Oxycodone-Naloxone Combination Hinders Opioid Consumption in Osteoarthritic Chronic Low Back Pain: A Retrospective Study with Two Years of Follow-Up
Abstract
:1. Introduction
1.1. Opioids for Chronic Pain: Misuse and Opioid Epidemic
1.2. Opioid-Induced Bowel Dysfunction (OIBD)
1.3. Opioid Tolerance
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Design and Procedures
2.2. Data Collection
2.3. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Treede, R.D.; Rief, W. A classification of chronic pain for ICD-11. Pain 2015, 156, 1003–1007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Vittori, A.; Petrucci, E.; Cascella, M.; Innamorato, M.; Cuomo, A.; Giarratano, A.; Petrini, F.; Marinangeli, F. Pursuing the Recovery of Severe Chronic Musculoskeletal Pain in Italy: Clinical and Organisational Perspectives from a SIAARTI Survey. J. Pain Res. 2021, 14, 3401–3410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheung, C.W.; Choi, S.W. Chronic opioid therapy for chronic non-cancer pain: A review and comparison of treatment guidelines. Pain Physician 2014, 17, 401–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reid, J.K.; Harker, J. Epidemiology of chronic non-cancer pain in Europe: Narrative review of prevalence, pain treatments and pain impact. Curr. Med. Res. Opin. 2011, 27, 449–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ballantyne, J.C.; Shin, N.S. Efficacy of opioids for chronic pain: A review of the evidence. Clin. J. Pain 2008, 24, 469–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Busse, J.W.; Craigie, S. Guideline for opioid therapy and chronic noncancer pain. CMAJ 2017, 189, E659–E666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- The British Pain Society. Opioids for persistent pain: Summary of guidance on good practice from the British Pain Society. Br. Pain Soc. 2010, 6, 9–10. [Google Scholar]
- Ballantyne, J.C. Opioid analgesia: Perspectives on right use and utility. Pain Physician 2007, 10, 479–491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, G.H.; Bruera, E. The Opioid Epidemic in the United States—Overview, origins, and potential solutions. Obstet. Gynaecol. Surv. 2019, 74, 278–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- The Lancet. A time of crisis for the opioid epidemic in the USA. Lancet 2021, 398, 277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dydyk, A.M.; Jain, N.K.; Gupta, M. Opioid Use Disorder. Available online: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK553166/ (accessed on 21 June 2022).
- Volkow, N.; Benveniste, H. Use and Misuse of Opioids in Chronic Pain. Annu. Rev. Med. 2018, 69, 451–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- John, W.S.; Zhu, H. Prevalence, patterns, and correlates of multiple substance use disorders among adult primary care patients. Drug Alcohol Depend 2018, 187, 79–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pappagallo, M. Incidence, prevalence, and management of opioid bowel dysfunction. Am. J. Surg. 2001, 182, 11S–18S. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ducrotté, P.; Caussé, C. The Bowel Function Index: A new validated scale for assessing opioid-induced constipation. Curr. Med. Res. Opin. 2012, 28, 457–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brock, C.; Olesen, S.S. Opioid-Induced Bowel Dysfunction. Drugs 2012, 72, 1847–1865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Schepper, H.U.; Cremonini, F. Opioids and the gut: Pharmacology and current clinical experience. Neurogastroenterol. Motil. 2004, 16, 383–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, H.K.; Nelson, L.S. Reducing the harm of opioid overdose with the safe use of naloxone: A pharmacologic review. Expert Opin. Drug Saf. 2015, 14, 1137–1146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sandner-Kiesling, A.; Leyendecker, P. Long term efficacy and safety of combined prolonged-release oxycodone and naloxone in the management of non-cancer chronic pain. Int. J. Clin. Pract. 2010, 64, 763–774. [Google Scholar] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Meissner, W.; Leyendecker, P. A randomised controlled trial with prolonged-release oral oxycodone and naloxone to prevent and reverse opioid-induced constipation. Eur. J. Pain 2009, 13, 56–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chindalore, V.L.; Craven, R.A. Adding ultra-low-dose naltrexone to oxycodone enhances and prolongs analgesia. J. Pain 2005, 6, 392–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Webster, L.R.; Butera, P.G. Oxytrex minimises physical dependence while providing effective analgesia: A randomised controlled trial in low-back pain. J. Pain 2006, 7, 937–946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stein, C. New concepts in opioid analgesia. Expert Opin. Investig. Drugs 2018, 27, 765–775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jeevendra, M.J.A.; Mao, J.; Bittner, E.A. Opioid tolerance in critical illness. New Engl. J. Med. 2019, 380, 365–378. [Google Scholar]
- Mercadante, S.; Ferrera, P. Frequency, indications, outcomes, and predictive factors of opioid switching in an acute palliative care unit. J. Pain Symptom. Manag. 2009, 37, 632–641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morgan, M.M.; MacDonald, J.C. Analysis of opioid efficacy, tolerance, addiction and dependence from cell culture to human. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2011, 164, 1322–1334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hayhurst, C.J.; Durieux, M.E. Differential Opioid Tolerance and Opioid-induced Hyperalgesia: A Clinical Reality. Anesthesiology 2016, 124, 483–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, J.T.; Ingram, S.L. Regulation of mu-opioid receptors: Desensitisation, phosphorylation, internalisation and tolerance. Pharmacol. Rev. 2013, 65, 223–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Koch, T.; Höllt, V. Role of receptor internalisation in opioid tolerance and dependence. Pharmacol. Ther. 2008, 117, 199–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sim-Selley, L.J.; Scoggins, K.L. Region-dependent attenuation of mu opioid receptor-mediated G-protein activation in mouse CNS as a function of morphine tolerance. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2007, 151, 1324–1333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Freynhagen, R.; Baron, R. The evaluation of neuropathic components in low back pain. Curr. Pain Headache Rep. 2009, 13, 185–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bian, J.M.; Wu, N. Opioid receptor trafficking and signalling: What happens after opioid receptor activation? Cell Mol. Neurobiol. 2012, 32, 167–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, B.; Du, L. Naloxone protects rat dopaminergic neurons against inflammatory damage through inhibition of microglia activation and superoxide generation. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 2000, 293, 607–617. [Google Scholar]
- Hutchinson, M.R.; Zhang, Y. Non-stereo selective reversal of neuropathic pain by naloxone and naltrexone: Involvement of toll-like receptor 4 (TLR4). Eur. J. Neurosci. 2008, 28, 20–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bruno, K.; Woller, S.A. Targeting toll-like receptor-4 (TLR4)-an emerging therapeutic target for persistent pain states. Pain 2018, 159, 1908–1915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Q. Antagonists of toll like receptor 4 may be a new strategy to counteract opioid-induced hyperalgesia and opioid tolerance. Med. Hypothesis 2012, 79, 754–756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, S.L.; Tsai, R.Y. Co-administration of ultra-low dose naloxone attenuates morphine tolerance in rats via attenuation of NMDA receptor neurotransmission and suppression of neuroinflammation in the spinal cords. Pharmacol. Biochem. Behav. 2010, 96, 236–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vondrackova, D.; Leyendecker, P. Analgesic efficacy and safety of oxycodone in combination with naloxone as prolonged release tablets in patients with moderate to severe chronic pain. J. Pain 2008, 9, 1144–1154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheatle, M.D.; Compton, P.A. Development of the Revised Opioid Risk Tool to Predict Opioid Use Disorder in Patients with Chronic Nonmalignant Pain. J. Pain 2019, 20, 842–851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simpson, K.; Leyendecker, P.; Hopp, M.; Müller-Lissner, S.; Löwenstein, O.; de Andrés, J.; Ferrarons, J.T.; Bosse, B.; Krain, B.; Nichols, T.; et al. Fixed-ratio combination oxycodone/naloxone compared with oxycodone alone for the relief of opioid-induced constipation in moderate-to-severe noncancer pain. Curr. Med. Res. Opin. 2008, 24, 3503–3512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leppert, W.; Zajaczkowska, R.; Wordliczek, J. Oxycodone/naloxone in the management of patients with pain and opioid–induced bowel dysfunction. Curr. Drug Targets 2014, 15, 124–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nadstawek, J.; Leyendecker, P.; Hopp, M.; Ruckes, C.; Wirz, S.; Fleischer, W.; Reimer, K. Patient assessment of a novel therapeutic approach for the treatment of severe, chronic pain. Int. J. Clin. Pract. 2008, 62, 1159–1167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kim, E.S. Oxycodone/Naloxone Prolonged Release: A Review in Severe Chronic Pain. Clin. Drug Investig. 2017, 37, 1191–1201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burness, C.B.; Keating, G.M. Oxycodone/Naloxone Prolonged-Release: A Review of Its Use in the Management of Chronic Pain While Counteracting Opioid-Induced Constipation. Drugs 2014, 74, 353–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Poelaert, J.; Koopmans-Klein, G.; Dioh, A.; Louis, F.; Gorissen, M.; Logé, D.; van Megen, Y.J. Treatment with Prolonged-Release Oxycodone/Naloxone Improves Pain Relief and Opioid-Induced Constipation Compared with Prolonged-Release Oxycodone in Patients with Chronic Severe Pain and Laxative-Refractory Constipation. Clin. Ther. 2015, 37, 784–792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Baron, R.; Likar, R.; Martin-Mola, E.; Blanco, F.J.; Kennes, L.; Müller, M.; Falke, D.; Steigerwald, I. Effectiveness of tapentadol prolonged release (PR) compared with oxycodone/naloxone PR for the management of severe chronic low back pain with a neuropathic component: A randomized, controlled, open-label, phase 3b/4 study. Pain Pract. 2016, 16, 580–599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ueda, H.; Fukushima, N. Low doses of naloxone produce analgesia in the mouse brain by blocking presynaptic autoinhibition of encephaline release. Neurosci. Lett. 1986, 278, 740–741. [Google Scholar]
- Gan, T.J.; Ginsberg, B. Opioid-sparing effects of a low-dose infusion of naloxone in patient-administered morphine sulphate. Anesthesiology 1997, 87, 1075–1081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Movafegh, A.; Shoeibi, G. Naloxone infusion and post-hysterectomy morphine consumption: A double blind, placebo-controlled study. Acta Anaesthesiol. Scand. 2012, 56, 1241–1249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burns, L.H.; Wang, H.Y. Ultra-Low-Dose Naloxone or Naltrexone to Improve Opioid Analgesia: The History, the Mystery and a Novel Approach. Clin. Med. Insights Ther. 2010, 2, 857–868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Demographics and Baseline Clinical Features Variables (n = 43) | ||
|---|---|---|
| Group OXN | Group OXY | |
| n = 22 | n = 21 | |
| Age (years) | 74.5 (70.0–78.0) | 73.0 (64.8–82.3) |
| Male | 7 | 7 |
| Female | 15 | 14 |
| Caucasians | 22 | 21 |
| Non Caucasians | 0 | 0 |
| VAS at baseline (0–100) | 75.5 (68.0–83.0) | 76.0 (65.8–85.3) |
| BFI at baseline (0–100) | 32.5 (22.0–50.0) | 37.8 (25.4–51.4) |
| Start opioid daily dosage (mg) | 10.0 (10.0–10.0) | 10.0 (10.0–10.0) |
| Non opioid analgesics (paracetamol, NSAIDs) | 18 | 19 |
| Gabapentinoids at baseline | 7 | 6 |
| SSRI at baseline | 4 | 3 |
| SNRI at baseline | 2 | 3 |
| TCA at baseline | 3 | 2 |
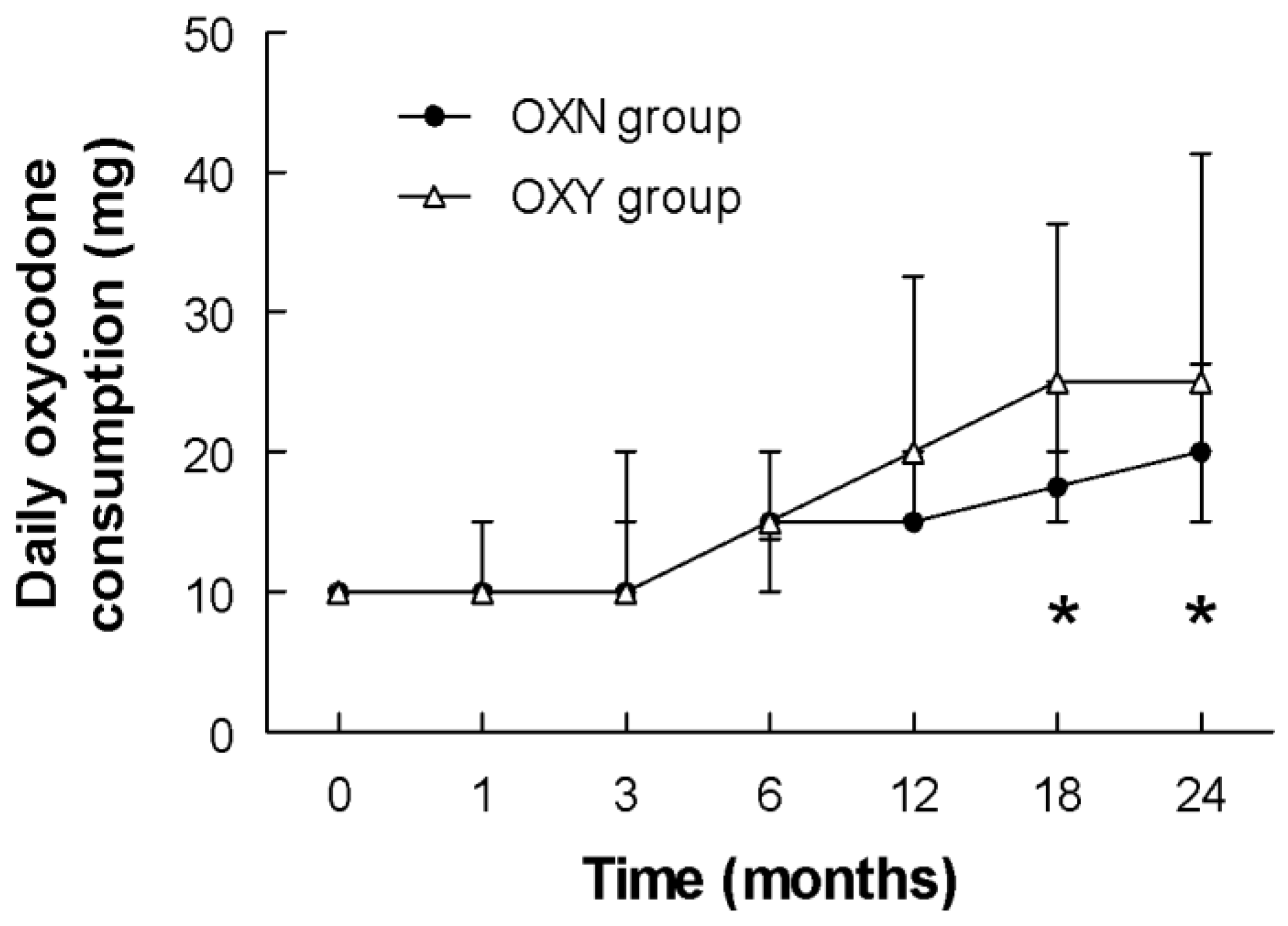
| Daily Oxycodone PR Consumption in mg | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Group | Time (months) | ||||||
| 0 | 1 | 3 | 6 | 12 | 18 | 24 | |
| OXY | 10.0 (10.0–10.0) | 10.0 (10.0–10.0) | 10.0 (10.0–15.0) | 15.0 (13.8–20.0) | 20.0 (15.0–32.5) | 25.0 (20.0–36.3) | 25.0 (20.0–41.3) |
| OXN | 10.0 (10.0–10.0) | 10.0 (10.0–15.0) | 10.0 (10.0–20.0) | 15.0 (10.0–20.0) | 15.0 (15.0–20.0) | 17.5 (15.0–25.0) | 20.0 (15.0–26.3) |
| p | 0.8181 | 0.4146 | 0.7503 | 0.1326 | 0.1067 | 0.0142 | 0.0052 |
| Reported Opioid Side Effects or Adverse Events | ||
|---|---|---|
| Group OXN | Group OXY | |
| n = 27 | n = 26 | |
| Nausea | 4 | 3 |
| Vomiting | 0 | 0 |
| Lightheadedness | 2 | 2 |
| Myoclonus | 1 | 0 |
| Itching | 1 | 0 |
| Moderate to severe constipation (BFI ≥ 60) | 4 | 11 * |
| Drowsiness/sedation | 5 | 6 |
| Strong sedation | 2 | 2 |
| Dizziness | 1 | 1 |
| Dry mouth | 0 | 0 |
| Fatigue | 0 | 1 |
| Cognitive impairment | 0 | 0 |
| Hyperalgesia/allodynia | 0 | 0 |
| Respiratory depression | 0 | 0 |
| Gastritis | 1 | 0 |
| Stupor | 1 | 0 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Polati, E.; Nizzero, M.; Rama, J.; Martini, A.; Gottin, L.; Donadello, K.; Del Balzo, G.; Varrassi, G.; Marinangeli, F.; Vittori, A.; et al. Oxycodone-Naloxone Combination Hinders Opioid Consumption in Osteoarthritic Chronic Low Back Pain: A Retrospective Study with Two Years of Follow-Up. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 13354. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph192013354
Polati E, Nizzero M, Rama J, Martini A, Gottin L, Donadello K, Del Balzo G, Varrassi G, Marinangeli F, Vittori A, et al. Oxycodone-Naloxone Combination Hinders Opioid Consumption in Osteoarthritic Chronic Low Back Pain: A Retrospective Study with Two Years of Follow-Up. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health. 2022; 19(20):13354. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph192013354
Chicago/Turabian StylePolati, Enrico, Marta Nizzero, Jacopo Rama, Alvise Martini, Leonardo Gottin, Katia Donadello, Giovanna Del Balzo, Giustino Varrassi, Franco Marinangeli, Alessandro Vittori, and et al. 2022. "Oxycodone-Naloxone Combination Hinders Opioid Consumption in Osteoarthritic Chronic Low Back Pain: A Retrospective Study with Two Years of Follow-Up" International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health 19, no. 20: 13354. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph192013354
APA StylePolati, E., Nizzero, M., Rama, J., Martini, A., Gottin, L., Donadello, K., Del Balzo, G., Varrassi, G., Marinangeli, F., Vittori, A., Secchettin, E., & Schweiger, V. (2022). Oxycodone-Naloxone Combination Hinders Opioid Consumption in Osteoarthritic Chronic Low Back Pain: A Retrospective Study with Two Years of Follow-Up. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 19(20), 13354. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph192013354









