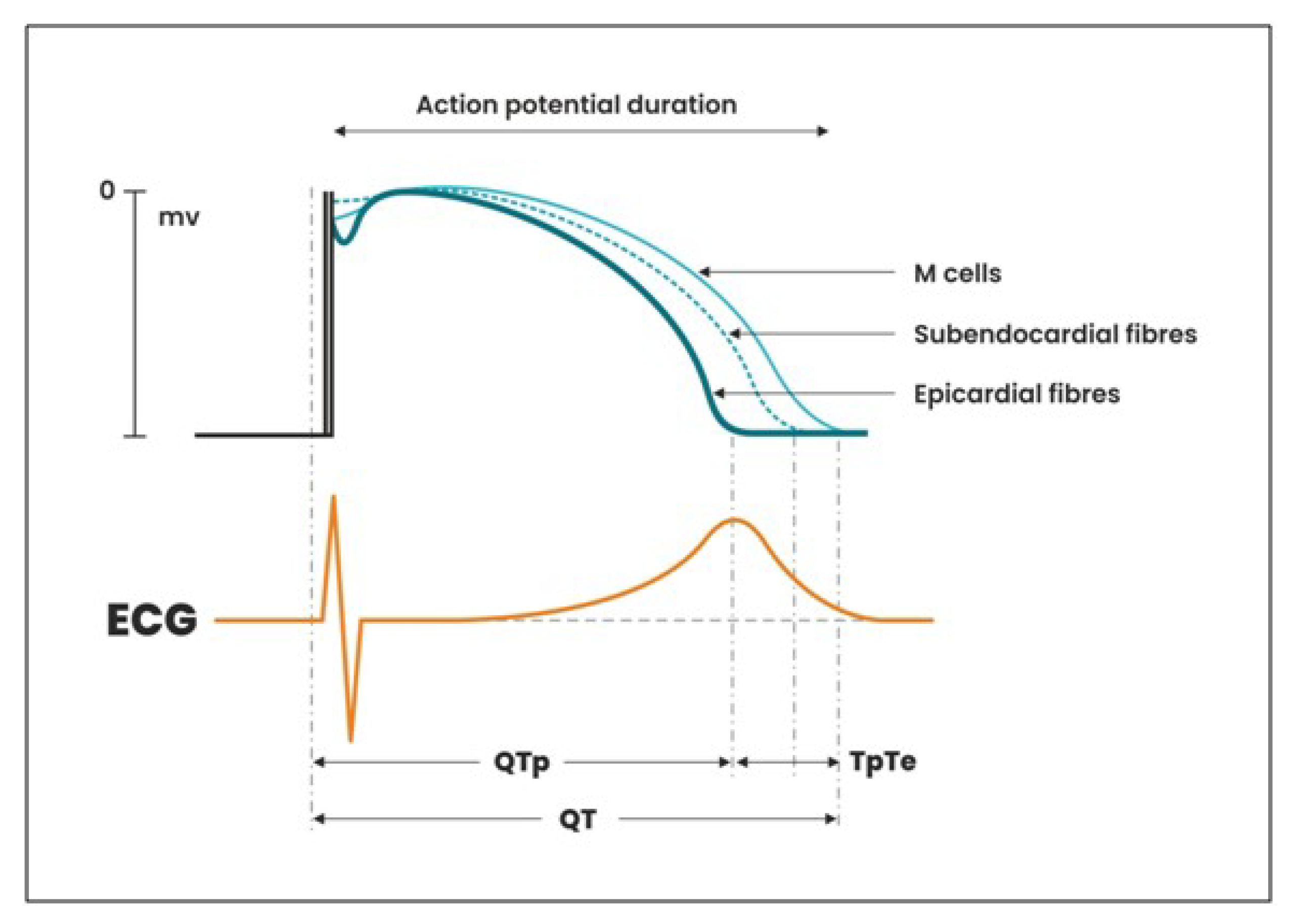
Tpeak-Tend Interval during Pregnancy and Postpartum
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| ECG | Electrocardiogram |
| LQTS | Long QT Syndrome |
| QTc | QT interval corrected with Bazett formula |
| QTp | (Q-Tpeak) |
| TpTe | Tpeak—Tend interval |
References
- Tamirisa, K.P.; Elkayam, U.; Briller, J.E.; Mason, P.K.; Pillarisetti, J.; Merchant, F.M.; Patel, H.; Lakkireddy, D.R.; Russo, A.M.; Volgman, A.S.; et al. Arrhythmias in Pregnancy. JACC Clin. Electrophysiol. 2021, 8, 120–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adamson, D.L.; Nelson-Piercy, C. Managing palpitations and arrhythmias during pregnancy. Postgrad. Med. J. 2008, 84, 66–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michels, G.; Kochanek, M.; Pfister, R. Life-threatening cardiac arrhythmias due to drug-induced QT prolongation. Med. Klin.-Intensiv. und Notfallmedizin 2015, 111, 302–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silversides, C.K.; Harris, L.; Haberer, K.; Sermer, M.; Colman, J.M.; Siu, S. Recurrence Rates of Arrhythmias During Pregnancy in Women With Previous Tachyarrhythmia and Impact on Fetal and Neonatal Outcomes. Am. J. Cardiol. 2006, 97, 1206–1212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, Q.; Lin, J. Risk factors for heart failure during pregnancy among Chinese women with cardiac disease. Int. J. Gynecol. Obstet. 2015, 130, 266–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rashba, E.J.; Zareba, W.; Moss, A.J.; Hall, W.J.; Robinson, J.; Locati, E.H.; Schwartz, P.J.; Andrews, M. Influence of Pregnancy on the Risk for Cardiac Events in Patients With Hereditary Long QT Syndrome. Circulation 1998, 97, 451–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishibashi, K.; Aiba, T.; Kamiya, C.; Miyazaki, A.; Sakaguchi, H.; Wada, M.; Nakajima, I.; Miyamoto, K.; Okamura, H.; Noda, T.; et al. Arrhythmia risk and Beta-blocker therapy in pregnant women with long QT syndrome. Heart 2017, 103, 1374–1379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khositseth, A.; Tester, D.J.; Will, M.L.; Bell, C.M.; Ackerman, M.J. Identification of a common genetic substrate underlying postpartum cardiac events in congenital long QT syndrome. Hear. Rhythm 2004, 1, 60–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heradien, M.J.; Goosen, A.; Crotti, L.; Durrheim, G.; Corfield, V.; Brink, P.; Schwartz, P.J. Does Pregnancy Increase Cardiac Risk for LQT1 Patients With the KCNQ1-A341V Mutation? J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2006, 48, 1410–1415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seth, R.; Moss, A.J.; McNitt, S.; Zareba, W.; Andrews, M.L.; Qi, M.; Robinson, J.L.; Goldenberg, I.; Ackerman, M.J.; Benhorin, J.; et al. Long QT Syndrome and Pregnancy. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2007, 49, 1092–1098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kirbas, A.; Kirbas, O.; Daglar, K.; Inal, H.A.; Kurmus, O.; Kara, O.; Timur, H.; Gencosmanoglu, G.; Danisman, N. Novel indexes of arrhythmogenesis in preeclampsia: QT dispersion, Tp-e interval, and Tp-e/QT ratio. Pregnancy Hypertens. Int. J. Women’s Cardiovasc. Health 2016, 6, 38–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Achmad, C.; Iqbal, M.; Karwiky, G.; Prameswari, H.S.; Febrianora, M. T-Peak to T-End Improvements After Beta-Blocker Administration in Peripartum Cardiomyopathy Patients. Cardiol. Res. 2020, 11, 185–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamaguchi, M.; Shimizu, M.; Ino, H.; Terai, H.; Uchiyama, K.; Oe, K.; Mabuchi, T.; Konno, T.; Kaneda, T.; Mabuchi, H. T wave peak-to-end interval and QT dispersion in acquired long QT syndrome: A new index for arrhythmogenicity. Clin. Sci. 2003, 105, 671–676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Topilski, I.; Rogowski, O.; Rosso, R.; Justo, D.; Copperman, Y.; Glikson, M.; Belhassen, B.; Hochenberg, M.; Viskin, S. The Morphology of the QT Interval Predicts Torsade de Pointes During Acquired Bradyarrhythmias. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2007, 49, 320–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Watanabe, N.; Kobayashi, Y.; Tanno, K.; Miyoshi, F.; Asano, T.; Kawamura, M.; Mikami, Y.; Adachi, T.; Ryu, S.; Miyata, A.; et al. Transmural dispersion of repolarization and ventricular tachyarrhythmias. J. Electrocardiol. 2004, 37, 191–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, G.-X.; Antzelevitch, C. Cellular Basis for the Normal T Wave and the Electrocardiographic Manifestations of the Long-QT Syndrome. Circulation 1998, 98, 1928–1936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Antzelevitch, C.; Shimizu, W.; Yan, G.-X.; Sicouri, S.; Weissenburger, J.; Nesterenko, V.V.; Burashnikov, A.; Diego, J.; Saffitz, J.; Thomas, G.P. The M Cell: Its Contribution to the ECG and to Normal and Abnormal Electrical Function of the Heart. J. Cardiovasc. Electrophysiol. 1999, 10, 1124–1152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Antzelevitch, C.; Oliva, A. Amplification of spatial dispersion of repolarization underlies sudden cardiac death associated with catecholaminergic polymorphic VT, long QT, short QT and Brugada syndromes. J. Intern. Med. 2005, 259, 48–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sucu, M.; Ozer, O.; Davutoglu, V.; Ercan, S.; Yuce, M.; Coskun, F.Y. Relationship between Neurocardiogenic Syncope and Ventricular Repolarization. Pacing Clin. Electrophysiol. 2015, 38, 625–629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hancock, E.W.; Deal, B.J.; Mirvis, D.M.; Okin, P.; Kligfield, P.; Gettes, L.S.; Bailey, J.J.; Childers, R.; Gorgels, A.; Josephson, M.; et al. AHA/ACCF/HRS Recommendations for the Standardization and Interpretation of the Electrocardiogram: Part V: Electrocardiogram Changes Associated With Cardiac Chamber Hypertrophy A Scientific Statement From the American Heart Association Electrocardiography and Arrhythmias Committee, Council on Clinical Cardiology; the American College of Cardiology Foundation; and the Heart Rhythm Society Endorsed by the International Society for Computerized Electrocardiology. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2009, 53, 992–1002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tanindi, A.; Akgun, N.; Pabuccu, E.G.; Gursoy, A.Y.; Yüce, E.; Tore, H.F.; Duvan, C.I. Electrocardiographic P-Wave Duration, QT Interval, T Peak to End Interval and Tp-e/QT Ratio in Pregnancy with Respect to Trimesters. Ann. Noninvasive Electrocardiol. 2015, 21, 169–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guillon, A.; Leyre, S.; Remérand, F.; Taihlan, B.; Perrotin, F.; Fusciardi, J.; Laffon, M. Modification of Tp-e and QTc intervals during caesarean section under spinal anaesthesia. Anaesthesia 2010, 65, 337–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gazi, E.; Gencer, M.; Temiz, A.; Barutcu, A.; Altun, B.; Gungor, A.N.C.; Hacivelioglu, S.; Uysal, A.; Cosar, E. Does pregnancy-induced hypertension affect the electrophysiology of the heart? J. Obstet. Gynaecol. 2015, 36, 183–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, J. Evidences of the gender-related differences in cardiac repolarization and the underlying mechanisms in different animal species and human. Fundam. Clin. Pharmacol. 2006, 20, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bidoggia, H.; Maciel, J.P.; Capalozza, N.; Mosca, S.; Blaksley, E.J.; Valverde, E.; Bertran, G.; Arini, P.; Biagetti, M.O.; Quinteiro, R.A. Sex differences on the electrocardiographic pattern of cardiac repolarization: Possible role of testosterone. Am. Heart J. 2000, 140, 678–683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vrtovec, B.; Starc, V.; Meden-Vrtovec, H. The effect of estrogen replacement therapy on ventricular repolarization dynamics in healthy postmenopausal women. J. Electrocardiol. 2001, 34, 277–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akboga, M.K. Tp-e interval and Tp-e/QTc ratio as novel surrogate markers for prediction of ventricular arrhythmic events in hypertrophic cardiomyopathy. Anatol. J. Cardiol. 2017, 18, 48–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alizade, E.; Avcı, A.; Fidan, S.; Tabakci, M.; Bulut, M.; Zehir, R.; Simsek, Z.; Evlice, M.; Arslantas, U.; Çakır, H.; et al. The Effect of Chronic Anabolic–Androgenic Steroid Use on Tp-E Interval, Tp-E/Qt Ratio, and Tp-E/Qtc Ratio in Male Bodybuilders. Ann. Noninvasive Electrocardiol. 2015, 20, 592–600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Braschi, A.; Abrignani, M.G.; Francavilla, V.C.; Abrignani, V.; Francavilla, G. Age- and sex-based reference ranges for non-invasive ventricular repolarisation parameters. Int. J. Clin. Pract. 2017, 71, e12949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haarmark, C.; Kyvik, K.O.; Vedel-Larsen, E.; Budtz-Jørgensen, E.; Kanters, J.K. Heritability of Tpeak-Tend Interval and T-Wave Amplitude. Circ. Cardiovasc. Genet. 2011, 4, 516–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Xianpei, W.; Sha, W.; Chuanyu, G.; Juanjuan, Y.; Chong, C.; Yongen, S.; Yu, F.; Zhenhao, L. Tpeak-Tend dispersion as a predictor for malignant arrhythmia events in patients with vasospastic angina. Int. J. Cardiol. 2017, 249, 61–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scott, P.A.; Rosengarten, J.A.; Shahed, A.; Yue, A.M.; Murday, D.C.; Roberts, P.R.; Peebles, C.R.; Harden, S.P.; Curzen, N.P.; Morgan, J.M. The relationship between left ventricular scar and ventricular repolarization in patients with coronary artery disease: Insights from late gadolinium enhancement magnetic resonance imaging. Europace 2012, 15, 899–906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haarmark, C.; Hansen, P.R.; Vedel-Larsen, E.; Pedersen, S.H.; Graff, C.; Andersen, M.P.; Toft, E.; Wang, F.; Struijk, J.J.; Kanters, J.K. The prognostic value of the Tpeak-Tend interval in patients undergoing primary percutaneous coronary intervention for ST-segment elevation myocardial infarction. J. Electrocardiol. 2009, 42, 555–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Onur, S.T.; Emet, S.; Sokucu, S.N.; Onur, I. T wave peak-to-end interval in COPD. Int. J. Chronic Obstr. Pulm. Dis. 2018, 13, 2157–2162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ilgenli, T.F.; Tokatli, A.; Akpinar, O.; Kilicaslan, F. The Effects of Cigarette Smoking on the Tp-e Interval, Tp-e/QT Ratio and Tp-e/QTc Ratio. Adv. Clin. Exp. Med. 2015, 24, 973–978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuzu, F. The effect of type 2 diabetes on electrocardiographic markers of significant cardiac events. Pak. J. Med. Sci. 2018, 34, 626–632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kayali, S.; Demir, F. The effects of cigarette smoking on ventricular repolarization in adolescents. Einstein (São Paulo) 2017, 15, 251–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yılmaz, M.; Kayançiçek, H.; Gözel, N.; Bilen, M.; Kurtoğlu, E.; Seçen, O.; Öner, P.; Demirkıran, S.; Uku, O.; Çekici, Y.; et al. Spotlights on some electrocardiographic paradigms: How should we evaluate normal reference values of Tp–Te interval, Tp–Te dispersion and Tp–Te/QT ratio? Adv. Clin. Exp. Med. 2020, 29, 1091–1099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ciobanu, A.; Tse, G.; Liu, T.; Deaconu, M.V.; Gheorghe, G.S.; Ilieşiu, A.M.; Nanea, I.T. Electrocardiographic measures of repolarization dispersion and their relationships with echocardiographic indices of ventricular remodeling and premature ventricular beats in hypertension. J. Geriatr. Cardiol. 2017, 14, 717–724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garg, L.; Garg, J.; Krishnamoorthy, P.; Ahnert, A.; Shah, N.; Dusaj, R.S.; Bozorgnia, B. Influence of Pregnancy in Patients With Congenital Long QT Syndrome. Cardiol. Rev. 2017, 25, 197–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
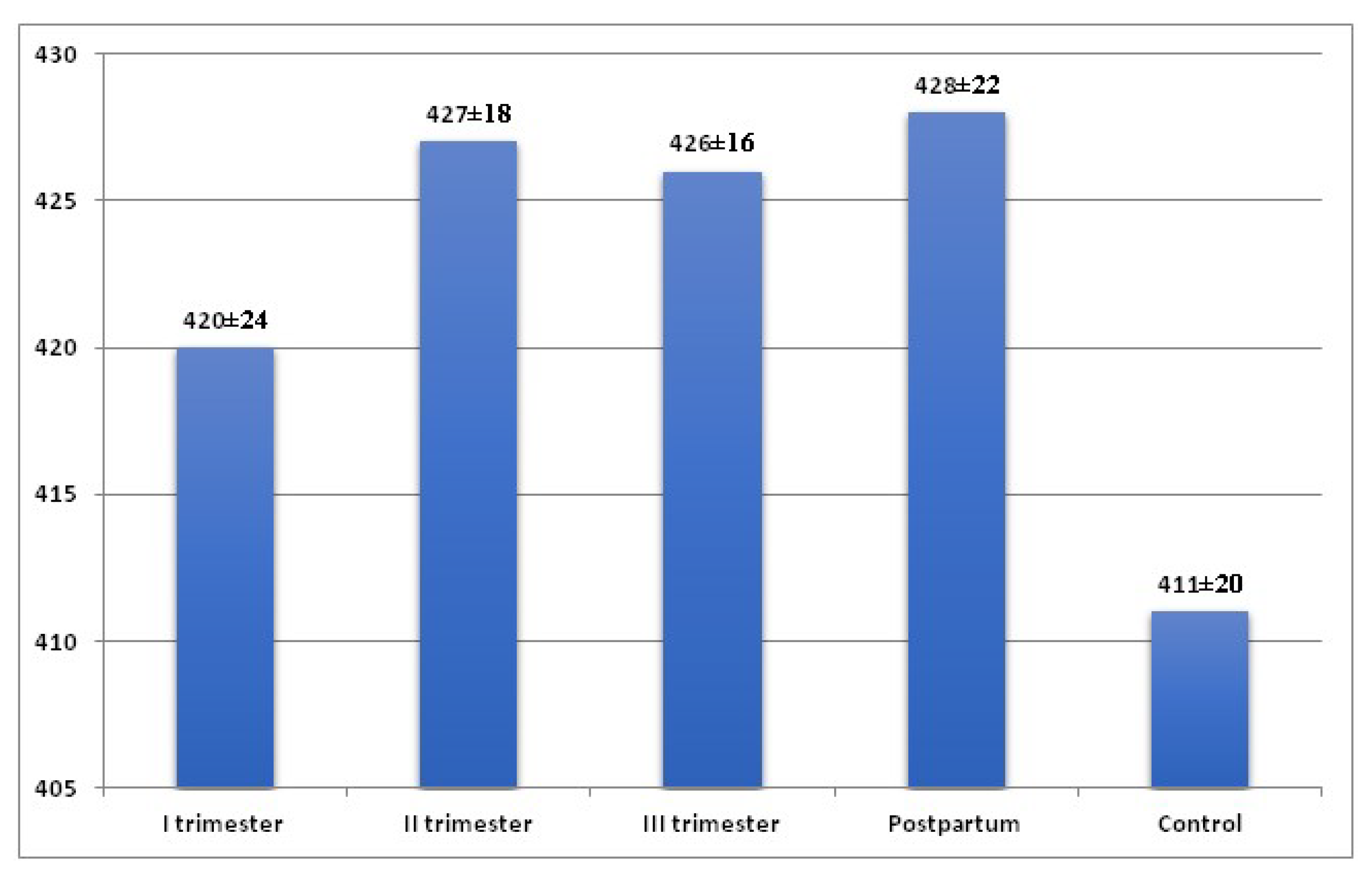
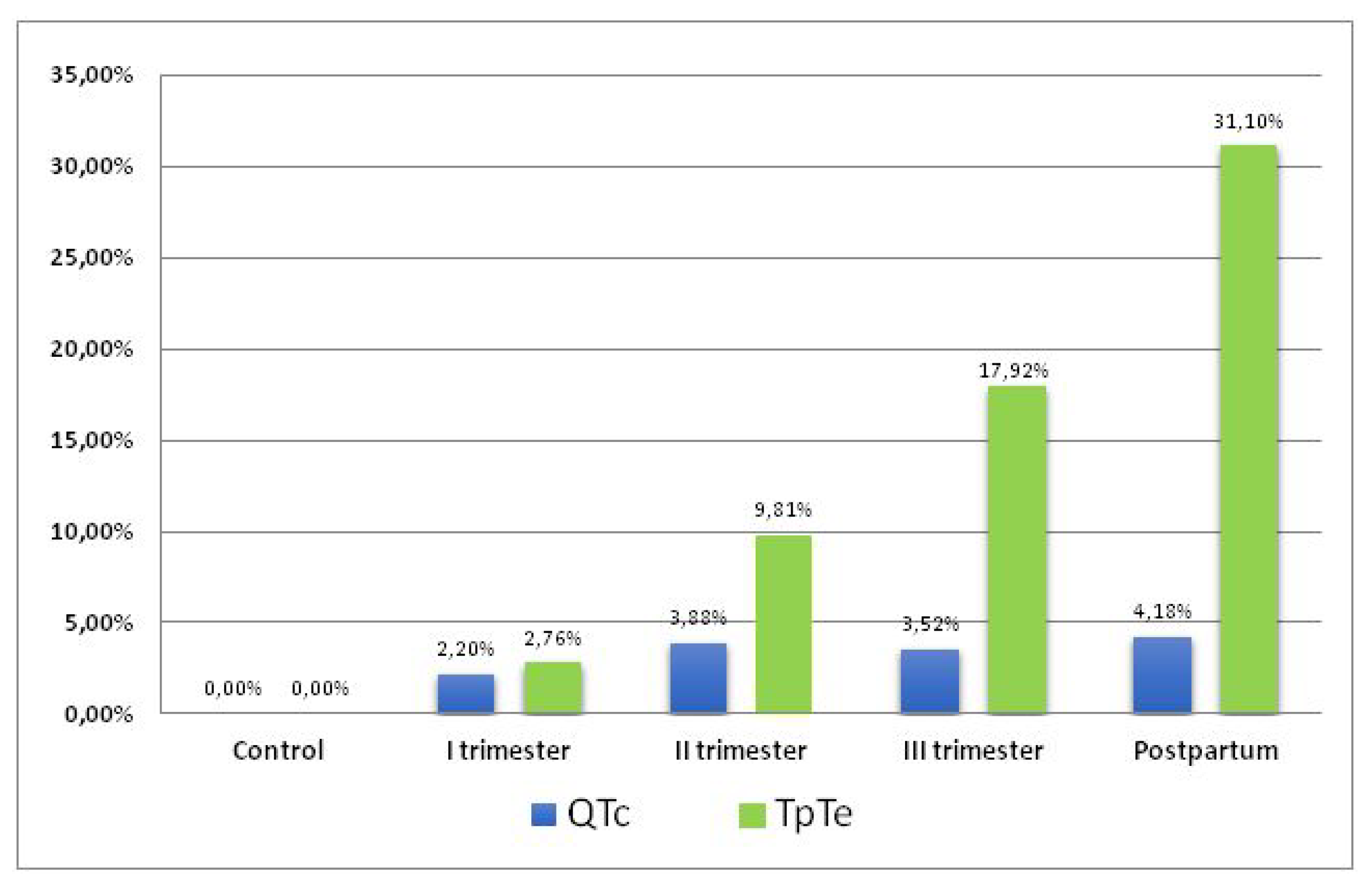
| QTcB [ms] | I Trimester | II Trimester | III Trimester | Postpartum | Control |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| N | 36 | 30 | 30 | 32 | 32 |
| Mean | 420.57 | 427.58 | 426.56 | 428.83 | 411.23 |
| SD | 24.91 | 18.61 | 16.12 | 22.52 | 20.84 |
| Minimum | 372.62 | 388.89 | 390.01 | 394.13 | 378.11 |
| Maximum | 466.16 | 460.93 | 466.69 | 505.96 | 455.96 |
| Median | 420.65 | 427.42 | 426.82 | 426.98 | 411.63 |
| I trimester | — | p = 0.212 | p = 0.306 | p = 0.163 | p = 0.110 |
| II trimester | p = 0.212 | — | p = 0.742 | p = 0.815 | p = 0.002 |
| III trimester | p = 0.306 | p = 0.742 | — | p = 0.589 | p = 0.003 |
| Postpartum | p = 0.163 | p = 0.815 | p = 0.589 | — | p = 0.002 |
| Control | p = 0.110 | p = 0.002 | p = 0.003 | p = 0.002 | — |
| (I-III trim.) vs. Control | p < 0.001 | ||||
| (I trim-post.) vs. Control | p < 0.001 | ||||
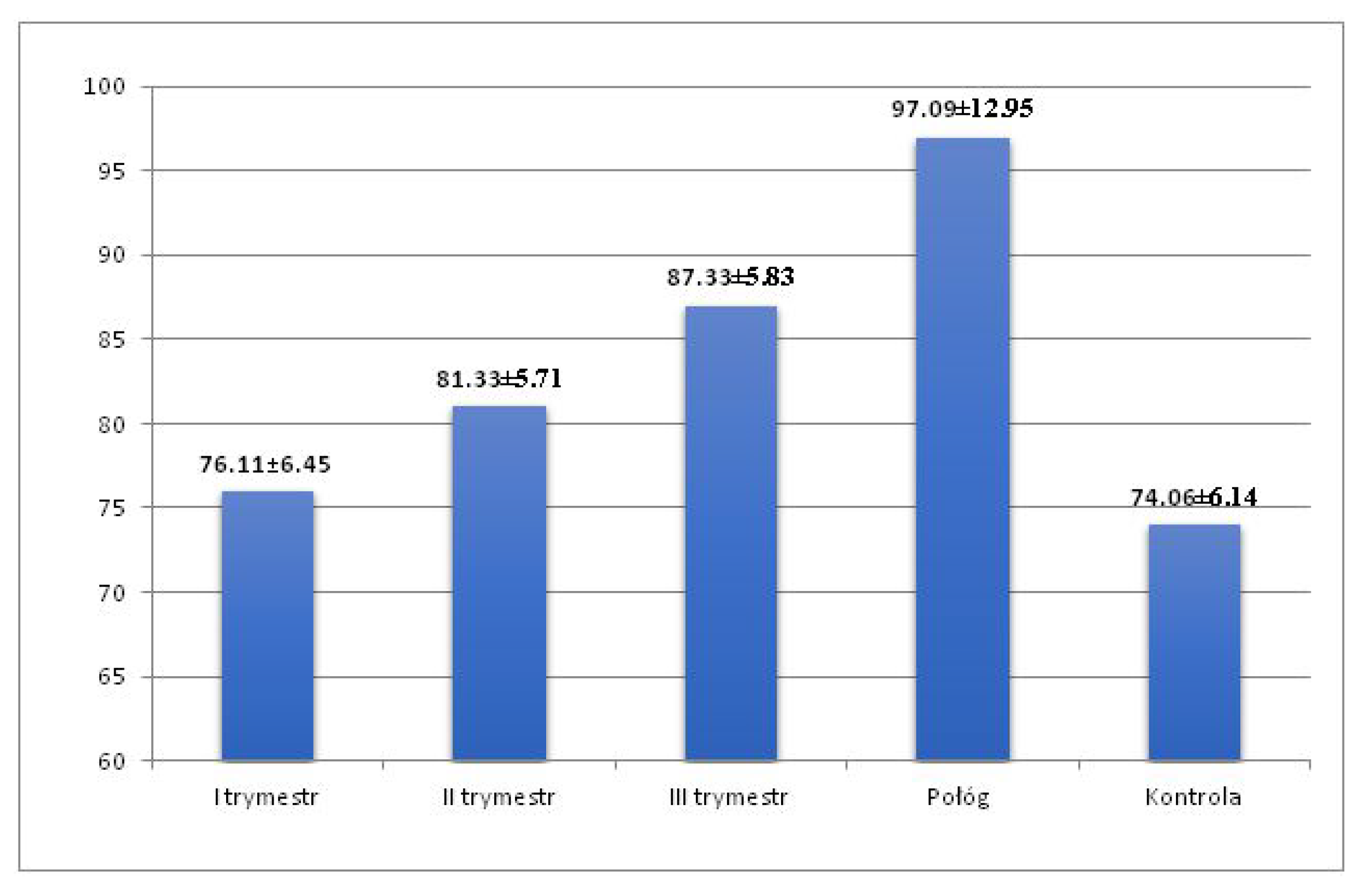
| TpTe | I Trimester | II Trimester | III Trimester | Postpartum | Control |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| N | 36 | 30 | 30 | 32 | 32 |
| Mean | 76.11 | 81.33 | 87.33 | 97.09 | 74.06 |
| SD | 6.45 | 5.71 | 5.83 | 12.95 | 6.14 |
| Minimum | 60.00 | 70,00 | 80.0 | 80.00 | 60.00 |
| Maximum | 90.00 | 90.00 | 100,00 | 130,00 | 80,00 |
| Median | 80.00 | 80.00 | 90.00 | 100.00 | 70.00 |
| I trimester | — | p < 0.001 | p < 0.001 | p < 0.001 | p = 0.186 |
| II trimester | p < 0.001 | — | p < 0.001 | p < 0.001 | p < 0.001 |
| III trimester | p < 0.001 | p < 0.001 | — | p < 0.001 | p < 0.001 |
| Postpartum | p < 0.001 | p < 0.001 | p < 0.001 | — | p < 0.001 |
| Control | p = 0.186 | p < 0.001 | p < 0.001 | p < 0.001 | — |
| (I-III trim.) vs. Control | p < 0.001 | ||||
| (I trim-post.) vs. Control | p < 0.001 | ||||
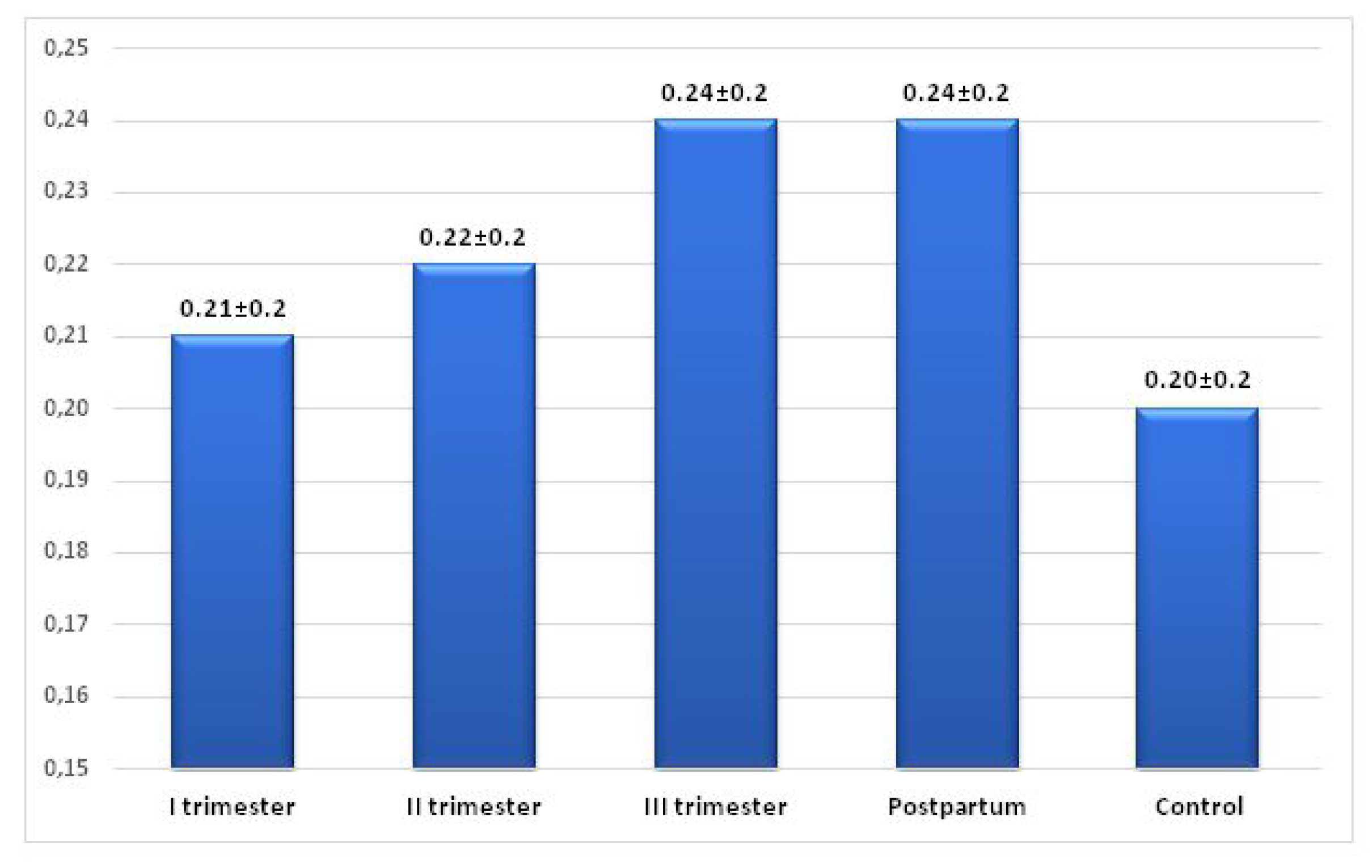
| TpTe/QT | I Trimester | II Trimester | III Trimester | Postpartum | Control |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| N | 36 | 30 | 30 | 32 | 32 |
| Mean | 0.21 | 0.22 | 0.24 | 0.24 | 0.20 |
| SD | 0.02 | 0.02 | 0.02 | 0.03 | 0.02 |
| Minimum | 0.16 | 0.19 | 0.20 | 0.16 | 0.14 |
| Maximum | 0.24 | 0.25 | 0.27 | 0.29 | 0.23 |
| Median | 0.21 | 0.22 | 0.24 | 0.25 | 0.20 |
| I trimester | — | p = 0.012 | p < 0.001 | p < 0.001 | p = 0.045 |
| II trimester | p = 0.012 | — | p < 0.001 | p < 0.001 | p < 0.001 |
| III trimester | p < 0.001 | p < 0.001 | — | p = 0.469 | p < 0.001 |
| Postpartum | p < 0.001 | p < 0.001 | p = 0.469 | — | p < 0.001 |
| Control | p = 0.045 | p < 0.001 | p < 0.001 | p < 0.001 | — |
| (I-III trim.) vs. Control | p < 0.001 | ||||
| (I trim-post.) vs. Control | p < 0.001 | ||||
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kandzia, T.; Markiewicz-Łoskot, G.; Binkiewicz, P. Tpeak-Tend Interval during Pregnancy and Postpartum. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 12638. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph191912638
Kandzia T, Markiewicz-Łoskot G, Binkiewicz P. Tpeak-Tend Interval during Pregnancy and Postpartum. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health. 2022; 19(19):12638. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph191912638
Chicago/Turabian StyleKandzia, Tomasz, Grażyna Markiewicz-Łoskot, and Przemysław Binkiewicz. 2022. "Tpeak-Tend Interval during Pregnancy and Postpartum" International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health 19, no. 19: 12638. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph191912638
APA StyleKandzia, T., Markiewicz-Łoskot, G., & Binkiewicz, P. (2022). Tpeak-Tend Interval during Pregnancy and Postpartum. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 19(19), 12638. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph191912638






