Using Stable Sulfur Isotope to Trace Sulfur Oxidation Pathways during the Winter of 2017–2019 in Tianjin, North China
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Method
2.1. Sample Collection
2.2. Chemical Composition Analysis
2.3. Determination of Sulfur Isotopic (δ34S) Ratios
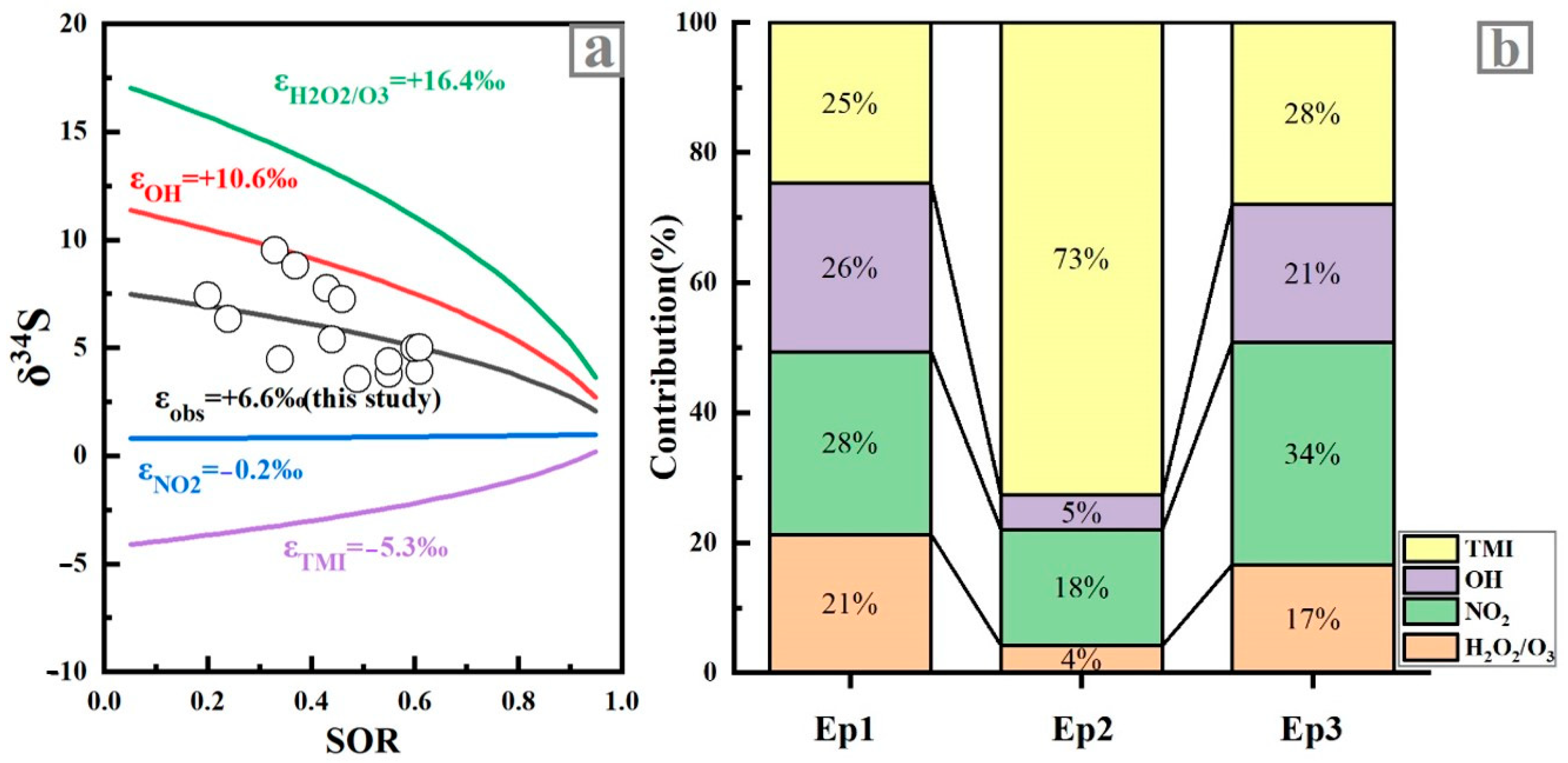
2.4. MIXSIAR Model to Calculate the Formation Pathways of Sulfate Aerosols
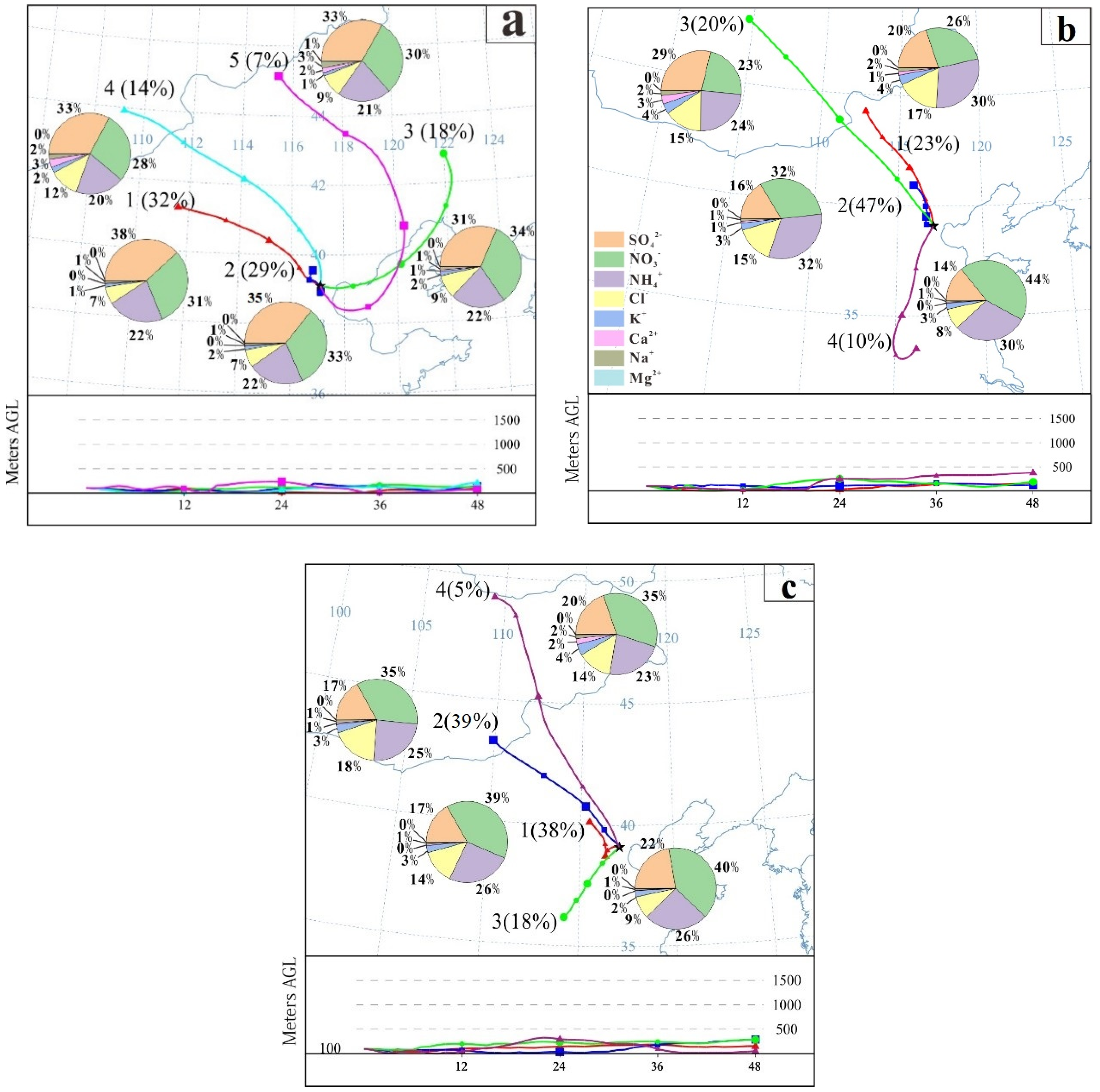
2.5. HYSPLIT Backward Trajectory Analysis
2.6. Boundary Layer Height (BLH) Simulation
3. Results and Discussion
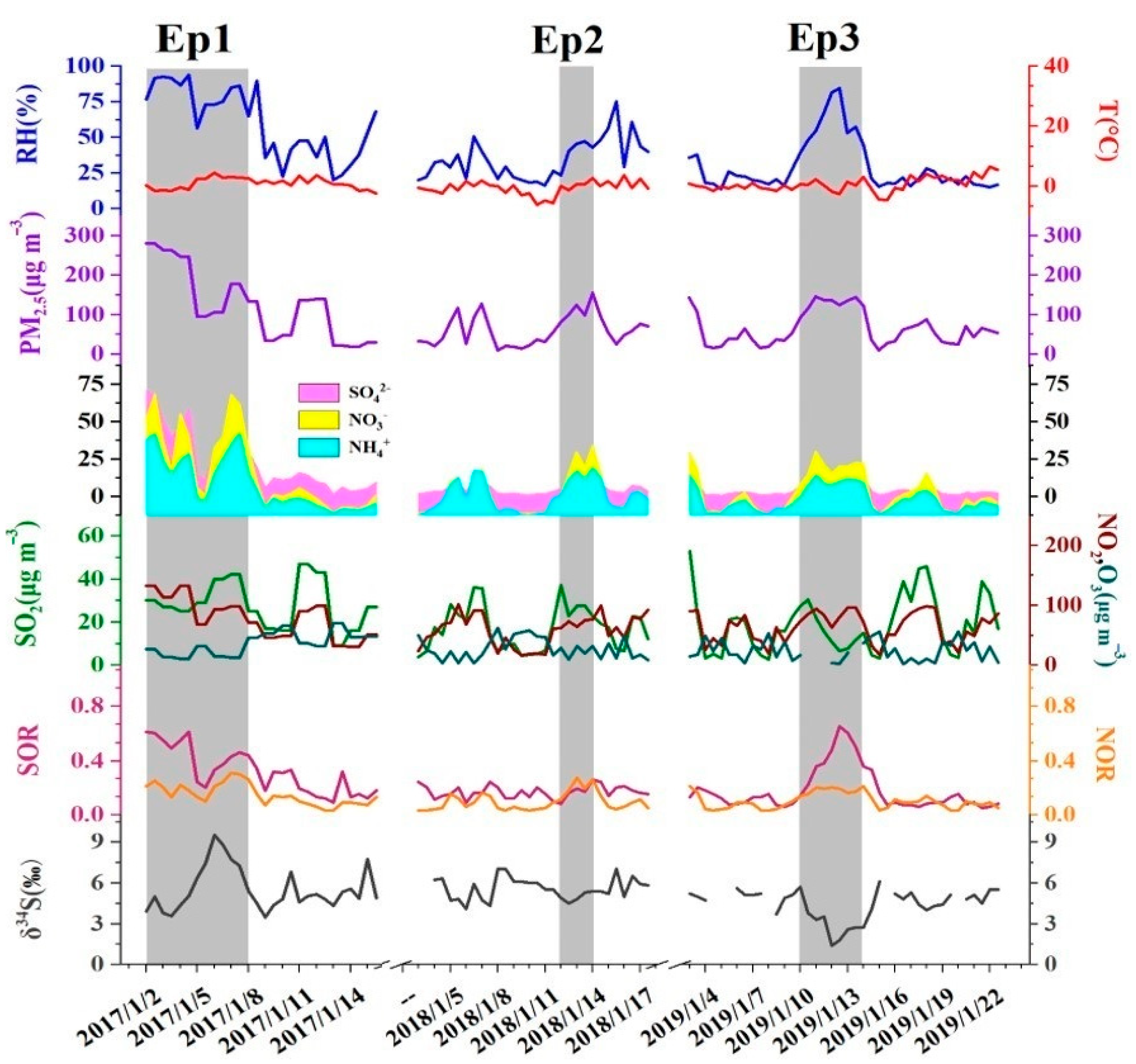
3.1. Effect of CRP on PM2.5 Loading and Its Composition
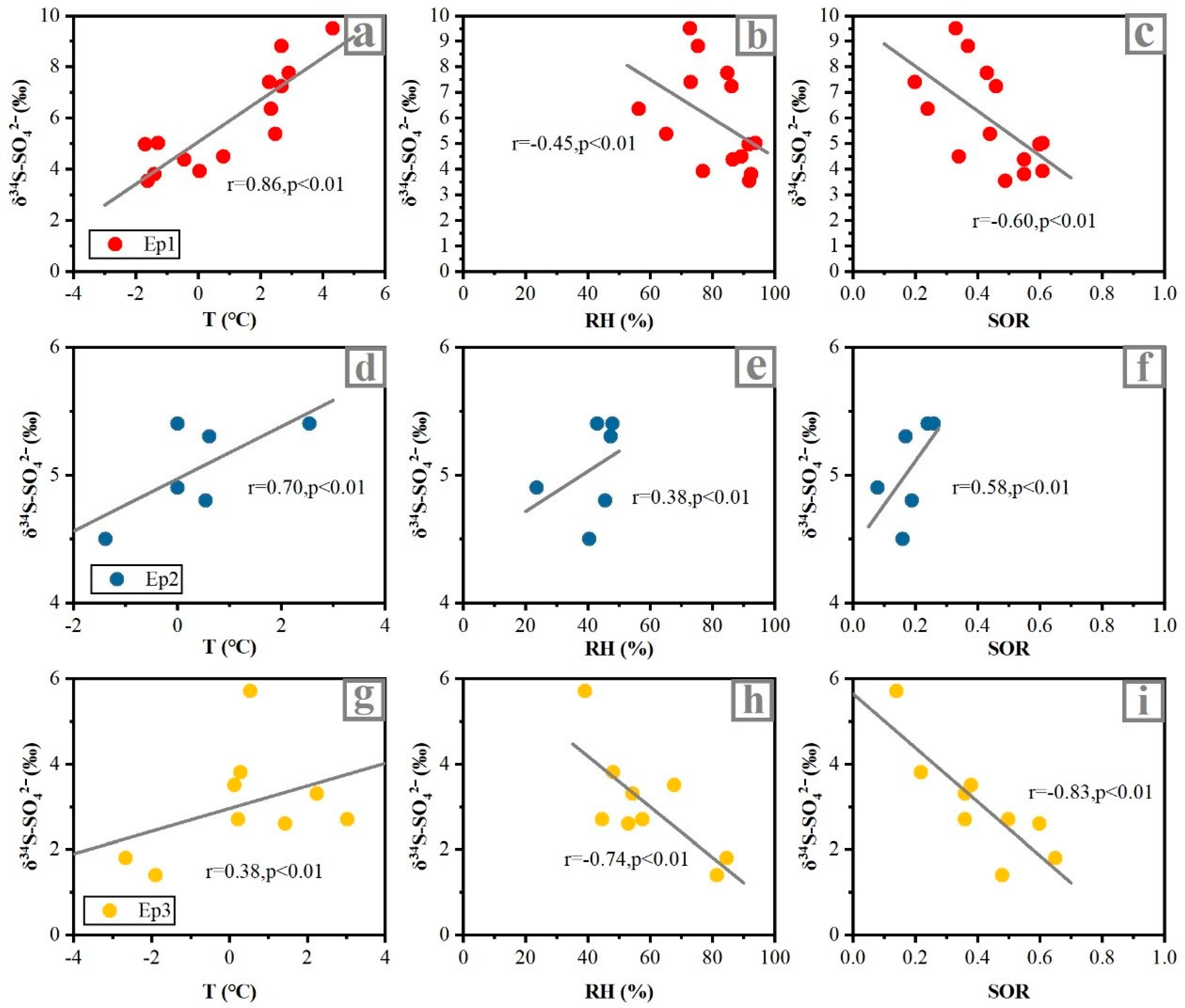
3.2. Sulfur Isotope Composition of Sulfate Aerosols
3.3. Sulfur Isotopic Characteristics during the Haze Episodes
3.3.1. Sulfur Isotopic Compositions of Sulfate during the Haze Episodes
3.3.2. Contributions of Oxidation Pathways to Sulfate Formation
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bai, W.; Zhao, X.; Yin, B.; Guo, L.; Zhang, W.; Wang, X.; Yang, W. Characteristics of PM2.5 in an industrial city of northern China: Mass concentrations, chemical composition, source apportionment, and health risk assessment. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 5443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ouyang, J.; Shao, Y.; Luo, M.; Zhang, J.L.; Dai, X.X.; Ma, L.L.; Xu, D.D. Exploration of the potential application of plutonium isotopes in source identification of sandstorm in the atmosphere of Beijing. Chin. Chem. Lett. 2022, 33, 3516–3521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Li, T.; Li, Z.; Fang, C. Study on the spatial and temporal distribution characteristics and influencing factors of particulate matter pollution in coal production cities in China. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 3228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- An, Z.; Huang, R.-J.; Zhang, R.; Tie, X.; Li, G.; Cao, J.; Zhou, W.; Shi, Z.; Han, Y.; Gu, Z.; et al. Severe haze in northern China: A synergy of anthropogenic emissions and atmospheric processes. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2019, 116, 8657–8666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.H.; Chen, Y.J.; Song, Y.Y.; Dong, C.; Cai, Z.W. Atmospheric pressure gas chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry analysis of fourteen emerging polycyclic aromatic sulfur heterocycles in PM2.5. Chin. Chem. Lett. 2021, 32, 801–804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, J.; Zhang, L.; Cao, J.; Zhang, R. A review of current knowledge concerning PM2.5 chemical composition, aerosol optical properties and their relationships across China. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2017, 17, 9485–9518. [Google Scholar]
- Feng, X.Q.; Li, Q.K.; Tao, Y.L.; Ding, S.Y.; Chen, Y.Y.; Li, X.D. Impact of Coal Replacing Project on atmospheric fine aerosol nitrate loading and formation pathways in urban Tianjin: Insights from chemical composition and 15N and 18O isotope ratios. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 708, 134797. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Wu, G.; Tian, W.; Zhang, L.; Yang, H. The Chinese spring festival impact on air quality in China: A critical review. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 9074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, C.; Sun, Y.L.; Xu, W.Q.; Du, W.; Zhou, L.B.; Han, T.T.; Wang, Q.Q.; Fu, P.Q.; Wang, Z.F.; Gao, Z.Q. Characteristics and sources of submicron aerosols above the urban canopy (260 m) in Beijing, China during 2014 APEC summit. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2015, 15, 12879–12895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, W.J.; Liu, C.; Hu, Q.H.; Fan, G.Q.; Xie, Z.Q.; Huang, X.; Zhang, T.S.; Chen, Z.Y.; Dong, Y.S.; Ji, X.G. Characterization of ozone in the lower troposphere during the 2016 G20 conference in Hangzhou. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 17368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Chen, W.Y. Potential impact of shifting coal to gas and electricity for building sectors in 28 major northern cities of China. Appl. Energy 2019, 236, 1049–1061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, B.; Jia, Z. Economic, energy and environmental impact of coal-to-electricity policy in China: A dynamic recursive CGE study. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 698, 134241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, C.Q.; Yang, J.J. Economic benefits assessments of “coal-to-electricity” project in rural residents heating based on life cycle cost. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 213, 217–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, Y.Q.; Wang, G.H.; Wu, C.; Wang, J.Y.; Li, J.J.; Zhang, L.; Han, Y.N.; Liu, L.; Cao, C.; Cao, J.J.; et al. Changes in concentration, composition and source contribution of atmospheric organic aerosols by shifting coal to natural gas in Urumqi. Atmos. Environ. 2017, 148, 306–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pang, J.; Jian, W.U.; Zhong, M.A.; Liang, L.N.; Zhang, T.T. Air pollution abatement effects of replacing coal with natural gas for central heating in cities of China. China Environ. Sci. 2015, 35, 55–61. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, J.P.; Ning, Y.C.; Liu, C.L.; Zheng, L.I.; Wang, H.H.; Chen, L. Monitoring and analysis of effect of project “Replacing Coal With Electricity” improving atmospheric environmental quality in mentougou district, Beijing. J. Ecol. Rural Environ. 2017, 33, 898–906. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, G.; Zhang, R.; Gomez, M.E.; Yang, L.; Zamora, M.L.; Hu, M.; Lin, Y.; Peng, J.; Guo, S.; Meng, J. Persistent sulfate formation from London Fog to Chinese haze. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2016, 113, 13630–13635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, R.J.; Zhang, Y.L.; Bozzetti, C.; Ho, K.F.; Cao, J.J.; Han, Y.M.; Daellenbach, K.R.; Slowik, J.G.; Platt, S.M.; Canonaco, F. High secondary aerosol contribution to particulate pollution during haze events in China. Nature 2014, 514, 218–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Guo, Z.; Guo, Z.; Guo, Q.; Zhang, Y.; Zhu, B.; Zhang, H. Sulfur isotopic fractionation and its implication: Sulfate formation in PM2.5 and coal combustion under different conditions. Atmos. Res. 2017, 194, 142–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leung, F.Y.; Colussi, A.J.; Hoffmann, M.R. Sulfur isotopic fractionation in the gas-phase oxidation of sulfur dioxide initiated by hydroxyl radicals. J. Phys. Chem. A 2001, 105, 8073–8076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.H.Y.; Zhang, Y.L.; Cao, F.; Zhang, W.Q.; Fan, M.Y.; Lee, X.H.; Michalski, G. Stable sulfur isotopes revealed a major role of transition-metal-ion catalyzed SO2 oxidation in haze episodes. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2020, 54, 2626–2634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, L.F.; Yue, S.Y.; Zhao, W.Y.; Yang, W.Y.; Zhang, Y.J.; Ren, L.J.; Han, X.K.; Guo, Q.J.; Sun, Y.L.; Wang, Z.F. Stable sulfur isotope ratios and chemical compositions of fine aerosols (PM2.5) in Beijing, China. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 633, 1156–1164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ding, T.; Valkiers, S.; Kipphardt, H.; De Bievre, P.; Taylor, P.; Gonfiantini, R.; Krouse, R. Calibrated sulfur isotope abundance ratios of three IAEA sulfur isotope reference materials and V-CDT with a reassessment of the atomic weight of sulfur. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 2001, 65, 2433–2437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Z.; Shi, L.; Chen, S.; Jiang, W.; Wei, Y.; Rui, M.; Zeng, G. Sulfur isotopic fractionation and source appointment of PM2.5 in Nanjing region around the second session of the Youth Olympic Games. Atmos. Res. 2016, 174, 9–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakata, M.; Ishikawa, T.; Mitsunobu, S. Effectiveness of sulfur and boron isotopes in aerosols as tracers of emissions from coal burning in Asian continent. Atmos. Environ. 2013, 67, 296–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sinha, B.; Hoppe, P.; Huth, J.; Foley, S.; Andreae, M. Sulfur isotope analyses of individual aerosol particles in the urban aerosol at a central European site (Mainz, Germany). Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2008, 8, 7217–7238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, Y.; Zheng, G.; Wei, C.; Mu, Q.; Zheng, B.; Wang, Z.; Gao, M.; Zhang, Q.; He, K.; Carmichael, G. Reactive nitrogen chemistry in aerosol water as a source of sulfate during haze events in China. Sci. Adv. 2016, 2, e1601530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harris, E.; Sinha, B.; Hoppe, P.; Crowley, J.; Ono, S.; Foley, S. Sulfur isotope fractionation during oxidation of sulfur dioxide: Gas-phase oxidation by OH radicals and aqueous oxidation by H2O2, O3 and iron catalysis. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2012, 12, 407–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, M.Y.; Zhang, Y.L.; Lin, Y.C.; Li, J.; Fu, P. Roles of sulfur oxidation pathways in the variability in stable sulfur isotopic composition of sulfate aerosols at an urban site in Beijing, China. Environ. Sci. Technol. Lett. 2020, 7, 883–888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tostevin, R.; Turchyn, A.V.; Farquhar, J.; Johnston, D.T.; Eldridge, D.L.; Bishop, J.K.; McIlvin, M. Multiple sulfur isotope constraints on the modern sulfur cycle. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 2014, 396, 14–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alexander, B.; Park, R.J.; Jacob, D.J.; Gong, S. Transition metal-catalyzed oxidation of atmospheric sulfur: Global implications for the sulfur budget. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2009, 114, D02309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, J.; Chen, Q.; Wang, Y.; Lu, X.; Alexander, B. Heterogeneous sulfate aerosol formation mechanisms during wintertime Chinese haze events: Air quality model assessment using observations of sulfate oxygen isotopes in Beijing. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2019, 19, 6107–6123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, J.; Yu, X.; Yuan, Z.; Griffith, S.M.; Lau, A.; Seinfeld, J.H.; Yu, J.Z. Efficient control of atmospheric sulfate production based on three formation regimes. Nat. Geosci. 2019, 12, 977–982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, S.Q.; Wu, J.H.; Zhang, Y.F.; Cai, Z.Y.; Feng, Y.C.; Yao, Q.; Li, X.J.; Liu, Y.W.; Zhang, M. Characteristics and formation mechanism of a winter haze–fog episode in Tianjin, China. Atmos. Environ. 2014, 98, 323–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| January 2017 | January 2018 | January 2019 | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| All (n = 28) | C (n = 6) | Ep1 (n = 14) | All (n = 30) | C (n = 19) | Ep2 (n = 6) | All (n = 40) | C (n = 27) | Ep3 (n = 9) | |
| PM2.5 | 151.6 ± 86.2 | 59.7 ± 19.2 | 217.5 ± 72.5 | 60.7 ± 39.2 | 35.5 ± 17.8 | 109.1 ± 26.5 | 65.4 ± 43.3 | 39.0 ± 18.2 | 127.9 ± 16.7 |
| Na+ | 0.7 ± 0.5 | 0.3 ± 0.1 | 1.1 ± 0.3 | 0.3 ± 0.2 | 0.2 ± 0.1 | 0.4 ± 0.1 | 0.3 ± 0.1 | 0.2 ± 0.1 | 0.4 ± 0.1 |
| NH4+ | 15.1 ± 13.2 | 3.1 ± 1.6 | 25.3 ± 11.3 | 9.2 ± 7.8 | 4.1 ± 3.4 | 18.1 ± 4.8 | 7.6 ± 6.1 | 3.9 ± 2.5 | 15.8 ± 3.1 |
| K+ | 1.0 ± 0.8 | 0.3 ± 0.1 | 1.7 ± 0.7 | 0.9 ± 0.6 | 0.5 ± 0.3 | 1.6 ± 0.3 | 0.9 ± 0.6 | 0.6 ± 0.4 | 1.4 ± 0.3 |
| Ca2+ | 0.3 ± 0.3 | 0.4 ± 0.2 | 0.4 ± 0.4 | 0.3 ± 0.2 | 0.2 ± 0.2 | 0.3 ± 0 | 0.1 ± 0.1 | 0.1 ± 0.1 | 0.2 ± 0.1 |
| Mg2+ | 0.04 ± 0.03 | 0.04 ± 0.04 | 0.04 ± 0.02 | 0.01 ± 0.02 | 0.01 ± 0.02 | 0.02 ± 0.00 | 0.03 ± 0.01 | 0.02 ± 0.10 | 0.03 ± 0.01 |
| Cl− | 5.2 ± 5.0 | 1.5 ± 0.7 | 8.4 ± 5.2 | 4.2 ± 4.3 | 2.0 ± 1.8 | 6.0 ± 1.4 | 4.0 ± 2.6 | 3.1 ± 2.3 | 5.0 ± 1.4 |
| NO3− | 22.3 ± 19.4 | 4.54 ± 2.65 | 37.3 ± 16.9 | 10.0 ± 9.8 | 3.82 ± 3.07 | 24.0 ± 8.9 | 11.5 ± 9.5 | 5.65 ± 3.83 | 24.1 ± 4.6 |
| SO42− | 24.6 ± 21.2 | 5.3 ± 3.2 | 40.8 ± 18.7 | 5.0 ± 3.2 | 3.0 ± 1.7 | 8.4 ± 2.4 | 5.6 ± 5.7 | 2.2 ± 1.1 | 14.7 ± 3.7 |
| RH | 60.6 ± 24.2 | 28.5 ± 7.4 | 81.1 ± 11.4 | 34.8 ± 14.4 | 31.2 ± 16.1 | 41.3 ± 9.1 | 29.4 ± 18.3 | 19.4 ± 3.6 | 58.9 ± 15.9 |
| T | 0.9 ± 1.9 | 0.5 ± 1.3 | 1.0 ± 2.0 | −0.7 ± 2.3 | 1.4 ± 2.5 | 0.4 ± 1.3 | 0.6 ± 2.4 | 0.5 ± 2.7 | 0.4 ± 1.8 |
| WS | 1.4 ± 0.7 | 2.3 ± 0.8 | 1.0 ± 0.4 | 1.5 ± 0.4 | 1.6 ± 0.5 | 1.4 ± 0.3 | 1.5 ± 0.7 | 1.7 ± 0.8 | 1.1 ± 0.3 |
| SO2 | 28.1 ± 11.3 | 13.8 ± 3.8 | 31.1 ± 6.7 | 17.0 ± 10.1 | 11.0 ± 6.1 | 26.2 ± 6.3 | 18.7 ± 13.1 | 16.2 ± 11.3 | 16.2 ± 8.5 |
| NO2 | 78.9 ± 33.8 | 36.5 ± 8.6 | 101.0 ± 25.2 | 57.8 ± 26.1 | 45.1 ± 23.1 | 74.7 ± 13.5 | 63.6 ± 24.9 | 52.9 ± 22.6 | 82.5 ± 11.8 |
| O3 | 36.1 ± 19.5 | 58.8 ± 11.1 | 21.9 ± 12.9 | 27.7 ± 17.8 | 33.3 ± 18.8 | 22.0 ± 10.3 | 22.9 ± 16.8 | 26.4 ± 17.4 | 14.8 ± 12.9 |
| SOR | 0.3 ± 0.2 | 0.2 ± 0.1 | 0.4 ± 0.1 | 0.2 ± 0.1 | 0.2 ± 0.1 | 0.2 ± 0.1 | 0.2 ± 0.2 | 0.1 ± 0.1 | 0.4 ± 0.2 |
| NOR | 0.1 ± 0.1 | 0.1 ± 0.1 | 0.2 ± 0.1 | 0.1 ± 0.1 | 0.05 ± 0.1 | 0.2 ± 0.1 | 0.1 ± 0.1 | 0.1 ± 0.1 | 0.2 ± 0.01 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ding, S.; Chen, Y.; Li, Q.; Li, X.-D. Using Stable Sulfur Isotope to Trace Sulfur Oxidation Pathways during the Winter of 2017–2019 in Tianjin, North China. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 10966. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph191710966
Ding S, Chen Y, Li Q, Li X-D. Using Stable Sulfur Isotope to Trace Sulfur Oxidation Pathways during the Winter of 2017–2019 in Tianjin, North China. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health. 2022; 19(17):10966. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph191710966
Chicago/Turabian StyleDing, Shiyuan, Yingying Chen, Qinkai Li, and Xiao-Dong Li. 2022. "Using Stable Sulfur Isotope to Trace Sulfur Oxidation Pathways during the Winter of 2017–2019 in Tianjin, North China" International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health 19, no. 17: 10966. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph191710966
APA StyleDing, S., Chen, Y., Li, Q., & Li, X.-D. (2022). Using Stable Sulfur Isotope to Trace Sulfur Oxidation Pathways during the Winter of 2017–2019 in Tianjin, North China. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 19(17), 10966. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph191710966






