Leachate Pretreatment before Pipe Transportation: Reduction of Leachate Clogging Potential and Upgrading of Landfill Gas
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Material and Column
2.2. Analytical Procedures
2.3. Main Experimental Methods
- (1)
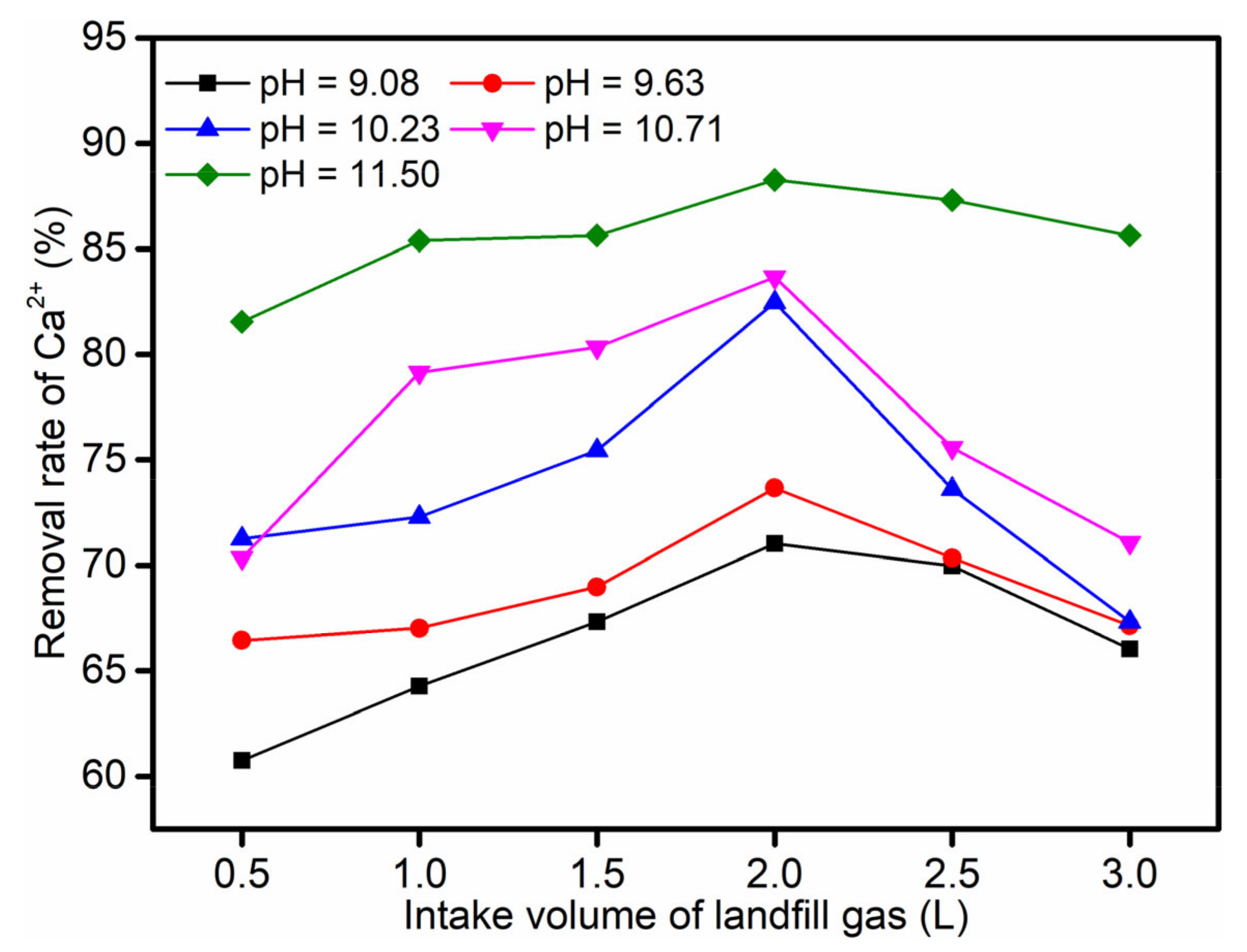
- Examining the volume of the landfill gas, the landfill gas intake flow rate was set at 0.05 L/min, and the leachate pH was adjusted to about 9.08, 9.63, 10.23, 10.71, and 11.50. The intake volumes were 0.5, 1.0, 1.5, 2.0, 2.5, and 3.0 L, respectively.
- (2)
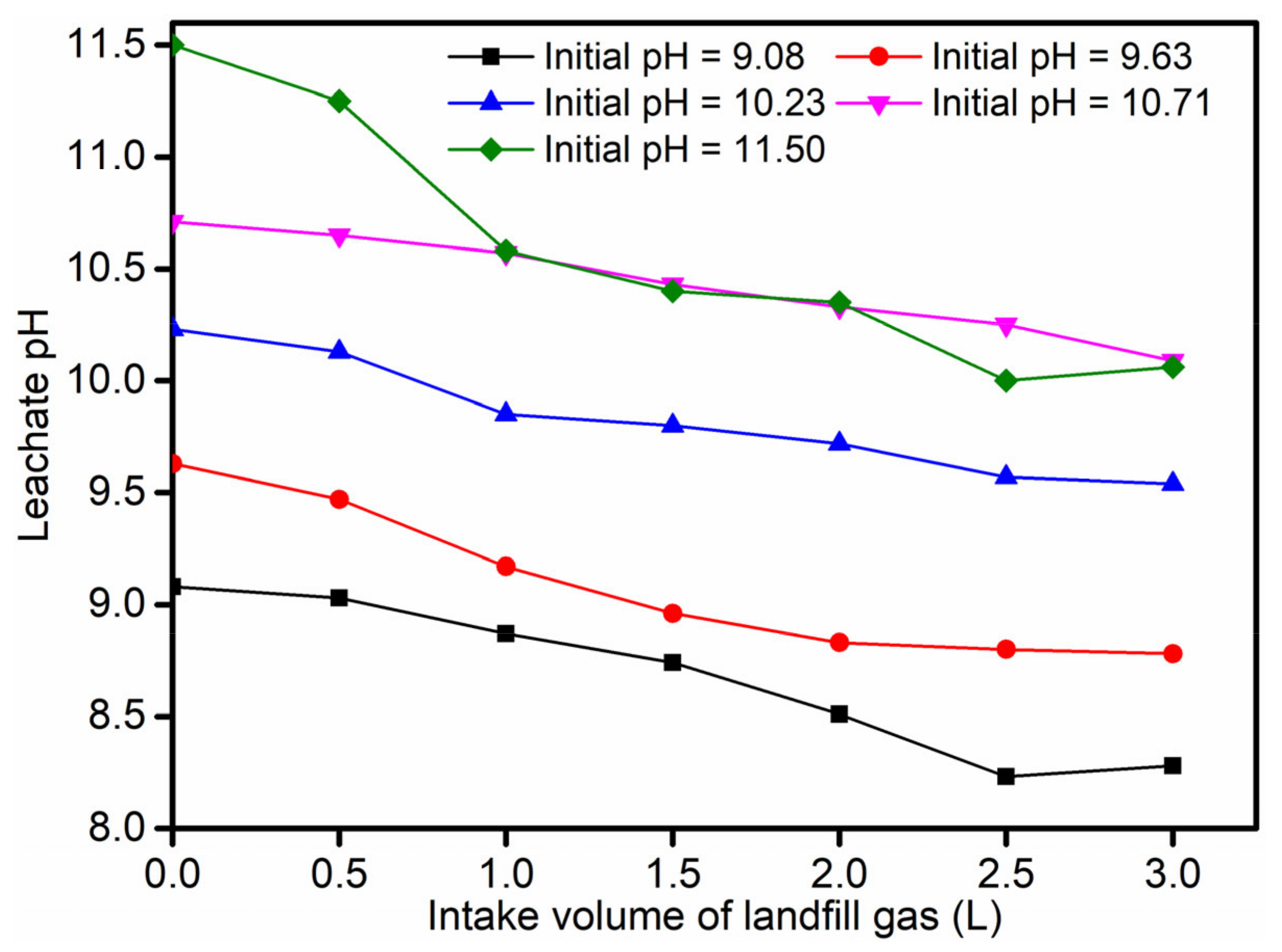
- Examining the intake flow rate of the landfill gas, the landfill gas volume was set at 2.0 L, and the pH of the leachate was adjusted to about 9.08, 9.63, 10.23, 10.71, and 11.50. The landfill gas intake flow rates were 0.05, 0.08, 0.1, 0.2, and 0.4 L/min, respectively.
- (3)
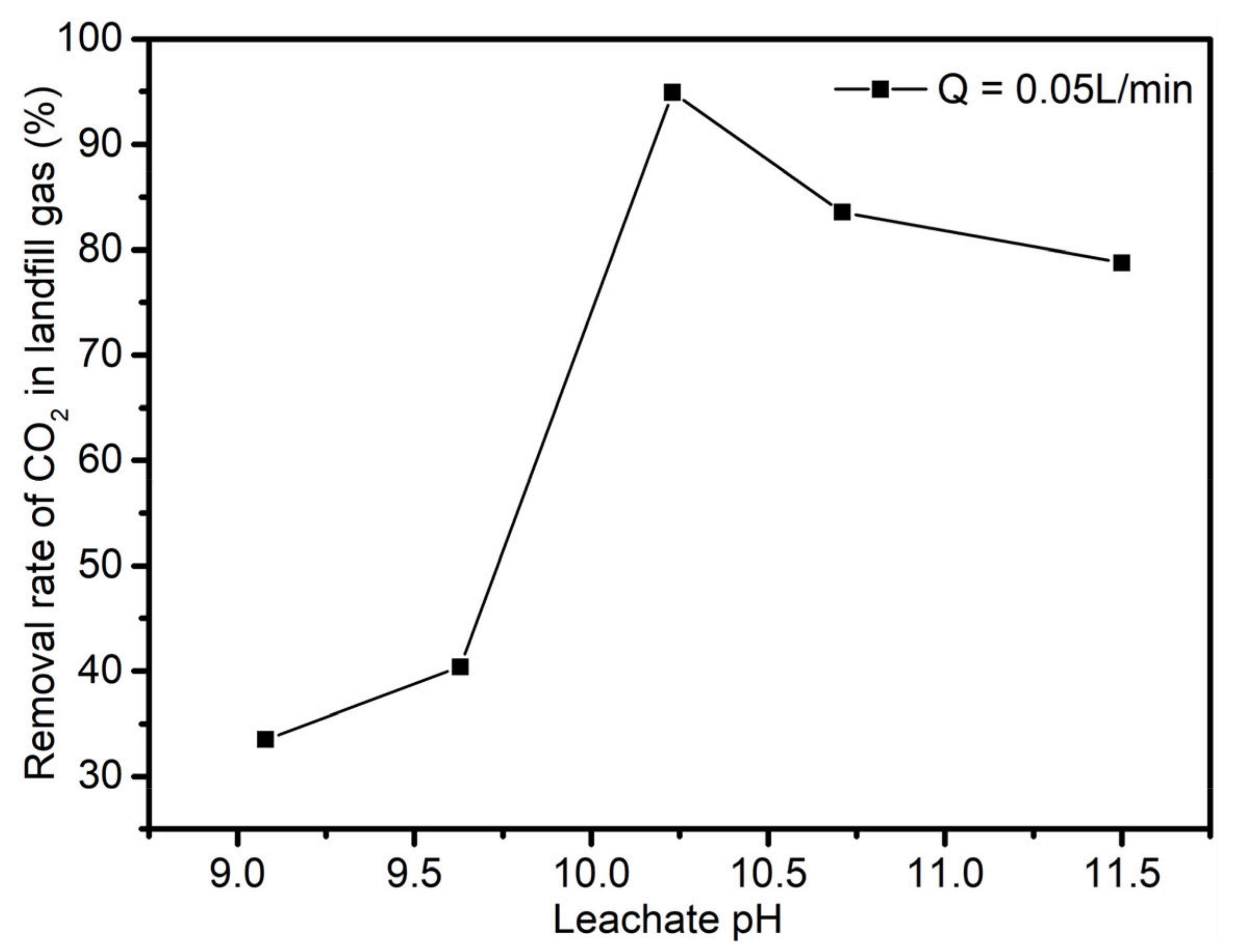
- Examining the pH of the leachate, the landfill gas intake volume was set at 2.0 L, and the landfill gas intake flow rates were set at 0.05, 0.08, 0.1, 0.2, and 0.4 L/min. The leachate pH was adjusted to about 9.08, 9.63, 10.23, 10.71, and 11.50, respectively.
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Effect of Volume of Landfill Gas Intake on the Rate of Calcium Removal
3.2. Effect of Landfill Gas Intake Flow Rate and Leachate pH on the Removal Rate of Calcium
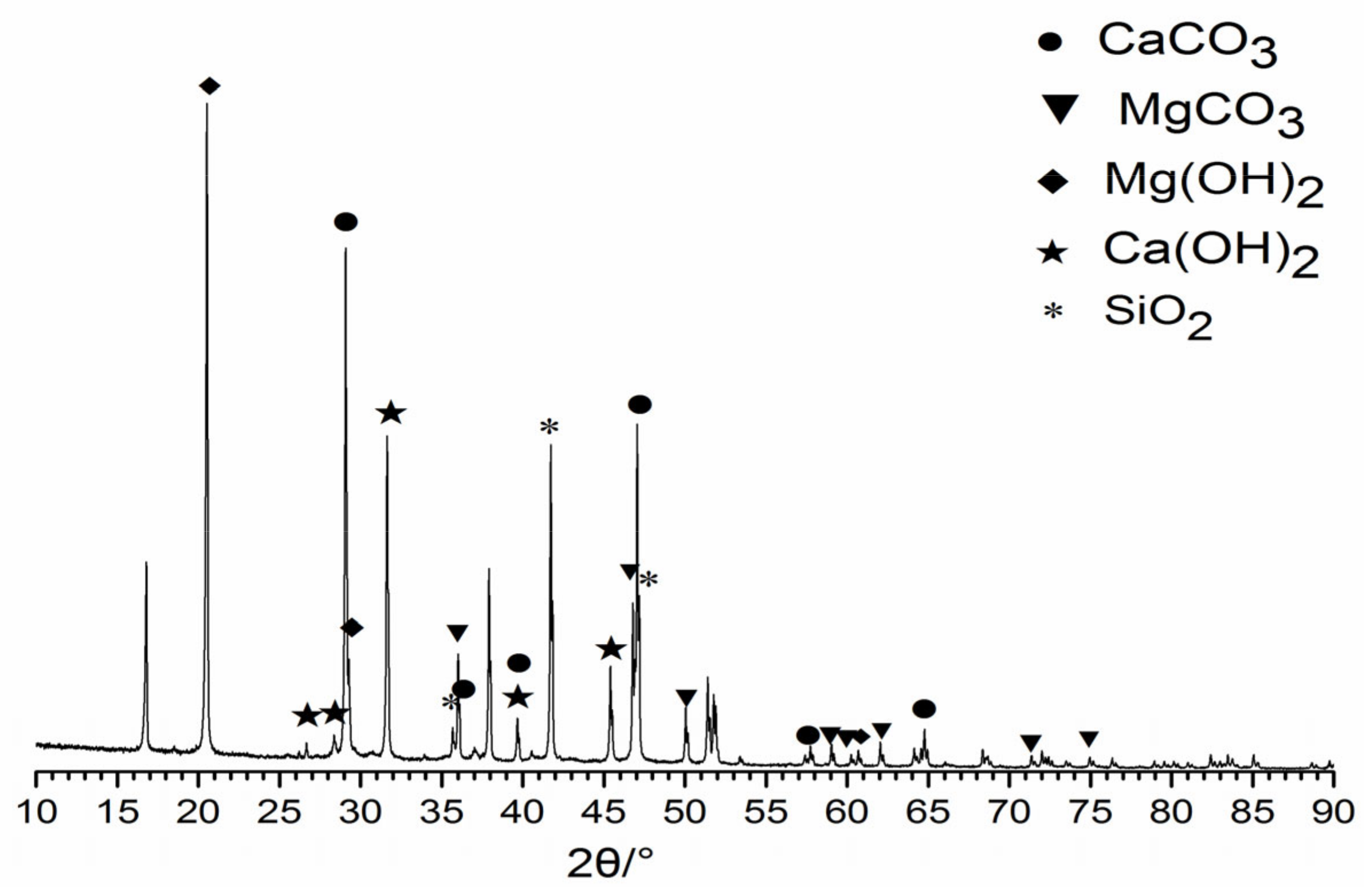
3.3. Characterizations of Precipitates
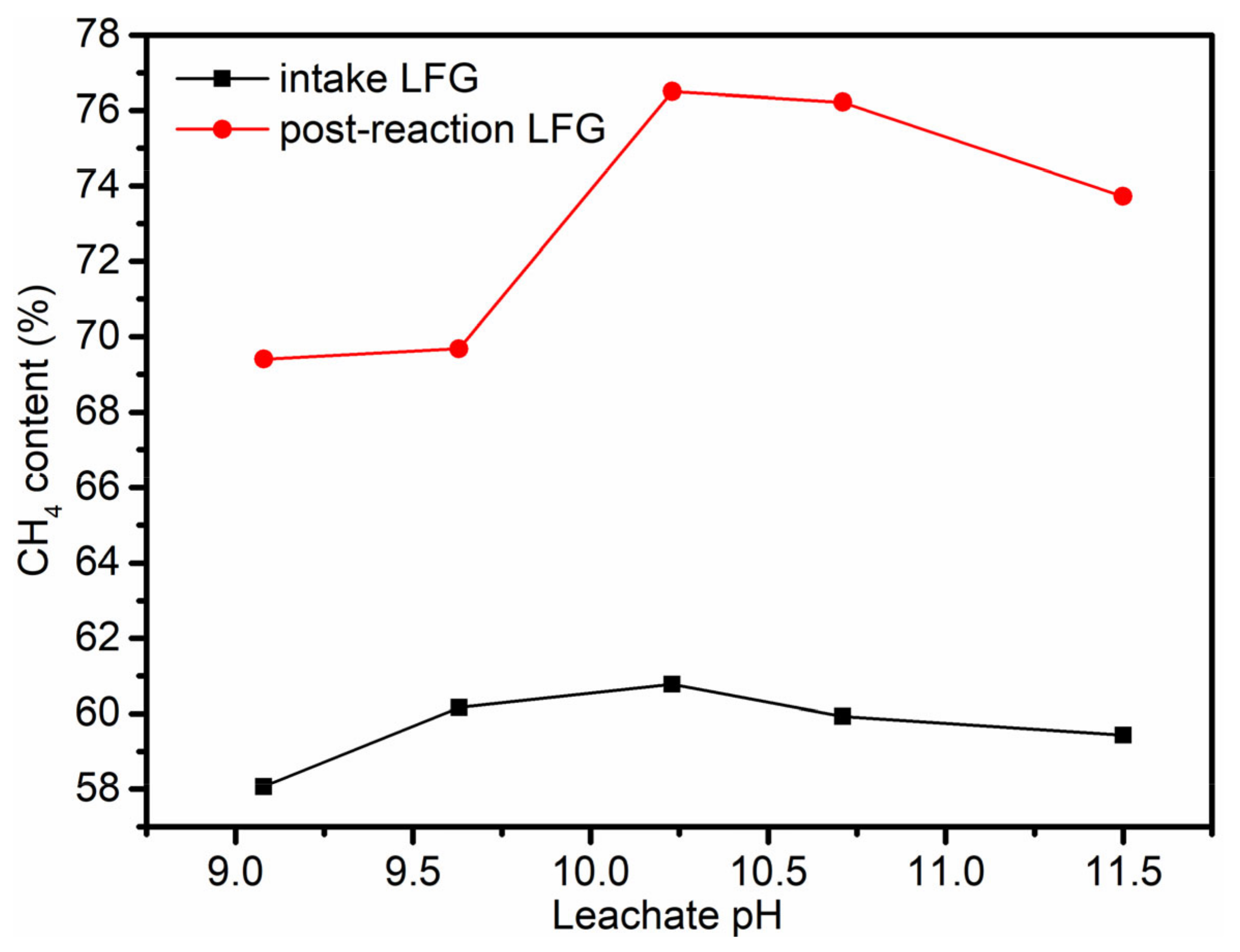
3.4. Analysis of CO2 and CH4 Content Changes in Landfill Gas
4. Conclusions
- (1)
- Most Ca2+ is removed prior to the leachate pipe transportation. This improves the service life of the relevant facilities and avoids the environmental pollution caused by the clogging of leachate pipes.
- (2)
- The CO2 component of the landfill gas was mostly removed, and the upgrade of landfill gas increased its calorific value, laying the foundation for the energy utilization of landfill gas.
- (3)
- CO2 is one of the main greenhouse gases, and landfills are one of its main sources; it is fixed by means of carbonate precipitation so as to reduce greenhouse gas emission.
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ke, H.; Hu, J.; Xu, X.B.; Wang, W.F.; Chen, Y.M.; Zhan, L.T. Evolution of saturated hydraulic conductivity with compression and degradation for municipal solid waste. Waste Manag. 2017, 65, 63–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, S.W.; Fu, G.F.; Zhu, X.J.; He, H.P. Temperature influence on the permeability of clay liner for landfills. J. Yangzhou Univ. 2018, 21, 17–21. [Google Scholar]
- Zhan, T.L.T.; Guan, C.; Xie, H.J.; Chen, Y.M. Vertical migration of leachate pollutants in clayey soils beneath an uncontrolled landfill at Huainan, China: A field and theoretical investigation. Sci. Total Environ. 2014, 470, 290–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rowe, R.K.; Yu, Y. Modeling of leachate collection systems with filter separators in municipal solid waste landfills. J. Environ. Eng. 2013, 139, 1042–1052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rowe, R.K.; Quigley, R.M.; Brachman, R.W.I.; Booker, J.R. Barrier Systems for Waste Disposal Facilities, 2nd ed.; Taylor & Francis: London, UK, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Abhilash, T.N.; Senthilnathan, J.; Shiva Nagendra, S.M. Application of the phycoremediation process for tertiary treatment of landfill leachate and carbon dioxide mitigation. J. Water Process Eng. 2019, 28, 322–330. [Google Scholar]
- Gong, H.J.; Zhou, S.Y.; Chen, Z.Z.; Chen, L. Effect of volatile organic compounds on carbon dioxide adsorption performance via pressure swing adsorption for landfill gas upgrading. Renew. Energy 2019, 135, 811–818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fleming, I.R.; Rowe, R.K.; Cullimore, D.R. Field observations of clogging in a landfill leachate collection system. Can. Geotech. J. 1999, 36, 685–707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lozecznik, S.; VanGulck, J. Full-scale laboratory study into clogging of pipes permeated with landfill leachate. Pract. Period. Hazard. Toxic Radio Waste Manag. 2009, 13, 261–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lozecznik, S.; Sparling, R.; Oleszkiewicz, J.A.; Clark, S.; VanGulck, J.F. Leachate treatment before injection into a bioreactor landfill: Clogging potential reduction and benefits of using methanogenesis. Waste Manag. 2010, 30, 2030–2036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lozecznik, S.; Oleszkiewicz, J.A.; Clark, S.P.; Sparling, R.; VanGulck, J.F. Effects of turbulence and temperature on leachate chemistry. J. Environ. Eng. 2012, 138, 562–569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maliva, R.G.; Missimer, T.M. Unusual calcite stromatolites and pisoids from a landfill leachate collection system. Geology 2000, 28, 931–934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nikolova-Kuscu, R.; Powrie, W.; Smallman, D.J. Mechanisms of clogging in granular drainage systems permeated with low organic strength leachate. Can. Geotech. J. 2013, 50, 632–649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- VanGulck, J.F.; Rowe, R.K. Influence of landfill leachate suspended solids on clog (biorock) formation. Waste Manag. 2004, 24, 723–738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.L.; Liu, J.G. Mechanism and dynamic evolution of leachate collection system clogging in MSW landfills in China. Waste Manag. 2021, 120, 314–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Huang, K.X.; Wang, K.H.; Meng, L. Countermeasures against the scaling of refuse leachate drainage pipe. Water Wastewater Eng. 2000, 26, 29–31. [Google Scholar]
- Man, R.L.; Bai, G.L.; Chen, S.L. Analysis of scales in landfill leachate drainage pipe. Guizhou Environ. Prot. Sci. Technol. 2002, 8, 4–7. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Y.L.; Liu, J.G. The biochemical clogging of landfill leachate collection system: Based on laboratory studies. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 2299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bennett, P.J.; Longstaffe, F.J.; Rowe, R.K. The stability of dolomite in landfill leachate collection systems. Can. Geotech. J. 2000, 37, 371–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rittmann, B.E.; Banaszak, J.E.; Cooke, A.; Rowe, R.K. Biogeochemical evaluation of mechanisms controlling CaCO3(s) precipitation in landfill leachate-collection systems. J. Environ. Eng. 2003, 129, 723–730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, D.D.; Liu, D.; Li, J. Analysis of scaling causation on pipes to convey waste leachate. Sichuan Environ. 2008, 27, 9–13. [Google Scholar]
- Beheshtian Ardakani, M.; Ebadi, T.; Mir Mohammad Hosseini, S.M. The effects of using reprocessable material on the durability and mechanical properties of landfill leachate collection HDPE pipes. J. Mater. Cycles Waste 2016, 19, 1166–1176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaha, B.N.; Meeroff, D.E.; Kohn, K.; Townsend, T.G.; Schert, J.D.; Mayer, N.; Schultz, R.; Telson, J. Effect of electronic water treatment system on calcium carbonate scale formation in landfill leachate collection piping. J. Environ. Eng. 2019, 145, 04019052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cardoso, A.J.; Levine, A.D.; Nayak, B.S.; Harwood, V.J.; Rhea, L.R. Lysimeter comparison of the role of waste characteristics in the formation of mineral deposits in leachate drainage systems. Waste Manag. Res. 2006, 24, 560–572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Riddick, S.N.; Hancock, B.R.; Robinson, A.D.; Connors, S.; Davies, S.; Allen, G.; Pitt, J.; Harris, N.R.P. Development of a low-maintenance measurement approach to continuously estimate methane emissions: A case study. Waste Manag. 2018, 73, 210–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scheutz, C.; Kjeldsen, P. Guidelines for landfill gas emission monitoring using the tracer gas dispersion method. Waste Manag. 2019, 85, 351–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, Z.H.; Kjeldsen, P.; Scheutz, C. Trace gas composition in landfill gas at Danish landfills receiving low-organic waste. Waste Manag. 2021, 122, 113–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, W.; Zhan, L.T.; Lan, J.W.; Chen, Y.M.; Zhang, H.H.; Zheng, X.J. Exploration on efficient collection of landfill gas in a landfill with a high leachate level. China Environ. Sci. 2017, 37, 1434–1441. [Google Scholar]
- Andriani, D.; Wresta, A.; Atmaja, T.D.; Saepudin, A. A review on optimization production and upgrading biogas through CO2 removal using various techniques. Appl. Biochem. Biotech. 2014, 172, 1909–1928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Desideri, U.; Di Maria, F.; Leonardi, D.; Proietti, S. Sanitary landfill energetic potential analysis: A real case study. Energy Convers. Manag. 2003, 44, 1969–1981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coskuner, G.; Jassim, M.S.; Nazeer, N.; Damindra, G.H. Quantification of Landfill Gas Generation and Renewable Energy Potential in Arid Countries: Case Study of Bahrain. Waste Manag. Res. 2020, 38, 1110–1118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baciocchi, R.; Carnevale, E.; Costa, G.; Lombardi, L.; Olivieri, T.; Paradisi, A.; Zanchi, L.; Zingaretti, D. Pilot-scale investigation of an innovative process for biogas upgrading with CO2 capture and storage. Energy Procedia 2013, 37, 6026–6034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jamil, A.; Ching, O.P.; Shariff, A.B.M. Current status and future prospect of polymer-layered silicate mixed-matrix membranes for CO2/CH4 separation. Chem. Eng. Technol. 2016, 39, 1393–1405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghafoori, M.S.; Loubar, K.; Marin-Gallego, M.; Tazerout, M. Techno-economic and sensitivity analysis of biomethane production via landfill biogas upgrading and power-to-gas technology. Energy 2022, 239, 122086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strevett, K.A.; Vieth, R.F.; Grass, D. Chemo-autotrophic biogas purification for methane enrichment: Mechanism and kinetics. Chem. Eng. J. 1995, 58, 71–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryckebosch, E.; Drouillon, M.; Vervaeren, H. Techniques for transformation of biogas to biomethane. Biomass Bioenerg. 2011, 35, 1633–1645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lombardi, L.; Corti, A.; Carnevale, E.; Baciocchi, R.; Daniela, Z. Carbon dioxide removal and capture for landfill gas up-grading. Energy Procedia 2011, 4, 465–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Qian, H.; Ma, Z.Y. Hydrogeochemistry, 1st ed.; Geological Publishing House: Beijing, China, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Ren, X.; Liu, D.; He, Y.J.; Zhong, S.Z.; Wang, F. Study on the chemical mechanism of removing scale ions from leachate by using landfill gas. Sichuan Environ. 2013, 32, 37–44. [Google Scholar]
- Cosmoa, R.P.; Pereira, F.A.R.; Soares, E.J.; Martins, A.L. Modeling and validation of the CO2 degassing effect on CaCO3 precipitation using oilfield data. Fuel 2022, 310, 122067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, M.X.; Yi, N.T.; Di, W.T.; Wang, T.; Wang, Q.H. Emission and control of flue gas pollutants in CO2 chemical absorption system—A review. Int. J. Greenh. Gas. Con. 2020, 93, 102904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sang, J.W.; Huang, J.B.; Zhou, R.; Xu, L.; Zhou, S.C. Impact of water influent pH on MBR treatment of landfill leachate. Water Technol. 2020, 14, 18–22. [Google Scholar]
- Tao, Q.; Chen, T.H.; Liu, H.B.; Zhu, S.C. The effect of potassium and sodium ions on the crystallization of struvite in RO concentrate of landfill leachate. Acta Petro. Min. 2019, 38, 417–423. [Google Scholar]
- Mullin, J.W. Crystallization, 4th ed.; Butterworth-Heinemann: Oxford, UK, 2001. [Google Scholar]



| (A) Raw Leachate | Concentration |
|---|---|
| pH | 7.8–8.3 |
| Chemical oxygen demand (mg/L) | 2100–5700 |
| Ammonia nitrogen (mg/L) | 780–1130 |
| Calcium (mg/L) | 280–370 |
| Magnesium (mg/L) | 200–350 |
| Total suspended solids (mg/L) | 1000–3000 |
| (B) Raw landfill gas | |
| CO2 (%) | 32–36 |
| CH4 (%) | 52–62 |
| Flow rate (mL/min) | 720 |
| Indicators | Method |
|---|---|
| COD | potassium dichromate titration |
| Ca2+, Mg2+ | atomic absorption spectrophotometry |
| TSS | gravimetric measurement |
| Ammonia nitrogen | distillation neutralization titration |
| pH | PHS-3C pH meter method |
| CO2, CH4 | gas chromatography |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Xie, M.; Guo, X.; Liu, D. Leachate Pretreatment before Pipe Transportation: Reduction of Leachate Clogging Potential and Upgrading of Landfill Gas. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 6349. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph19106349
Xie M, Guo X, Liu D. Leachate Pretreatment before Pipe Transportation: Reduction of Leachate Clogging Potential and Upgrading of Landfill Gas. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health. 2022; 19(10):6349. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph19106349
Chicago/Turabian StyleXie, Mingde, Xi Guo, and Dan Liu. 2022. "Leachate Pretreatment before Pipe Transportation: Reduction of Leachate Clogging Potential and Upgrading of Landfill Gas" International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health 19, no. 10: 6349. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph19106349
APA StyleXie, M., Guo, X., & Liu, D. (2022). Leachate Pretreatment before Pipe Transportation: Reduction of Leachate Clogging Potential and Upgrading of Landfill Gas. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 19(10), 6349. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph19106349





