Nitrate in Maternal Drinking Water during Pregnancy and Measures of Male Fecundity in Adult Sons
Abstract
:1. Introduction
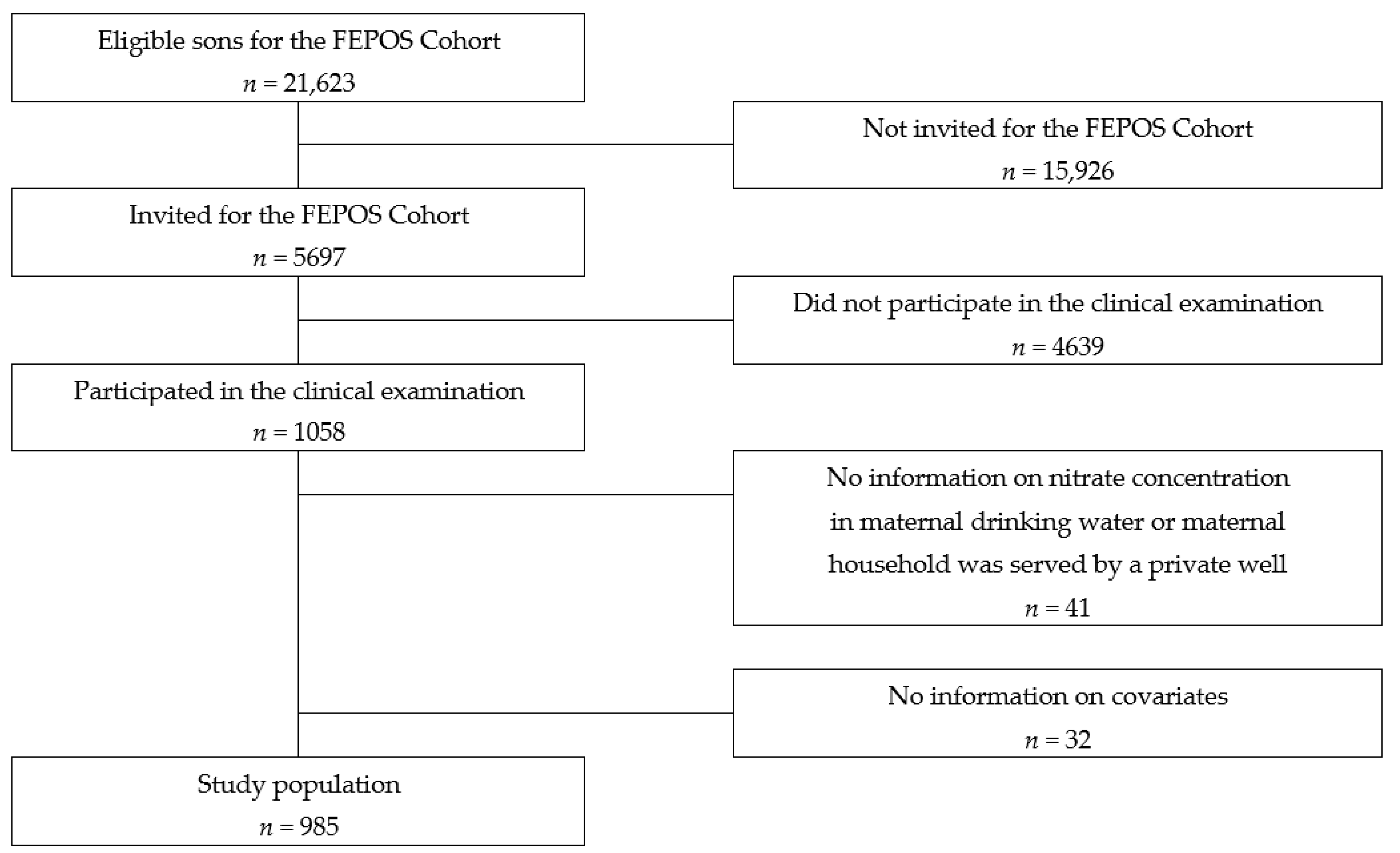
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
References
- Skakkebaek, N.E.; Rajpert-De Meyts, E.; Buck Louis, G.M.; Toppari, J.; Andersson, A.-M.; Eisenberg, M.L.; Jensen, T.K.; Jørgensen, N.; Swan, S.H.; Sapra, K.J.; et al. Male Reproductive Disorders and Fertility Trends: Influences of Environment and Genetic Susceptibility. Physiol. Rev. 2016, 96, 55–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Virtanen, H.E.; Jorgensen, N.; Toppari, J. Semen quality in the 21(st) century. Nat. Rev. Urol. 2017, 14, 120–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Levine, H.; Jørgensen, N.; Martino-Andrade, A.; Mendiola, J.; Weksler-Derri, D.; Mindlis, I.; Pinotti, R.; Swan, S.H. Temporal trends in sperm count: A systematic review and meta-regression analysis. Hum. Reprod. Update 2017, 23, 646–659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Skakkebæk, N.E.; Lindahl-Jacobsen, R.; Levine, H.; Andersson, A.-M.; Jørgensen, N.; Main, K.M.; Lidegaard, Ø.; Priskorn, L.; Holmboe, S.A.; Bräuner, E.V.; et al. Environmental factors in declining human fertility. Nat. Rev. Endocrinol. 2022, 18, 139–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bonde, J.P.; Flachs, E.M.; Rimborg, S.; Glazer, C.H.; Giwercman, A.; Ramlau-Hansen, C.H.; Hougaard, K.S.; Høyer, B.B.; Hærvig, K.K.; Petersen, S.B.; et al. The epidemiologic evidence linking prenatal and postnatal exposure to endocrine disrupting chemicals with male reproductive disorders: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Hum. Reprod. Update 2016, 23, 104–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ward, M.H.; Jones, R.R.; Brender, J.D.; de Kok, T.M.; Weyer, P.J.; Nolan, B.T.; Villanueva, C.M.; van Breda, S.G. Drinking Water Nitrate and Human Health: An Updated Review. Int. J. Env. Res. Public Health 2018, 15, 1557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Manassaram, D.M.; Backer, L.C.; Moll, D.M. A review of nitrates in drinking water: Maternal exposure and adverse reproductive and developmental outcomes. Cienc. Saude Coletiva 2007, 12, 153–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Stayner, L.T.; Jensen, A.S.; Schullehner, J.; Coffman, V.R.; Trabjerg, B.B.; Olsen, J.; Hansen, B.; Pedersen, M.; Pedersen, C.B.; Sigsgaard, T. Nitrate in drinking water and risk of birth defects: Findings from a cohort study of over one million births in Denmark. Lancet Reg. Health Eur. 2022, 14, 100286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blaisdell, J.; Turyk, M.E.; Almberg, K.S.; Jones, R.M.; Stayner, L.T. Prenatal exposure to nitrate in drinking water and the risk of congenital anomalies. Env. Res. 2019, 176, 108553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World Health Organization. Nitrate and nitrite in drinking-water. In Background Document for Development of WHO Guidelines for Drinking-Water Quality; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Poulsen, R.; Cedergreen, N.; Hayes, T.; Hansen, M. Nitrate: An Environmental Endocrine Disruptor? A Review of Evidence and Research Needs. Env. Sci. Technol. 2018, 52, 3869–3887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edwards, T.M.; Hamlin, H.J. Reproductive endocrinology of environmental nitrate. Gen. Comp. Endocrinol. 2018, 265, 31–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Panesar, N.S.; Chan, K.W. Decreased steroid hormone synthesis from inorganic nitrite and nitrate: Studies in vitro and in vivo. Toxicol. Appl. Pharm. 2000, 169, 222–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Neto, F.T.; Bach, P.V.; Najari, B.B.; Li, P.S.; Goldstein, M. Spermatogenesis in humans and its affecting factors. Semin. Cell Dev. Biol. 2016, 59, 10–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gabrielsen, J.S.; Tanrikut, C. Chronic exposures and male fertility: The impacts of environment, diet, and drug use on spermatogenesis. Andrology 2016, 4, 648–661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aly, H.A.A.; Mansour, A.M.; Abo-Salem, O.M.; Abd-Ellah, H.F.; Abdel-Naim, A.B. Potential testicular toxicity of sodium nitrate in adult rats. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2010, 48, 572–578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pant, N.; Srivastava, S.P. Testicular and spermatotoxic effect of nitrate in mice. Hum. Exp. Toxicol. 2002, 21, 37–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Attia, Y.A.; Abd El Hamid, E.A.; Ismaiel, A.M.; El-Nagar, A. The detoxication of nitrate by two antioxidants or a probiotic, and the effects on blood and seminal plasma profiles and reproductive function of New Zealand White rabbit bucks. Animal 2013, 7, 591–601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Montenegro, M.F.; Sundqvist, M.L.; Nihlén, C.; Hezel, M.; Carlström, M.; Weitzberg, E.; Lundberg, J.O. Profound differences between humans and rodents in the ability to concentrate salivary nitrate: Implications for translational research. Redox Biol. 2016, 10, 206–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Djekoun-Bensoltane, S.; Kammerer, M.; Larhantec, M.; Pilet, N.; Thorin, C. Nitrate and nitrite concentrations in rabbit saliva: Comparison with rat saliva. Environ. Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2007, 23, 132–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Owumi, S.E.; Adedara, I.A.; Duro-Ladipo, A.; Farombi, E.O. Acute diethyl nitrosamine and cadmium co-exposure exacerbates deficits in endocrine balance, sperm characteristics and antioxidant defence mechanisms in testes of pubertal rats. Andrologia 2019, 51, e13230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamino, K.; Seiler, F.; Emura, M.; Thomale, J.; Rajewsky, M.F.; Mohr, U. Formation of O6-ethylguanine in spermatogonial DNA of adult Syrian golden hamster by intraperitoneal injection of diethylnitrosamine. Exp. Toxicol. Pathol. 1995, 47, 443–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stocks, S.J.; Agius, R.M.; Cooley, N.; Harrison, K.L.; Brison, D.R.; Horne, G.; Gibbs, A.; Povey, A.C. Alkylation of sperm DNA is associated with male factor infertility and a reduction in the proportion of oocytes fertilised during assisted reproduction. Mutat. Res./Genet. Toxicol. Environ. Mutagen. 2010, 698, 18–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Keglberg Hærvig, K.; Bonde, J.P.; Ramlau-Hansen, C.A.-O.; Toft, G.; Hougaard, K.A.-O.; Specht, I.A.-O.; Giwercman, A.; Nybo Andersen, A.A.-O.; Olsen, J.; Lindh, C.A.-O.; et al. Fetal Programming of Semen Quality (FEPOS) Cohort—A DNBC Male-Offspring Cohort. Clin. Epidemiol. 2020, 12, 757–770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Olsen, J.; Melbye, M.; Olsen, S.F.; Sorensen, T.I.A.; Aaby, P.; Andersen, A.M.N.; Taxbol, D.; Hansen, K.D.; Juhl, M.; Schow, T.B.; et al. The Danish National Birth Cohort—Its background, structure and aim. Scand. J. Public Health 2001, 29, 300–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andersen, A.M.; Olsen, J. The Danish National Birth Cohort: Selected scientific contributions within perinatal epidemiology and future perspectives. Scand. J. Public Health 2011, 39, 115–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Schullehner, J.; Jensen, N.L.; Thygesen, M.; Hansen, B.; Sigsgaard, T. Drinking water nitrate estimation at household-level in Danish population-based long-term epidemiologic studies. J. Geochem. Explor. 2017, 183, 178–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schullehner, J. Danish Water Supply Areas and their links to water production facilities: An open-access data set. GEUS Bull. 2022, 49, 8319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- The Danish Civil Registration Office. The Civil Registration System in Denmark. Available online: https://cpr.dk/english (accessed on 1 September 2022).
- Bliddal, M.; Broe, A.; Pottegard, A.; Olsen, J.; Langhoff-Roos, J. The Danish Medical Birth Register. Eur. J. Epidemiol. 2018, 33, 27–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Coffman, V.R.; Jensen, A.S.; Trabjerg, B.B.; Pedersen, C.B.; Hansen, B.; Sigsgaard, T.; Olsen, J.; Schaumburg, I.; Schullehner, J.; Pedersen, M.; et al. Prenatal Exposure to Nitrate from Drinking Water and Markers of Fetal Growth Restriction: A Population-Based Study of Nearly One Million Danish-Born Children. Environ. Health Perspect. 2021, 129, 27002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World Health Organization. WHO Laboratory Manual for the Examination and Processing of Human Semen, 5th ed.; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Ramlau-Hansen, C.H.; Thulstrup, A.M.; Bonde, J.P.; Ernst, E. Is self-measuring of testicular volume by a Prader orchidometer a valid method? Fertil Steril 2007, 87, 1480–1482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lubin, J.H.; Colt Js Fau-Camann, D.; Camann D Fau-Davis, S.; Davis S Fau-Cerhan, J.R.; Cerhan Jr Fau-Severson, R.K.; Severson Rk Fau-Bernstein, L.; Bernstein L Fau-Hartge, P.; Hartge, P. Epidemiologic evaluation of measurement data in the presence of detection limits. Env. Health Perspect. 2004, 12, 1691–1696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Centre for Integrated Register-based Research at Aarhus University. CIRRAU. Available online: https://cirrau.au.dk/ (accessed on 1 September 2022).
- Greenland, S.; Pearl, J.; Robins, J.M. Causal diagrams for epidemiologic research. Epidemiology 1999, 10, 37–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harrell, F.E., Jr. Regression Modeling Strategies: With Applications to Linear Models, Logistic and Ordinal Regression, and Survival Analysis; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Hernán, M.A.; Hernández-Díaz, S.; Robins, J.M. A Structural Approach to Selection Bias. Epidemiology 2004, 15, 615–625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lotti, F.; Maggi, M. Ultrasound of the male genital tract in relation to male reproductive health. Hum. Reprod. Update 2015, 21, 56–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ebdrup, N.H.; Knudsen, U.B.; Schullehner, J.; Arendt, L.H.; Liew, Z.; Lyngsø, J.; Bay, B.; Clemmensen, P.J.; Sigsgaard, T.; Hansen, B.; et al. Nitrate in Drinking Water and Time to Pregnancy or Medically Assisted Reproduction in Women and Men: A Nationwide Cohort Study in the Danish National Birth Cohort. Clin. Epidemiol. 2022, 14, 475–487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schullehner, J.; Hansen, B. Nitrate exposure from drinking water in Denmark over the last 35 years. Environ. Res. Lett. 2014, 9, 95001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sherris, A.R.; Baiocchi, M.; Fendorf, S.; Luby, S.P.; Yang, W.; Shaw, G.M. Nitrate in Drinking Water during Pregnancy and Spontaneous Preterm Birth: A Retrospective Within-Mother Analysis in California. Env. Health Perspect 2021, 129, 57001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schullehner, J.; Hansen, B.; Thygesen, M.; Pedersen, C.B.; Sigsgaard, T. Nitrate in drinking water and colorectal cancer risk: A nationwide population-based cohort study: Nitrate in drinking water and CRC. Int. J. Cancer 2018, 143, 73–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brender, J.D.; Weyer, P.J.; Romitti, P.A.; Mohanty, B.P.; Shinde, M.U.; Vuong, A.M.; Sharkey, J.R.; Dwivedi, D.; Horel, S.A.; Kantamneni, J.; et al. Prenatal nitrate intake from drinking water and selected birth defects in offspring of participants in the national birth defects prevention study. Environ. Health Perspect. 2013, 121, 1083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Stayner, L.T.; Schullehner, J.; Semark, B.D.; Jensen, A.S.; Trabjerg, B.B.; Pedersen, M.; Olsen, J.; Hansen, B.; Ward, M.H.; Jones, R.R.; et al. Exposure to nitrate from drinking water and the risk of childhood cancer in Denmark. Env. Int. 2021, 155, 106613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vested, A.; Ramlau-Hansen Cecilia, H.; Olsen Sjurdur, F.; Bonde Jens, P.; Kristensen Susanne, L.; Halldorsson Thorhallur, I.; Becher, G.; Haug Line, S.; Ernst Emil, H.; Toft, G. Associations of in Utero Exposure to Perfluorinated Alkyl Acids with Human Semen Quality and Reproductive Hormones in Adult Men. Environ. Health Perspect. 2013, 121, 453–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hærvig Katia, K.; Petersen Kajsa, U.; Hougaard Karin, S.; Lindh, C.; Ramlau-Hansen Cecilia, H.; Toft, G.; Giwercman, A.; Høyer Birgit, B.; Flachs Esben, M.; Bonde Jens, P.; et al. Maternal Exposure to Per- and Polyfluoroalkyl Substances (PFAS) and Male Reproductive Function in Young Adulthood: Combined Exposure to Seven PFAS. Environ. Health Perspect. 2022, 130, 107001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Axelsson, J.; Rylander, L.; Rignell-Hydbom, A.; Lindh, C.H.; Jönsson, B.A.G.; Giwercman, A. Prenatal phthalate exposure and reproductive function in young men. Environ. Res. 2015, 138, 264–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schullehner, J.; Stayner, L.; Hansen, B. Nitrate, Nitrite, and Ammonium Variability in Drinking Water Distribution Systems. Int. J. Env. Res. Public Health 2017, 14, 276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


| Nitrate Concentration in Maternal Drinking Water (mg/L) | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| ≤2 (n = 548) | 2–5 (n = 346) | >5 (n = 91) | |
| Maternal characteristics | |||
| Age at delivery in years | |||
| Mean (±SD) | 31 (4) | 30 (4) | 30 (4) |
| Highest social class of parents, n (%) | |||
| High grade professional | 203 (37.0) | 116 (33.5) | 23 (25.3) |
| Low grade professional | 189 (34.5) | 102 (29.5) | 32 (35.2) |
| Skilled worker or unskilled worker | 122 (22.3) | 117 (33.8) | ≥31 (~34.0) |
| Student or economically inactive | 34 (6.2) | 11 (3.2) | ≤5 (~5.5) a |
| Daily number of cigarettes in 1st trimester, n (%) | |||
| Non-smoker | 436 (79.6) | 259 (74.9) | ≥60 (~65.9) |
| ≤10 cigarettes/day | 97 (17.7) | 68 (19.7) | 26 (28.6) |
| >10 cigarettes/day | 15 (2.7) | 19 (5.5) | ≤5 (~5.5) a |
| Characteristics of the clinical examination | |||
| Place of semen sample collection, n (%) | |||
| At home | 82 (15.0) | 43 (12.4) | 5 (5.5) |
| At the clinic | 466 (85.0) | 303 (87.6) | 86 (94.5) |
| Interval between ejaculation and time of analysis in minutes, n (%) | |||
| ≤60 | 451 (82.3) | 292 (84.4) | 81 (89.0) |
| >60 | 97 (17.7) | 54 (15.6) | 10 (11.0) |
| Abstinence time in days, n (%) | |||
| ≤2 | 301 (54.9) | 199 (57.5) | 45 (49.5) |
| 2–3 | 138 (25.2) | 88 (25.4) | 28 (30.8) |
| >3 | 109 (19.9) | 59 (17.1) | 18 (19.8) |
| Spillage, n (%) | |||
| No | 458 (83.6) | 280 (80.9) | 76 (83.5) |
| Yes | 90 (16.4) | 66 (19.1) | 15 (16.5) |
| Time at blood sample, n (%) | |||
| Morning <12 PM | 207 (37.8) | 110 (31.8) | 38 (41.8) |
| Afternoon 12–18 PM | 289 (52.7) | 192 (55.5) | 43 (47.3) |
| Evening >18 PM | 52 (9.5) | 44 (12.7) | 10 (11.0) |
| Nitrate Concentration in Drinking Water (mg/L) | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| ≤2 (n = 548) | 2– 5 (n = 346) | > 5 (n = 91) | |
| Semen quality characteristics a | |||
| Volume (mL) b | 3 (1;5) | 3 (1;4) | 3 (1;5) |
| Concentration (million/mL) | 40 (8;115) | 36 (6;102) | 42 (7117) |
| Total sperm count (million) b | 102 (19;339) | 96 (17;310) | 122 (14;410) |
| Normal morphology (%) c | 6 (1;13) | 6 (1;13) | 8 (1;15) |
| Motility, non-progressive and immotile (%) c | 37 (19;60) | 37 (21;61) | 34 (19;55) |
| Testes volume a | |||
| Average volume (mL) | 15 (9;23) | 15 (9;25) | 15 (9;23) |
| Reproductive hormones a | |||
| Estradiol (pmol/L) | 53 (18;96) | 52 (12;90) | 54 (28;107) |
| Follicle stimulating hormone (IU/L) | 4 (2;7) | 4 (2;7) | 3 (1;7) |
| Luteninizing hormone (IU/L) | 5 (3;8) | 5 (3;8) | 5 (3;9) |
| Sex hormone binding globulin (nmol/L) | 33 (21;51) | 32 (20;52) | 31 (19;47) |
| Testosterone (nmol/L) | 18 (12;26) | 18 (11;26) | 18 (12;25) |
| Free androgen index (%) | 56 (36;79) | 54 (34;85) | 57 (40;91) |
| Nitrate mg/L | n a | Crude | Adjusted b (95% CI) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Semen quality characteristics | ||||
| Volume (mL) c | >790 | |||
| ≤2 | ref | ref | ||
| 2–5 | −3% | 0% (−7;7) | ||
| >5 | 7% | 8% (−4;22) | ||
| Per 1 mg/L nitrate | 0% | 0% (−1;1) | ||
| Concentration (million/mL) d | >950 | |||
| ≤2 | ref | ref | ||
| 2–5 | −10% | −6% (−16;6) | ||
| >5 | −4% | 0% (−17;19) | ||
| Per 1 mg/L nitrate | −1% | 0% (−2;1) | ||
| Total sperm count (million) c | >790 | |||
| ≤2 | ref | ref | ||
| 2–5 | −6% | 2% (−10;16) | ||
| >5 | 16% | 16% (−4;39) | ||
| Per 1 mg/L nitrate | 0% | 0% (−1;2) | ||
| Normal morphology (%) e | >930 | |||
| ≤2 | ref | ref | ||
| 2–5 | −3% | −2% (−11;8) | ||
| >5 | 19% | 22% (4;42) | ||
| Per 1 mg/L nitrate | 1% | 1% (−1;2) | ||
| Motility, non-pregressive and immotile (%) e,f | >935 | |||
| ≤2 | ref | ref | ||
| 2–5 | 1% | 0% (−5;6) | ||
| >5 | −8% | −9% (−17;−1) | ||
| Per 1 mg/L nitrate | −1% | −1% (−2;0) | ||
| Testes volume | ||||
| Average volume (mL) g | >950 | |||
| ≤2 | ref | ref | ||
| 2–5 | 1% | 1% (−3;6) | ||
| >5 | 1% | 1% (−7;9) | ||
| Per 1 mg/L nitrate | 0% | 0% (−1;1) | ||
| Reproductive hormones | ||||
| Estradiol (pmol/L) h | >950 | |||
| ≤2 | ref | ref | ||
| 2–5 | −5% | −4% (−11;3) | ||
| >5 | 9% | 8% (−3;22) | ||
| Per 1 mg/L nitrate | 1% | 1% (0;2) | ||
| Follicle stimulating hormone (IU/L) h | >950 | |||
| ≤2 | ref | ref | ||
| 2–5 | −1% | −1% (−11;10) | ||
| >5 | −15% | −15% (−27;−1) | ||
| Per 1 mg/L nitrate | −1% | −1% (−2%;1) | ||
| Luteninizing hormone (IU/L) h | >950 | |||
| ≤2 | ref | ref | ||
| 2–5 | −3% | −2% (−8;5) | ||
| >5 | −8% | −8% (−18;2) | ||
| Per 1 mg/L nitrate | 0% | 0% (−1;1) | ||
| Sex hormone binding globulin (nmol/L) h | >950 | |||
| ≤2 | ref | ref | ||
| 2–5 | −2% | −1% (−6;4) | ||
| >5 | −9% | −8% (−16;0) | ||
| Per 1 mg/L nitrate | 0% | 0% (−1;0) | ||
| Testosterone (nmol/L) h | >950 | |||
| ≤2 | ref | ref | ||
| 2–5 | −3% | −1% (−6;3) | ||
| >5 | −3% | −3% (−9;3) | ||
| Per 1 mg/L nitrate | 0% | 0% (0;1) | ||
| Free androgen index (%) h | >950 | |||
| ≤2 | ref | ref | ||
| 2–5 | 3% | 3% (−4;10) | ||
| >5 | 6% | 3% (−5;11) | ||
| Per 1 mg/L nitrate | 0% | 0% (0;1) | ||
| Nitrate mg/L | n a | Adjusted b (95% CI) | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Semen quality characteristics | |||
| Volume (mL) c | >625 | ||
| ≤2 | ref | ||
| 2–5 | 2% (−7;12) | ||
| >5 | 2% (−12;18) | ||
| Per 1 mg/L nitrate | 0% (−1;1) | ||
| Concentration (million/mL) d | >765 | ||
| ≤2 | ref | ||
| 2–5 | 9% (−6;26) | ||
| >5 | −17% (−36;8) | ||
| Per 1 mg/L nitrate | −1% (−3;1) | ||
| Total sperm count (million) c | >630 | ||
| ≤2 | ref | ||
| 2–5 | 6% (−10;24) | ||
| >5 | −10% (−33;22) | ||
| Per 1 mg/L nitrate | −1% (−3;1) | ||
| Normal morphology (%) e | >745 | ||
| ≤2 | ref | ||
| 2–5 | 11% (−1;25) | ||
| >5 | 7% (−16;37) | ||
| Per 1 mg/L nitrate | 1% (−1;3) | ||
| Motility, non-progressive and immotile (%) e,f | >750 | ||
| ≤2 | ref | ||
| 2–5 | −9% (−16;−2) | ||
| >5 | −9% (−21;5) | ||
| Per 1 mg/L nitrate | −1% (−2;0) | ||
| Testes volume | |||
| Average volume (mL) g | >760 | ||
| ≤2 | ref | ||
| 2–5 | 1% (−5;7) | ||
| >5 | 5% (−5;16) | ||
| Per 1 mg/L nitrate | 0% (−1;1) | ||
| Reproductive hormones | |||
| Estradiol (pmol/L) h | >765 | ||
| ≤2 | ref | ||
| 2–5 | −7% (−16;4) | ||
| >5 | 3% (−13;20) | ||
| Per 1 mg/L nitrate | 0% (−1;1) | ||
| Follicle stimulating hormone (IU/L) h | >760 | ||
| ≤2 | ref | ||
| 2–5 | 0% (−10;11) | ||
| >5 | −5% (−27;24) | ||
| Per 1 mg/L nitrate | −1% (−2;1) | ||
| Luteninizing hormone (IU/L) h | >760 | ||
| ≤1 | ref | ||
| 2–5 | 1% (−6;8) | ||
| >5 | −3% (−19;15) | ||
| Per 1 mg/L nitrate | −1% (−2;0) | ||
| Sex hormone binding globulin (nmol/L) h | >760 | ||
| ≤2 | ref | ||
| 2–5 | 4% (−2;11) | ||
| >5 | 5% (−5;17) | ||
| Per 1 mg/L nitrate | 0% (0;1) | ||
| Testosterone (nmol/L) h | >765 | ||
| ≤1 | ref | ||
| 2–5 | 4% (−1;10) | ||
| >5 | −1% (−9,8) | ||
| Per 1 mg/L nitrate | 0% (−1;1) | ||
| Free androgen index (%) h | >760 | ||
| ≤2 | ref | ||
| 2–5 | 6% (−2;16) | ||
| >5 | −6% (−15;4) | ||
| Per 1 mg/L nitrate | 0% (−1;0) | ||
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Clemmensen, P.J.; Brix, N.; Schullehner, J.; Gaml-Sørensen, A.; Toft, G.; Tøttenborg, S.S.; Ebdrup, N.H.; Hougaard, K.S.; Hansen, B.; Sigsgaard, T.; et al. Nitrate in Maternal Drinking Water during Pregnancy and Measures of Male Fecundity in Adult Sons. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 14428. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph192114428
Clemmensen PJ, Brix N, Schullehner J, Gaml-Sørensen A, Toft G, Tøttenborg SS, Ebdrup NH, Hougaard KS, Hansen B, Sigsgaard T, et al. Nitrate in Maternal Drinking Water during Pregnancy and Measures of Male Fecundity in Adult Sons. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health. 2022; 19(21):14428. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph192114428
Chicago/Turabian StyleClemmensen, Pernille Jul, Nis Brix, Jörg Schullehner, Anne Gaml-Sørensen, Gunnar Toft, Sandra Søgaard Tøttenborg, Ninna Hinchely Ebdrup, Karin Sørig Hougaard, Birgitte Hansen, Torben Sigsgaard, and et al. 2022. "Nitrate in Maternal Drinking Water during Pregnancy and Measures of Male Fecundity in Adult Sons" International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health 19, no. 21: 14428. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph192114428
APA StyleClemmensen, P. J., Brix, N., Schullehner, J., Gaml-Sørensen, A., Toft, G., Tøttenborg, S. S., Ebdrup, N. H., Hougaard, K. S., Hansen, B., Sigsgaard, T., Kolstad, H. A., Bonde, J. P. E., & Ramlau-Hansen, C. H. (2022). Nitrate in Maternal Drinking Water during Pregnancy and Measures of Male Fecundity in Adult Sons. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 19(21), 14428. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph192114428









