Abstract
Helicobacter species can colonize the gastrointestinal tract of both humans and animals, and are associated with gastrointestinal and extra-gastrointestinal diseases. Some studies indicate that animals, health professionals, and people in close contact with animals might be at higher risk for infection with gastric Helicobacter spp. Considering that veterinarians are professionals at risk for infection with zoonotic gastric Helicobacters and are also seen by many as health communicators concerning zoonoses, the aim of this study was to evaluate the Portuguese veterinarians’ perception and knowledge of Helicobacter spp. infection and its zoonotic risk/potential. Therefore, a structured questionnaire composed of 34 dichotomic, multiple-choice, rating scale, matrix, drop-down, and open-ended questions was developed and given to Portuguese veterinarians via an online platform from May 2021 to July 2021, and statistical analysis was used to obtain results. There was a total of 149 respondents, most of them (73.8%) being females. Evidently, Portuguese veterinarians have a limited perception regarding Helicobacter spp. infections. Of the respondents that “have heard of Helicobacter”, 17.6% do not know which animal species can be affected by it. Most of the companion animal veterinarians (76.2%) do not consider Helicobacter spp. infection a differential diagnosis when evaluating animals with gastritis. A significant percentage (37.2%) of the respondents that have “heard of H. suis” do not consider it a zoonotic bacterium. There is a need for education and sensitization of veterinarians regarding the potential zoonotic risk of Helicobacter spp. in order to elucidate these professionals to this One Health issue, as the number of reports of non-Helicobacter pylori Helicobacter in livestock, companion, and wild animals is increasing.
Keywords:
awareness; NHPH; One Health; public health; occupational health; risk communication; zoonosis 1. Introduction
Helicobacter species can colonize the gastrointestinal tract of both humans and animals and are characterized as Gram-negative, spiral-shaped motile bacteria associated with several diseases [1,2,3,4].
In 1994, the World Health Organization (WHO) classified Helicobacter pylori (H. pylori) in the first group of carcinogenic agents, and its eradication remains a public health concern worldwide [5].
In humans, H. pylori is the most common gastric pathogen, affecting more than half of the world’s population, playing a major role in the development of gastritis, gastroduodenal ulcers, gastric adenocarcinoma, mucosa-associated lymphoid tissue (MALT) lymphoma, and extra-digestive diseases [1,6,7,8].
Gastric non-Helicobacter pylori Helicobacter (NHPH) have been associated with a wide range of pathologies, from MALT lymphoma to extra-digestive diseases, and have been diagnosed in 0.2–6% of human gastric biopsies [2,4,9].
In humans, Helicobacter suis (H. suis), naturally hosted by pigs, is the most prevalent NHPH and has also been associated with a range of gastric and extra-digestive pathologies [1,4,10,11,12,13]. Recent reports reinforce that these infections most likely originate from pigs, emphasizing their zoonotic potential [12,13,14,15].
H. pylori infection is acquired predominantly during childhood and persists throughout life without treatment [5]. The route of transmission is not 100% known and the human stomach is considered the only known reservoir, despite having been identified in other species’ stomachs [5,14,16,17]. Human-to-human transmission may occur through different pathways (such as gastro-oral, oral-oral, and fecal-oral), but there are other routes also hypothesized to be foodborne transmissions as the organism has been identified in food and water [5,17,18]. Indeed, H. pylori has been detected in drinking water, seawater, vegetables, and foods of animal origin. H. pylori survives in complex foodstuffs such as milk, vegetables, and ready-to-eat foods [19] and it has been demonstrated to transmit between humans and animals [20]. These types of contaminations are hypothesized to be the cause of new infections [5]. H. suis DNA was detected on pork carcasses in slaughterhouses, and the bacterium can persist for up to 48 h in experimentally contaminated pork. Therefore, pork consumption may constitute a new route of H. suis transmission in humans [21]. H. suis has also been associated with gastric disease in animal health professionals, emphasizing its zoonotic importance [12]. Thus, as some studies indicate, animals, health professionals, and people in close contact with animals might be at a higher risk for infection [22].
Considering that veterinarians are professionals at risk for infection with zoonotic species of gastric Helicobacters, and are also seen by many as health communicators concerning zoonoses, the aim of this study was to evaluate the Portuguese veterinarians’ perception and knowledge of Helicobacter spp. infection and its zoonotic risk/potential.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Data Collection
Data collection was performed using a structured questionnaire, specifically developed for this study in Portuguese. The draft questionnaire was designed based on the bibliographic review and three focus groups with veterinarians. Then, it was tested before being released. The questionnaire includes information related to general demographic (date of birth, gender, region), contact with animals (specifically pigs and wild boars), and the context and duration of the contact. Information regarding food consumption, consumption of pig and wild boar meat or meat products, as well as the frequency of weekly consumption and food safety, was also assessed. Moreover, data regarding perception and knowledge of Helicobacter spp., H. suis, H. pylori, infection, and zoonotic risk was assessed. Data regarding the possible gastric disease of each participant presumably associated or not with Helicobacter spp. infection was also addressed. Finally, these data were collected regarding the participants’ interest in receiving further information about Helicobacter spp. infection in animals and humans and how they would like to receive any further information.
The following variables were considered for the present study: general demographic characteristics, contact with animals, nutritional habits, food safety habits, veterinarians’ knowledge of Helicobacter spp., perception of each individual gastric pathology, and receptiveness to obtain more information regarding the survey topic.
This process resulted in the final survey, composed of 34 dichotomic, multiple-choice, rating scale, matrix, drop-down, and open-ended questions.
2.2. Study Design and Participants
A cross-sectional study using data from an online survey based on the snowball sampling method was performed [23]. A virtual snowball sampling survey was disseminated, firstly, through closed social networking channels (namely, Facebook®, Menlo Park, CA, USA) and, secondly, through the researcher’s mailing lists to work colleagues and veterinarian friends. The inclusion criteria consisted of age ≥23, being a certified veterinarian, and being based in Portugal. Everyone who followed the link accepted to participate. Since the survey did not have information on where the participants were recruited (e.g., Facebook or mailing list), due to confidentiality, we cannot calculate the proportion of participants that come from each networking channel. For the present study, data was gathered from May 2021 to July 2021, corresponding to a convenience sample of 149 individuals.
2.3. Ethics Approval and Consent to Participate
Ethical approval was obtained from the i3S Animal Welfare and Ethics Review Body (ref.2021-4). According to the Ethical Principles for Medical Research involving human subjects expressed in the Declaration of Helsinki and the current national legislation, all participants were asked to give their informed consent. Since this was an online survey, participants had to select the option: “accept to participate in the study to proceed with the survey”. The questionnaire was confidential, and no data that allowed the identification of the participants was collected.
2.4. Statistical Analysis
These data were analyzed using IBM SPSS® Statistics v27 (IBM, Armonk, NY, USA). Descriptive statistics were generated to verify the variables described above. Cross-tables and chi-square analyses were used to explore possible associations between nominal variables and Cramer’s V test, with an oscillation between 0 and 1, to assess the intensity of the relationship between variables. Statistical significance was set at p < 0.05.
3. Results
3.1. Sociodemographic Distribution
Of the 149 questionnaires were completed, 73.8% (110/149) of the respondents were female veterinarians and 26.2% (39/149) were male veterinarians. The mean age was 37.2 years-old and 71.1% (106/149) were companion animal veterinarians.
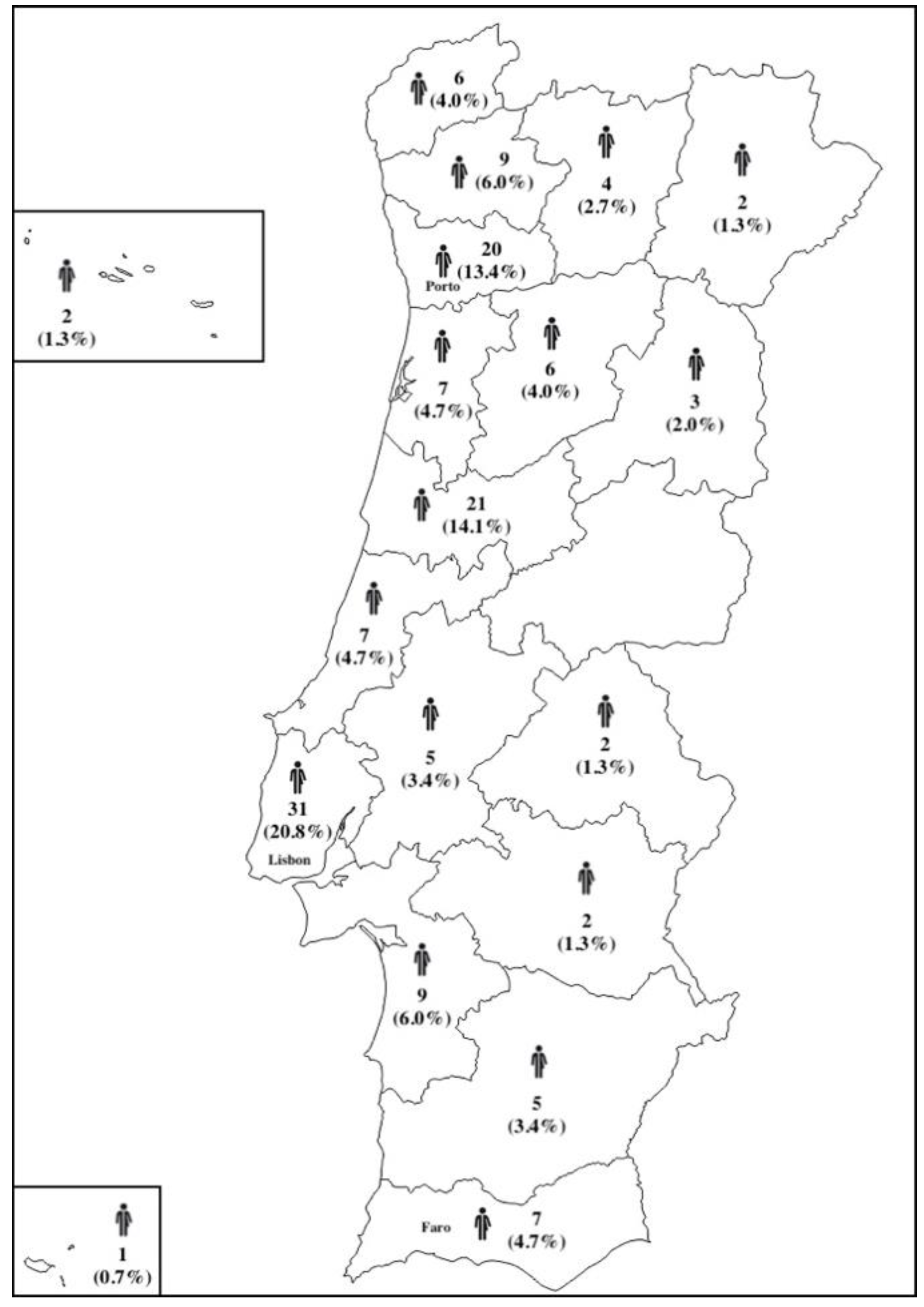
There were respondents from 17 of the 18 districts of Portugal with the greater percentages of respondents from Lisbon (20.8%), Coimbra (14.1%), and Porto (13.4%) in concordance with the most populated regions in Portugal (Figure 1).
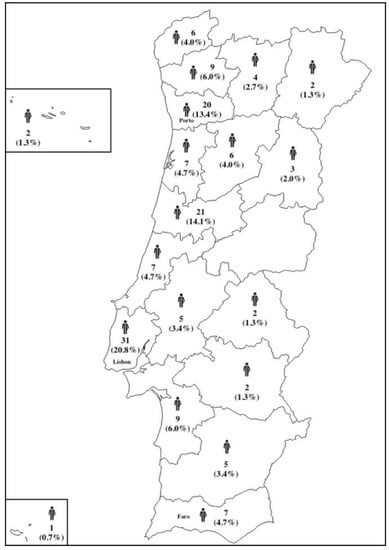
Figure 1.
Distributions of the respondents enrolled in the questionnaire.
3.2. Knowledge about Helicobacter spp. Infection
When the questionnaire asked “have you heard of Helicobacter?”, only 0.7% (1/149) chose “no” and 99.3% (148/149) chose “yes”. Of the respondents that chose “yes”, 97.3% (144/148) answered “yes, I know what it is” and 2.7% (4/148) “yes, but I don’t know what it is”.
Of the 148 respondents that “have heard of Helicobacter”, when asked the question “have you heard of H. suis?”, 47.0% replied “no”, 38.3% replied “yes, and I know what it is”, 13.4% replied “yes, but I don’t know what it is”, and 0.7% preferred not to answer. Regarding the question “Have you heard of H. pylori?”, 2.0% selected “no”, 92.6% selected “yes, and I know what it is”, and 4.7% selected “yes, but I don’t know what it is”.
From the 148 respondents that “have heard of Helicobacter,” 17.6% did not know which animal species could be affected by Helicobacter, and only 4.0% stated that they “do not know” clinical signs associated with Helicobacter spp. infection in animals or humans.
Of the 106 respondent veterinarians who practice in companion animal clinics, the majority never (22.6%) or rarely (50.0%) consider Helicobacter spp. infection as a differential diagnosis of gastritis in companion animals; on the other hand, 21.6% frequently and 3.8% always consider it.
Of those 106 companion animal veterinarians, 22.6% have already diagnosed gastritis associated with Helicobacter spp. infection while 54.7% never have. Within the 24 companion animal veterinarians that have diagnosed gastritis associated with Helicobacter spp. infection, 22.6% diagnosed it in dogs, 8.3% in cats, and 12.5% in other species.
Of the 149 respondents, 47.7% consider Helicobacter spp. a zoonotic bacteria, 13.4% do not consider it a zoonotic bacteria, and 38.9% “do not know”.
Although 71 veterinarians consider the zoonotic potential of Helicobacter spp., most (45.1%, 32/71) referred to an ambiguous answer when asked how the transmission between animals and humans occurs. Some indicated “food contamination” (21.1%, 15/71), “feco-oral route” (16.9%, 12/71), or “oral-oral route” (8.5%, 6/71), while 11.2% (8/71) stated that they “do not know”.
3.3. Contact with Pigs and Wild Boars and Consumption of Their Meat or Meat Products
Of the total respondents, 79.2% (118/149) had contact with pigs and/or wild boars: 31.4% (37/118) as livestock animal veterinarians, 23.7% (28/118) as companion animal veterinarians, 11.9% (14/118) as meat inspectors, 10.2% (12/118) when they were students, 1.7% (2/118) as hunters, 1.7% (2/118) as livestock farmers, and 19.5% (23/118) in other circumstances.
Of the 118 veterinarians who had contact with pigs and or wild boars, 52.5% have been in contact with pigs for less than 5 years and 47.5% for more than 5 years.
Regarding consumption of pig and wild boar meat or meat products: 89.9% (134/149) consumed pork at least once per week and 90.6% (135/149) consumed pork products, 38.9% (58/149) consumed wild boar meat at least once per week, and 18.1% (27/149) consumed wild boar meat products at least once per week.
3.4. Food Safety and Hygiene
More than one-fourth of the veterinarians (28.8%, 34/149) refer to the use of borehole water during food preparation or for ingestion.
Regarding the preparation of food at home, 98.7% (147/149) prepare food at home at least once per week.
Of the 147 respondents that prepare food at home, 97.9% (144/147) state that they “have hygiene and safety measures during food preparation”, 0.7% (1/147) state that do not have hygiene and safety measures during food preparation, and 1.4% (2/147) state they “do not know if they have hygiene and safety measures during food preparation”. When questioned about which type of hygiene and safety measures they practice: 81.3% (117/144) mentioned “food washing”, 45.1% (65/144) “cooking”, 27.8% (40/144) “food separation to avoid cross-contamination”, 10.4% (15/144) “refrigeration”, and 3.5% (5/144) “hand washing”.
3.5. Gastric Pathology among Veterinarians
Of the respondent veterinarians, 83.9% (125/149) admitted to having “gastric pain”, 69.1% (103/149) “had gastritis”, 77.2% (115/149) “suffered from gastric reflux/heartburn”, and 30.9% (46/149) did some type of gastric diagnostic test (Table 1). Finally, 21.5% (32/149) of the respondents are medicated for gastric disease.

Table 1.
Assessment of veterinarians’ gastric pathology: questions and answers (numbers and percentages).
A total of 22 (14.7%) of the 149 participants responded that they had gastric disease associated with Helicobacter. Of this number, 100% (22/22) claim to have been treated for Helicobacter pylori infection, with 50.0% (11/22) cured or eradicated, 18.2% (4/22) not cured or eradicated, and 31.8% (7/22) did not know if they got cured or if eradication was achieved.
3.6. Interest in Receiving Information on Helicobacter spp. Infections
Lastly, the respondents were questioned if they would like to receive more information about Helicobacter spp. infection in livestock animals, companion animals, or humans. Most (85.9%, 128/149) said “yes”, and 32.0% (41/149) responded that they would like to get it through the Portuguese Order of Veterinarians (Ordem dos Médicos Veterinários, OMV).
3.7. Statistical Associations between Variables
When applying statistical analysis to determine if there was any association between them, it was possible to conclude that there are some statistically significant associations (with green background in Table 2) whose strengths vary from weak (<0.1) to moderate (<0.3) considering the Cramer’s V and the degree of freedom =1.

Table 2.
Statistical association between variables.
4. Discussion
There are several species of gastric Helicobacters, with H. pylori being one of the most studied since humans remain the natural host. H. pylori is associated with gastric disease as it may cause gastritis, peptic ulcer disease, gastric carcinoma, and mucosa-associated lymphoid tissue (MALT) lymphoma. Besides this species, other NHPHs with zoonotic potential, such as H. suis, have been associated with gastric and neurologic pathologies in humans [2,4,10,24,25]. Considering the close contact between humans and animals and the late reports of Helicobacter spp. in humans [26], the late reports of H. pylori human-animal transmission and infection [20], or the detection of H. pylori DNA in other animal species [14,16], and also the description of human H. suis infection [1,27], including a report in a veterinarian [12], our goal was to investigate the awareness of veterinarians regarding Helicobacter species, such as H. pylori and H. suis.
However, there are two limitations that should be pointed out: one is the small sample size and the other is that the majority of the respondents were female veterinarians, so the generalizability of our findings is limited.
Most of the 149 questionnaire respondents were females (73.8%), as expected according to the 2018 European veterinary survey applied and published by the Federation of Veterinarians of Europe (FVE) [28]. Additionally, according to the OMV, on the 12th February 2020, there were 4071 (61%) female veterinarians and 2551 (39%) male veterinarians registered in Portugal. Therefore, when associating different variables with gender, there is expected to be a deviation towards the female gender.
Despite some of the NHPHs being considered zoonotic or with zoonotic potential [25,29], in this study 37.2% of the respondents that “heard of H. suis” do not consider it a zoonosis (p < 0.001; cv = 0.322). However, people directly affected by H. pylori infection seem to be aware of this hypothesis since 68.2% of the respondents that “had gastric disease associated with Helicobacter” (p = 0.037; cv = 0.171) and 68.2% that “had treatment for Helicobacter infection” (p = 0.029; cv = 0.219) consider it a zoonosis.
Interestingly, 59.0% of the respondents between the ages of 25 and 35 years-old consider Helicobacter spp. infections a zoonosis, while only 39.8% of the respondents between the ages of 36 and 68 years-old do (p = 0.021; cv = 0.189). We hypothesize that the recent emergence of zoonoses globally [30] may have made younger professionals more aware of these diseases.
Some studies report the presence of H. suis on pig carcasses and retail meat which can pose a transmission route [21,31]. Intriguingly, 42.4% of the respondents to the questionnaire that claim “to eat pork” regularly also “have gastric pain” (p = 0.047; cv = 0.163). Although no direct association can be made, this result should be explored in further studies.
Regarding food safety and hygiene, despite 97.9% of the respondents that prepare food at home stating that they “have hygiene and safety measures during food preparation” (p < 0.01; cv = 0.398), only 3.5% mention “hand washing” as a food safety practice. Similar findings were reported in a study by Stratev et al. (2017) concluded that, despite the high level of awareness of food safety, these practices were low among veterinary medicine students in Bulgaria [32].
With our study we were able to assess that most of the respondents have limited perception and knowledge about the zoonotic/anthropozoonotic risks of H. suis and H. pylori infections. When questioned “have you heard of Helicobacter”, 99.3% chose“yes” with the majority of the respondents (97.3%) knowing H. pylori but only 51.7% acknowledging H. suis, and interestingly, 17.6% of respondents that “have heard of Helicobacter” did not know which animals’ species could be affected. Furthermore, 13.4% do not consider Helicobacter spp. a zoonotic bacteria and 38.9% “do not know”, even though 96.6% claimed that they “have heard of Helicobacter and know what it is” and 38.3% “have heard of H. suis and know what it is”.
It can also be hypothesized that Helicobacter spp. infections among animals could be underdiagnosed due to a lack of knowledge/awareness of veterinarians regarding this bacterial infection. In fact, 17.6% did not know the animal species that could be affected, and of the 106 veterinarians that practice at companion animals’ clinics, 72.6% never (22.6%) or rarely (50.0%) consider Helicobacter spp. infection as a differential diagnosis of gastritis in companion animals.
When assessing gastric pathology among the respondents, 59.4% of females responded positively to “did you use to have gastric pain” and 68.2% of females “have had treatment for Helicobacter” (p = 0.003; cv = 0.277), which follows the study published by Khoder et al. (2021) that reports a higher occurrence of H. pylori infections in females [33].
We also concluded that veterinarians with higher contact time (>5 years) with pigs (52.9%) also “had had treatment for Helicobacter infection” (p = 0.020; cv = 0.268), which again may indicate the occupational risk of these professionals as reported by Joosten et al. (2013) [12].
Remarkably, 86.5% of the respondents that “have heard of Helicobacter spp.” (p = 0.013; cv = 0.203), 85.7% that “have not heard of H. suis” (p = 0.045; cv = 0.204), 87.2% that “have heard of H. pylori” (p = 0.001; cv = 0.299), 100% that “take medication for gastric pain” (p = 0.010; cv = 0.212), 100% that “have gastric problems associated with Helicobacter infection” (p = 0.040; cv = 0.169), and 100% that “had treatment for H. pylori infection” (p = 0.023; cv = 0.226) would like to receive more information about this bacterial infection in livestock, companion animals, and humans. This may suggest that despite having some insights about the subject, they would like to get further information and enrich their knowledge.
On the other side, we should not neglect that a surprising percentage of veterinarians (14.1%) do not wish to receive additional information.
To the authors’ best knowledge there are no studies that assess the perception, awareness, and knowledge of veterinarians regarding Helicobacter spp. infections. This makes our results the first to be reported and challenging to compare since there are no similar studies among veterinarians that are up to date.
It is known that zoonotic diseases are a growing concern, amounting to approximately 60% of the existing human pathogens, and over 75% of those can be tracked to animals [34]. Sometimes, zoonotic diseases manifest in animals before they infect humans [35], so veterinarians possess specialty training in zoonoses and, thereafter, should be a great resource of information on this subject [36]. In addition, m according to Spear et al. (2015), people would be willing to consult with a veterinarian on the advice of their physician if they had a zoonotic disease [36]. Some studies also show that veterinarians should be active not only in controlling zoonotic diseases in animals but also in providing information for patients and physicians, and that physicians assign them the duty of educating populations about zoonoses [36,37,38]. This happens because physicians are uncomfortable with their knowledge about zoonoses [36,38]. Therefore, physicians consign veterinarians the duty of educating the public about zoonoses, yet neither of these experts communicate with the other [35].
Despite the results of our study being suggestive of limited knowledge and awareness of veterinarians regarding Helicobacter spp. infections, they continue to play an important role in the promotion of public health [35,39]. Pet owners are more likely to contact their veterinarian than their physician regarding information about zoonoses [40], along with the fact that they consider the role of veterinarians important as public health promoters [39]. So further training programs addressing vet communication skills should take into account the particular issues of emerging zoonoses, and veterinarians need to have proper knowledge so they can assess and explain the risks to their clients [41].
The medical and veterinary communities should collaborate closely in clinical, public health, and research contexts since zoonoses can infect both animals and humans [42].
Veterinarians are in the perfect position to give animal owners trustworthy information since they are more aware of the possible hazards of zoonotic diseases and how to minimize them.
There is a need for collaboration between animal, human, and environmental professionals in an objective One Health perspective due to the increase in emerging zoonotic diseases. Veterinarians seem to show greater awareness of the importance of cooperation activities and continuous cross-sectional formation than physicians [34].
Nonetheless, communication between veterinarians and physicians seems to be insufficient [37], so it is important to create awareness of this need and promote cooperation and communication since the One Health initiative aims to reduce this professional gap between veterinarians and physicians [43], and both parts can and should play a role on public health education.
5. Conclusions
There is a need for education and sensitization of veterinarians regarding the zoonotic risk of Helicobacter spp. in order to elucidate these professionals to this One Health issue since the number of reports of NHPH in livestock, companion, and wild animals are increasing.
The results of this study allowed us to conclude that communication and sensibilization regarding Helicobacter spp. infections in animals and its zoonotic potential should be done by veterinarians since there are 37.2% of them that heard of H. suis but do not consider it a zoonosis. A special focus should be implemented regarding veterinarians older than 35 years since only 39.8% of these consider Helicobacter spp. infections as potential zoonoses.
The veterinarian respondents demonstrated interest in receiving more information regarding Helicobacter spp. infections in production animals, companion animals, or humans which could, in fact, increase their awareness on this topic, and improve their role as clinicians and public health agents.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, F.C.N., R.L.M., I.A. and T.L.M.; methodology, F.C.N., R.L.M., I.A. and T.L.M.; software, F.C.N. and R.L.M.; validation, R.L.M., T.L.M. and I.A.; formal analysis, F.C.N., R.L.M., I.A. and T.L.M.; investigation, F.C.N.; data curation, F.C.N., R.L.M., I.A. and T.L.M.; writing—original draft preparation, F.C.N.; writing—review and editing, S.T., R.L.M., I.A. and T.L.M.; supervision, I.A. and T.L.M. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by FCT-the Portuguese Foundation for Science and Technology, MCTES-Ministry of Science, Technology and Higher Education, FSE- European Social Fund and UE-European Union (SFRH/BD/147761/2019). The participation of Teresa Letra Mateus was supported by the projects UIDB/CVT/00772/2020 and LA/P/0059/2020 funded by the Portuguese Foundation for Science and Technology (FCT).
Institutional Review Board Statement
Ethical approval was obtained from the i3S Animal Welfare and Ethics Review Body (ref.2021-4) in March 2021. According to the Ethical Principles for Medical Research involving human subjects expressed in the Declaration of Helsinki and the current national legislation, all participants were asked to give their informed consent. Since this was an online survey, participants must select the option: to accept to participate in the study to proceed with the survey. The questionnaire was confidential, and no data that allow the identification of the participants was collected.
Informed Consent Statement
Informed consent was obtained from all subjects involved in the study.
Data Availability Statement
Not applicable.
Acknowledgments
We would like to thank all the veterinarian respondents that participated in this questionnaire.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Ali, B.; Chloë, W.; Mehmet, A.; Sofie, B.; Annemieke, S.; Gökhan, T.; Tülin, G.G.; Freddy, H.; Fatih, K. Presence of gastric Helicobacter species in children suffering from gastric disorders in Southern Turkey. Helicobacter 2018, 23, e12511. [Google Scholar]
- Haesebrouck, F.; Pasmans, F.; Flahou, B.; Chiers, K.; Baele, M.; Meyns, T.; Decostere, A.; Ducatelle, R. Gastric helicobacters in domestic animals and nonhuman primates and their significance for human health. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2009, 22, 202–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, Y.K.; Han, J.H.; Joo, H.S. Identification of novel Helicobacter species in pig stomachs by PCR and partial sequencing. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2001, 39, 3311–3315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gorlé, N.; Bauwens, E.; Haesebrouck, F.; Smet, A.; Vandenbroucke, R.E. Helicobacter and the Potential Role in Neurological Disorders: There Is More Than Helicobacter pylori. Front. Immunol. 2020, 11, 584165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kayali, S.; Manfredi, M.; Gaiani, F.; Bianchi, L.; Bizzarri, B.; Leandro, G.; Di Mario, F.; Angelis, G.L.D. Helicobacter pylori, transmission routes and recurrence of infection: State of the art. Acta Biomed. 2018, 89, 72–76. [Google Scholar]
- Lopo, I.; Libânio, D.; Pita, I.; Dinis-Ribeiro, M.; Pimentel-Nunes, P. Helicobacter pylori antibiotic resistance in Portugal: Systematic review and meta-analysis. Helicobacter 2018, 23, e12493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guevara, B.; Cogdill, A.G. Helicobacter pylori: A Review of Current Diagnostic and Management Strategies. Dig. Dis. Sci. 2020, 65, 1917–1931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baj, J.; Forma, A.; Flieger, W.; Morawska, I.; Michalski, A.; Buszewicz, G.; Sitarz, E.; Portincasa, P.; Garruti, G.; Flieger, M.; et al. Helicobacter pylori Infection and Extragastric Diseases-A Focus on the Central Nervous System. Cells 2021, 10, 2191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baele, M.; Decostere, A.; Vandamme, P.; Ceelen, L.; Hellemans, A.; Mast, J.; Chiers, K.; Ducatelle, R.; Haesebrouck, F. Isolation and characterization of Helicobacter suis sp. nov. from pig stomachs. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2008, 58 Pt 6, 1350–1358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Augustin, A.D.; Savio, A.; Nevel, A.; Ellis, R.J.; Weller, C.; Taylor, D.; Tucker, R.M.; Ibrahim, M.A.A.; Bjarnason, I.; Dobbs, S.M.; et al. Helicobacter suis Is Associated With Mortality in Parkinson’s Disease. Front. Med. 2019, 6, 188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bosschem, I.; Flahou, B.; Van Deun, K.; De Koker, S.; Volf, J.; Smet, A.; Ducatelle, R.; Devriendt, B.; Haesebrouck, F. Species-specific immunity to Helicobacter suis. Helicobacter 2017, 22, e12375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joosten, M.; Flahou, B.; Meyns, T.; Smet, A.; Arts, J.; De Cooman, L.; Pasmans, F.; Ducatelle, R.; Haesebrouck, F. Case report: Helicobacter suis infection in a pig veterinarian. Helicobacter 2013, 18, 392–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flahou, B.; Rossi, M.; Bakker, J.; Langermans, J.A.; Heuvelman, E.; Solnick, J.V.; E Martin, M.; O’Rourke, J.; Ngoan, L.D.; Hoa, N.X.; et al. Evidence for a primate origin of zoonotic Helicobacter suis colonizing domesticated pigs. Isme J. 2018, 12, 77–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cortez Nunes, F.; Letra Mateus, T.; Teixeira, S.; Barradas, P.; de Witte, C.; Haesebrouck, F.; Amorim, I.; Gärtner, F. Presence of Helicobacter pylori and H. suis DNA in Free-Range Wild Boars. Animals 2021, 11, 1269. [Google Scholar]
- Rimbara, E.; Suzuki, M.; Matsui, H.; Nakamura, M.; Morimoto, M.; Sasakawa, C.; Masuda, H.; Nomura, S.; Osaki, T.; Nagata, N.; et al. Isolation and characterization of Helicobacter suis from human stomach. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2021, 118, e2026337118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cortez Nunes, F.; Mateus, T.L.; Teixeira, S.; Barradas, P.F.; Gärtner, F.; Haesebrouck, F.; Amorim, I. Molecular Detection of Human Pathogenic Gastric Helicobacter Species in Wild Rabbits (Oryctolagus cuniculus) and Wild Quails (Coturnix coturnix). Zoonotic Dis. 2021, 1, 42–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leja, M.; Grinberga-Derica, I.; Bilgilier, C.; Steininger, C. Review: Epidemiology of Helicobacter pylori infection. Helicobacter 2019, 24 (Suppl. 1), e12635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burucoa, C.; Axon, A. Epidemiology of Helicobacter pylori infection. Helicobacter 2017, 22, e12403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quaglia, N.C.; Dambrosio, A. Helicobacter pylori: A foodborne pathogen? World J. Gastroenterol. 2018, 24, 3472–3487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kubota-Aizawa, S.; Matsubara, Y.; Kanemoto, H.; Mimuro, H.; Uchida, K.; Chambers, J.; Tsuboi, M.; Ohno, K.; Fukushima, K.; Kato, N.; et al. Transmission of Helicobacter pylori between a human and two dogs: A case report. Helicobacter 2021, 26, e12798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Cooman, L.; Flahou, B.; Houf, K.; Smet, A.; Ducatelle, R.; Pasmans, F.; Haesebrouck, F. Survival of Helicobacter suis bacteria in retail pig meat. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2013, 166, 164–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sabry, M.A.; Abdel-Moein, K.A.; Seleem, A. Evidence of Zoonotic Transmission of Helicobacter canis Between Sheep and Human Contacts. Vector Borne Zoonotic Dis. 2016, 16, 650–653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aguiar, A.; Pinto, M.; Duarte, R. Psychological Impact of the COVID-19 Pandemic and Social Determinants on the Portuguese Population: Protocol for a Web-Based Cross-sectional Study. JMIR Res. Protoc. 2021, 10, e28071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taillieu, E.; Chiers, K.; Amorim, I.; Gärtner, F.; Maes, D.; Van Steenkiste, C.; Haesebrouck, F. Gastric Helicobacter species associated with dogs, cats and pigs: Significance for public and animal health. Vet. Res. 2022, 53, 42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flahou, B.; Haesebrouck, F.; Smet, A. Non-Helicobacter pylori Helicobacter Infections in Humans and Animals, in Helicobacter pylori Research: From Bench to Bedside; Backert, S., Yamaoka, Y., Eds.; Springer: Tokyo, Japan, 2016; pp. 233–269. [Google Scholar]
- Matos, R.; Taillieu, E.; De Bruyckere, S.; De Witte, C.; Rêma, A.; Santos-Sousa, H.; Nogueiro, J.; Reis, C.A.; Carneiro, F.; Haesebrouck, F.; et al. Presence of Helicobacter Species in Gastric Mucosa of Human Patients and Outcome of Helicobacter Eradication Treatment. J. Pers. Med. 2022, 12, 181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakamura, M.; Øverby, A.; Michimae, H.; Matsui, H.; Takahashi, S.; Mabe, K.; Shimoyama, T.; Sasaki, M.; Terao, S.; Kamada, T.; et al. PCR analysis and specific immunohistochemistry revealing a high prevalence of non-Helicobacter pylori Helicobacters in Helicobacter pylori-negative gastric disease patients in Japan: High susceptibility to an Hp eradication regimen. Helicobacter 2020, 25, e12700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Federation of Veterinarians of Europe. 9 June 2022. Available online: https://fve.org/cms/wp-content/uploads/FVE_Survey_2018_WEB.pdf (accessed on 13 July 2022).
- Mladenova-Hristova, I.; Grekova, O.; Patel, A. Zoonotic potential of Helicobacter spp. J. Microbiol. Immunol. Infect. 2017, 50, 265–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McArthur, D.B. Emerging Infectious Diseases. Nurs. Clin. N. Am. 2019, 54, 297–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Cooman, L.; Houf, K.; Smet, A.; Flahou, B.; Ducatelle, R.; De Bruyne, E.; Pasmans, F.; Haesebrouck, F. Presence of Helicobacter suis on pork carcasses. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2014, 187, 73–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stratev, D.; Odeyemi, O.A.; Pavlov, A.; Kyuchukova, R.; Fatehi, F.; Bamidele, F.A. Food safety knowledge and hygiene practices among veterinary medicine students at Trakia University, Bulgaria. J. Infect. Public Health 2017, 10, 778–782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khoder, G.; Muhammad, J.S.; Mahmoud, I.; Soliman, S.S.M.; Burucoa, C. Prevalence of Helicobacter pylori and Its Associated Factors among Healthy Asymptomatic Residents in the United Arab Emirates. Pathogens 2019, 8, 44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Giusti, M.; Barbato, D.; Lia, L.; Colamesta, V.; Lombardi, A.M.; Cacchio, D.; Villari, P.; La Torre, G. Collaboration between human and veterinary medicine as a tool to solve public health problems. Lancet Planet. Health 2019, 3, e64–e65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mateus, T.L.; Teixeira, P.; Maia, R.L. We Know One Health, but We Also Need One Communication, in Sustainable Policies and Practices in Energy, Environment and Health Research: Addressing Cross-Cutting Issues; Filho, W.L., Vidal, D.G., Dinis, M.A.P., Dias, R.C., Eds.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2022; pp. 245–259. [Google Scholar]
- Speare, R.; Mendez, D.; Judd, J.; Reid, S.; Tzipori, S.; Massey, P.D. Willingness to Consult a Veterinarian on Physician’s Advice for Zoonotic Diseases: A Formal Role for Veterinarians in Medicine? PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0131406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mateus, T.L.; Castro, A.; Ribeiro, J.N.; Vieira-Pinto, M. Multiple zoonotic parasites identified in dog feces collected in Ponte de Lima, Portugal-a potential threat to human health. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2014, 11, 9050–9067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mateus, T.L.; Ribeiro, J.N.; Castro, A.; Vieira-Pinto, M. Limited Knowledge About Hydatidosis Among Farmers in Northwest Portugal: A Pressing Need for a One Health Approach. Ecohealth 2016, 13, 480–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- do Vale, B.; Lopes, A.P.; Fontes, M.D.C.; Silvestre, M.; Cardoso, L.; Coelho, A.C. A Cross-Sectional Study of Knowledge on Ownership, Zoonoses and Practices among Pet Owners in Northern Portugal. Animals 2021, 11, 3543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Powell, L.; Lavender, T.M.; Reinhard, C.L.; Watson, B. Pet Owners’ Perceptions of COVID-19, Zoonotic Disease, and Veterinary Medicine: The Impact of Demographic Characteristics. Vet. Sci. 2022, 9, 195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mendez, D.H.; Büttner, P.; Kelly, J.; Nowak, M.; Speare, R. Difficulties experienced by veterinarians when communicating about emerging zoonotic risks with animal owners: The case of Hendra virus. BMC Vet. Res. 2017, 13, 56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shanko, K.; Kemal, J.; Kenea, D. A Review on Confronting Zoonoses: The Role of Veterinarian and Physician. J. Vet. Sci. Technol. 2015, 221, 1000221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Overgaauw, P.A.M.; Vinke, C.M.; Van Hagen, M.A.; Lipman, L.J. A One Health Perspective on the Human-Companion Animal Relationship with Emphasis on Zoonotic Aspects. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 3789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).