiolitis, weather conditions and air pollution in an Italian urban area: An observational study. Environ. Res. 2017, 158, 188–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Su, W.; Wu, X.; Geng, X.; Zhao, X.; Liu, Q.; Liu, T. The short-term effects of air pollutants on influenza-like illness in Jinan, China. BMC Public Health 2019, 19, 1319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boda, E.; Rigamonti, A.E.; Bollati, V. Understanding the effects of air pollution on neurogenesis and gliogenesis in the growing and adult brain. Curr. Opin. Pharmacol. 2020, 50, 61–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Y.-K.; Chang, C.-K.; Chang, S.-C.; Chen, P.-S.; Lin, C.; Wang, Y.-C. Temperature, nitrogen dioxide, circulating respiratory viruses and acute upper respiratory infections among children in Taipei, Taiwan: A population-based study. Environ. Res. 2013, 120, 109–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stieb, D.M.; Shutt, R.; Kauri, L.M.; Roth, G.; Szyszkowicz, M.; Dobbin, N.A.; Chen, L.; Rigden, M.; Van Ryswyk, K.; Kulka, R. Cardiorespiratory effects of air pollution in a panel study of winter outdoor physical activity in older adults. J. Occup. Environ. Med. 2018, 60, 673–682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shabani, S. A mechanistic view on the neurotoxic effects of air pollution on central nervous system: Risk for autism and neurodegenerative diseases. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2021, 28, 6349–6373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Reeth, K. Cytokines in the pathogenesis of influenza. Vet. Microbiol. 2000, 74, 109–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, C.-G.; Chien, W.-C.; Lin, H.-C.; Lin, H.-C.; Chung, C.-H.; Cheng, C.-A. Hearing impairment in young and middle-aged septicemia survivors. Medicine 2020, 99, e21050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, I.Y.; Elkind, M.S.; Boehme, A.K. Risk factors for stroke in patients with sepsis and bloodstream infections. Stroke 2019, 50, 1046–1051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Fu, Y.-Y.; Zhang, T.-Y. Role of viral infection in sudden hearing loss. J. Int. Med. Res. 2019, 47, 2865–2872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, W.; Dai, Q.; Liu, J.; Liu, Y.; Hellström, S.; Duan, M. Analysis of clinical and laboratory findings of idiopathic sudden sensorineural hearing loss. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 6057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taiwanese Center of Disease Control. The Received Rate of Influzena Vaccine in Taiwan; Taiwanese Center of Disease Control: Taipei, Taiwan, 2021. Available online: https://www.cdc.gov.tw/Category/MPage/JNTC9qza3F_rgt9sRHqV2Q (accessed on 1 April 2021).
- Tsai, Y.-W.; Huang, W.-F.; Wen, Y.-W.; Chen, P.-F. The relationship between influenza vaccination and outpatient visits for upper respiratory infection by the elderly in Taiwan. Value Health 2007, 10, 117–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Wu, H.-H.; Chang, Y.-Y.; Kuo, S.-C.; Chen, Y.-T. Influenza vaccination and secondary prevention of cardiovascular disease among Taiwanese elders-A propensity score-matched follow-up study. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0219172. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, K.K.; Miller, M.R.; Shah, A.S. Air pollution and stroke. J. Stroke 2018, 20, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsuzuki, N.; Wasano, K.; Oishi, N.; Hentona, K.; Shimanuki, M.; Nishiyama, T.; Hiraga, Y.; Shinden, S.; Ogawa, K. Severe sudden sensorineural hearing loss related to risk of stroke and atherosclerosis. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 20204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mustafić, H.; Jabre, P.; Caussin, C.; Murad, M.H.; Escolano, S.; Tafflet, M.; Périer, M.-C.; Marijon, E.; Vernerey, D.; Empana, J.-P. Main air pollutants and myocardial infarction: A systematic review and meta-analysis. JAMA 2012, 307, 713–721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, K.-H.; Tsai, S.C.-S.; Lee, C.-Y.; Chou, R.-H.; Fan, H.-C.; Lin, F.C.-F.; Lin, C.-L.; Hsu, Y.-C. Increased risk of sensorineural hearing loss as a result of exposure to air pollution. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 1969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ho, C.-H.; Tan, T.-Y.; Hwang, C.-F.; Lin, W.-C.; Wu, C.-N.; Yang, C.-H. Association of carotid intima-media thickness with the risk of sudden sensorineural hearing loss. PeerJ 2020, 8, e9276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammadi, M.; Taziki Balajelini, M.H.; Rajabi, A. Migraine and risk of sudden sensorineural hearing loss: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Laryngoscope Investig. Otolaryngol. 2020, 5, 1089–1095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsai, Y.-T.; Chang, I.-J.; Hsu, C.-M.; Yang, Y.-H.; Liu, C.-Y.; Tsai, M.-S.; Chang, G.-H.; Lee, Y.-C.; Huang, E.I.; Lin, M.-H. Association between Sudden Sensorineural Hearing Loss and Preexisting Thyroid Diseases: A Nationwide Case-Control Study in Taiwan. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Pollutant | Mean ± Standard Deviation | 25% | 50% | 75% | Minimum | Maximum |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PM2.5 (ppm) | 18 ± 10.64 | 12 | 18 | 26 | 2 | 85 |
| PM10 (ppm) | 36.57 ± 18.15 | 24 | 36.57 | 45 | 5 | 147 |
| O3 (ppm) | 25.6 ± 10.39 | 19.2 | 25.6 | 32.8 | 2.8 | 90 |
| NO2 (ppb) | 19.83 ± 7.26 | 15.86 | 19.83 | 24.26 | 2.38 | 65.63 |
| SO2 (ppb) | 2.6 ± 1.54 | 1.9 | 2.6 | 3.6 | 0.2 | 20.8 |
| CO (ppm) | 0.46 ± 0.2 | 0.37 | 0.46 | 0.58 | 0.08 | 2.63 |
| Air temperature (°C) | 23.79 ± 5.55 | 19.03 | 23.79 | 28.48 | 5.5 | 33.3 |
| Relative Humidity (%) | 73.42 ± 9.54 | 66.34 | 73.42 | 81 | 24.57 | 95.01 |
| PM2.5 | PM10 | O3 | NO2 | SO2 | CO | Temperature | RH | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PM2.5 | 0.843 *** | 0.233 *** | 0.520 *** | 0.441 *** | 0.557 *** | −0.127 *** | −0.222 *** | |
| PM10 | 0.843 *** | 0.348 *** | 0.451 *** | 0.384 *** | 0.473 *** | −0.186 *** | −0.359 *** | |
| O3 | 0.233 *** | 0.348 *** | −0.126 *** | 0.001 | −0.187 *** | −0.173 *** | −0.266 *** | |
| NO2 | 0.52 *** | 0.451 *** | −0.126 ** | 0.456 *** | 0.859 *** | −0.273 *** | 0.117 *** | |
| SO2 | 0.441 *** | 0.384 *** | 0.001 | 0.456 *** | 0.333 *** | 0.174 *** | −0.157 *** | |
| CO | 0.557 *** | 0.473 *** | −0.187 *** | 0.859 *** | 0.333 *** | −0.167 *** | 0.103 *** | |
| Temperature | −0.127 *** | −0.186 *** | −0.173 *** | −0.273 *** | 0.174 *** | −0.167 *** | −0.254 *** | |
| Relative Humidity | −0.222 *** | −0.359 *** | −0.266 *** | 0.117 *** | −0.157 *** | 0.103 *** | −0.254 *** | |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Cheng, C.-G.; Chen, Y.-H.; Yen, S.-Y.; Lin, H.-C.; Lin, H.-C.; Chou, K.-R.; Cheng, C.-A. Air Pollution Exposure and the Relative Risk of Sudden Sensorineural Hearing Loss in Taipei. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 6144. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph19106144
Cheng C-G, Chen Y-H, Yen S-Y, Lin H-C, Lin H-C, Chou K-R, Cheng C-A. Air Pollution Exposure and the Relative Risk of Sudden Sensorineural Hearing Loss in Taipei. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health. 2022; 19(10):6144. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph19106144
Chicago/Turabian StyleCheng, Chun-Gu, Yu-Hsuan Chen, Shang-Yih Yen, Hui-Chen Lin, Hung-Che Lin, Kuei-Ru Chou, and Chun-An Cheng. 2022. "Air Pollution Exposure and the Relative Risk of Sudden Sensorineural Hearing Loss in Taipei" International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health 19, no. 10: 6144. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph19106144
APA StyleCheng, C.-G., Chen, Y.-H., Yen, S.-Y., Lin, H.-C., Lin, H.-C., Chou, K.-R., & Cheng, C.-A. (2022). Air Pollution Exposure and the Relative Risk of Sudden Sensorineural Hearing Loss in Taipei. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 19(10), 6144. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph19106144






