Geographical Distribution and Pattern of Pesticides in Danish Drinking Water 2002–2018: Reducing Data Complexity
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Data Sources
2.2. Public Water Supply
2.3. Data Management
2.4. Data Exploration
2.4.1. Pesticide Groups
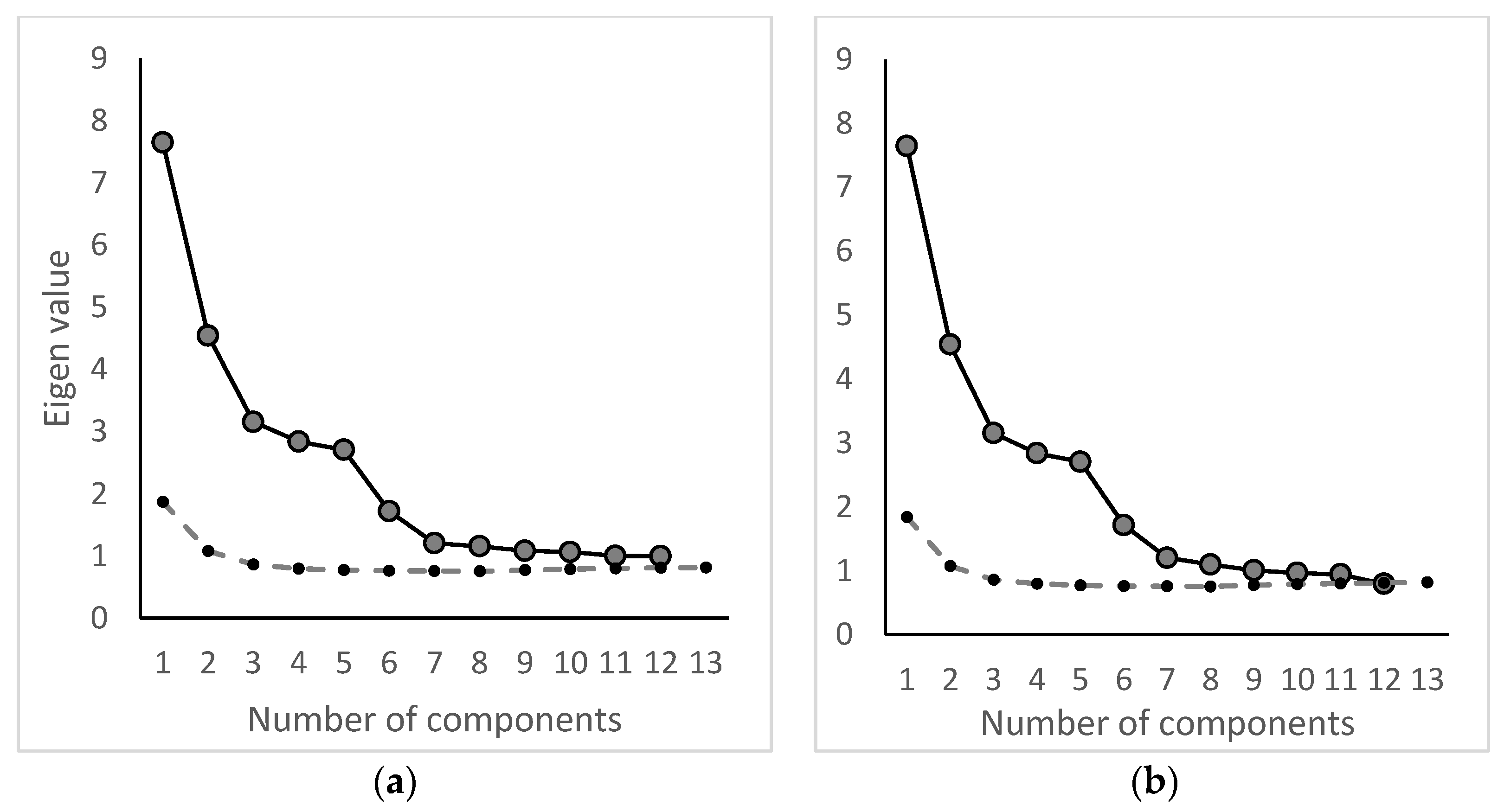
2.4.2. Factor Analysis
- (1)
- Perform factor analysis with the specifications listed above;
- (2)
- Evaluate MSA, eigenvalues, and scree plot, including Horn’s parallel analysis, and select optimum number of factor components;
- (3)
- Perform factor analysis, specifying number of components and rotation;
- (4)
- Evaluate factor pattern—if pesticides are observed with poor loadings (i.e., −0.45 to 0.45) to the factor components (not reaching the pre-set criteria for inclusion), the pesticides are removed and steps 1–4 are repeated.
2.4.3. Sensitivity Analysis
3. Results
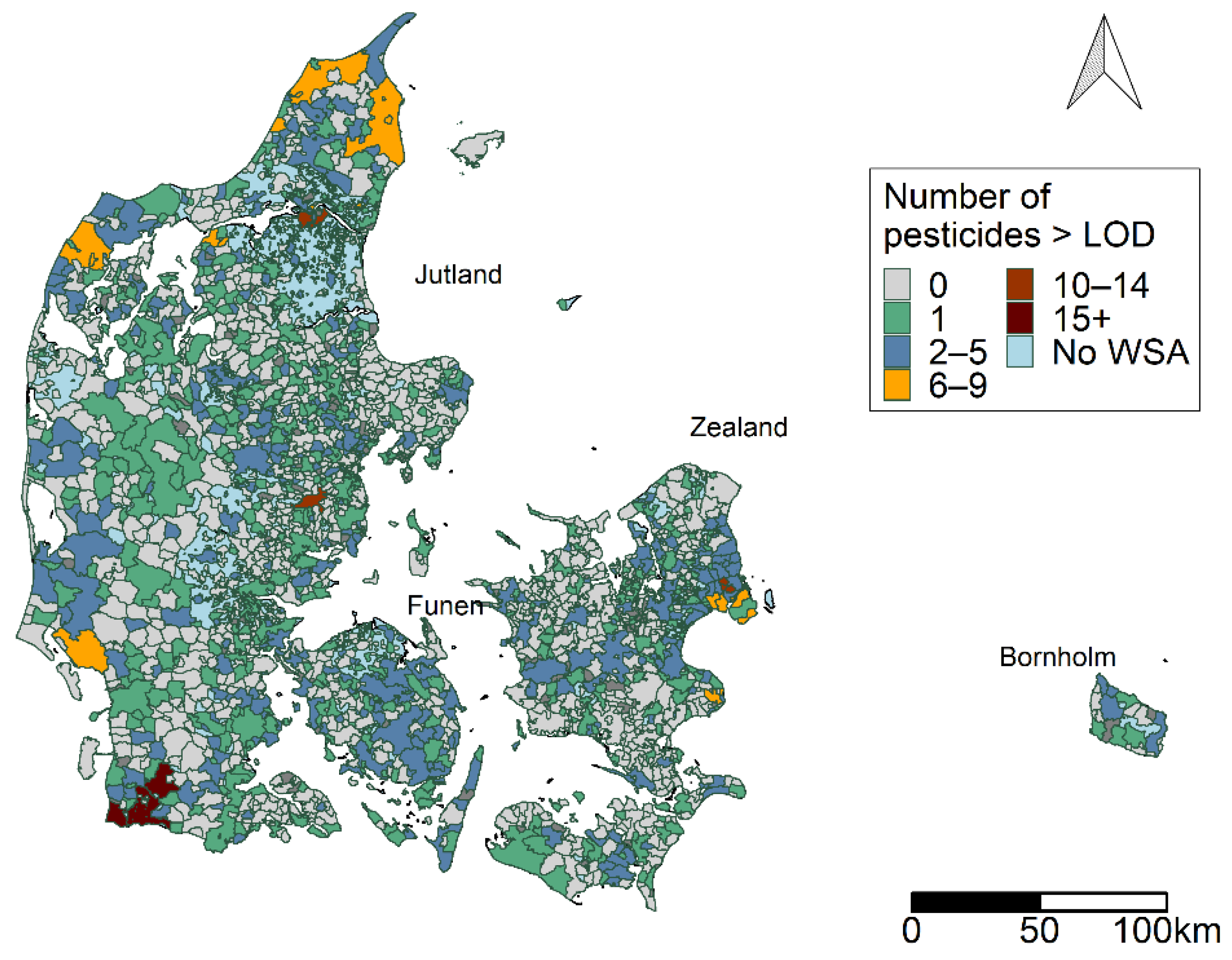
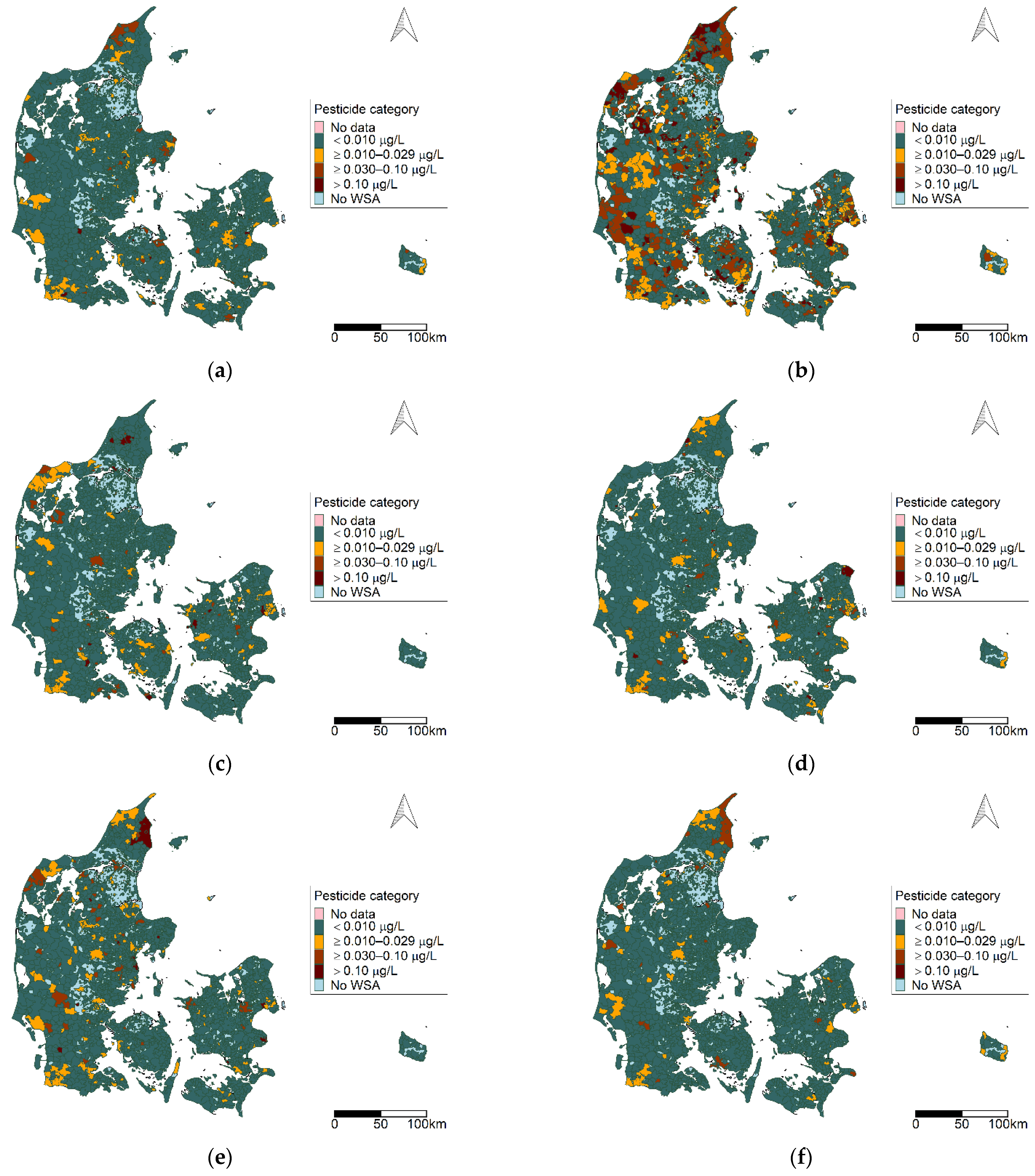
3.1. Descriptive Results
3.2. Pesticide Groups
Variation over Time
3.3. Factor Analysis
3.3.1. Factor Analysis 2002–2011
3.3.2. Factor Analysis 2012–2018
3.3.3. Sensitivity Analysis
3.4. Compare Patterns
4. Discussion
4.1. Summary of Findings
4.2. Comparison with Similar Studies
4.3. Strengths
4.4. Limitations
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Casida, J.E. Pest toxicology: The primary mechanisms of pesticide action. Chem. Res. Toxicol. 2009, 22, 609–619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hernández, A.F.; Parrón, T.; Tsatsakis, A.M.; Requena, M.; Alarcón, R.; López-Guarnido, O. Toxic effects of pesticide mixtures at a molecular level: Their relevance to human health. Toxicology 2013, 307, 136–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- European Commission. EU Pesticides Database (v.2.2) Search Active Substances, Safeners and Synergists. 2021. Available online: https://ec.europa.eu/food/plant/pesticides/eu-pesticides-database/active-substances/index.cfm?event=search.as&s=3&a_from=&a_to=&e_from=&e_to=&additionalfilter__class_p1=&additionalfilter__class_p2=&string_tox_1=&string_tox_1=&string_tox_2=&string_tox_2=&s (accessed on 21 July 2021).
- The European Parliament; The Council of the European Union. Regulation (EC) No 1107/2009 of the European Parliament and of the Council of 21 October 2009. Off. J. Eur. Union 2009, 309, 1–50. Available online: https://eur-lex.europa.eu/legal-content/EN/TXT/?uri=celex%3A32009R1107 (accessed on 19 August 2021).
- The Council of the European Union. Council Directive 98/83/EC of 3 November 1998 on the Quality of Water Intended for Human Consumption. Off. J. Eur. Union 1998, 330, 32–54. Available online: https://eur-lex.europa.eu/legal-content/EN/TXT/?uri=celex%3A31998L0083 (accessed on 19 August 2021).
- Ministry of Environment and Food (Miljø- og Fødevareministeriet). Drikkevandsbekendtgørelsen, BEK nr 1110 af 30/05/2021. Retsinformation. 2021. Available online: https://www.retsinformation.dk/eli/lta/2021/1110 (accessed on 30 August 2021).
- Chen, M.; Chang, C.H.; Tao, L.; Lu, C. Residential exposure to pesticide during childhood and childhood cancers: A meta-analysis. Pediatrics 2015, 136, 719–729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Malagoli, C.; Costanzini, S.; Heck, J.E.; Malavolti, M.; De Girolamo, G.; Oleari, P.; Palazzi, G.; Teggi, S.; Vinceti, M. Passive exposure to agricultural pesticides and risk of childhood leukemia in an Italian community. Int. J. Hyg. Environ. Health 2016, 219, 742–748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kim, K.H.; Kabir, E.; Jahan, S.A. Exposure to pesticides and the associated human health effects. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 575, 525–535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baudry, J.; Assmann, K.E.; Touvier, M.; Allès, B.; Seconda, L.; Latino-Martel, P.; Ezzedine, K.; Galan, P.; Hercberg, S.; Lairon, D.; et al. Association of Frequency of Organic Food Consumption with Cancer Risk: Findings from the NutriNet-Santé Prospective Cohort Study. JAMA Intern. Med. 2018, 178, 1597–1606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- International Agency for Research on Cancer. List of Classifications by Cancer Sites with Sufficient or Limited Evidence in Humans. IARC Monographs. 2020. Available online: https://monographs.iarc.fr/wp-content/uploads/2019/07/Classifications_by_cancer_site.pdf (accessed on 17 August 2021).
- IARC. IARC Monographs Volume 112: Evaluation of Five Organophosphate Insecticides and Herbicides 20. IARC Monogr. 2015, 112, 235–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hansen, M.; Pjetursson, B. Free, online Danish shallow geological data. Geol. Surv. Den. Greenl. Bull. 2011, 23, 53–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Voutchkova, D.D.; Schullehner, J.; Skaarup, C.; Wodschow, K.; Ersbøll, A.K.; Hansen, B. Estimating pesticides in public drinking water at the household level in Denmark. GEUS Bull. 2021, 47, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schullehner, J.; Hansen, B. Nitrate exposure from drinking water in Denmark over the last 35 years. Environ. Res. Lett. 2014, 9, 095001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wodschow, K.; Hansen, B.; Schullehner, J.; Ersbøll, A.K. Stability of major geogenic cations in drinking water-an issue of public health importance: A danish study, 1980–2017. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2018, 15, 1212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sharma, S. Applied Multivariate Techniques; J. Wiley: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 1996; ISBN 0-471-31064-6. [Google Scholar]
- Hornung, R.W.; Reed, L.D. Estimation of Average Concentration in the Presence of Nondetectable Values. Appl. Occup. Environ. Hyg. 1990, 5, 46–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- SAS Institute Inc. SAS Help Center: SAS 9.4 Language Reference: Concepts, 6th ed.; SAS Institute Inc.: Cary, NC, USA, 2016; Available online: https://documentation.sas.com/doc/en/pgmsascdc/9.4_3.5/lrcon/titlepage.htm (accessed on 22 April 2021).
- Ali, I.; Jain, C.K. Groundwater contamination and health hazards by some of the most commonly used pesticides. Curr. Sci. 1998, 75, 1011–1014. [Google Scholar]
- Bexfield, L.M.; Belitz, K.; Lindsey, B.D.; Toccalino, P.L.; Nowell, L.H. Pesticides and Pesticide Degradates in Groundwater Used for Public Supply across the United States: Occurrence and Human-Health Context. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2021, 55, 362–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kolpin, D.W.; Barbash, J.E.; Gilliom, R.J. Occurrence of pesticides in shallow groundwater of the United States: Initial results from the National Water-Quality Assessment program. Environ. Sci. Technol. 1998, 32, 558–566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lapworth, D.J.; Baran, N.; Stuart, M.E.; Manamsa, K.; Talbot, J. Persistent and emerging micro-organic contaminants in Chalk groundwater of England and France. Environ. Pollut. 2015, 203, 214–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Maanen, J.M.S.; De Vaan, M.A.J.; Veldstra, A.W.F.; Hendrix, W.P.A.M. Pesticides and nitrate in groundwater and rainwater in the province of Limburg in the Netherlands. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2001, 72, 95–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ryberg, K.R.; Vecchia, A.V.; Martin, J.D.; Gilliom, R.J. Trends in Pesticide Concentrations in Urban Streams in the United States, 1992–2008. U.S. Geological Survey Scientific Investigations Report 2010-5139, 101p. Available online: https://pubs.usgs.gov/sir/2010/5139/ (accessed on 17 August 2021). [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sjerps, R.M.A.; Kooij, P.J.F.; van Loon, A.; Van Wezel, A.P. Occurrence of pesticides in Dutch drinking water sources. Chemosphere 2019, 235, 510–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schipper, P.N.M.; Vissers, M.J.M.; Van Der Linden, A.M.A. Pesticides in groundwater and drinking water wells: Overview of the situation in the Netherlands. Water Sci. Technol. 2008, 57, 1277–1286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Syafrudin, M.; Kristanti, R.A.; Yuniarto, A.; Hadibarata, T.; Rhee, J.; Al-onazi, W.A.; Algarni, T.S.; Almarri, A.H.; Al-Mohaimeed, A.M. Pesticides in Drinking Water—A Review. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tröger, R.; Ren, H.; Yin, D.; Postigo, C.; Nguyen, P.D.; Baduel, C.; Golovko, O.; Been, F.; Joerss, H.; Boleda, M.R.; et al. What’s in the water?—Target and suspect screening of contaminants of emerging concern in raw water and drinking water from Europe and Asia. Water Res. 2021, 198, 117099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, C.W.; Lin, K.H.; Kuo, Y.M. Application of factor analysis in the assessment of groundwater quality in a blackfoot disease area in Taiwan. Sci. Total Environ. 2003, 313, 77–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.; Swartz, M.D.; Langlois, P.H.; Romitti, P.A.; Weyer, P.; Mitchell, L.E.; Luben, T.J.; Ramakrishnan, A.; Malik, S.; Lupo, P.J.; et al. Estimated maternal pesticide exposure from drinkingwater and heart defects in offspring. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2017, 14, 889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- McLeod, L.; Bharadwaj, L.; Epp, T.; Waldner, C. Use of Principal Components Analysis and Kriging to Predict Groundwater-Sourced Rural Drinking Water Quality in Saskatchewan. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2017, 14, 1065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Samanic, C.; Hoppin, J.A.; Lubin, J.H.; Blair, A.; Alavanja, M.C.R. Factor analysis of pesticide use patterns among pesticide applicators in the Agricultural Health Study. J. Expo. Anal. Environ. Epidemiol. 2005, 15, 225–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weissenburger-Moser, L.; Meza, J.; Yu, F.; Shiyanbola, O.; Romberger, D.J.; Levan, T.D. A principal factor analysis to characterize agricultural exposures among Nebraska veterans. J. Expo. Sci. Environ. Epidemiol. 2017, 27, 214–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Alavanja, M.C.R.; Sandler, D.P.; McMaster, S.B.; Zahm, S.H.; McDonnell, C.J.; Lynch, C.F.; Pennybacker, M.; Rothman, N.; Dosemeci, M.; Bond, A.E.; et al. The agricultural health study. Environ. Health Perspect. 1996, 104, 362–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- US EPA. 2018 Edition of the Drinking Water Standards and Health Advisories Tables. 2018. Available online: https://www.epa.gov/sites/production/files/2018-03/documents/dwtable2018.pdf (accessed on 17 August 2021).
- US EPA. Chemicals Evaluated for Carcinogenic Potential Annual Cancer Report 2020. 2020. Available online: https://www.epa.gov/risk/guidelines-carcinogen-risk-assessment (accessed on 17 August 2021).
- Ministry of Environment and Food. Bekendtgørelse Om Helt Eller Delvist Forbud Mod Visse Bekæmpelsesmidler, BEK nr 790 af 30/08/1996. Retsinformation. 1996. Available online: https://www.retsinformation.dk/eli/lta/1996/790 (accessed on 17 August 2021).
- Ministry of Environment and Food (Miljø- og Fødevareministeriet). Bekendtgørelse Om Begrænsning af Import, Salg Og Anvendelse af Biocidholdig Bundmaling, BEK nr 1278 af 12/12/2005. Retinformation. 2005. Available online: https://www.retsinformation.dk/eli/lta/2005/1278 (accessed on 17 August 2021).
- Ministry of Environment and Food (Miljø- og Fødevareministeriet). Bekendtgørelse Om Ændring af Bekendtgørelse Om Bekæmpelsesmidler, BEK nr 102 af 05/02/2009. Retsinformation. 2009. Available online: https://www.retsinformation.dk/eli/lta/2009/102 (accessed on 17 August 2021).
- European Commission. Commission Directive 2010/17/EU of 9 March 2010. 2010. Available online: https://eur-lex.europa.eu/legal-content/EN/ALL/?uri=CELEX%3A32010L0017 (accessed on 13 September 2021).
- European Commision. Commission Decision 2007/389/EC. Available online: https://eur-lex.europa.eu/legal-content/GA/TXT/?uri=CELEX:32007D0389 (accessed on 13 September 2021).
- Ministry of Environment and Food (Miljø- og Fødevareministeriet). Bekendtgørelse Om Ændring af Bekendtgørelse Om Bekæmpelsesmidler, BEK nr 919 af 13/09/2012. Retsinformation. 2012. Available online: https://www.retsinformation.dk/eli/lta/2012/919 (accessed on 17 August 2021).
- Ministry of Environment and Food. Lov Om Ændring af Lov Om Kemiske Stoffer Og Produkter (Forbud Mod Bekæmpelsesmidler, Der Indeholder Visse Aktivstoffer), LOV nr 438 af 01/06/1994. Retsinformation. 1994. Available online: https://www.retsinformation.dk/eli/lta/1994/438 (accessed on 17 August 2021).
- The European Commission. Commission Implementing Regulation (EU) 2019/1090 of 26 June 2019. 2019. Available online: https://eur-lex.europa.eu/legal-content/EN/TXT/?qid=1562078470492&uri=CELEX:32019R1090 (accessed on 13 September 2021).
- Ministry of Environment and Food. BEK nr 824 af 23/07/2004. Retsinformation. 2004. Available online: https://www.retsinformation.dk/eli/lta/2004/824 (accessed on 17 August 2021).
- Ministry of Environment and Food (Miljø- og Fødevareministeriet). Bekendtgørelse Om Ændring af Bekendtgørelse Om Bekæmpelsesmidler, BEK nr 1481 af 16/12/2005. Retsinformation. 2005. Available online: https://www.retsinformation.dk/eli/lta/2005/1481 (accessed on 17 August 2021).
- Ministry of Environment and Food (Miljø- og Fødevareministeriet). Bekendtgørelse Om Forbud Mod Bekæmpelsesmidler, Der Indeholder Visse Virksomme Stoffer, BEK nr 208 af 26/03/1992. Retsinformation. 1992. Available online: https://www.retsinformation.dk/eli/lta/1992/208 (accessed on 17 August 2021).
- Ministry of Environment and Food (Miljø- og Fødevareministeriet). Bekendtgørelse Om Helt Eller Delvist Forbud Mod Visse Bekæmpelsesmidler, BEK nr 189 af 22/03/1999. Retsinformation. 1999. Available online: https://www.retsinformation.dk/eli/lta/1999/189 (accessed on 17 August 2021).





| Pesticide Group | Factor 1 | Factor 2 | Factor 3 | Factor 4 | Factor 5 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MCPA | Phenoxy | 0.959 | 0.003 | −0.001 | −0.011 | 0.001 |
| Dichlorprop | Phenoxy | 0.958 | −0.002 | −0.001 | 0.011 | −0.001 |
| Atrazine | Triazine | 0.002 | 0.817 | 0.050 | −0.031 | −0.011 |
| Atrazine, desethyl- | Triazine | 0.001 | 0.784 | 0.297 | −0.012 | −0.019 |
| Atrazine, hydroxy- | Triazine | 0.002 | −0.632 | 0.458 | −0.073 | −0.064 |
| Simazine | Triazine | −0.002 | −0.131 | 0.820 | 0.062 | 0.066 |
| Atrazine, desisopropy | Triazine | 0.000 | 0.209 | 0.733 | −0.013 | −0.031 |
| Diuron | Urea | 0.014 | −0.032 | 0.024 | 0.815 | −0.017 |
| 4-CPP | Phenoxy | −0.014 | 0.037 | 0.024 | 0.807 | 0.010 |
| Cyanazine | Triazine | 0.001 | −0.019 | 0.073 | −0.033 | 0.679 |
| 2,4-D | Phenoxy | 0.001 | 0.019 | −0.009 | −0.004 | 0.637 |
| DNOC | Dinitrophenol | −0.001 | 0.019 | −0.017 | 0.027 | 0.560 |
| Variance explained | 2.177 | 1.841 | 1.333 | 1.193 | 1.097 |
| Pesticide Group | Factor 1 | Factor 2 | Factor 3 | Factor 4 | Factor 5 | Factor 6 | Factor 7 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2-(2,6-dichlorphenoxy) propanoic acid | Phenoxy acid | 0.988 | −0.010 | 0.004 | 0.004 | −0.011 | −0.011 | 0.007 |
| Terbuthylazine-desethyl | Triazine | 0.985 | −0.007 | 0.000 | 0.019 | −0.013 | −0.012 | 0.007 |
| Simazine, hydroxy | Triazine | 0.984 | −0.007 | 0.000 | 0.019 | −0.013 | −0.012 | 0.007 |
| 4-Nitrophenol | Organophosphate | 0.976 | −0.025 | 0.006 | 0.015 | −0.013 | −0.011 | 0.007 |
| 4-CPP | Phenoxy | 0.967 | −0.004 | 0.004 | 0.000 | −0.008 | −0.014 | 0.005 |
| DEIA | Triazine | 0.959 | −0.014 | −0.008 | 0.022 | −0.014 | 0.072 | 0.008 |
| AMPA | Organophosphate | 0.749 | −0.007 | −0.007 | −0.013 | 0.010 | −0.009 | −0.042 |
| Glyphosate | Organophosphate | 0.480 | 0.010 | −0.024 | −0.022 | 0.184 | −0.009 | −0.091 |
| Metribuzin | Triazinone | 0.011 | 0.944 | −0.067 | −0.078 | −0.001 | −0.005 | 0.053 |
| Metribuzin-diketo | Triazinone | −0.044 | 0.942 | −0.079 | 0.124 | 0.001 | −0.004 | 0.036 |
| Metribuzin-desamino-diketo | Triazinone | −0.044 | 0.942 | −0.079 | 0.124 | 0.001 | −0.004 | 0.036 |
| Diuron | Phenylurea | 0.042 | 0.877 | −0.062 | −0.073 | −0.003 | −0.008 | 0.059 |
| CGA 62826 | Acylamino acid | −0.006 | 0.742 | 0.204 | −0.051 | 0.000 | 0.019 | −0.125 |
| CGA 108906 | Acylamino acid | −0.006 | 0.742 | 0.204 | −0.051 | 0.000 | 0.020 | −0.125 |
| Methyl-desphenyl-chloridazon | Pyridazinone | −0.001 | −0.005 | 0.916 | 0.009 | −0.009 | 0.024 | 0.043 |
| Desphenyl chloridazon | Pyridazinone | −0.002 | −0.014 | 0.894 | 0.018 | −0.008 | 0.026 | 0.046 |
| 1,2,4-Triazole | Conazole | −0.010 | 0.065 | 0.780 | 0.014 | 0.006 | −0.056 | −0.028 |
| N,N-dimethylsulfamide (DMS) | Phenylsulfamide | −0.003 | 0.022 | 0.753 | 0.012 | 0.009 | −0.052 | −0.035 |
| Chloridazon | Pyridazinone | 0.004 | −0.034 | 0.653 | −0.019 | 0.010 | 0.050 | 0.046 |
| Desethyl-hydroxy-atrazine | Triazine | −0.013 | −0.014 | 0.008 | 0.992 | 0.002 | −0.001 | 0.001 |
| Deisopropyl-hydroxyatrazine | Triazine | −0.013 | −0.014 | 0.008 | 0.992 | 0.002 | −0.001 | 0.001 |
| 2,6-dichlorobenzoic acid | Nitrile herbicides | −0.007 | −0.010 | 0.004 | 0.986 | 0.002 | −0.002 | 0.000 |
| Didealkyl-hydroxy-atrazine | Triazine | 0.284 | 0.060 | 0.012 | 0.482 | −0.002 | 0.004 | −0.034 |
| Mecoprop | Phenoxy | 0.005 | 0.004 | 0.006 | 0.006 | 0.971 | 0.002 | 0.020 |
| Dichlorprop | Phenoxy | 0.009 | −0.014 | 0.013 | 0.004 | 0.967 | 0.002 | 0.022 |
| MCPA | Phenoxy | 0.046 | 0.009 | −0.011 | −0.006 | 0.960 | −0.001 | −0.022 |
| Atrazin, desisopropyl | Triazine | 0.000 | −0.004 | −0.030 | 0.031 | 0.001 | 0.805 | 0.000 |
| Hexazinone | Triazinone | −0.021 | 0.010 | 0.024 | 0.028 | 0.000 | 0.657 | 0.000 |
| Atrazine, desethyl- | Triazine | 0.027 | 0.009 | −0.002 | −0.085 | 0.001 | 0.606 | −0.005 |
| Atrazine | Triazine | −0.014 | 0.003 | 0.003 | 0.018 | 0.002 | 0.504 | 0.001 |
| Atrazine, hydroxy- | Triazine | −0.167 | −0.097 | 0.035 | 0.005 | 0.014 | 0.000 | 0.902 |
| Ethylenthiourea | Dithiocarbamate | 0.318 | 0.149 | 0.036 | −0.036 | 0.003 | −0.005 | 0.630 |
| Variance explained | 7.645 | 4.540 | 3.153 | 2.838 | 2.705 | 1.714 | 1.204 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Skaarup, C.; Wodschow, K.; Voutchkova, D.D.; Schullehner, J.; Raaschou-Nielsen, O.; Andersen, H.R.; Hansen, B.; Ersbøll, A.K. Geographical Distribution and Pattern of Pesticides in Danish Drinking Water 2002–2018: Reducing Data Complexity. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 823. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph19020823
Skaarup C, Wodschow K, Voutchkova DD, Schullehner J, Raaschou-Nielsen O, Andersen HR, Hansen B, Ersbøll AK. Geographical Distribution and Pattern of Pesticides in Danish Drinking Water 2002–2018: Reducing Data Complexity. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health. 2022; 19(2):823. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph19020823
Chicago/Turabian StyleSkaarup, Carina, Kirstine Wodschow, Denitza D. Voutchkova, Jörg Schullehner, Ole Raaschou-Nielsen, Helle Raun Andersen, Birgitte Hansen, and Annette Kjær Ersbøll. 2022. "Geographical Distribution and Pattern of Pesticides in Danish Drinking Water 2002–2018: Reducing Data Complexity" International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health 19, no. 2: 823. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph19020823
APA StyleSkaarup, C., Wodschow, K., Voutchkova, D. D., Schullehner, J., Raaschou-Nielsen, O., Andersen, H. R., Hansen, B., & Ersbøll, A. K. (2022). Geographical Distribution and Pattern of Pesticides in Danish Drinking Water 2002–2018: Reducing Data Complexity. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 19(2), 823. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph19020823






