Changes in Otorhinolaryngologic Disease Incidences before and during the COVID-19 Pandemic in Korea
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methods
2.1. Ethics
2.2. Study Population
2.3. Otorhinolarynologic Diseases
2.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
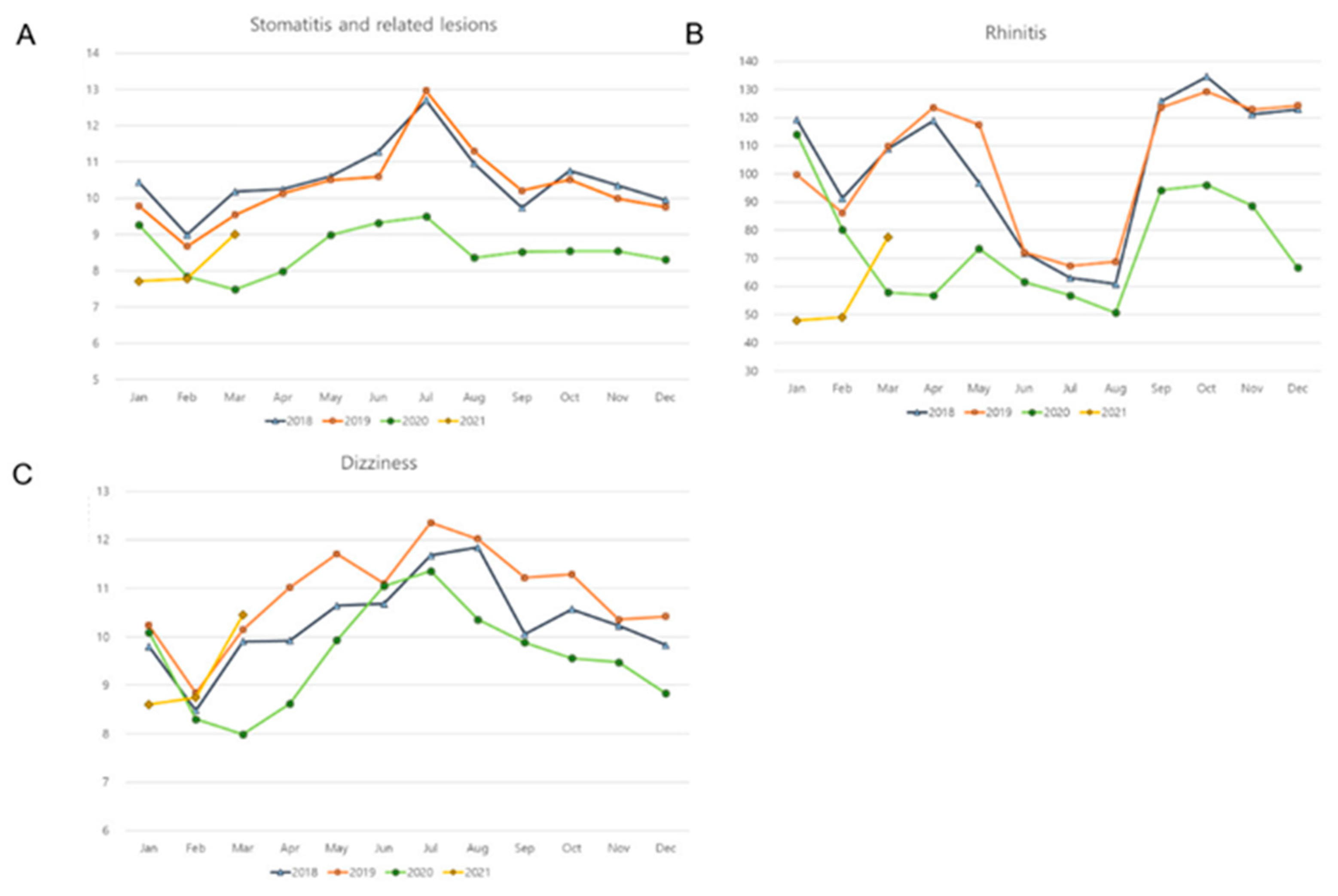
3.1. Incidences of Infectious Diseases
3.2. Incidences of Noninfectious Diseases
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sahoo, S.K.; Dhandapani, S.; Singh, A.; Gendle, C.; Karthigeyan, M.; Salunke, P.; Aggarwal, A.; Singla, N.; Singla, R.; Tripathi, M.; et al. COVID-19: Changing patterns among neurosurgical patients from North India, efficacy of repeat testing, and inpatient prevalence. Neurosurg. Focus 2020, 49, E7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goyal, N.; Venkataram, T.; Singh, V.; Chaturvedi, J. Collateral damage caused by COVID-19: Change in volume and spectrum of neurosurgery patients. J. Clin. Neurosci. 2020, 80, 156–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bambra, C.; Riordan, R.; Ford, J.; Matthews, F. The COVID-19 pandemic and health inequalities. J. Epidemiol. Commun. Health 2020, 74, 964–968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cowling, B.J.; Ali, S.T.; Ng, T.W.Y.; Tsang, T.K.; Li, J.C.M.; Fong, M.W.; Liao, Q.; Kwan, M.Y.; Lee, S.L.; Chiu, S.S.; et al. Impact assessment of non-pharmaceutical interventions against coronavirus disease 2019 and influenza in Hong Kong: An observational study. Lancet Public Health 2020, 5, e279–e288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, X. COVID-19 changes the lifestyle of the population and subtly reduces the incidence of metabolic disease. Med. Hypotheses 2021, 146, 110416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, K.H.; Lee, S.W.; Kim, T.S.; Huh, H.J.; Lee, J.; Kim, S.Y.; Park, J.-S.; Kim, G.J.; Sung, H.; Roh, K.H.; et al. Guidelines for Laboratory Diagnosis of Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19) in Korea. Ann. Lab. Med. 2020, 40, 351–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choi, Y.; Kim, J.S.; Choi, H.; Lee, H.; Lee, C.H. Assessment of Social Distancing for Controlling COVID-19 in Korea: An Age-Structured Modeling Approach. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 7474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eccles, R. An Explanation for the Seasonality of Acute Upper Respiratory Tract Viral Infections. Acta Oto-Laryngol. 2002, 122, 183–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Price, R.H.M.; Graham, C.; Ramalingam, S. Association between viral seasonality and meteorological factors. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torretta, S.; Cantoni, B.; Bertolozzi, G.; Capaccio, P.; Milani, G.; Pignataro, L.; Aleo, S.; Marchisio, P. Has Otitis Media Disappeared during COVID-19 Pandemic? A Fortuitus Effect of Domestic Confinement. J. Clin. Med. 2021, 10, 2851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nordstokke, D.W.; Zumbo, B.D. A New Nonparametric Levene Test for Equal Variances. Psicológica 2010, 31, 401–430. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, B.; Wang, M.; Huang, X.; Xie, M.; Pan, L.; Liu, H.; Liu, Z.; Zhou, P. Changes in Incidence of Notifiable Infectious Diseases in China Under the Prevention and Control Measures of COVID-19. Front. Public Health 2021, 9, 1548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Diesner-Treiber, S.C.; Voitl, P.; Voitl, J.J.M.; Langer, K.; Kuzio, U.; Riepl, A.; Patel, P.; Mühl-Riegler, A.; Mühl, B. Respiratory Infections in Children During a Covid-19 Pandemic Winter. Front. Pediatr. 2021, 9, 740785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soo, R.J.J.; Chiew, C.J.; Ma, S.; Pung, R.; Lee, V. Decreased Influenza Incidence under COVID-19 Control Measures, Singapore. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2020, 26, 1933–1935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wong, N.-S.; Leung, C.-C.; Lee, S.-S. Abrupt Subsidence of Seasonal Influenza after COVID-19 Outbreak, Hong Kong, China. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2020, 26, 2752–2754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noh, J.Y.; Seong, H.; Yoon, J.G.; Song, J.Y.; Cheong, H.J.; Kim, W.J. Social Distancing against COVID-19: Implication for the Control of Influenza. J. Korean Med. Sci. 2020, 35, e182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamamoto, T.; Komiya, K.; Fujita, N.; Okabe, E.; Hiramatsu, K.; Kadota, J.-I. COVID-19 pandemic and the incidence of community-acquired pneumonia in elderly people. Respir. Investig. 2020, 58, 435–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, C. The COVID-19 Pandemic and the Incidence of the Non-COVID-19 Pneumonia in Adults. Front. Med. 2021, 8, 737999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torretta, S.; Capaccio, P.; Coro, I.; Bosis, S.; Pace, M.E.; Bosi, P.; Pignataro, L.; Marchisio, P. Incidental lowering of otitis-media complaints in otitis-prone children during COVID-19 pandemic: Not all evil comes to hurt. Eur. J. Pediatrics 2021, 180, 649–652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qualls, N.; Levitt, A.; Kanade, N.; Wright-Jegede, N.; Dopson, S.; Biggerstaff, M.; Reed, C.; Uzicanin, A.; Frank, M.; Holloway, R.; et al. Community Mitigation Guidelines to Prevent Pandemic Influenza—United States, 2017. MMWR. Recomm. Rep. 2017, 66, 1–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baker, R.E.; Park, S.W.; Yang, W.; Vecchi, G.A.; Metcalf, C.J.E.; Grenfell, B.T. The impact of COVID-19 nonpharmaceutical interventions on the future dynamics of endemic infections. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2020, 117, 30547–30553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahmed, F.; Zviedrite, N.; Uzicanin, A. Effectiveness of workplace social distancing measures in reducing influenza transmission: A systematic review. BMC Public Health 2018, 18, 518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, J.-Y.; Yun, J.-G.; Noh, J.-Y.; Cheong, H.-J.; Kim, W.-J. Covid-19 in South Korea—Challenges of Subclinical Manifestations. New Engl. J. Med. 2020, 382, 1858–1859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bardsley, M.; Morbey, R.A.; Hughes, H.E.; Beck, C.R.; Watson, C.H.; Zhao, H.; Ellis, J.; Smith, G.E.; Elliot, A.J. Epidemiology of respiratory syncytial virus in children younger than 5 years in England during the COVID-19 pandemic, measured by laboratory, clinical, and syndromic surveillance: A retrospective observational study. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2022, (in press). [CrossRef]
- Stockmann, C.; Ampofo, K.; Hersh, A.L.; Carleton, S.T.; Korgenski, K.; Sheng, X.; Pavia, A.T.; Byington, C.L. Seasonality of Acute Otitis Media and the Role of Respiratory Viral Activity in Children. Pediatr. Infect. Dis. J. 2013, 32, 314–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Audi, A.; Al Ibrahim, M.; Kaddoura, M.; Hijazi, G.; Yassine, H.M.; Zaraket, H. Seasonality of Respiratory Viral Infections: Will COVID-19 Follow Suit? Front. Public Health 2020, 8, 567184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.Y.; Kim, D.W. Does the Clinical Spectrum of Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19) Show Regional Differences? Clin. Exp. Otorhinolaryngol. 2020, 13, 83–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, J.-H.; Jang, W.; Kim, S.-W.; Lee, J.; Lim, Y.-S.; Cho, C.-G.; Park, S.-W.; Kim, B.H. The Clinical Manifestations and Chest Computed Tomography Findings of Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19) Patients in China: A Proportion Meta-Analysis. Clin. Exp. Otorhinolaryngol. 2020, 13, 95–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prevention KCfDCa. Coronavirus Disease. 2019–2020. Available online: http://ncov.mohw.go.kr (accessed on 5 October 2020).
- Choi, W.S. The National Influenza Surveillance System of Korea. Infect. Chemother. 2019, 51, 98–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, J.-E.; Ryu, Y. Transmissibility and severity of influenza virus by subtype. Infect. Genet. Evol. 2018, 65, 288–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Diseases | Before COVID-19 | During COVID-19 | p Values of Difference | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mean | SD | Mean | SD | Mean | Variance | |
| URI | 1,819,884.7 | 381,893.5 | 792,754.8 | 154,661.7 | <0.001 * | 0.008 † |
| Influenza | 221,636.5 | 350,137.6 | 1776.9 | 1167.4 | <0.001 * | 0.048 † |
| Acute tonsillitis | 659,617.9 | 118,633.2 | 279,773.2 | 49,945.3 | <0.001 * | 0.008 † |
| Peritonsillar abscess | 86,037.4 | 15,697.1 | 36,877.9 | 5960.2 | <0.001 * | 0.008 † |
| Retropharyngeal and parapharyngeal abscess | 57,056.0 | 11,596.6 | 24,739.4 | 4299.3 | <0.001 * | 0.008 † |
| Acute laryngitis and bronchitis | 419,958.0 | 100,744.8 | 181,879.4 | 31,304.8 | <0.001 * | 0.008 † |
| Stomatitis and related lesions | 102,796.3 | 10,744.6 | 84,670.7 | 6224.4 | <0.001 * | 0.077 |
| Acute sinusitis | 539,828.7 | 124,631.7 | 243,105.9 | 58,250.4 | <0.001 * | 0.030 † |
| Rhinitis | 1,028,775.8 | 238,879.4 | 675,294.8 | 170,040.4 | <0.001 * | 0.055 |
| Otitis media | 343,229.7 | 55,749.3 | 148,861.7 | 23,754.1 | <0.001 * | 0.008 † |
| Dizziness | 104,910.8 | 10,232.1 | 96,040.7 | 10,232.2 | 0.022 * | 0.537 |
| Diseases | Before COVID-19 | During COVID-19 | p Values of Difference | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mean | SD | Mean | SD | Mean | Variance | |
| Men | ||||||
| URI | 808,009.1 | 166,143.8 | 345,512.2 | 67,529.2 | <0.001 * | 0.008 † |
| Influenza | 102,389.1 | 161,148.9 | 817.0 | 540.9 | <0.001 * | 0.074 |
| Acute tonsillitis | 292,892.4 | 50,747.4 | 119,724.5 | 20,979.9 | <0.001 * | 0.008 † |
| Peritonsillar abscess | 38,552.1 | 6811.1 | 16,007.3 | 2472.9 | <0.001 * | 0.008 † |
| Retropharyngeal and parapharyngeal abscess | 24,954.4 | 4882.1 | 10,892.8 | 1827.7 | <0.001 * | 0.008 † |
| Acute laryngitis and Bronchitis | 179,642.1 | 43,109.3 | 78,923.5 | 13,443.6 | <0.001 * | 0.008 † |
| Stomatitis and related lesions | 46,071.0 | 4914.4 | 37,484.5 | 2251.5 | <0.001 * | 0.069 |
| Acute sinusitis | 257,029.9 | 57,383.9 | 121,754.1 | 29,431.8 | <0.001 * | 0.038 † |
| Rhinitis | 493,887.1 | 113,755.6 | 340,218.0 | 87,028.1 | <0.001 * | 0.134 |
| Otitis media | 169,809.7 | 27,017.7 | 72,879.5 | 11,794.7 | <0.001 * | 0.008 † |
| Dizziness | 37,218.4 | 4031.7 | 34,242.0 | 3812.3 | 0.043 * | 0.610 |
| Women | ||||||
| URI | 1,011,875.6 | 216,322.6 | 447,242.6 | 87,408.5 | <0.001 * | 0.006 † |
| Influenza | 119,247.3 | 189,106.3 | 959.9 | 627.6 | <0.001 * | 0.037 † |
| Acute tonsillitis | 366,725.5 | 68337.2 | 160,048.6 | 29,027.1 | <0.001 * | 0.006 † |
| Peritonsillar abscess | 47,485.3 | 8947.4 | 20,870.6 | 3507.1 | <0.001 * | 0.006 † |
| Retropharyngeal and parapharyngeal abscess | 32,101.6 | 6739.1 | 13,846.5 | 2491.6 | <0.001 * | 0.006 † |
| Acute laryngitis and bronchitis | 240,315.9 | 57,726.4 | 102,955.8 | 17,975.3 | <0.001 * | 0.006 † |
| Stomatitis and related lesions | 56,725.3 | 5947.9 | 47186.2 | 4027.3 | <0.001 * | 0.035 † |
| Acute sinusitis | 282,798.8 | 67,455.3 | 121,351.8 | 28,910.2 | <0.001 * | 0.020 † |
| Rhinitis | 534,888.8 | 125,704.1 | 335,076.8 | 83,425.7 | <0.001 * | 0.333 |
| Otitis media | 173,419.9 | 28,775.7 | 75,982.2 | 11,992.1 | <0.001 * | 0.006 † |
| Dizziness | 67,692.4 | 6259.8 | 61,798.7 | 6524.2 | 0.008 * | 0.926 |
| Diseases | Before COVID-19 | During COVID-19 | p Values of Difference | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mean | SD | Mean | SD | Mean | Variance | |
| Age 0–19 years old | ||||||
| URI | 718,215.0 | 128,970.4 | 316,330.5 | 115,637.1 | <0.001 * | 0.022 † |
| Influenza | 118,451.5 | 180,263.3 | 609.6 | 412.3 | <0.001 * | 0.050 |
| Acute tonsillitis | 248,149.3 | 48,522.3 | 97,814.2 | 32,298.2 | <0.001 * | 0.026 † |
| Peritonsillar abscess | 25,512.7 | 4769.3 | 10281.5 | 3223.4 | <0.001 * | 0.023 † |
| Retropharyngeal and parapharyngeal abscess | 19,341.0 | 3642.8 | 7731.1 | 2781.8 | <0.001 * | 0.012 † |
| Acute laryngitis and bronchitis | 110,269.8 | 27,491.9 | 41,969.3 | 14,762.1 | <0.001 * | 0.017 † |
| Stomatitis and related lesions | 23,150.9 | 8331.2 | 16,477.1 | 1903.5 | <0.001 * | 0.475 |
| Acute sinusitis | 290,623.6 | 67,944.1 | 131,921.8 | 50,112.8 | <0.001 * | 0.143 |
| Rhinitis | 466,588.7 | 109,804.7 | 302,083.9 | 103,858.1 | <0.001 * | 0.569 |
| Otitis media | 227,843.8 | 49,043.2 | 68,770.6 | 20,508.9 | <0.001 * | 0.008 † |
| Dizziness | 5336.8 | 1149.6 | 4584.1 | 1436.5 | 0.089 | 0.210 |
| Age 20–59 years old | ||||||
| URI | 784,291.7 | 227,502.8 | 311,720.8 | 53,937.4 | <0.001 * | 0.008 † |
| Influenza | 85,726.2 | 147,894.7 | 814.1 | 582.5 | <0.001 * | 0.124 |
| Acute tonsillitis | 328,817.8 | 77,712.5 | 138,490.6 | 20,547.8 | <0.001 * | 0.008 † |
| Peritonsillar abscess | 46,454.8 | 10,447.3 | 19,399.9 | 2918.4 | <0.001 * | 0.008 † |
| Retropharyngeal and parapharyngeal abscess | 29,282.9 | 7288.1 | 12,392.9 | 2123.3 | <0.001 * | 0.012 † |
| Acute laryngitis and bronchitis | 221,135.6 | 59,408.4 | 91,148.6 | 16,522.8 | <0.001 * | 0.008 † |
| Stomatitis and related lesions | 44,485.5 | 3424.8 | 35,926.8 | 2579.5 | <0.001 * | 0.052 |
| Acute sinusitis | 198,909.4 | 52,964.1 | 84,172.0 | 14,543.4 | <0.001 * | 0.012 † |
| Rhinitis | 412,045.3 | 111,175.6 | 259,300.3 | 73,503.3 | <0.001 * | 0.151 |
| Otitis media | 72,384.2 | 7520.6 | 44,657.5 | 3794.8 | <0.001 * | 0.008 † |
| Dizziness | 44,766.6 | 4387.5 | 39478.7 | 4007.3 | 0.001 * | 0.993 |
| Age 60+ years old | ||||||
| URI | 317,955.5 | 106,564.2 | 164,960.2 | 29,720.8 | <0.001 * | 0.019 † |
| Influenza | 17,514.0 | 34,873.4 | 353.5 | 191.7 | <0.001 * | 0.204 |
| Acute tonsillitis | 82,870.0 | 22,396.6 | 43,566.0 | 5408.0 | <0.001 * | 0.030 † |
| Peritonsillar abscess | 14,101.9 | 3850.2 | 7210.1 | 1037.9 | <0.001 * | 0.023 † |
| Retropharyngeal and parapharyngeal abscess | 8451.3 | 2324.4 | 4626.0 | 659.8 | <0.001 * | 0.045 † |
| Acute laryngitis and bronchitis | 88,750.5 | 23,658.4 | 48,867.8 | 6315.1 | <0.001 * | 0.027 † |
| Stomatitis and related lesions | 35,194.9 | 2313.6 | 32,297.7 | 2474.2 | 0.002 * | 0.581 |
| Acute sinusitis | 50,521.8 | 14,750.5 | 27,119.8 | 3757.3 | <0.001 * | 0.029 † |
| Rhinitis | 150,577.6 | 40,633.5 | 114,227.2 | 20,862.3 | 0.004 * | 0.013 † |
| Otitis media | 43,161.5 | 2499.3 | 35,538.9 | 2120.9 | <0.001 * | 0.012 † |
| Dizziness | 54,853.7 | 5045.5 | 52,020.8 | 4923.0 | 0.101 | 0.679 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kim, S.Y.; Yoo, D.M.; Kim, J.H.; Kwon, M.J.; Kim, J.-H.; Chung, J.; Choi, H.G. Changes in Otorhinolaryngologic Disease Incidences before and during the COVID-19 Pandemic in Korea. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 13083. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph192013083
Kim SY, Yoo DM, Kim JH, Kwon MJ, Kim J-H, Chung J, Choi HG. Changes in Otorhinolaryngologic Disease Incidences before and during the COVID-19 Pandemic in Korea. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health. 2022; 19(20):13083. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph192013083
Chicago/Turabian StyleKim, So Young, Dae Myoung Yoo, Ji Hee Kim, Mi Jung Kwon, Joo-Hee Kim, Juyong Chung, and Hyo Geun Choi. 2022. "Changes in Otorhinolaryngologic Disease Incidences before and during the COVID-19 Pandemic in Korea" International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health 19, no. 20: 13083. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph192013083
APA StyleKim, S. Y., Yoo, D. M., Kim, J. H., Kwon, M. J., Kim, J.-H., Chung, J., & Choi, H. G. (2022). Changes in Otorhinolaryngologic Disease Incidences before and during the COVID-19 Pandemic in Korea. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 19(20), 13083. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph192013083







