Abstract
Dam removal is considered an effective measure to solve the adverse ecological effects caused by dam construction and has started to be considered in China. The sediment migration and habitat restoration of river ecosystems after dam removal have been extensively studied abroad but are still in the exploratory stage in China. However, there are few studies on the ecological response of fishes at different growth stages. Considering the different habitat preferences of Schizothorax prenanti (S. prenanti) in the spawning and juvenile periods, this study coupled field survey data and a two-dimensional hydrodynamic model to explore the changes in river morphology at different scales and the impact of changes in hydrodynamic conditions on fish habitat suitability in the short term. The results show that after the dam is removed, in the upstream of the dam, the riverbed is eroded and cut down and the riverbed material coarsens. With the increase in flow velocity and the decrease in flow area, the weighted usable area (WUA) in the spawning and juvenile periods decreases by 5.52% and 16.36%, respectively. In the downstream of the dam, the riverbed is markedly silted and the bottom material becomes fine. With the increase in water depth and flow velocity, the WUA increases by 79.91% in the spawning period and decreases by 67.90% in the juvenile period, which is conducive to adult fish spawning but not to juvenile fish growth. The changes in physical habitat structure over a short time period caused by dam removal have different effects on different fish development periods, which are not all positive. The restoration of stream continuity increases adult fish spawning potential while limiting juvenile growth. Thus, although fish can spawn successfully, self-recruitment of fish stocks can still be affected if juvenile fish do not grow successfully. This study provides a research basis for habitat assessment after dam removal and a new perspective for the subsequent adaptive management strategy of the project.
1. Introduction
The excessive and disorderly development of small hydropower groups is the main reason for the habitat degradation and fragmentation of tributary river networks. Dams hinder the migration route of fish, change the runoff process and lead to the degradation and loss of river habitats. According to the IUCN (International Union for Conservation of Nature), dams have been the main reason for the extinction or endangerment of nearly one-fifth of the fish species worldwide in the past 100 years [1,2]. With a large number of small dams reaching the end of their design life and their management and maintenance requirements not being met, potential safety hazards are becoming increasingly prominent. Under the condition that maintenance and reinforcement still cannot solve their potential safety hazards, the removal of low-head dams as an eco-friendly strategy has attracted increasing attention [3,4]. The effect of dam removal on restoring the interaction between geomorphic and hydrological processes and on reshaping the river channel through erosion and sedimentation processes have been well discussed [5,6,7,8,9]. In addition, dam removal has been proven to be an effective way to increase the diversity of river ecosystems, as it reconnects rivers and promotes gene exchange between populations [10,11,12]. For example, O’Donnell et al. [13] found that within one year after the removal of the Edwards dam on the Kennebec River, a large number of American eel (Anguilla rostrata), Alewife (Alosa pseudoharengus) and Atlantic sturgeon (Acipenser oxyrinchus) were observed in the upstream habitat, which had disappeared for over 150 years. Catalano et al. [14] and Kanehl et al. [15] found that after dam removal, the static water environment becomes a torrent environment, and the number of shoals, bends and torrents increases. Fish that prefer river habitats gradually replace fish that prefer lake habitats. However, although studies on the habitat and ecological response after dam removal have been carried out in recent years, as mentioned above, most of them have only focused on the impact of dam removal on adult fish, especially on spawning activities [6,16,17,18]. Indeed, habitat preference is far more complicated for fish at different periods, and the impact of physical habitat changes on other sensitive growth periods is less studied.
The replenishment of fish populations is highly dependent on habitat availability and habitat quality [19,20,21,22]. Only when external environmental conditions such as water temperature, hydrology and hydraulic power are met and sufficient energy is accumulated can fish complete the corresponding life activities [23,24]. Spawning activity, which bonds parents and offspring and is believed to be key to boosting stocks, has been well discussed by scholars [25,26,27,28]. Shen et al. [29] found that the delay of the spawning time of Chinese sturgeons was attributed to the increase in water temperature and the decrease in downstream discharge through model simulation. Warren et al. [30] reviewed the impact of flow on the number and distribution of salmon and found that improper hydraulic and ecological hydrological conditions delay the spawning time and reduce the number of eggs, which may further lead to the aging of fish populations and reduce the replenishment of fish resources. The juvenile period, where fish begin to store energy by increasing feeding for the maturation of internal organs, is another critical period. Although the living habits of juvenile fish are roughly the same as those of adult fish, studies have shown that environmental interference may lead to the death of a large number of juvenile fish, meaning that they are more sensitive to environmental changes than adult fish [31,32,33]. As a major source of parental supplementation, the successful growth of juvenile fish is very important to maintain the sustainable regeneration of fishery resources so fish can mate once sexually mature [34,35]. However, the habitat needs of juvenile fish are usually ignored in the study of river ecological restoration. With the development of environmental awareness in various countries, higher requirements have been put forward for the protection of fish diversity, which highlights the need for a deeper understanding of the potential role of the removal of low-head dams in the protection and restoration of key habitats.
At present, the impact assessment of dam removal is mainly carried out via two different approaches: actual monitoring data analysis and theoretical model prediction [36]. The site monitoring and assessment of dam removal cases is the most direct and convincing research method, but due to cost and some noncontrollable factors, monitoring data are sometimes not comprehensive. Numerical simulation can predict the ecological impact of dam removal because of its fast speed, low cost and strong simulation ability. However, sometimes the accuracy of the simulation cannot be guaranteed [37]. In recent years, both methods have been widely used in the ecological impact assessment of dam removal [38,39]. Comprehensively considering the advantages and disadvantages of the two evaluation methods, the best way to evaluate the ecological impact and provide a reliable basis for the dam removal decision is to use the numerical simulation method to quickly grasp the changes in fish habitat in different spatial locations, determine the impact of dam removal on fish and use the monitoring data to provide evidence for the simulation results and to verify the correctness of the model-based analysis.
Taking the Laomuhe Dam removal project of the Heishui River as an example, this study investigates the impact of dam removal on river morphology and fish critical habitats in the short term (within three years after dam removal) by incorporating the juvenile and spawning habitat requirements into the ecological impact assessment of dam removal by coupling the numerical simulation and field survey methods. It further discusses how to develop and manage river ecological restoration measures to more comprehensively maintain river fish habitat quality at a high level in small and medium mountainous rivers. Compared with our previous research results in the Heishui River [23,40], this study is a continuation and extension of the research on the impact of external environmental changes on fish. The research results can provide theoretical support for the environmental impact assessment and adaptive management of subsequent river restoration projects.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Area
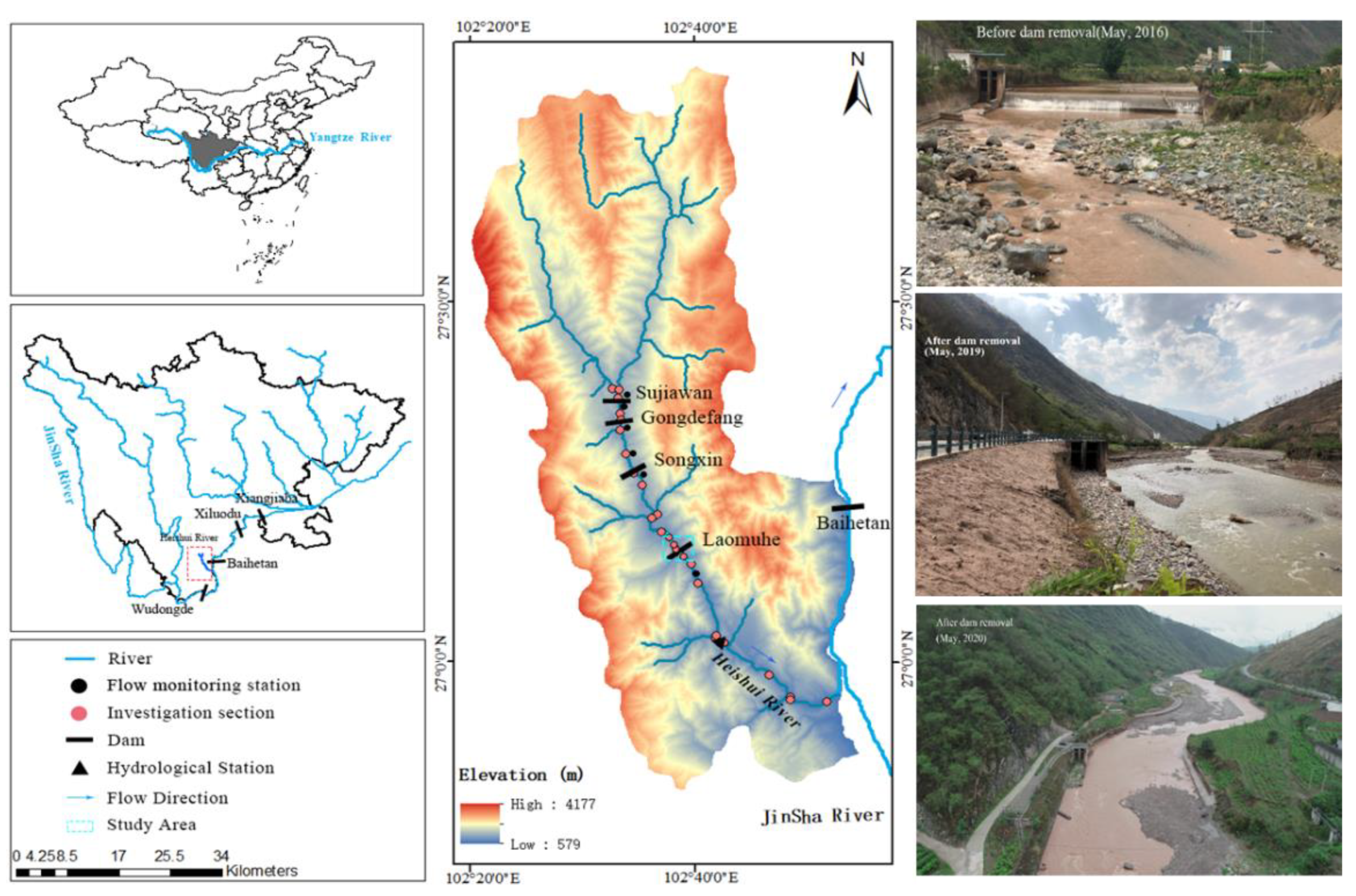
The Heishui River is the first-class tributary on the left bank of the Jinsha River and a typical mountain river in Southwest China. With a total length of 173.0 km, the riverbed bottom is mainly composed of pebbles and gravel, with occasional large boulders. There are four cascade dams in the Heishui River, namely Sujiawan Dam (SJWD), Gongdefang Dam (GDFD), Songxin Dam (SXD) and Laomuhe Dam (LMHD), from upstream to downstream. The four dams are all run-of-river hydropower stations without regulation capability (Figure 1).
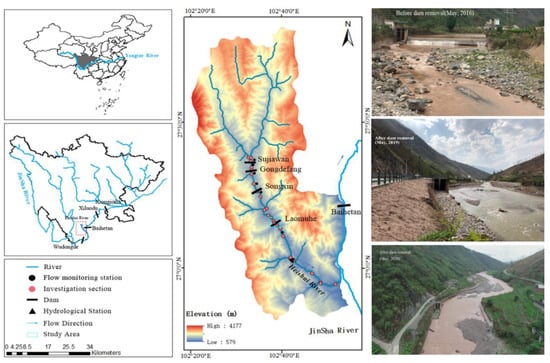
Figure 1.
Location (left) and basin elevation (center) of the Heishui River. The picture shows the river reach near the dam site before (2018, top right), during (2019, middle right) and two years after (2021, bottom right) removal.
The LMHD (102°38’ E, 27°10’ N) is 7.8 m high and 56 m wide. Water diversion has greatly changed the natural hydrological conditions of the river section, making the downstream river section severely dehydrated. As a result, the biological habitat in this area has been severely degraded, and there are great differences in fish population structures between the upstream and downstream sections. To repair the local harsh habitats, restore river connectivity and extend the length of natural river sections, the LMHD was removed in December 2018. The study area of this study is the river section where the habitat quality is severely disturbed between 1 km upstream and 0.5 km downstream of the LMHD. According to the flow monitoring data of Ningnan hydrological station for the last 20 years, under natural conditions, the average flow during the centralized spawning period from March to May was 23.55 m3/s. After the completion of the LMHD, the average flow downstream of the dam was 2.95 m3/s (Figure 1).
2.2. Field Data Collection and Target Fish
Since December 2018, 25 monitoring sections along the main stream of the Heishui River have been tracked in spring and autumn every year (organized by Shanghai Investigation, Design and Research Institute Corporation Limited, Shanghai, China). Four monitoring sections are included in the study area of this manuscript. The four monitoring sections are located 1 km upstream of LMHD, 400 m upstream of LMHD, LMHD site and 400 m below the LMHD. The monitoring content includes velocity, water depth, discharge, riverbed substrate and channel topography. Hydrodynamic indexes (velocity and water depth) were performed by Acoustic Doppler Current Profiler (ADCP), portable flow rate meter and depth sounder RTK according to the actual situation of the river. During each tracking and monitoring, the sand shovel was used to collect appropriate riverbed materials at each monitoring section and put them into plastic buckets. After drying in the laboratory, electric mesh screen was used to screen the bed material with different particle sizes, and the weight of sediment with different particle sizes was recorded. Finally, the percentage was calculated and the sediment grain grading curve was drawn. In addition, a total of six automatic monitoring stations were set up in the Heishui River (Figure 1), and each station monitored the flow in the reach on a daily basis to provide the required flow data for the numerical simulation of the study. In order to understand the changes in riverbed topography before and after the removal of LMHD, the riverbed and the topography of both sides of the study area were mapped in May 2018, May 2019 and May 2021, respectively. The survey contents included river topography and sectional topography. According to the measurement data of river elevation in the study area, the measured data of limited river section topography were used to construct refined river topography by encrypting sections and interpolation, which was used to analyze the changes in river topography before and after dam removal.
According to the preliminary survey results of fish resources, Schizothorax prenanti (S. prenanti) is the main dominant fish in the Heishui River [41,42]. Due to overfishing, hydropower development and water pollution, its resources have decreased significantly in recent years [43]. The Sichuan provincial government has listed S. prenanti as a priority protected species. Considering the economic status and degree of endangerment of S. prenanti in the Heishui River, this study selected S. prenanti as the target fish [40,44]. S. prenanti is a typical plateau fish species that mainly lives in mountainous rivers with fast flow velocity and high oxygen content and exhibits short-distance reproductive migration. The breeding period of S. prenanti in the study area is from December to May, during which time the peak spawning period is from March to May. Its eggs are heavy and sticky and are mostly deposited on the gravel of the rapids [42].
2.3. Habitat Simulation Model
2.3.1. Hydrodynamic Model
The two-dimensional hydrodynamic model of MIKE is applied to explore the changes in hydrodynamic conditions before and after dam removal. The hydrodynamic model of the research is based on the Navier–Stokes equation with three-dimensional incompressibility and uniform Reynolds values, and is subject to the Boussinesq assumption and the assumption of hydrostatic pressure [45,46,47]. The shallow water equations, including continuity and momentum equations, are given by
where , are the Cartesian coordinates; and (m/s) are the components of velocity in the x and y directions; and (m/s) are, respectively, defined by ; (s) is the time; (m) is the total water depth, ; (m) is the height of the water surface relative to the undisturbed base surface, (m) is the still water depth ; S is the magnitude of the discharge due to point sources; f is the Coriolis parameter and is equal to ( is the angular rate of revolution and is the geographic latitude); g is gravitational acceleration, g = 9.81 m/s2; (kg/m3) is the density of water; (kg/m3) is the reference density of water); (, ) (N/m2) and (, ) (N/m2) are the components of the surface wind and bottom stresses in the x and y directions; (Pa) is the atmospheric pressure; (, ) is the velocity at which the water is discharged into ambient water.
2.3.2. Habitat Suitability Index
Three indicators, the habitat suitability index (HSI), weighted usable area (WUA) and overall suitability index (OSI), were used to evaluate habitat quality. HSI is used to quantitatively describe the relationship between habitat preference and habitat factors [48]. The higher the habitat suitability value is, the higher the frequency of species. OSI [49,50] is the ratio of the WUA to the total computational domain area. For rivers with the best habitat quality, the theoretical OSI is 1, while 0 represents the worst habitat quality.
where , and are the suitability of velocity, water depth and substrate, respectively. HSIi is the habitat suitability index of cell i. Each variable was quantified using a suitability curve between 0 and 1, with 0 indicating the lowest suitability and 1 indicating the highest; Ai is the area of the i-th element, m2; n are the total number of elements in the study area.
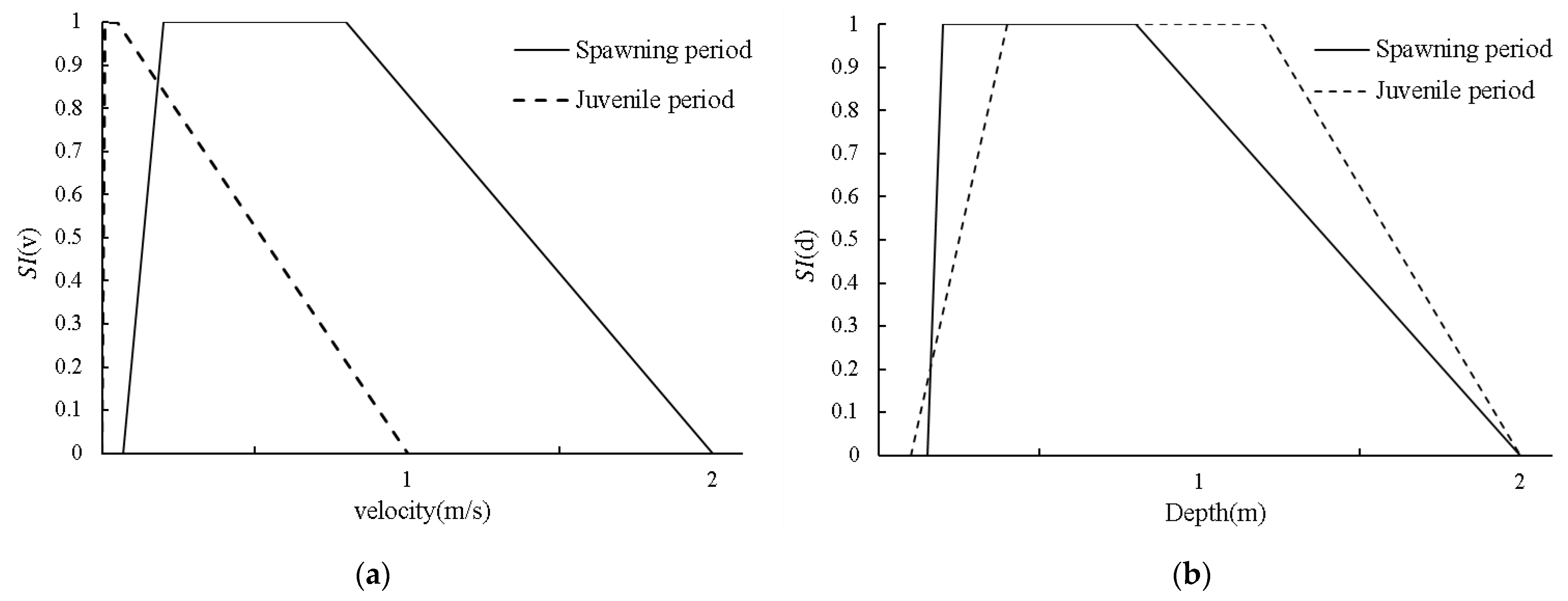
In this study, by investigating the historical natural spawning habitats of schizothoracids in the Heishui River estuary and combining these data with those from other relevant studies of S. prenanti [51,52,53,54,55,56], the flow velocity and water depth preferences in different periods were determined (Figure 2). For S. prenanti, the suitable water depth range during the spawning period is 0.15~2.00 m, and the most suitable water depth is 0.20~0.80 m. The suitable flow velocity range is 0.07~2.00 m/s, the best flow velocity range is 0.20~0.8 m/s and the bottom material suitable for spawning is pebbles and gravel (diameter range is 2–256 mm). In the juvenile fish period, the suitable water depth range is 0.10~2.00 m, and the most suitable water depth is 0.40~1.20 m. The suitable flow velocity range is 0.00~1.00 m/s, the best flow velocity range is 0.10~0.50 m/s and the bottom material suitable for juvenile fish is pebbles and gravel (diameter range is 2–256 mm).
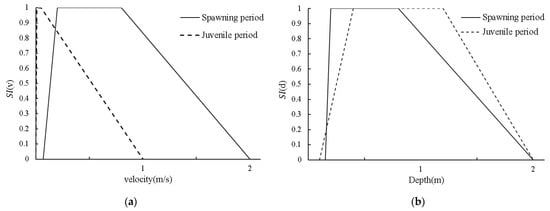
Figure 2.
Suitability index (SI), (a) suitability index of velocity (SI(v)), (b) suitability index of depth (SI(d)).
3. Results
3.1. Morphological Changes
Terrain monitoring was carried out in the study area before (2018), after (2019) and two years after (2021) dam removal. Limited by the monitoring conditions, only the river channel within the range of 300 m upstream to 400 m downstream of the dam site was measured in May 2019, and the terrain monitoring range in the other two periods was 1 km above the dam to 500 m below the dam.
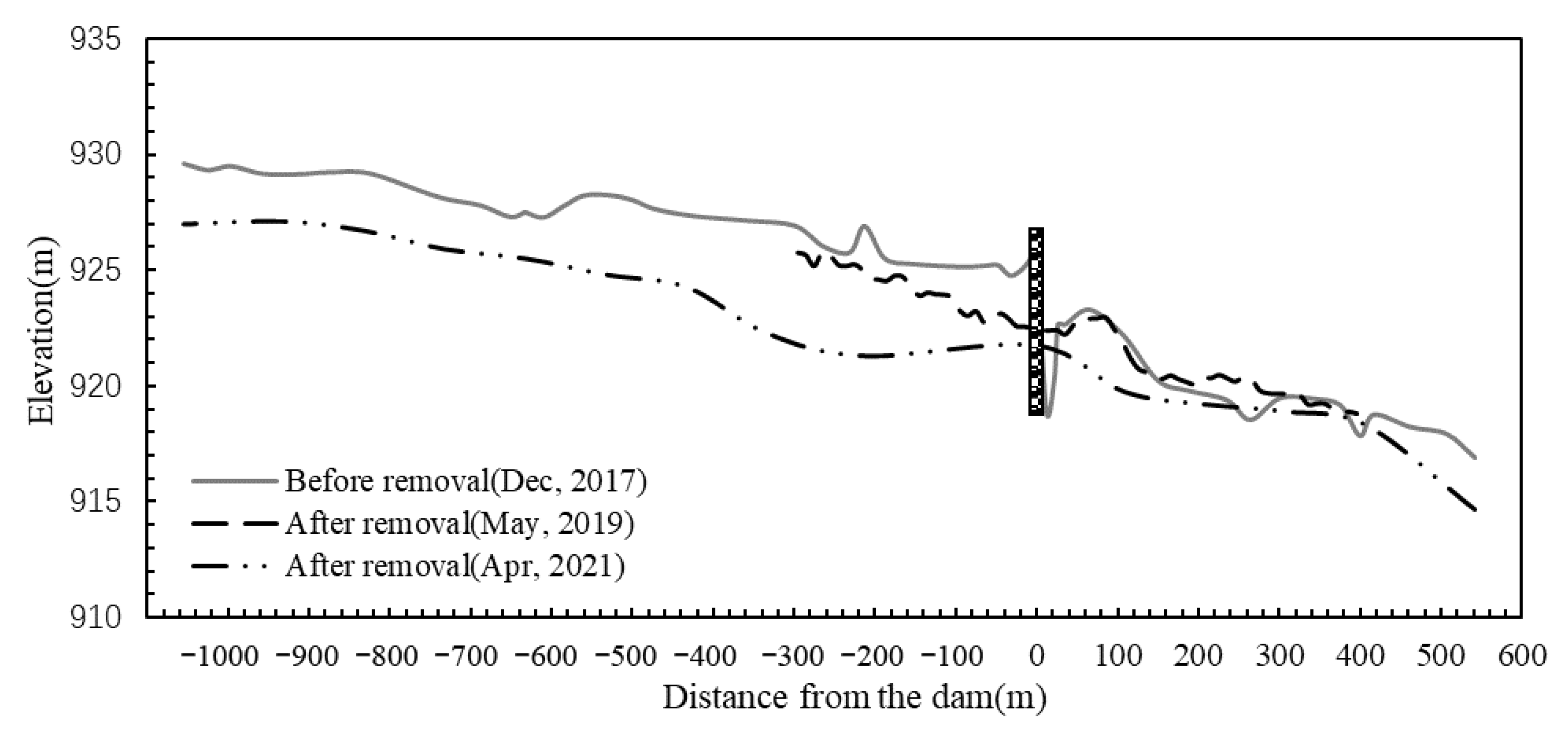
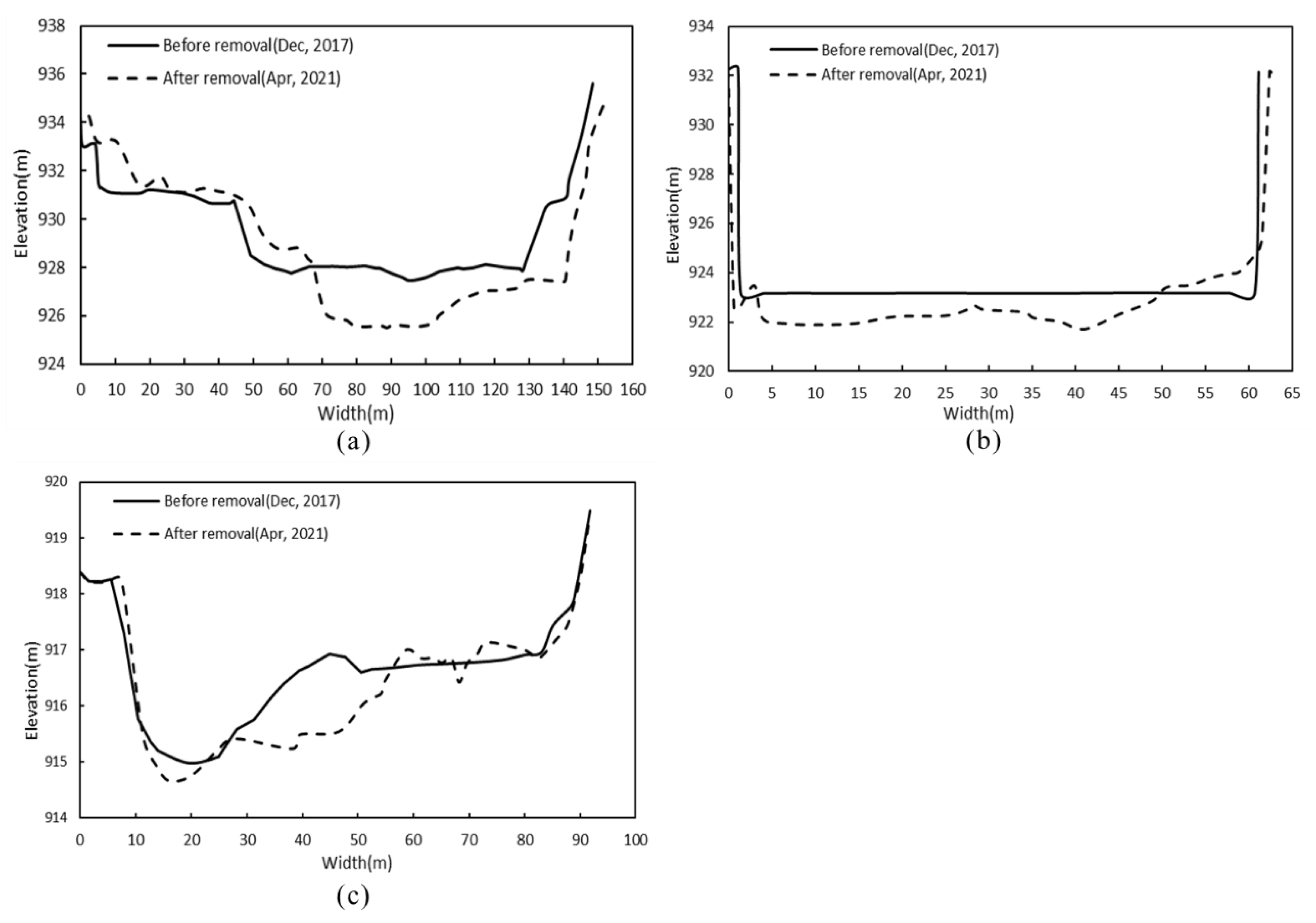
The elevation change map of the river profile is drawn according to the measured topographic data of the study area, as shown in Figure 3. Topography monitoring results show that after dam removal, a large amount of sediment particles accumulated in the upstream reservoir are transported downstream, causing erosion of the upstream riverbed. Half a year after the dam was removed, the erosion depth in the reservoir area was approximately 0.5~2.93 m. Two years after the dam was removed, the riverbed erosion deepened, reaching 1.55~5.58 m. To minimize water pollution caused by sediment discharge, the riverbed near the dam site was manually dredged before dam removal, which is the main reason for the significant change in river morphology there. Half a year after dam removal, the riverbed at the dam site decreased by approximately 1.14 m, and two years later, it decreased by 3.67 m. Sediment deposition and erosion occurred in the riverbed downstream of the dam, and sediment deposition was more considerable. The sediment deposition was mainly concentrated in the river section 160 m~300 m downstream of the dam. The deposition height was approximately 0~1.17 m after half a year and 0~1.88 m after two years.
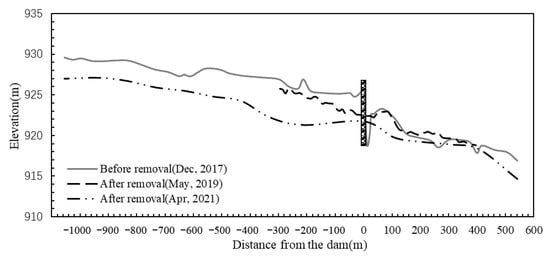
Figure 3.
Changes in the longitudinal profiles of elevation with dam removal.
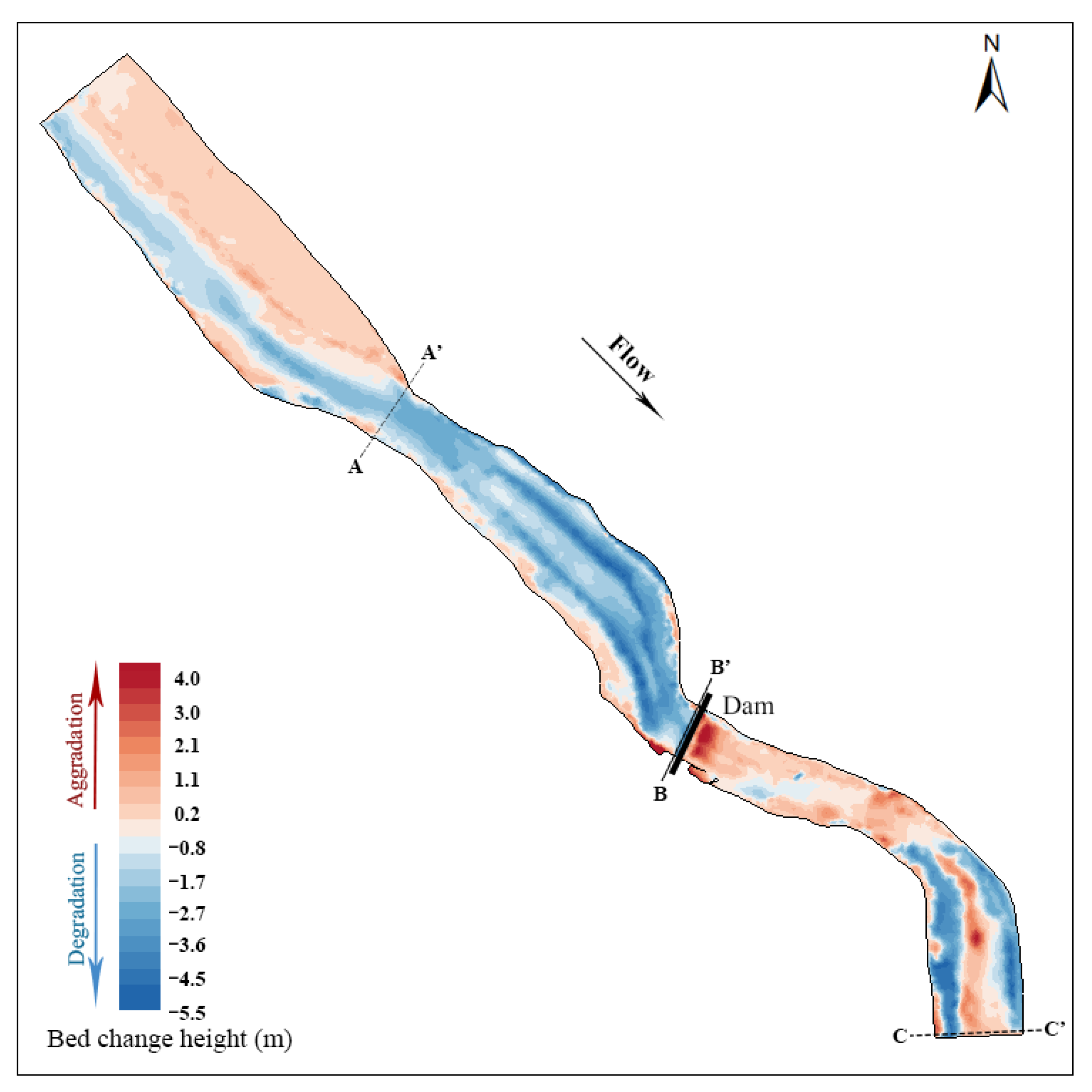
Figure 4 shows the elevation change in the riverbed two years after dam removal. The red area is the riverbed aggradation area. The darker the red is, the greater the aggradation. The blue area is the riverbed degradation area. The deeper the blue is, the greater the riverbed degradation degree is. Two years after dam removal, the riverbed upstream of the dam showed a general degradation trend, and the erosion of the main channel was clear. However, the left and right riverbeds immediately upstream of the dam site were raised by aggradation. These areas are vegetated floodplains where reduced flow velocity may be the main reason for sediment particle deposition. The sediment downstream of the dam was mainly deposited in the middle of the riverbed and left bank of the riverbed, and the riverbed on the right bank was clearly eroded. In the bend section 300 m~500 m downstream of the dam site, the river erosion depth on the left and right sides was relatively large, and the sediment deposition in the main channel was considerable. According to the field investigation, there is a relatively substantial central beach in this area, and the sediment deposition in the middle of the riverbed seems to be related to the central beach.
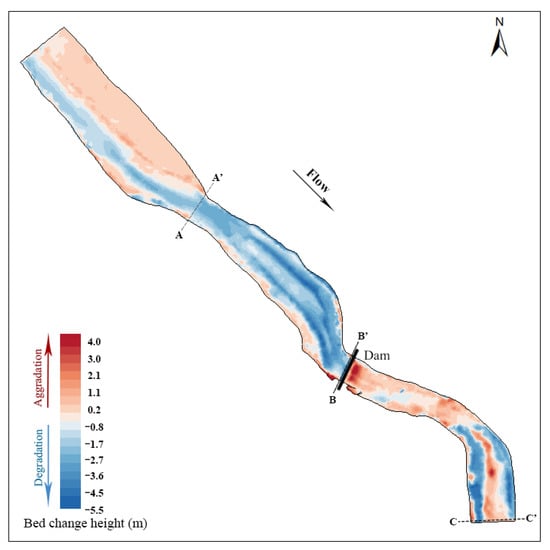
Figure 4.
Bed elevation change before and after dam removal.
Figure 5 shows the morphological changes in typical sections before and after dam removal. The A–A’ section is located 600 m upstream of the dam site and is approximately 100 m wide (Figure 5a). After the dam was removed, there was marked sediment deposition on the right bank of the section, and the deposition height was between 0.6 and 1.5 m. The maximum erosion depth of the main channel was approximately 2.5 m. Section B–B’ corresponds to the dam site section and is approximately 60 m wide. After the dam was removed, the riverbed was degraded by approximately 1.4 m (Figure 5b). The riverbed erosion may have been influenced by the manual dredging, but, unfortunately, the specific dredging depth cannot be determined. The C–C’ section is located 500 m downstream of the dam site (Figure 5c). The channel on the right bank is obviously eroded, and the sediment is mainly deposited on the left bank, with a maximum deposition height of approximately 0.3 m. The specific positions of the three typical sections in the river are shown in Figure 4.
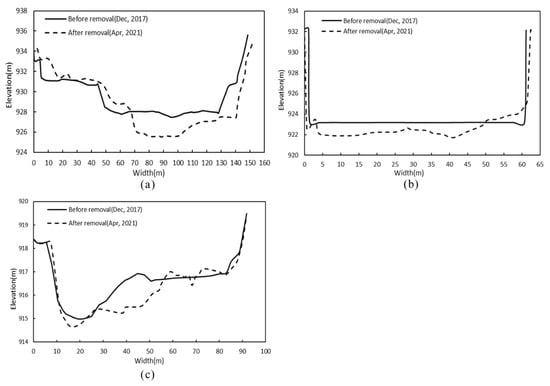
Figure 5.
Changes in the channel cross-section after dam removal. The positions of (a) section A–A’, (b) section B–B’ and (c) section C–C’ are shown in Figure 4. The water flow direction is vertical and faces outward.
To study the influence of dam removal on riverbed materials, the change in average particle size before and after dam removal was compared and analyzed (Table 1). Limited by the scope of investigation, only two sections, 1 km upstream and 1 km downstream of the dam site, were investigated. The median particle size (D50) was measured at each cross-section to represent the sediment size of the reach. Sediments with particle sizes greater than 8 mm were not investigated before dam removal, and were determined by referring to the study of Tang et al. [6]. The median particle size of sediment after dam removal was determined according to the investigation results in spring 2021. The results show that the downstream sediment changed from coarse grain to fine grain, and the upstream sediment changed from fine grain to coarse grain. Before and after dam removal, the overburden layer of the upstream and downstream riverbed was mostly gravel or pebbles with diameters between 2 mm and 100 mm, which are suitable for the spawning and growth of S. prenanti.

Table 1.
Variation in median substrate size (D50).
3.2. Fish Habitat Quality Assessment
3.2.1. Model Calibration and Validation
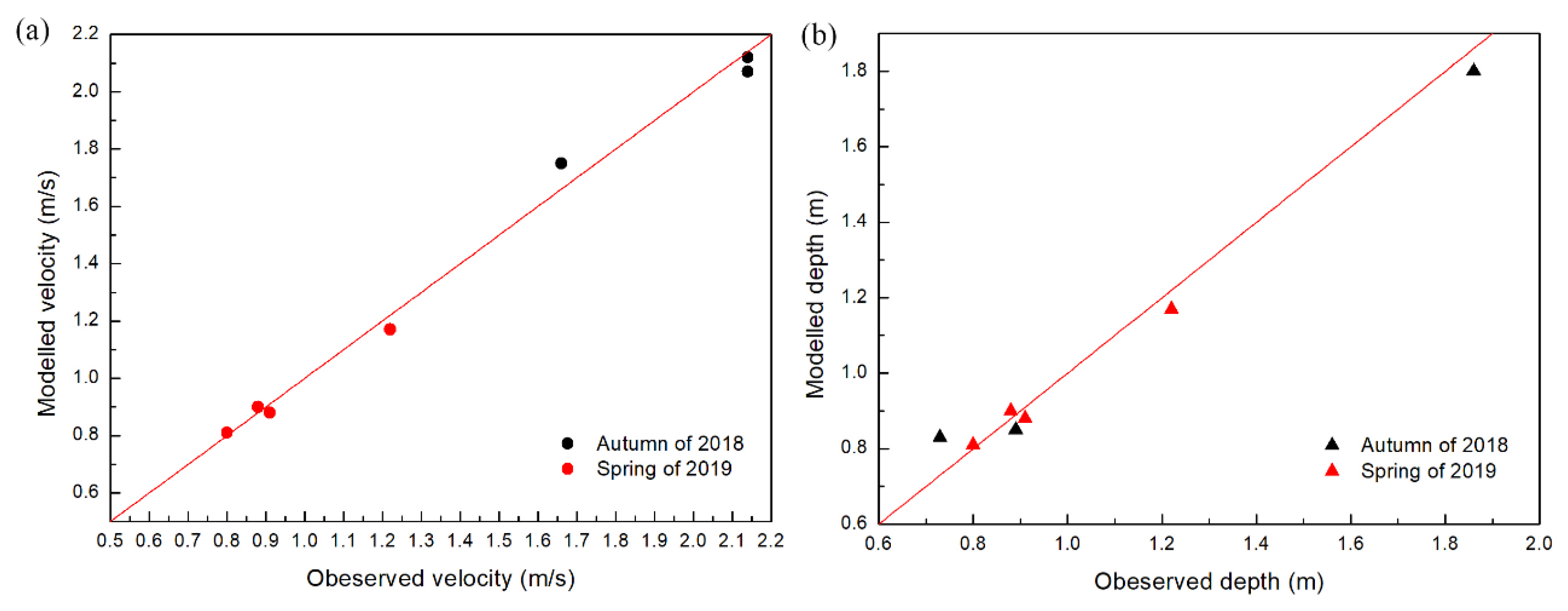
In the calculation of the two-dimensional fluid dynamics model, the upstream boundary is set as the flow provided by the automatic monitoring station of SXD, and the downstream boundary is the water level calculated according to the daily flow data of Ningnan hydrological station and the riverbed slope. The hydrodynamic models before and after dam removal were calibrated using the maximum water depth and maximum velocity data from the measured hydrological data of each survey section (Figure 1) in November 2018 (autumn) and March 2019 (spring), and the calculated roughness n in the model was 0.035~0.042 [57]. The comparison between model simulation results and actual measurement results is shown in Figure 6. The mean absolute error (MAE), root mean square error (RMSE) and R squared (R2) were introduced to the error analysis. The error analysis result is shown in Table 2, which indicates a good match between our model and the real river hydrodynamic conditions [58].
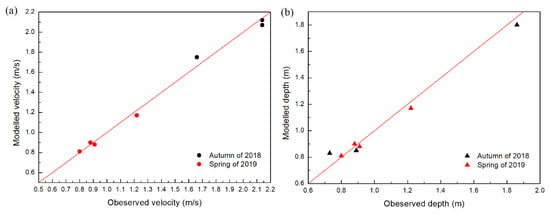
Figure 6.
Comparison of observed velocity and water depth data with modelled results: (a) flow velocity and (b) water depth. The magnitude of the values varies with the flow in different periods.

Table 2.
Error analysis of velocity (V) and depth (D) simulation results.
3.2.2. Flow Characteristics
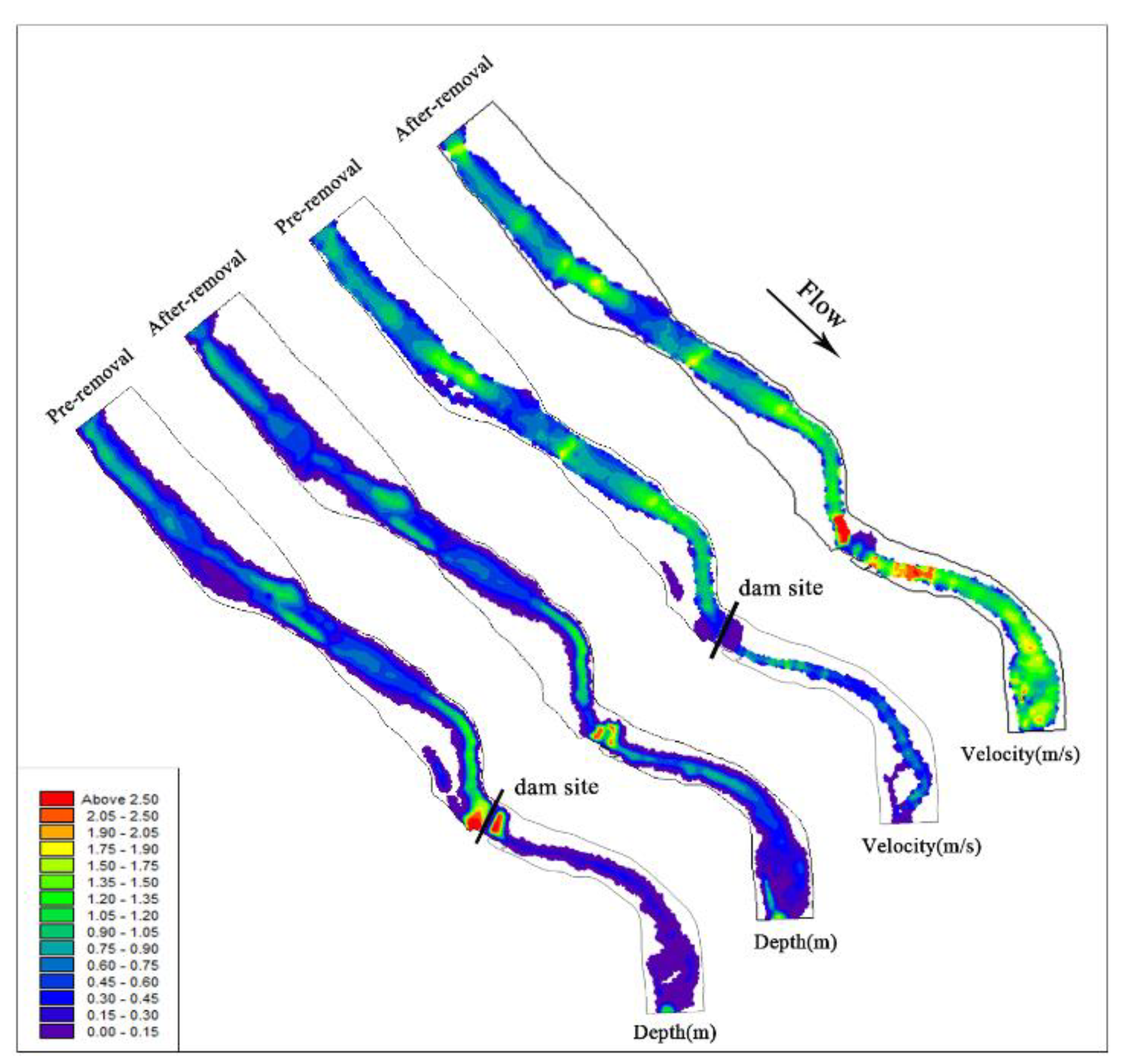
According to the simulation results, the influence of dam removal on the river flow pattern was compared and analyzed. The short-term changes in velocity and water depth after dam removal are shown in Figure 7. The river barrier point disappears, and the upstream overflow area decreases after the dam is removed. The water depth tends to decrease and varies from 0.04 to 1 m. The area near the dam site may be affected by artificial dredging, and the flow velocity increases significantly. The removal of the power station and diversion tunnel restored the natural flow of the river downstream of the dam and eliminated dehydration downstream. With the increase in discharge, the downstream water depth and velocity increased significantly, and the width of the water surface almost doubled, which increased the living space of aquatic organisms. According to the model calculation, the river area increased from 81,844.59 m2 to 84,745.06 m2, representing an increase of approximately 3.5%. After dam removal, the remolding of river morphology and the change in water flow distribution lead to the diversification of water flow structure, which promotes the formation of heterogeneous habitats, thus cultivating a rich river ecosystem [59].
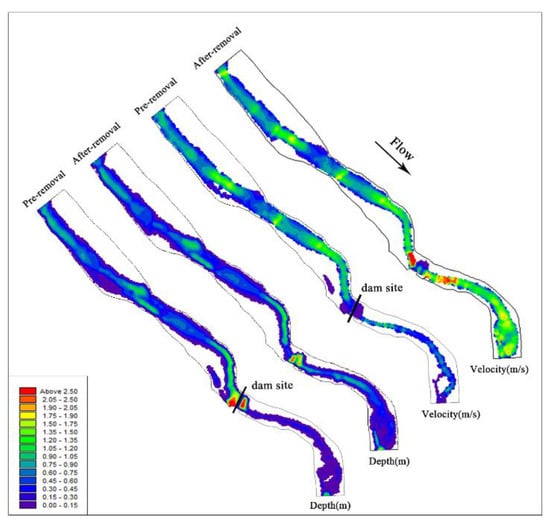
Figure 7.
Velocity and water depth distribution map of the river before and after dam removal.
3.2.3. Physical Habitat
- (1)
- Changes in habitat during the spawning period
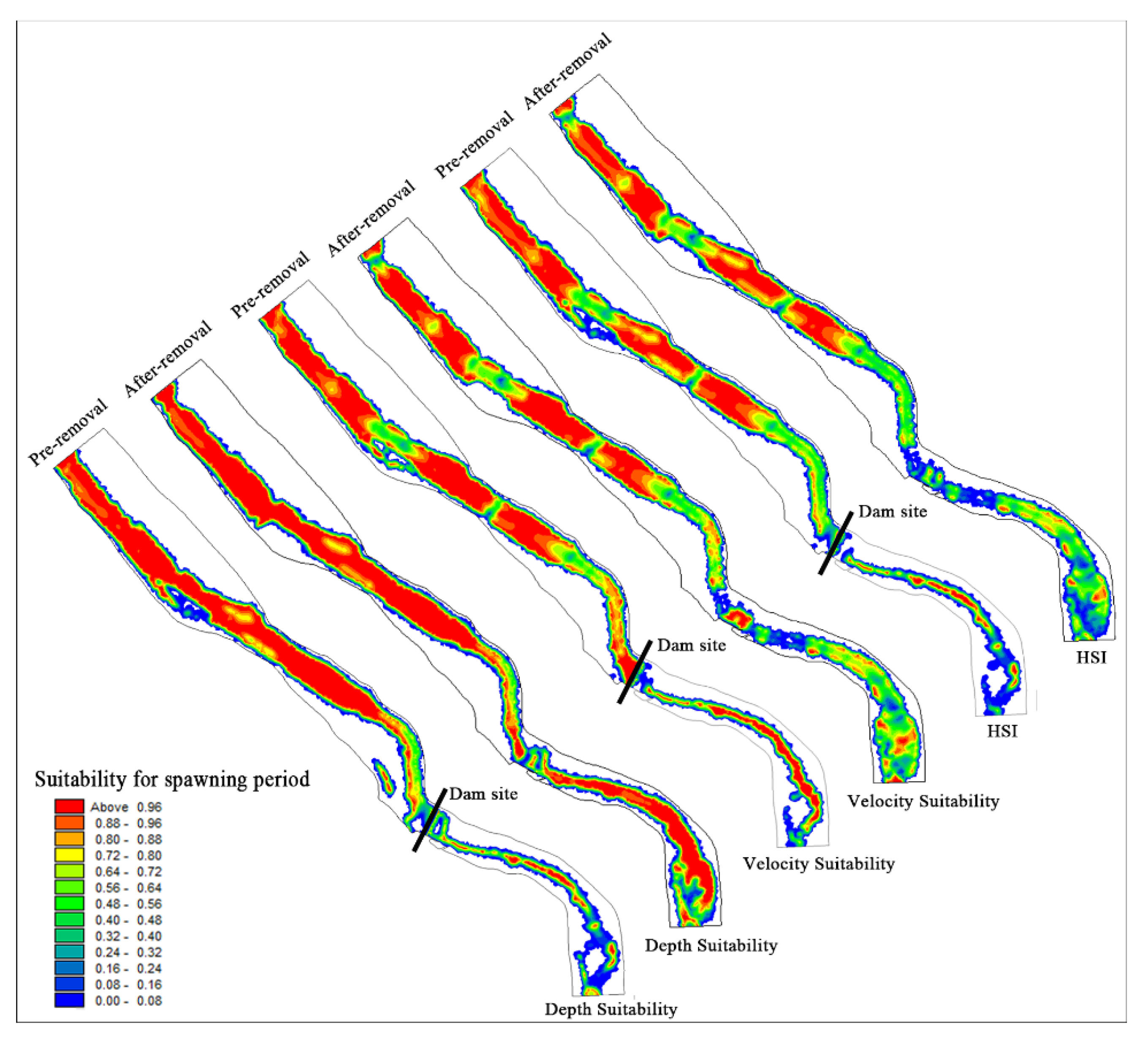
Hydraulic variables such as flow velocity and water depth were correlated with the habitat requirements of S. prenanti. The habitat suitability distribution of S. prenanti during the spawning season is shown in Figure 8. After dam removal, the water depth suitability increases but the velocity suitability decreases. According to the analysis, the flow velocity is the main factor limiting the comprehensive suitability for S. prenanti spawning. As shown in Figure 8 and Table 3, after dam demolition, the WUA of S. prenanti in the upstream of the LMHD decreased from 47,146.39 m2 to 44,542.88 m2, a decrease of 5.52%.
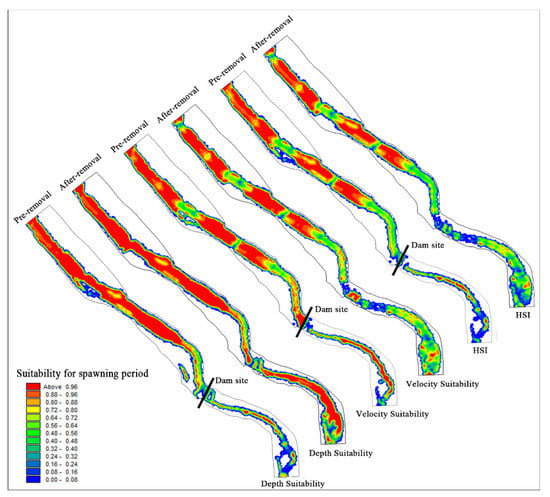
Figure 8.
Distribution map of velocity suitability, water depth suitability and habitat suitability before and after dam demolition during the spawning period.

Table 3.
Changes in weighted usable area (WUA) values for S. prenanti before and after dam removal.
The change in hydraulic conditions after dam removal has a significant impact on the downstream habitat. The recovery of the natural flow pattern increases the activity space of aquatic organisms and the suitable water depth area. After the dam was removed, the increased flow rate promoted the frequent exchange of matter and energy, making the water rich in oxygen. The high flow velocity and high dissolved oxygen content in the middle of the channel are not conducive to the adhesion of viscous fish eggs [60,61], leading to the gradual shift of suitable spawning habitats to both sides of the river bank. As seen from Table 3, the WUA of S. prenanti increased from 6206.9 m2 to 11,166.83 m2 in the downstream of the dam, with an increase of approximately 79.91%.
In terms of the overall suitable area of the river section during the spawning period, the WUA increased by 4.42% after the dam was removed. The removal of the dam improved the spawning habitat quality of S. prenanti in the study area, especially in the section downstream of the dam.
- (2)
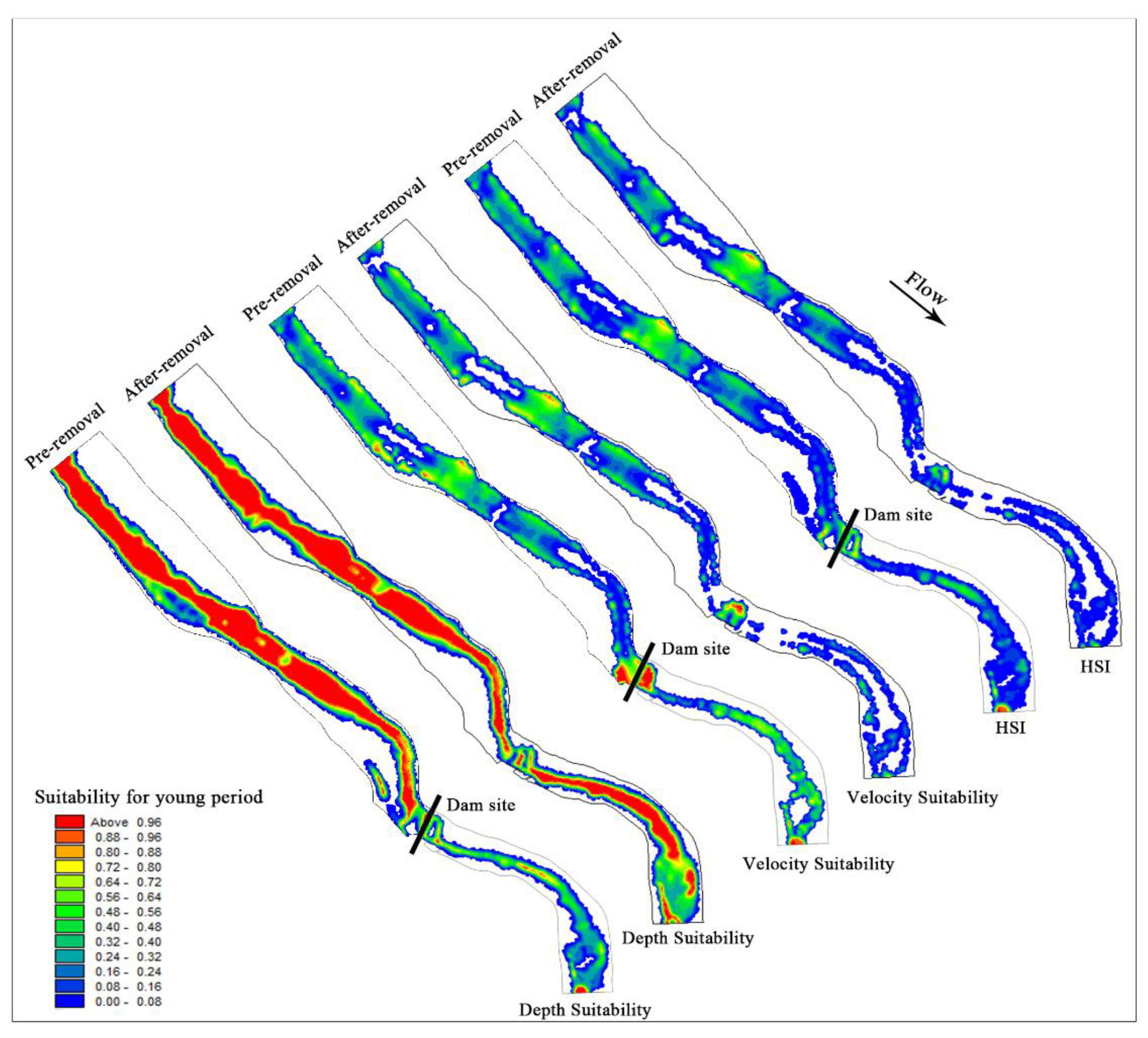
- Changes in habitat during the juvenile period
There is no apparent change in water depth suitability in the channel upstream of the dam after dam removal. However, the massive discharge of water and sediment reduces the area of the upstream river and the area suitable for juvenile fish. With the increase in flow velocity, the suitability of flow velocity decreases significantly, and flow velocity is the main factor limiting the comprehensive suitability. As shown in Table 3, the WUA of juvenile fish upstream decreased from 14,329.24 m2 to 11,984.44 m2, a decrease of 16.36%.
After dam removal, the natural flow was restored downstream of the dam. With the increase in water depth, the water depth suitability is significantly improved. As the flow velocity increased, the suitability of the flow velocity in the middle of the river channel decreased significantly, and the suitable growth area of juvenile fish gradually shifted from the river channel to the riparian slow-flow area. Figure 9 shows that after dam removal, the comprehensive suitability of juvenile fish growth downstream of the dam decreased significantly, and the flow velocity was the main indicator limiting their habitat suitability. The WUA of juvenile fish downstream of the dam decreased from 3599.93 m2 to 1155.49 m2, a decrease of 67.90%.
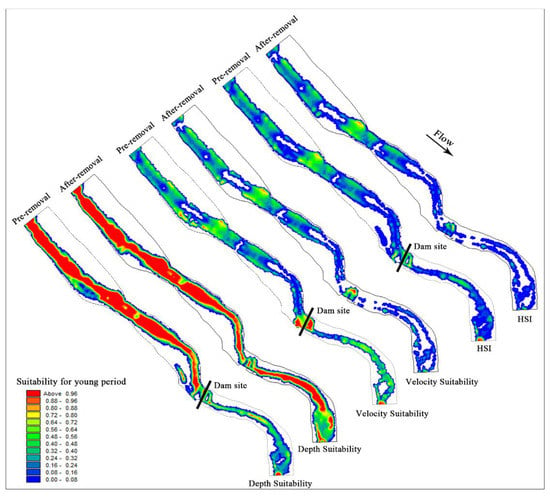
Figure 9.
Comparative analysis of velocity suitability, water depth suitability and comprehensive suitability before and after dam demolition at the juvenile stage.
The changes in hydrodynamic conditions caused by dam removal had a great impact on the habitat quality of juvenile fish, and the overall WUA decreased by 26.71% in the study area.
3.2.4. Habitat Sensitivity Analysis
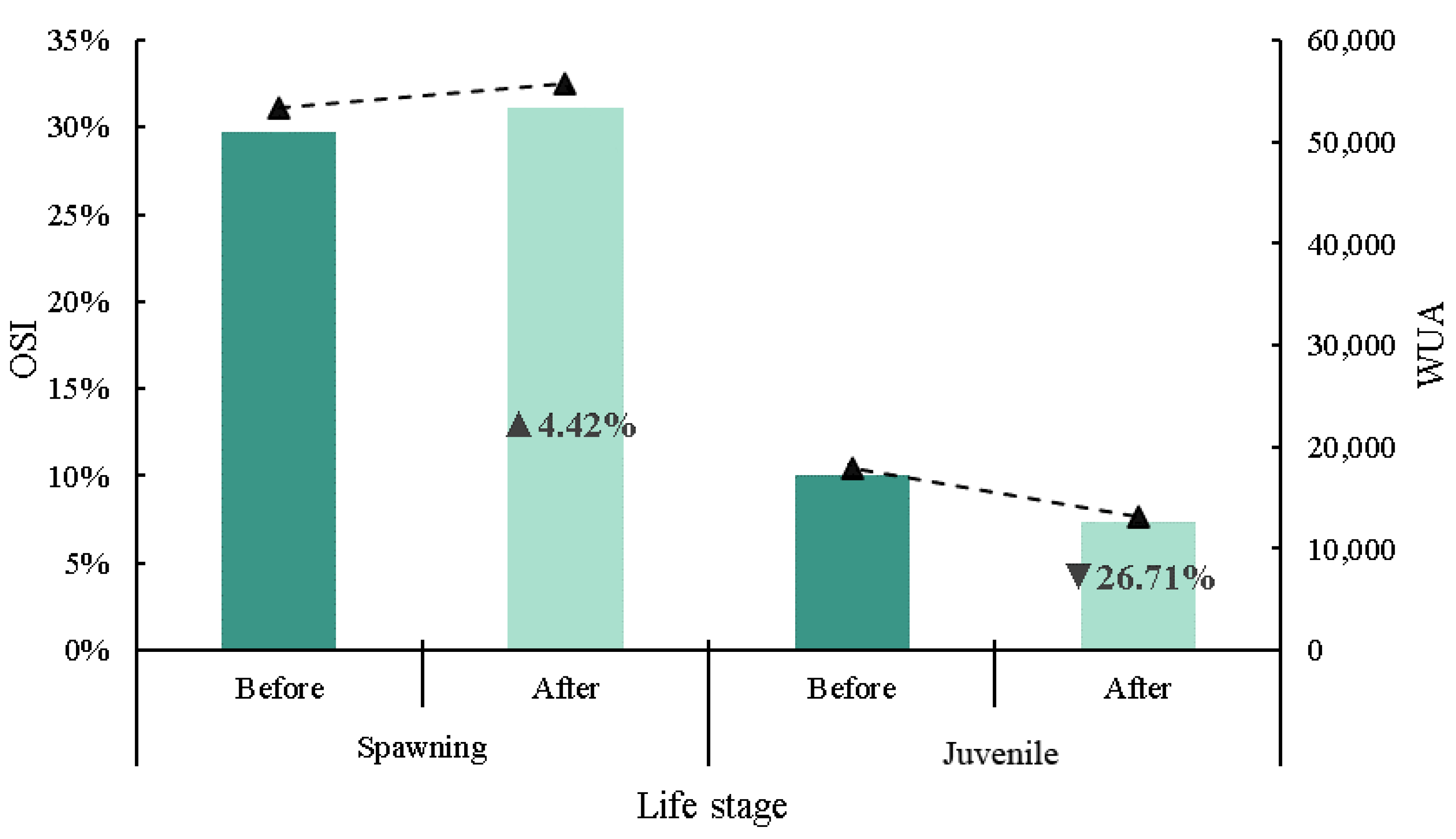
Habitat sensitivities at the juvenile and spawning periods of S. prenanti were analyzed according to the WUA and OSI. It is noted that WUA and OSI had exactly the same trend, while OSI had different values at different critical periods of S. prenanti growth. Figure 10 shows that the OSI value of the spawning period is higher than that of the juvenile period. After dam removal, both the WUA and OSI in the spawning period increased from 29.78% to 31.09%, with an increase of 1.31%. The WUA and OSI decreased from 10.01% to 7.33%, with a decrease of 2.68% in the juvenile period. This shows that dam demolition has a positive impact on fish spawning but a negative impact on the growth of juvenile fish. From the above analysis, it can be seen that juvenile fish in this area are more sensitive to habitat changes.
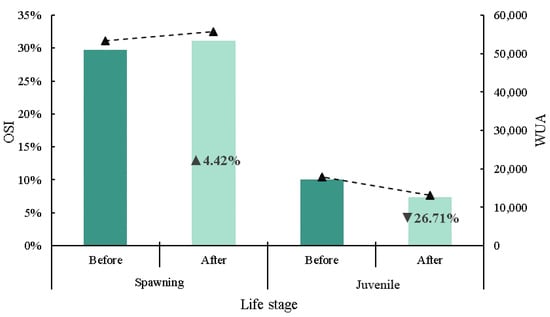
Figure 10.
Changes in OSI (overall suitability index) and WUA (weighted usable area) values for S. prenanti before and after dam removal. ▲: increase and ▼: decrease.
4. Discussion
The change in hydrodynamic conditions caused by dam removal has different effects on the habitat quality of fishes in different growth periods. It can improve the spawning habitat but negatively affect the growth of juvenile fishes. The increase in flow velocity seems to be the main factor limiting habitat quality in this area. According to the calculation results, with the increase in the flow rate in the channel after dam removal, the suitable area for fish spawning is wider than the suitable growth area for juvenile fish, and the suitable habitat for juvenile fish is mainly distributed in the bank beach with slow flow velocity. This may be because juveniles do not have enough energy or muscle strength to develop in habitats with high flow velocity [62], and the low flow velocity on both banks can reduce energy losses during juvenile activity. In addition, juvenile fish need to accumulate a large amount of energy for growth and development, and the abundant bait resources in the river beach can provide the necessary energy for the growth of juvenile fish [63]. This suggests that shallow slow-flow areas may be an important survival area for juveniles [64]. In view of the characteristics of high flow velocity and shallow water depth in the southwestern mountainous areas of China, although the increase in velocity caused by dam removal can stimulate fish spawning, the number of fish stocks may not increase due to the low survival rate of juvenile fish under high velocity. In the early period of fish life, especially in the rapidly growing embryo and juvenile period, small changes in environmental factors may lead to developmental arrest of fish at this period, thus affecting the growth and development of individuals in the later period [65,66]. According to this analysis and previous work, the periods when fish are more sensitive to habitat changes, such as the juvenile and spawning periods, may be better suited for assessing environmental pressures on aquatic organisms.
Dam removal is a very important opportunity to restore the geomorphology and ecological function of river ecosystems. In the short term after dam removal, the river morphology upstream and downstream of the dam changes to different degrees. The headwater erosion of the upstream river makes the upstream river narrower and deeper, and the riverbed elevation decreases [67,68]. The large amount of fine sediment discharge makes the upstream sediment size coarser and the downstream sediment size finer [69]. The size changes downstream are minimal, probably due to fine sediment particles being moved further downstream by the current. Changes in river morphology and flow structure will further affect the distribution of deep pools and riffles in the river, diversifying the natural habitat structure and thus improving habitat quality in the river [6,7]. The river continuity restored by the removal of the dam allows migratory fish to normally use the habitat upstream of the dam site and to swim to suitable sites to spawn [70]. Dam removal increases fish migration and reproduction opportunities, but strategies to remove the LMHD may be limited in restoring river connectivity due to differences in the needs of different fish species. For fish with long-distance migration needs, the existence of the SXD will still restrict their migration and reproduction activities. In a follow-up study, whether the SXD and the two upstream dam sites need to be demolished to meet the needs of different protected fish needs to be further studied.
This study only considered the effects of velocity and water depth on the habitat suitability of S. prenanti. These two variables were chosen because they were assumed to be the most important variables to explain their habitat selection. Furthermore, these variables are used in physical habitat studies and are known as habitat templates [71,72]. In this study, the change in bed materials was analyzed based on field monitoring but using only the survey data of cross-sections. Since no model has been established to simulate bed material change, it is assumed that the change in the reach is similar to that in the section. S. prenanti prefer to spawn on pebbles and gravel at the bottom of rapids and move to shallow areas to feed after spawning, where juveniles generally live. While these qualitative descriptions are helpful, quantitative data on habitat substrates for S. prenanti are almost nonexistent. By comparing the changes in substrates, we believe that the changes in substrates are still within the suitable range of the target fish, so the effects of substrate changes on habitat suitability are not considered in this study. However, the substrate preference of fish in different growth periods is still a future research focus. Moreover, the environmental factors affected by dam removal are not limited to hydrodynamic parameters but also include the dissolved oxygen and water temperature [73,74]. According to the environmental factor requirements in different life periods, future studies should further consider other variables that may play an important role in habitat assessment to provide more comprehensive theoretical support for project management.
As an emerging river ecological restoration technology, the restoration effect of dam demolition is complex and uncertain. Habitat loss of fish at different growth periods may reduce the effectiveness of ecological restoration or even lead to ineffective restoration [3]. Therefore, successfully restoring the river ecological environment requires not simply dismantling dams but must also be combined with other river ecological restoration measures to carry out comprehensive river ecological management to achieve results [75]. Through the analysis, it can be seen that after dam removal, many parts of the downstream channel have become the main silting areas, and a large amount of sediment cover will affect the quality of fish spawning grounds until the river reaches a new balance. Therefore, in the section of the river with considerable silt accumulation, a T-shaped dam can be built after the flood season, and water diversion and sediment discharge can be carried out by improving the hydrodynamic conditions of the river section to achieve the purpose of further improving the quality the habitat of the fish. Planned stocking can promote the sustainable development of fish resources, restore the food chain and achieve long-term ecological restoration effects. The restoration and reconstruction of fish habitats can select sections of rivers with low flow rates as fish habitats and consider adding gravel, logs and aquatic weeds to the downstream riverbed to increase the growth environment of the fish. The protection of spawning grounds and nursery areas in rivers as part of subsequent fisheries management is also an effective way to increase the self-replenishment of fish stocks [76].
5. Conclusions
In China, many low-head dams are about to be removed due to poor management or economic efficiency. To explore the impact of low-head dam removal on the habitat suitability of S. prenanti in mountainous rivers, this study took LMHD removal in the Heishui River as an example and combined field survey data with numerical simulation results to study the changes in river morphology and fish habitat after dam removal, and drew the following conclusions.
After dam removal, the change in water and sediment conditions leads to the erosion and deposition of particles upstream and downstream of the dam, respectively. The riverbed material upstream becomes coarse, and the riverbed material downstream becomes fine. However, the riverbed material before and after dam removal is within the size range of coarse-grained stone. The change in river morphology affects the hydraulic conditions in the river to a certain extent, which may change the existing distribution of deep pools and shoals, increase the diversity of riverbed geomorphology, and further affect the quality of the biological habitat in the river.
The habitat suitability calculated by the model shows that with the restoration of natural hydraulic conditions, the quality of the spawning habitat is significantly improved in the downstream reaches and decreased in the upstream reaches. For the juvenile period, the habitat quality of the upstream and downstream reaches of the dam site tends to decrease, which is not conducive to the growth and development of juvenile fish. The dam removal restored the continuity of the river habitat, and the WUA increased by 4.42% during the spawning period and decreased by 26.71% during the juvenile period throughout the reach. The influence of hydraulic conditions on the juvenile period was greater than that on the spawning period, and the flow velocity was the main limiting factor for the quality of the fish habitat in this area.
In general, our research results provide a new idea for dam removal management. According to the needs of fish in different growing stages, the method of dam removal can be discussed and designed in detail, which can minimize the disturbance of the fish population caused by the change in hydrodynamic conditions in the river. However, it is also crucial to track and monitor the changes in fish stocks after dam removal because the changes in biological resources can more intuitively reflect the link between fish reproduction and the benefits of barrier removal. What is more, the subsequent protection or restoration of the habitat should also be emphasized to ensure that dam removal can achieve the best effect and provide theoretical support for the adaptive management of restoration measures.
Author Contributions
Y.L. (Yun Lu): responsible for numerical simulation calculation, data analysis and manuscript writing. Q.-Y.L.: responsible for study about juvenile fish and manuscript revision; Y.L. (Yong Li): responsible for the proposal of methods in different life periods, review and supervision of texts. W.-Y.Z., H.-W.T., Z.-Y.Z. and Z.-H.W.: responsible for data collection, literature research in related research fields and collation of original data. B.-X.C. and G.S.: responsible for resources and project administration. J.Q. and X.Y.: responsible for field monitoring and data verification. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was financially supported by the China Three Gorges Projects Development Co., Ltd., Scientific Research Program (JG/18056B, JG/18057B).
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
Not applicable.
Acknowledgments
This consensus paper represents many rounds of discussions among the authors. They all agreed on the major issues presented herein.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interest or personal relationship that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
References
- Reynalte-Tataje, D.A.; Agostinho, A.A.; Bialetzki, A. Temporal and spatial distributions of the fish larval assemblages of the Ivinheima River sub-basin (Brazil). Environ. Biol. Fishes 2013, 96, 811–822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nunes, D.M.F.; Magalhães, A.L.B.; Weber, A.A.; Gomes, R.Z.; Normando, F.T.; Santiago, K.B.; Rizzo, E.; Bazzoli, N. Influence of a large dam and importance of an undammed tributary on the reproductive ecology of the threatened fish matrinxã Brycon orthotaenia Günther, 1864 (Characiformes: Bryconidae) in southeastern Brazil. Neotrop. Ichthyol. 2015, 13, 317–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foley, M.M.; Bellmore, J.R.; O’Connor, J.E.; Duda, J.J.; East, A.E.; Grant, G.E.; Anderson, C.W.; Bountry, J.A.; Collins, M.J.; Connolly, P.J. Dam removal: Listening in. Water Resour. Res. 2017, 53, 5229–5246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, S.; Wu, S.; Fan, Z. Discussion on the negative effects and countermeasures of small reservoirs. Water Resour. Dev. Res. 2004, 4, 33–36. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doyle, M.W.; Stanley, E.H.; Orr, C.H.; Selle, A.R.; Sethi, S.A.; Harbor, J.M. Stream ecosystem response to small dam removal: Lessons from the Heartland. Geomorphology 2005, 71, 227–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, L.; Mo, K.; Zhang, J.; Wang, J.; Chen, Q.; He, S.; Zhu, C.; Lin, Y. Removing tributary low-head dams can compensate for fish habitat losses in dammed rivers. J. Hydrol. 2021, 598, 126204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bednarek, A.T. Undamming rivers: A review of the ecological impacts of dam removal. Environ. Manag. 2001, 27, 803–814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brew, A.K. Analysis of Variations in Channel Width and Sediment Supply on Riffle-Pool Dynamics, Before and After Dam Removal; Colorado State University: Fort Collins, CO, USA, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Gardner, C.; Coghlan, S., Jr.; Zydlewski, J.; Saunders, R. Distribution and abundance of stream fishes in relation to barriers: Implications for monitoring stream recovery after barrier removal. River Res. Appl. 2013, 29, 65–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pess, G.; Quinn, T.; Gephard, S.R.; Saunders, R. Re-colonization of Atlantic and Pacific rivers by anadromous fishes: Linkages between life history and the benefits of barrier removal. Rev. Fish Biol. Fish. 2014, 24, 881–900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kornis, M.S.; Weidel, B.C.; Powers, S.M.; Diebel, M.W.; Cline, T.J.; Fox, J.M.; Kitchell, J.F. Fish community dynamics following dam removal in a fragmented agricultural stream. Aquat. Sci. 2015, 77, 465–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magilligan, F.J.; Graber, B.E.; Nislow, K.H.; Chipman, J.W.; Sneddon, C.S.; Fox, C.A. River restoration by dam removal: Enhancing connectivity at watershed scalesRiver restoration by dam removal. Elem. Sci. Anthr. 2016, 4, 000108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Donnell, M.; Gray, N.; Wippelhauser, G.; Christman, P. Kennebec River Diadromous Fish Restoration; Annual Progress Report; Maine Department of Marine Resources: Augusta, GA, USA, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Catalano, M.J.; Bozek, M.A.; Pellett, T.D. Effects of dam removal on fish assemblage structure and spatial distributions in the Baraboo River, Wisconsin. North Am. J. Fish. Manag. 2007, 27, 519–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanehl, P.D.; Lyons, J.; Nelson, J.E. Changes in the habitat and fish community of the Milwaukee River, Wisconsin, following removal of the Woolen Mills Dam. North Am. J. Fish. Manag. 1997, 17, 387–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gillenwater, D.; Granata, T.; Zika, U. GIS-based modeling of spawning habitat suitability for walleye in the Sandusky River, Ohio, and implications for dam removal and river restoration. Ecol. Eng. 2006, 28, 311–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hill, N.L.; Trueman, J.R.; Prévost, A.D.; Fraser, D.J.; Ardren, W.R.; Grant, J.W. Effect of dam removal on habitat use by spawning Atlantic salmon. J. Great Lakes Res. 2019, 45, 394–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wippelhauser, G.S.; Zydlewski, G.B.; Kieffer, M.; Sulikowski, J.; Kinnison, M.T. Shortnose Sturgeon in the Gulf of Maine: Use of spawning habitat in the Kennebec system and response to dam removal. Trans. Am. Fish. Soc. 2015, 144, 742–752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melcher, A.H.; Schmutz, S. The importance of structural features for spawning habitat of nase Chondrostoma nasus (L.) and barbel Barbus barbus (L.) in a pre-Alpine river. River Syst. 2010, 19, 33–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCormick, M.; Moore, J.; Munday, P. Influence of habitat degradation on fish replenishment. Coral Reefs 2010, 29, 537–546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shima, J.S.; Osenberg, C.W. Cryptic density dependence: Effects of covariation between density and site quality in reef fish. Ecology 2003, 84, 46–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watson, J.R.; Siegel, D.A.; Kendall, B.E.; Mitarai, S.; Rassweiller, A.; Gaines, S.D. Identifying critical regions in small-world marine metapopulations. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2011, 108, E907–E913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q.; Zhang, P.; Cheng, B.; Li, Y.; Li, J.; Zhou, H.; Sun, G.; Qing, J.; Zhu, Z.; Lu, Y. Incorporating the life stages of fish into habitat assessment frameworks: A case study in the Baihetan Reservoir. J. Environ. Manag. 2021, 299, 113663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McBride, R.S.; Somarakis, S.; Fitzhugh, G.R.; Albert, A.; Yaragina, N.A.; Wuenschel, M.J.; Alonso-Fernández, A.; Basilone, G. Energy acquisition and allocation to egg production in relation to fish reproductive strategies. Fish Fish. 2015, 16, 23–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- VanOverzee, H.M.J.; Rijnsdorp, A.D. Effects of fishing during the spawning period: Implications for sustainable management. Rev. Fish Biol. Fish. 2015, 25, 65–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hutchings, J.A.; Myers, R.A. Effect of age on the seasonality of maturation and spawning of Atlantic cod, Gadus morhua, in the Northwest Atlantic. Can. J. Fish. Aquat. Sci. 1993, 50, 2468–2474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wieland, K.; Teichmann, J.A.; Horbowa, K. Changes in the timing of spawning of Baltic cod: Possible causes and implications for recruitment. ICES J. Mar. Sci. 2000, 57, 452–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malcolm, I.A.; Gibbins, C.N.; Soulsby, C.; Tetzlaff, D.; Moir, H.J. The influence of hydrology and hydraulics on salmonids between spawning and emergence: Implications for the management of flows in regulated rivers. Fish. Manag. Ecol. 2012, 19, 464–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, Y.; Wang, P.; Wang, C.; Yu, Y.; Kong, N. Potential causes of habitat degradation and spawning time delay of the Chinese sturgeon (Acipenser sinensis). Ecol. Inform. 2018, 43, 96–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Warren, M.; Dunbar, M.; Smith, C. River flow as a determinant of salmonid distribution and abundance: A review. Environ. Biol. Fishes 2015, 98, 1695–1717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cerqueira, V.; Tsuzuki, M. A review of spawning induction, larviculture, and juvenile rearing of the fat snook, Centropomus parallelus. Fish Physiol. Biochem. 2009, 35, 17–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kihslinger, R.L.; Nevitt, G.A. Early rearing environment impacts cerebellar growth in juvenile salmon. J. Exp. Biol. 2006, 209, 504–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- OuYang, L.; ZhuGe, Y.; Wen, S.; Du, Q. Research and Application of Instream Ecological Water Requirement Based on Fish Biomass Method. South-North Water Transf. Water Sci. Technol. 2014, 12, 62–67. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Donelson, J.M.; Munday, P.L.; McCormick, M.I. Parental effects on offspring life histories: When are they important? Biol. Lett. 2009, 5, 262–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lavin, C.P.; Jones, G.P.; Williamson, D.H.; Harrison, H.B. Minimum size limits and the reproductive value of numerous, young, mature female fish. Proc. R. Soc. B 2021, 288, 20202714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuqing, L.; Junxiu, M.; Qiuwen, C. Research on effects of dam removal on river ecosystem and review of its assessment methods. Adv. Sci. Technol. Water Resour. 2017, 37, 9–15+21. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, W.; Li, Y.; Cheng, T.; Cui, X. Progress of habitat suitability index model in fish habitat assessment. Fish. Inf. Strategy 2020, 35, 48–54. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burroughs, B.A.; Hayes, D.B.; Klomp, K.D.; Hansen, J.F.; Mistak, J. The effects of the Stronach Dam removal on fish in the Pine River, Manistee County, Michigan. Trans. Am. Fish. Soc. 2010, 139, 1595–1613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomsic, C.A.; Granata, T.C.; Murphy, R.P.; Livchak, C.J. Using a coupled eco-hydrodynamic model to predict habitat for target species following dam removal. Ecol. Eng. 2007, 30, 215–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Z.; Li, Y.; Li, K.; Cheng, B.; Yang, S.; Liu, Q.; Qing, J.; Zhang, B.; Yan, X.; Liang, R. Study of quality maintenance of fish habitats in small-and medium-sized mountain rivers with low flow rate. Ecol. Eng. 2020, 147, 105780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z.; Gong, Y.; Dong, C.; Tang, H.Y.; Ye, Q. Fish resource status of the lower reaches of the Heishui River and the measures for their conservation. Resour. Environ. Yangtze Basin 2017, 26, 847–855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teng, H.; Tian, H.W.; Liu, H.W.; Cheng, B.X.; Yang, S.R. Fish resources status in Heishui River, a tributary of the lower reach of Jinsha River. Chin. J. Ecol. 2021, 40, 1499–1511. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, J.; Song, Z.; Yue, B.; Zheng, W. Assessing genetic diversity of wild populations of Prenantȁ9s schizothoracin, Schizothorax prenanti, using AFLP markers. Environ. Biol. Fishes 2006, 77, 79–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Y.Q.; Cheng, B.X.; Hu, W. Quantitative analysis of conservation priority for fis h species in Heishui River. J. Hydroecol. 2018, 39, 65–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DHI. MIKE 21 & MIKE 3 Flow Model FM. Hydrodynamic and Transport Module. In Scientific Documentation; Danish Hydraulic Institute: Hørsholm, Denmark, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Ahmad, S.; Simonovic, S.P. Comparison of one-dimensional and two-dimensional hydrodynamic modeling approaches for Red river basin. In Civil & Environmental Engineering and Construction Faculty Publications; University of Nevada: Reno, NV, USA, 1999. [Google Scholar]
- Leclerc, M.; Boudreault, A.; Bechara, T.A.; Corfa, G. Two-dimensional hydrodynamic modeling: A neglected tool in the instream flow incremental methodology. Trans. Am. Fish. Soc. 1995, 124, 645–662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yi, Y.; Wang, Z.; Yang, Z. Two-dimensional habitat modeling of Chinese sturgeon spawning sites. Ecol. Model. 2010, 221, 864–875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moir, H.; Gibbins, C.N.; Soulsby, C.; Youngson, A. PHABSIM modelling of Atlantic salmon spawning habitat in an upland stream: Testing the influence of habitat suitability indices on model output. River Res. Appl. 2005, 21, 1021–1034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, W.; Bui, M.D.; Rutschmann, P. Application of habitat and population modeling in river management. In Proceedings of the Internationales Symposium Wasserund Flussbau im Alpenraum, Zürich, Germany, 25–27 June 2014; pp. 207–216. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, Z.; Zhang, J.; Zhao, J.; Peng, W.; Fu, Y.; Wang, Q.; Zhang, Y. A new method for calculating the downstream ecological flow of diversion-type small hydropower stations. Ecol. Indic. 2021, 125, 107530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, T.; Wang, Y.; Xu, S. Response relationship between flow changing and habitat indicators of schizothorax prenanti. Resour. Environ. Yangtze Basin 2015, 24, 85–91. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Sun, Y.; Niu, T.X.; Wang, Y.R. Design of simulative restoration of fish habitat based on terrain remolding. Environ. Impact Assess. 2015, 37, 29–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, J.C. Effects and Evaluation of Yalong River Hydropower Development on Physiological Adaptability of Fishes. Master’s Thesis, China Three Gorges University, Yichang, China, 2010. (In Chinese). [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, J.C.; Huang, Y.P.; Yuan, X.; Liu, G.Y.; Ma, Z.K. Analysis on habitat suitability index of schizothorax based on fuzzy logic. Yangtze River 2011, 42, 65–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, H.; Li, M.; Zeng, R.; Liu, X.; Yang, K.; Song, Z. Substrate type and brightness preference of Schizothorax wangchiachii and Percocypris pingi juveniles. Aquac. Res. 2020, 51, 2790–2798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Z.; He, J. Hydraulics; Tsinghua University Press: Beijing, China, 2010. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Vozinaki, A.-E.K.; Morianou, G.G.; Alexakis, D.D.; Tsanis, I.K. Comparing 1D and combined 1D/2D hydraulic simulations using high-resolution topographic data: A case study of the Koiliaris basin, Greece. Hydrol. Sci. J. 2017, 62, 642–656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palmer, M.; Ruhi, A. Linkages between flow regime, biota, and ecosystem processes: Implications for river restoration. Science 2019, 365, eaaw2087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moss, S.; McFarland, W. The influence of dissolved oxygen and carbon dioxide on fish schooling behavior. Mar. Biol. 1970, 5, 100–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Facey, D.E.; Grossman, G.D. The metabolic cost of maintaining position for four North American stream fishes: Effects of season and velocity. Physiol. Zool. 1990, 63, 757–776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lapointe, N.W.; Corkum, L.D.; Mandrak, N.E. Seasonal and ontogenic shifts in microhabitat selection by fishes in the shallow waters of the Detroit River, a large connecting channel. Trans. Am. Fish. Soc. 2007, 136, 155–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, P.; Li, K.; Liu, Q.; Liu, R.; Qin, L.; Wang, H.; Zhang, Z.; Wang, K.; Wang, Y.; Liang, R. Linking bait and feeding opportunities to fish foraging habitat for the assessment of environmental flows and river restoration. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 768, 144580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Branigan, P.R.; Quist, M.C.; Shepard, B.B.; Ireland, S.C. Microhabitat use of native fishes in the K ootenai R iver: A fine-scale evaluation of large-scale habitat rehabilitation efforts. River Res. Appl. 2018, 34, 1267–1277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amado, L.L.; Monserrat, J.M. Oxidative stress generation by microcystins in aquatic animals: Why and how. Environ. Int. 2010, 36, 226–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnston, I.; Vieira, V.; Temple, G. Functional consequences and population differences in the developmental plasticity of muscle to temperature in Atlantic herring Clupea harengus. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2001, 213, 285–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Burroughs, B.A.; Hayes, D.B.; Klomp, K.D.; Hansen, J.F.; Mistak, J. Effects of Stronach dam removal on fluvial geomorphology in the Pine River, Michigan, United States. Geomorphology 2009, 110, 96–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, J. Erosion, Deposition of Sediment and Morphologic Response to the Removal of the Small Dams; Chongqing Jiaotong University: Chongqing, China, 2017. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Warrick, J.A.; Duda, J.J.; Magirl, C.S.; Curran, C.A. River turbidity and sediment loads during dam removal. Eos Trans. Am. Geophys. Union 2012, 93, 425–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hogg, R.S.; Coghlan, S.M., Jr.; Zydlewski, J.; Gardner, C. Fish community response to a small-stream dam removal in a maine coastal river tributary. Trans. Am. Fish. Soc. 2015, 144, 467–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spence, R.; Hickley, P. The use of PHABSIM in the management of water resources and fisheries in England and Wales. Ecol. Eng. 2000, 16, 153–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bornette, G.; Henry, C.; Barrat, M.-H.; Amoros, C. Theoretical habitat templets, species traits, and species richness: Aquatic Coleoptera in the Upper Rhône River and its floodplain. Freshw. Biol. 1994, 31, 487–505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stahlberg-Meinhardt, S.; Kertadikara, D.S. Verteilung, Habitatansprüche und Bewegungen von Mühlkoppe (Cottus gobio Linnaeus, 1758) und Bachforelle (Salmo trutta Linnaeus, 1758) in Zwei Unterschiedlich Anthropogen Beeinflußten Fließgewässern im Vorharz: Einfluß der Landnutzungsänderungen auf das Abflußverhalten des Ciliwung in West-Java (Indonesien); Inst. f. Wasserwirtschaft, Hydrologie u. Landwirtschaftl. Wasserbau d. Univ. Hannover: Hannover, Germany, 1994. [Google Scholar]
- Null, S.E.; Mouzon, N.R.; Elmore, L.R. Dissolved oxygen, stream temperature, and fish habitat response to environmental water purchases. J. Environ. Manag. 2017, 197, 559–570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pan, B.; Yuan, J.; Zhang, X.; Wang, Z.; Chen, J.; Lu, J.; Yang, W.; Li, Z.; Zhao, N.; Xu, M. A review of ecological restoration techniques in fluvial rivers. Int. J. Sediment Res. 2016, 31, 110–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kinney, M.J.; Simpfendorfer, C.A. Reassessing the value of nursery areas to shark conservation and management. Conserv. Lett. 2009, 2, 53–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).