Risk Factors Attributable to Hypertension among HIV-Infected Patients on Antiretroviral Therapy in Selected Rural Districts of the Eastern Cape Province, South Africa
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Design and Setting
2.2. Eligibility Criteria
2.3. Ethical Approval
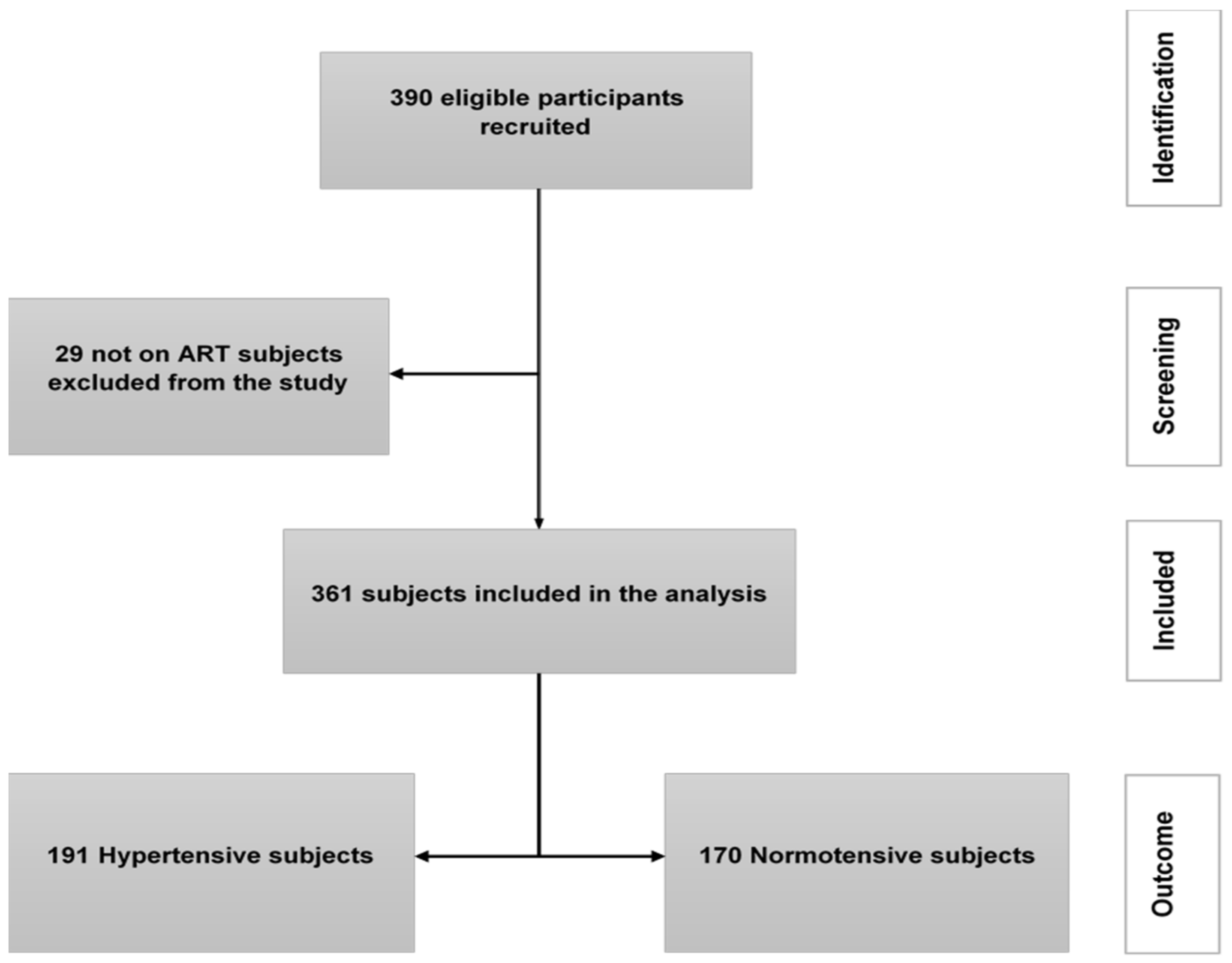
2.4. Sample Size and Sampling
2.5. Sampling Procedure
2.6. Data Collection
2.7. Definitions
2.7.1. Hypertension
2.7.2. Assessment of Overweight/Obesity
2.7.3. Immunological Status
2.7.4. Renal Function
2.7.5. Socioeconomic and Environmental Variables
2.8. Data Analysis
2.9. Validity and Reliability
3. Results
3.1. Characteristics of the Study Population
3.2. Characteristics of the Study Population
3.3. Risk Factors Associated with the Development of Hypertension
3.4. Impact of the Identified Risk Factors on the Incidence of Hypertension
3.5. Kaplan–Meier Curves
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Marcus, J.L.; Leyden, W.A.; Alexeeff, S.E.; Anderson, A.N.; Hechter, R.C.; Hu, H.; Lam, J.O.; Towner, W.J.; Yuan, Q.; Horberg, M.A.; et al. Comparison of Overall and Comorbidity-Free Life Expectancy Between Insured Adults with and without HIV Infection, 2000–2016. JAMA Netw. Open 2020, 3, e207954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smit, M.; Smit, C.; Geerlings, S.; Gras, L.; Brinkman, K.; Hallett, T.B.; de Wolf, F.; Athena Observational Cohort. Changes in first-line cART regimens and short-term clinical outcome between 1996 and 2010 in The Netherlands. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e76071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smit, M.; Brinkman, K.; Geerlings, S.; Smit, C.; Thyagarajan, K.; van Sighem, A.; de Wolf, F.; Hallett, T.B. Future challenges for clinical care of an ageing population infected with HIV: A modelling study. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2015, 15, 810–818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World Health Organisation. Hypertension. Available online: https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/hypertension (accessed on 16 May 2022).
- World Health Organisation. Noncommunicable Diseases Progress Monitor; World Health Organisation: Geneva, Switzerland, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- World Health Organisation. A Global Brief on Hypertension: Silent Killer, Global Public Health Crisis: World Health Day 2013. Available online: https://apps.who.int/iris/handle/10665/79059 (accessed on 16 May 2022).
- Matthew, J.F.; Priscilla, Y.; Laura, A.B.; Gerald, S.B.; Judith, S.C.; Matthew, S.F.; Steven, K.G.; Jules, L.; Chris, T.L.; Wendy, S. Characteristics, Prevention, and Management of Cardiovascular Disease in People Living with HIV: A Scientific Statement from the American Heart Association. Circulation 2019, 140, e98–e124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stats SA. Mortality and Causes of Death in South Africa, 2016: Findings from Death Notification; Stats SA: Pretoria, South Africa, 2019; p. 19. [Google Scholar]
- UNAIDS. Ending AIDS towards the 90–90–90 Targets; UNAIDS: Geneva, Switzerland, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Kandala, N.B.; Nnanatu, C.C.; Dukhi, N.; Sewpaul, R.; Davids, A.; Reddy, S.P. Mapping the Burden of Hypertension in South Africa: A Comparative Analysis of the National 2012 SANHANES and the 2016 Demographic and Health Survey. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 5445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Daniels, A.; Hoffman, M.; Lombard, C.; Steyn, K.; Levitt, N.; Katzenellenbogen, J. Blood pressure and social support observations from Mamre, South Africa, during social and political transition. J. Hum. Hypertens. 1999, 13, 689–693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Metcalf, C.A.; Hoffman, M.N.; Steyn, K.; Katzenellenbogen, J.M.; Fourie, J.M. Design and baseline characteristics of a hypertension intervention program in a South African village. J. Hum. Hypertens. 1996, 10, 21–26. [Google Scholar]
- Steyn, K.; Gaziano, T.A.; Bradshaw, D.; Laubscher, R.; Fourie, J. Hypertension in South African adults: Results from the Demographic and Health Survey, 1998. J. Hypertens. 2001, 19, 1717–1725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bärnighausen, T.; Welz, T.; Hosegood, V.; Bätzing-Feigenbaum, J.; Tanser, F.; Herbst, K.; Hill, C.; Newell, M.L. Hiding in the shadows of the HIV epidemic: Obesity and hypertension in a rural population with very high HIV prevalence in South Africa. J. Hum. Hypertens. 2008, 22, 236–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berry, K.M.; Parker, W.A.; McHiza, Z.J.; Sewpaul, R.; Labadarios, D.; Rosen, S.; Stokes, A. Quantifying unmet need for hypertension care in South Africa through a care cascade: Evidence from the SANHANES, 2011–2012. BMJ Glob. Health 2017, 2, e000348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- National Department of Health; Statistics South Africa; South African Medical Research Council; ICF. South Africa Demographic Health Survey 2016; National Department of Health: Pretoria, South Africa, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Adeloye, D.; Basquill, C. Estimating the prevalence and awareness rates of hypertension in Africa: A systematic analysis. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e104300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fahme, S.A.; Bloomfield, G.S.; Peck, R. Hypertension in HIV-Infected Adults: Novel Pathophysiologic Mechanisms. Hypertension 2018, 72, 44–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, K.A.; Peer, N.; Mills, E.J.; Kengne, A.P. Burden, Determinants, and Pharmacological Management of Hypertension in HIV-Positive Patients and Populations: A Systematic Narrative Review. AIDS Rev. 2015, 17, 83–95. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Schouten, J.; Wit, F.W.; Stolte, I.G.; Kootstra, N.A.; van der Valk, M.; Geerlings, S.E.; Prins, M.; Reiss, P. Cross-sectional comparison of the prevalence of age-associated comorbidities and their risk factors between HIV-infected and uninfected individuals: The AGEhIV cohort study. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2014, 59, 1787–1797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Zoest, R.A.; van den Born, B.H.; Reiss, P. Hypertension in people living with HIV. Curr. Opin. HIV AIDS 2017, 12, 513–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, Y.; Chen, X.; Wang, K. Global prevalence of hypertension among people living with HIV: A systematic review and meta-analysis. J. Am. Soc. Hypertens. 2017, 11, 530–540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- World Health Organisation. South Africa HIV Country Profile 2019. Available online: https://cfs.hivci.org/country-factsheet.html (accessed on 17 May 2022).
- Ataguba, J.E. The Impact of Financing Health Services on Income Inequality in an Unequal Society: The Case of South Africa. Appl. Health Econ. Health Policy 2021, 19, 721–733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, I.M.; Shiroma, E.J.; Lobelo, F.; Puska, P.; Blair, S.N.; Katzmarzyk, P.T. Effect of physical inactivity on major non-communicable diseases worldwide: An analysis of burden of disease and life expectancy. Lancet 2012, 380, 219–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deeks, S.G. HIV infection, inflammation, immunosenescence, and aging. Annu. Rev. Med. 2011, 62, 141–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zanni, M.V.; Schouten, J.; Grinspoon, S.K.; Reiss, P. Risk of coronary heart disease in patients with HIV infection. Nat. Rev. Cardiol. 2014, 11, 728–741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, C.; Gange, S.J.; Moore, R.D.; Justice, A.C.; Buchacz, K.; Abraham, A.G.; Rebeiro, P.F.; Koethe, J.R.; Martin, J.N.; Horberg, M.A.; et al. Multimorbidity Among Persons Living with Human Immunodeficiency Virus in the United States. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2018, 66, 1230–1238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Patel, P.; Rose, C.E.; Collins, P.Y.; Nuche-Berenguer, B.; Sahasrabuddhe, V.V.; Peprah, E.; Vorkoper, S.; Pastakia, S.D.; Rausch, D.; Levitt, N.S. Noncommunicable diseases among HIV-infected persons in low-income and middle-income countries: A systematic review and meta-analysis. AIDS 2018, 32 (Suppl. 1), S5–S20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mpondo, B.C. HIV Infection in the Elderly: Arising Challenges. J. Aging Res. 2016, 2016, 2404857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hennessey, C.; Hurter, T. TIER.net HIV Electronic Register Training Guide. 2011. Available online: https://tieredstrategy.files.wordpress.com/2011/2008/ndoh_data_clerk_part2014.pdf (accessed on 26 November 2021).
- Desai, M.; Joyce, V.; Bendavid, E.; Olshen, R.A.; Hlatky, M.; Chow, A.; Holodniy, M.; Barnett, P.; Owens, D.K. Risk of cardiovascular events associated with current exposure to HIV antiretroviral therapies in a US veteran population. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2015, 61, 445–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mulenga, L.; Musonda, P.; Mwango, A.; Vinikoor, M.J.; Davies, M.A.; Mweemba, A.; Calmy, A.; Stringer, J.S.; Keiser, O.; Chi, B.H.; et al. Effect of baseline renal function on tenofovir-containing antiretroviral therapy outcomes in Zambia. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2014, 58, 1473–1480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stats SA. Census 2022; Stats SA: Pretoria, South Africa, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- The World Medical Association. World Medical Association declaration of Helsinki. Recommendations guiding physicians in biomedical research involving human subjects. JAMA 1997, 277, 925–926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Medina-Torne, S.; Ganesan, A.; Barahona, I.; Crum-Cianflone, N.F. Hypertension is common among HIV-infected persons, but not associated with HAART. J. Int. Assoc. Physicians AIDS Care 2012, 11, 20–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harris, P.A.; Taylor, R.; Thielke, R.; Payne, J.; Gonzalez, N.; Conde, J.G. Research electronic data capture (REDCap)—A metadata-driven methodology and workflow process for providing translational research informatics support. J. Biomed. Inform. 2009, 42, 377–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- James, P.A.; Oparil, S.; Carter, B.L.; Cushman, W.C.; Dennison-Himmelfarb, C.; Handler, J.; Lackland, D.T.; LeFevre, M.L.; MacKenzie, T.D.; Ogedegbe, O.; et al. 2014 evidence-based guideline for the management of high blood pressure in adults: Report from the panel members appointed to the Eighth Joint National Committee (JNC 8). JAMA 2014, 311, 507–520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- WHO. Obesity: Preventing and managing the global epidemic. Report of a WHO consultation. WHO Tech. Rep. Ser. 2000, 894, i–xii + 1–253. [Google Scholar]
- Stevens, P.E.; Levin, A. Evaluation and management of chronic kidney disease: Synopsis of the kidney disease: Improving global outcomes 2012 clinical practice guideline. Ann. Intern. Med. 2013, 158, 825–830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- WHO. Global Recommendations on Physical Activity for Health; WHO: Geneva, Switzerland, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Monakali, S.; Ter Goon, D.; Seekoe, E.; Owolabi, E.O. Prevalence, awareness, control and determinants of hypertension among primary health care professional nurses in Eastern Cape, South Africa. Afr. J. Prim. Health Care Fam. Med. 2018, 10, e1–e5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Guwatudde, D.; Nankya-Mutyoba, J.; Kalyesubula, R.; Laurence, C.; Adebamowo, C.; Ajayi, I.; Bajunirwe, F.; Njelekela, M.; Chiwanga, F.S.; Reid, T.; et al. The burden of hypertension in sub-Saharan Africa: A four-country cross sectional study. BMC Public Health 2015, 15, 1211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Joffres, M.; Falaschetti, E.; Gillespie, C.; Robitaille, C.; Loustalot, F.; Poulter, N.; McAlister, F.A.; Johansen, H.; Baclic, O.; Campbell, N. Hypertension prevalence, awareness, treatment and control in national surveys from England, the USA and Canada, and correlation with stroke and ischaemic heart disease mortality: A cross-sectional study. BMJ Open 2013, 3, e003423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mills, K.T.; Bundy, J.D.; Kelly, T.N.; Reed, J.E.; Kearney, P.M.; Reynolds, K.; Chen, J.; He, J. Global Disparities of Hypertension Prevalence and Control: A Systematic Analysis of Population-Based Studies from 90 Countries. Circulation 2016, 134, 441–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kagaruki, G.B.; Mayige, M.T.; Ngadaya, E.S.; Kimaro, G.D.; Kalinga, A.K.; Kilale, A.M.; Kahwa, A.M.; Materu, G.S.; Mfinanga, S.G. Magnitude and risk factors of non-communicable diseases among people living with HIV in Tanzania: A cross sectional study from Mbeya and Dar es Salaam regions. BMC Public Health 2014, 14, 904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Currier, J.S.; Taylor, A.; Boyd, F.; Dezii, C.M.; Kawabata, H.; Burtcel, B.; Maa, J.F.; Hodder, S. Coronary heart disease in HIV-infected individuals. J. Acquir. Immune Defic. Syndr. 2003, 33, 506–512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klein, D.; Hurley, L.B.; Quesenberry, C.P., Jr.; Sidney, S. Do protease inhibitors increase the risk for coronary heart disease in patients with HIV-1 infection? J. Acquir. Immune Defic. Syndr. 2002, 30, 471–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rodriguez-Arboli, E.; Mwamelo, K.; Kalinjuma, A.V.; Furrer, H.; Hatz, C.; Tanner, M.; Battegay, M.; Letang, E.; Group, K.S. Incidence and risk factors for hypertension among HIV patients in rural Tanzania—A prospective cohort study. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0172089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weimann, A.; Dai, D.; Oni, T. A cross-sectional and spatial analysis of the prevalence of multimorbidity and its association with socioeconomic disadvantage in South Africa: A comparison between 2008 and 2012. Soc. Sci. Med. 2016, 163, 144–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Ramirez, S.S.; Enquobahrie, D.A.; Nyadzi, G.; Mjungu, D.; Magombo, F.; Ramirez, M.; Sachs, S.E.; Willett, W. Prevalence and correlates of hypertension: A cross-sectional study among rural populations in sub-Saharan Africa. J. Hum. Hypertens. 2010, 24, 786–795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cappuccio, F.P.; Micah, F.B.; Emmett, L.; Kerry, S.M.; Antwi, S.; Martin-Peprah, R.; Phillips, R.O.; Plange-Rhule, J.; Eastwood, J.B. Prevalence, detection, management, and control of hypertension in Ashanti, West Africa. Hypertension 2004, 43, 1017–1022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bosu, W.K.; Reilly, S.T.; Aheto, J.M.K.; Zucchelli, E. Hypertension in older adults in Africa: A systematic review and meta-analysis. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0214934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ataro, Z.; Ashenafi, W.; Fayera, J.; Abdosh, T. Magnitude and associated factors of diabetes mellitus and hypertension among adult HIV-positive individuals receiving highly active antiretroviral therapy at Jugal Hospital, Harar, Ethiopia. HIV AIDS 2018, 10, 181–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fiseha, T.; Belete, A.G.; Dereje, H.; Dires, A. Hypertension in HIV-Infected Patients Receiving Antiretroviral Therapy in Northeast Ethiopia. Int. J. Hypertens. 2019, 2019, 4103604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mulugeta, H.; Afenigus, A.D.; Haile, D.; Amha, H.; Kassa, G.M.; Wubetu, M.; Abebaw, E.; Jara, D. Incidence and Predictors of Hypertension Among HIV Patients Receiving ART at Public Health Facilities, Northwest Ethiopia: A One-Year Multicenter Prospective Follow-Up Study. HIV AIDS 2021, 13, 889–901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berhane, T.; Yami, A.; Alemseged, F.; Yemane, T.; Hamza, L.; Kassim, M.; Deribe, K. Prevalence of lipodystrophy and metabolic syndrome among HIV positive individuals on Highly Active Anti-Retroviral treatment in Jimma, South West Ethiopia. Pan Afr. Med. J. 2012, 13, 43. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Alberts, M.; Urdal, P.; Steyn, K.; Stensvold, I.; Tverdal, A.; Nel, J.H.; Steyn, N.P. Prevalence of cardiovascular diseases and associated risk factors in a rural black population of South Africa. Eur. J. Prev. Cardiol. 2005, 12, 347–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mkhonto, S.S.; Labadarios, D.; Mabaso, M.L.H. Retraction: Association of body weight and physical activity with blood pressure in a rural population in the Dikgale village of Limpopo Province in South Africa. BMC Res. Notes 2013, 6, 422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thorogood, M.; Connor, M.; Tollman, S.; Lewando Hundt, G.; Fowkes, G.; Marsh, J. A cross-sectional study of vascular risk factors in a rural South African population: Data from the Southern African Stroke Prevention Initiative (SASPI). BMC Public Health 2007, 7, 326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dalal, S.; Beunza, J.J.; Volmink, J.; Adebamowo, C.; Bajunirwe, F.; Njelekela, M.; Mozaffarian, D.; Fawzi, W.; Willett, W.; Adami, H.O.; et al. Non-communicable diseases in sub-Saharan Africa: What we know now. Int. J. Epidemiol. 2011, 40, 885–901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Owolabi, E.O.; Goon, D.T.; Adeniyi, O.V.; Seekoe, E. Social epidemiology of hypertension in Buffalo City Metropolitan Municipality (BCMM): Cross-sectional study of determinants of prevalence, awareness, treatment and control among South African adults. BMJ Open 2017, 7, e014349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kotwani, P.; Kwarisiima, D.; Clark, T.D.; Kabami, J.; Geng, E.H.; Jain, V.; Chamie, G.; Petersen, M.L.; Thirumurthy, H.; Kamya, M.R.; et al. Epidemiology and awareness of hypertension in a rural Ugandan community: A cross-sectional study. BMC Public Health 2013, 13, 1151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sander, L.D.; Newell, K.; Ssebbowa, P.; Serwadda, D.; Quinn, T.C.; Gray, R.H.; Wawer, M.J.; Mondo, G.; Reynolds, S. Hypertension, cardiovascular risk factors and antihypertensive medication utilisation among HIV-infected individuals in Rakai, Uganda. Trop. Med. Int. Health 2015, 20, 391–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brennan, A.T.; Jamieson, L.; Crowther, N.J.; Fox, M.P.; George, J.A.; Berry, K.M.; Stokes, A.; Maskew, M.; Sanne, I.; Long, L.; et al. Prevalence, incidence, predictors, treatment, and control of hypertension among HIV-positive adults on antiretroviral treatment in public sector treatment programs in South Africa. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0204020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jayedi, A.; Rashidy-Pour, A.; Khorshidi, M.; Shab-Bidar, S. Body mass index, abdominal adiposity, weight gain and risk of developing hypertension: A systematic review and dose-response meta-analysis of more than 2.3 million participants. Obes. Rev. 2018, 19, 654–667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Angeli, F.; Reboldi, G.; Verdecchia, P. Hypertension around the world: New insights from developing countries. J. Hypertens. 2013, 31, 1358–1361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, Z.; Yan, W.; Yu, Q.; Wu, P.; Bigambo, F.M.; Chen, J. Association between Exercise and Blood Pressure in Hypertensive Residents: A Meta-Analysis. Evid.-Based Complementary Altern. Med. 2022, 2022, 2453805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, O.; Bickel, M.; Ditting, T.; Rickerts, V.; Welk, T.; Helm, E.B.; Staszewski, S.; Geiger, H. Hypertension in HIV-1-infected patients and its impact on renal and cardiovascular integrity. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 2004, 19, 2250–2258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gazzaruso, C.; Bruno, R.; Garzaniti, A.; Giordanetti, S.; Fratino, P.; Sacchi, P.; Filice, G. Hypertension among HIV Patients: Prevalence and Relationships to Insulin Resistance and Metabolic Syndrome; Scientific IRCCS Network: Milan, Italy, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Okello, S.; Kanyesigye, M.; Muyindike, W.R.; Annex, B.H.; Hunt, P.W.; Haneuse, S.; Siedner, M.J. Incidence and predictors of hypertension in adults with HIV-initiating antiretroviral therapy in south-western Uganda. J. Hypertens. 2015, 33, 2039–2045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peck, R.N.; Shedafa, R.; Kalluvya, S.; Downs, J.A.; Todd, J.; Suthanthiran, M.; Fitzgerald, D.W.; Kataraihya, J.B. Hypertension, kidney disease, HIV and antiretroviral therapy among Tanzanian adults: A cross-sectional study. BMC Med. 2014, 12, 125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mogadam, E.; King, K.; Shriner, K.; Chu, K.; Sondergaard, A.; Young, K.; Naghavi, M.; Kloner, R.A. The association of nadir CD4-T cell count and endothelial dysfunction in a healthy HIV cohort without major cardiovascular risk factors. SAGE Open Med. 2020, 8, 2050312120924892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Njelekela, M.; Muhihi, A.; Aveika, A.; Spiegelman, D.; Hawkins, C.; Armstrong, C.; Liu, E.; Okuma, J.; Chalamila, G.; Kaaya, S.; et al. Prevalence of Hypertension and Its Associated Risk Factors among 34,111 HAART Naive HIV-Infected Adults in Dar es Salaam, Tanzania. Int. J. Hypertens. 2016, 2016, 5958382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hatleberg, C.I.; Ryom, L.; d’Arminio Monforte, A.; Fontas, E.; Reiss, P.; Kirk, O.; El-Sadr, W.; Phillips, A.; de Wit, S.; Dabis, F.; et al. Association between exposure to antiretroviral drugs and the incidence of hypertension in HIV-positive persons: The Data Collection on Adverse Events of Anti-HIV Drugs (D:A:D) study. HIV Med. 2018, 19, 605–618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ascher, S.B.; Scherzer, R.; Peralta, C.A.; Tien, P.C.; Grunfeld, C.; Estrella, M.M.; Abraham, A.; Gustafson, D.R.; Nowicki, M.; Sharma, A.; et al. Association of Kidney Function and Early Kidney Injury with Incident Hypertension in HIV-Infected Women. Hypertension 2017, 69, 304–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Remais, J.V.; Zeng, G.; Li, G.; Tian, L.; Engelgau, M.M. Convergence of non-communicable and infectious diseases in low- and middle-income countries. Int. J. Epidemiol. 2013, 42, 221–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vecchiet, J.; Ucciferri, C.; Falasca, K.; Mancino, P.; Di Iorio, A.; De Caterina, R. Antihypertensive and metabolic effects of telmisartan in hypertensive HIV-positive patients. Antivir. Ther. 2011, 16, 639–645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ucciferri, C.; Falasca, K.; Vecchiet, J. Hypertension in HIV: Management and Treatment. AIDS Rev. 2017, 19, 198–211. [Google Scholar]
- Kahn, K.; Tollman, S.M.; Collinson, M.A.; Clark, S.J.; Twine, R.; Clark, B.D.; Shabangu, M.; Gómez-Olivé, F.X.; Mokoena, O.; Garenne, M.L. Research into health, population and social transitions in rural South Africa: Data and methods of the Agincourt Health and Demographic Surveillance System1. Scandinavian J. Public Health 2007, 35, 8–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]


| Hypertensive | Normotensive | Total | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Age, Median (IQR) | 51 (39.0–59.0) | 43 (33.0–54.5) | 45 (35–56) |
| 15–30 years, n (%) | +20 (10.5) | 31 (18.2) | 51 (14.1) |
| 31–40 years, n (%) | 42 (22.0) | 52 (30.6) | 94 (26.0) |
| 35–45 years, n (%) | 129 (67.5) | 87 (30.6) | 216 (59.8) |
| Gender, n (%) | |||
| Female | 160 (83.8) | 161 (94.7) | 321 (88.9) |
| Male | 31 (16.2) | 9 (5.3) | 40 (11.1) |
| Current smokers, n (%) | |||
| Non-Smoker | 166 (86.9) | 165 (97.1) | 331 (91.7) |
| Smoker | 25 (13.1) | 5 (2.9) | 30 (8.3) |
| Consume alcohol, n (%) | |||
| No | 161 (84.3) | 157 (92.4) | 318 (88.1) |
| Yes | 30 (15.7) | 13 (7.2) | 43 (11.9) |
| Exercise, n (%) | |||
| No | 110 (57.6) | 41 (24.1) | 151 (41.8) |
| Yes | 81 (42.4) | 129 (75.9) | 210 (58.2) |
| Hypertension heredity, n (%) | |||
| No | 90 (47.1) | 126 (74.1) | 216 (59.8) |
| Yes | 101 (52.9) | 44 (25.9) | 145 (40.2) |
| Diabetes history, n (%) | |||
| No | 137 (71.7) | 152 (89.4) | 289 (80.1) |
| Yes | 54 (28.3) | 18 (10.6) | 72 (19.9) |
| BMI categories, n (%) | |||
| <25 (kg/m2) | 48 (25.1) | 87 (48.8) | 131 (36.3) |
| ≥25 (kg/m2) | 143 (74.9) | 83 (51.2) | 230 (63.7) |
| eGFR, n (%) | |||
| <60 mL/min/1.73 m² | 123 (64.4) | 6 (3.5) | 129 (35.7) |
| ≥60 mL/min/1.73 m² | 68 (35.6) | 164 (96.5) | 232 (64.3) |
| VL category, n (%) | |||
| <50 (copies/mL) | 139 (72.8) | 131 (77.1) | 270 (74.8) |
| 50–1000 (copies/mL) | 28 (14.7) | 38 (22.4) | 66 (18.3) |
| >1000 (copies/mL) | 24 (12.6) | 1 (0.6) | 25 (6.9) |
| CD4 count, n (%) | |||
| Mild | 53 (27.7) | 161 (94.7) | 214 (59.3) |
| Advanced | 56 (29.3) | 5 (2.9) | 61 (16.9) |
| Severe | 82 (42.9) | 4 (2.4) | 86 (23.8) |
| ART regimen, n (%) | |||
| 1S3E | 14 (7.3) | 12 (7.1) | 26 (7.2) |
| 1T3E | 26 (13.6) | 22 (12.9) | 48 (13.3) |
| 1T3N | 11 (5.8) | 11 (6.5) | 22 (6.1) |
| 1TFE | 140 (73.3) | 125 (73.3) | 265 (73.4) |
| ART duration, n (%) | |||
| <5 years | 106 (55.5) | 106 (62.4) | 212 (58.7) |
| 5–10 years | 66 (34.6) | 53 (31.2) | 119 (33.0) |
| >10 years | 19 (9.9) | 11 (6.2) | 30 (8.3) |
| Univariate Model | Multivariate Model | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Unadjusted HR (95% CI) | p Value | Adjusted HR (95% CI) | p Value | |
| Gender MALE | 1.66 (1.13–2.45) | 0.0106 | 2.83 (1.76–4.56) | 0.0000 |
| Age 31–40 (years) | 0.96 (0.56–1.64) | 0.8790 | 0.72 (0.41–1.26) | 0.2467 |
| Age > 40 years | 1.26 (0.79–2.03) | 0.3330 | 0.97 (0.58–1.61) | 0.8991 |
| Consume alcohol Yes | 1.51 (1.02–2.23) | 0.0414 | 1.26 (0.82–1.94) | 0.2932 |
| Exercise Yes | 0.62 (0.47–0.83) | 0.0015 | 0.91 (0.66–1.26) | 0.5756 |
| Diabetes history Yes | 1.39 (1.01–1.91) | 0.0422 | 1.26 (0.90–1.76) | 0.1706 |
| Hypertension heredity Yes | 1.93 (1.45–2.57) | 0.0000 | 1.66 (1.21–2.27) | 0.0015 |
| BMI ≥ 25 kg/m2 | 1.69 (1.21–2.34) | 0.0019 | 1.97 (1.35–2.87) | 0.0005 |
| eGFR ≥ 60 mL/min/1.73 m² | 0.38 (0.29–0.52) | 0.0000 | 0.54 (0.36–0.71) | 0.0000 |
| ART regimen 1T3E | 1.93 (0.99–3.73) | 0.0515 | 3.39 (1.62–7.09) | 0.0012 |
| ART regimen 1T3N | 1.20 (0.53–2.71) | 0.6633 | 1.01 (0.43–2.37) | 0.9868 |
| ART regimen 1TFE | 3.92 (2.22–6.93) | 0.0000 | 5.99 (3.19–11.27) | 0.0000 |
| CD4 count Advanced | 3.74 (2.57–5.45) | 0.0000 | 2.28 (1.50–3.45) | 0.0001 |
| CD4 count Severe | 3.10 (2.19–4.39) | 0.0000 | 2.48 (1.71–3.61) | 0.0000 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tsuro, U.; Oladimeji, K.E.; Pulido-Estrada, G.-A.; Apalata, T.R. Risk Factors Attributable to Hypertension among HIV-Infected Patients on Antiretroviral Therapy in Selected Rural Districts of the Eastern Cape Province, South Africa. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 11196. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph191811196
Tsuro U, Oladimeji KE, Pulido-Estrada G-A, Apalata TR. Risk Factors Attributable to Hypertension among HIV-Infected Patients on Antiretroviral Therapy in Selected Rural Districts of the Eastern Cape Province, South Africa. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health. 2022; 19(18):11196. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph191811196
Chicago/Turabian StyleTsuro, Urgent, Kelechi E. Oladimeji, Guillermo-Alfredo Pulido-Estrada, and Teke R. Apalata. 2022. "Risk Factors Attributable to Hypertension among HIV-Infected Patients on Antiretroviral Therapy in Selected Rural Districts of the Eastern Cape Province, South Africa" International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health 19, no. 18: 11196. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph191811196
APA StyleTsuro, U., Oladimeji, K. E., Pulido-Estrada, G.-A., & Apalata, T. R. (2022). Risk Factors Attributable to Hypertension among HIV-Infected Patients on Antiretroviral Therapy in Selected Rural Districts of the Eastern Cape Province, South Africa. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 19(18), 11196. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph191811196





