Digital Addiction and Sleep
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Digital Addiction: A New Problem Worldwide
2.1. Instant Availability of the “Digital Drug”
2.2. From Loss of Impulse Control to Insomnia and Depression
2.3. Dysfunctional Sleep as a Key Variable
3. What Happens in the Brain?
3.1. From Habit and Reward to Craving
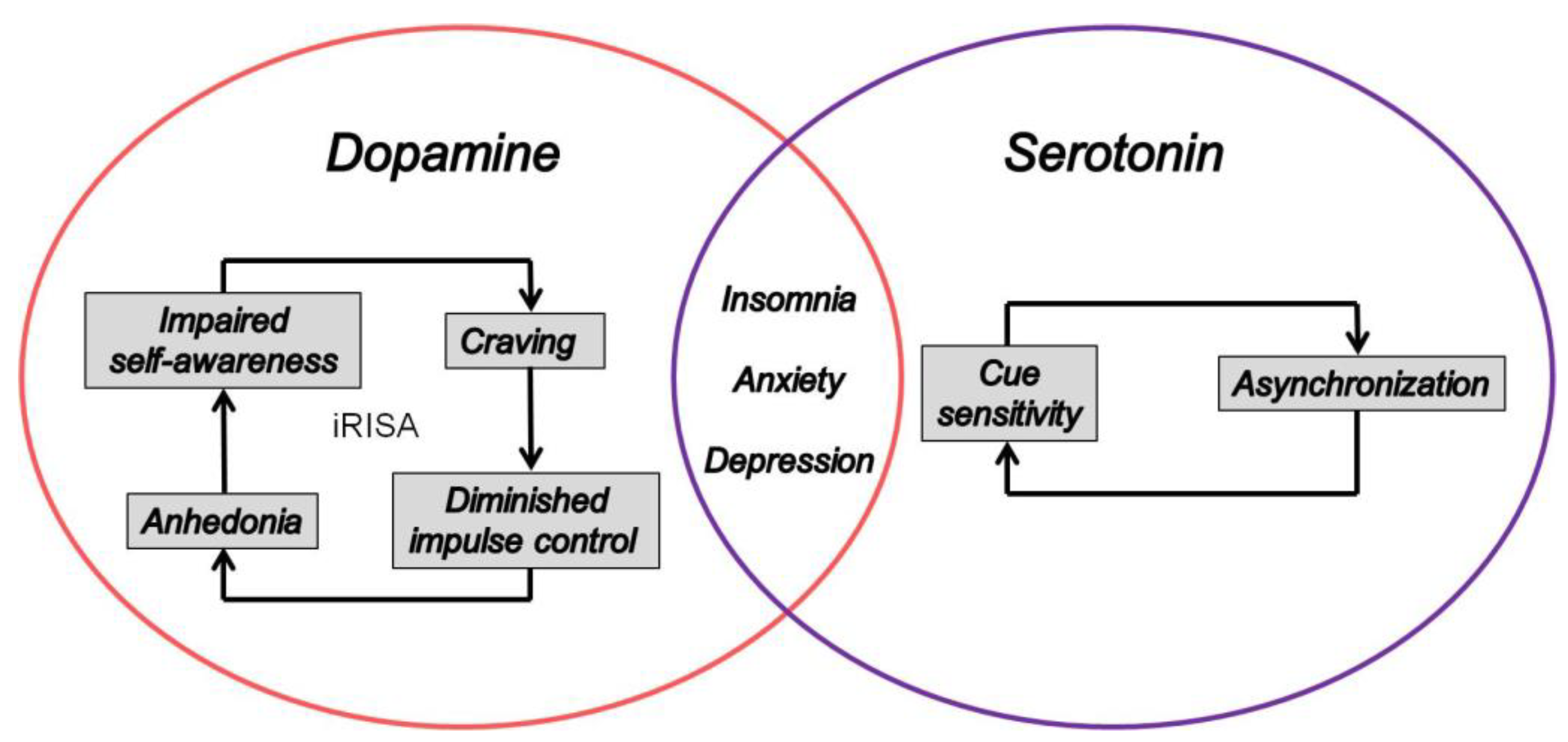
3.2. From Craving to Anxiety, Sleeplessness, and Anhedonia
4. The Dopamine–Serotonin Imbalance Hypothesis
4.1. Synaptic Plasticity and Pathological Adaptation
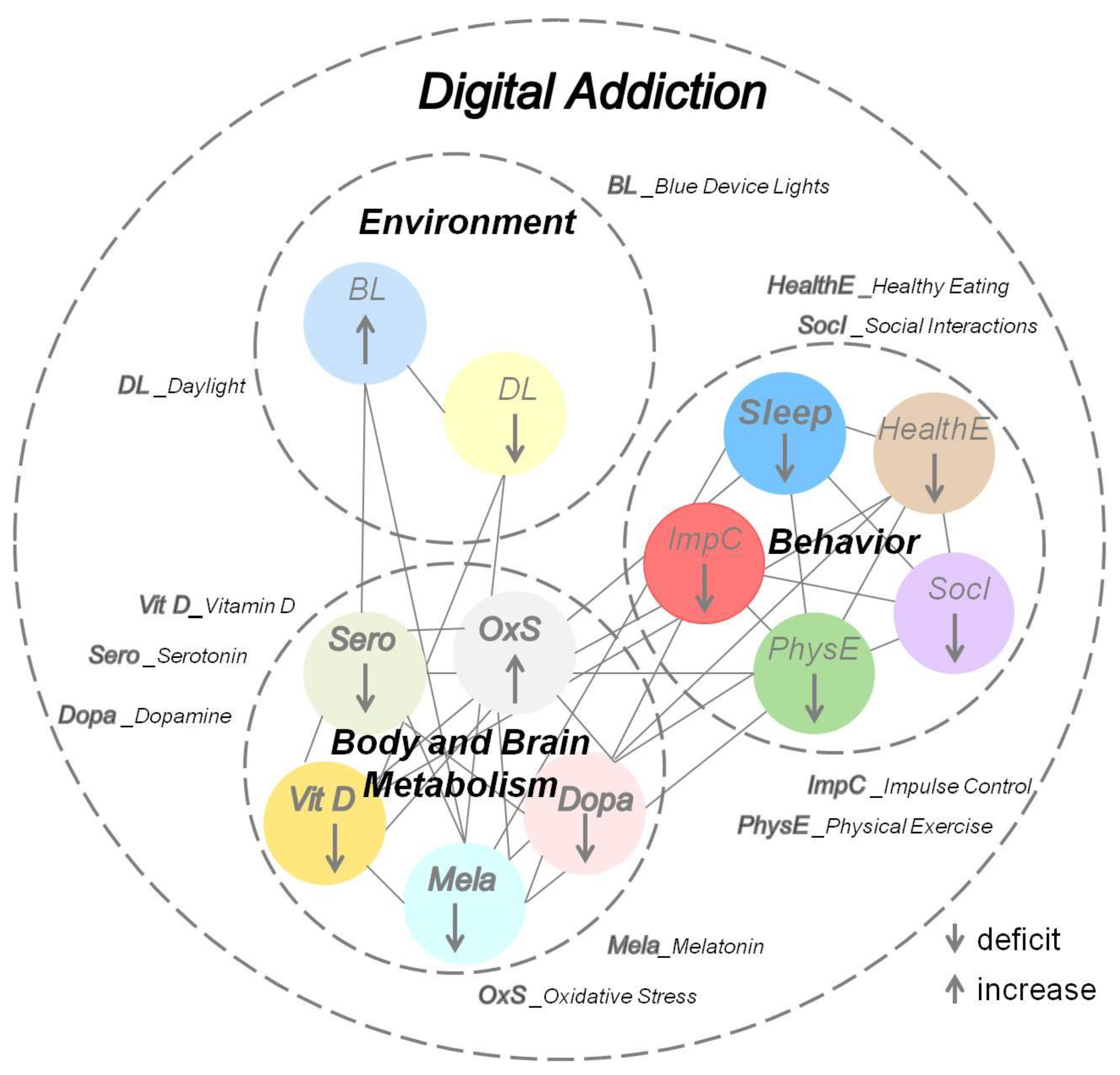
4.2. Lifestyle-Induced Metabolic Changes
5. Perspectives for Clinical Research and Treatment
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ryan, P. Technology: The New Addiction. US Naval Institute Publications. Proceedings. September 2018; 144, e387. Available online: https://www.usni.org/magazines/proceedings/2018/september/technology-new-addiction (accessed on 3 June 2022).
- Smith, A.; Anderson, M. Social Media Use in 2018; The Pew Research Center: Washington, DC, USA, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Yau, Y.H.; Potenza, M.N. Gambling disorder and other behavioral addictions: Recognition and treatment. Harv. Rev. Psychiatry 2015, 23, 134–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Greenfield, D. Treatment Considerations in Internet and Video Game Addiction: A Qualitative Discussion. Child Adolesc. Clin. N. Am. 2018, 27, 327–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Twenge, J.M. Have Smartphones Destroyed a Generation? The Atlantic, September 2017. Available online: https://www.theatlantic.com/magazine/archive/2017/09/has-the-smartphone-destroyed-a-generation/534198/ (accessed on 3 June 2022).
- Shaw, M.; Black, D.W. Internet addiction: Definition, assessment, epidemiology and clinical management. CNS Drugs 2008, 22, 353–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuss, D.J.; Griffiths, M.D.; Karila, L.; Billieux, J. Internet addiction: A systematic review of epidemiological research for the last decade. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2014, 20, 4026–4052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Rumpf, H.; Achab, S.; Billieux, J.; Bowden-Jones, H.; Carragher, N.; Demetrovics, Z.; Higuchi, S.; King, D.; Mann, K.; Potenza, M.; et al. Including gaming disorder in the ICD-11: The need to do so from a clinical and public health perspective. J. Behav. Addict. 2018, 7, 556–561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- World Health Organization. International Classification of Diseases for Mortality and Morbidity Statistics (11th Revision). 2020. Available online: https://icd.who.int/browse11/l-m/en (accessed on 3 June 2022).
- American Psychiatric Association. DSM-5—Manuel Diagnostique et Statistique des Troubles Mentaux; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Kemp, S. Global Digital Overview. 2019. Available online: https://datareportal.com/reports/digital-2019-global-digital-overview (accessed on 3 June 2022).
- Griffiths, M.D.; Pontes, H.M. Internet Addiction Disorder and Internet Gaming Disorder are not the same. J. Addict. Res. Ther. 2014, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dresp-Langley, B. Children’s Health in the Digital Age. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 3240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, G.; Shen, Y.; Huang, J.; Du, X. Impaired error-monitoring function in people with Internet addiction disorder: An event-related FMRI study. Eur. Addict. Res. 2013, 19, 269–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, C.; Li, A.Y. Internet addiction prevalence and quality of (real) life: A meta-analysis of 31 nations across seven world regions. Cyberpsychol. Behav. Soc. Netw. 2014, 17, 755–760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wallace, P. Internet addiction disorder and youth: There are growing concerns about compulsive online activity and that this could impede students’ performance and social lives. EMBO Rep. 2014, 15, 12–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nalwa, K.; Anand, A.P. Internet addiction in students: A cause of concern. Cyberpsychol. Behav. 2003, 6, 653–656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cao, F.; Su, L. Internet addiction among Chinese adolescents: Prevalence and psychological features. Child Care Health Dev. 2006, 33, 275–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, K.W.; Chan, W.S.; Wong, P.W.; Yip, P.S. Internet addiction: Prevalence, discriminant validity and correlates among adolescents in Hong Kong. Br. J. Psychiatry 2010, 196, 486–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saikia, A.M.; Das, J.; Barman, P.; Bharali, M.D. Internet Addiction and its Relationships with Depression, Anxiety, and Stress in Urban Adolescents of Kamrup District, Assam. J. Fam. Community Med. 2019, 26, 108–112. [Google Scholar]
- Dalbudak, E.; Evren, C.; Aldemir, S.; Coskun, K.S.; Ugurlu, H.; Yildirim, F.G. Relationship of internet addiction severity with depression, anxiety and alexithymia, temperament, and character in university students. Cyberpsychol. Behav. Soc. Netw. 2013, 16, 272–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shakya, H.B.; Christakis, N.A. Association of ‘Facebook’ use with compromised well-being: A longitudinal study. Am. J. Epidemiol. 2017, 185, 203–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lau, J.T.F.; Walden, D.L.; Wu, A.M.S.; Cheng, K.M.; Lau, M.C.M.; Mo, P.K.H. Bidirectional predictions between Internet addiction and probable depression among Chinese adolescents. J. Behav. Addict. 2018, 7, 633–643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hinojo-Lucena, F.J.; Aznar-Díaz, I.; Cáceres-Reche, M.P.; Trujillo-Torres, J.M.; Romero-Rodríguez, J.M. Problematic Internet Use as a Predictor of Eating Disorders in Students: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis Study. Nutrients 2019, 11, 2151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Moreno, M.A.; Eickhoff, J.; Zhao, Q.; Suris, J.C. College Students and Problematic Internet Use: A Pilot Study Assessing Self-Appraisal and Independent Behavior Change. J. Adolesc. Health 2019, 64, 131–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krishnamurthy, S.; Chetlapalli, S.K. Internet addiction: Prevalence and risk factors: A cross-sectional study among college students in Bengaluru, the Silicon Valley of India. Indian J. Public Health 2015, 59, 115–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.B.; Lau, J.T.F.; Mo, P.K.H.; Su, X.F.; Tang, J.; Qin, Z.G.; Gross, D.L. Insomnia partially mediates the association between problematic Internet use and depression among secondary school students in China. J. Behav. Addict. 2017, 6, 554–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.L.; Gau, S.S. Sleep problems and internet addiction among children and adolescents: A longitudinal study. J. Sleep Res. 2016, 25, 458–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kim, K.; Ryu, E.; Chon, M.-Y.; Yeun, E.-J.; Choi, S.-Y.; Seo, J.-S.; Nam, B.-W. Internet addiction in Korean adolescents and its relation to depression and suicidal ideation: A questionnaire survey. Int. J. Nurs. Stud. 2006, 43, 185–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Keles, B.; McCrae, N.; Grealish, A. A systematic review: The influence of social media on depression, anxiety and psychological distress in adolescents. Int. J. Adolesc. Youth 2020, 25, 79–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- CESDS. The Center for Epidemiological Studies Depression Scale Revised. 2020. Available online: https://cesd-r.com/ (accessed on 3 June 2022).
- PQI. The Pittsburgh Sleep Quality Index. 2020. Available online: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Pittsburgh_Sleep_Quality_Index (accessed on 3 June 2022).
- YDQIA. Young’s Diagnostic Questionnaire for Internet Addiction. 2020. Available online: https://journals.plos.org/plosone/article/file?type=supplementary&id=info:doi/10.1371/journal.pone.0107379906.s001 (accessed on 3 June 2022).
- Shahnawaz, M.G.; Rehman, U. Social Networking Addiction Scale. Cogent Psychol. 2020, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Demirci, K.; Akgönül, M.; Akpinar, A. Relationship of smartphone use severity with sleep quality, depression, and anxiety in university students. J. Behav. Addict. 2015, 4, 85–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dong, G.; Huang, J.; Du, X. Enhanced reward sensitivity and decreased loss sensitivity in Internet addicts: An fMRI study during a guessing task. J. Psychiatr. Res. 2011, 45, 1525–1529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petry, N.M.; Rehbein, F.; Gentile, D.A.; Lemmens, J.S.; Rumpf, H.-J.; Mößle, T.; Bischof, G.; Tao, R.; Fung, D.S.S.; Borges, G.; et al. An international consensus for assessing internet gaming disorder using the new DSM-5 approach. Addiction 2014, 109, 1399–1406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuss, D.J.; Lopez-Fernandez, O. Internet addiction and problematic Internet use: A systematic review of clinical research. World J. Psychiatry 2016, 6, 143–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuss, D.J.; Griffiths, M.D.; Pontes, H.M. Chaos and confusion in DSM-5 diagnosis of Internet Gaming Disorder: Issues, concerns, and recommendations for clarity in the field. J. Behav. Addict. 2017, 6, 103–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Petry, N.M.; Zajac, K.; Ginley, M.K. Behavioral Addictions as Mental Disorders: To Be or Not to Be? Annu. Rev. Clin. Psychol. 2018, 14, 399–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alavi, S.S.; Ferdosi, M.; Jannatifard, F.; Eslami, M.; Alaghemandan, H.; Setare, M. Behavioral Addiction versus Substance Addiction: Correspondence of Psychiatric and Psychological Views. Int. J. Prev. Med. 2012, 3, 290–294. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Raouf, S.Y.A.; Gabr, H.M.; Al-Wutayd, O.; Al-Batanony, M.A. Video game disorder and mental wellbeing among university students: A cross-sectional study. Pan Afr. Med J. 2022, 41, 89. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Hamre, R.; Smith, O.R.F.; Samdal, O.; Haug, E. Gaming Behaviors and the Association with Sleep Duration, Social Jetlag, and Difficulties Falling Asleep among Norwegian Adolescents. Int. J. Env. Res. Public Health. 2022, 19, 1765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al Shareef, S.M. Excessive daytime sleepiness and associations with sleep-related motor vehicle accidents: Results from a nationwide survey. Sleep Breath. 2021, 25, 1671–1676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gharibi, V.; Mokarami, H.; Cousins, R.; Jahangiri, M.; Eskandari, D. Excessive Daytime Sleepiness and Safety Performance: Comparing Proactive and Reactive Approaches. Int. J. Occup. Environ. Med. 2020, 11, 95–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Monti, J.M.; Jantos, H. The roles of dopamine and serotonin, and of their receptors, in regulating sleep and waking. Prog. Brain Res. 2008, 172, 625–646. [Google Scholar]
- Racagni, G.; Riva, M.A.; Popoli, M. The interaction between the internal clock and antidepressant efficacy. Int. Clin. Psychopharmacol. 2007, 22, S9–S14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, C.Y.; Lee, M.B.; Liao, S.C.; Chang, L.R. Risk factors of internet addiction among internet users: An online questionnaire survey. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0137506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Restrepo, A.; Scheininger, T.; Clucas, J.; Alexander, L.; Salum, G.A.; Georgiades, K.; Paksarian, D.; Merikangas, K.R.; Milham, M.P. Problematic internet use in children and adolescents: Associations with psychiatric disorders and impairment. BMC Psychiatry 2020, 20, 252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Otsuka, Y.; Kaneita, Y.; Itani, O.; Matsumoto, Y.; Jike, M.; Higuchi, S.; Kanda, H.; Kuwabara, Y.; Kinjo, A.; Osaki, Y. The association between Internet usage and sleep problems among Japanese adolescents: Three repeated cross-sectional studies. Sleep 2021, 44, zsab175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tan, Y.; Chen, Y.; Lu, Y.; Li, L. Exploring Associations between Problematic Internet Use, Depressive Symptoms and Sleep Disturbance among Southern Chinese Adolescents. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2016, 13, 313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Jain, A.; Sharma, R.; Gaur, K.L.; Yadav, N.; Sharma, P.; Sharma, N.; Khan, N.; Kumawat, P.; Jain, G.; Maanju, M.; et al. Study of internet addiction and its association with depression and insomnia in university students. J. Fam. Med. Prim. Care 2020, 9, 1700–1706. [Google Scholar]
- Alimoradi, Z.; Lin, C.Y.; Broström, A.; Bülow, P.H.; Bajalan, Z.; Griffiths, M.D.; Ohayon, M.M.; Pakpour, A.H. Internet addiction and sleep problems: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Sleep Med. Rev. 2019, 47, 51–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kokka, I.; Mourikis, I.; Nicolaides, N.C.; Darviri, C.; Chrousos, G.P.; Kanaka-Gantenbein, C.; Bacopoulou, F. Exploring the Effects of Problematic Internet Use on Adolescent Sleep: A Systematic Review. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Younes, F.; Halawi, G.; Jabbour, H.; El Osta, N.; Karam, L.; Hajj, A.; Khabbaz, L.R. Internet Addiction and Relationships with Insomnia, Anxiety, Depression, Stress and Self-Esteem in University Students: A Cross-Sectional Designed Study. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0161126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Islamie Farsani, S.; Allahbakhshi, K.; Valipour, A.A.; Mohammadian-Hafshejani, A. Some Facts on Problematic Internet Use and Sleep Disturbance among Adolescents. Iran. J. Public Health 2016, 45, 1531–1532. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Wang, W.; Du, X.; Guo, Y.; Li, W.; Zhang, S.; Guo, L.; Lu, C. Association between problematic internet use and behavioral/emotional problems among Chinese adolescents: The mediating role of sleep disorders. PeerJ 2021, 9, e10839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, L.; Luo, M.; Wang, W.X.; Huang, G.L.; Xu, Y.; Gao, X.; Lu, C.Y.; Zhang, W.H. Association between problematic Internet use, sleep disturbance, and suicidal behavior in Chinese adolescents. J. Behav. Addict. 2018, 7, 965–975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Canan, F.; Yildirim, O.; Sinani, G.; Ozturk, O.; Ustunel, T.Y.; Ataoglu, A. Internet addiction and sleep disturbance symptoms among Turkish high school students. Sleep Biol. Rhythms 2013, 11, 210–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Çelebioğlu, A.; Aytekin Özdemir, A.; Küçükoğlu, S.; Ayran, G. The effect of Internet addiction on sleep quality in adolescents. J. Child Adolesc. Psychiatr. Nurs. 2020, 33, 221–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van den Bulck, J. Television viewing, computer game playing, and internet use and self-reported time in bed and time out of bed in secondary-school children. Sleep 2004, 27, 101–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Do, K.Y.; Lee, K.S. Relationship between Problematic Internet Use, Sleep Problems, and Oral Health in Korean Adolescents: A National Survey. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2018, 15, 1870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Fernández-Villa, T.; Ojeda, J.A.; Gómez, A.A.; Carral, J.; Cancela, M.; Delgado-Rodríguez, M.; García-Martín, M.; Jiménez-Mejías, E.; Llorca, J.; Molina, A.J. Problematic Internet Use in University Students: Associated factors and differences of gender. Adicciones 2015, 27, 265–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- An, J.; Sun, Y.; Wan, Y.; Chen, J.; Wang, X.; Tao, F. Associations between problematic internet use and adolescents’ physical and psychological symptoms: Possible role of sleep quality. J. Addict. Med. 2014, 8, 282–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cain, N.; Gradisar, M. Electronic media use and sleep in school-aged children and adolescents: A review. Sleep Med. 2010, 11, 735–742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tahir, M.J.; Malik, N.I.; Ullah, I.; Khan, H.R.; Perveen, S.; Ramalho, R.; Siddiqi, A.R.; Waheed, S.; Shalaby, M.M.M.; De Berardis, D.; et al. Internet addiction and sleep quality among medical students during the COVID-19 pandemic: A multinational cross-sectional survey. PLoS ONE 2021, 16, e0259594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Griffiths, M.D. A ‘components’ model of addiction within a biopsychosocial framework. J. Subst. Use 2005, 10, 191–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leshner, A.I. Addiction is a brain disease, and it matters. Science 1997, 278, 45–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Laviolette, S.R.; van der Kooy, D. GABA(A) receptors in the ventral tegmental area control bidirectional reward signalling between dopaminergic and non-dopaminergic neural motivational systems. Eur. J. Neurosci. 2001, 13, 1009–1015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wise, R.A.; Robble, M.A. Dopamine and Addiction. Annu. Rev. Psychol. 2020, 71, 79–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Volkow, N.D.; Michaelides, M.; Baler, R. The Neuroscience of Drug Reward and Addiction. Physiol. Rev. 2019, 99, 2115–2140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scaplen, K.M.; Kaun, K.R. Reward from bugs to bipeds: A comparative approach to understanding how reward circuits function. J. Neurogenet. 2016, 30, 133–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Blum, K.; Gondré-Lewis, M.; Steinberg, B.; Elman, I.; Baron, D.; Modestino, E.J.; Badgaiyan, R.D.; Gold, M.S. Our evolved unique pleasure circuit makes humans different from apes: Reconsideration of data derived from animal studies. J. Syst. Integr. Neurosci. 2018, 4, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wise, R.A. Dopamine and Reward: The Anhedonia Hypothesis 30 years on. Neurotox Res. 2008, 14, 169–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Koob, G.F.; Volkow, N.D. Neurobiology of addiction: A neurocircuitry analysis. Lancet Psychiatry 2016, 3, 760–773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goldstein, R.Z.; Volkow, N.D. Dysfunction of the prefrontal cortex in addiction: Neuroimaging findings and clinical implications. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 2011, 12, 652–669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maniaci, G.; Picone, F.; van Holst, R.J.; Bolloni, C.; Scardina, S.; Cannizzaro, C. Alterations in the Emotional Regulation Process in Gambling Addiction: The Role of Anger and Alexithymia. J. Gambl. Stud. 2017, 33, 633–647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, G.; Hu, Y.; Lin, X.; Lu, Q. What makes Internet addicts continue playing online even when faced by severe negative consequences? Possible explanations from an fMRI study. Biol. Psychol. 2013, 94, 282–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Juárez, B.; Han, M.H. Diversity of Dopaminergic Neural Circuits in Response to Drug Exposure. Neuropsychopharmacology 2016, 41, 2424–2446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Baler, R.D.; Volkow, N.D. Drug addiction: The neurobiology of disrupted self-control. Trends Mol. Med. 2006, 12, 559–566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, H.J.; Lee, J.H.; Yun, K.; Kim, J.H. Alterations in Striatal Circuits Underlying Addiction-Like Behaviors. Mol. Cells 2017, 40, 379–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Luo, S.X.; Huang, E.J. Dopaminergic Neurons and Brain Reward Pathways: From Neurogenesis to Circuit Assembly. Am. J. Pathol. 2016, 186, 478–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Simmons, S.C.; Wheeler, K.; Mazei-Robison, M.S. Determination of circuit-specific morphological adaptations in ventral tegmental area dopamine neurons by chronic morphine. Mol. Brain 2019, 12, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Pierce, R.C.; Vanderschuren, L.J. Kicking the habit: The neural basis of ingrained behaviors in cocaine addiction. Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev. 2010, 35, 212–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Volkow, N.D.; Koob, G.F.; McLellan, A.T. Neurobiologic Advances from the Brain Disease Model of Addiction. N. Engl. J. Med. 2016, 374, 363–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Y.; Salmeron, B.J.; Gu, H.; Stein, E.A.; Yang, Y. Impaired functional connectivity within and between frontostriatal circuits and its association with compulsive drug use and trait impulsivity in cocaine addiction. JAMA Psychiatry 2015, 72, 584–592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Koob, G.F.; Le Moal, M. Addiction and the brain’s anti-reward system. Annu. Rev. Psychol. 2008, 59, 29–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bouarab, C.; Thompson, B.; Polter, A.M. VTA GABA Neurons at the Interface of Stress and Reward. Front. Neural Circuits 2019, 13, 78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Parolaro, D.; Viganò, D.; Rubino, T. Endocannabinoids and drug dependence. Curr. Drug Targets CNS Neurol. Disord. 2005, 4, 643–655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, W.X.; Pun, C.L.; Zhou, Y. Psychostimulants Induce Low-Frequency Oscillations in the Firing Activity of Dopamine Neurons. Neuropsychopharmacology 2004, 29, 2160–2167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schultz, W. Dopamine signals for reward value and risk: Basic and recent data. Behav. Brain Funct. 2010, 6, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kobayashi, S.; Schultz, W. Reward contexts extend dopamine signals to unrewarded stimuli. Curr. Biol. 2014, 24, 56–62. [Google Scholar]
- Trifilieff, P.; Martinez, D. Imaging addiction: D2 receptors and dopamine signaling in the striatum as biomarkers for impulsivity. Neuropharmacology 2014, 76, 498–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Olds, J.; Milner, P. Positive reinforcement produced by electrical stimulation of septal area and other regions of rat brain. J. Comp. Physiol. Psychol. 1954, 47, 419–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Milner, P.M. Brain-stimulation reward: A review. Can. J. Psychol. 1991, 45, 1–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yuodelis-Flores, C.; Ries, R.K. Addiction and suicide: A review. Am. J. Addict. 2015, 24, 98–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weinstein, A.; Curtiss Feder, L.; Rosenberg, K.P.; Dannon, P. Internet addiction disorder: Overview and controversies. In Behavioral Addictions; Rosenberg, K.P., Feder, L.C., Eds.; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2014; pp. 99–117. [Google Scholar]
- Weinstein, A.M. Computer and video game addiction—A comparison between game users and non-game users. Am. J. Drug Alcohol Abus. 2010, 36, 268–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robbins, T.W.; Ersche, K.D.; Everitt, B.J. Drug addiction and the memory systems of the brain. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2008, 1141, 1–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kätsyri, J.; Hari, R.; Ravaja, N.; Nummenmaa, L. Just watching the game is not enough: Striatal fMRI reward responses to successes and failures in a video game during active and vicarious playing. Front. Hum. Neurosci. 2013, 7, e278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gould, T.J. Addiction and cognition. Addict. Sci. Clin. Pract. 2010, 5, 4–14. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Goodman, J.; Packard, M.G. Memory Systems and the Addicted Brain. Front. Psychiatry 2016, 7, e24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Von der Goltz, C.; Kiefer, F. Learning and memory in the aetiopathogenesis of addiction: Future implications for therapy? Eur. Arch. Psychiatry Clin. Neurosci. 2009, 259, S183–S187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ladewig, D. Biologische und lerntheoretische Aspekte süchtigen Verhaltens (Biological and learning-theory aspects of addictive behavior). Schweiz. Med. Wochenschr. 1974, 104, 545–550. [Google Scholar]
- Kauer, J.A. Learning mechanisms in addiction: Synaptic plasticity in the ventral tegmental area as a result of exposure to drugs of abuse. Annu. Rev. Physiol. 2004, 66, 447–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pantic, I. Online social networking and mental health. Cyberpsychol. Behav. Soc. Netw. 2014, 17, 652–657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kauer, J.A.; Malenka, R.C. Synaptic plasticity and addiction. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 2007, 8, 844–858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalivas, P.W.; Volkow, N.; Seamans, J. Unmanageable motivation in addiction: A pathology in prefrontal-accumbens glutamate transmission. Neuron 2005, 45, 647–650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Moeller, S.J.; London, E.D.; Northoff, G. Neuroimaging markers of glutamatergic and GABAergic systems in drug addiction: Relationships to resting-state functional connectivity. Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev. 2016, 61, 35–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Behar, K.L.; Rothman, D.L.; Petersen, K.F.; Hooten, M.; Delaney, R.; Petroff, O.A.; Shulman, G.I.; Navarro, V.; Petrakis, I.L.; Charney, D.S.; et al. Preliminary evidence of low cortical GABA levels in localized 1H–MR spectra of alcohol-dependent and hepatic encephalopathy patients. Am. J. Psychiatry 1999, 156, 952–954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lovinger, D.M.; Roberto, M. Synaptic effects induced by alcohol. Curr. Top. Behav. Neurosci. 2013, 13, 31–86. [Google Scholar] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hyman, S.E. Addiction: A disease of learning and memory. Am. J. Psychiatry 2005, 162, 1414–1422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Widyanto, L.; Griffiths, M.; Brunsden, V.; McMurran, M. The Psychometric Properties of the Internet Related Problem Scale: A Pilot Study. Int. J. Ment. Health Addict. 2008, 6, 205–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brand, M.; Young, K.S.; Laier, C. Prefrontal control and internet addiction: A theoretical model and review of neuropsychological and neuroimaging findings. Front. Hum. Neurosci. 2014, 8, e375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trotzke, P.; Starcke, K.; Müller, A.; Brand, M. Cue-induced craving and symptoms of online-buying-shopping disorder interfere with performance on the Iowa Gambling Task modified with online-shopping cues. Addict. Behav. 2019, 96, 82–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perry, C.J.; Zbukvic, I.; Kim, J.H.; Lawrence, A.J. Role of cues and contexts on drug-seeking behaviour. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2014, 171, 4636–4672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kasanetz, F.; Deroche-Gamonet, V.; Berson, N.; Balado, E.; Lafourcade, M.; Manzoni, O.; Piazza, P.V. Transition to addiction is associated with a persistent impairment in synaptic plasticity. Science 2010, 328, 1709–1712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ojeda, J.; Ávila, A. Early Actions of Neurotransmitters During Cortex Development and Maturation of Reprogrammed Neurons. Front. Synaptic Neurosci. 2019, 11, e33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Avchalumov, Y.; Mandyam, C.D. Plasticity in the Hippocampus, Neurogenesis, and Drugs of Abuse. Brain Sci. 2021, 11, 404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mameli, M.; Lüscher, C. Synaptic plasticity and addiction: Learning mechanisms gone awry. Neuropharmacology 2011, 61, 1052–1059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hyman, S.E.; Malenka, R.C. Addiction and the brain: The neurobiology of compulsion and its persistence. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 2001, 2, 695–703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kalivas, P.W.; Volkow, N.D. The neural basis of addiction: A pathology of motivation and choice. Am. J. Psychiatry 2005, 162, 1403–1413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cools, R.; Froböse, M.; Aarts, E.; Hofmans, L. Dopamine and the motivation of cognitive control. Handb. Clin. Neurol. 2019, 163, 123–143. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Hou, H.; Jia, S.; Hu, S.; Fan, R.; Sun, W.; Sun, T.; Zhang, H. Reduced striatal dopamine transporters in people with internet addiction disorder. J. Biomed. Biotechnol. 2012, 2012, 854524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.H.; Baik, S.-H.; Park, C.S.; Kim, S.J.; Choi, S.W.; Kim, S.E. Reduced striatal dopamine D2 receptors in people with Internet addiction. NeuroReport 2011, 22, 407–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, B.; Friston, K.; Liu, J.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, G.; Cao, F.; Su, L.; Yao, S.; Lu, H.; Hu, D. Impaired Frontal-Basal Ganglia Connectivity in Adolescents with Internet Addiction. Sci. Rep. 2014, 4, 5027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Harada, T.; Morikuni, M.; Yoshii, S.; Yamashita, Y.; Takeuchi, H. Usage of mobile phone in the evening or at night makes Japanese students evening-typed and night sleep uncomfortable. Sleep Hypn. 2002, 4, 149–153. [Google Scholar]
- Weaver, E.; Gradisar, M.; Dohnt, H.; Lovato, N.; Douglas, P. The effect of pre-sleep video game playing on adolescent sleep. J. Clin. Sleep Med. 2010, 6, 184–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Levenson, J.C.; Shensa, A.; Sidani, J.E.; Colditz, J.B.; Primack, B.A. The association between social media use and sleep disturbance among young adults. Prev. Med. 2016, 85, 36–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Medic, G.; Wille, M.; Hemels, M.E. Short- and long-term health consequences of sleep disruption. Nat. Sci. Sleep 2017, 9, 151–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lopez, R.B.; Brand, G.; Gilbert-Diamond, D. Media Multitasking Is Associated with Higher Body Mass Index in Pre-Adolescent Children. Front. Psychol. 2019, 10, 2534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lopez, R.B.; Heatherton, T.F.; Wagner, D.D. Media multitasking is associated with higher risk for obesity and increased responsiveness to rewarding food stimuli. Brain Imaging Behav. 2019, 14, 1050–1061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ariatama, B.; Effendy, E.; Amin, M.M. Relationship between Internet Gaming Disorder with Depressive Syndrome and Dopamine Transporter Condition in Online Game Players. Open Access Maced. J. Med. Sci. 2019, 7, 2638–2642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Weinstein, A.; Livny, A.; Weizman, A. New developments in brain research of internet and gaming disorder. Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev. 2017, 75, 314–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, H.X.; Jiang, W.Q.; Lin, Z.G.; Du, Y.S.; Vance, A. Comparison of psychological symptoms and serum levels of neurotransmitters in Shanghai adolescents with and without internet addiction disorder: A case-control study. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e63089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Petit, A.; Karila, L.; Estellat, C.; Moisan, D.; Reynaud, M.; D’Ortho, M.P.; Lejoyeux, M.; Levy, F. Les troubles du sommeil dans l’addiction à Internet (Sleep disorders in Internet addiction). La Presse Médicale. 2016, 45, 1170–1177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kohyama, J. A newly proposed disease condition produced by light exposure during night: Asynchronization. Brain Dev. 2009, 31, 255–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trinko, J.R.; Land, B.B.; Solecki, W.B.; Wickham, R.J.; Tellez, L.A.; Maldonado-Aviles, J.; de Araujo, I.E.; Addy, N.A.; DeLeone, R.J. Vitamin D3: A Role in Dopamine Circuit Regulation, Diet-Induced Obesity, and Drug Consumption. eNeuro 2016, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Menon, V.; Kar, S.K.; Suthar, N.; Nebhinani, N. Vitamin D and Depression: A Critical Appraisal of the Evidence and Future Directions. Indian J. Psychol. Med. 2020, 42, 11–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, G.; Cao, J.; Li, Y.; Cheng, P.; Liu, B.; Hao, Z.; Yao, H.; Shi, D.; Peng, L.; Guo, L.; et al. Association Between Internet Addiction and the Risk of Musculoskeletal Pain in Chinese College Freshmen—A Cross-Sectional Study. Front. Psychol. 2019, 10, 1959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Homberg, J.R. Serotonin and decision making processes. Neurosci. Biobehav. 2012, 36, 218–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wood, M.D.; Wren, P.B. Serotonin-dopamine interactions: Implications for the design of novel therapeutic agents for psychiatric disorders. Prog. Brain Res. 2008, 172, 213–230. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Sepede, G.; Tavino, M.; Santacroce, R.; Fiori, F.; Salerno, R.M.; Di Giannantonio, M. Functional magnetic resonance imaging of internet addiction in young adults. World J. Radiol. 2016, 8, 210–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Liu, M.; Luo, J. Relationship between peripheral blood dopamine level and internet addiction disorder in adolescents: A pilot study. Int. J. Clin. Exp. Med. 2015, 8, 9943–9948. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Juárez Olguín, H.; Calderón Guzmán, D.; Hernández García, E.; Barragán Mejía, G. The Role of Dopamine and Its Dysfunction as a Consequence of Oxidative Stress. Oxid. Med. Cell. Longev. 2016, 2016, e9730467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Winstanley, C.; Theobald, D.; Dalley, J.; Robbins, T.W. Interactions between Serotonin and Dopamine in the Control of Impulsive Choice in Rats: Therapeutic Implications for Impulse Control Disorders. Neuropsychopharmacology 2005, 30, 669–682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patrick, R.P.; Ames, B.N. Vitamin D hormone regulates serotonin synthesis. Part 1: Relevance for autism. FASEB J. 2014, 28, 2398–2413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sellnow, R.C.; Newman, J.H.; Chambers, N.; West, A.R.; Steece-Collier, K.; Sandoval, I.M.; Benskey, M.J.; Bishop, C.; Manfredsson, F.P. Regulation of dopamine neurotransmission from serotonergic neurons by ectopic expression of the dopamine D2 autoreceptor blocks levodopa-induced dyskinesia. Acta Neuropathol. Commun. 2019, 7, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muñoz, A.; Lopez-Lopez, A.; Labandeira, C.M.; Labandeira-Garcia, J.L. Interactions Between the Serotonergic and Other Neurotransmitter Systems in the Basal Ganglia: Role in Parkinson’s Disease and Adverse Effects of L-DOPA. Front. Neuroanat. 2020, 14, 26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hyman, S.E.; Malenka, R.C.; Nestler, E.J. Neural mechanisms of addiction: The role of reward-related learning and memory. Annu. Rev. Neurosci. 2006, 29, 565–598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cash, H.; Rae, C.D.; Steel, A.H.; Winkler, A. Internet Addiction: A Brief Summary of Research and Practice. Curr. Psychiatry Rev. 2012, 8, 292–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Everitt, B.J.; Robbins, T.W. Neural systems of reinforcement for drug addiction: From actions to habits to compulsion. Nat. Neurosci. 2005, 8, 1481–1489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carroll, K.M.; Onken, L.S. Behavioral therapies for drug abuse. Am. J. Psychiatry 2005, 162, 1452–1460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Quinones, C.; Griffiths, M.D. Reducing compulsive Internet use and anxiety symptoms via two brief interventions: A comparison between mindfulness and gradual muscle relaxation. J. Behav. Addict. 2019, 8, 530–536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ong, J.C.; Smith, C.E. Using Mindfulness for the Treatment of Insomnia. Curr. Sleep Med. Rep. 2017, 3, 57–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wani, A.; Trevino, K.; Marnell, P.; Husain, M.M. Advances in brain stimulation for depression. Ann. Clin. Psychiatry 2013, 25, 217–224. [Google Scholar]
- Krack, P.; Hariz, M.I.; Baunez, C.; Guridi, J.; Obeso, J.A. Deep brain stimulation: From neurology to psychiatry. Trends Neurosci. 2010, 33, 474–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Veerakumar, A.; Berton, O. Cellular mechanisms of deep brain stimulation: Activity-dependent focal circuit reprogramming. Curr. Opin. Behav. Sci. 2015, 4, 48–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Deniau, J.M.; Degos, B.; Bosch, C.; Maurice, N. Deep brain stimulation mechanisms: Beyond the concept of local functional inhibition. Eur. J. Neurosci. 2010, 32, 1080–1091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delaloye, S.; Holtzheimer, P.E. Deep brain stimulation in the treatment of depression. Dialog. Clin. Neurosci. 2014, 16, 83–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schlaepfer, T.E.; Cohen, M.X.; Frick, C.; Kosel, M.M.; Brodesser, D.; Axmacher, N.; Joe, A.Y.; Kreft, M.; Lenartz, D.; Sturm, V. Deep brain stimulation to reward circuitry alleviates anhedonia in refractory major depression. Neuropsychopharmacology 2008, 33, 368–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bewernick, B.H.; Hurlemann, R.; Matusch, A.; Kayser, S.; Grubert, C.; Hadrysiewicz, B.; Axmacher, N.; Lemke, M.; Cooper-Mahkorn, D.; Cohen, M.X.; et al. Nucleus accumbens deep brain stimulation decreases ratings of depression and anxiety in treatment-resistant depression. Biol. Psychiatry 2010, 67, 110–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bewernick, B.H.; Kayser, S.; Sturm, V.; Schlaepfer, T.E. Long-term effects of nucleus accumbens deep brain stimulation in treatment-resistant depression: Evidence for sustained efficacy. Neuropsychopharmacology 2012, 37, 1975–1985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Corripio, I.; Roldán, A.; Sarró, S.; McKenna, P.J.; Alonso-Solís, A.; Rabella, M.; Díaz, A.; Puigdemont, D.; Pérez-Solà, V.; Álvarez, E.; et al. Deep brain stimulation in treatment resistant schizophrenia: A pilot randomized cross-over clinical trial. eBioMedicine 2020, 51, 102568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kisely, S.; Hall, K.; Siskind, D.; Frater, J.; Olson, S.; Crompton, D. Deep brain stimulation for obsessive-compulsive disorder: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Psychol. Med. 2014, 44, 3533–3542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Da Cunha, C.; Boschen, S.L.; Gómez, A.; Ross, E.K.; Gibson, W.S.J.; Min, H.-K.; Lee, K.H.; Blaha, C.D. Toward sophisticated basal ganglia neuromodulation: Review on basal ganglia deep brain stimulation. Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev. 2015, 58, 186–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sabatino, M.; La Grutta, V.; Ferraro, G.; La Grutta, G. Relations between basal ganglia and hippocampus: Action of substantia nigra and pallidum. Rev. Electroencephalogr. Neurophysiol. Clin. 1986, 16, 179–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gálvez, G.; Recuero, M.; Canuet, L.; Del-Pozo, F. Short-Term Effects of Binaural Beats on EEG Power, Functional Connectivity, Cognition, Gait and Anxiety in Parkinson’s Disease. Int. J. Neural Syst. 2018, 28, 1750055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia-Argibay, M.; Santed, M.A.; Reales, J.M. Efficacy of binaural auditory beats in cognition, anxiety, and pain perception: A meta-analysis. Psychol. Res. 2019, 83, 357–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, M.; Song, C.B.; Shin, G.H.; Lee, S.W. Possible Effect of Binaural Beat Combined With Autonomous Sensory Meridian Response for Inducing Sleep. Front. Hum. Neurosci. 2019, 13, 425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chaieb, L.; Wilpert, E.C.; Reber, T.P.; Fell, J. Auditory beat stimulation and its effects on cognition and mood States. Front. Psychiatry 2015, 6, 70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Engelbregt, H.; Meijburg, N.; Schulten, M.; Pogarell, O.; Deijen, J.B. The Effects of Binaural and Monoaural Beat Stimulation on Cognitive Functioning in Subjects with Different Levels of Emotionality. Adv. Cogn. Psychol. 2019, 15, 199–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jirakittayakorn, N.; Wongsawat, Y. Brain Responses to a 6-Hz Binaural Beat: Effects on General Theta Rhythm and Frontal Midline Theta Activity. Front. Neurosci. 2017, 11, 365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Orozco Perez, H.D.; Dumas, G.; Lehmann, A. Binaural Beats through the Auditory Pathway: From Brainstem to Connectivity Patterns. eNeuro 2020, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wahbeh, H.; Calabrese, C.; Zwickey, H.; Zajdel, D. Binaural beat technology in humans: A pilot study to assess neuropsychological, physiological, and electroencephalographic effects. J. Altern. Complement. Med. 2007, 13, 199–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yusim, A.; Grigaitis, J. Efficacy of Binaural Beat Meditation Technology for Treating Anxiety Symptoms: A Pilot Study. J. Nerv. Ment. Dis. 2020, 208, 155–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weinstein, A.M. An update overview on brain imaging studies of Internet gaming disorder. Front Psychiatry 2017, 8, 185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seton, C.; Fitzgerald, D.A. Chronic sleep deprivation in teenagers: Practical ways to help. Paediatr. Respir. Rev. 2021, 40, 73–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Statista. Number of Smartphone Users from 2016 to 2021 (in Billions). Technology and Telecommunications. 2021. Available online: https://www.statista.com/statistics/330695/number-of-smartphone-users-worldwide/ (accessed on 3 June 2022).
- Chaudron, S. Young Children (0–8) and Digital Technology: A Qualitative Exploratory Study across Seven Countries; Publications Office of the European Union: Luxembourg, 2015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carreazo, Y. Association between social media use (Twitter, Instagram, Facebook) and depressive symptoms: Are Twitter users at higher risk? Int. J. Soc. Psychiatry 2019, 65, 14–19. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, Q.; Chen, T.; Zhong, N.; Bao, J.; Zhao, Y.; Du, J.; Zhao, M. Changes of internet behavior of adolescents across the period of COVID-19 pandemic in China. Psychol. Health Med. 2022, 1–11, Epub ahead of print. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masaeli, N.; Farhadi, H. Prevalence of Internet-based addictive behaviors during COVID-19 pandemic: A systematic review. J. Addict. Dis. 2021, 39, 468–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Z.L.; Liu, R.; He, F.; Li, S.Y.; Zhao, Y.J.; Zhang, W.Y.; Zhang, Y.; Cheung, T.; Jackson, T.; Tang, Y.L.; et al. Prevalence of Internet Addiction Disorder and Its Correlates among Clinically Stable Adolescents with Psychiatric Disorders in China during the COVID-19 Outbreak. Front. Psychiatry 2021, 12, 686177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Dresp-Langley, B.; Hutt, A. Digital Addiction and Sleep. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 6910. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph19116910
Dresp-Langley B, Hutt A. Digital Addiction and Sleep. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health. 2022; 19(11):6910. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph19116910
Chicago/Turabian StyleDresp-Langley, Birgitta, and Axel Hutt. 2022. "Digital Addiction and Sleep" International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health 19, no. 11: 6910. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph19116910
APA StyleDresp-Langley, B., & Hutt, A. (2022). Digital Addiction and Sleep. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 19(11), 6910. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph19116910





