Analysis of the Dilemma of Promoting Circular Logistics Packaging in China: A Stochastic Evolutionary Game-Based Approach
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Literature Review
2.1. Green Logistics-Packaging Recycling and Management
2.2. Stochastic Evolutionary Game
3. Problem Formulation and Model Construction
3.1. Problem Description and Parameter Setting
3.2. Payoff Matrix and Replicator Dynamics Equations
4. Construction of the Stochastic Evolutionary Game Model
4.1. Stochastic Evolutionary Game Model
4.2. Analysis of the Existence and Stability of Equilibrium Solutions
- (a)
- If a positive constant exists, such that , then the zero solution of Equation (19) is an exponentially stable P-order moment, which holds .
- (b)
- If there exists a positive constant , such that , then the zero solution of Equation (19) with the P-order moment exponent is unstable and holds .
4.3. Taylor Expansion of the Evolution Equation
5. Simulation and Discussion
5.1. Data Collection
- JD Logistics has invested 300,000 “Qingliu” circular logistics boxes into society. The cost of this kind of logistics box is about CNY 15, and the number of cycles is about 20. The cost of an ordinary logistics box is about CNY 1; therefore, the use of ordinary logistics packaging cost is CNY 300,000. The cost of using circular logistics box is CNY 225,000.
- According to China’s Hainan Provincial Development and Reform Commission, each circular logistics box is subsidized by CNY 0.4. The subsidy of logistics companies obtained from environmental regulators is CNY 120,000. Assuming that the subsidy strength is 0.5, referring to Shanghai’s policy of penalizing enterprises with excessive carbon emissions, we can infer that logistics enterprises are fined CNY 100,000 for not using circular packaging, assuming that the penalty intensity is 0.5 at this point.
- The cost of a green packaging recycling box is about CNY 500 per piece. According to “China Logistics Packaging Waste Generation Characteristics and Management Status Study Report,” it is estimated that 300,000 circular logistics boxes require about 100 recycling bins for their recovery. The personnel management cost of each recycling bin is about CNY 2000. Therefore, the additional cost for logistics enterprises to promote circular packaging can be obtained as CNY 250,000. JD Logistics returns 20 “Jingdou” to consumers who take the initiative to recycle the packaging. “Jingdou” can be spent in JD Mall, and 20 “Jingdou” is about CNY 0.2. The incentive given by logistics companies to consumers for using circular packaging can be obtained as CNY 60,000.
- The additional regulatory cost is set at CNY 50,000 with reference to the public data of Shanghai Environmental Protection Bureau. Other parameters, which are more difficult to determine economically, are determined through expert interviews and visits to research organizations, where is 0.6, is 0.3, and and are both set to 2.
- The Chinese government is actively enacting various policies to reduce social carbon emissions and to achieve the goal of “carbon neutrality” and “carbon peaking”. Therefore, the probability of initial “weak regulation” by the environmental regulator x is 0.2. Most logistics companies are still in a wait-and-see situation, and the promotion of circular packaging is uncommon. Therefore, the initial “no promotion” probability y for logistics companies is 0.5. The survey shows that currently, only about 20% of consumers are actively recycling packaging. Therefore, the initial “negative use” probability z of the consumer is set to 0.8.
5.2. Simulation and Discussion
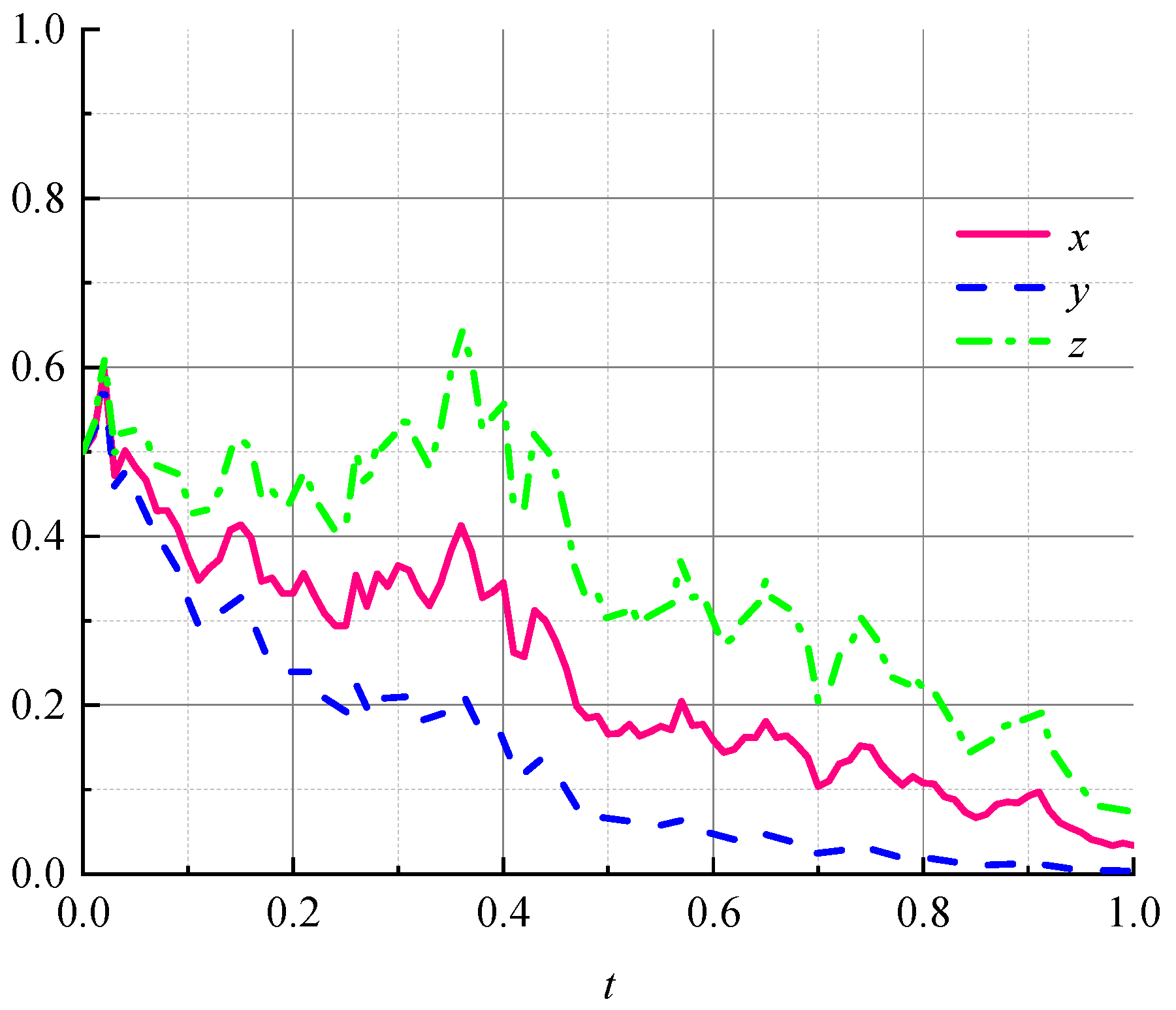
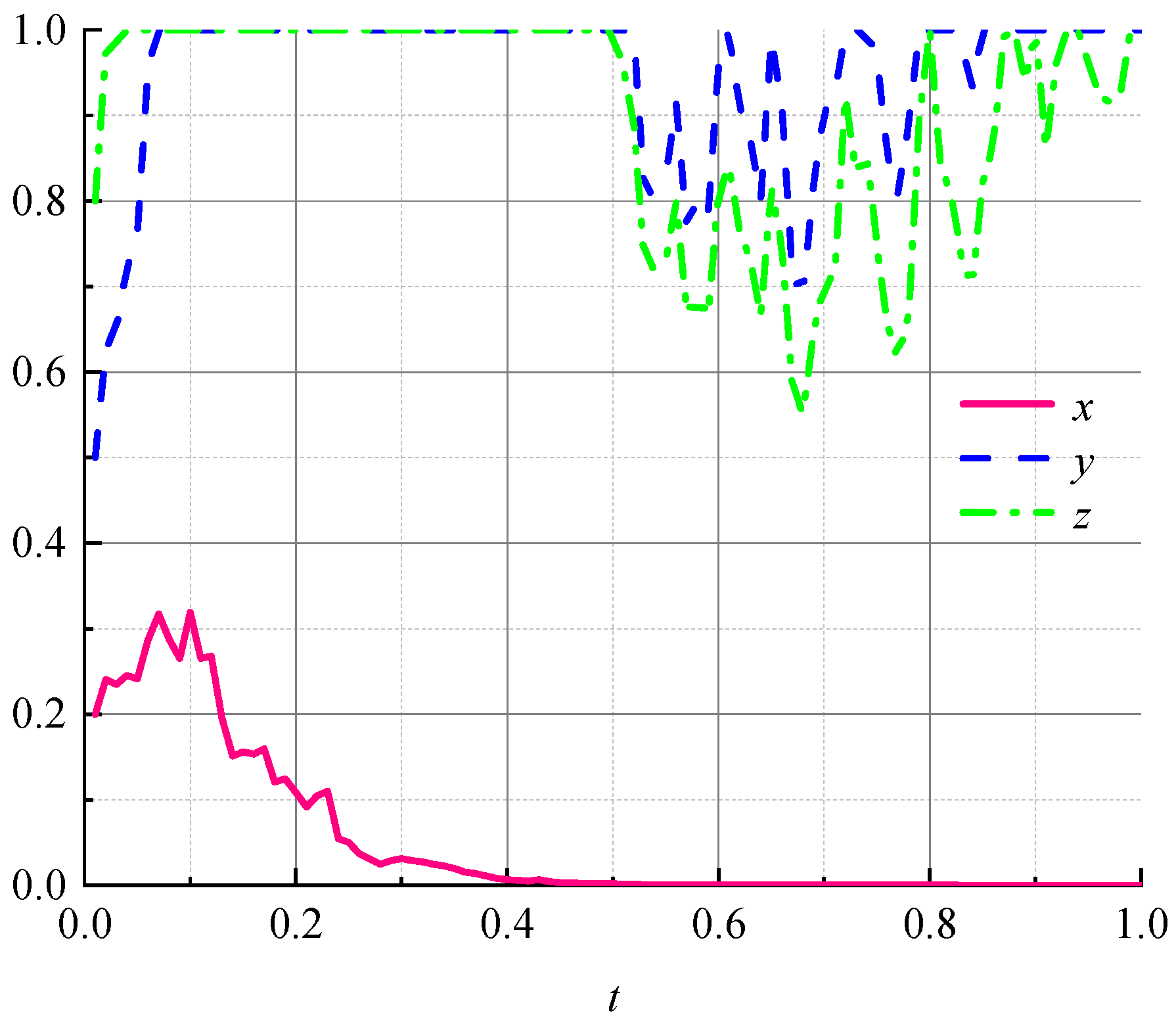
- (1)
- Impact of initial probability changes on evolutionary results
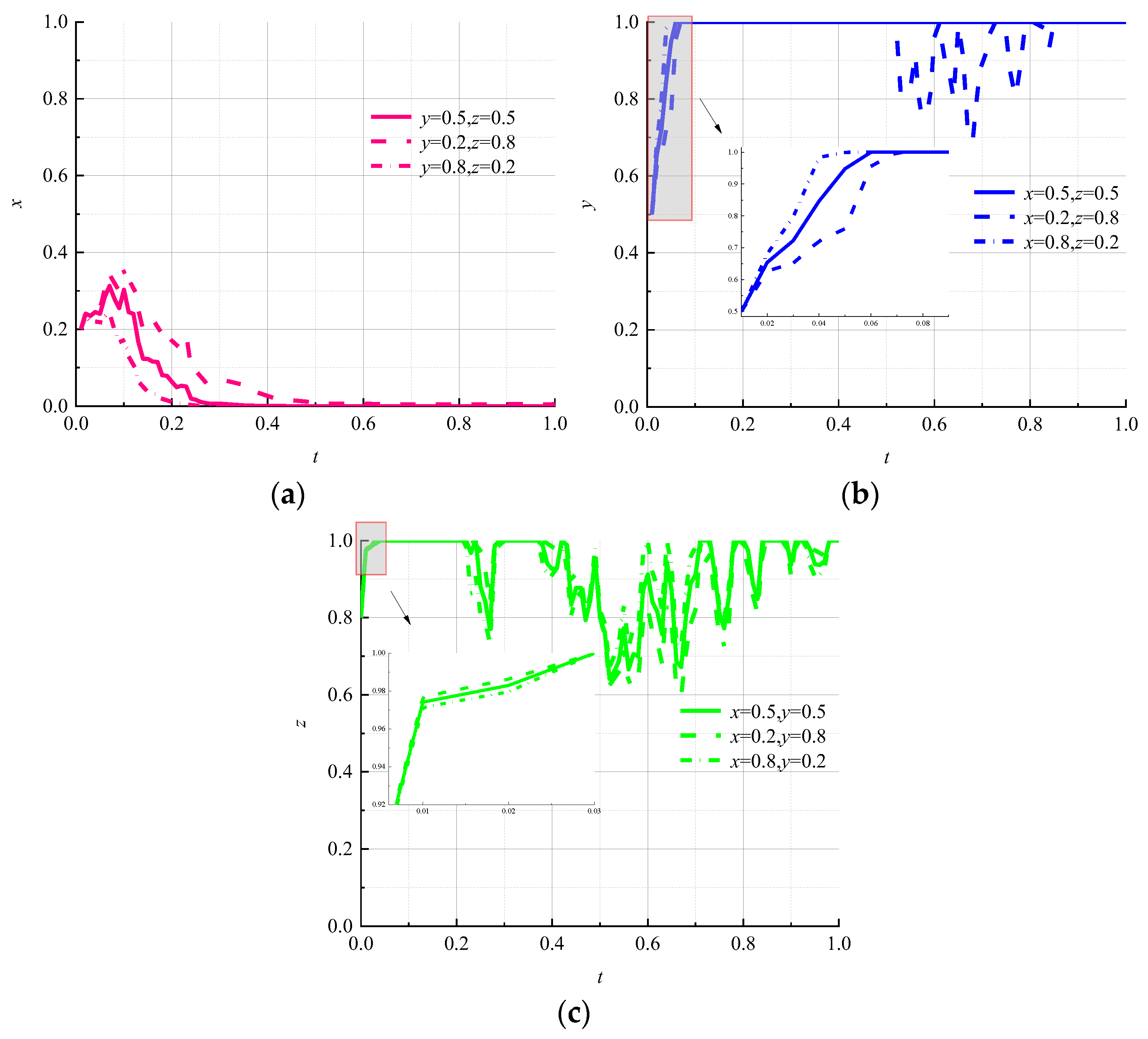
- (2)
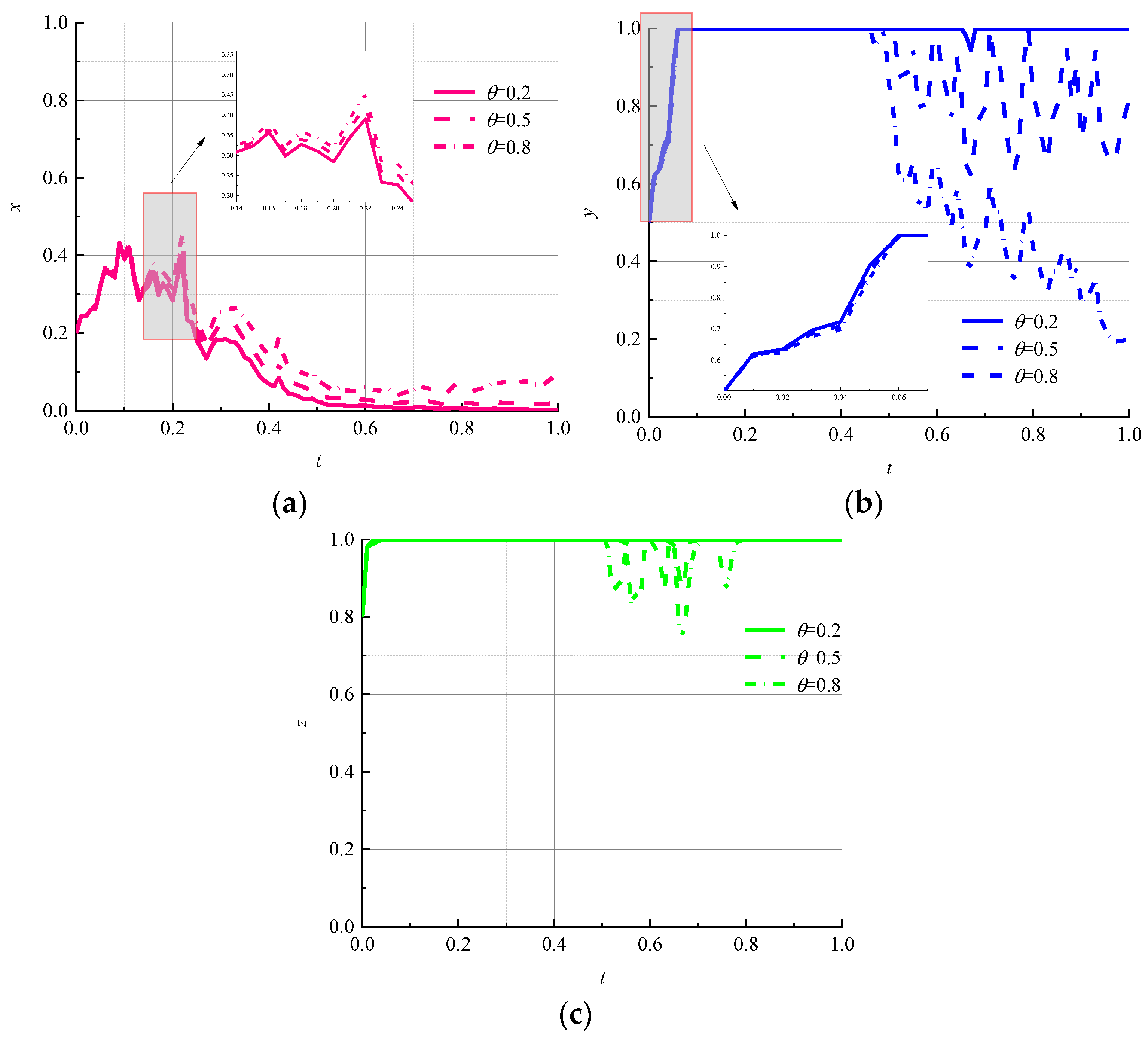
- Impact of information disclosure intensity on evolutionary results
- (3)
- Impact of penalty intensity on evolutionary results
- (4)
- Impact of subsidy intensity on evolutionary results
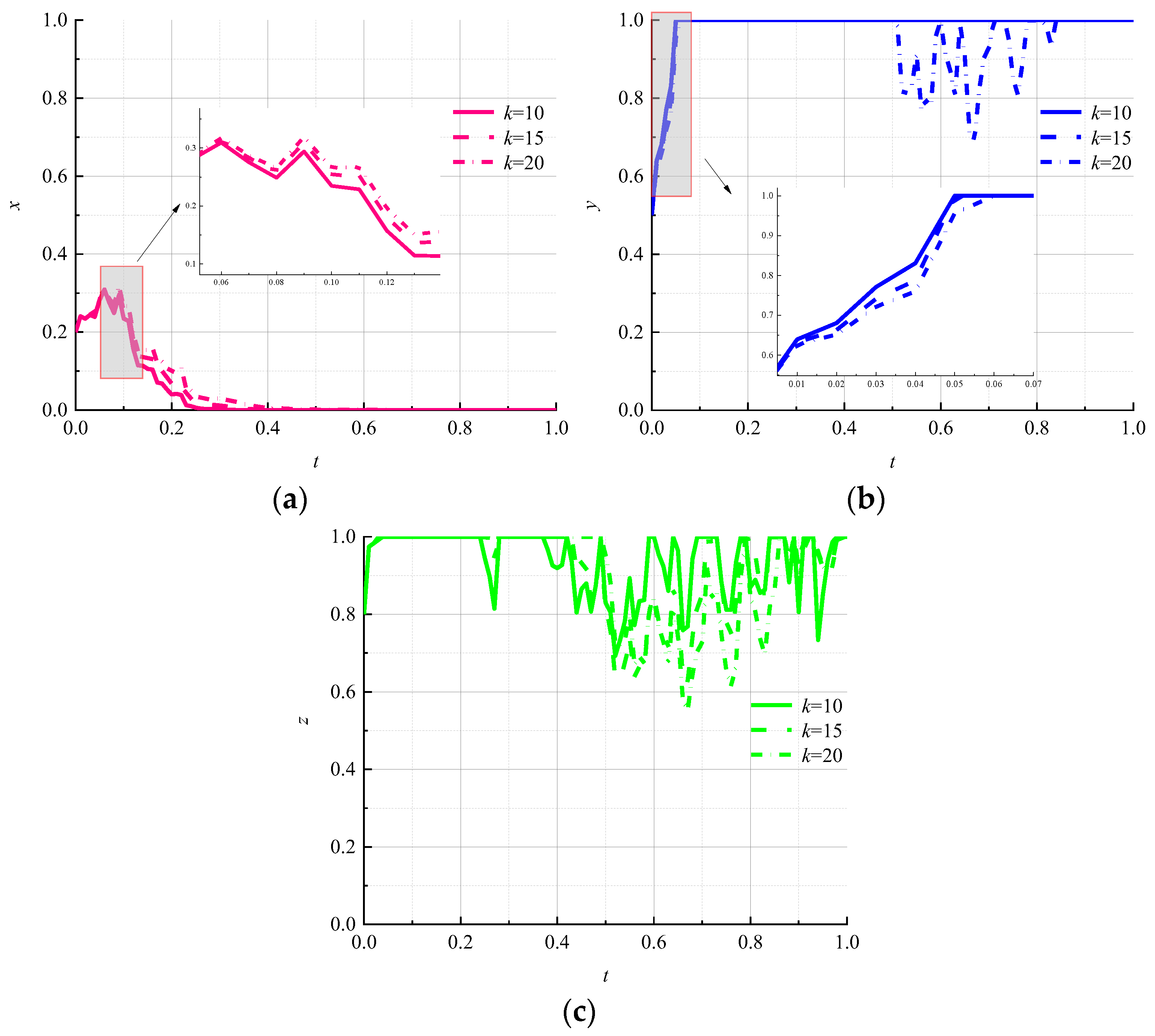
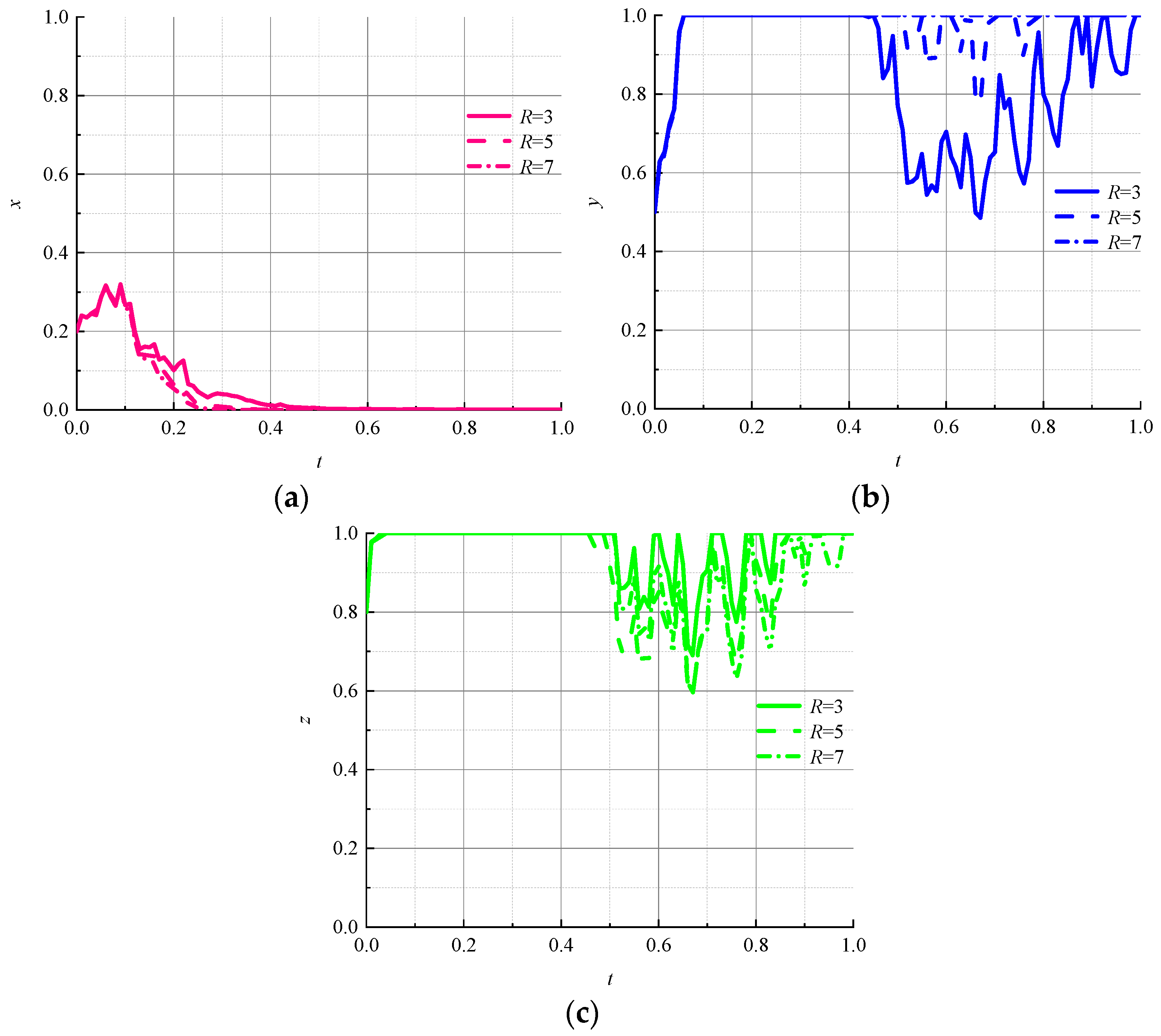
- (5)
- Impact of the number by cycles on the evolutionary results
- (6)
- Impact of recycling incentives on evolutionary results
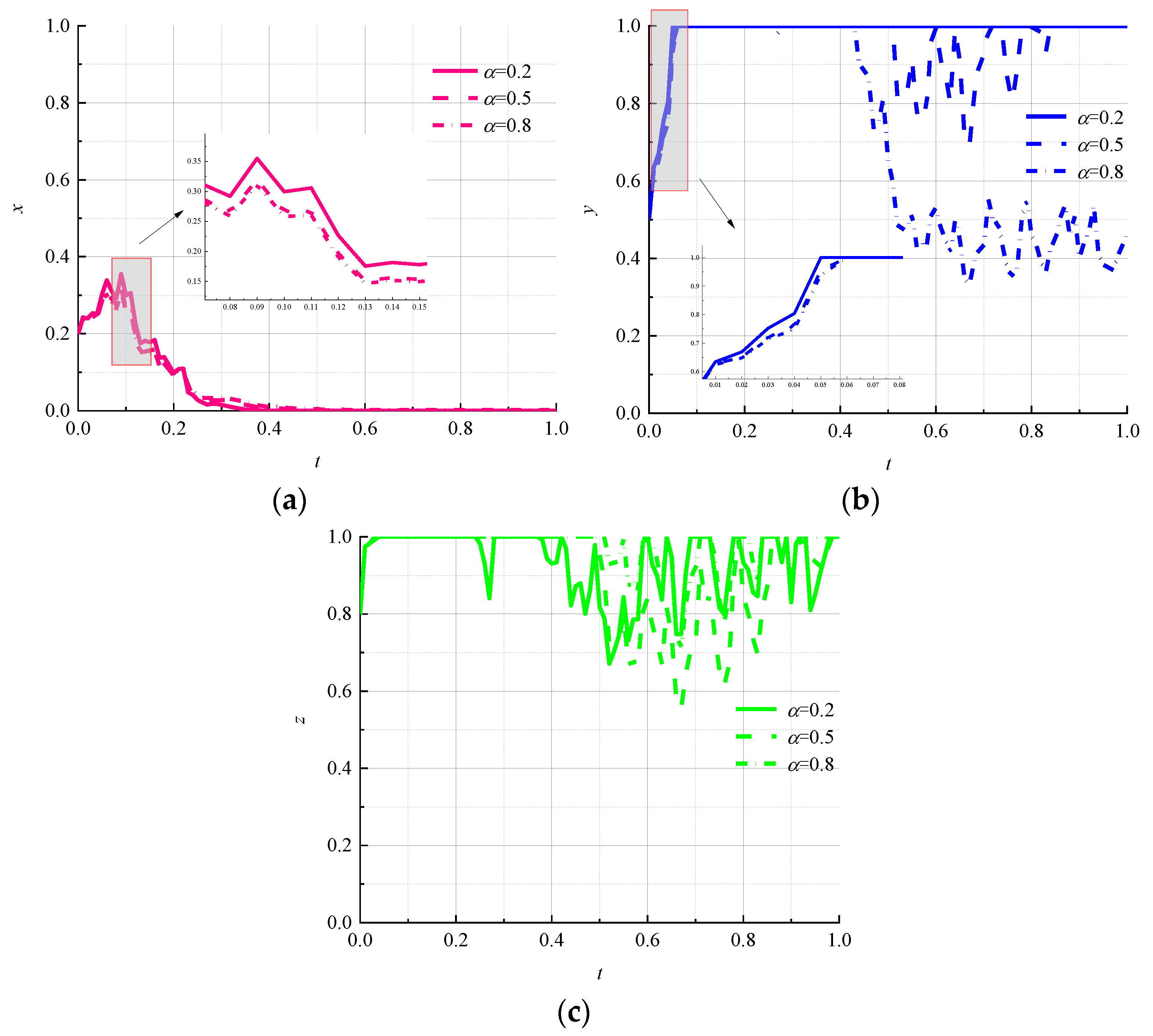
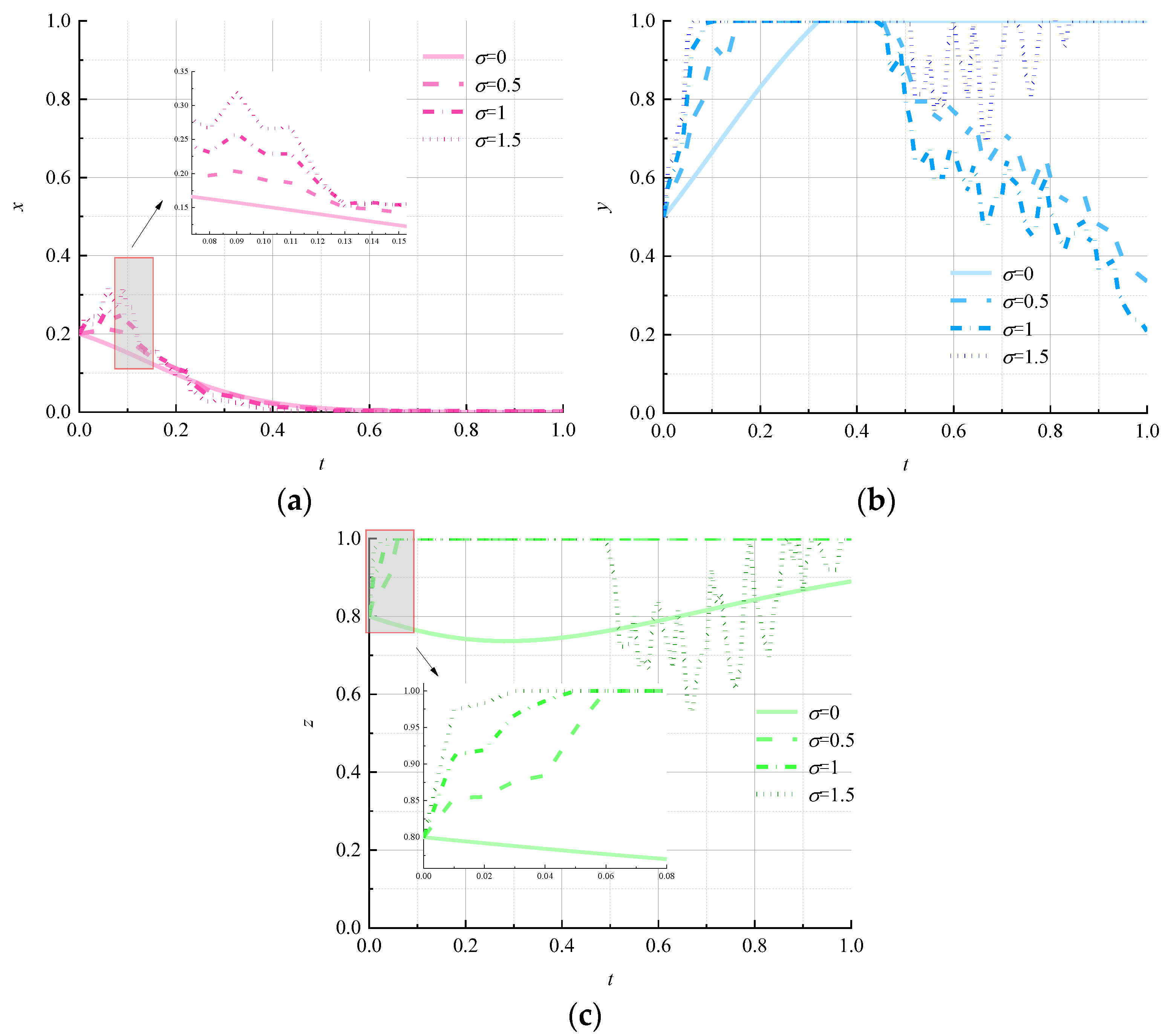
- (7)
- Impact of random disturbance strength on evolutionary results
6. Conclusions and Policy Implications
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Garcia-Arca, J.; Comesana-Benavides, J.A.; Garrido, A.; Prado-Prado, J.C. Rethinking the Box for Sustainable Logistics. Sustainability 2020, 12, 1870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Xiang, N.; Xu, F.; Sha, J.H. Simulation Analysis of China’s Energy and Industrial Structure Adjustment Potential to Achieve a Low-carbon Economy by 2020. Sustainability 2013, 5, 5081–5099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Olivo, F.; Junqueira, M.C.; Furlan, M.B.; Justi, P.A.; Lima, P.D. Monetary losses caused by the absence of packaging reverse logistics: Environmental and economic impacts. J. Mater. Cycles Waste Manag. 2020, 22, 1801–1817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molina-Besch, K.; Palsson, H. A Supply Chain Perspective on Green Packaging Development-Theory Versus Practice. Packag. Technol. Sci. 2016, 29, 45–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Da Cruz, N.F.; Simoes, P.; Marques, R.C. Economic cost recovery in the recycling of packaging waste: The case of Portugal. J. Clean. Prod. 2012, 37, 8–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Marques, R.C.; da Cruz, N.F.; Simoes, P.; Ferreira, S.F.; Pereira, M.C.; De Jaeger, S. Economic viability of packaging waste recycling systems: A comparison between Belgium and Portugal. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2014, 85, 22–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kuo, T.C.; Chiu, M.C.; Chung, W.H.; Yang, T.I. The circular economy of LCD panel shipping in a packaging logistics system. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2019, 149, 435–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.Y.; Li, J.; Li, Y.; Chen, G.Q. Evolution Process of Recycling Chain of Takeout Packages Based on Behavioural Science. Neuroquantology 2018, 16, 215–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.F.; Liu, S.C.; Liu, Y.; Li, R. Smart box-enabled product-service system for cloud logistics. Int. J. Prod. Res. 2016, 54, 6693–6706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, S.; Gong, X.; Wang, Y.; Cao, J. Consumer Cognition and Management Perspective on Express Packaging Pollution. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 4895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, Z.H.; Sun, J.; Wang, Y.W.; Jiang, X.H.; Liu, R.; Sun, W.B.; Mou, Y.P.; Wang, D.A.W.; Liu, M.Z. Research on the influence of anthropomorphic design on the consumers’ express packaging recycling willingness: The moderating effect of psychological ownership. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2021, 168, 105269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, F.Y.; Chen, H.; Yang, J.H.; Long, R.Y.; Li, W.B. Impact of regulatory focus on express packaging waste recycling behavior: Moderating role of psychological empowerment perception. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2019, 26, 8862–8874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tan, Y.; Guo, C.X. Research on Two-Way Logistics Operation with Uncertain Recycling Quality in Government Multi-Policy Environment. Sustainability 2019, 11, 882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sun, D.S.; Xie, D.L.; Jiang, P.; Xie, J.C.; Xu, Y.; Ren, Y.N. Simulating the Effect of Mixed Subsidy Policies on Urban Low-Value Recyclable Waste in China: A System Dynamics Approach. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 10636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, X.M.; Bai, X.L. How to motivate the producers’ green innovation in WEEE recycling in China?—An analysis based on evolutionary game theory. Waste Manag. 2021, 122, 26–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gorji, M.A.; Jamali, M.B.; Iranpoor, M. A game-theoretic approach for decision analysis in end-of-life vehicle reverse supply chain regarding government subsidy. Waste Manag. 2021, 120, 734–747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.L.; He, L.Y.; Zhong, Z.Q.; Wang, D.Q. How does China’s green institutional environment affect renewable energy investments? The nonlinear perspective. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 727, 138689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.B.; Long, R.Y.; Chen, H.; Dou, B.Q.; Chen, F.Y.; Zheng, X.; He, Z.X. Public Preference for Electric Vehicle Incentive Policies in China: A Conjoint Analysis. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kwon, Y.; Son, S.; Jang, K. Evaluation of incentive policies for electric vehicles: An experimental study on Jeju Island. Transp. Res. Part A Policy Pract. 2018, 116, 404–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, C.J.; Brannon, D.C.; Salas, J.; Troncoza, M. Advertising, incentives, and the upsell: How advertising differentially moderates customer- vs. retailer-directed price incentives’ impact on consumers’ preferences for premium products. J. Acad. Mark. Sci. 2021, 49, 1043–1064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Yan, L. An Analytical Study of the External Environment of the Coevolution between Manufacturing and Logistics Based on the Logistic Model. Complexity 2021, 2021, 9914076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, L.A.; Li, L.; Tang, L. What can mass media do to control public panic in accidents of hazardous chemical leakage into rivers? A multi-agent-based online opinion dissemination model. J. Clean. Prod. 2017, 143, 1203–1214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.M.; Zhou, G.G.; Cao, J.; Wu, A.Q. Evolving strategies of e-commerce and express delivery enterprises with public supervision. Res. Transp. Econ. 2020, 80, 100810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bo, Y.; Shao, W.T. Empirical statistical analysis on the influencing factors of Co-opetition behavior of enterprises in logistics park. Int. J. Electr. Eng. Educ. 2020, 6, 0020720920931080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.Q.; Liu, S.; Ye, D.P.; Tang, H.; Wang, F. Dynamic impact of negative public sentiment on agricultural product prices during COVID-19. J. Retail. Consum. Serv. 2022, 64, 102790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Lin, K.; Wang, L. Stochastic evolutionary game analysis of e-waste recycling in environmental regulation from the perspective of dual governance system. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 319, 128685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, X.X.; Zheng, H.D. Environmental Concerns, Environmental Policy and Green Investment. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2017, 14, 1570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cao, H.; Guan, X.; Fan, T.J.; Zhou, L. The Acquisition of Quality Information in a Supply Chain with Voluntary vs. Mandatory Disclosure. Prod. Oper. Manag. 2020, 29, 595–616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, S.Q.; Liao, W.Z.; Huang, Y.Q. Heterogeneous fleet recyclables collection routing optimization in a two-echelon collaborative reverse logistics network from circular economic and environmental perspective. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 758, 144062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.Y.; Huo, L.J. Problems and Solutions for Express Logistic Packaging. In Proceedings of the China Academic Conference on Printing, Packaging Engineering and Media Technology, China Academy of Printing Technology, Xian, China, 25–27 November 2016; pp. 705–710. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, G.R.; Zhao, Z.J. Green Packaging Management of Logistics Enterprises. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Applied Physics and Industrial Engineering (ICAPIE), Wuhan, China, 1–2 March 2012; pp. 900–905. [Google Scholar]
- Kumar, M.; Kumar, D. Green Logistics Optimization Model for Forward and Reverse Logistics Using Genetic Algorithm. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Industrial Engineering and Engineering Management (IEEM), Singapore, 6–9 December 2015; pp. 717–720. [Google Scholar]
- Renugala, S.; Chin, T.A.; Henga, L.H. Drivers of Green Logistics Practices for Sustainability Performance: A Review. Adv. Sci. Lett. 2018, 24, 3858–3863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laguir, I.; Stekelorum, R.; El Baz, J. Going green? Investigating the relationships between proactive environmental strategy, GSCM practices and performances of third-party logistics providers (TPLs). Prod. Plan. Control 2021, 32, 1049–1062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, H.X.; Li, J.L. Behavioural choice of governments, enterprises and consumers on recyclable green logistics packaging. Sustain. Prod. Consum. 2021, 28, 459–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.Z.; Tsai, Z.L.; Fu, J.; Zhao, L.Y.; Yang, L.L. Internalization of negative external cost of green logistics and incentive mechanism. Adv. Mech. Eng. 2017, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wandosell, G.; Parra-Merono, M.C.; Alcayde, A.; Banos, R. Green Packaging from Consumer and Business Perspectives. Sustainability 2021, 13, 1356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.T. Research on application and innovation of green ecological concept in packaging design. Fresenius Environ. Bull. 2022, 31, 2653–2658. [Google Scholar]
- Hao, Y.; Liu, H.; Chen, H.J.; Sha, Y.H.; Ji, H.F.; Fan, J.J. What affect consumers’ willingness to pay for green packaging? Evidence from China. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2019, 141, 21–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, J.M.; Price, G.R. The Logic of Animal Conflict. Nature 1973, 246, 15–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, J.M. The theory of games and the evolution of animal conflicts. J. Theor. Biol. 1974, 47, 209–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Taylor, P.D.; Jonker, L. B Evolutionarily Stable Strategies and Game Dynamics. Math. Biosci. Eng. 1978, 40, 145–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foster, D.; Young, P.J. Stochastic evolutionary game dynamics. Theor. Popul. Biol. 1990, 38, 219–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cobb, L.; Ragade, R.K. Applications of Catastrophe Theory in the Behavioral and Life Sciences; Behavioral Science: New York, NY, USA, 1978; Volume 23. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, B.S.; Yeh, C.H. Stochastic noncooperative and cooperative evolutionary game strategies of a population of biological networks under natural selection. Biosystems 2017, 162, 90–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, H.M.; Wang, F.Q.; Wang, L.Y.; Su, L.M.; Zhang, C.Y. The Stochastic Evolution Game of Knowledge Sharing in the Infrastructure PPP Supply Chain Network. Complexity 2020, 2020, 8858845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Du, Y. Technical standard competition: An ecosystem-view analysis based on stochastic evolutionary game theory. Technol. Soc. 2021, 67, 101794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, W.-Q.; Wang, Y.-J.; Su, C.-H.; Chen, M.-H.; Kot, H.W. A comprehensive analysis of package tour quality: A stochastic evolutionary game. Tour. Manag. 2022, 91, 104478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Ren, H.; Wang, M. How to escape the dilemma of charging infrastructure construction? A multi-sectorial stochastic evolutionary game model. Energy 2021, 231, 120807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cobb, L.; Zacks, S. Applications of Catastrophe Theory for Statistical Modeling in the Biosciences. J. Am. Stat. Assoc. 1985, 80, 793–802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Parameters | Descriptions |
|---|---|
| Basic benefits for environmental regulators | |
| Basic benefits for logistics companies | |
| Basic benefits for consumers | |
| Additional regulatory costs when environmental regulators choose a “strong regulation” strategy | |
| Subsidies from environmental regulators for logistics companies choosing “promotion” strategies | |
| The intensity of subsidies from environmental regulators for logistics companies choosing “promotion” strategies | |
| Environmental regulators fine logistics companies for choosing a “nonpromotion” strategy | |
| The intensity of penalty from environmental regulators for logistics companies choosing “nonpromotion” strategies | |
| Reputational damage of a logistics company’s choice of “nonpromotion” strategy when information is made public | |
| Reputational benefits of a logistics company’s choice of “promotion” strategy when information is made public | |
| The intensity of information disclosure by environmental regulators | |
| Cost of ordinary logistics packaging | |
| Cost of circular logistics packaging | |
| The maximum number of cycles that can be made in a circular package | |
| Cost of environmental governance for environmental regulators | |
| Cost of developing circular packaging for logistics companies | |
| Additional costs for logistics companies to promote circular packaging | |
| Incentives for consumers to actively use circular packaging | |
| The cost of time and physical effort for consumers to actively use circular packaging | |
| The psychological loss of consumers after unsuccessful recycling | |
| Potential losses for logistics companies |
| Variable | Description |
|---|---|
| Probability of environmental regulators choosing a “weak regulation” strategy | |
| The probability of logistics companies choosing the “nonpromotion” strategy | |
| Probability of consumers choosing the “negative use” strategy |
| Strategic Choice | Environmental Regulators | Logistics Companies | Consumers |
|---|---|---|---|
| (x, y, z) | |||
| (1 − x, y, z) | |||
| (x, 1 − y, z) | |||
| (1 − x, 1 − y, z) | |||
| (x, y, 1 − z) | |||
| (1 − x, y, 1 − z) | |||
| (x, 1 − y, 1 − z) | |||
| (1 − x, 1 − y, 1−z) |
| Parameters | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Value | 30 | 22.5 | 12 | 10 | 25 | 6 | 5 | 0.6 | 0.3 | 2 | 2 | 0.5 | 0.5 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Xu, X.; Yang, Y. Analysis of the Dilemma of Promoting Circular Logistics Packaging in China: A Stochastic Evolutionary Game-Based Approach. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 7363. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph19127363
Xu X, Yang Y. Analysis of the Dilemma of Promoting Circular Logistics Packaging in China: A Stochastic Evolutionary Game-Based Approach. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health. 2022; 19(12):7363. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph19127363
Chicago/Turabian StyleXu, Xinyang, and Yang Yang. 2022. "Analysis of the Dilemma of Promoting Circular Logistics Packaging in China: A Stochastic Evolutionary Game-Based Approach" International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health 19, no. 12: 7363. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph19127363
APA StyleXu, X., & Yang, Y. (2022). Analysis of the Dilemma of Promoting Circular Logistics Packaging in China: A Stochastic Evolutionary Game-Based Approach. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 19(12), 7363. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph19127363





