Can Communication Technologies Reduce Loneliness and Social Isolation in Older People? A Scoping Review of Reviews
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. State of Research and Review Questions
- RQ1:
- Which types of CTs have been investigated in the context of loneliness and/or social isolation reduction among older people by previous research reviews—considering both targeted interventions and self-directed behaviors?
- RQ2:
- Which theoretical frameworks have been adopted to link CT use with loneliness and/or social isolation reduction among older people by previous research reviews—considering both targeted interventions and self-directed behaviors?
- RQ3:
- Which study designs have been applied to investigate CTs in the context of loneliness and/or social isolation reduction among older people by previous research reviews—considering both targeted interventions and self-directed behaviors?
- RQ4:
- Which effects on loneliness and/or social isolation reduction among older people have been found in connection with the use of CTs by previous research reviews—considering both targeted interventions and self-directed behaviors?
3. Results
3.1. Eligibility and Exclusion Criteria
3.1.1. Eligibility Criteria
3.1.2. Exclusion Criteria
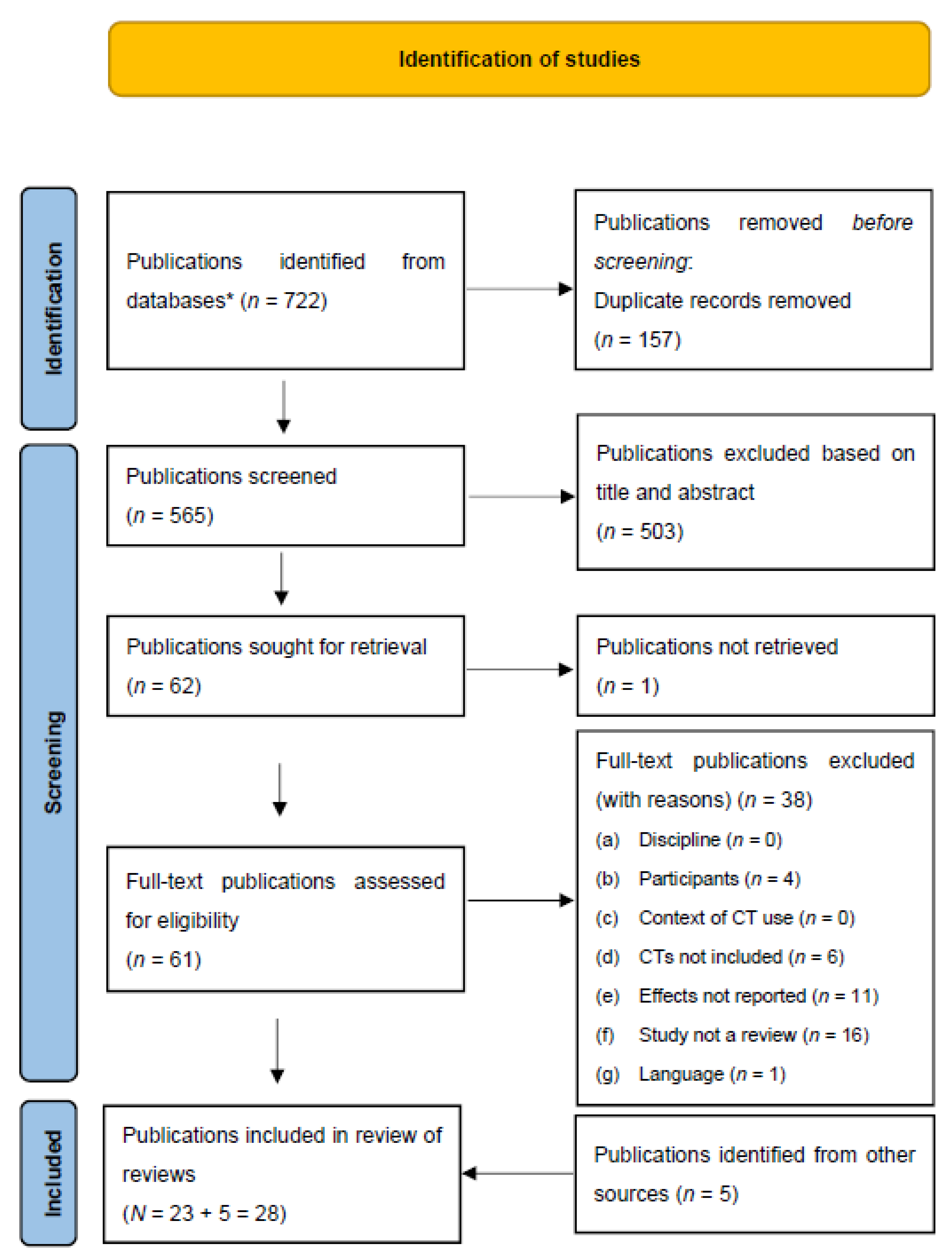
3.2. Information Sources and Search Strategy
3.2.1. Electronic Search
3.2.2. Manual Search
3.3. Study Selection
3.4. Data Collection and Charting
3.5. Methods of Data Analysis
3.5.1. Reporting of Descriptive Characteristics
3.5.2. Statistical Analysis
- If an included review covered only primary studies addressing CT-related interventions and/or self-directed behaviors, the general conclusions of the review were used to report the effects.
- If an included review covered both CT-related and non-CT-related interventions and/or self-directed behaviors, only the technology-related effects were used to report the effect. The aforementioned technology-related effects were extracted from the results section, individual tables, or specific sections in the overall conclusions of the respective included reviews.
4. Results
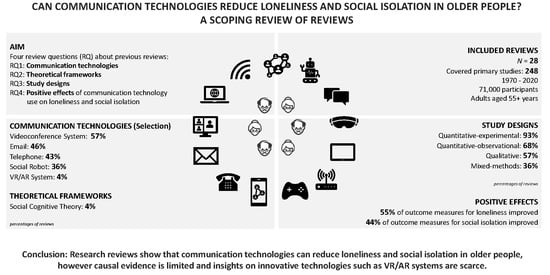
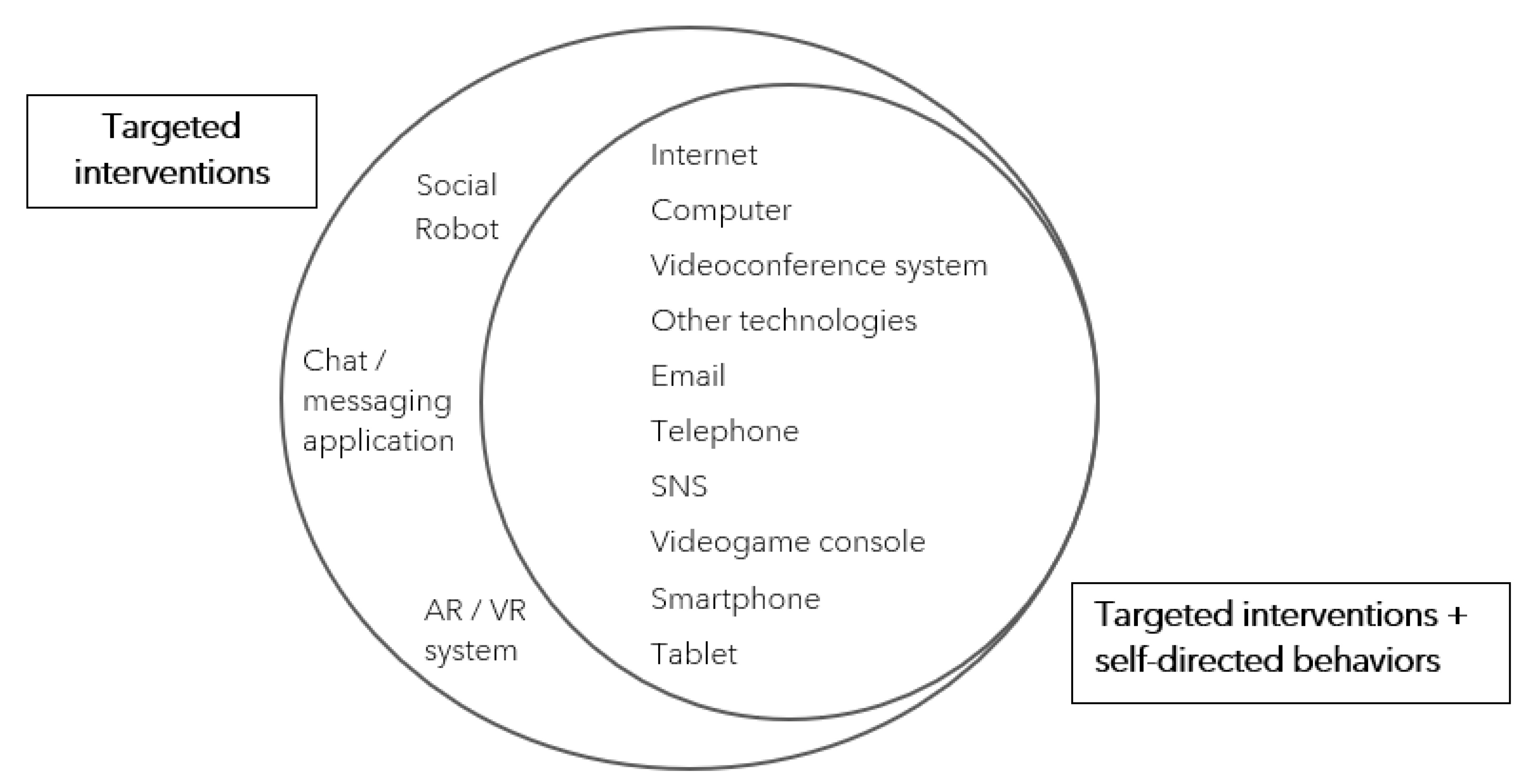
4.1. Types of Communication Technologies
4.2. Theoretical Frameworks
4.3. Study Designs
4.4. Effects on Loneliness and Social Isolation
5. Discussion
5.1. Interpretation of Main Results
5.2. Limitations and Strengths
5.3. Outlook on Future Research and Practice
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- World Health Organization. Aging and Health. Available online: https://www.who.int/news–room/fact–sheets/detail/ageing–and–health (accessed on 4 October 2021).
- De Jong-Gierveld, J. Developing and testing a model of loneliness. J. Personal. Soc. Psychol. 1987, 53, 119–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chipps, J.; Jarvis, M.A.; Ramlall, S. The effectiveness of e–Interventions on reducing social isolation in older persons: A systematic review of systematic reviews. J. Telemed. Telecare 2017, 23, 817–827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dahlberg, L.; Agahi, N.; Lennartsson, C. Lonelier than ever? Loneliness of older people over two decades. Arch. Gerontol. Geriatr. 2018, 75, 96–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Victor, C.R.; Bowling, A. A longitudinal analysis of loneliness among older people in Great Britain. J. Psychol. 2012, 146, 313–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Jong-Gierveld, J.; Van Tilburg, T.; Dykstra, P.A. Loneliness and social isolation. In Cambridge Handbook of Personal Relationships; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2006; pp. 485–500. [Google Scholar]
- Russell, D.; Peplau, L.A.; Ferguson, M.L. Developing a measure of loneliness. J. Personal. Assess. 1978, 42, 290–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zavaleta, D.; Samuel, K.; Mills, C.T. Measures of social isolation. Soc. Indic. Res. 2017, 131, 367–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Evans, I.E.; Martyr, A.; Collins, R.; Brayne, C.; Clare, L. Social isolation and cognitive function in later life: A systematic review and meta–analysis. J. Alzheimer’s Dis. 2019, 70, S119–S144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barbosa Neves, B.; Baecker, R. Mixing methods and sciences: A longitudinal cross-disciplinary mixed methods study on technology to address social isolation and loneliness in later life. J. Mix. Methods Res. 2022, 16, 88–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perissinotto, C.; Holt-Lunstad, J.; Periyakoil, V.S.; Covinsky, K. A practical approach to assessing and mitigating loneliness and isolation in older adults. J. Am. Geriatr. Soc. 2019, 67, 657–662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, B. Social isolation and loneliness among older adults in the context of COVID19: A global challenge. Glob. Health Res. Policy 2020, 5, 1–3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ong, A.D.; Uchino, B.N.; Wethington, E. Loneliness and health in older adults: A mini–review and synthesis. Gerontology 2016, 62, 443–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kharicha, K.; Manthorpe, J.; Iliffe, S.; Davies, N.; Walters, K. Strategies employed by older people to manage loneliness: Systematic review of qualitative studies and model development. Int. Psychogeriatr. 2018, 30, 1767–1781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vogel, E.A. Millennials Stand out for Their Technology Use, but Older Generations also Embrace Digital Life. Pew Research Center. Available online: https://pewrsr.ch/2A3kD6X (accessed on 9 September 2019).
- Fakoya, O.A.; McCorry, N.K.; Donnelly, M. Loneliness and social isolation interventions for older adults: A scoping review of reviews. BMC Public Health 2020, 20, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jarvis, M.A.; Padmanabhanunni, A.; Balakrishna, Y.; Chipps, J. The effectiveness of interventions addressing loneliness in older persons: An umbrella review. Int. J. Afr. Nurs. Sci. 2020, 12, 100177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arksey, H.; O’Malley, L. Scoping studies: Towards a methodological framework. Int. J. Soc. Res. Methodol. 2005, 8, 19–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tricco, A.C.; Lillie, E.; Zarin, W.; O’Brien, K.K.; Colquhoun, H.; Levac, D.; Moher, D.; Peters, M.D.J.; Horsley, T.; Weeks, L.; et al. PRISMA extension for scoping reviews (PRISMA–ScR): Checklist and explanation. Ann. Intern. Med. 2018, 169, 467–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, S.H.; Shin, I.S. A reporting quality assessment of systematic reviews and meta–analyses in sports physical therapy: A review of reviews. Healthcare 2021, 9, 1368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fujioka, J.K.; Budhwani, S.; Thomas–Jacques, T.; De Vera, K.; Challa, P.; Fuller, K.; Hogeveen, S.; Gordon, D.; Shahid, S.; Seto, E.; et al. Challenges and strategies for promoting health equity in virtual care: Protocol for a scoping review of reviews. JMIR Res. Protoc. 2020, 9, e22847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shea, B.J.; Reeves, B.C.; Wells, G.; Thuku, M.; Hamel, C.; Moran, J.; Moher, D.; Tugwell, P.; Welch, V.; Kristjansson, E.; et al. AMSTAR 2: A critical appraisal tool for systematic reviews that include randomised or non–randomised studies of healthcare interventions, or both. BMJ 2017, 358, j4008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dettori, J.R.; Skelly, A.C.; Brodt, E.D. Critically low confidence in the results produced by spine surgery systematic reviews: An AMSTAR–2 evaluation from 4 spine journals. Glob. Spine J. 2020, 10, 667–673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Matthias, K.; Rissling, O.; Pieper, D.; Morche, J.; Nocon, M.; Jacobs, A.; Wegewitz, U.; Schirm, J.; Lorenz, R.C. The methodological quality of systematic reviews on the treatment of adult major depression needs improvement according to AMSTAR 2: A cross–sectional study. Heliyon 2020, 6, e04776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliveira Almeida, M.; Parma Yamato, T.; Silva Parreira, P.D.C.; Oliveira Pena Costa, L.; Kamper, S.; Tirotti Saragiotto, B. Overall confidence in the results of systematic reviews on exercise therapy for chronic low back pain: A cross–sectional analysis using the Assessing the Methodological Quality of Systematic Reviews (AMSTAR) 2 tool. Braz. J. Phys. Ther. 2020, 24, 103–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pieper, D.; Lorenz, R.C.; Rombey, T.; Jacobs, A.; Rissling, O.; Freitag, S.; Matthias, K. Authors should clearly report how they derived the overall rating when applying AMSTAR 2—A cross–sectional study. J. Clin. Epidemiol. 2021, 129, 97–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Storman, M.; Storman, D.; Jasinska, K.W.; Swierz, M.J.; Bala, M.M. The quality of systematic reviews/meta-analyses published in the field of bariatrics: A cross-sectional systematic survey using AMSTAR 2 and ROBIS. Obes. Rev. 2020, 21, e12994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baker, S.; Warburton, J.; Waycott, J.; Batchelor, F.; Hoang, T.; Dow, B.; Ozanne, E.; Vetere, F. Combatting social isolation and increasing social participation of older adults through the use of technology: A systematic review of existing evidence. Australas. J. Ageing 2018, 37, 184–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brimelow, R.E.; Wollin, J.A. Loneliness in old age: Interventions to curb loneliness in long–term care facilities. Act. Adapt. Aging 2017, 41, 301–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Casanova, G.; Zaccaria, D.; Rolandi, E.; Guaita, A. The effect of information and communication technology and social networking site use on older people’s well–being in relation to loneliness: Review of experimental studies. J. Med. Internet Res. 2021, 23, e23588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cattan, M.; White, M.; Bond, J.; Learmouth, A. Preventing social isolation and loneliness among older people: A systematic review of health promotion interventions. Ageing Soc. 2005, 25, 41–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, E.; Wood, D.; Ysseldyk, R. Online social networking and mental health among older adults: A scoping review. Can. J. Aging 2021. Advance online publication. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.-R.; Schulz, P.J. The effect of information communication technology interventions on reducing social isolation in the elderly: A systematic review. J. Med. Internet Res. 2016, 18, e18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, H.K.; Lee, S.H. Trends and effectiveness of ICT interventions for the elderly to reduce loneliness: A systematic review. Healthcare 2021, 9, 293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choi, M.; Kong, S.; Jung, D. Computer and internet interventions for loneliness and depression in older adults: A meta–analysis. Healthc. Inform. Res. 2012, 18, 191–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cohen–Mansfield, J.; Perach, R. Interventions for alleviating loneliness among older persons: A critical review. Am. J. Health Promot. 2015, 29, e109–e125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dickens, A.P.; Richards, S.H.; Greaves, C.J.; Campbell, J.L. Interventions targeting social isolation in older people: A systematic review. BMC Public Health 2011, 11, 647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Franck, L.; Molyneux, N.; Parkinson, L. Systematic review of interventions addressing social isolation and depression in aged care clients. Qual. Life Res. 2016, 25, 1395–1407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gardiner, C.; Geldenhuys, G.; Gott, M. Interventions to reduce social isolation and loneliness among older people: An integrative review. Health Soc. Care Community 2018, 26, 147–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gasteiger, N.; Loveys, K.; Law, M.; Broadbent, E. Friends from the future: A scoping review of research into robots and computer agents to combat loneliness in older people. Clin. Interv. Aging 2021, 16, 941–971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gorenko, J.A.; Moran, C.; Flynn, M.; Dobson, K.; Konnert, C. Social isolation and psychological distress among older adults related to COVID–19: A narrative review of remotely–delivered interventions and recommendations. J. Appl. Gerontol. 2021, 40, 3–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hagan, R.; Manktelow, R.; Taylor, B.J.; Mallett, J. Reducing loneliness amongst older people: A systematic search and narrative review. Aging Ment. Health 2014, 18, 683–693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heins, P.; Boots, L.; Koh, W.Q.; Neven, A.; Verhey, F.; de Vugt, M.E. The effects of technological interventions on social participation of community-dwelling older adults with and without dementia: A systematic review. J. Clin. Med. 2021, 10, 2308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ibarra, F.; Baez, M.; Cernuzzi, L.; Casati, F. A systematic review on technology–supported interventions to improve old–age social wellbeing: Loneliness, social isolation, and connectedness. J. Healthc. Eng. 2020, 2020, 2036842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ibrahim, A.F.; Tan, M.P.; Teoh, G.K.; Muda, S.M.; Chong, M.C. Health benefits of social participation interventions among community–dwelling older persons: A review article. Exp. Aging Res. 2022, 48, 234–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Isabet, B.; Pino, M.; Lewis, M.; Benveniste, S.; Rigaud, A.-S. Social telepresence robots: A narrative review of experiments involving older adults before and during the COVID-19 pandemic. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 3597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khosravi, P.; Ghapanchi, A.H. Investigating the effectiveness of technologies applied to assist seniors: A systematic literature review. Int. J. Med. Inform. 2016, 85, 17–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khosravi, P.; Rezvani, A.; Wiewiora, A. The impact of technology on older adults’ social isolation. Comput. Hum. Behav. 2016, 63, 594–603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Erdt, M.; Chen, L.; Cao, Y.; Lee, S.-Q.; Theng, Y.-L. The social effects of exergames on older adults: Systematic review and metric analysis. J. Med. Internet Res. 2018, 20, e10486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Masi, C.M.; Chen, H.Y.; Hawkley, L.C.; Cacioppo, J.T. A meta–analysis of interventions to reduce loneliness. Personal. Soc. Psychol. Rev. 2011, 15, 219–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morris, M.E.; Adair, B.; Ozanne, E.; Kurowski, W.; Miller, K.J.; Pearce, A.J.; Santamaria, N.; Long, M.; Ventura, C.; Said, C.M. Smart technologies to enhance social connectedness in older people who live at home. Australas. J. Ageing 2014, 33, 142–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noone, C.; McSharry, J.; Smalle, M.; Burns, A.; Dwan, K.; Devane, D.; Morrissey, E.C. Video calls for reducing social isolation and loneliness in older people: A rapid review. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2020, 5, 1–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Rourke, H.M.; Collins, L.; Sidani, S. Interventions to address social connectedness and loneliness for older adults: A scoping review. BMC Geriatr. 2018, 18, 214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Poscia, A.; Stojanovic, J.; La Milia, D.I.; Duplaga, M.; Grysztar, M.; Moscato, U.; Onder, G.; Collamati, A.; Ricciardi, W.; Magnavita, N. Interventions targeting loneliness and social isolation among the older people: An update systematic review. Exp. Gerontol. 2018, 102, 133–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shah, S.G.S.; Nogueras, D.; van Woerden, H.C.; Kiparoglou, V. Evaluation of the effectiveness of digital technology interventions to reduce loneliness in older adults: Systematic review and meta–analysis. J. Med. Internet Res. 2021, 23, e24712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cacioppo, J.T.; Hawkley, L.C.; Ernst, J.M.; Burleson, M.; Berntson, G.G.; Nouriani, B.; Spiegel, D. Loneliness within a nomological net: An evolutionary perspective. J. Res. Personal. 2006, 40, 1054–1085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cacioppo, J.T.; Fowler, J.H.; Christakis, N.A. Alone in the crowd: The structure and spread of loneliness in a large social network. J. Personal. Soc. Psychol. 2009, 97, 977–991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bandura, A. Social Foundations of thought and Action: A Social Cognitive Theory; Prentice-Hall: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 1986. [Google Scholar]
- De Jong–Gierveld, J.; Van Tilburg, T. Manual of the Loneliness Scale; Vrije Universiteit: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 1990. [Google Scholar]
- Hawthorne, G. Measuring social isolation in older adults: Development and initial validation of the friendship scale. Soc. Indic. Res. 2006, 77, 521–548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lubben, J.E. Assessing social networks among elderly populations. Fam. Community Health J. Health Promot. Maint. 1988, 11, 42–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- George, L.K.; Blazer, D.G.; Hughes, D.C.; Fowler, N. Social support and the outcome of major depression. Br. J. Psychiatry 1989, 154, 478–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moyle, W.; Jones, C.; Murfield, J.; Liu, F. ‘For me at 90, it’s going to be difficult’: Feasibility of using iPad video-conferencing with older adults in long-term aged care. Aging Ment. Health 2020, 24, 349–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inoue, K.; Sasaki, C.; Nakamura, M. Communication Robots for Elderly People and Their Families to Support Their Daily Lives-Case Study of Two Families Living with the Communicaton Robot. In Assistive Technology; IOS Press: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2021; pp. 980–983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pirhonen, J.; Tiilikainen, E.; Pekkarinen, S.; Lemivaara, M.; Melkas, H. Can robots tackle late-life loneliness? Scanning of future opportunities and challenges in assisted living facilities. Futures 2020, 124, 102640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mannheim, I.; Schwartz, E.; Xi, W.; Buttigieg, S.C.; McDonnell-Naughton, M.; Wouters, E.J.; Van Zaalen, Y. Inclusion of older adults in the research and design of digital technology. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2019, 16, 3718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- March, S.T.; Smith, G.F. Design and natural science research on information technology. Decis. Support Syst. 1995, 15, 251–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Ref. | Authors | Range of Publication Years of Primary Studies | Number of Primary Studies Addressing CTs | Total Sample of Primary Studies Addressing CTs | AMSTAR 2 Quality Score of Review |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| [28] | Baker et al. (2018) | 2000–2016 1 | 36 | N/A | 4 |
| [29] | Brimelow and Wollin (2017) | 1996–2013 | 4 | 233 | 4 |
| [30] | Casanova et al. (2021) | 2002–2019 | 11 | 953 | 2 |
| [31] | Cattan et al. (2005) | 1970–2002 | 7 | 745 | 3 |
| [32] | Chen et al. (2021) | 2007–2018 | 52 | 5844 | 4 |
| [33] | Chen and Schulz (2016) | 2002–2015 | 30 | N/A | 2 |
| [34] | Choi and Lee (2021) | 2003–2019 | 21 | 1323 2 | 2 |
| [35] | Choi et al. (2012) | 2001–2011 | 6 | 373 | 2 |
| [36] | Cohen-Mansfield and Perach (2015) | 1996–2011 | 12 | 694 | 2 |
| [37] | Dickens et al. (2011) | 1976–2009 | 6 | 767 | 2 |
| [38] | Franck et al. (2016) | 2010–2011 | 1 | 36 | 2 |
| [39] | Gardiner et al. (2018) | 2003–2016 | 9 | N/A | 4 |
| [40] | Gasteiger et al. (2021) | 2003–2020 | 29 | 632 | 3 |
| [41] | Gorenko et al. (2021) | 2007–2018 | 19 3 | N/A | 4 |
| [42] | Hagan et al. (2014) | 2000–2012 | 6 | 439 | 4 |
| [43] | Heins et al. (2021) | 2005–2020 | 36 | N/A | 1 |
| [44] | Ibarra et al. (2020) | until 2020 1 | 25 | N/A | 4 |
| [45] | Ibrahim et al. (2021) | 1978–2018 | 4 | 162 | 4 |
| [46] | Isabet et al. (2021) | 2003–2018 | 24 | 377 | 4 |
| [47] | Khosravi and Ghapanchi (2016) | 2002–2013 | 41 4 | N/A | 4 |
| [48] | Khosravi et al. (2016) | 2002–2015 | 34 | 8895 | 4 |
| [49] | Li et al. (2018) | 2009–2017 | 10 | 382 | 2 |
| [50] | Masi et al. (2011) | 1982–2009 | 8 | 410 | 3 |
| [51] | Morris et al. (2014) | 2000–2013 | 18 | 2343 | 2 |
| [52] | Noone et al. (2020) | 2010–2020 | 3 | 201 | 1 |
| [53] | O’Rourke et al. (2018) | 1984–2014 | 4 | N/A | 4 |
| [54] | Poscia et al. (2018) | 2012–2015 | 4 | 319 | 2 |
| [55] | Shah et al. (2021) | 2010–2019 | 6 | 646 | 1 |
| CTs | Total No. of Reviews (No. of Reviews with SDB) | Reviews |
|---|---|---|
| Internet | 23 (2) | [28] *, [29,30,31], [32] *, [33,34,35,36,37,39,41,42,43,44,45,47,48,50,51,53,54,55] |
| Computer | 23 (1) | [28] *, [29,30,31,33,34,35,36,37,39,40,41,43,44,45,47,48,50,51,52,53,54,55] |
| Videoconference system | 16 (2) | [28] *, [29], [32] *, [33,34,36,39,41,42,43,44,48,52,53,54,55] |
| Other technologies | 14 (2) | [28] *, [32] *, [33,34,39,40,42,43,44,45,48,51,54,55] |
| 13 (2) | [28] *, [30], [32] *, [33,34,35,36,43,44,45,50,53,54] | |
| Telephone | 12 (1) | [28] *, [31,33,36,37,39,41,43,44,45,50,53] |
| SNS | 11 (2) | [28] *, [30], [32] *, [33,34,39,41,43,44,48,55] |
| Videogame console | 10 (1) | [28] *, [29,33,34,38,42,43,48,49,51] |
| Social robot | 10 (0) | [29,34,39,40,42,46,47,48,53,54] |
| Smartphone | 8 (2) | [28] *, [30], [32] *, [33,34,43,44,52] |
| Tablet | 7 (1) | [28] *, [30,33,34,43,44,52] |
| Chat/messaging app | 6 (0) | [33,34,43,44,51,55] |
| AR/VR system | 1 (0) | [48] |
| Review | Theoretical Framework | No. of Primary Studies Applying Theoretical Framework | Link between CT Use and Reduced Loneliness and/or Isolation |
|---|---|---|---|
| Masi et al. (2011) [50] | Social Cognitive Theory (SCT) | 1 (social cognitive training through telephone calls) | Interventions that address maladaptive social cognition will have a greater impact than those addressing social skills, social support, and social interaction. Outcome measures for loneliness were obtained by applying the 10-item UCLA Loneliness Scale. No outcome measures for social isolation were reported. |
| Qualitative Designs (16 Reviews) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ref. | Author(s) | CTs | Primary Studies with Qualitative Design | AMSTAR 2 Quality Score of Review | Effects on L/SI |
| [28] | Baker et al. (2018) | Telephone, smartphone, tablet, computer, videogame console, videoconference system, email, SNS, internet, other technologies | 24 | 4 | L = n/a SI = unclear effect |
| [33] | Chen and Schulz (2016) | Telephone, smartphone, tablet, computer, videogame console, messaging app, videoconference system, email, SNS, internet, other technologies | 14 | 2 | L = unclear effect SI = positive effect |
| [43] | Heins et al. (2021) | Telephone, smartphone, tablet, computer, videogame console, messaging app, videoconference system, email, SNS, internet, other technologies | 14 | 1 | L = unclear effect SI = unclear effect |
| [53] | O’Rourke et al. (2018) | Telephone, computer, social robot, videoconference system, email, internet, other technologies | 12 | 4 | L = n/a 1 SI = n/a 1 |
| [39] | Gardiner et al. (2018) | Telephone, computer, social robot, videoconference system, SNS, internet, other technologies | 10 | 4 | L = positive effect SI = n/a |
| [32] | Chen et al. (2021) | Smartphone, videoconference system, email, SNS, internet, other technologies | 8 | 4 | L = positive effect SI = positive effect |
| [40] | Gasteiger et al. (2021) | Computer, social robot, other technologies | 7 | 3 | L = positive effect SI = n/a |
| [44] | Ibarra et al. (2020) | Telephone, smartphone, tablet, computer, messaging app, videoconference system, email, SNS, internet, other technologies | 6 | 4 | L = positive effect SI = no effect |
| [34] | Choi and Lee (2021) | Smartphone, tablet, computer, social robot, videogame console, messaging app, videoconference system, email, SNS, internet, other technologies | 5 | 2 | L = unclear effect SI = positive effect |
| [49] | Li et al. (2018) | Videogame console | 5 | 2 | L = positive effect SI = n/a |
| [54] | Poscia et al. (2018) | Telephone, smartphone, tablet, computer, social robot, videogame console, AR/VR system, messaging app, videoconference system, email, SNS, internet, other technologies | 5 | 2 | L = positive effect SI = n/a |
| [46] | Isabet et al. (2021) | Social robot | 5 | 4 | L = unclear effect SI = unclear effect |
| [48] | Khosravi et al. (2016) | Computer, social robot, videogame console, AR/VR system, videoconference system, SNS, internet, other technologies | 4 | 4 | L = positive effect SI = positive effect |
| [41] | Gorenko et al. (2021) | Telephone, computer, videoconference system, SNS, internet, other technologies | 3 | 4 | L = positive effect 2 SI = positive effect 2 |
| [45] | Ibrahim et al. (2021) | Telephone, computer, email, internet, other technologies | 3 | 4 | L = no effect SI = unclear effect |
| [36] | Cohen-Mansfield and Perach (2015) | Telephone, computer, videoconference system, email, internet | 1 | 2 | L = positive effect SI = n/a |
| Total | Positive effect: L (9), SI (5) No effect: L (1), SI (1) Unclear effect: L (4), SI (4) | ||||
| Quantitative-Observational Designs (19 Reviews) | |||||
| Ref. | Author(s) | CTs | Primary Studies with Quantitative-Observational Design | Quality Score | Effects on L/SI |
| [39] | Gardiner et al. (2018) | Telephone, computer, social robot, videoconference system, SNS, internet, other technologies | 21 | 4 | L = positive effect SI = n/a |
| [32] | Chen et al. (2021) | Smartphone, videoconference system, email, SNS, internet, other technologies | 20 | 4 | L = positive effect SI = positive effect |
| [53] | O’Rourke et al. (2018) | Telephone, computer, social robot, videoconference system, email, internet, other technologies | 16 | 4 | L = n/a 1 SI = n/a 1 |
| [48] | Khosravi et al. (2016) | Computer, social robot, videogame console, AR/VR system, videoconference system, SNS, internet, other technologies | 15 | 4 | L = positive effect SI = positive effect |
| [44] | Ibarra et al. (2020) | Telephone, smartphone, tablet, computer, messaging app, videoconference system, email, SNS, internet, other technologies | 14 | 4 | L = positive effect SI = no effect |
| [33] | Chen and Schulz (2016) | Telephone, smartphone, tablet, computer, videogame console, messaging app, videoconference system, email, SNS, internet, other technologies | 10 | 2 | L = unclear effect SI = positive effect |
| [28] | Baker et al. (2018) | Telephone, smartphone, tablet, computer, videogame console, videoconference system, email, SNS, internet, other technologies | 9 | 4 | L = n/a SI = unclear effect |
| [46] | Isabet et al. (2021) | Social robot | 8 | 4 | L = unclear effect SI = unclear effect |
| [54] | Poscia et al. (2018) | Telephone, smartphone, tablet, computer, social robot, videogame console, AR/VR system, messaging app, videoconference system, email, SNS, internet, other technologies | 7 | 2 | L = positive effect SI = n/a |
| [51] | Morris et al. (2014) | Computer, videogame console, messaging app, internet, other technologies | 6 | 2 | L = unclear effect SI = unclear effect |
| [34] | Choi and Lee (2021) | Smartphone, tablet, computer, social robot, videogame console, messaging app, videoconference system, email, SNS, internet, other technologies | 5 | 2 | L = unclear effect SI = positive effect |
| [36] | Cohen-Mansfield and Perach (2015) | Telephone, computer, videoconference system, email, internet | 5 | 2 | L = positive effect SI = n/a |
| [40] | Gasteiger et al. (2021) | Computer, social robot, other technologies | 5 | 3 | L = positive effect SI = n/a |
| [49] | Li et al. (2018) | Videogame console | 5 | 2 | L = positive effect SI = n/a |
| [42] | Hagan et al. (2014) | Social robot, videogame console, videoconference system, internet, other technologies | 2 | 4 | L = unclear effect SI = n/a |
| [43] | Heins et al. (2021) | Telephone, smartphone, tablet, computer, videogame console, messaging app, videoconference system, email, SNS, internet, other technologies | 2 | 1 | L = unclear effect SI = unclear effect |
| [45] | Ibrahim et al. (2021) | Telephone, computer, email, internet, other technologies | 2 | 4 | L = no effect SI = unclear effect |
| [47] | Khosravi and Ghapanchi (2016) | Computer, social robot, internet | 1 | 4 | L = n/a SI = positive effect |
| [55] | Shah et al. (2021) | Computer, messaging app, videoconference system, SNS, internet, other technologies | 1 | 1 | L = positive effect SI = n/a |
| Total | Positive effect: L (9), SI (5) No effect: L (1), SI (1) Unclear effect: L (6), SI (5) | ||||
| Quantitative-Experimental Designs (26 Reviews) | |||||
| Ref. | Author(s) | CTs | Primary Studies with Quantitative-–Experimental Design | Quality Score | Effects on L/SI |
| [50] | Masi et al. (2011) | Telephone, computer, email, internet | 50 | 3 | L = no effect SI = no effect |
| [37] | Dickens et al. (2011) | Telephone, computer, internet | 32 | 2 | L = no effect SI = n/a |
| [31] | Cattan et al. (2005) | Telephone, computer, internet | 30 | 3 | L = no effect SI = no effect |
| [36] | Cohen-Mansfield and Perach (2015) | Telephone, computer, videoconference system, email, internet | 28 | 2 | L = positive effect SI = n/a |
| [53] | O’Rourke et al. (2018) | Telephone, computer, social robot, videoconference system, email, internet, other technologies | 25 | 4 | L = n/a 1 SI = n/a 1 |
| [45] | Ibrahim et al. (2021) | Telephone, computer, email, internet, other technologies | 18 | 4 | L = no effect SI = unclear effect |
| [48] | Khosravi et al. (2016) | Computer, social robot, videogame console, AR/VR system, videoconference system, SNS, internet, other technologies | 15 | 4 | L = positive effect SI = positive effect |
| [51] | Morris et al. (2014) | Computer, videogame console, messaging app, internet, other technologies | 12 | 2 | L = unclear effect SI = unclear effect |
| [30] | Casanova et al. (2021) | Smartphone, tablet, computer, email, SNS, internet | 11 | 2 | L = positive effect SI = n/a |
| [43] | Heins et al. (2021) | Telephone, smartphone, tablet, computer, videogame console, messaging app, videoconference system, email, SNS, internet, other technologies | 10 | 1 | L = unclear effect SI = unclear effect |
| [32] | Chen et al. (2021) | Smartphone, videoconference system, email, SNS, internet, other technologies | 8 | 4 | L = positive effect SI = positive effect |
| [40] | Gasteiger et al. (2021) | Computer, social robot, other technologies | 7 | 3 | L = positive effect SI = n/a |
| [47] | Khosravi and Ghapanchi (2016) | Computer, social robot, internet | 7 | 4 | L = n/a SI = positive effect |
| [54] | Poscia et al. (2018) | Telephone, smartphone, tablet, computer, social robot, videogame console, AR/VR system, messaging app, videoconference system, email, SNS, internet, other technologies | 7 | 2 | L = positive effect SI = n/a |
| [33] | Chen and Schulz (2016) | Telephone, smartphone, tablet, computer, videogame console, messaging app, videoconference system, email, SNS, internet, other technologies | 6 | 2 | L = unclear effect SI = positive effect |
| [34] | Choi and Lee (2021) | Smartphone, tablet, computer, social robot, videogame console, messaging app, videoconference system, email, SNS, internet, other technologies | 6 | 2 | L = unclear effect SI = positive effect |
| [35] | Choi et al. (2012) | Computer, email, internet, other technologies | 6 | 2 | L = positive effect SI = n/a |
| [39] | Gardiner et al. (2018) | Telephone, computer, social robot, videoconference system, SNS, internet, other technologies | 6 | 4 | L = positive effect SI = n/a |
| [44] | Ibarra et al. (2020) | Telephone, smartphone, tablet, computer, messaging app, videoconference system, email, SNS, internet, other technologies | 6 | 4 | L = positive effect SI = no effect |
| [38] | Franck et al. (2016) | Videogame console | 5 | 2 | L = positive effect SI = n/a |
| [55] | Shah et al. (2021) | Computer, messaging app, videoconference system, SNS, internet, other technologies | 5 | 1 | L = positive effect SI = n/a |
| [41] | Gorenko et al. (2021) | Telephone, computer, videoconference system, SNS, internet, other technologies | 4 | 4 | L = positive effect 2 SI = positive effect 2 |
| [42] | Hagan et al. (2014) | Social robot, videogame console, videoconference system, internet, other technologies | 4 | 4 | L = unclear effect SI = n/a |
| [52] | Noone et al. (2020) | Smartphone, tablet, computer, videoconference system | 3 | 1 | L = unclear effect SI = unclear effect |
| [46] | Isabet et al. (2021) | Social robot | 3 | 4 | L = unclear effect SI = unclear effect |
| [29] | Brimelow and Wollin (2017) | Computer, social robot, videogame console, videoconference system, internet | 2 | 4 | L = unclear effect SI = n/a |
| Total | Positive effect: L (12), SI (6) No effect: L (4), SI (3) Unclear effect: L (8), SI (5) | ||||
| Mixed-Methods Designs (10 Reviews) | |||||
| Ref. | Author(s) | CTs | Primary studies with Mixed-Methods Design | Quality Score | Effects on L/SI |
| [40] | Gasteiger et al. (2021) | Computer, social robot, other technologies | 10 | 3 | L = positive effect SI = n/a |
| [43] | Heins et al. (2021) | Telephone, smartphone, tablet, computer, videogame console, messaging app, videoconference system, email, SNS, internet, other technologies | 10 | 1 | L = unclear effect SI = unclear effect |
| [32] | Chen et al. (2021) | Smartphone, videoconference system, email, SNS, internet, other technologies | 8 | 4 | L = positive effect SI = positive effect |
| [46] | Isabet et al. (2021) | Social robot | 8 | 4 | L = unclear effect SI = unclear effect |
| [28] | Baker et al. (2018) | Telephone, smartphone, tablet, computer, videogame console, videoconference system, email, SNS, internet, other technologies | 3 | 4 | L = n/a SI = unclear effect |
| [34] | Choi and Lee (2021) | Smartphone, tablet, computer, social robot, videogame console, messaging app, videoconference system, email, SNS, internet, other technologies | 3 | 2 | L = unclear effect SI = positive effect |
| [39] | Gardiner et al. (2018) | Telephone, computer, social robot, videoconference system, SNS, internet, other technologies | 2 | 4 | L = positive effect SI = n/a |
| [45] | Ibrahim et al. (2021) | Telephone, computer, email, internet, other technologies | 2 | 4 | L = no effect SI = unclear effect |
| [53] | O’Rourke et al. (2018) | Telephone, computer, social robot, videoconference system, email, internet, other technologies | 1 | 4 | L = n/a 1 SI = n/a 1 |
| [54] | Poscia et al. (2018) | Telephone, smartphone, tablet, computer, social robot, videogame console, AR/VR system, messaging app, videoconference system, email, SNS, internet, other technologies | 1 | 2 | L = positive effect SI = n/a |
| Total | Positive effect: L (4), SI (2) No effect: L (1), SI (0) Unclear effect: L (3), SI (4) | ||||
| Study Design | No. of Outcome Measures for Loneliness (%) | Positive Effect (%) | No Effect (%) | Unclear Effect (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Qualitative | 14 (22%) | 9 (15%) | 1 (2%) | 4 (6%) |
| Quantitative-observational | 16 (26%) | 9 (15%) | 1 (2%) | 6 (10%) |
| Quantitative-experimental | 24 (39%) | 12 (19%) | 4 (6%) | 8 (13%) |
| Mixed methods | 8 (13%) | 4 (6%) | 1 (2%) | 3 (5%) |
| Total | 62 (100%) | 34 (55%) * | 7 (12%) * | 21 (34%) * |
| Study Design | No. of Outcome Measures for Social Isolation (%) | Positive Effect (%) | No Effect (%) | Unclear Effect (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Qualitative | 10 (24%) | 5 (12%) | 1 (2%) | 4 (10%) |
| Quantitative-observational | 11 (27%) | 5 (12%) | 1 (2%) | 5 (12%) |
| Quantitative-experimental | 14 (34%) | 6 (15%) | 3 (7%) | 5 (12%) |
| Mixed methods | 6 (15%) | 2 (5%) | 0 (0%) | 4 (10%) |
| Total | 41 (100%) | 18 (44%) * | 5 (11%) * | 18 (44%) * |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Döring, N.; Conde, M.; Brandenburg, K.; Broll, W.; Gross, H.-M.; Werner, S.; Raake, A. Can Communication Technologies Reduce Loneliness and Social Isolation in Older People? A Scoping Review of Reviews. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 11310. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph191811310
Döring N, Conde M, Brandenburg K, Broll W, Gross H-M, Werner S, Raake A. Can Communication Technologies Reduce Loneliness and Social Isolation in Older People? A Scoping Review of Reviews. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health. 2022; 19(18):11310. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph191811310
Chicago/Turabian StyleDöring, Nicola, Melisa Conde, Karlheinz Brandenburg, Wolfgang Broll, Horst-Michael Gross, Stephan Werner, and Alexander Raake. 2022. "Can Communication Technologies Reduce Loneliness and Social Isolation in Older People? A Scoping Review of Reviews" International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health 19, no. 18: 11310. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph191811310
APA StyleDöring, N., Conde, M., Brandenburg, K., Broll, W., Gross, H.-M., Werner, S., & Raake, A. (2022). Can Communication Technologies Reduce Loneliness and Social Isolation in Older People? A Scoping Review of Reviews. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 19(18), 11310. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph191811310