Metabolic-Syndrome-Related Comorbidities in Narcolepsy Spectrum Disorders: A Preliminary Cross-Sectional Study in Japan
Abstract
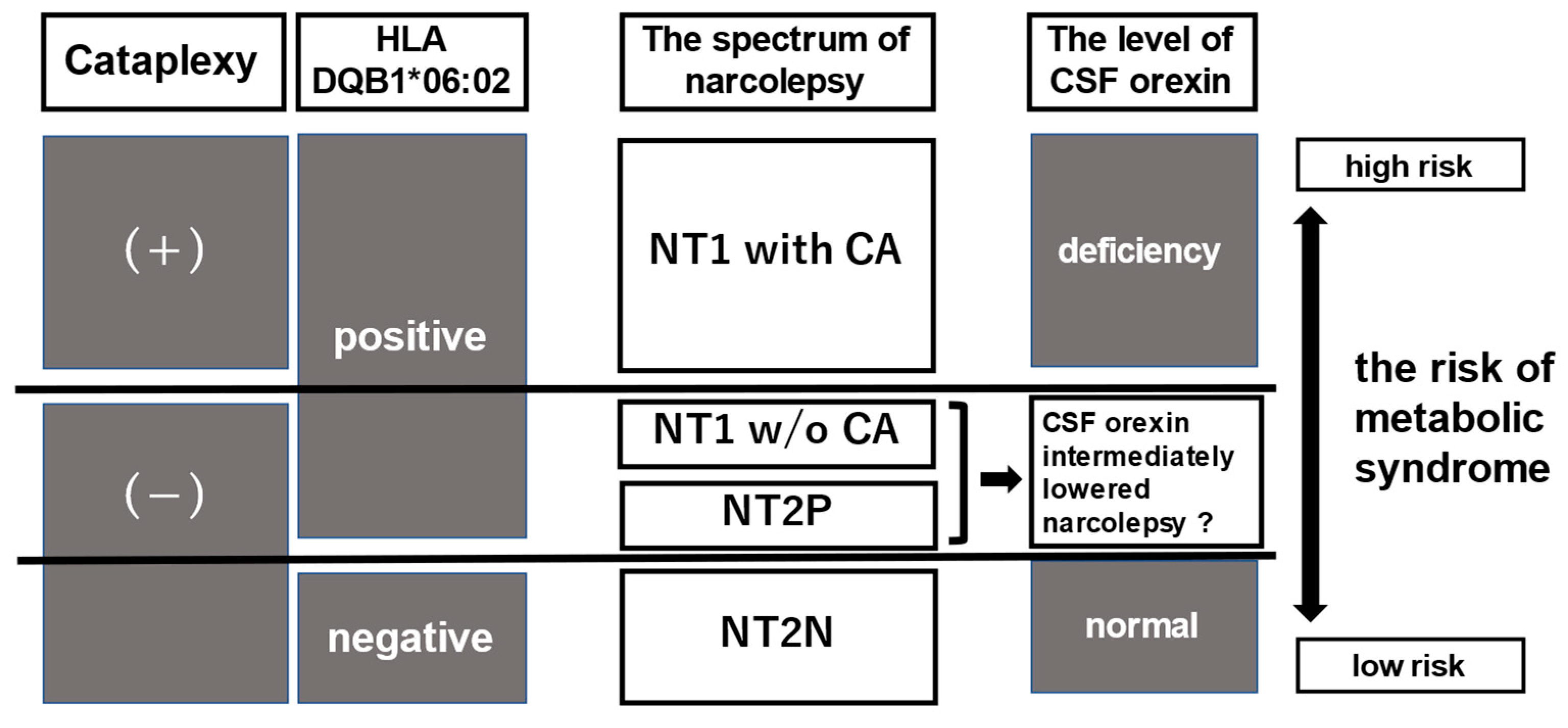
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Surveyed Participants and Procedures
2.2. Statistical Analyses
3. Results
3.1. Comparison of Demographic Variables and the Incidence of Complications among Patients with NSD
3.2. Comparison of Demographic Variables and Incidence of Complications between Patients Who Are NT2P and NT2N
3.3. Factors Associated with the Incidence of MRD
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| AHI | apnea–hypopnea index |
| ANOVA | one-way analysis of variance |
| BMI | body mass index |
| CSF | cerebrospinal fluid |
| EDS | excessive daytime sleepiness |
| HLA | human leukocyte antigen |
| ICSD-2 | the International Classification of Sleep Disorders, Second Edition |
| ICSD-3 | the International Classification of Sleep Disorders, Third Edition |
| IH | idiopathic hypersomnia |
| LST | long sleep time |
| MRD | metabolic-syndrome-related disorder |
| MSLT | multiple sleep latency tests |
| nCPAP | nasal continuous positive airway pressure |
| NSD | narcolepsy spectrum disorder |
| NT1 | narcolepsy type 1 |
| NT2 | narcolepsy type 2 |
| NT2P | human leukocyte antigen DQB1*06:02 positive narcolepsy type 2 |
| NT2N | human leukocyte antigen DQB1*06:02 negative narcolepsy type 2 |
| OSA | obstructive sleep apnea |
| PSG | polysomnography |
| REM | rapid eye movement |
| SD | standard deviation |
References
- Reading, P. Cataplexy. Pract. Neurol. 2019, 19, 21–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Slowik, J.M.; Collen, J.F.; Yow, A.G. Narcolepsy. In StatPearls; StatPearls Publishing: Treasure Island, FL, USA, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- The International Classification of Sleep Disorders, 3rd ed.; American Academy of Sleep Medicine: Darien, IL, USA, 2014; ISBN 099-154-340-8.
- The International Classification of Sleep Disorders, 2nd ed.; American Academy of Sleep Medicine: Darien, IL, USA, 2005; ISBN 0-9657220-2-3.
- Sonka, K.; Susta, M.; Billiard, M. Narcolepsy with and without cataplexy, idiopathic hypersomnia with and without long sleep time: A cluster analysis. Sleep Med. 2015, 16, 225–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sasai, T.; Inoue, Y.; Komada, Y.; Sugiura, T.; Matsushima, E. Comparison of clinical characteristics among narcolepsy with and without cataplexy and idiopathic hypersomnia without long sleep time, focusing on HLA-DRB1(*)1501/DQB1(*)0602 finding. Sleep Med. 2009, 10, 961–966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aldrich, M.S. The clinical spectrum of narcolepsy and idiopathic hypersomnia. Neurology 1996, 46, 393–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takei, Y.; Komada, Y.; Namba, K.; Sasai, T.; Nakamura, M.; Sugiura, T.; Hayashida, K.; Inoue, Y. Differences in findings of nocturnal polysomnography and multiple sleep latency test between narcolepsy and idiopathic hypersomnia. Clin. Neurophysiol. 2012, 123, 137–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nishino, S.; Ripley, B.; Overeem, S.; Lammers, G.J.; Mignot, E. Hypocretin (orexin) deficiency in human narcolepsy. Lancet 2000, 355, 39–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barateau, L.; Dauvilliers, Y. Recent advances in treatment for narcolepsy. Ther. Adv. Neurol. Disord. 2019, 12, 1756286419875622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dauvilliers, Y.; Baumann, C.R.; Carlander, B.; Bischof, M.; Blatter, T.; Lecendreux, M.; Maly, F.; Besset, A.; Touchon, J.; Billiard, M.; et al. CSF hypocretin-1 levels in narcolepsy, Kleine-Levin syndrome, and other hypersomnias and neurological conditions. J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatry 2003, 74, 1667–1673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mignot, E.; Lammers, G.J.; Ripley, B.; Okun, M.; Nevsimalova, S.; Overeem, S.; Vankova, J.; Black, J.; Harsh, J.; Bassetti, C.; et al. The role of cerebrospinal fluid hypocretin measurement in the diagnosis of narcolepsy and other hypersomnias. Arch. Neurol. 2002, 59, 1553–1562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohayon, M.M.; Black, J.; Lai, C.; Eller, M.; Guinta, D.; Bhattacharyya, A. Increased mortality in narcolepsy. Sleep 2014, 37, 439–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jennum, P.; Thorstensen, E.W.; Pickering, L.; Ibsen, R.; Kjellberg, J. Morbidity and mortality of middle-aged and elderly narcoleptics. Sleep Med. 2017, 36, 23–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meigs, J.B. Epidemiology of the metabolic syndrome, 2002. Am. J. Manag. Care 2002, 8, S283–S292. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Dominguez, L.J.; Barbagallo, M. The biology of the metabolic syndrome and aging. Curr. Opin. Clin. Nutr. Metab. Care 2016, 19, 5–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shimamoto, K.; Ando, K.; Fujita, T.; Hasebe, N.; Higaki, J.; Horiuchi, M.; Imai, Y.; Imaizumi, T.; Ishimitsu, T.; Ito, M.; et al. The Japanese Society of Hypertension Guidelines for the Management of Hypertension (JSH 2014). Hypertens. Res. 2014, 37, 253–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Seino, Y.; Nanjo, K.; Tajima, N.; Kadowaki, T.; Kashiwagi, A.; Araki, E.; Ito, C.; Inagaki, N.; Iwamoto, Y.; Kasuga, M.; et al. Report of the committee on the classification and diagnostic criteria of diabetes mellitus. J. Diabetes Investig. 2010, 1, 212–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kinoshita, M.; Yokote, K.; Arai, H.; Iida, M.; Ishigaki, Y.; Ishibashi, S.; Umemoto, S.; Egusa, G.; Ohmura, H.; Okamura, T.; et al. Japan Atherosclerosis Society (JAS) Guidelines for Prevention of Atherosclerotic Cardiovascular Diseases 2017. J. Atheroscler. Thromb. 2018, 25, 846–984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Japan Society for the Study of Obesity. The 42th Annual Meeting of Japan Society for the Study of Obesity (JASSO 42)/The 39th Annual Meeting of the Japanese Society for Treatment of Obesity (JSTO 39). Available online: http://www.jasso.or.jp/contents/english/index.html (accessed on 10 April 2022).
- Kribbs, N.B.; Pack, A.I.; Kline, L.R.; Smith, P.L.; Schwartz, A.R.; Schubert, N.M.; Redline, S.; Henry, J.N.; Getsy, J.E.; Dinges, D.F. Objective measurement of patterns of nasal CPAP use by patients with obstructive sleep apnea. Am. Rev. Respir. Dis. 1993, 147, 887–895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pepin, J.L.; Krieger, J.; Rodenstein, D.; Cornette, A.; Sforza, E.; Delguste, P.; Deschaux, C.; Grillier, V.; Levy, P. Effective compliance during the first 3 months of continuous positive airway pressure. A European prospective study of 121 patients. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 1999, 160, 1124–1129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanda, Y. Investigation of the freely available easy-to-use software ‘EZR’ for medical statistics. Bone Marrow Transplant. 2013, 48, 452–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Eckel, R.H.; Grundy, S.M.; Zimmet, P.Z. The metabolic syndrome. Lancet 2005, 365, 1415–1428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schuld, A.; Hebebrand, J.; Geller, F.; Pollmacher, T. Increased body-mass index in patients with narcolepsy. Lancet 2000, 355, 1274–1275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ponziani, V.; Gennari, M.; Pizza, F.; Balsamo, A.; Bernardi, F.; Plazzi, G. Growing up with type 1 narcolepsy: Its anthropometric and endocrine features. J. Clin. Sleep Med. 2016, 12, 1649–1657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakamura, M.; Kanbayashi, T.; Sugiura, T.; Inoue, Y. Relationship between clinical characteristics of narcolepsy and CSF orexin-A levels. J. Sleep Res. 2011, 20, 45–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Z.; Wu, H.; Stone, W.S.; Zhuang, J.; Qiu, L.; Xu, X.; Wang, Y.; Zhao, Z.; Han, F.; Zhao, Z. Body weight and basal metabolic rate in childhood narcolepsy: A longitudinal study. Sleep Med. 2016, 25, 139–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Fronczek, R.; Overeem, S.; Reijntjes, R.; Lammers, G.J.; van Dijk, J.G.; Pijl, H. Increased heart rate variability but normal resting metabolic rate in hypocretin/orexin-deficient human narcolepsy. J. Clin. Sleep Med. 2008, 4, 248–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- National Health and Nutrition Survey (2018). Ministry of Health, Labor and Welfare, Japan. Available online: https://www.mhlw.go.jp/content/10900000/000688863.pdf (accessed on 10 April 2022).
- Ohayon, M.M. Narcolepsy is complicated by high medical and psychiatric comorbidities: A comparison with the general population. Sleep Med. 2013, 14, 488–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cohen, A.; Mandrekar, J.; St Louis, E.K.; Silber, M.H.; Kotagal, S. Comorbidities in a community sample of narcolepsy. Sleep Med. 2018, 43, 14–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kayaba, Y.; Nakamura, A.; Kasuya, Y.; Ohuchi, T.; Yanagisawa, M.; Komuro, I.; Fukuda, Y.; Kuwaki, T. Attenuated defense response and low basal blood pressure in orexin knockout mice. Am. J. Physiol. Integr. Comp. Physiol. 2003, 285, R581–R593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bastianini, S.; Silvani, A.; Berteotti, C.; Elghozi, J.L.; Franzini, C.; Lenzi, P.; Lo Martire, V.; Zoccoli, G. Sleep related changes in blood pressure in hypocretin-deficient narcoleptic mice. Sleep 2011, 34, 213–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dauvilliers, Y.; Jaussent, I.; Krams, B.; Scholz, S.; Lado, S.; Levy, P.; Pepin, J.L. Non-dipping blood pressure profile in narcolepsy with cataplexy. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e38977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drager, L.F.; Togeiro, S.M.; Polotsky, V.Y.; Lorenzi-Filho, G. Obstructive sleep apnea: A cardiometabolic risk in obesity and the metabolic syndrome. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2013, 62, 569–576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Coughlin, S.R.; Mawdsley, L.; Mugarza, J.A.; Calverley, P.M.A.; Wilding, J.P.H. Obstructive sleep apnoea is independently associated with an increased prevalence of metabolic syndrome. Eur. Heart J. 2004, 25, 735–741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wolf, J.; Hering, D.; Narkiewicz, K. Non-dipping pattern of hypertension and obstructive sleep apnea syndrome. Hypertens. Res. 2010, 33, 867–871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Mignot, E.; Hayduk, R.; Black, J.; Grumet, F.C.; Guilleminault, C. HLA DQB1*0602 is associated with cataplexy in 509 narcoleptic patients. Sleep 1997, 20, 1012–1020. [Google Scholar] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Andlauer, O.; Moore, H.T.; Hong, S.C.; Dauvilliers, Y.; Kanbayashi, T.; Nishino, S.; Han, F.; Silber, M.H.; Rico, T.; Einen, M.; et al. Predictors of hypocretin (orexin) deficiency in narcolepsy without cataplexy. Sleep 2012, 35, 1247–1255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Postiglione, E.; Barateau, L.; Pizza, F.; Lopez, R.; Antelmi, E.; Rassu, A.L.; Vandi, S.; Chenini, S.; Mignot, E.; Dauvilliers, Y.; et al. Narcolepsy with intermediate cerebrospinal level of hypocretin-1. Sleep 2022, 45, zsab285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakanishi, N.; Takatorige, T.; Suzuki, K. Cigarette smoking and the risk of the metabolic syndrome in middle-aged Japanese male office workers. Ind. Health 2005, 43, 295–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yokoyama, H.; Hiroshi, H.; Ohgo, H.; Hibi, T.; Saito, I. Effects of excessive ethanol consumption on the diagnosis of the metabolic syndrome using its clinical diagnostic criteria. Intern. Med. 2007, 46, 1345–1352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bosco, A.; Lopez, R.; Barateau, L.; Chenini, S.; Pesenti, C.; Pepin, J.L.; Jaussent, I.; Dauvilliers, Y. Effect of psychostimulants on blood pressure profile and endothelial function in narcolepsy. Neurology 2018, 90, e479–e491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- The National Institute of Health. What Is Metabolic Syndrome? Available online: https://www.nhlbi.nih.gov/health-topics/metabolic-syndrome (accessed on 10 April 2022).
| NT1 | NT2 [NT2P/NT2N] | IH | |
|---|---|---|---|
| n | 94 | 83 [36/47] | 57 |
| Mean age (SD) | 50.7 (14.4) *a, *b | 45.8 (7.8) [45.6 (7.9)/45.9 (7.8)] | 45.5 (9.6) |
| Sex: male (%) | 56 (59.6) | 45 (54.2) [13 (36.1) *c/32 (68.1)] | 35 (63.8) |
| BMI (SD) | 26.7 (4.4) *a, *b | 24.1 (2.1) [24.0 (1.6)/24.2 (2.5)] | 24.1 (4.3) |
| BMI ≥ 25 (%) | 54 (57.4) *d | 21 (25.3) *c [7 (19.4)/14 (29.8)] | 18 (31.6) |
| OSA with AHI ≥ 15/h (%) | 16 (17.0) | 10 (12.0) [5 (13.9)/5 (10.6)] | 9 (15.8) |
| NT1 | NT2 [NT2P/NT2N] | IH | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Hypertension (%) | 46 (48.9) *a | 22 (26.5) *b [14 (38.9) *a/8 (17.0)] | 18 (31.6) |
| Diabetes (%) | 22 (23.4) | 10 (12.0) [7 (19.4)/3 (6.4)] | 6 (10.5) |
| Dyslipidemia (%) | 24 (25.5) | 17 (20.5) [13 (36.1) *a/4 (8.5) *b] | 9 (15.8) |
| MRD (%) | 55 (58.5) *c | 33 (39.8) [20 (55.6) *a/13 (27.7)] | 26 (45.6) |
| Odds Ratio | 95% Confidence Interval | p-Value | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Age | 0.95 | 0.93–0.98 | <0.01 * |
| Sex: male | 1.47 | 0.82–2.64 | 0.20 |
| BMI | 0.85 | 0.78–0.93 | <0.01 * |
| OSA with AHI ≥ 15/h | 2.50 | 1.04–6.00 | <0.05 * |
| Category of NSD | 0.73 | ||
| NT1 (ref. IH) | 0.99 | 0.46–2.16 | 0.99 |
| NT2 (ref. IH) | 1.27 | 0.60–2.66 | 0.53 |
| Odds Ratio | 95% Confidence Interval | p-Value | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Age | 1.05 | 1.01–1.09 | <0.01 * |
| Sex: male | 1.16 | 0.45–3.01 | 0.77 |
| BMI | 1.13 | 1.01–1.27 | <0.05 * |
| OSA with AHI ≥ 15/h | 3.84 | 0.74–20.00 | 0.11 |
| Odds Ratio | 95% Confidence Interval | p-Value | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Age | 1.03 | 0.97–1.10 | 0.32 |
| Sex: male | 0.51 | 0.18–1.45 | 0.21 |
| BMI | 1.49 | 1.09–2.02 | <0.05 * |
| OSA with AHI ≥ 15/h | 1.07 | 0.21–5.54 | 0.93 |
| HLA DQB1*06:02 positivity | 3.64 | 1.28–10.40 | <0.05 * |
| Odds Ratio | 95% Confidence Interval | p-Value | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Age | 1.09 | 1.01–1.18 | <0.05 * |
| Sex: male | 0.53 | 0.15–1.90 | 0.33 |
| BMI | 1.17 | 0.99–1.38 | 0.07 |
| OSA with AHI ≥ 15/h | 2.42 | 0.43–13.60 | 0.32 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Futenma, K.; Takaesu, Y.; Nakamura, M.; Hayashida, K.; Takeuchi, N.; Inoue, Y. Metabolic-Syndrome-Related Comorbidities in Narcolepsy Spectrum Disorders: A Preliminary Cross-Sectional Study in Japan. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 6285. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph19106285
Futenma K, Takaesu Y, Nakamura M, Hayashida K, Takeuchi N, Inoue Y. Metabolic-Syndrome-Related Comorbidities in Narcolepsy Spectrum Disorders: A Preliminary Cross-Sectional Study in Japan. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health. 2022; 19(10):6285. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph19106285
Chicago/Turabian StyleFutenma, Kunihiro, Yoshikazu Takaesu, Masaki Nakamura, Kenichi Hayashida, Noboru Takeuchi, and Yuichi Inoue. 2022. "Metabolic-Syndrome-Related Comorbidities in Narcolepsy Spectrum Disorders: A Preliminary Cross-Sectional Study in Japan" International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health 19, no. 10: 6285. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph19106285
APA StyleFutenma, K., Takaesu, Y., Nakamura, M., Hayashida, K., Takeuchi, N., & Inoue, Y. (2022). Metabolic-Syndrome-Related Comorbidities in Narcolepsy Spectrum Disorders: A Preliminary Cross-Sectional Study in Japan. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 19(10), 6285. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph19106285







