A Deep Learning-Based Model for Predicting Abnormal Liver Function in Workers in the Automotive Manufacturing Industry: A Cross-Sectional Survey in Chongqing, China
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
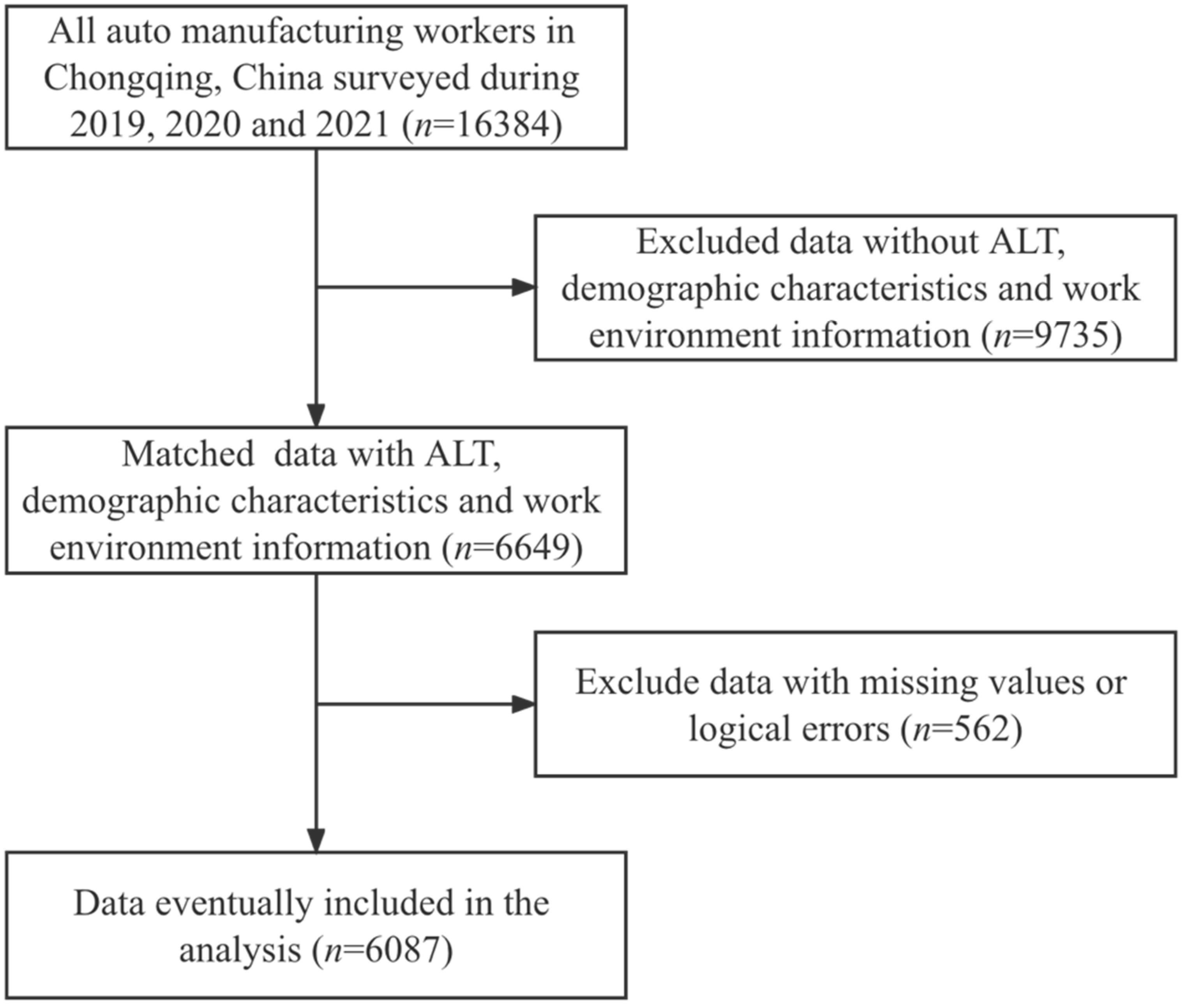
2.1. Study Subjects
2.2. Data Collection
2.3. Statistical Analysis
2.3.1. Identification of Influencing Factors
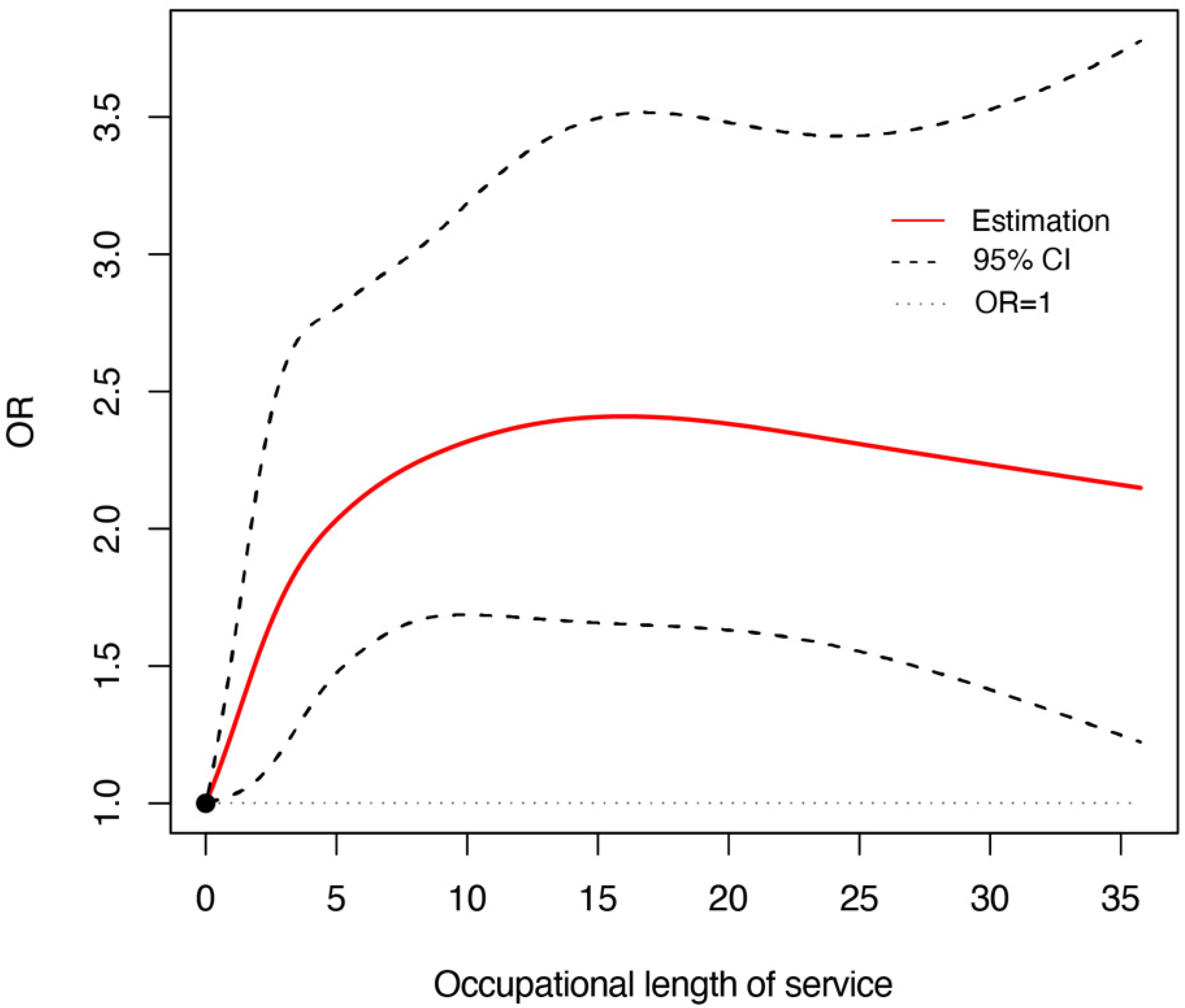
2.3.2. Restricted Cubic Spline Analysis
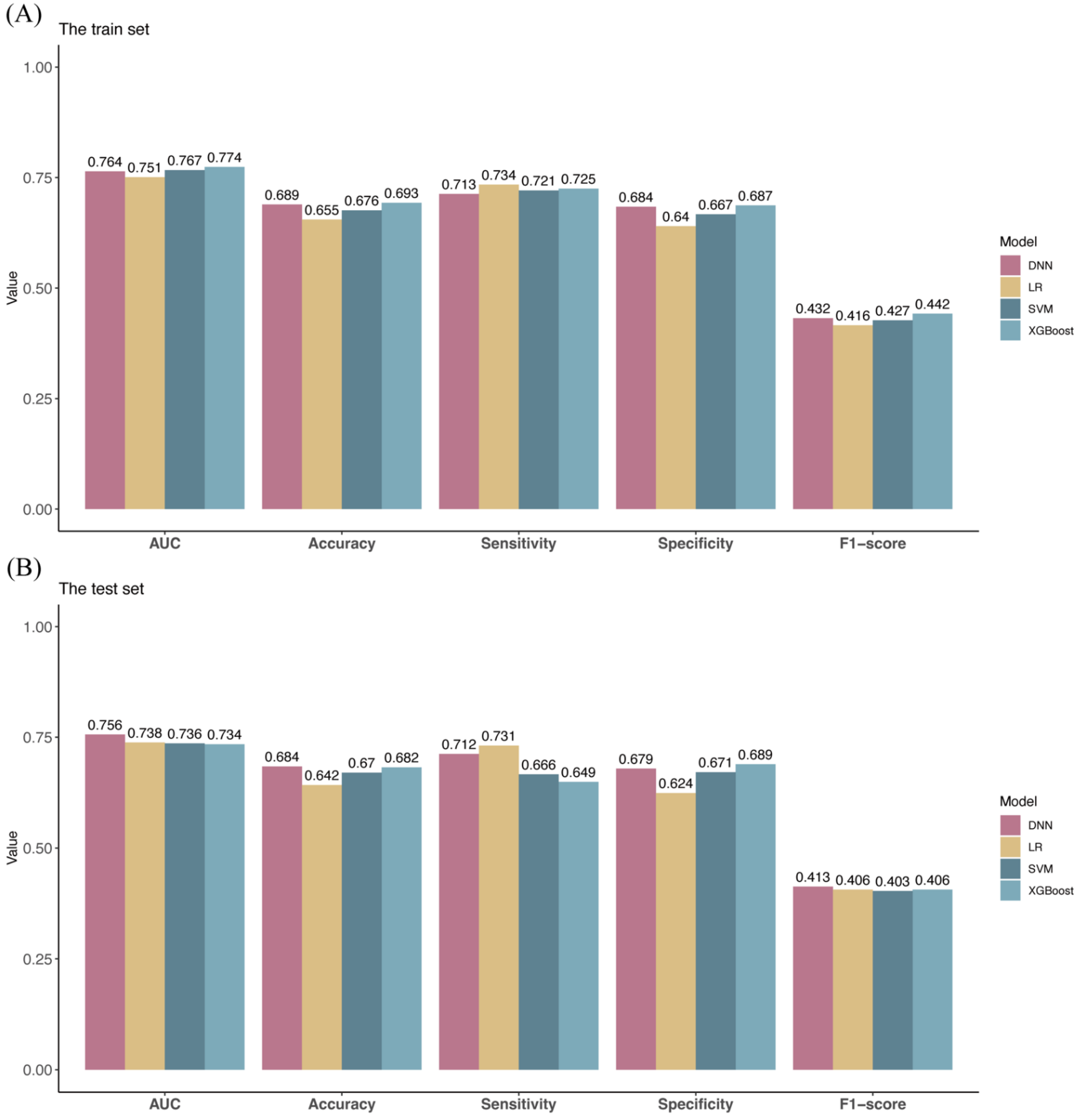
2.4. Development and Evaluation of DNN Model
3. Results
3.1. Demographic Characteristics and Work Environment Information of Workers
3.2. Comparison of Characteristics between the Normal Liver Function Group and Abnormal Liver Function Group
3.3. Identification of Risk Factors for Abnormal Liver Function
3.4. The Relationship between Length of Service and Risk of Abnormal Liver Function
3.5. A predictive Model for Abnormal Liver Function in Workers in the Automotive Manufacturing Industry
4. Discussion
Study Limitations and Future Works
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| BMI | body mass index |
| DBP | diastolic blood pressure |
| SBP | systolic blood pressure |
| ROC curve | receiver operating characteristic curve |
| AUC | area under curve |
| DNN | deep neural networks |
| LR | logistic regression |
| XGBoost | eXtreme gradient boosting |
| SVM | support vector machine |
References
- Trefts, E.; Gannon, M.; Wasserman, D.H. The liver. Curr. Biol. 2017, 27, R1147–R1151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mokdad, A.A.; Lopez, A.D.; Shahraz, S.; Lozano, R.; Mokdad, A.H.; Stanaway, J.; Murray, C.J.; Naghavi, M. Liver cirrhosis mortality in 187 countries between 1980 and 2010: A systematic analysis. BMC Med. 2014, 12, 145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Asrani, S.K.; Devarbhavi, H.; Eaton, J.; Kamath, P.S. Burden of liver diseases in the world. J. Hepatol. 2019, 70, 151–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Døssing, M. Occupational toxic liver damage. J. Hepatol. 1986, 3, 131–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahimi Moghadam, S.; Afshari, M.; Ganjali, A.; Moosazadeh, M. Effect of occupational exposure to petrol and gasoline components on liver and renal biochemical parameters among gas station attendants, a review and meta-analysis. Rev. Environ. Health 2020, 35, 517–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, Q.; Liu, J.; Li, Q.; Chen, K.; Liu, Z.; Shen, Y.; Niu, P.; Yang, Y.; Zou, Y.; Yang, X. Interaction of occupational manganese exposure and alcohol drinking aggravates the increase of liver enzyme concentrations from a cross-sectional study in China. Environ. Health 2013, 12, 30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lippmann, S.J.; Richardson, D.B.; Chen, J.C. Elevated serum liver enzymes and fatty liver changes associated with long driving among taxi drivers. Am. J. Ind. Med. 2011, 54, 618–627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sturgeon, T.; Memedovic, O.; Van Biesebroeck, J.; Gereffi, G. Globalisation of the automotive industry: Main features and trends. Int. J. Technol. Learn. Innov. Dev. 2009, 1, 7–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azam, S.F.; Yusoff, S.K.M. Investment and Financing Analysis: An Investigation of the Automotive Industry of China. Syst. Rev. Pharm. 2020, 11, 913–919. [Google Scholar]
- Assunção, A.; Moniz-Pereira, V.; Fujão, C.; Bernardes, S.; Veloso, A.P.; Carnide, F. Predictive Factors of Short-Term Related Musculoskeletal Pain in the Automotive Industry. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public. Health 2021, 18, 13062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, L.; Jiang, J.; Huang, S.L.; He, J.; Li, J.M. Analysis on characteristics of hearing loss in occupational noise-exposed workers in automotive manufacturing industry. Chin. J. Ind. Hyg. Occup. Dis. 2018, 36, 445–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Travill, A.L.; Soeker, F.; Overmeyer, D.; Rickers, F. Cardiovascular and metabolic risk factors of shift workers within the automotive industry. Health SA 2019, 24, 1227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sancini, A.; Casale, T.; De Sio, S.; Rosati, M.V.; Sacco, C.; Montuori, L.; Nardone, N.; Giubilati, R.; Iannattone, G.; Nieto, H.A.; et al. Liver damage in automotive and industrial workers of the glass. Ann. Ig. 2014, 26, 148–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, X.; Zhao, L.; Yu, D.; Ma, S.; Liu, X. Effects of extremely low frequency electromagnetic field on the health of workers in automotive industry. Electromagn. Biol. Med. 2013, 32, 551–559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rînjea, C.; Chivu, O.R.; Darabont, D.-C.; Feier, A.I.; Borda, C.; Gheorghe, M.; Nitoi, D.F. Influence of the Thermal Environment on Occupational Health and Safety in Automotive Industry: A Case Study. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 8572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dehghani, F.; Golbabaei, F.; Abolfazl Zakerian, S.; Omidi, F.; Mansournia, M.A. Health risk assessment of exposure to volatile organic compounds (BTEX) in a painting unit of an automotive industry. J. Health Saf. Work. 2018, 8, 55–64. [Google Scholar]
- Karmen, A.; Wroblewski, F.; Ladue, J.S. Transaminase activity in human blood. J. Clin. Investig. 1955, 34, 126–131. Available online: https://www.jci.org/articles/view/103055 (accessed on 2 October 2022). [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lala, V.; Goyal, A.; Minter, D.A. Liver Function Tests. In StatPearls; StatPearls Publishing Copyright © 2022; StatPearls Publishing LLC.: St. Petersburg, FL, USA, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Abdalrada, A.S.; Yahya, O.H.; Alaidi, A.H.M.; Hussein, N.A.; Alrikabi, H.T.; Al-Quraishi, T.A.-Q. A predictive model for liver disease progression based on logistic regression algorithm. Period. Eng. Nat. Sci. (PEN) 2019, 7, 1255–1264. [Google Scholar]
- Yip, T.F.; Ma, A.; Wong, V.S.; Tse, Y.K.; Chan, H.Y.; Yuen, P.C.; Wong, G.H. Laboratory parameter-based machine learning model for excluding non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) in the general population. Aliment. Pharmacol. Ther. 2017, 46, 447–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ma, X.; Yang, C.; Liang, K.; Sun, B.; Jin, W.; Chen, L.; Dong, M.; Liu, S.; Xin, Y.; Zhuang, L. A predictive model for the diagnosis of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease based on an integrated machine learning method. Am. J. Transl. Res. 2021, 13, 12704–12713. [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, N.; Zhao, Z.; Xu, P. Predictive Analysis and Evaluation Model of Chronic Liver Disease Based on BP Neural Network with Improved Ant Colony Algorithm. J. Healthc. Eng. 2021, 2021, 3927551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, H.; Xu, C.F.; Shen, Z.; Yu, C.H.; Li, Y.M. Application of Machine Learning Techniques for Clinical Predictive Modeling: A Cross-Sectional Study on Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease in China. Biomed. Res. Int. 2018, 2018, 4304376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wang, F.S.; Fan, J.G.; Zhang, Z.; Gao, B.; Wang, H.Y. The global burden of liver disease: The major impact of China. Hepatology 2014, 60, 2099–2108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Maeso-Díaz, R.; Ortega-Ribera, M.; Fernández-Iglesias, A.; Hide, D.; Muñoz, L.; Hessheimer, A.J.; Vila, S.; Francés, R.; Fondevila, C.; Albillos, A.; et al. Effects of aging on liver microcirculatory function and sinusoidal phenotype. Aging Cell 2018, 17, e12829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tajiri, K.; Shimizu, Y. Liver physiology and liver diseases in the elderly. World J. Gastroenterol. 2013, 19, 8459–8467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmucker, D.L. Age-Related changes in liver structure and function: Implications for disease? Exp. Gerontol. 2005, 40, 650–659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horvath, S.; Erhart, W.; Brosch, M.; Ammerpohl, O.; von Schönfels, W.; Ahrens, M.; Heits, N.; Bell, J.T.; Tsai, P.C.; Spector, T.D.; et al. Obesity accelerates epigenetic aging of human liver. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2014, 111, 15538–15543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Goodman, Z.D. The impact of obesity on liver histology. Clin. Liver Dis. 2014, 18, 33–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cuzmar, V.; Alberti, G.; Uauy, R.; Pereira, A.; García, C.; De Barbieri, F.; Corvalán, C.; Santos, J.L.; Mericq, V.; Villarroel, L.; et al. Early Obesity: Risk Factor for Fatty Liver Disease. J. Pediatr. Gastroenterol. Nutr. 2020, 70, 93–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahman, S.; Islam, S.; Haque, T.; Kathak, R.R.; Ali, N. Association between serum liver enzymes and hypertension: A cross-sectional study in Bangladeshi adults. BMC Cardiovasc. Disord. 2020, 20, 128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Z.; Wang, G.; Jonas, J.B.; Ji, C.; Chen, S.; Yuan, Y.; Shen, C.; Wu, Y.; Wu, S. Blood pressure control and progression of arteriosclerosis in hypertension. J. Hypertens. 2021, 39, 1221–1229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Campollo, O. Alcohol and the Liver: The Return of the Prodigal Son. Ann. Hepatol. 2019, 18, 6–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chembazhi, U.V.; Bangru, S.; Hernaez, M.; Kalsotra, A. Cellular plasticity balances the metabolic and proliferation dynamics of a regenerating liver. Genome Res. 2021, 31, 576–591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schmidhuber, J. Deep learning in neural networks: An overview. Neural Netw. 2015, 61, 85–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Wang, L.; Su, Y.; Zhong, L.; Peng, B. Prediction model for the onset risk of impaired fasting glucose: A 10-year longitudinal retrospective cohort health check-up study. BMC Endocr. Disord. 2021, 21, 211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Study Subjects | Sample Size | Independent Variables | Model | Performance Index | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Abdalrada [19] | Indian Liver Patient Dataset | 583 | Demographic characteristics and laboratory data | Logistic regression | AUC Accuracy Sensitivity Specificity |
| Yip [20] | Patients in hospital | 922 | Demographic characteristics and laboratory data | Logistic regression Ridge regression AdaBoost Decision tree | AUC Sensitivity Specificity |
| Ma [21] | Patients in hospital | 98 | Demographic characteristics and laboratory data | Logistic regression Random forest Support vector machine | AUC |
| Jiang [22] | Patients in hospital | 35 | Laboratory data | BP neutral network | AUC Accuracy MSE |
| Ma [23] | Patients in hospital | 10,508 | Demographic characteristics and laboratory data | Bayesian network | F-measure Accuracy Sensitivity Specificity Precision |
| X1 | X2 | X3 | X4 | X5 | X6 | X7 | X8 | X9 | y | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| S1 | 1 | 0.139899 | 0.149886 | 1 | 0 | 0.136555 | 0.463415 | 0.34375 | 0 | 0 |
| S2 | 0 | 0.313271 | 0.30896 | 0 | 1 | 0.132353 | 0.353659 | 0.242188 | 1 | 0 |
| S3 | 1 | 0.450327 | 0.410568 | 0 | 0 | 0.058824 | 0.463415 | 0.382813 | 1 | 1 |
| S4 | 0 | 0.499732 | 0.317005 | 1 | 1 | 0.428571 | 0.329268 | 0.40625 | 0 | 1 |
| Total (n = 6087) | |
|---|---|
| Age (years) | |
| Mean ± SD | 36.8 ± 10.5 |
| BMI (kg/m2) | |
| Mean ± SD | 23.5 ± 3.5 |
| DBP (mmHg) | |
| Mean ± SD | 80.6 ± 10.9 |
| SBP (mmHg) | |
| Mean ± SD | 125.0 ± 15.3 |
| Length of service (years) | |
| Mean ± SD | 6.9 ± 7.05 |
| Sex | |
| Female | 909 (14.9%) |
| Male | 5178 (85.1%) |
| Exposure to benzene | |
| No | 4970 (81.6%) |
| Yes | 1117 (18.4%) |
| Exposure to noise | |
| No | 2203 (36.2%) |
| Yes | 3884 (63.8%) |
| Scale of enterprise | |
| Small and under | 929 (15.3%) |
| Medium | 1189 (19.5%) |
| Large | 3969 (65.2%) |
| Normal Liver Function (n = 5069) | Abnormal Liver Function (n = 1018) | p-Value | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Age (years) | 37.0 ± 10.7 | 35.4 ± 9.39 | <0.0001 *** |
| BMI (kg/cm2) | 23.1 ± 3.32 | 25.6 ± 3.39 | <0.0001 *** |
| Length of service (years) | 6.80 ± 7.03 | 7.59 ± 7.09 | 0.0011 ** |
| DBP (mmHg) | 79.9 ± 10.6 | 84.2 ± 11.6 | <0.0001 *** |
| SBP (mmHg) | 124 ± 15.0 | 130 ± 15.7 | <0.0001 *** |
| Sex (male) | 4212 (83.1%) | 966 (94.9%) | <0.0001 *** |
| Exposure to benzene | 952 (18.8%) | 165 (16.2%) | 0.0587 |
| Exposure to noise | 3203 (63.2%) | 681 (66.9%) | 0.0271 * |
| Size of enterprise | <0.0001 *** | ||
| Small and under | 813 (16.0%) | 116 (11.4%) | |
| Medium | 1006 (19.8%) | 183 (18.0%) | |
| Large | 3250 (64.1%) | 719 (70.6%) |
| Univariate | Multivariate | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Variables | OR | 95% CI | p-Value | OR | 95% CI | p-Value |
| Age | 0.985 | 0.979–0.992 | <0.0001 *** | 0.969 | 0.960–0.978 | <0.0001 *** |
| BMI | 1.232 | 1.207–1.258 | <0.0001 *** | 1.218 | 1.192–1.244 | <0.0001 *** |
| Length of service | 1.015 | 1.006–1.024 | 0.0011 ** | 1.022 | 1.010–1.034 | 0.0002 *** |
| DBP | 1.036 | 1.03–1.042 | <0.0001 *** | 1.017 | 1.007–1.027 | 0.0011 ** |
| SBP | 1.025 | 1.021–1.029 | <0.0001 *** | 1.008 | 1.000–1.015 | 0.0393 * |
| Sex (vs. Female) | 3.78 | 2.832–5.044 | <0.0001 *** | 3.272 | 2.418–4.428 | <0.0001 *** |
| Exposure to benzene (vs. No) | 0.837 | 0.698–1.002 | 0.0532 | – | – | – |
| Exposure to noise (vs. No) | 1.177 | 1.021–1.358 | 0.0248 * | 1.142 | 0.974–1.340 | 0.1023 |
| Size of enterprise (vs. Small and under) | – | – | – | – | – | – |
| Medium | 1.275 | 0.993–1.638 | 0.0572 | 1.047 | 0.801–1.368 | 0.7375 |
| Large | 1.551 | 1.256–1.914 | <0.0001 *** | 1.11 | 0.874–1.408 | 0.3924 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ni, L.; Chen, F.; Ran, R.; Li, X.; Jin, N.; Zhang, H.; Peng, B. A Deep Learning-Based Model for Predicting Abnormal Liver Function in Workers in the Automotive Manufacturing Industry: A Cross-Sectional Survey in Chongqing, China. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 14300. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph192114300
Ni L, Chen F, Ran R, Li X, Jin N, Zhang H, Peng B. A Deep Learning-Based Model for Predicting Abnormal Liver Function in Workers in the Automotive Manufacturing Industry: A Cross-Sectional Survey in Chongqing, China. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health. 2022; 19(21):14300. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph192114300
Chicago/Turabian StyleNi, Linghao, Fengqiong Chen, Ruihong Ran, Xiaoping Li, Nan Jin, Huadong Zhang, and Bin Peng. 2022. "A Deep Learning-Based Model for Predicting Abnormal Liver Function in Workers in the Automotive Manufacturing Industry: A Cross-Sectional Survey in Chongqing, China" International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health 19, no. 21: 14300. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph192114300
APA StyleNi, L., Chen, F., Ran, R., Li, X., Jin, N., Zhang, H., & Peng, B. (2022). A Deep Learning-Based Model for Predicting Abnormal Liver Function in Workers in the Automotive Manufacturing Industry: A Cross-Sectional Survey in Chongqing, China. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 19(21), 14300. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph192114300







