Alcohol and Nicotine Use among Adolescents: An Observational Study in a Sicilian Cohort of High School Students
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Experimental Design
2.2. Assessment of Alcohol Consumption
2.3. Assessment of Nicotine Dependence
2.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Pattern of Alcohol Consumption
3.2. Pattern of Nicotine Consumption
3.3. Correlation between Alcohol and Nicotine Consumption
4. Discussion
5. Study Limitations
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Ethic Statement
References
- World Health Organization. Harmful Use of Alcohol Kills More than 3 Million People Each Year, Most of Them Men. 2018. Available online: www.who.int (accessed on 16 April 2022).
- Grant, M. Alcohol Policies. Copenhagen: WHO Regional Publications European Series 18; WHO: Copenhagen, Denmark, 1985. [Google Scholar]
- Gual, A.; Colom, J. Why has alcohol consumption declined in countries of southern Europe? Addiction 1997, 92, S21–S31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- World Health Organization. Global Information System on Alcohol and Health; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Istituto Nazionale di Statistica. Il Consumo di Alcol in Italia. 2020. Available online: www.istat.it/archivio/244222 (accessed on 12 May 2022).
- Pollard, M.S.; Tucker, J.S.; Green, H.D. Changes in Adult Alcohol Use and Consequences During the COVID-19 Pandemic in the US. JAMA 2020, 3, e2022942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cirrincione, L.; Rapisarda, V.; Mazzucco, W.; Provenzano, R.; Cannizzaro, E. SARS-CoV-2 and the Risk Assessment Document in Italian Work; Specific or Generic Risk Even If Aggravated? Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 3729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cirrincione, L.; Plescia, F.; Ledda, C.; Rapisarda, V.; Martorana, D.; Lacca, G.; Argo, A.; Zerbo, S.; Vitale, E.; Vinnikov, D.; et al. COVID-19 Pandemic: New Prevention and Protection Measures. Sustainability 2022, 14, 4766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Di, Y.; Ye, J.; Wei, W. Study on the public psychological states and its related factors during the outbreak of coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) in some regions of China. Psychol. Health Med. 2021, 26, 13–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cannizzaro, E.; Cirrincione, L.; Mazzucco, W.; Scorciapino, A.; Catalano, C.; Ramaci, T.; Ledda, C.; Plescia, F. Night-Time Shift Work and Related Stress Responses: A Study on Security Guards. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Boscarino, J.A.; Adams, R.E.; Galea, S. Alcohol use in New York after the terrorist attacks: A study of the effects of psychological trauma on drinking behavior. Addict. Behav. 2006, 31, 606–621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brancato, A.; Lavanco, G.; Cavallaro, A.; Plescia, F.; Cannizzaro, C. Acetaldehyde, Motivation and Stress: Behavioral Evidence of an Addictive ménage à trois. Front. Behav. Neurosci. 2017, 11, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Plescia, F.; Cirrincione, L.; Martorana, D.; Ledda, C.; Rapisarda, V.; Castelli, V.; Martines, F.; Vinnikov, D.; Cannizzaro, E. Alcohol Abuse and Insomnia Disorder: Focus on a Group of Night and Day Workers. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 13196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuntsche, E.; Rehm, J.; Gmel, G. Characteristics of binge drinkers in Europe. Soc. Sci. Med. 2004, 59, 113–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- NIAAA. Drinking Levels Defined. Available online: https://www.niaaa.nih.gov/alcohol-health/overview-alcohol-consumption/moderate-binge-drinking (accessed on 2 November 2017).
- Windle, M. Alcohol use among adolescents and young adults. Alcohol Res. Health 2003, 27, 79–85. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Waller, R.; Murray, L.; Shaw, D.S.; Forbes, E.E.; Hyde, L.W. Accelerated alcohol use across adolescence predicts early adult symptoms of alcohol use disorder via reward-related neural function. Psychol. Med. 2019, 49, 675–684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Roy, B.; Veenstra, M.; Clench-Aas, J. Construct validity of the five-factor Strengths and Difficulties Questionnaire (SDQ) in pre-, early, and late adolescence. J. Child Psychol. Psychiatry 2008, 49, 1304–1312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuntsche, E.; Gmel, G. Alcohol consumption in late adolescence and early adulthood—Where is the problem? Swiss Med. Wkly. 2013, 143, w13826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Santangelo, O.E.; Provenzano, S.; Piazza, D.; Firenze, A. Factors associated with risky con-sumption of alcohol in a sample of university students. Ann. Ig. 2018, 30, 502–508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Briones, T.L.; Woods, J. Chronic binge-like alcohol consumption in adolescence causes depression-like symptoms possibly mediated by the effects of BDNF on neurogenesis. Neuroscience 2013, 254, 324–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- McBride, O.; Cheng, H.G. Exploring the emergence of alcohol use disorder symptoms in the two years after onset of drinking: Findings from the National Surveys on drug use and health. Addiction 2011, 106, 555–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Golub, A.; Johnson, B.D. The shifting importance of alcohol and marijuana as gateway substances among serious drug abusers. J. Stud. Alcohol 1994, 55, 607–614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Davila, V.R.; Stahl, D.L.; Bhandary, S.P.; Papadimos, T.J. What’s New in Critical Illness and Injury Science? The association between initial blood alcohol concentration and polysubstance use may be indicative of a gateway drug effect. Int. J. Crit. Illn. Inj. Sci. 2018, 8, 181–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nunes, P.T.; Kipp, B.T.; Reitz, N.L.; Savage, L.M. Aging with alcohol-related brain damage: Critical brain circuits associated with cognitive dysfunction. Int. Rev. Neurobiol. 2019, 148, 101–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sartor, C.E.; Lynskey, M.T.; Heath, A.C.; Jacob, T.; True, W. The role of childhood risk factors in initiation of alcohol use and progression to alcohol dependence. Addiction 2007, 102, 216–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brancato, A.; Castelli, V.; Lavanco, G.; Tringali, G.; Micale, V.; Kuchar, M.; D’Amico, C.; Pizzolanti, G.; Feo, S.; Cannizzaro, C. Binge-like Alcohol Exposure in Adolescence: Behavioural, Neuroendocrine and Molecular Evidence of Abnormal Neuroplasticity and Return. Biomedicines 2021, 9, 1161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tapia-Rojas, C.; Carvajal, F.J.; Mira, R.G.; Arce, C.; Lerma-Cabrera, J.M.; Orellana, J.A.; Cerpa, W.; Quintanilla, R.A. Adolescent Binge Alcohol Exposure Affects the Brain Function Through Mitochondrial Impairment. Mol. Neurobiol. 2018, 55, 4473–4491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- West, R.K.; Maynard, M.E.; Leasure, J.L. Binge ethanol effects on prefrontal cortex neurons, spatial working memory and task-induced neuronal activation in male and female rats. Physiol. Behav. 2018, 188, 79–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Voos, N.; Goniewicz, M.L.; Eissenberg, T. What is the nicotine delivery profile of electronic cigarettes? Expert Opin. Drug Deliv. 2019, 16, 1193–1203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jordt, S.E. Synthetic nicotine has arrived. Tob. Control 2021, 7, 56626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Istituto Superiore di Sanità. Fumo Informazioni Generali. Available online: www.epicentro.iss.it/fumo/ (accessed on 16 April 2022).
- Torres, O.V.; Tejeda, H.A.; Natividad, L.A.; O’Dell, L.E. Enhanced vulnerability to the rewarding effects of nicotine during the adolescent period of development. Pharmacol. Biochem. Behav. 2008, 90, 658–663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Colby, S.M.; Tiffany, S.T.; Shiffman, S.; Niaura, R.S. Are adolescent smokers dependent on nicotine? A review of the evidence. Drug Alcohol Depend. 2000, 59, S83–S95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coulton, S.; Alam, M.F.; Boniface, S.; Deluca, P.; Donoghue, K.; Gilvarry, E.; Kaner, E.; Lynch, E.; Maconochie, I.; McArdle, P.; et al. Opportunistic screening for alcohol use problems in adolescents attending emergency departments: An evaluation of screening tools. J. Public Health 2019, 41, e53–e60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Caputo, A. Comparing Theoretical Models for the Understanding of Health-Risk Behaviour: Towards an Integrative Model of Adolescent Alcohol Consumption. Eur. J. Psychol. 2020, 16, 418–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Zheng, H.; Steve, S.; Gong, J.; Stacy, A.; Xia, J.; Gallaher, P.; Dent, C.; Azen, S.; Shan, J.; et al. Use of the fagerstrom tolerance questionnaire for measuring nicotine dependence among adolescent smokers in China: A pilot test. Psychol. Addict. Behav. 2002, 16, 260–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fekketich, A.K.; Fossati, R.; Apolone, G. An Evaluation of the Italian Version of the Fagerström Test for Nicotine Dependence. Psychol. Rep. 2008, 102, 687–694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patrick, M.E.; Schulenberg, J.E.; Martz, M.E.; Maggs, J.L.; O’Malley, P.M.; Johnston, L.D. Extreme binge drinking among 12th-grade students in the United States: Prevalence and predictors. JAMA Pediatr. 2013, 167, 1019–1025, Erratum in JAMA Pediatr. 2013, 167, 117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Martinotti, G.; Lupi, M.; Carlucci, L.; Santacroce, R.; Cinosi, E.; Acciavatti, T.; Sarchione, F.; Verrastro, V.; Diotaiuti, P.; Petruccelli, I.; et al. Alcohol drinking patterns in young people: A survey-based study. J. Health Psychol. 2017, 22, 1889–1896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuntsche, E.; Müller, S. Why do young people start drinking? Motives for first-time alcohol consumption and links to risky drinking in early adolescence. Eur. Addict. Res. 2012, 18, 34–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chung, T.; Creswell, K.G.; Bachrach, R.; Clark, D.B.; Martin, C.S. Adolescent Binge Drinking. Alcohol Res. 2018, 39, 5–15. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Alcol e Salute, la Situazione Globale nel Report Oms (iss.it). Available online: www.epicentro.iss.it/alcol/GlobalStatusReportAlcol2018 (accessed on 20 April 2022).
- Chassin, L.; Pitts, S.C.; Prost, J. Binge drinking trajectories from adolescence to emerging adulthood in a high-risk sample: Predictors and substance abuse outcomes. J. Consult Clin. Psychol. 2002, 70, 67–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sudhinaraset, M.; Wigglesworth, C.; Takeuchi, D.T. Social and Cultural Contexts of Alcohol Use: Influences in a Social-Ecological Framework. Alcohol Res. 2016, 38, 35–45. [Google Scholar]
- Halim, A.; Hasking, P.; Allen, F. The role of social drinking motives in the relationship between social norms and alcohol consumption. Addict. Behav. 2012, 37, 1335–1341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Popova, S.; Rehm, J.; Patra, J.; Zatonski, W. Comparing alcohol consumption in central and eastern Europe to other European countries. Alcohol Alcohol. 2007, 42, 465–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, J.W.; Naimi, T.S.; Brewer, R.D.; Jones, S.E. Binge drinking and associated health risk behaviors among high school students. Pediatrics 2007, 119, 76–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dube, S.R.; Miller, J.W.; Brown, D.W.; Giles, W.H.; Felitti, V.J.; Dong, M.; Anda, R.F. Adverse childhood experiences and the association with ever using alcohol and initiating alcohol use during adolescence. J. Adolesc. Health 2006, 38, 444-e1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paus, T.; Zijdenbos, A.; Worsley, K.; Collins, D.L.; Blumenthal, J.; Giedd, J.N.; Rapoport, J.L.; Evans, A.C. Structural maturation of neural pathways in children and adolescents: In vivo study. Science 1999, 283, 1908–1911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Day, E.; Rudd, J.H.F. Alcohol use disorders and the heart. Addiction 2019, 114, 1670–1678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shimpi, T.R.; Shikhare, S.N.; Chung, R.; Wu, P.; Peh, W.C.G. Imaging of Gastrointestinal and Abdominal Emergencies in Binge Drinking. Can. Assoc. Radiol. J. 2019, 70, 52–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bava, S.; Tapert, S.F. Adolescent brain development and the risk for alcohol and other drug problems. Neuropsychol. Rev. 2010, 20, 398–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- De Luca, C.R.; Wood, S.J.; Anderson, V.; Buchanan, J.A.; Proffitt, T.M.; Mahony, K.; Pantelis, C. Normative data from the CANTAB. I: Development of executive function over the lifespan. J. Clin. Exp. Neuropsychol. 2003, 25, 242–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clark, D.B.; Thatcher, D.L.; Tapert, S.F. Alcohol, psychological dysregulation, and adolescent brain development. Alcohol Clin. Exp. Res. 2008, 32, 375–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plescia, F.; Brancato, A.; Venniro, M.; Maniaci, G.; Cannizzaro, E.; Sutera, F.M.; De Caro, V.; Giannola, L.I.; Cannizzaro, C. Acetaldehyde self-administration by a two-bottle choice paradigm: Consequences on emotional reactivity, spatial learning, and memory. Alcohol 2015, 49, 139–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cranford, J.A.; Eisenberg, D.; Serras, A.M. Substance use behaviors, mental health problems, and use of mental health services in a probability sample of college students. Addict. Behav. 2009, 34, 134–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, R.; Wang, L.; Xie, Y. An analysis of factors influencing drinking relapse among patients with alcohol-induced psychiatric and behavioral disorders. Shanghai Arch. Psychiatry 2016, 28, 147–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sutera, F.M.; De Caro, V.; Cannizzaro, C.; Giannola, L.I.; Lavanco, G.; Plescia, F. Effects of DA-Phen, a dopamine-aminoacidic conjugate, on alcohol intake and forced abstinence. Behav. Brain Res. 2016, 1, 109–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sullivan, L.E.; Fiellin, D.A.; O’Connor, P.G. The prevalence and impact of alcohol problems in major depression: A systematic review. Am. J. Med. 2005, 118, 330–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Robinson, J.; Sareen, J.; Cox, B.; Bolton, J. Role of Self-medication in the Development of Comorbid Anxiety and Substance Use Disorders: A Longitudinal Investigation. Arch. Gen. Psychiatry 2011, 68, 800–807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Degenhardt, L.; Dierker, L.; Chiu, W.T.; Medina-Mora, M.E.; Neumark, Y.; Sampson, N.; Alonso, J.; Angermeyer, M.; Anthony, J.C.; Bruffaerts, R.; et al. Evaluating the drug use “gateway” theory using cross-national data: Consistency and associations of the order of initiation of drug use among participants in the WHO World Mental Health Surveys. Drug Alcohol Depend. 2010, 108, 84–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Samet, J.M. Tobacco smoking: The leading cause of preventable disease worldwide. Thorac. Surg. Clin. 2013, 23, 103–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sansone, N.; Fong, G.T.; Lee, W.B.; Laux, F.L.; Sirirassamee, B.; Seo, H.G.; Omar, M.; Jiang, Y. Comparing the experience of regret and its predictors among smokers in four asian countries: Findings from the itc surveys in Tailand, South Korea, Malaysia, and China. Nicotine Tob. Res. 2013, 15, 1663–1672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alotaibi, S.A.; Alsuliman, M.A.; Durgampudi, P.K. Smoking tobacco prevalence among college students in the Kingdom of Saudi Arabia: Systematic review and meta-analysis. Tob. Induc. Dis. 2019, 17, 35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- ESPAD ITALIA. European School Survey Project on Alcohol and other Drugs—Italy. Available online: www.espad.it (accessed on 22 April 2022).
- Becker, J.B.; McClellan, M.L.; Reed, B.G. Sex differences, gender and addiction. J. Neurosci. Res. 2017, 95, 136–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gelernter, J.; Panhuysen, C.; Weiss, R.; Brady, K.; Poling, J.; Krauthammer, M. Genomewide linkage scan for nicotine dependence: Identification of a chromosome 5 risk locus. Biol. Psychiatry 2007, 61, 119–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bierut, L.J.; Madden, P.A.; Breslau, N.; Johnson, E.O.; Hatsukami, D.; Pomerleau, O.F. Novel genes identified in a high-density genome wide association study for nicotine dependence. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2007, 16, 24–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ring, H.Z.; Valdes, A.M.; Nishita, D.M.; Prasad, S.; Jacob, P.; Tyndale, R.F.; Swan, G.E.; Benowitz, N.L. Gene-gene interactions between CYP2B6 and CYP2A6 in nicotine metabolism. Pharm. Genom. 2007, 17, 1007–1015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bierut, L.J.; Stitzel, J.A.; Wang, J.C.; Hinrichs, A.L.; Grucza, R.A.; Xuei, X.; Saccone, N.L.; Saccone, S.F.; Bertelsen, S.; Fox, L.; et al. Variants in nicotinic receptors and risk for nicotine dependence. Am. J. Psychiatry 2008, 165, 1163–1171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oscarson, M. Genetic polymorphisms in the cytochrome P450 2A6 (CYP2A6) gene: Implications for interindividual differences in nicotine metabolism. Drug Metab. Dispos. 2001, 29, 91–95. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Yoshida, R.; Nakajima, M.; Nishimura, K.; Tokudome, S.; Kwon, J.T.; Yokoi, T. Effects of polymorphism in promoter region of human CYP2A6 gene (CYP2A6*9) on expression level of messenger ribonucleic acid and enzymatic activity in vivo and in vitro. Clin. Pharmacol. Ther. 2003, 74, 69–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colombo, S.F.; Mazzo, F.; Pistillo, F.; Gotti, C. Biogenesis, trafficking and up-regulation of nicotinic ACh receptors. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2013, 86, 1063–1073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karp, I.; O’Loughlin, J.; Hanley, J.; Tyndale, R.F.; Paradis, G. Risk factors for tobacco dependence in adolescent smokers. Tob. Control 2006, 15, 199–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, F.; Chen, H.; Steketee, J.D.; Sharp, B.M. Upregulation of ionotropic glutamate receptor subunits within specific mesocorticolimbic regions during chronic nicotine self-administration. Neuropsychopharmacol 2007, 32, 103–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szumlinski, K.K.; Woodward, J.J. Glutamate signaling in alcohol abuse and dependence. Neurobiol Alcohol Depend. 2014, 173, 206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castelli, V.; Brancato, A.; Cavallaro, A.; Lavanco, G.; Cannizzaro, C. Homer2 and Alcohol: A Mutual Interaction. Front. Psychiatry 2017, 8, 268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Verplaetse, T.L.; McKee, S.A. An overview of alcohol and tobacco/nicotine interactions in the human laboratory. Am. J. Drug Alcohol Abus. 2017, 43, 186–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- McKee, S.A.; Falba, T.; O’Malley, S.S.; Sindelar, J.; O’Connor, P.G. Smoking status as a clinical indicator for alcohol misuse in US adults. Arch. Intern. Med. 2007, 167, 716–721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grant, B.F. Age at smoking onset and its association with alcohol consumption and DSM-IV alcohol abuse and dependence: Results from the National Longitudinal Alcohol Epidemiologic Survey. J. Subst. Abus. 1998, 10, 59–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Chiara, G. Role of dopamine in the behavioural actions of nicotine related to addiction. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2000, 393, 295–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mansvelder, H.D.; McGehee, D.S. Long-term potentiation of excitatory inputs to brain reward areas by nicotine. Neuron 2000, 27, 349–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Miyata, H.; Yanagita, T. Neurobiological mechanisms of nicotine craving. Alcohol 2001, 24, 87–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gogtay, N.; Giedd, J.N.; Lusk, L.; Hayashi, K.M.; Greenstein, D.; Vaituzis, A.C.; Nugent, T.F.; Herman, D.H.; Clasen, L.S.; Toga, A.W.; et al. Dynamic mapping of human cortical development during childhood through early adulthood. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2004, 101, 8174–8179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Casey, B.; Jones, R.M.; Somerville, L.H. Braking and accelerating of the adolescent brain. J. Res. Adolesc. 2011, 21, 21–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Singer, W. Dynamic formation of functional networks by synchronization. Neuron 2011, 69, 191–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]

| Male | na | % | Mean | SD | Min | Med | Max |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Students | 224 | 100 | |||||
| Age | 16.83 | 1.295 | 14 | 17 | 19 | ||
| Height (cm) | 1.73 | 0.0768 | 1.50 | 1.73 | 1.97 | ||
| Weight (kg) | 67.37 | 11.89 | 40 | 65 | 98 | ||
| Body Mass Index (BMI) | |||||||
| Under weight | 17 | 7.6 | 17.39 | 1.198 | 14.87 | 17.99 | 18.37 |
| Normal weight | 164 | 73.2 | 21.62 | 1.855 | 18.64 | 21.22 | 24.82 |
| Overweight | 30 | 13.4 | 27.26 | 1.307 | 25.14 | 27.45 | 29.39 |
| Obese | 13 | 5.8 | 34.49 | 7.474 | 30.12 | 31.22 | 51.20 |
| Female | na | % | Mean | SD | Min | Med | Max |
| Students | 125 | 100 | |||||
| Age | 15.82 | 1.240 | 14 | 15 | 19 | ||
| Height (cm) | 1.64 | 0.0766 | 1.43 | 1.61 | 1.80 | ||
| Weight (kg) | 55.79 | 9.33 | 40 | 56 | 78 | ||
| Body Mass Index (BMI) | |||||||
| Under weight | 31 | 24.8 | 16.88 | 0.966 | 15.63 | 16.61 | 18.38 |
| Normal weight | 83 | 66.4 | 21.63 | 2.04 | 18.59 | 21.37 | 29.05 |
| Overweight | 11 | 8.8 | 26.72 | 1.758 | 25.06 | 25.86 | 28.91 |
| Obese | 0 | - | - | - | - | - | |
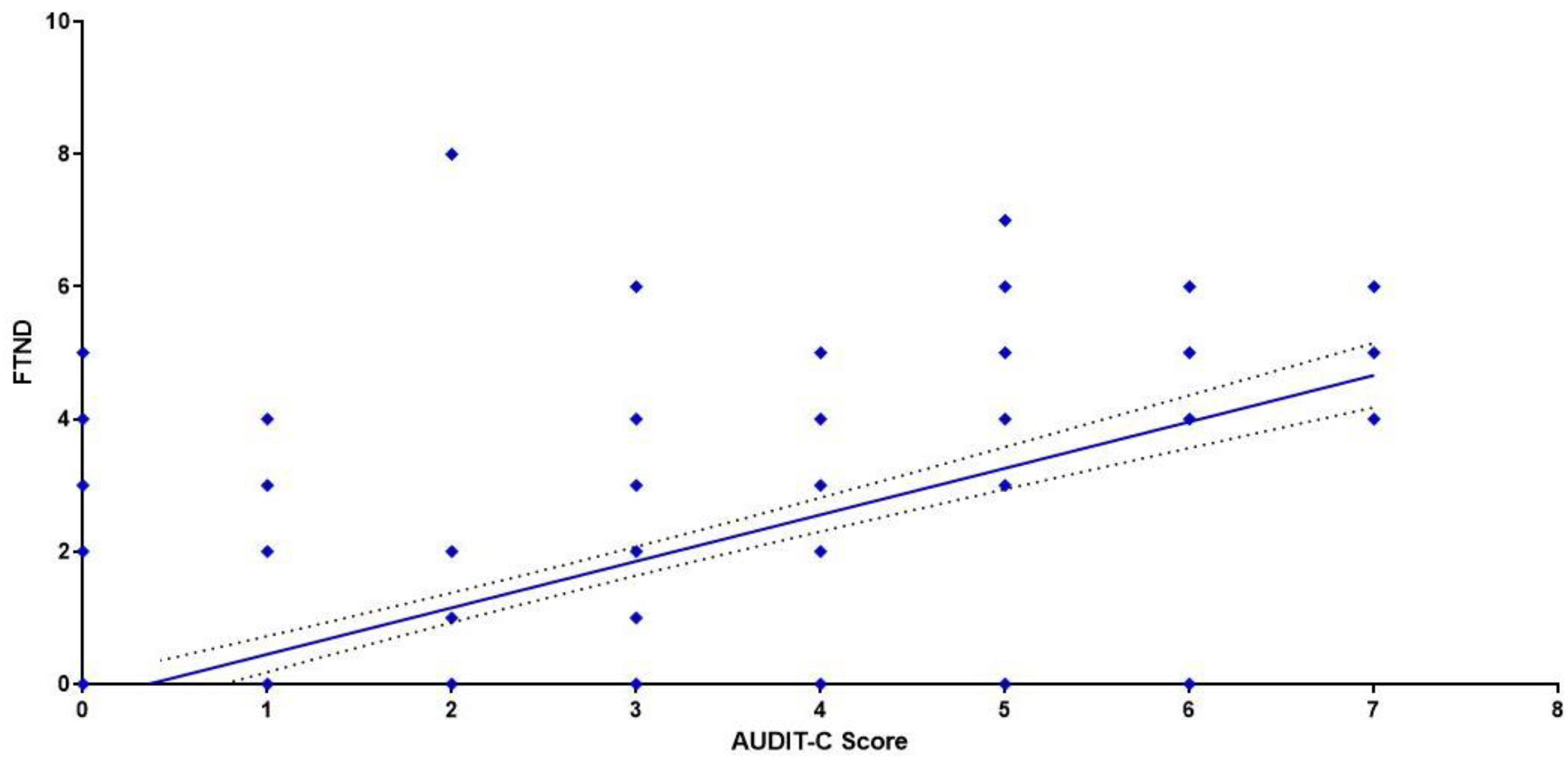
| Male | n | % | AUDIT-C Score Index Mean | 95% CI |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 224 | 100 | 2.652 | 2.368–2.936 | |
| Non drinkers | 51 | 22.8 | - | - |
| Drinkers | 173 | 77.2 | 3.497 | 3.206–3.788 |
| Among students reporting alcohol intake | ||||
| Occasional drinkers | 48 | 27.7 | 1.604 | 1.319–1.890 |
| Monthly drinkers | 65 | 37.6 | 3.185 | 2.878–3.491 |
| Weekly drinkers | 60 | 34.7 | 5.133 | 4.827–5.440 |
| Harmful drinkers | 54 | 31.2 | 5.648 | 5.463–5.833 |
| Binging drinkers | 96 | 55.5 | 4.688 | 4.421–4.954 |
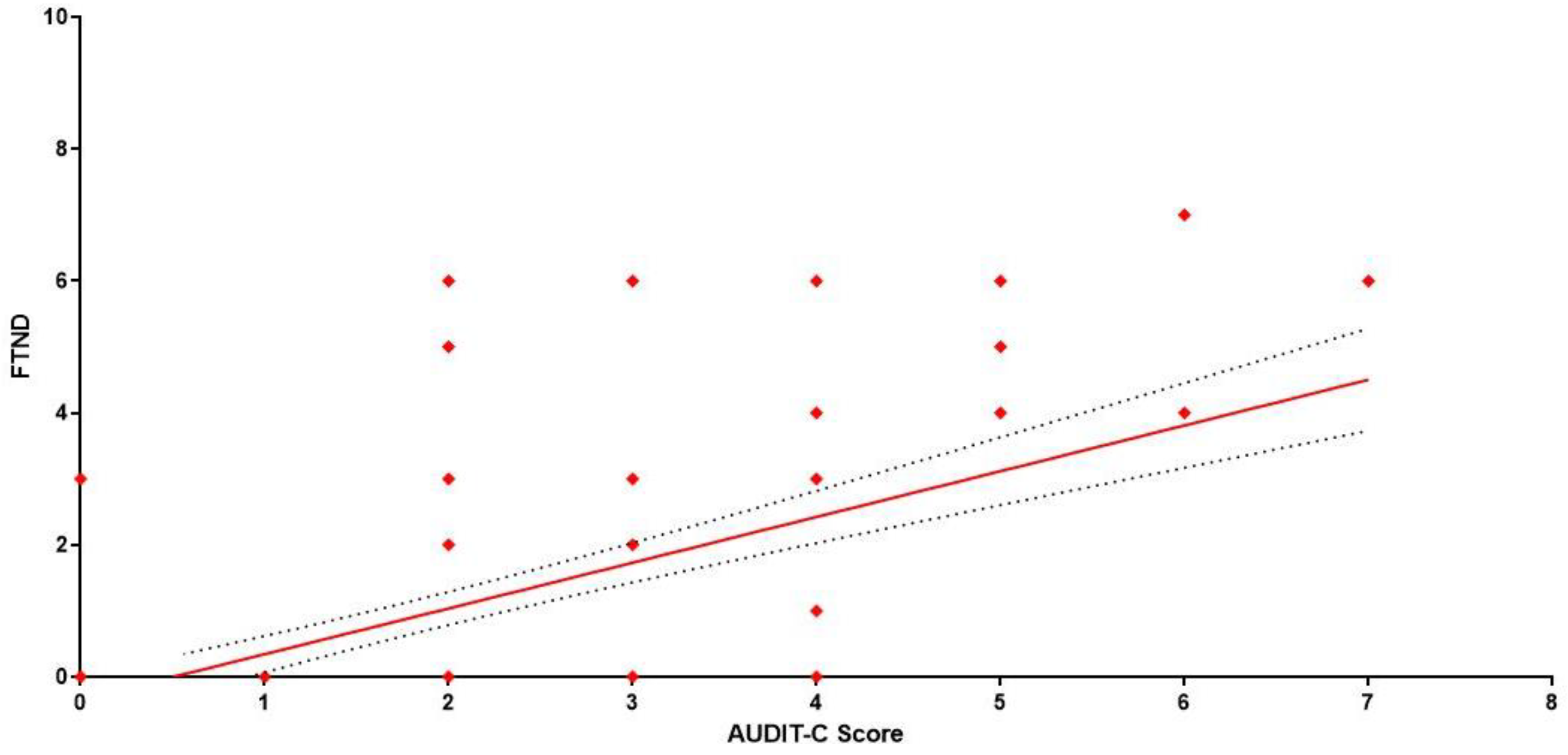
| Female | n | % | AUDIT-C Score Index Mean | 95% CI |
| 125 | 100 | 1.832 | 1.520–2.144 | |
| Non drinkers | 38 | 30.4 | - | - |
| Drinkers | 87 | 69.6 | 2.793 | 2.412–3.174 |
| Among students reporting alcohol intake | ||||
| Occasional drinkers | 37 | 42.5 | 1.432 | 1.165–1.699 |
| Monthly drinkers | 30 | 34.5 | 3.933 | 2.542–3.325 |
| Weekly drinkers | 20 | 23.0 | 4.400 | 3.824–4.976 |
| Harmful drinkers | 39 | 42.5 | 4.000 | 3.676–4.324 |
| Binging drinkers | 38 | 43.7 | 3.947 | 3.543–4.351 |
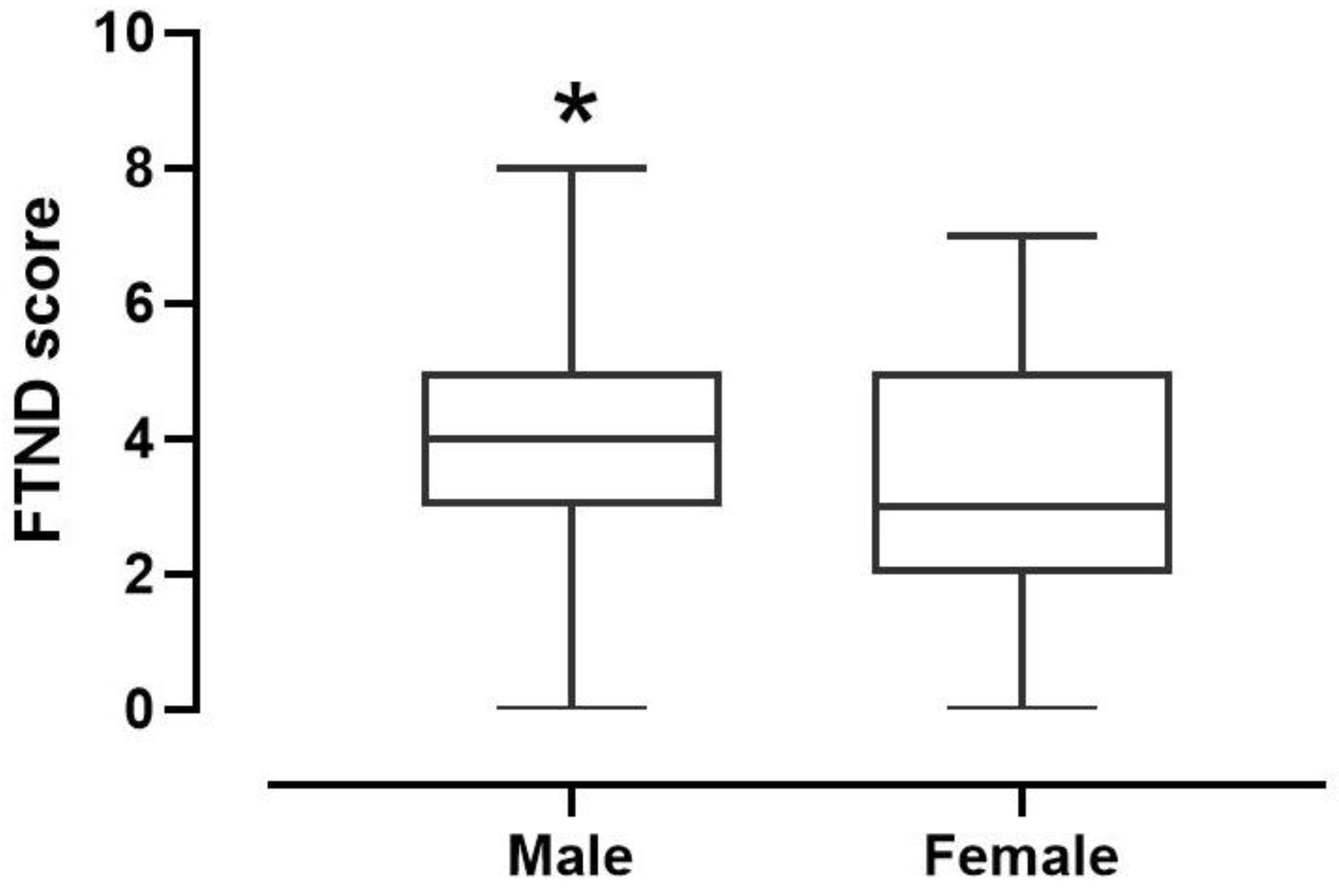
| Male | n | % | FTND Score Index Mean | 95% CI |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 224 | 100 | 1.612 | 1.318–1.905 | |
| Smoking habit | ||||
| Non smokers | 131 | 58.5 | - | - |
| Smokers | 93 | 41.5 | 3.882 | 3.519–4.245 |
| Degree of dependence | ||||
| Mild | 21 | 22.6 | 1.429 | 0.860–1.997 |
| Medium | 30 | 32.2 | 3.633 | 3.450–3.816 |
| Severe | 40 | 43.0 | 5.275 | 5.130–5.420 |
| Very severe | 2 | 2.2 | 7.500 | 1.147–13.85 |
| Female | n | % | FTND Score Index Mean | 95% CI |
| 125 | 100 | 0.9200 | 0.590–1.249 | |
| Smoking habit | ||||
| Non smokers | 90 | 72 | - | - |
| Smokers | 35 | 28 | 3.286 | 2.547–4.024 |
| Degree of dependence | ||||
| Mild | 13 | 37.1 | 1.000 | 0.4484–1.552 |
| Medium | 11 | 31.5 | 3.455 | 3.104–3.805 |
| Severe | 9 | 25.7 | 5.556 | 5.150–5.961 |
| Very severe | 2 | 5.7 | 7.000 | 7.000–7.000 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Cannizzaro, E.; Lavanco, G.; Castelli, V.; Cirrincione, L.; Di Majo, D.; Martines, F.; Argo, A.; Plescia, F. Alcohol and Nicotine Use among Adolescents: An Observational Study in a Sicilian Cohort of High School Students. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 6152. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph19106152
Cannizzaro E, Lavanco G, Castelli V, Cirrincione L, Di Majo D, Martines F, Argo A, Plescia F. Alcohol and Nicotine Use among Adolescents: An Observational Study in a Sicilian Cohort of High School Students. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health. 2022; 19(10):6152. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph19106152
Chicago/Turabian StyleCannizzaro, Emanuele, Gianluca Lavanco, Valentina Castelli, Luigi Cirrincione, Danila Di Majo, Francesco Martines, Antonina Argo, and Fulvio Plescia. 2022. "Alcohol and Nicotine Use among Adolescents: An Observational Study in a Sicilian Cohort of High School Students" International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health 19, no. 10: 6152. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph19106152
APA StyleCannizzaro, E., Lavanco, G., Castelli, V., Cirrincione, L., Di Majo, D., Martines, F., Argo, A., & Plescia, F. (2022). Alcohol and Nicotine Use among Adolescents: An Observational Study in a Sicilian Cohort of High School Students. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 19(10), 6152. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph19106152








