Comparative Analysis of Composite Mortality Prediction Scores in Intensive Care Burn Patients
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methods
2.1. Study Design and Data Extraction
- The Ryan score published by Ryan et al. in 1998. It is based on the presence of scaled risk factors using the parameters age, TBSA and inhalation injury [10].
- The Belgian Outcome in Burn Injury (BOBI) score published by the Belgian Outcome in Burn Injury Study Group in 2009. This model is based on the parameters age, TBSA and inhalation injury [11].
- The revised Baux score as published by Osler et al. in 2010. This relies on the risk factors age, TBSA and inhalation injury [12].
- The Burn Mortality Prediction (BUMP) score published by Bagheri et al. in 2022 is based on the parameters age, TBSA, presence of inhalation injury, full-thickness burns, and the circumstances and risk factors present [13].
2.2. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Limitations and Future Work
6. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Grant, E.J. Burn Injuries. Clin. Plast. Surg. 2017, 44, 451–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brusselaers, N.; Monstrey, S.; Vogelaers, D.; Hoste, E.; Blot, S. Severe Burn Injury in Europe: A Systematic Review of the Incidence, Etiology, Morbidity, and Mortality. Crit. Care 2010, 14, R188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meshulam-Derazon, S.; Nachumovsky, S.; Ad-El, D.; Sulkes, J.; Hauben, D.J. Prediction of Morbidity and Mortality on Admission to a Burn Unit. Plast. Reconstr. Surg. 2006, 118, 116–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brusselaers, N.; Monstrey, S.J.; Vandijck, D.M.; Blot, S.I. Prediction of Morbidity and Mortality on Admission to a Burn Unit. Plast. Reconstr. Surg. 2007, 120, 360–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thombs, B.D. Do More Predictors Improve Mortality Risk Estimates among Burn Patients? Burns 2009, 35, 303–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Halgas, B.; Bay, C.; Foster, K. A Comparison of Injury Scoring Systems in Predicting Burn Mortality. Ann. Burns Fire Disasters 2018, 31, 89–93. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Obed, D.; Schroeter, A.; Gruber, L.; Bucher, F.; Salim, M.; Bingoel, A.S.; Krezdorn, N.; Dastagir, K.; Vogt, P.M. Epidemiology and Outcome Analysis of 1359 Intensive Care Burn Patients: A 14-Year Retrospective Study in a Major Burn Center in Germany. Burns 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melo, F.D.L.; Gragnani, A.; de Oliveira, A.F.; Ferreira, L.M. Predicting Mortality for Critically Ill Burns Patients, Using the Abbreviated Burn Severity Index and Simplified Acute Physiology Score 3. Injury 2022, 53, 453–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tobiasen, J.; Hiebert, J.M.; Edlich, R.F. The Abbreviated Burn Severity Index. Ann. Emerg. Med. 1982, 11, 260–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryan, C.M.; Schoenfeld, D.A.; Thorpe, W.P.; Sheridan, R.L.; Cassem, E.H.; Tompkins, R.G. Objective Estimates of the Probability of Death from Burn Injuries. N. Engl. J. Med. 1998, 338, 362–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- The Belgian Outcome in Burn Injury Study Group; Blot, S. Development and Validation of a Model for Prediction of Mortality in Patients with Acute Burn Injury. Br. J. Surg. 2008, 96, 111–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osler, T.; Glance, L.G.; Hosmer, D.W. Simplified Estimates of the Probability of Death After Burn Injuries: Extending and Updating the Baux Score. J. Trauma Acute Care Surg. 2010, 68, 690–697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bagheri, M.; Fuchs, P.C.; Lefering, R.; Daniels, M.; Schulz, A.; the German Burn Registry; Schiefer, J.L. The BUrn Mortality Prediction (BUMP) Score—An Improved Mortality Prediction Score Based on Data of the German Burn Registry. Burns, 2022; in press. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Woods, J.F.C.; Quinlan, C.S.; Shelley, O.P. Predicting Mortality in Severe Burns—What Is the Score?: Evaluation and Comparison of 4 Mortality Prediction Scores in an Irish Population. Plast. Reconstr. Surg.—Glob. Open 2016, 4, e606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pantet, O.; Faouzi, M.; Brusselaers, N.; Vernay, A.; Berger, M.M. Comparison of Mortality Prediction Models and Validation of SAPS II in Critically Ill Burns Patients. Ann. Burns Fire Disasters 2016, 29, 123–129. [Google Scholar]
- Wardhana, A.; Valeria, M.; Apriza, R.P.; Basuki, A. Comparison between ABSI and BOBI Score for Burns Mortality Prediction in Indonesia’s National Referral Burn Center: A 5-Year Study. Burns Open 2022, 6, 92–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romanowski, K.S.; Sen, S. Wound Healing in Older Adults with Severe Burns: Clinical Treatment Considerations and Challenges. Burns Open 2022, 6, 57–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lundgren, R.S.; Kramer, C.B.; Rivara, F.P.; Wang, J.; Heimbach, D.M.; Gibran, N.S.; Klein, M.B. Influence of Comorbidities and Age on Outcome Following Burn Injury in Older Adults. J. Burn Care Res. 2009, 30, 307–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bayuo, J.; Botchway, A.E. Burns among Older Persons: A Narrative Review. Burns Open 2017, 1, 2–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, P.; Burrell, A.; Bailey, M.; Moore, E.; Pilcher, D.; Cleland, H. Performance of BEAMS Risk of Death Score for Mortality Prediction in Australian and New Zealand Burns Patients. J. Burn Care Res. 2022, irac053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Usmani, A.; Pipal, D.K.; Bagla, H.; Verma, V.; Kumar, P.; Yadav, S.; Garima, G.; Rani, V.; Pipal, R.K. Prediction of Mortality in Acute Thermal Burn Patients Using the Abbreviated Burn Severity Index Score: A Single-Center Experience. Cureus 2022, 14, e26161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hassan, Z.; Burhamah, W.; Alabdulmuhsen, S.; Al Saffar, A.; Oroszlányová, M.; Aziz, H. The Analysis and Accuracy of Mortality Prediction Scores in Burn Patients Admitted to the Intensive Care Burn Unit (ICBU). Ann. Med. Surg. 2021, 65, 102249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Germann, G.; Barthold, U.; Lefering, R.; Raff, T.; Hartmann, B. The Impact of Risk Factors and Pre-Existing Conditions on the Mortality of Burn Patients and the Precision of Predictive Admission-Scoring Systems. Burns 1997, 23, 195–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, S.; Tandon, R. Predicting Burn Mortality Using a Simple Novel Prediction Model. Indian J. Plast. Surg. 2021, 54, 46–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jaskille, A.D.; Shupp, J.W.; Jordan, M.H.; Jeng, J.C. Critical Review of Burn Depth Assessment Techniques: Part I. Historical Review. J. Burn Care Res. 2009, 30, 937–947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rennekampff, H.-O.; Tenenhaus, M. Damage Control Surgery after Burn Injury: A Narrative Review. Eur. Burn J. 2022, 3, 278–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masud, D.; Norton, S.; Smailes, S.; Shelley, O.; Philp, B.; Dziewulski, P. The Use of a Frailty Scoring System for Burns in the Elderly. Burns 2013, 39, 30–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clark, A.; Neyra, J.A.; Madni, T.; Imran, J.; Phelan, H.; Arnoldo, B.; Wolf, S.E. Acute Kidney Injury after Burn. Burns 2017, 43, 898–908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brusselaers, N.; Monstrey, S.; Colpaert, K.; Decruyenaere, J.; Blot, S.I.; Hoste, E.A.J. Outcome of Acute Kidney Injury in Severe Burns: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Intensive Care Med. 2010, 36, 915–925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knowlin, L.T.; Purcell, L.; Cairns, B.A.; Charles, A.G. Burn Injury Mortality in Patients with Preexisting and New Onset Renal Disease. Am. J. Surg. 2018, 215, 1011–1015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, Z.; Cai, G.; Li, J.; Chen, F.; Chen, X. Meta-Analysis of Renal Replacement Therapy for Burn Patients: Incidence Rate, Mortality, and Renal Outcome. Front. Med. 2021, 8, 708533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colpaert, K.; Hoste, E.A. Acute Kidney Injury in Burns: A Story of Volume and Inflammation. Crit. Care 2008, 12, 192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chrysopoulo, M.T.; Jeschke, M.G.; Dziewulski, P.; Barrow, R.E.; Herndon, D.N. Acute Renal Dysfunction in Severely Burned Adults. J. Trauma Acute Care Surg. 1999, 46, 141–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cumming, J.; Purdue, G.F.; Hunt, J.L.; E O’Keefe, G. Objective Estimates of the Incidence and Consequences of Multiple Organ Dysfunction and Sepsis after Burn Trauma. J. Trauma Acute Care Surg. 2001, 50, 510–515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coban, Y.K.; Aral, M. Serum IL-18 Is Increased at Early Postburn Period in Moderately Burned Patients. Mediat. Inflamm. 2006, 2006, 16492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lavrentieva, A.; Kontakiotis, T.; Lazaridis, L.; Tsotsolis, N.; Koumis, J.; Kyriazis, G.; Bitzani, M. Inflammatory Markers in Patients with Severe Burn Injury. Burns 2007, 33, 189–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brusselaers, N.; Agbenorku, P.; Hoyte-Williams, P.E. Assessment of Mortality Prediction Models in a Ghanaian Burn Population. Burns 2013, 39, 997–1003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herlianita, R.; Purwanto, E.; Wahyuningsih, I.; Pratiwi, I.D. Clinical Outcome and Comparison of Burn Injury Scoring Systems in Burn Patient in Indonesia. Afr. J. Emerg. Med. 2021, 11, 331–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wong, D.T.; Knaus, W.A. Predicting Outcome in Critical Care: The Current Status of the APACHE Prognostic Scoring System. Can. J. Anaesth. 1991, 38, 374–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taylor, S.L.; Lawless, M.; Curri, T.; Sen, S.; Greenhalgh, D.G.; Palmieri, T.L. Predicting Mortality from Burns: The Need for Age-Group Specific Models. Burns 2014, 40, 1106–1115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Prognostic Score | Year | Parameters Used | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Age | TBSA | IHT | Full-Thickness Burn | Sex | Comorbidities | Circumstances | ||
| ABSI | 1982 | x | x | x | x | x | ||
| Ryan | 1998 | x | x | x | ||||
| BOBI | 2009 | x | x | x | ||||
| Revised Baux | 2010 | x | x | x | ||||
| BUMP | 2022 | x | x | x | x | x | x | |
| Variable | Total (n = 617) | Survivors (n = 528) | Non-Survivors (n = 89) | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Age (years) (mean ± SD) | 48.9 ± 19 | 46.7 ± 18.3 | 61.9 ± 18.7 | <0.001 |
| TBSA (%) (mean ± SD) | 23.2 ± 16 | 19.8 ± 10.6 | 43.5 ± 13.9 | <0.001 |
| Male Gender, n (%) | 441 (71.5) | 379 (71.8) | 63 (70.8) | 0.06 |
| Age Group, n (%) | ||||
| 14–24 | 74 (12.0) | 70 (13.3) | 4 (4.5) | 0.139 |
| 25–44 | 189 (30.6) | 177 (33.5) | 12 (13.5) | 0.029 |
| 45–64 | 225 (36.5) | 190 (36.0) | 35 (39.3) | 0.057 |
| ≥65 | 129 (20.9) | 91 (17.2) | 38 (42.7) | <0.001 |
| TBSA, n (%) | ||||
| 10–19.9 | 329 (53.3) | 315 (59.7) | 14 (15.7) | <0.001 |
| 20–29.9 | 140 (22.7) | 120 (22.7) | 20 (22.5) | 0.283 |
| ≥30 | 148 (24.0) | 93 (17.6) | 55 (61.8) | <0.001 |
| Inhalational Injury, n (%) | 98 (15.9) | 79 (15.0) | 19 (21.3) | 0.016 |
| Full-Thickness Burns, n (%) | 264 (42.8) | 185 (35.0) | 79 (88.8) | <0.001 |
| Comorbidities, n (%) | ||||
| Hypertension | 129 (20.9) | 110 (20.8) | 19 (21.3) | 0.211 |
| Diabetes | 53 (8.6) | 43 (8.1) | 10 (11.2) | 0.084 |
| Peripheral Arterial Disease | 9 (1.5) | 6 (1.1) | 3 (3.4) | 0.072 |
| Coronary artery Disease | 30 (4.9) | 19 (3.6) | 11 (12.4) | <0.001 |
| Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease | 19 (3.1) | 13 (2.5) | 6 (6.7) | 0.015 |
| Arrhythmia | 89 (14.4) | 50 (9.5) | 39 (43.8) | <0.001 |
| Heart Insufficiency | 16 (2.6) | 9 (1.7) | 7 (7.9) | 0.001 |
| Renal Insufficiency | 59 (9.6) | 17 (3.2) | 42 (47.2) | <0.001 |
| Burn Etiology, n (%) | ||||
| Flame/Contact | 341 (55.3) | 272 (51.5) | 69 (77.5) | <0.001 |
| Scalding | 115 (18.6) | 107 (20.3) | 8 (9) | 0.182 |
| Explosion/Deflagration | 140 (22.7) | 130 (24.6) | 10 (11.2) | 0.141 |
| Chemical | 11 (1.8) | 10 (1.9) | 1 (1.1) | 0.999 |
| Electricity | 11 (1.8) | 10 (1.9) | 1 (1.1) | 0.999 |
| Body Area, n (%) | ||||
| Face/Neck/Scalp | 360 (58.3) | 301 (57.0) | 59 (66.3) | 0.004 |
| Arms | 436 (70.7) | 363 (68.8) | 73 (82) | <0.001 |
| Hands | 313 (50.7) | 265 (50.2) | 48 (53.9) | 0.032 |
| Legs | 331 (53.6) | 270 (51.1) | 61 (68.5) | <0.001 |
| Feet | 87 (14.1) | 65 (12.3) | 22 (24.7) | <0.001 |
| Thorax | 291 (47.2) | 233 (44.1) | 58 (65.2) | <0.001 |
| Abdomen | 157 (25.4) | 126 (23.9) | 31 (34.4) | 0.002 |
| Back/Flanks | 199 (32.3) | 148 (28.0) | 51 (56.7) | <0.001 |
| Genital area | 51 (8.3) | 34 (6.4) | 17 (18.9) | <0.001 |
| Place of Burn Incident, n (%) | ||||
| Home | 341 (55.3) | 278 (52.7) | 63 (70) | <0.001 |
| Recreational | 146 (23.7) | 134 (25.4) | 12 (13.3) | 0.295 |
| Workplace | 96 (15.6) | 88 (16.7) | 8 (8.9) | 0.423 |
| Other | 34 (5.5) | 28 (5.3) | 6 (6.7) | 0.27 |
| Traffic Accident, n (%) | 5 (0.8) | 3 (0.6) | 2 (2.2) | 0.101 |
| Suicide Attempt, n (%) | 31 (5.0) | 20 (3.8) | 11 (12.2) | <0.001 |
| LOS (days) (mean ± SD) | 25.7 ± 23.3 | 27.4 ± 24.2 | 16 ± 3.7 | <0.001 |
| LOS on ICU (days) (mean ± SD) | 15.9 ± 20.2 | 15.9 ± 21.1 | 15.8 ± 13.7 | 0.966 |
| Surgical Intervention Rate (mean ± SD) | 3.5 ± 3.7 | 3.4 ± 3.8 | 3.9 ± 2.9 | 0.237 |
| Mechanical Ventilation, n (%) | 227 (36.8) | 180 (33.9) | 47 (52.2) | <0.001 |
| Mechanical Ventilation (hours) (mean ± SD) | 73.6 ± 253.3 | 57.8 ± 245.3 | 166.6 ± 276.8 | <0.001 |
| Variable | p-Value | OR | CI (95%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Age | <0.001 | 1.053 | 1.029–1.079 |
| TBSA | <0.001 | 1.095 | 1.069–1.127 |
| Full-Thickness Burns | <0.001 | 4.78 | 2.043–12.27 |
| Coronary Artery Disease | 0.451 | 1.541 | 0.4850–4.675 |
| Arrhythmia | 0.198 | 1.669 | 0.7575–3.621 |
| Heart Insufficiency | 0.354 | 1.854 | 0.4948–6.911 |
| Renal Insufficiency | <0.001 | 9.042 | 4.000–21.33 |
| Home | 0.777 | 0.799 | 0.189–4.455 |
| Recreational | 0.124 | 0.255 | 0.0472–1.616 |
| Workplace | 0.22 | 0.28 | 0.0357–2.235 |
| Suicide Attempt | 0.6 | 0.66 | 0.128–2.902 |
| Mechanical Ventilation | 0.934 | 1.031 | 0.501–2.097 |
| Inhalation Injury | 0.058 | 2.293 | 0.961–5.402 |
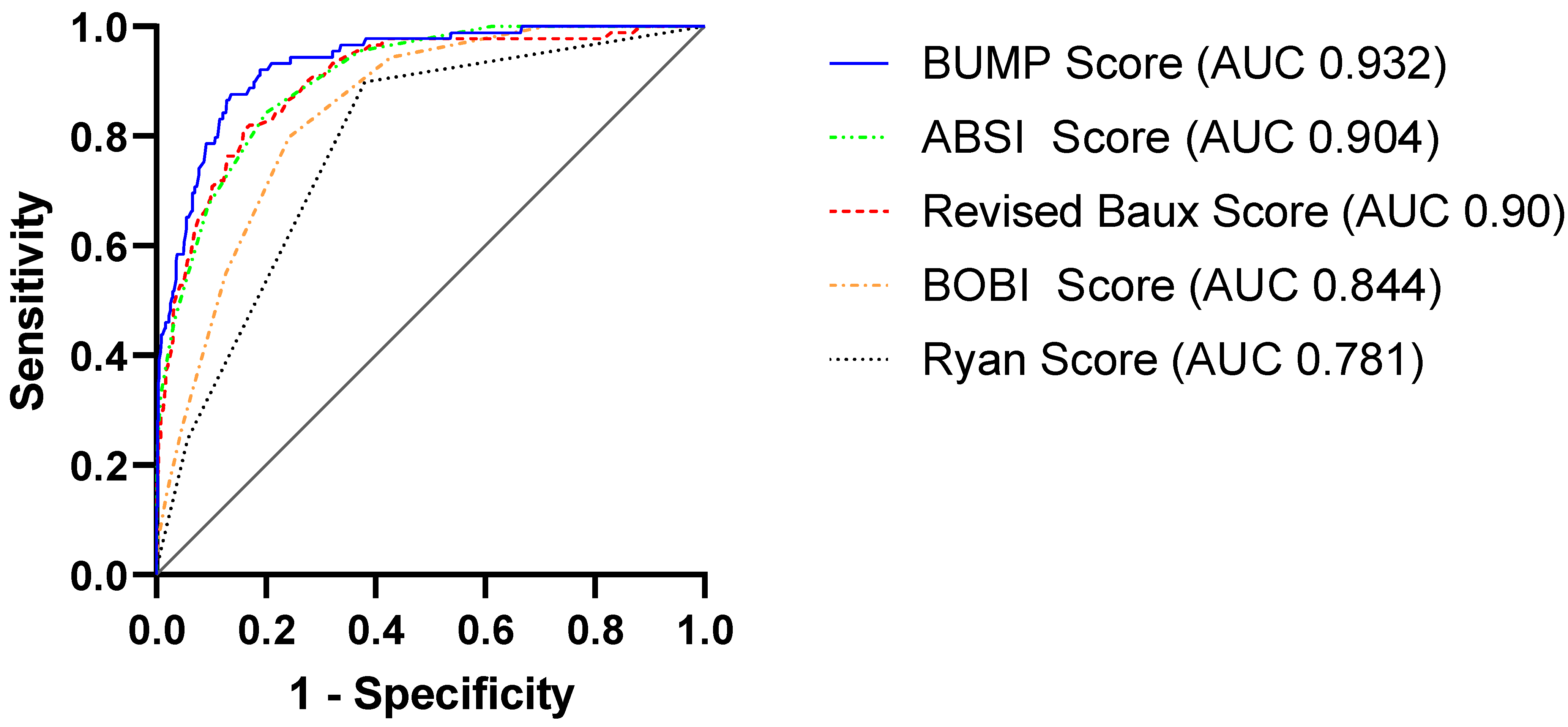
| Burn Mortality Score | Total (n = 619) | Survivors (n = 530) | Non-Survivors (n = 89) | Sensitivity | Specificity | AUC (95% CI) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ABSI (mean ± SD) | 6.6 ± 2.2 | 6.1 ± 1.7 | 9.7 ± 2.2 | 0.843 | 0.629 | 0.904 (0.875–0.934) |
| Ryan (mean ± SD) | 0.5 ± 0.7 | 0.4 ± 0.6 | 1.2 ± 0.6 | 0.899 | 0.619 | 0.781 (0.734–0.828) |
| BOBI (mean ± SD) | 1.9 ± 1.7 | 1.6 ± 1.5 | 3.8 ± 1.6 | 0.798 | 0.758 | 0.844 (0.807–0.881) |
| Revised Baux (mean ± SD) | 74.9 ± 25.7 | 69.2 ± 21.2 | 108.9 ± 23.6 | 0.809 | 0.841 | 0.900 (0.866–0.935) |
| BUMP (mean ± SD) | −3.1 ± 2.1 | −3.6 ± 1.6 | 0.01 ± 1.8 | 0.876 | 0.864 | 0.932 (0.906–0.958) |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Obed, D.; Salim, M.; Dastagir, N.; Knoedler, S.; Dastagir, K.; Panayi, A.C.; Vogt, P.M. Comparative Analysis of Composite Mortality Prediction Scores in Intensive Care Burn Patients. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 12321. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph191912321
Obed D, Salim M, Dastagir N, Knoedler S, Dastagir K, Panayi AC, Vogt PM. Comparative Analysis of Composite Mortality Prediction Scores in Intensive Care Burn Patients. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health. 2022; 19(19):12321. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph191912321
Chicago/Turabian StyleObed, Doha, Mustafa Salim, Nadjib Dastagir, Samuel Knoedler, Khaled Dastagir, Adriana C. Panayi, and Peter M. Vogt. 2022. "Comparative Analysis of Composite Mortality Prediction Scores in Intensive Care Burn Patients" International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health 19, no. 19: 12321. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph191912321
APA StyleObed, D., Salim, M., Dastagir, N., Knoedler, S., Dastagir, K., Panayi, A. C., & Vogt, P. M. (2022). Comparative Analysis of Composite Mortality Prediction Scores in Intensive Care Burn Patients. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 19(19), 12321. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph191912321







