Insights into Asparaginase from Endophytic Fungus Lasiodiplodia theobromae: Purification, Characterization and Antileukemic Activity
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Microorganism
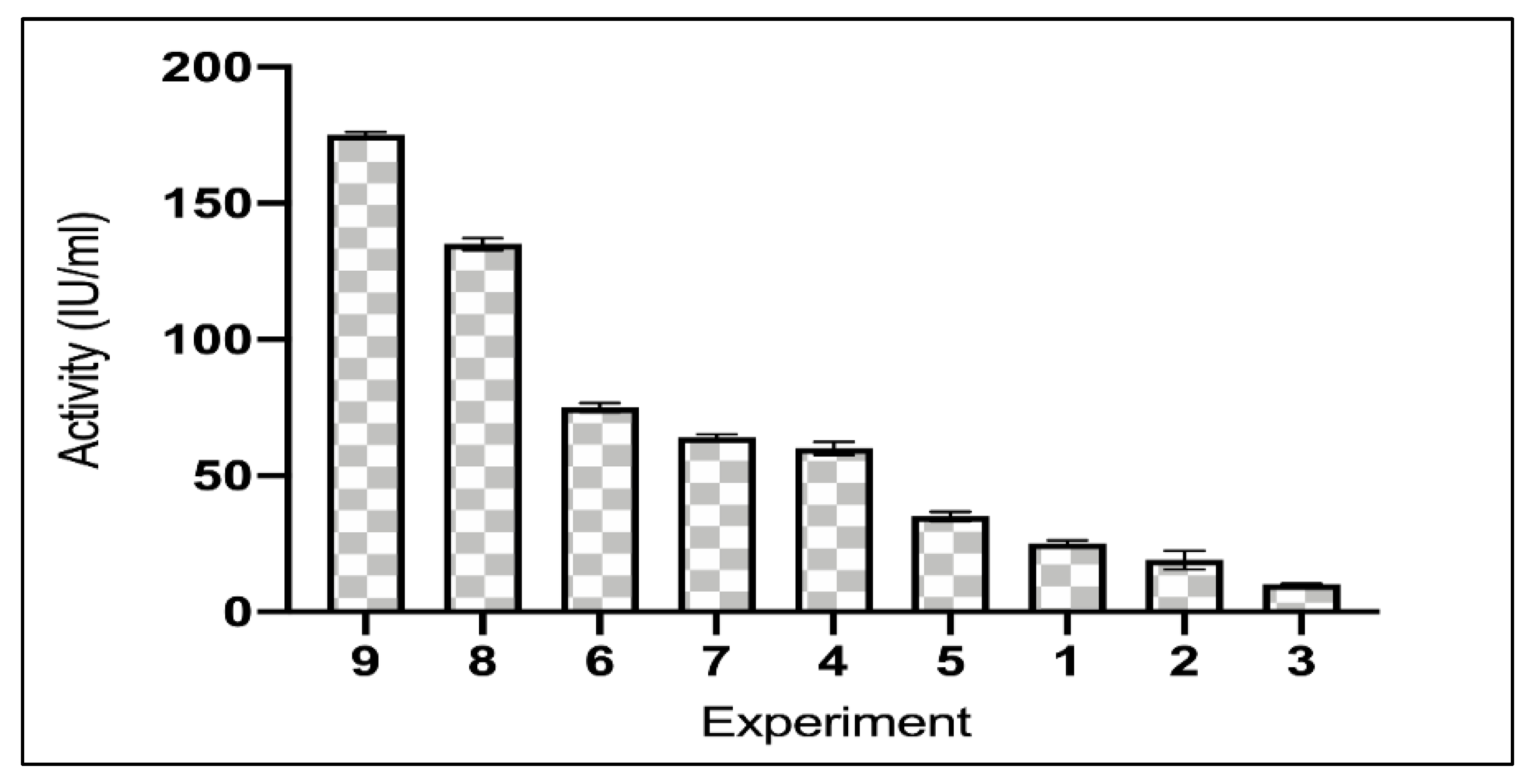
2.2. Optimization of Media Conditions and Asparaginase Induction
2.3. Purification of Asparaginase
2.3.1. Total Protein Precipitation
2.3.2. Ion Exchange Chromatography
2.3.3. Size Exclusion Gel-Filtration Chromatography
2.4. Estimation of Total Protein
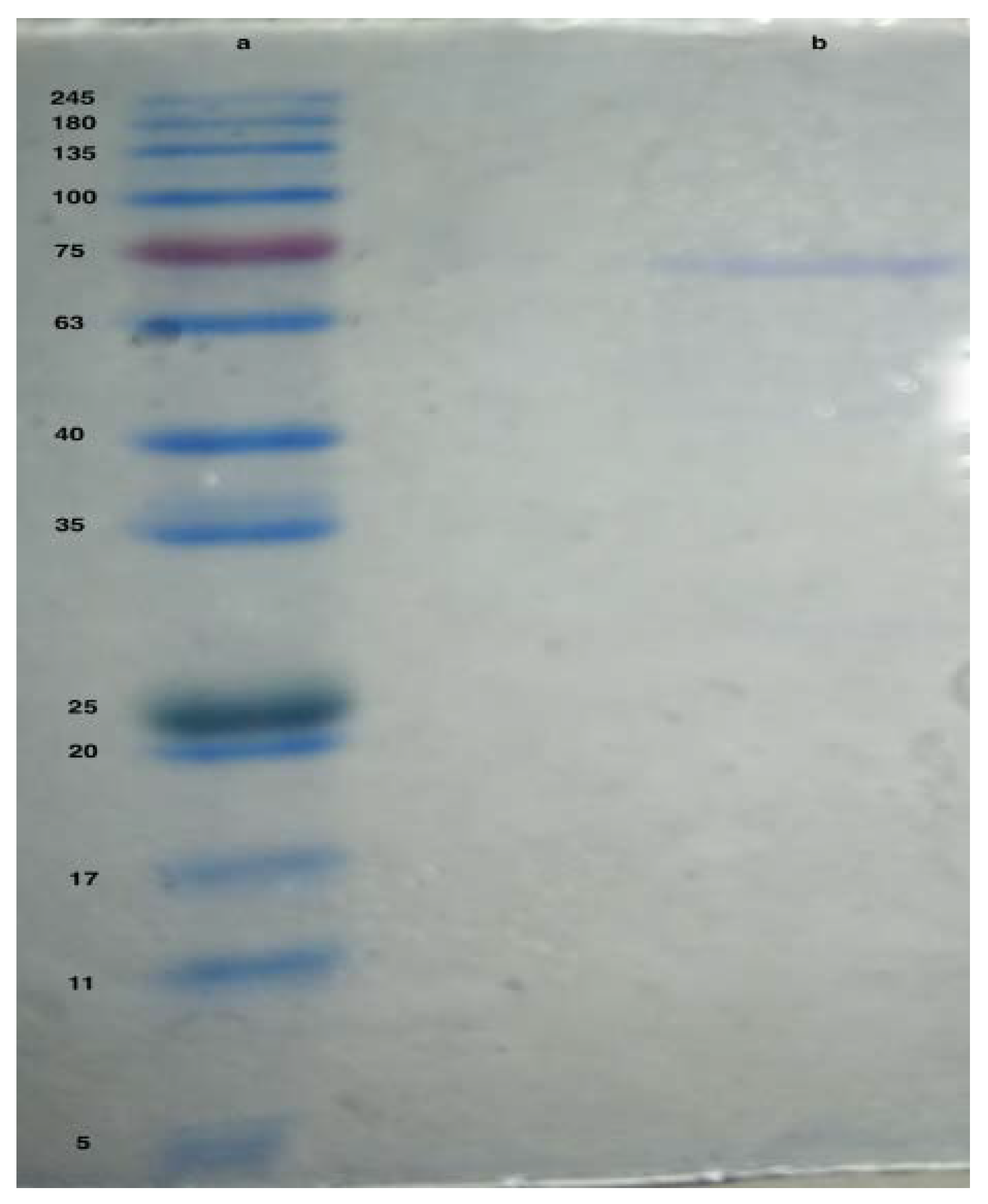
Estimation of Enzyme Molecular Weight Using SDS PAGE
2.5. Enzyme Characterization
2.5.1. Determination of the Optimum Reaction Temperature and Stability
2.5.2. Effect of pH on Asparaginase Activity
2.5.3. Effect of Inhibitors, Activators on Asparaginase Activity
2.5.4. Enzyme Kinetics
2.6. Testing the Antileukemic Activity
Cytotoxicity Evaluation Using the Viability Assay
2.7. Statistics
3. Results
3.1. Optimization of Media Conditions
3.2. Purification of Asparaginase
Estimation of Enzyme Molecular Weight
3.3. Enzyme Characterization
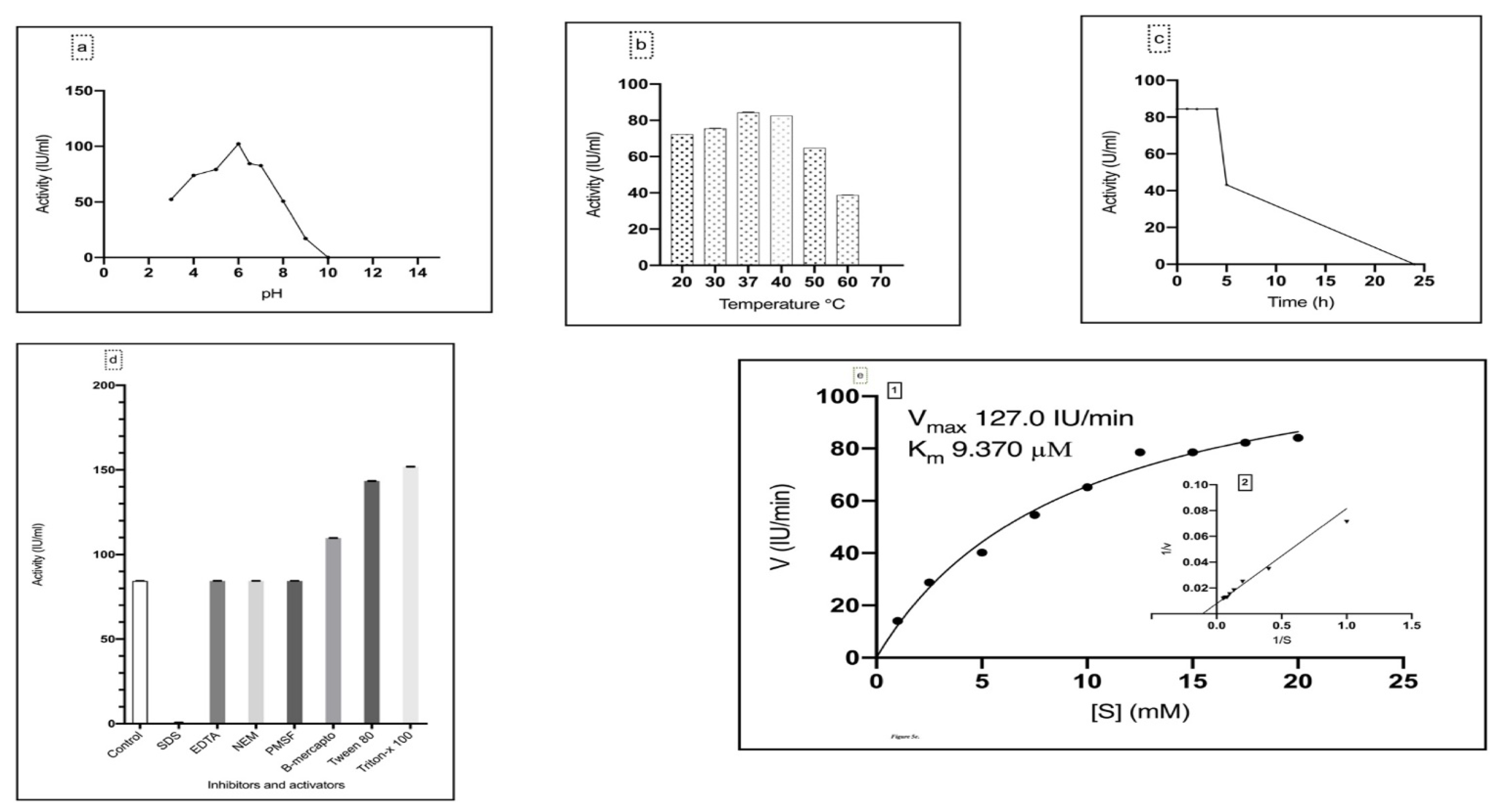
3.3.1. Effect of pH on Asparaginase Activity
3.3.2. Effect of Temperature on Asparaginase Activity
3.3.3. Effect of Inhibitors and Activators on Asparaginase Activity
3.3.4. Determination of Enzyme Kinetics
3.4. Estimation of Asparaginase Antileukemic Activity
3.4.1. Evaluation of Cytotoxicity against M-NFS-60 Cell Line
3.4.2. Evaluation of Cytotoxicity against WI-38 Cell Line
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Rodriguez, R.J.; White, J.F., Jr.; Arnold, A.E.; Redman, R.S. Fungal endophytes: Diversity and functional roles. New Phytol. 2009, 182, 314–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gouda, S.; Kerry, R.G.; Das, G.; Paramithiotis, S.; Shin, H.-S.; Patra, J.K. Revitalization of plant growth promoting rhizobacteria for sustainable development in agriculture. Microbiol. Res. 2018, 206, 131–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdel-Azeem, A.M.; Zaki, S.M.; Khalil, W.F.; Makhlouf, N.A.; Farghaly, L.M. Anti-Rheumatoid Activity of Secondary Metabolites Produced by Endophytic Chaetomium globosum. Front. Microbiol. 2016, 7, 1477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kumar, D.; Sobha, K. L-Asparaginase from Microbes: A Comprehensive Review. Adv. Biores. 2012, 3, 137–157. [Google Scholar]
- Clementi, A. La Désamidation Enzymatique De L’asparagine Chez Les Différentes Espéces Animales Et La Signification Physio Logique De Sa Presence Dans L’organisme. Arch. Int. Physiol. 1922, 19, 369–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mashburn, L.T.; Wriston, J.C. Tumor inhibitory effect of l-asparaginase from Escherichia coli. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 1964, 105, 450–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pieters, R.; Hunger, S.P.; Boos, J.; Rizzari, C.; Silverman, L.; Baruchel, A.; Goekbuget, N.; Schrappe, M.; Pui, C.-H. L-asparaginase treatment in acute lymphoblastic leukemia: A Focus on Erwinia Asparaginase. Cancer 2011, 117, 238–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- El-Naggar, N.E.-A.; El-Ewasy, S.M.; El-Shweihy, N.M. Microbial L-Asparaginase as a Potential Therapeutic Agent for the Treatment of Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia: The Pros and Cons. Int. J. Pharmacol. 2014, 10, 182–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Fan, J.; Venneti, S.; Cross, J.R.; Takagi, T.; Bhinder, B.; Djaballah, H.; Kanai, M.; Cheng, E.H.; Judkins, A.R.; et al. Asparagine Plays a Critical Role in Regulating Cellular Adaptation to Glutamine Depletion. Mol. Cell 2014, 56, 205–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fung, M.K.L.; Chan, G.C.-F. Drug-induced amino acid deprivation as strategy for cancer therapy. J. Hematol. Oncol. 2017, 10, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- More, S.S.; Thakur, L.L.M. Isolation, Purification and Characterization of Fungal Extracellular L-Asparaginase from Mucor hiemalis. J. Biocatal. Biotransform. 2013, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verma, N.; Kumar, K.; Kaur, G.; Anand, S. L-Asparaginase: A Promising Chemotherapeutic Agent. Crit. Rev. Biotechnol. 2007, 27, 45–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Bessoumy, A.A.; Sarhan, M.; Mansour, J. Production, isolation, and purification of L-asparaginase from Pseudomonas aeruginosa 50071 using solid-state fermentation. J. Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2004, 37, 387–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kafkewitz, D.; Goodman, D. L-Asparaginase Production by the Rumen Anaerobe Vibrio succinogenes. Appl. Microbiol. 1974, 27, 206–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hatamzadeh, S.; Rahnama, K.; Nasrollahnejad, S.; Fotouhifar, K.B.; Hemmati, K.; White, J.F.; Taliei, F. Isolation and identification of L-asparaginase-producing endophytic fungi from the Asteraceae family plant species of Iran. PeerJ 2020, 8, e8309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Egler, R.A.; Ahuja, S.P.; Matloub, Y. L-asparaginase in the treatment of patients with acute lymphoblastic leukemia. J. Pharmacol. Pharmacother. 2016, 7, 62–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Souza, P.M.; de Freitas, M.M.; Cardoso, S.L.; Pessoa, A.; Guerra, E.N.S.; Magalhães, P.O. Optimization and purification of L-asparaginase from fungi: A systematic review. Crit. Rev. Oncol. 2017, 120, 194–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mishra, A. Production of L-asparaginase, an anticancer agent, from Aspergillus niger using agricultural waste in solid state fermentation. Appl. Biochem. Biotechnol. 2006, 135, 33–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Archana, J.; Raja, P. Production, Purification and Characterization of L-Asparaginase from Aspergillus nidulans by Solid State Fermentation. Eur. J. Biotechnol. Biosci. 2014, 2, 51–58. [Google Scholar]
- Saied, E.M.; El-Maradny, Y.A.; Osman, A.A.; Darwish, A.M.G.; Abo Nahas, H.H.; Niedbała, G.; Piekutowska, M.; Abdel-Rahman, M.A.; Balbool, B.A.; Abdel-Azeem, A.M. A Comprehensive Review about the Molecular Structure of Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2): Insights into Natural Products against COVID-19. Pharmaceutics 2021, 13, 1759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagarajan, A.; Thirunavukkarasu, N.; Suryanarayanan, T.S.; Gummadi, N.S. Screening and Isolation of Novel Glutaminase Free L-Asparaginase from Fungal Endophytesitle. Res. J. Microbiol. 2014, 9, 163–176. [Google Scholar]
- Salini, G.; Madhusoodhanan, A.; Joseph, A.; Mohan, A.; Navya, R.K.; Nair, V.V. Glutaminase Free L-Asparaginase Producing Endophytes from Mangroves. Asian J. Pharm. Clin. Res. 2016, 9, 360–362. [Google Scholar]
- Gaber, A.; Alsanie, W.F.; Kumar, D.N.; Refat, M.S.; Saied, E.M. Novel Papaverine Metal Complexes with Potential Anticancer Activities. Molecules 2020, 25, 5447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Balbool, B.A.; Abdel-Azeem, A.M. Diversity of the Culturable Endophytic Fungi Producing L-Asparaginase in Arid Sinai, Egypt. Ital. J. Mycol. 2020, 49, 8–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaber, A.; Refat, M.S.; Belal, A.A.M.; El-Deen, I.M.; Hassan, N.; Zakaria, R.; Alhomrani, M.; Alamri, A.S.; Alsanie, W.F.; M. Saied, E. New Mononuclear and Binuclear Cu(II), Co(II), Ni(II), and Zn(II) Thiosemicarbazone Complexes with Potential Biological Ac-tivity: Antimicrobial and Molecular Docking Study. Molecules 2021, 26, 2288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ali, D.; Ouf, S.; Eweis, M.; Solieman, D. Optimization of L-Asparaginase production from some filamentous fungi with potential pharmaceutical properties. Egypt. J. Bot. 2018, 58, 355–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wriston, J.C. Asparaginase. In Methods in Enzymology—Metabolism of Amino Acids and Amines Part A; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 1970; Volume 17, pp. 732–742. [Google Scholar]
- Wessel, D.; Flügge, U. A method for the quantitative recovery of protein in dilute solution in the presence of detergents and lipids. Anal. Biochem. 1984, 138, 141–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laemmli, U.K. Cleavage of Structural Proteins during the Assembly of the Head of Bacteriophage T4. Nature 1970, 227, 680–685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharar, M.; Saied, E.M.; Rodriguez, M.C.; Arenz, C.; Montes-Bayón, M.; Linscheid, M.W. Elemental Labelling and Mass Spec-trometry for the Specific Detection of Sulfenic Acid Groups in Model Peptides: A Proof of Concept. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2017, 409, 2015–2027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yadav, N.; Sarkar, S. Production of L-Asparaginase by Fusarium Oxysporum Using Submerged Fermentation. Int. J. Pharm. Sci. Invent. 2014, 3, 32–40. [Google Scholar]
- Kothari, M.N.; Baig, M.M.V. Production and characterization of extracellular polygalacturonase by Erwinia carotovora MTCC 1428. Int. J. Adv. Biotechnol. Res. 2013, 4, 981–998. [Google Scholar]
- Pu, X.; Yu, S.; Fan, W.; Liu, L.; Ma, X.; Ren, J. Guiqi polysaccharide protects the normal human fetal lung fibroblast WI-38 cells from H2O2-induced premature senescence. Int. J. Clin. Exp. Pathol. 2015, 8, 4398–4407. [Google Scholar]
- Shafek, R.; Michael, H.; Sayed, A.; Ibrahim, A.; Al-Sayed, A. Phytochemical study, antioxidant and cytotoxic activities of Brassica rapa L. leaves extract and its silver nanoparticles. Egypt. J. Chem. 2018, 61, 237–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mosmann, T. Rapid colorimetric assay for cellular growth and survival: Application to proliferation and cytotoxicity assays. J. Immunol. Methods 1983, 65, 55–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.; Shan, T.; Mou, Y.; Zhou, L. Plant-Derived Bioactive Compounds Produced by Endophytic Fungi. Mini-Rev. Med. Chem. 2011, 11, 159–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jia, M.; Chen, L.; Xin, H.-L.; Zheng, C.-J.; Rahman, K.; Han, T.; Qin, L.-P. A Friendly Relationship between Endophytic Fungi and Medicinal Plants: A Systematic Review. Front. Microbiol. 2016, 7, 906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Schulz, B.; Boyle, C. The endophytic continuum. Mycol. Res. 2005, 109, 661–686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Matsuura, H.; Nakamori, K.; Omer, E.; Hatakeyama, C.; Yoshihara, T.; Ichihara, A. Three lasiodiplodins from lasiodiplodia theobromae IFO 31059. Phytochemistry 1998, 49, 579–584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Navaratnam, P.; Arasaratnam, V.; Mahendran, S.; Balasubramaniam, K. Formulation of medium and recycling of biomass for glucoamylase production by Botryodiplodia theobromae. Process. Biochem. 1996, 31, 77–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashok, A.; Doriya, K.; Rao, J.V.; Qureshi, A.; Tiwari, A.K.; Kumar, D.S. Microbes Producing L-Asparaginase free of Glutaminase and Urease isolated from Extreme Locations of Antarctic Soil and Moss. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 1423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Félix, C.; Salvatore, M.M.; DellaGreca, M.; Ferreira, V.; Duarte, A.S.; Salvatore, F.; Naviglio, D.; Gallo, M.; Alves, A.; Esteves, A.C.; et al. Secondary metabolites produced by grapevine strains of Lasiodiplodia theobromae grown at two different temperatures. Mycologia 2019, 111, 466–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Narayana, K.J.P.; Kumar, K.G.; Vijayalakshmi, M. L-asparaginase production by Streptomyces albidoflavus. Indian J. Microbiol. 2008, 48, 331–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nossal, N.G.; Heppel, L.A. The Release of Enzymes by Osmotic Shock from Escherichia coli in Exponential Phase. J. Biol. Chem. 1996, 241, 3055–3062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohamed, S.A.; Elshal, M.F.; Kumosani, T.A.; Aldahlawi, A. Purification and Characterization of Asparaginase from Phaseolus vulgaris Seeds. Evid.-Based Complement. Altern. Med. 2015, 2015, 309214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ahmed, M.M.A.; Dahad, F.N.A.; Taha, M.T.; Hassan, S.M.F. Production, Purification and Characterization of L-Asparaginase from Marine Endophytic Aspergillus sp. ALAA-2000 under Submerged and Solid State Fermentation. J. Microb. Biochem. Technol. 2015, 7, 165–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, L.; Liu, Y.; Sun, Y.; Yan, Q.; Jiang, Z. Biochemical Characterization of a Novel L-Asparaginase with Low Glutaminase Activity from Rhizomucor miehei and Its Application in Food Safety and Leukemia Treatment. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2013, 80, 1561–1569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hong, S.-J.; Lee, Y.-H.; Khan, A.R.; Ullah, I.; Lee, C.; Park, C.K.; Shin, J.-H. Cloning, expression, and characterization of thermophilic L-asparaginase from Thermococcus kodakarensis KOD1. J. Basic Microbiol. 2014, 54, 500–508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cedar, H.; Schwartz, J.H. Localization of the Two L-Asparaginases in Anaerobically Grown Escherichia coli. J. Biol. Chem. 1967, 242, 3753–3755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shifrin, S.; Parrott, C.L.; Luborsky, S.W. Substrate Binding and Intersubunit Interactions in L-Asparaginase. J. Biol. Chem. 1974, 249, 1335–1340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scheetz, R.W.; Whelan, H.A.; Wriston, J.C. Purification and properties of an L-asparaginase from Fusarium tricinctum. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 1971, 142, 184–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manna, S.; Sinha, A.; Sadhukhan, R.; Chakrabarty, S.L. Purification, characterization and antitumor activity of L-asparaginase isolated from Pseudomonas stutzeri MB-405. Curr. Microbiol. 1995, 30, 291–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanjotha, G.; Manawadi, S.I. Isolation, Screening, Optimization and Production of Anti-Tumor L-Asparaginase by Fungi from Karwar Coastal Region. Res. J. Recent Sci. 2017, 6, 1–7. [Google Scholar]
- Gaffar, S.A.; Shethna, Y.I. Purification and Some Biological Properties of Asparaginase from Azotobacter vinelandii. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 1977, 33, 508–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mesas, J.M.; Gil, J.A.; Martin, J.F. Characterization and Partial Purification of L-Asparaginase from Corynebacterium Glutamicum. J. Gen. Microbiol. 1990, 136, 515–519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sakamoto, T.; Araki, C.; Beppu, T.; Arima, K. Partial purification and some properties of extracellular asparaginase from Candida utilis. Agric. Biol. Chem. 1977, 41, 1359–1364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sonaimuthu, V.; Krishnamoorthy, S.; Johnpaul, M. Taxol producing endophytic fungus Fusarium culmorum SVJM072 from medicinal plant of Tinospora cordifolia—A first report. J. Biotechnol. 2010, 150, 425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raha, S.K.; Roy, S.K.; Dey, S.K.; Chakrabarty, S.L. Purification and properties of an L-asparaginase from Cylindrocarpon obtusisporum MB-10. Biochem. Int. 1990, 21, 987–1000. [Google Scholar]
- Qin, M.; Wang, W.; Thirumalai, D. Protein folding guides disulfide bond formation. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2015, 112, 11241–11246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, S.; Xie, Y.; Zhang, C.; Bie, X.; Zhao, H.; Lu, F.; Lu, Z. Biochemical characterization of a novel L-asparaginase from Bacillus megaterium H-1 and its application in French fries. Food Res. Int. 2015, 77, 527–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamza, M.A.; Engel, P.C. Enhancing long-term thermal stability in mesophilic glutamate dehydrogenase from Clostridium symbiosum by eliminating cysteine residues. Enzym. Microb. Technol. 2007, 41, 706–710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patro, K.R. Extraction, purification and characterization of L-asparaginase from Penicillium sp. by submerged fermentation. Int. J. Biotechnol. Mol. Biol. Res. 2012, 3, 30–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lewies, A.; Du Plessis, L.H.; Wentzel, J.F. The Cytotoxic, Antimicrobial and Anticancer Properties of the Antimicrobial Peptide Nisin Z Alone and in Combination with Conventional Treatments. In Cytotoxicity; IntechOpen: London, UK, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Ben Tanfous, M.; Sharif-Askari, B.; Ceppi, F.; Laaribi, H.; Gagné, V.; Rousseau, J.; Labuda, M.; Silverman, L.B.; Sallan, S.E.; Neuberg, D.; et al. Polymorphisms of Asparaginase Pathway and Asparaginase-Related Complications in Children with Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia. Clin. Cancer Res. 2015, 21, 329–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Broome, J.D. Evidence That the L-Asparaginase of Guinea Pig Serum is Responsible for Its Antilymphoma Effects: I. Properties of The L-Asparaginase of Guinea Pig Serum in Relation to Those of The Antilymphoma Substance. J. Exp. Med. 1963, 118, 99–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kidd, J.G. Regression of Transplanted Lymphomas Induced in Vivo by Means of Normal Guinea Pig Serum. II. Studies on the Nature of the Active Serum Constituent: Histological Mechanism of the Regression: Tests for Effects of Guinea Pig Serum on Lymphoma Cells in Vitro. J. Exp. Med. 1953, 98, 583–606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neuman, R.E.; McCoy, T.A. Dual Requirement of Walker Carcinosarcoma 256 in vitro for Asparagine and Glutamine. Science 1956, 124, 124–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Mei, L.; Ontiveros, E.P.; Griffiths, E.A.; Thompson, J.E.; Wang, E.S.; Wetzler, M. Pharmacogenetics predictive of response and toxicity in acute lymphoblastic leukemia therapy. Blood Rev. 2015, 29, 243–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gervasini, G.; Vagace, J.M. Impact of genetic polymorphisms on chemotherapy toxicity in childhood acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Front. Genet. 2012, 3, 249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]


| Step | Total Protein (mg) | Activity * (IU/mL) | Specific Activity (IUmg−1) | Purification Fold | Yield % |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Induced enzyme | 9.21 | 315.00 | 34.20 | 1.00 | 100.00 |
| Acetone | 6.81 | 250.00 | 36.71 | 1.07 | 79.37 |
| Q-FF (0.3M NaCl) | 1.31 | 138.91 | 105.88 | 3.10 | 44.10 |
| Sephadex G-100 | 0.18 | 84.40 | 468.03 | 13.68 | 26.79 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Moubasher, H.A.; Balbool, B.A.; Helmy, Y.A.; Alsuhaibani, A.M.; Atta, A.A.; Sheir, D.H.; Abdel-Azeem, A.M. Insights into Asparaginase from Endophytic Fungus Lasiodiplodia theobromae: Purification, Characterization and Antileukemic Activity. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 680. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph19020680
Moubasher HA, Balbool BA, Helmy YA, Alsuhaibani AM, Atta AA, Sheir DH, Abdel-Azeem AM. Insights into Asparaginase from Endophytic Fungus Lasiodiplodia theobromae: Purification, Characterization and Antileukemic Activity. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health. 2022; 19(2):680. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph19020680
Chicago/Turabian StyleMoubasher, Hani A., Bassem A. Balbool, Yosra A. Helmy, Amnah Mohammed Alsuhaibani, Ahmed A. Atta, Donia H. Sheir, and Ahmed M. Abdel-Azeem. 2022. "Insights into Asparaginase from Endophytic Fungus Lasiodiplodia theobromae: Purification, Characterization and Antileukemic Activity" International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health 19, no. 2: 680. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph19020680
APA StyleMoubasher, H. A., Balbool, B. A., Helmy, Y. A., Alsuhaibani, A. M., Atta, A. A., Sheir, D. H., & Abdel-Azeem, A. M. (2022). Insights into Asparaginase from Endophytic Fungus Lasiodiplodia theobromae: Purification, Characterization and Antileukemic Activity. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 19(2), 680. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph19020680








