Accounting for Sampling Weights in the Analysis of Spatial Distributions of Disease Using Health Survey Data, with an Application to Mapping Child Health in Malawi and Mozambique
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methods
2.1. General Notation
2.2. The Horvitz–Thompson Estimator
2.3. Bayesian Hierarchical Spatial Smoothing Models
2.4. Incorprating Survey Sampling Weights in Hierarchical Spatial Model Analysis
2.5. Bayesian Inference, Computation, and Model Evaluation
3. Application
3.1. Data Sources: Malawi and Mozambique
3.2. Outcomes
3.3. Malawi: District Variation in the Prevalence of Child Malnutrition
3.4. Mozambique: Pronvicial Variations in the Prevalence Child Fver and Diarrhoea
4. Discussion and Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| AS | Arcsine square-root transformation |
| DEFF | Design effect |
| DIC | Deviance information criterion |
| EAs | Enumeration areas |
| ES | Effective sample size |
| ES-deff | Effective sample size using design effect |
| GMRF | Gaussian random field |
| HT | Horvitz–Thompson |
| ICAR | Intrinsic conditional autoregressive |
| IMASIDA | Indicators of Immunization, Malaria and HIV/AIDS Survey |
| INLA | Integrated nested Laplace approximations |
| LN | Logit Normal |
| MCMC | Markov chain Monte Carlo |
| MDHS | Malawi Demographic and Health Survey |
| PL | Pseudo-likelihood |
| PSUs | Primary sample units |
| SAE | Small area estimation |
| SDGs | Sustainable Development Goals |
| SSA | Sub Saharan Africa |
| UB | Unadjusted binomial |
| UW | Unweighted |
| WHO | World Health Organization |
Appendix A. The Integrated Nested Laplace Approximation
Appendix B
Appendix B.1. Malawi Results
| Stunting | Wasting | Underweight | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| District | N. Respondents | (Stunted, %) | N. Respondents | (Wasted, %) | N. Respondents | (Underweighted,%) |
| Chitipa | 139 | 43 (33.08) | 144 | 2 (1.39) | 141 | 18 (13.89) |
| Karonga | 142 | 38 (28.00) | 143 | 2 (1.56) | 144 | 14 (9.18) |
| Nkhata Bay | 149 | 47 (31.33) | 150 | 1 (0.17) | 152 | 10 (5.89) |
| Rumphi | 147 | 44 (31.87) | 147 | 3 (1.74) | 147 | 20 (13.75) |
| Mzimba | 158 | 70 (44.79) | 159 | 5 (3.19) | 158 | 22 (13.45) |
| Likoma | 128 | 33 (26.99) | 128 | 5 (4.26) | 129 | 11 (9.13) |
| Mzuzu City | 39 | 7 (15.44) | 39 | 1 (2.72) | 39 | 1 (2.72) |
| Kasungu | 211 | 73 (35.90) | 215 | 5 (2.73) | 216 | 14 (6.56) |
| Nkhotakota | 202 | 69 (32.58) | 204 | 7 (1.82) | 202 | 32 (13.05) |
| Ntchisi | 181 | 68 (40.55) | 182 | 4 (1.80) | 186 | 20 (11.53) |
| Dowa | 199 | 74 (39.42) | 199 | 2 (1.05) | 200 | 17 (9.31) |
| Salima | 212 | 78 (36.75) | 214 | 4 (1.60) | 213 | 28 (13.81) |
| Lilongwe Rural | 147 | 63 (43.28) | 149 | 1 (0.64) | 150 | 14 (9.42) |
| Mchinji | 210 | 95 (45.88) | 214 | 8 (3.35) | 213 | 26 (12.20) |
| Dedza | 177 | 72 (41.18) | 177 | 5 (2.85) | 179 | 28 (15.41) |
| Ntcheu | 200 | 78 (40.77) | 199 | 8 (3.74) | 201 | 26 (12.99) |
| Lilongwe City | 74 | 15 (19.55) | 74 | 3 (4.14) | 74 | 6 (8.07) |
| Mangochi | 244 | 107 (44.33) | 246 | 2 (0.90) | 255 | 32 (12.08) |
| Machinga | 247 | 95 (38.50) | 247 | 9 (3.71) | 253 | 40 (15.58) |
| Zomba Rural | 182 | 67 (36.90) | 179 | 8 (4.50) | 183 | 22 (11.93) |
| Chiradzulu | 140 | 48 (33.62) | 144 | 9 (6.53) | 145 | 19 (12.81) |
| Blantyre Rural | 86 | 28 (32.84) | 87 | 5 (5.53) | 86 | 7 (8.00) |
| Mwanza | 143 | 46 (31.24) | 143 | 12 (7.03) | 150 | 23 (14.55) |
| Thyolo | 151 | 54 (34.43) | 149 | 6 (3.78) | 150 | 22 (13.29) |
| Mulanje | 172 | 66 (36.91) | 172 | 6 (3.58) | 174 | 29 (16.30) |
| Phalombe | 211 | 68 (33.09) | 216 | 4 (2.03) | 212 | 21 (10.31) |
| Chikwawa | 180 | 55 (30.18) | 181 | 8 (4.80) | 184 | 21 (11.27) |
| Nsanje | 159 | 48 (31.70) | 161 | 17 (9.92) | 162 | 27 (18.85) |
| Balaka | 213 | 69 (32.73) | 212 | 0 (0.00) | 214 | 26 (13.19) |
| Neno | 165 | 72 (45.28) | 164 | 7 (4.70) | 168 | 30 (18.44) |
| Zomba City | 49 | 8 (17.75) | 48 | 3 (5.56) | 50 | 1 (1.93) |
| Blantyre City | 92 | 28 (30.47) | 92 | 2 (2.10) | 93 | 7 (7.57) |
| Total | 5149 | 1826 (36.82) | 5178 | 164 (2.79) | 5223 | 634 (11.58) |
Appendix B.2. Mozambique Results
| Fever | Diarrhea | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| District | N. Respondents | (N, %) | N. Respondents | (N, %) |
| Niassa | 546 | 146 (30.16) | 546 | 94 (17.19) |
| Cabo Delgado | 380 | 86 (21.94) | 383 | 37 (9.90) |
| Nampula | 595 | 228 (39.49) | 597 | 64 (11.28) |
| Zambezia | 555 | 264 (51.67) | 556 | 90 (16.95) |
| Tete | 448 | 65 (14.37) | 449 | 39 (6.80) |
| Manica | 479 | 81 (16.59) | 479 | 43 (8.90) |
| Sofala | 505 | 109 (21.58) | 506 | 46 (8.43) |
| Inhambane | 323 | 68 (18.23) | 323 | 27 (7.24) |
| Gaza | 530 | 141 (27.00) | 530 | 61 (11.79) |
| Maputo Provincia | 340 | 53 (15.86) | 340 | 23 (8.25) |
| Maputo Cidade | 271 | 70 (24.99) | 271 | 28 (9.99) |
| Total | 4972 | 1311 (29.37) | 4980 | 549 (11.11) |
References
- Giorgi, E.; Diggle, P.J.; Snow, R.W.; Noor, A.M. Geostatistical Methods for Disease Mapping and Visualisation Using Data from Spatio-temporally Referenced Prevalence Surveys. Int. Stat. Rev. 2018, 86, 571–597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Manda, S.; Haushona, N.; Bergquist, R. A scoping review of spatial analysis approaches using health survey data in sub-Saharan Africa. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 3070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Okango, E.; Mwambi, H.; Ngesa, O. Spatial modeling of HIV and HSV-2 among women in Kenya with spatially varying coefficients. BMC Public Health 2016, 16, 355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Chen, C.; Wakefield, J.; Lumely, T. The use of sampling weights in Bayesian hierarchical models for small area estimation. Spat. Spatiotemporal. Epidemiol. 2014, 11, 33–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mercer, L.D.; Wakefield, J.; Chen, C.; Lumley, T. A comparison of spatial smoothing methods for small area estimation with sampling weights. Spat. Stat. 2014, 8, 69–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vandendijck, Y.; Faes, C.; Kirby, R.S.; Lawson, A.; Hens, N. Model-based inference for small area estimation with sampling weights. Spat. Stat. 2016, 18, 455–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Watjou, K.; Faes, C.; Lawson, A.; Kirby, R.S.; Aregay, M.; Carroll, R.; Vandendijck, Y. Spatial small area smoothing models for handling survey data with nonresponse. Stat. Med. 2017, 36, 3708–3745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- NSO Malawi Demographic and Health Survey 2015–16; National Statistical Office: Zomba, Malawi; The DHS Program ICF: Rockville, MD, USA, 2017; pp. 1–658.
- MISAU. INE Inquérito de Indicadores de Imunização, Malária e HIV SIDA em Moçambique (IMASIDA)-2015; INS: Maputo, Mozambique, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Lumley, T. Analysis of complex survey samples. J. Stat. Softw. 2004, 9, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horvitz, D.G.; Thompson, D.J. A Generalization of Sampling without Replacement from a Finite Universe. Am. Stat. Assoc. 1952, 47, 663–685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ICF International. Demographic and Health Survey Sampling and Household Listing Manual; MEASURE DHS: Rockville, MD, USA, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Rao, J.N.; Molina, I. Small Area Estimation; Jonh Wiley & Wiley Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Pfeffermann, D. New important developments in small area estimation. Stat. Sci. 2013, 28, 40–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Besag, J.; York, J.; Mollié, A. Bayesian image restoration, with two applications in spatial statistics. Ann. Inst. Stat. Math. 1991, 43, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rue, H.; Martino, S. Approximate Bayesian inference for latent Gaussian models by using integrated nested Laplace approximations. J. R. Stat. Soc. Ser. B Stat. Methodol. 2009, 71, 319–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raghunathan, T.E.; Xie, D.; Schenker, N.; Van Parsons, L.; Davis, W.W.; Dodd, K.W.; Feuer, E.J. Combining information from two surveys to estimate county-level prevalence rates of cancer risk factors and screening. J. Am. Stat. Assoc. 2007, 102, 474–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rabe-Hesketh, S.; Skrondal, A. Multilevel modelling of complex survey data. J. R. Stat. Soc. Ser. A Stat. Soc. 2006, 169, 805–827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kish, L. Methods for design effects. J. Off. Stat. 1995, 11, 55–77. [Google Scholar]
- Schrödle, B.; Held, L. Spatio-temporal disease mapping using INLA. Environmetrics 2011, 22, 725–734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bivand, R.; Gómez-Rubio, V.; Rue, H. Spatial Data Analysis with R-INLA with Some Extensions. J. Stat. Softw. 2015, 68, 1–31. [Google Scholar]
- Blangiardo, M.; Cameletti, M. Spatial and Spatio-Temporal Bayesian Models with R-INLA; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2015; ISBN 1118326555. [Google Scholar]
- Spiegelhalter, D.J.; Best, N.G.; Carlin, B.P.; Van Der Linde, A. Bayesian measures of model complexity and fit. J. R. Stat. Soc. Ser. B Stat. Methodol. 2002, 64, 583–639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- UNICEF. The State of the World’s Children 2019. Children, Food and Nutrition: Growing well in a Changing World. 2019. Available online: https://data.unicef.org/resources/state-of-the-worlds-children-2019/ (accessed on 21 July 2021).
- World Health Organization. Levels and Trends in Child Malnutrition. Joint Child Malnutrition Estimates. Key Findings of the 2017. Available online: https://www.unscn.org/en/resource-center/global-trends-and-emerging-issues?idnews=1709 (accessed on 21 July 2021).
- Institute for Health Metrics and Evaluation GBD Compare 2018. Available online: https://www.healthdata.org/gbd/publications (accessed on 21 July 2021).
- UNICEF. DATA Diarrhoeal Disease-UNICEF DATA 2019. Available online: https://data.unicef.org/topic/child-health/diarrhoeal-disease/ (accessed on 21 July 2021).
- United Nations. The Sustainable Development Goals Report 2016; UN: New York, NY, USA, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- World Health Organization. High risk group. Available online: https://www.who.int/ (accessed on 21 July 2021).
- Orunmoluyi, O.S.; Gayawan, E.; Manda, S. Spatial Co-Morbidity of Childhood Acute Respiratory Infection, Diarrhoea and Stunting in Nigeria. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 1838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kinyoki, D.K.; Kandala, N.B.; Manda, S.O.; Krainski, E.T.; Fuglstad, G.A.; Moloney, G.M.; Berkley, J.A.; Noor, A.M. Assessing comorbidity and correlates of wasting and stunting among children in Somalia using cross-sectional household surveys: 2007 to 2010. BMJ Open 2016, 6, e009854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


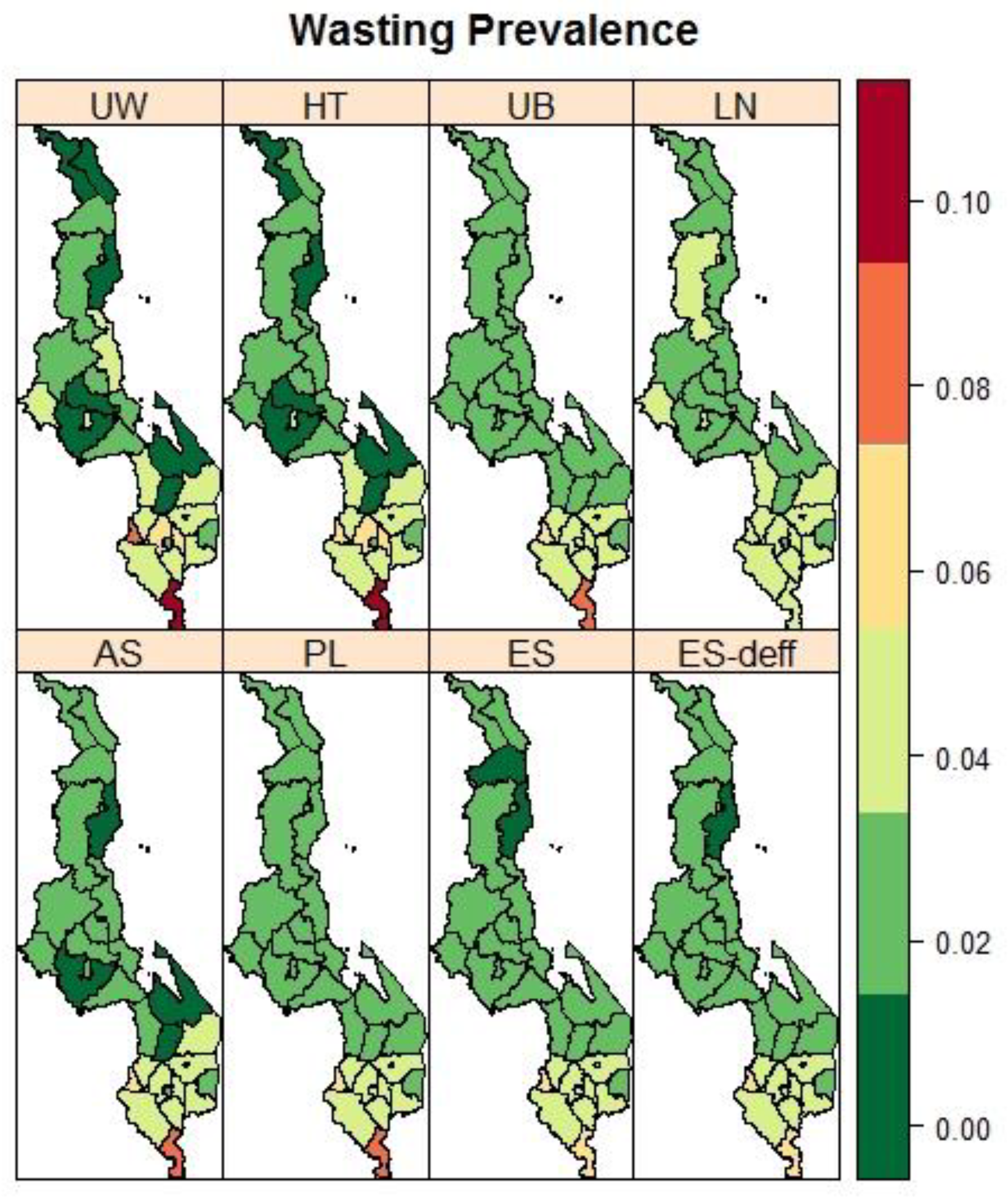
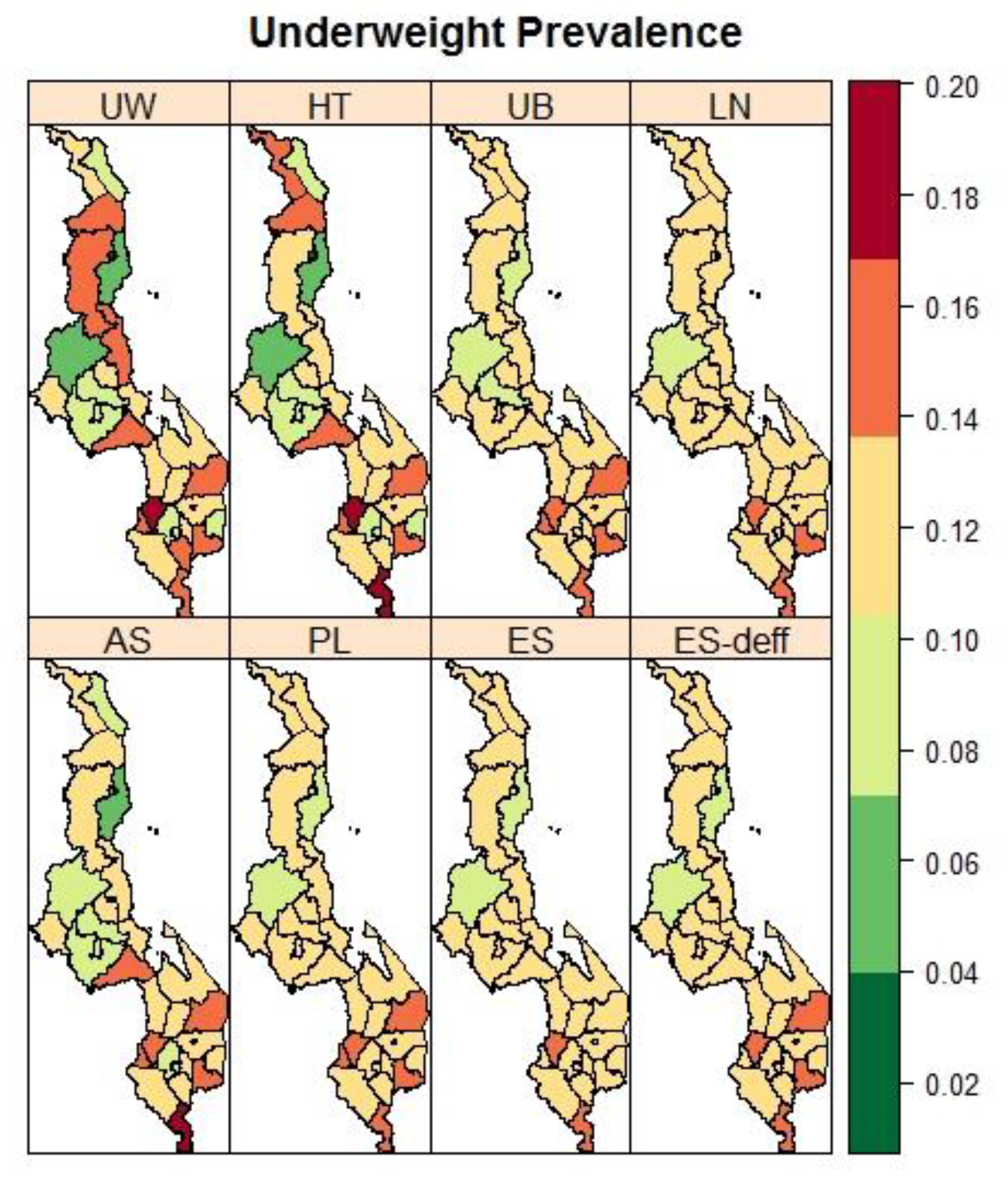
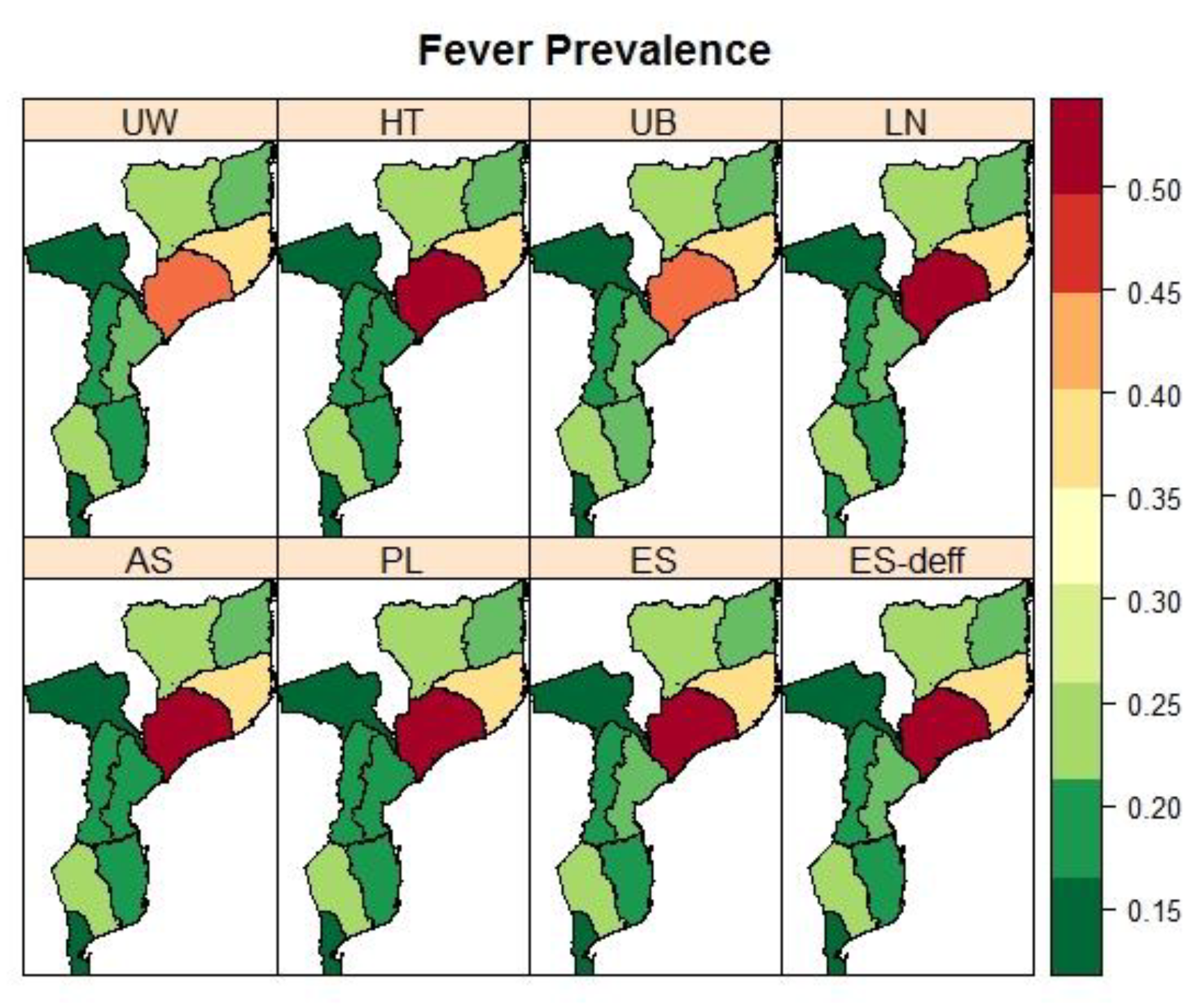
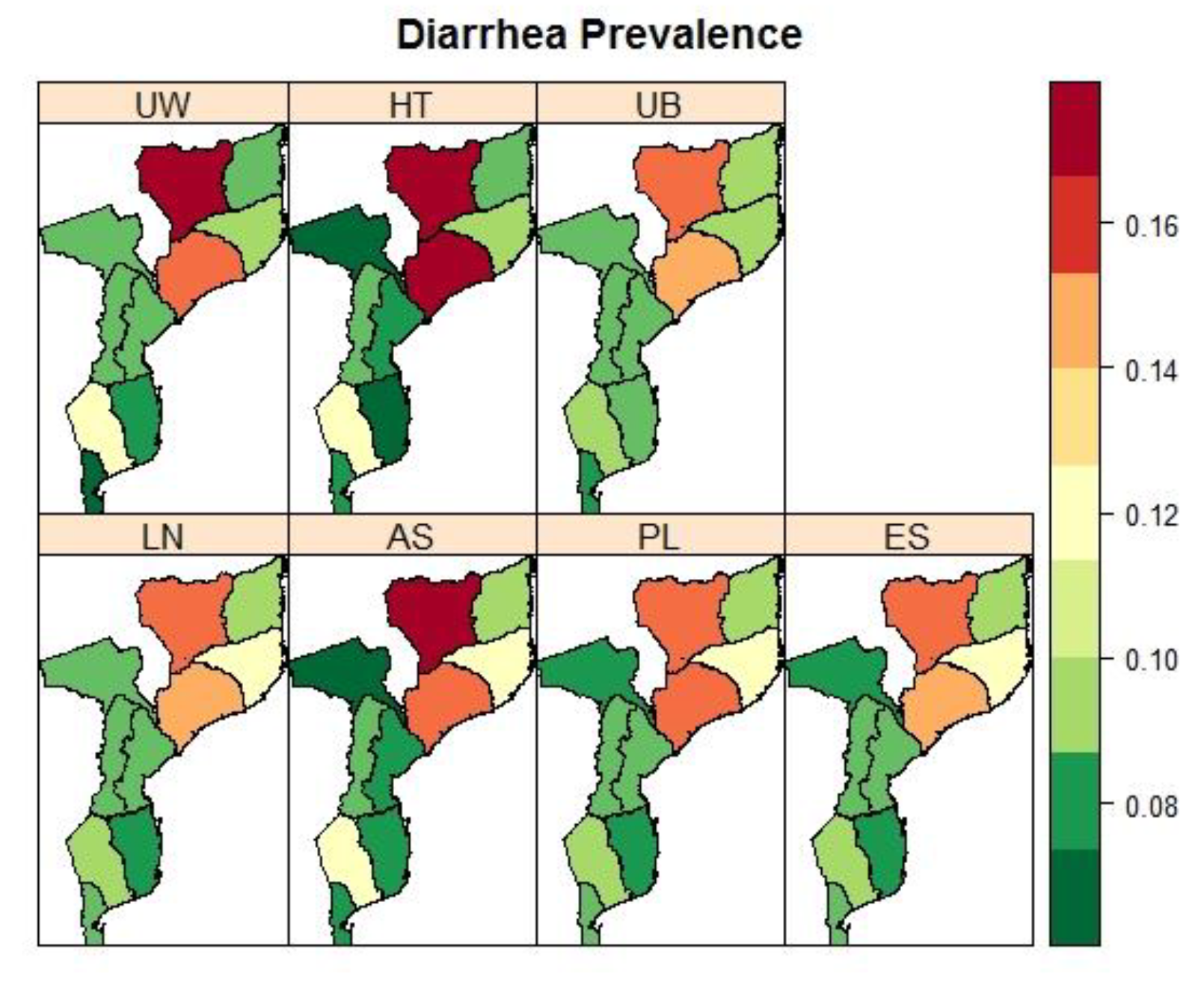
| Parameters | Model 1 | Model 2 | Model 3 | Model 4 | Model 5 | Model 6 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| (CI) | −0.605 | −0.585 | 0.634 | −0.607 | −0.594 | −0.609 |
| (−0.706; −0.547) | (−0.67; −0.505) | (0.608; 0.659) | (−0.691; −0.526) | (−0.68; −0.512) | (−0.694; −0.528) | |
| Sd | 0.04 | 0.042 | 0.013 | 0.042 | 0.043 | 0.042 |
| 0.210 | 0.170 | 0.069 | 0.219 | 0.188 | 0.218 | |
| 0.114 | 0.115 | 0.053 | 0.125 | 0.125 | 0.126 | |
| −135.88 | −24.45 | 12.88 | −137.78 | −133.44 | −137.21 | |
| 18.54 | 16.47 | 23.56 | 19.55 | 17.64 | 19.32 | |
| 226.85 | 6.24 | −86.69 | 229.23 | 222.80 | 228.22 |
| Parameters | Model 1 | Model 2 | Model 3 | Model 4 | Model 5 | Model 6 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| (CI) | −3.514 | −3.458 | 0.166 | −3.577 | −3.658 | −3.609 |
| (−3.715; −3.325) | (−3.661; −3.257) | (0.143; 0.19) | (−3.78; −3.386) | (−3.87; −3.457) | (−3.814; −3.416) | |
| Sd | 0.099 | 0.103 | 0.012 | 0.1 | 0.105 | 0.101 |
| 0.493 | 0.353 | 0.061 | 0.486 | 0.519 | 0.467 | |
| 0.148 | 0.121 | 0.0481 | 0.144 | 0.152 | 0.143 | |
| −95.22 | −48.39 | 18.11 | −94.04 | −93.43 | −92.31 | |
| 13.94 | 9.68 | 22.59 | 13.13 | 13.22 | 12.44 | |
| 150.84 | 60.80 | −94.76 | 148.73 | 147.06 | 145.98 |
| Parameters | Model 1 | Model 2 | Model 3 | Model 4 | Model 5 | Model 6 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| (CI) | −2 | −1.981 | 0.344 | −2.003 | −2.022 | −2.008 |
| (−2.109; –1.897) | (−2.09; −1.877) | (0.32; 0.368) | (−2.112; −1.901) | (−2.133;−1.916) | (−2.116; −1.905) | |
| Sd | 0.054 | 0.054 | 0.012 | 0.053 | 0.055 | |
| 0.1390 | 0.1197 | 0.0634 | 0.1523 | 0.1400 | 0.1420 | |
| 0.1371 | 0.1139 | 0.0495 | 0.1286 | 0.1261 | 0.1321 | |
| −117.62 | −29.98 | 15.99 | −117.38 | −113.23 | −115.35 | |
| 13.38 | 10.42 | 22.91 | 13.41 | 12.23 | 12.91 | |
| 197.75 | 24.96 | −89.77 | 197.28 | 190.55 | 193.68 |
| Parameters | Model 1 | Model 2 | Model 3 | Model 4 | Model 5 | Model 6 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| (CI) | −1.137 | −1.123 | 0.523 | −1.129 | −1.13 | −1.13 |
| (−1.433; −0.844) | (−1.453; −1.123) | (−0.45; 0.597) | (−1.496; −0.767) | (−1.458; −0.805) | (−1.458; −0.805) | |
| Sd | 0.146 | 0.162 | 0.036 | 0.183 | 0.161 | |
| 0.1734 | 0.1863 | 0.1046 | 0.1854 | 0.1848 | 0.1848 | |
| 0.4660 | 0.5123 | 0.1094 | 0.5241 | 0.5172 | 0.5172 | |
| −62.86 | −16.20 | −0.834 | −63.98 | −61.28 | −61.28 | |
| 10.52 | 10.28 | 10.66 | 10.60 | 10.50 | 10.50 | |
| 89.60 | 0.135 | −37.64 | 89.54 | 86.86 | 86.86 |
| Parameters | Model 1 | Model 2 | Model 3 | Model 4 | Model 5 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| (CI) | −2.145 | −2.14 | 0.329 | −1.945 | −2.152 |
| (−2.319;−1.979) | (−2.335; −1.956) | (0.283; 0.374) | (−2.189; −1.708) | (−2.34; −1.975) | |
| Sd | 0.085 | 0.095 | 0.023 | 0.118 | 0.091 |
| 0.1651 | 0.1799 | 0.0748 | 0.2303 | 0.1724 | |
| 0.2257 | 0.2231 | 0.0640 | 0.3438 | 0.2442 | |
| −50.27 | −10.40 | 4.37 | −53.70 | −48.96 | |
| 8.75 | 7.90 | 10.15 | 9.83 | 8.64 | |
| 81.04 | 4.30 | −39.23 | 81.71 | 78.83 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Cassy, S.R.; Manda, S.; Marques, F.; Martins, M.d.R.O. Accounting for Sampling Weights in the Analysis of Spatial Distributions of Disease Using Health Survey Data, with an Application to Mapping Child Health in Malawi and Mozambique. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 6319. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph19106319
Cassy SR, Manda S, Marques F, Martins MdRO. Accounting for Sampling Weights in the Analysis of Spatial Distributions of Disease Using Health Survey Data, with an Application to Mapping Child Health in Malawi and Mozambique. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health. 2022; 19(10):6319. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph19106319
Chicago/Turabian StyleCassy, Sheyla Rodrigues, Samuel Manda, Filipe Marques, and Maria do Rosário Oliveira Martins. 2022. "Accounting for Sampling Weights in the Analysis of Spatial Distributions of Disease Using Health Survey Data, with an Application to Mapping Child Health in Malawi and Mozambique" International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health 19, no. 10: 6319. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph19106319
APA StyleCassy, S. R., Manda, S., Marques, F., & Martins, M. d. R. O. (2022). Accounting for Sampling Weights in the Analysis of Spatial Distributions of Disease Using Health Survey Data, with an Application to Mapping Child Health in Malawi and Mozambique. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 19(10), 6319. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph19106319









