Prevalence, Characteristics, and Risk Factors of Retinal Hemorrhage among Full-Term Neonates in Southern China
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Design and Subjects
2.2. Examination Method
2.3. Determination and Classification of Neonatal Retinal Hemorrhage
2.4. Data Collection
2.5. Statistical Analysis
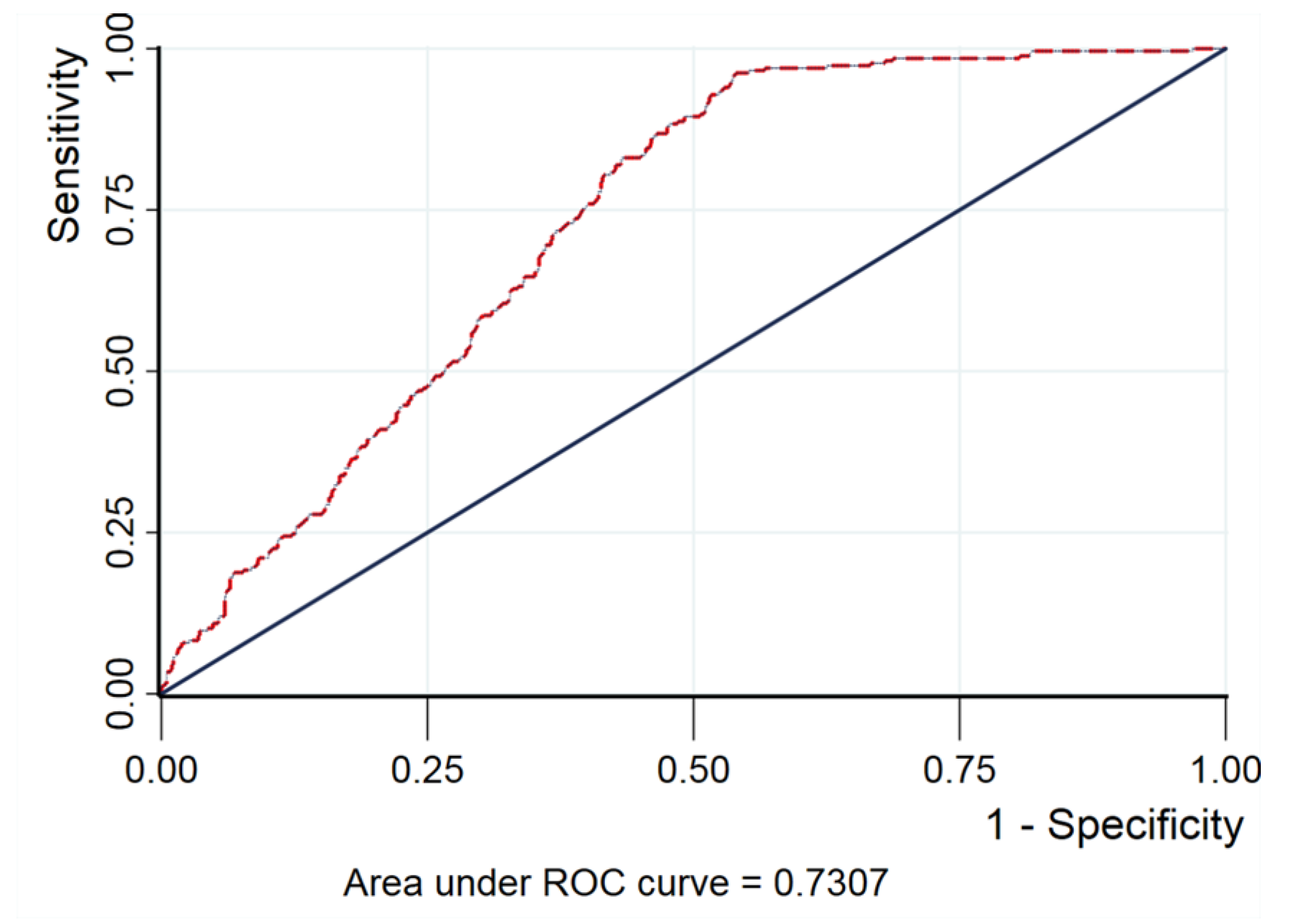
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Giles, C.L. Retinal hemorrhages in the newborn. Am. J. Ophthalmol. 1960, 49, 1005–1011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaur, B.; Taylor, D. Fundus hemorrhages in infancy. Surv. Ophthalmol. 1992, 37, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watts, P.; Maguire, S.; Kwok, T.; Talabani, B.; Mann, M.; Wiener, J.; Lawson, Z.; Kemp, A. Newborn retinal hemorrhages: A systematic review. J. AAPOS 2013, 17, 70–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hughes, L.A.; May, K.; Talbot, J.F.; Parsons, M.A. Incidence, distribution, and duration of birth-related retinal hemorrhages: A prospective study. J. AAPOS 2006, 10, 102–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, S.Y.; Morgan, L.A.; Baldwin, A.J.; Suh, D.W. Comparison of the characteristics of retinal hemorrhages in abusive head trauma versus normal vaginal delivery. J. AAPOS 2018, 22, 139–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Emerson, M.V.; Pieramici, D.J.; Stoessel, K.M.; Berreen, J.P.; Gariano, R.F. Incidence and rate of disappearance of retinal hemorrhage in newborns. Ophthalmology 2001, 108, 36–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paris, C.L.; Peyman, G.A.; Breen, C.; Blinder, K.J. Neonatal macular hemorrhage. Int. Ophthalmol. 1991, 15, 153–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, I.H.; Kim, M.S.; Heo, N.H.; Kim, S.Y. Birth-related retinal hemorrhages: The Soonchunhyang University Cheonan Hospital universal newborn eye screening (SUCH-NES) study. PLoS ONE 2021, 16, e0259378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, Y.J.; Jung, M.S.; Kim, S.Y. Retinal hemorrhage associated with perinatal distress in newborns. Korean J. Ophthalmol. 2011, 25, 311–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zwaan, J.; Cardenas, R.; O’Connor, P.S. Long-term outcome of neonatal macular hemorrhage. J. Pediatr. Ophthalmol. Strabismus 1997, 34, 286–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, M.C.; Knuppel, R.A.; O’Brien, W.F.; Weiss, A.; Spellacy, W.N.; Pietrantoni, M. Obstetric correlates of neonatal retinal hemorrhage. Obstet. Gynecol. 1993, 81, 688–694. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Besio, R.; Caballero, C.; Meerhoff, E.; Schwarcz, R. Neonatal retinal hemorrhages and influence of perinatal factors. Am. J. Ophthalmol. 1979, 87, 74–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sezen, F. Retinal haemorrhages in newborn infants. Br. J. Ophthalmol. 1971, 55, 248–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ji, M.H.; Ludwig, C.A.; Callaway, N.F.; Moshfeghi, D.M. Birth-related subconjunctival and retinal haemorrhages in the Newborn Eye Screening Test (NEST) Cohort. Eye 2019, 33, 1819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Svenningsen, L.; Lindemann, R.; Eidal, K.; Jensen, O. Neonatal retinal hemorrhages and neurobehavior related to tractive force in vacuum extraction. Acta Obstet. Gynecol. Scand. 1987, 66, 165–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Svenningsen, L.; Eidal, K. Lack of correlation between umbilical artery pH, retinal hemorrhages and Apgar score in the newborn. Acta Obstet. Gynecol. Scand. 1987, 66, 639–642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Egge, K.; Lyng, G.; Maltau, J.M. Effect of instrumental delivery on the frequency and severity of retinal hemorrhages in the newborn. Acta Obstet. Gynecol. Scand. 1981, 60, 153–155. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Planten, J.T.; von der Schaaf, P.C. Retinal haemorrhage in the newborn. An attempt to indicate and explain its cause and significance. Ophthalmologica 1971, 162, 213–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gonzalez Viejo, I.; Ferrer Novella, C.; Pueyo Subias, M.; Ronchera Oms, J.M.; Bueno Lozano, J.; Ferrer Novella, E.; Vicente Aznar, E.; Honrubia Lopez, F.M. Hemorrhagic retinopathy in newborns: Frequency, form of presentation, associated factors and significance. Eur. J. Ophthalmol. 1995, 5, 247–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bist, H.K.; Singh, M.; Satsangi, S.K.; Mishra, B.; Singh, R.S.; Pandey, D.N.; Singh, Y.P.; Prasad, R. Retinal hemorrhages in newborn—Fetal causative factors. Indian Pediatr. 1989, 26, 558–565. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Matieli, L.C.; Martins, E.N.; Moraes, N.S.; Berezovsky, A.; Salomao, S.R. Electroretinographic findings in a full-term newborn with retinal hemorrhages. J. Pediatr. Ophthalmol. Strabismus 2003, 40, 236–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eris, E.; Eris, D.; Seymen, Z.; Karasu, B.; Diracoglu, A.; Perente, I.; Comert, S. Retinal haemorrhage rates and resolution time of retinal haemorrhage in newborns after hypothermic treatment for hypoxic-ischemic encephalopathy. Arch. Pediatr. 2020, 27, 29–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Laghmari, M.; Skiker, H.; Handor, H.; Mansouri, B.; Ouazzani Chahdi, K.; Lachkar, R.; Salhi, Y.; Cherkaoui, O.; Ouazzani Tnacheri, B.; Ibrahimy, W.; et al. Birth-related retinal hemorrhages in the newborn: Incidence and relationship with maternal, obstetric and neonatal factors. Prospective study of 2031 cases. J. Fr. Ophtalmol. 2014, 37, 313–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Egge, K.; Lyng, G.; Maltau, J.M. Retinal haemorrhages in the newborn. Acta Ophthalmol. 1980, 58, 231–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bergen, R.; Margolis, S. Retinal hemorrhages in the newborn. Ann. Ophthalmol. 1976, 8, 53–56. [Google Scholar]
- Sitorus, R.S.; Pambudy, I.M.; Rohsiswatmo, R.; Barliana, J.D.; Yulia, D.E.; Widyahening, I.S. Retinal abnormalities in universal eye screening of healthy, full-term newborn infants in Jakarta. The incidence and its risk factors: A pilot study. Int. J. Retin. Vitr. 2021, 7, 67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vinekar, A.; Govindaraj, I.; Jayadev, C.; Kumar, A.K.; Sharma, P.; Mangalesh, S.; Simaldi, L.; Avadhani, K.; Shetty, B.; Bauer, N. Universal ocular screening of 1021 term infants using wide-field digital imaging in a single public hospital in India—A pilot study. Acta Ophthalmol. 2015, 93, e372–e376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, B.; Shao, X.; Cao, Y.; Xia, S.; Yue, H. Neonatal-perinatal medicine in a transitional period in China. Arch. Dis. Child Fetal Neonatal Ed. 2013, 98, F440–F444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Pu, Q.; Li, P.; Jiang, H.; Wang, H.; Zhou, Q.; Liu, J.; Zhong, W.; Huang, H. Factors related to retinal haemorrhage in infants born at high risk. Acta Ophthalmol. 2017, 95, e477–e480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zhao, Q.; Zhang, Y.; Yang, Y.; Li, Z.; Lin, Y.; Liu, R.; Wei, C.; Ding, X. Birth-related retinal hemorrhages in healthy full-term newborns and their relationship to maternal, obstetric, and neonatal risk factors. Graefes Arch. Clin. Exp. Ophthalmol. 2015, 253, 1021–1025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yanli, Z.; Qi, Z.; Yu, L.; Haike, G. Risk Factors Affecting the Severity of Full-Term Neonatal Retinal Hemorrhage. J. Ophthalmol. 2017, 2017, 4231489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, L.N.; He, X.P.; Huang, L.P. A survey of high risk factors affecting retinopathy in full-term infants in China. Int. J. Ophthalmol. 2012, 5, 177–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pu, Q.L.; Zhou, Q.Y.; Liu, J.; Li, P.; Huang, H.F.; Jiang, H.Q. Clinical observation and related factors analysis of neonatal asphyxia complicated with retinal hemorrhage. Chin. J. Ophthalmol. 2017, 53, 358–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Callaway, N.F.; Ludwig, C.A.; Blumenkranz, M.S.; Jones, J.M.; Fredrick, D.R.; Moshfeghi, D.M. Retinal and Optic Nerve Hemorrhages in the Newborn Infant: One-Year Results of the Newborn Eye Screen Test Study. Ophthalmology 2016, 123, 1043–1052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Simkin, S.K.; Misra, S.L.; Battin, M.; McGhee, C.N.J.; Dai, S. Prospective observational study of universal newborn eye screening in a hospital and community setting in New Zealand. BMJ Paediatr. Open 2019, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Goyal, P.; Padhi, T.R.; Das, T.; Pradhan, L.; Sutar, S.; Butola, S.; Behera, U.C.; Jain, L.; Jalali, S. Outcome of universal newborn eye screening with wide-field digital retinal image acquisition system: A pilot study. Eye 2018, 32, 67–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ma, Y.; Deng, G.; Ma, J.; Liu, J.; Li, S.; Lu, H. Universal ocular screening of 481 infants using wide-field digital imaging system. BMC Ophthalmol. 2018, 18, 283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fei, P.; Liu, Z.; He, L.; Li, N.; Xu, L.; Zhang, M.; Zhou, Y.; Li, F.; Wang, H.; Zhang, Q.; et al. Early detection of ocular abnormalities in a Chinese multicentre neonatal eye screening programme-1-year result. Acta Ophthalmol. 2021, 99, e415–e422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.H.; Wu, W.C.; Li, N.; Lu, J.; Zhang, G.M.; Zhao, J.Y.; Ma, Y. Full-Term Neonatal Ophthalmic Screening in China: A Review of 4-Year Outcomes. Ophthalmic Surg. Lasers Imaging Retin. 2017, 48, 983–992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Schenker, J.G.; Gombos, G.M. Retinal hemorrhage in the newborn. Obstet. Gynecol. 1966, 27, 521–524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lashutka, M.K.; Chandra, A.; Murray, H.N.; Phillips, G.S.; Hiestand, B.C. The relationship of intraocular pressure to intracranial pressure. Ann. Emerg. Med. 2004, 43, 585–591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Byrne, M.P.; McMillan, K.R.; Coats, B. Morphological Analysis of Retinal Microvasculature to Improve Understanding of Retinal Hemorrhage Mechanics in Infants. Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2020, 61, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hsu, K.H.; Liao, P.J.; Hwang, C.J. Factors affecting Taiwanese women’s choice of Cesarean section. Soc. Sci. Med. 2008, 66, 201–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


| Characteristics | Total (n = 1072) | Mild RHs (n = 103) | Moderate RHs (n = 40) | Severe RHs (n = 123) | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Fetal information | |||||
| Gender | |||||
| Male (n, %) | 608(56.7) | 49(47.6) | 20(50) | 71(57.7) | 0.294 |
| Female (n, %) | 464(43.3) | 54(52.4) | 20(50) | 52(42.3) | |
| Gestational age (weeks) | 39.3 ± 0.99 | 39.3 ± 0.96 | 39.1 ± 1.01 | 39.3 ± 0.98 | 0.770 |
| Birth weight (g) | 3209.5 ± 363.4 | 3139.4 ± 366.6 | 3143.5 ± 370.9 | 3177.3 ± 341.8 | 0.047 |
| Agar score (IQR) | 10(10, 10) | 10(10, 10) | 10(10, 10) | 10(10, 10) | 0.999 |
| Age at examination (days) | |||||
| <48 h | 639(59.6) | 84(81.6) | 30(75.0) | 103(83.7) | 0.464 |
| >48+ h | 433(40.4) | 19(18.4) | 10(25.0) | 20(16.3) | |
| Position of the fetus | |||||
| Left occipitoanterior | 726(67.7) | 74(71.8) | 28(70.0) | 94(76.4) | 0.626 |
| Other | 346(32.3) | 29(28.2) | 12(30.0) | 29(23.6) | |
| UCAN | |||||
| No | 738(68.8) | 75(72.8) | 30(75.0) | 88(71.5) | 0.911 |
| Yes | 334(31.2) | 28(27.2) | 10(25.0) | 35(28.5) | |
| Fetal distress | |||||
| No | 1004(93.7) | 98(95.2) | 37(92.5) | 120(97.6) | 0.338 |
| Yes | 68(6.34) | 5(4.85) | 3(7.50) | 3(2.44) | |
| Scalp hematoma | |||||
| No | 1032(96.3) | 97(94.2) | 35(87.5) | 118(95.9) | 0.149 |
| Yes | 40(3.73) | 6(5.83) | 5(12.5) | 5(4.07) | |
| Mother’s information | |||||
| BMI before production | 26.3 ± 3.23 | 26.0 ± 3.06 | 26.6 ± 3.71 | 25.9 ± 3.11 | 0.230 |
| PIH | |||||
| No | 1042(97.2) | 103(100) | 40(100) | 122(97.2) | 0.558 |
| Yes | 30(2.80) | 0 | 0 | 1(0.81) | |
| GDM | |||||
| No | 918(85.6) | 92(89.3) | 30(75.0) | 108(87.8) | 0.067 |
| Yes | 154(14.4) | 11(10.7) | 10(25.0) | 15(12.2) | |
| Delivery method, n (%) | |||||
| Vaginal | 689(64.3) | 98(95.2) | 38(95.0) | 119(96.8) | 0.798 |
| Cesarean section | 383(35.7) | 5(4.85) | 2(5.00) | 4(3.25) | |
| Parity | |||||
| First birth | 358(33.4) | 47(45.6) | 13(32.5) | 37(30.1) | 0.046 |
| Non first birth | 714(66.6) | 56(54.4) | 27(67.5) | 86(69.9) | |
| Amniotic fluid index | |||||
| Normal | 953(88.9) | 92(89.3) | 38(95.0) | 108(87.8) | 0.435 |
| Abnormal | 119(11.1) | 11(10.7) | 2(5.00) | 15(12.2) | |
| Use obstetric apparatus | |||||
| No | 1059(98.8) | 101(98.1) | 38(95.0) | 123(100) | 0.070 |
| Yes | 13(1.21) | 2(1.94) | 2(5.00) | 0 | |
| Laceration of perineum | |||||
| No | 457(42.6) | 19(18.5) | 8(20.0) | 14(11.4) | 0.234 |
| Yes | 615(57.4) | 84(81.6) | 32(80.0) | 109(88.6) | |
| PROM | |||||
| No | 820(76.5) | 76(73.8) | 30(75.0) | 101(82.1) | 0.291 |
| Yes | 252(23.5) | 27(26.2) | 10(25.0) | 22(17.9) | |
| Placental abruption | |||||
| No | 1069(99.7) | 102(99.0) | 40(100) | 123(100) | 0.452 |
| Yes | 3(0.28) | 1(0.97) | 0 | 0 |
| Left Eye | Right Eye | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| None | Mild RHs | Moderate RHs | Severe RHs | Total | |
| None | 806(92.4) | 38(46.3) | 4(13.8) | 8(8.99) | 856(79.9) |
| Mild RHs | 46(5.28) | 20(24.4) | 7(24.1) | 18(20.2) | 91(8.49) |
| Moderate RHs | 13(1.49) | 5(6.10) | 10(34.5) | 7(7.87) | 35(3.26) |
| Severe RHs | 7(0.80) | 19(23.2) | 8(27.6) | 56(62.9) | 90(8.40) |
| Total | 872(100) | 82(100) | 29(100) | 89(100) | 1072(100) |
| Total | Mild RHs | Moderate RHs | Severe RHs | p-Value | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Eyes with RHs | 266 | 103 (9.61%) | 40(3.73%) | 123(11.5%) | |
| All Macular Hemorrhages | 223 | 57(25.6) | 37(17.5) | 127(56.9) | |
| Extrafoveal involvement | |||||
| Yes | 216(81.2) | 56(54.4) | 37(92.5) | 123(100) | <0.001 |
| No | 50(18.8) | 47(45.6) | 3(7.5) | 0 | |
| Foveal involvement | |||||
| Yes | 7(2.63) | 1(0.97) | 2(5.00) | 4(3.25) | 0.338 |
| No | 259(96.8) | 102(99.0) | 38(95.0) | 119(96.8) | |
| Optic involvement | |||||
| Yes | 63(23.7) | 2(1.94) | 3(7.50) | 58(47.2) | <0.001 |
| No | 203(76.3) | 101(98.1) | 37(92.5) | 65(52.8) |
| Factors | Univariate Analysis | Multivariate Analysis | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| OR (95%CI) | p | OR (95%CI) | p | |
| Fetal information | ||||
| Female | 1.27(0.96, 1.68) | 0.091 | ||
| Gestational age (days) | 1.00(0.87, 1.15) | 0.987 | ||
| Birth weight (kg) | 0.58(0.39, 0.85) | 0.006 | 0.63(0.40, 0.99) | 0.043 |
| Agar score | 0.88(0.59, 1.33) | 0.558 | ||
| Age at examination | ||||
| <48 h | 1.0 (reference) | 1.0 (reference) | ||
| 48+ h | 0.25(0.18, 0.35) | <0.001 | 0.97(0.64, 1.47) | 0.891 |
| Position of the fetus | ||||
| Left occipitoanterior | 1.0 (reference) | 1.0 (reference) | ||
| Other | 0.70(0.52, 0.96) | 0.025 | 1.16(0.82, 1.63) | 0.414 |
| UCAN | 0.77(0.57, 1.05) | 0.097 | ||
| Fetal distress | 0.57(0.29, 1.10) | 0.092 | ||
| Scalp hematoma | 3.04(0.19, 48.7) | 0.433 | ||
| Mother’s information | ||||
| BMI before production | 0.96(0.92, 1.00) | 0.079 | ||
| PIH | 0.10(0.01, 0.75) | 0.025 | 0.21(0.03, 1.70) | 0.144 |
| GDM | 0.91(0.61, 1.36) | 0.656 | ||
| Delivery method | ||||
| Cesarean section | 1.0 (reference) | 1.0 (reference) | ||
| Vaginal | 19.9(10.7, 36.9) | <0.001 | 20.6(9.10, 46.5) | <0.001 |
| First birth | 1.23(0.92, 1.64) | 0.170 | ||
| Amniotic fluid index | 0.97(0.62, 1.52) | 0.905 | ||
| Use obstetric apparatus | 1.35(0.41, 4.43) | 0.618 | ||
| Laceration of perineum | 5.85(4.08, 8.39) | <0.001 | 0.92(0.56, 1.50) | 0.664 |
| PROM | 0.91(0.65, 1.26) | 0.556 | ||
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yang, T.; Hu, R.; Chen, J.; Lu, Y.; Guo, Y.; Liu, Y.; Yu, R.; Jin, G. Prevalence, Characteristics, and Risk Factors of Retinal Hemorrhage among Full-Term Neonates in Southern China. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 13927. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph192113927
Yang T, Hu R, Chen J, Lu Y, Guo Y, Liu Y, Yu R, Jin G. Prevalence, Characteristics, and Risk Factors of Retinal Hemorrhage among Full-Term Neonates in Southern China. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health. 2022; 19(21):13927. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph192113927
Chicago/Turabian StyleYang, Tingting, Rongsheng Hu, Jiansu Chen, Yamei Lu, Yonglong Guo, Yao Liu, Ruixia Yu, and Guangming Jin. 2022. "Prevalence, Characteristics, and Risk Factors of Retinal Hemorrhage among Full-Term Neonates in Southern China" International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health 19, no. 21: 13927. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph192113927
APA StyleYang, T., Hu, R., Chen, J., Lu, Y., Guo, Y., Liu, Y., Yu, R., & Jin, G. (2022). Prevalence, Characteristics, and Risk Factors of Retinal Hemorrhage among Full-Term Neonates in Southern China. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 19(21), 13927. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph192113927







