Effect of Different Acid and Base Potassium Ferrate Pretreatment on Organic Acid Recovery by Anaerobic Digestion of Sludge
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Characteristics of Excess Sludge
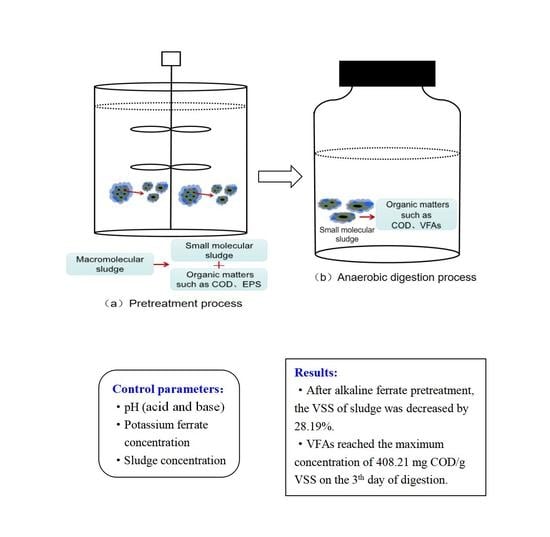
2.2. Experimental Method
2.3. Determination Index and Analysis Method
2.4. VFAs Analysis Method
2.5. Extracellular Polymeric Substances (EPS), PN, and PS Analysis Method
2.6. Microbiological Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Changes in Sludge Characteristics after Pretreatment
3.1.1. Changes in Liquid Phase in Sludge after Pretreatment
3.1.2. Changes of Solid Phase of Sludge after Pretreatment
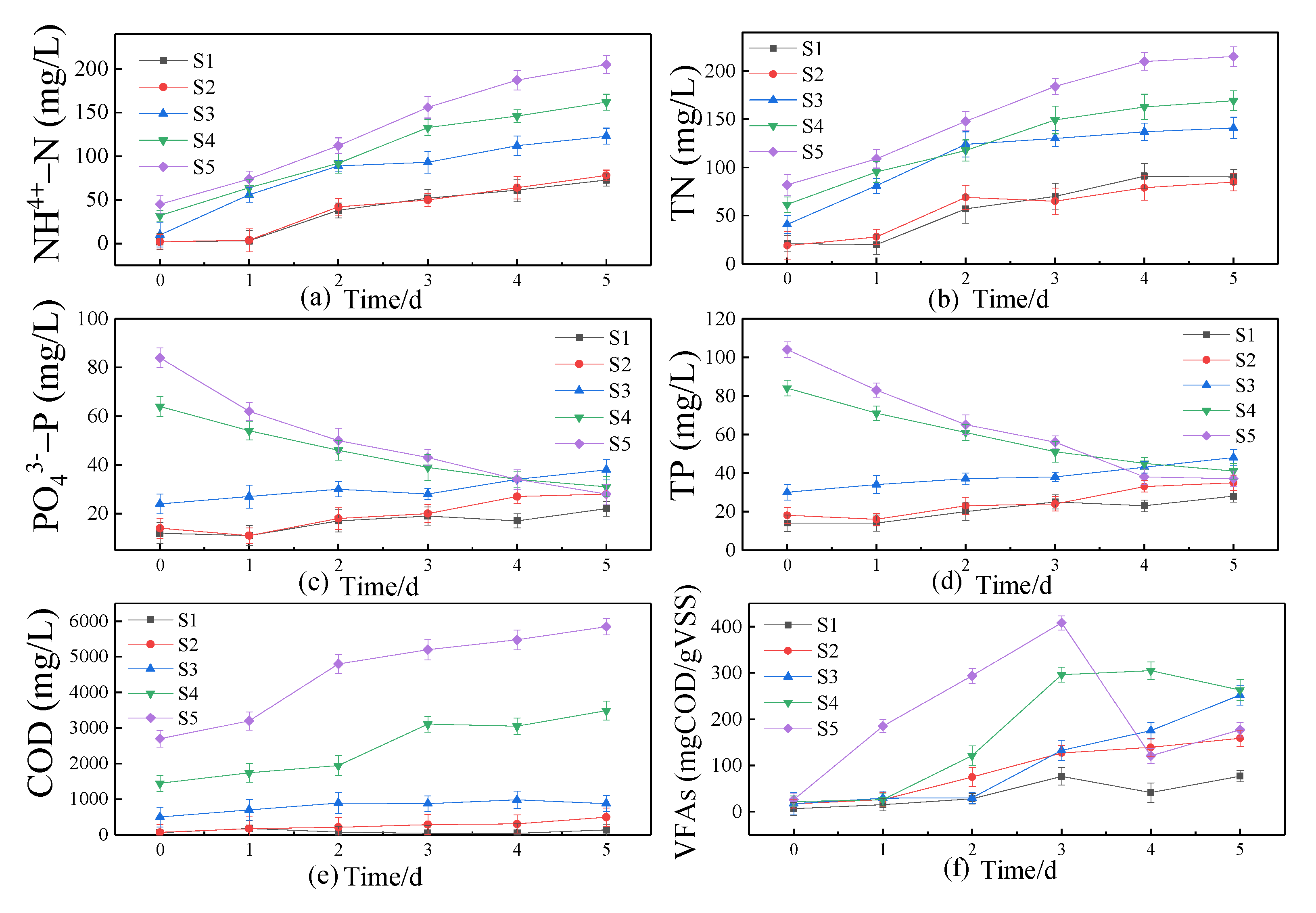
3.2. Analysis of Pretreated Sludge Characteristics during Digestion
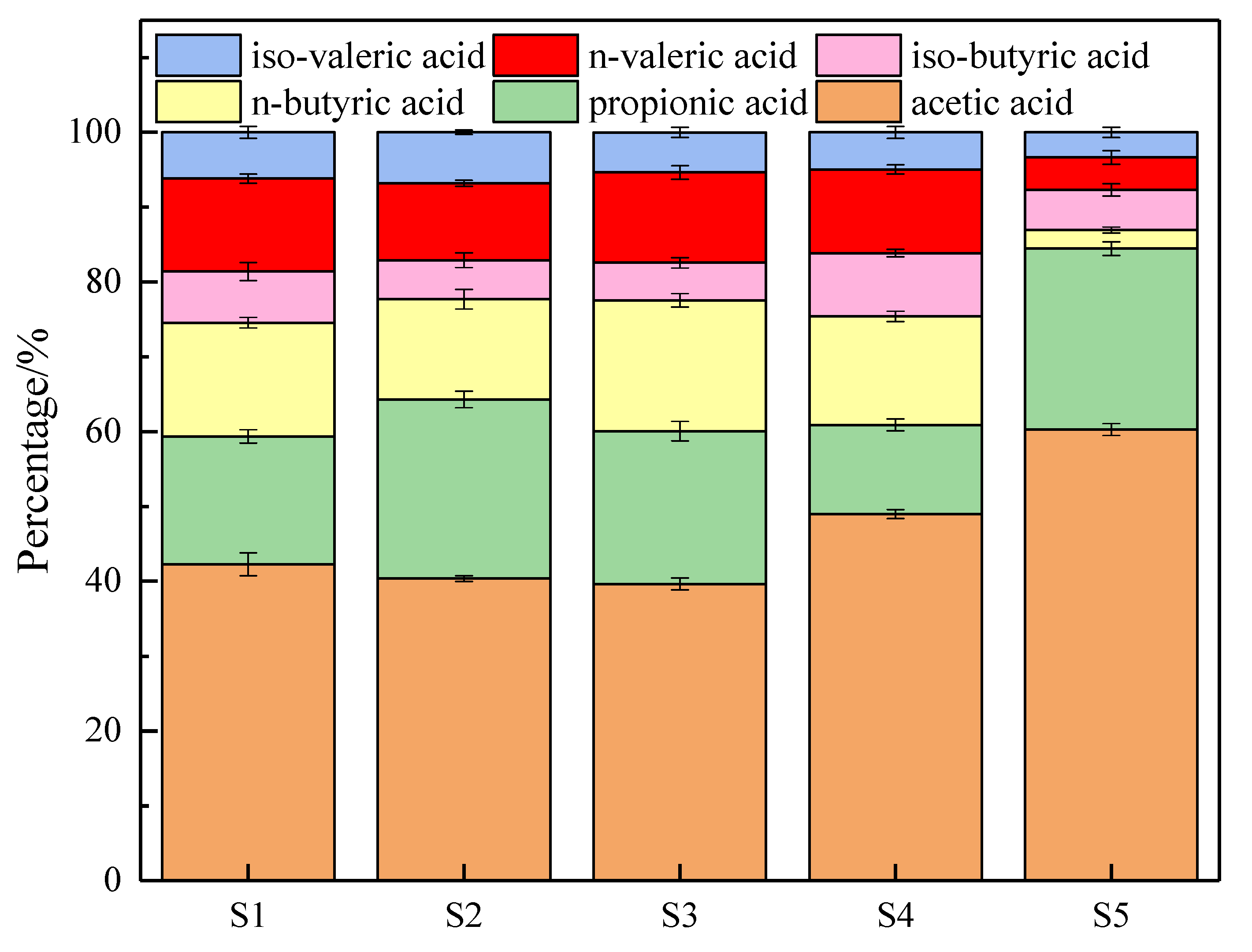
3.2.1. Liquid Phase Analysis of Pretreated Sludge during Digestion
3.2.2. Solid Phase Analysis of Sludge during Digestion
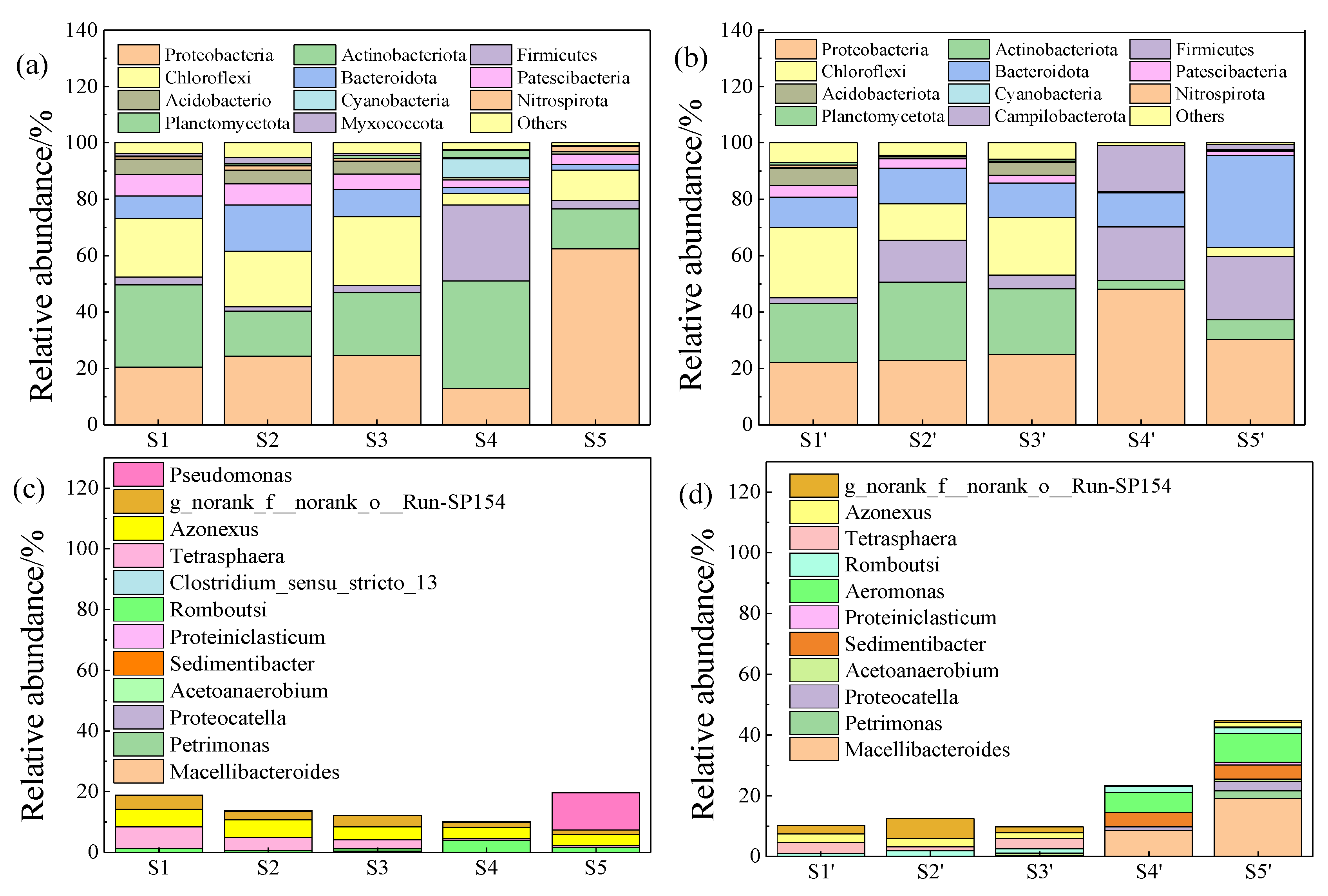
3.3. Microbial Characteristics Analysis
3.3.1. Microbial Analysis at Phylum Level
3.3.2. Microbial Analysis at Genus Level
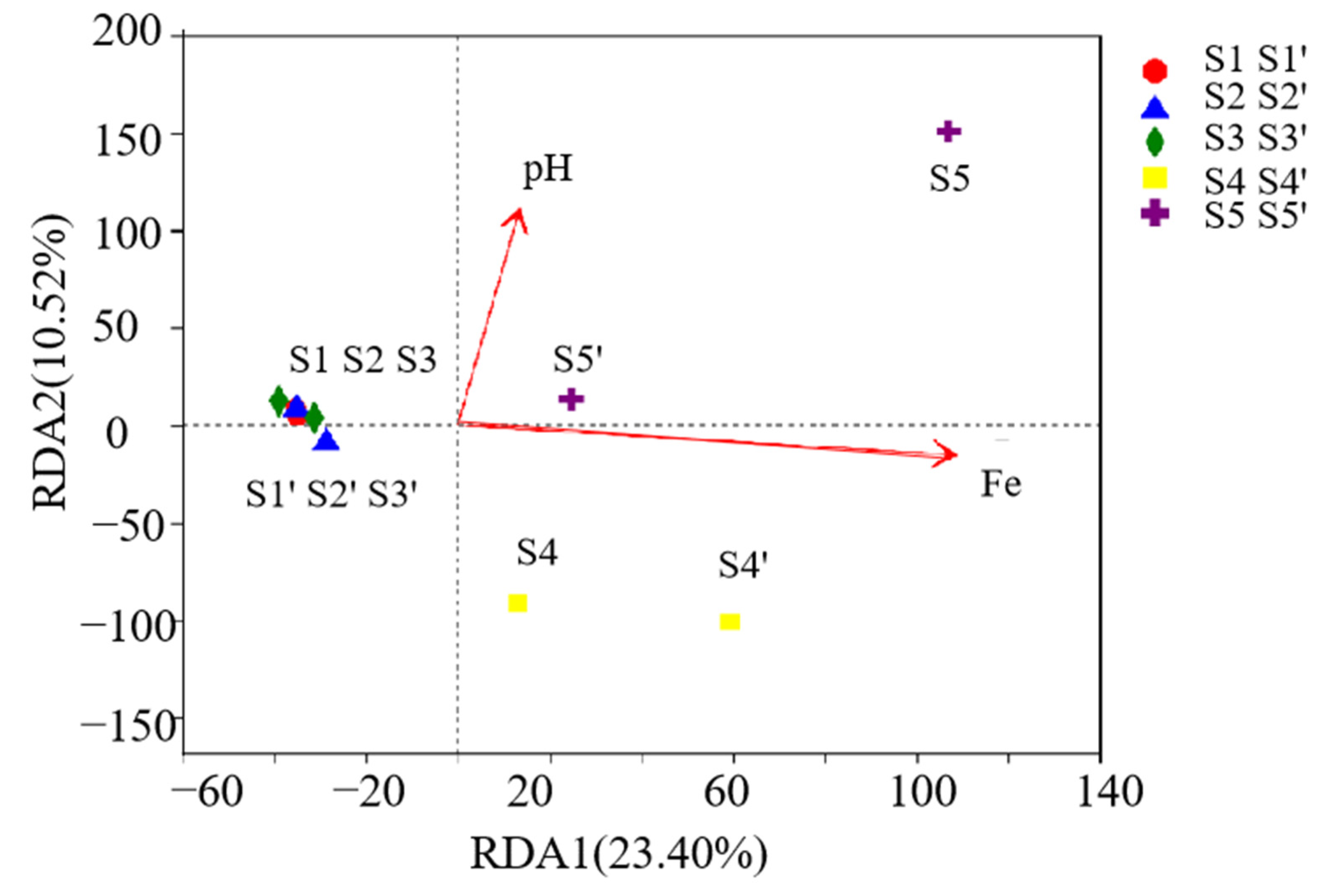
3.3.3. Correlation Analysis of Environmental Factors and Microorganisms
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Feng, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Chen, S.; Quan, X. Enhanced production of methane from waste activated sludge by the combination of high-solid anaerobic digestion and microbial electrolysis cell with iron-graphite electrode. Chem. Eng. J. 2015, 259, 787–794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; He, J.; Xin, X.; Wang, M.; Xu, J.; Zhang, J. Enhanced bioproduction of short-chain fatty acids from waste activated sludge by potassium ferrate pretreatment. Chem. Eng. J. 2018, 332, 456–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alloul, A.; Ganigué, R.; Spiller, M.; Meerburg, F.; Cagnetta, C.; Rabaey, K.; Vlaeminck, S.E. Capture–Ferment–Upgrade: A Three-Step Approach for the Valorization of Sewage Organics as Commodities. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2018, 52, 6729–6742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, L.; Xu, C.C.; Champagne, P.; Mabee, W. Overview of current biological and thermo-chemical treatment technologies for sustainable sludge management. Waste Manag. Res. 2014, 32, 586–600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Z.; Liu, T.; Duan, H.; Song, Y.; Lu, X.; Hu, S.; Yuan, Z.; Batstone, D.; Zheng, M. Post-treatment options for anaerobically digested sludge: Current status and future prospect. Water Res. 2021, 205, 117665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Wang, Y.; Yin, B.; Zhu, Y.; Fu, B.; Liu, H. Improving volatile fatty acid yield from sludge anaerobic fermentation through self-forming dynamic membrane separation. Bioresour. Technol. 2016, 218, 92–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kampas, P.; Parsons, S.A.; Pearce, P.; Ledoux, S.; Vale, P.; Cartmell, E.; Soares, A. An internal carbon source for improving biological nutrient removal. Bioresour. Technol. 2009, 100, 149–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, J.; Feng, L.; Zhang, W.; Li, X.; Chen, H.; Wang, D.; Chen, Y. Improved production of short-chain fatty acids from waste activated sludge driven by carbohydrate addition in continuous-flow reactors: Influence of SRT and temperature. Appl. Energy 2014, 113, 51–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morgan-Sagastume, F.; Hjort, M.; Cirne, D.; Gérardin, F.; Lacroix, S.; Gaval, G.; Karabegovic, L.; Alexandersson, T.; Johansson, P.; Karlsson, A.; et al. Integrated production of polyhydroxyalkanoates (PHAs) with municipal wastewater and sludge treatment at pilot scale. Bioresour. Technol. 2015, 181, 78–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; He, Z.; Guo, Z.; Sangeetha, T.; Yang, C.; Gao, L.; Wang, A.; Liu, W. Microbial community development on different cathode metals in a bioelectrolysis enhanced methane production system. J. Power Sources 2019, 444, 227306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xin, X.; Hong, J.; He, J.; Qiu, W. An integrated approach for waste activated sludge management towards electric energy production/resource reuse. Bioresour. Technol. 2019, 274, 225–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yan, Y.; Feng, L.; Zhang, C.; Wisniewski, C.; Zhou, Q. Ultrasonic enhancement of waste activated sludge hydrolysis and volatile fatty acids accumulation at pH 10.0. Water Res. 2010, 44, 3329–3336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xin, X.; She, Y.; Hong, J. Insights into microbial interaction profiles contributing to volatile fatty acids production via acidogenic fermentation of waste activated sludge assisted by calcium oxide pretreatment. Bioresour. Technol. 2021, 320, 124287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, Q.; Liu, X.; Fu, Y.; Li, Y.; Wang, D.; Wang, Q.; Liu, Y.; An, H.; Zhao, J.; Wu, Y.; et al. Feasibility of enhancing short-chain fatty acids production from waste activated sludge after free ammonia pretreatment: Role and significance of rhamnolipid. Bioresour. Technol. 2018, 267, 141–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, Z.-W.; Liu, W.-Z.; Gao, Q.; Tang, C.-C.; Wang, L.; Guo, Z.-C.; Zhou, A.-J.; Wang, A.-J. Potassium ferrate addition as an alternative pre-treatment to enhance short-chain fatty acids production from waste activated sludge. Bioresour. Technol. 2018, 247, 174–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Yuan, Y.; Jin, R.; Huang, Y.; Ma, J. High efficiency of excess sludge reduction and dewaterability using newly prepared alkaline ferrate pretreatment combined with anaerobic digestion. J. Environ. Manag. 2019, 243, 350–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; He, J.; Wang, M.; Xin, X.; Xu, J.; Zhang, J. Efficient Volatile Fatty Acids Production from Waste Activated Sludge after Ferrate Pretreatment with Alkaline Environment and the Responding Microbial Community Shift. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2018, 6, 16819–16827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Liu, X.; Liu, X.; Xu, Q.; Wang, W.; Wang, D.; Yang, G.; Fu, Q.; Kang, Z.; Yang, Q.; et al. Enhanced dark fermentative hydrogen production from waste activated sludge by combining potassium ferrate with alkaline pretreatment. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 707, 136105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Angelidaki, I. Microbial electrolysis cells turning to be versatile technology: Recent advances and future challenges. Water Res. 2014, 56, 11–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Water Environmental Federation; APHA. Standard Methods for the Examination of Water and Wastewater; American Public Health Association (APHA): Washington, DC, USA, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Geng, Y.-K.; Yuan, L.; Liu, T.; Li, Z.-H.; Zheng, X.; Sheng, G.-P. Thermal/alkaline pretreatment of waste activated sludge combined with a microbial fuel cell operated at alkaline pH for efficient energy recovery. Appl. Energy 2020, 275, 115291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, C.; Zhang, P.; Wang, H.; Ye, J. Conditioning of sewage sludge via combined ultrasonication-flocculation-skeleton building to improve sludge dewaterability. Ultrason. Sonochem. 2018, 40, 353–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharma, V.K. Potassium ferrate(VI): An environmentally friendly oxidant. Adv. Environ. Res. 2002, 6, 143–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Lou, Y.; Feng, K.; Zhou, H.; Liu, B.; Xie, G.; Xing, D. Enhancing the decomposition of extracellular polymeric substances and the recovery of short-chain fatty acids from waste activated sludge: Analysis of the performance and mechanism of co-treatment by free nitrous acid and calcium peroxide. J. Hazard. Mater. 2022, 423, 127022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leiyu, F.; Yinguang, C.; Xiong, Z. Enhancement of waste activated sludge protein conversion and volatile fatty acids accumulation during waste activated sludge anaerobic fermentation by carbohydrate substrate addition: The effect of pH. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2009, 43, 4373–4380. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, B.-B.; Liu, X.-T.; Chen, J.-M.; Peng, D.-C.; He, F. Composition and functional group characterization of extracellular polymeric substances (EPS) in activated sludge: The impacts of polymerization degree of proteinaceous substrates. Water Res. 2018, 129, 133–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, X.R.; Liu, Y.L. Enhancement of Waste Activated Sludge Dewaterability by Potassium Ferrate Pretreatment. Adv. Mater. Res. 2015, 1073–1076, 937–940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Lei, H.; Chen, K.; Liu, Z.; Wu, H.; Liang, H. Effect of potassium ferrate (K2FeO4) on sludge dewaterability under different pH conditions. Chem. Eng. J. 2012, 210, 467–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghosh, M.; Manoli, K.; Renaud, J.B.; Sabourin, L.; Nakhla, G.; Sharma, V.K.; Ray, A.K. Rapid removal of acesulfame potassium by acid-activated ferrate(VI) under mild alkaline conditions. Chemosphere 2019, 230, 416–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, Y.; Lu, Y.; Li, Q. Comparative Study on the Performances and Bacterial Diversity from Anaerobic Digestion and Aerobic Composting in Treating Solid Organic Wastes. Waste Biomass Valorization 2017, 8, 425–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, D.; Liu, X.; Apul, O.G.; Zhang, L.; Ryan, D.K.; Zhang, X. Optimization of biomethane production from anaerobic Co-digestion of microalgae and septic tank sludge. Biomass Bioenergy 2019, 127, 105266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Quan, X.; Chen, S. Enhanced anaerobic digestion of waste activated sludge digestion by the addition of zero valent iron. Water Res. 2014, 52, 242–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qian, P.; Zhipeng, Z.; Xiaohu, D.; Yongmei, L. Novel CaO2 beads used in the anaerobic fermentation of iron-rich sludge for simultaneous short-chain fatty acids and phosphorus recovery under ambient conditions. Bioresour. Technol. 2021, 322, 124553. [Google Scholar]
- Ni, M.; Chen, Y.; Pan, Y.; Huang, Y.; Li, D.-p.; Li, L.; Huang, B.; Song, Z. Study on community structure and metabolic mechanism of dominant polyphosphate-accumulating organisms (PAOs) and glycogen-accumulating organisms (GAOs) in suspended biofilm based on phosphate recovery. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 815, 152678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, J.; Zhang, Q.; Wu, L.; Feng, Q.; Fang, F.; Xue, Z.; Li, C.; Cao, J. Improving anaerobic fermentation of waste activated sludge using iron activated persulfate treatment. Bioresour. Technol. 2018, 268, 68–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, J.; Wu, Y.; Zhao, J.; Jin, S.; Aleem, M.; Zhang, Q.; Fang, F.; Xue, Z.; Luo, J. Phosphorus recovery as vivianite from waste activated sludge via optimizing iron source and pH value during anaerobic fermentation. Bioresour. Technol. 2019, 293, 122088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.; Yuan, Y.; Huang, Y.; Guo, C.-r.; Jin, R.; Liu, T.-t.; Ma, J. Transformation and migration of phosphorus in excess sludge reduction pretreatment by alkaline ferrate oxidation combined with anaerobic digestion. J. Environ. Sci. 2020, 92, 224–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Z.; Li, Y.; Quan, X.; Zhang, Y. Towards engineering application: Potential mechanism for enhancing anaerobic digestion of complex organic waste with different types of conductive materials. Water Res. 2017, 115, 266–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Jiang, S.; Yuan, H.; Zhou, Q.; Gu, G. Hydrolysis and acidification of waste activated sludge at different pHs. Water Res. 2007, 41, 683–689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, Q.; Liu, B.; Chen, Z. Simultaneous recovery of vivianite and produce short-chain fatty acids from waste activated sludge using potassium ferrate as pre-oxidation treatment. Environ. Res. 2022, 208, 112661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.; Huang, Y.; Xu, Q.; Liu, X.; Yang, Q.; Li, X. Free ammonia aids ultrasound pretreatment to enhance short-chain fatty acids production from waste activated sludge. Bioresour. Technol. 2019, 275, 163–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Wu, S.; Du, C.; Zhong, Y.; Yang, C. Preparation, Performances, and Mechanisms of Microbial Flocculants for Wastewater Treatment. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 1360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, J.; Gui, L.; Wang, Q.; Liu, Y.; Wang, D.; Ni, B.-J.; Li, X.; Xu, R.; Zeng, G.; Yang, Q. Aged refuse enhances anaerobic digestion of waste activated sludge. Water Res. 2017, 123, 724–733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nelson, M.C.; Morrison, M.; Yu, Z. A meta-analysis of the microbial diversity observed in anaerobic digesters. Bioresour. Technol. 2011, 102, 3730–3739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, J.; Chen, Y.; Feng, L. Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbon Affects Acetic Acid Production during Anaerobic Fermentation of Waste Activated Sludge by Altering Activity and Viability of Acetogen. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2016, 50, 6921–6929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barragán-Trinidad, M.; Carrillo-Reyes, J.; Buitrón, G. Hydrolysis of microalgal biomass using ruminal microorganisms as a pretreatment to increase methane recovery. Bioresour. Technol. 2017, 244, 100–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Chang, S. Impact of temperatures on microbial community structures of sewage sludge biological hydrolysis. Bioresour. Technol. 2017, 245, 502–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, J.; Feng, L.; Chen, Y.; Sun, H.; Shen, Q.; Li, X.; Chen, H. Alkyl polyglucose enhancing propionic acid enriched short-chain fatty acids production during anaerobic treatment of waste activated sludge and mechanisms. Water Res. 2015, 73, 332–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Parameters | Value (mg/L) | Parameters | Value (mg/L) |
|---|---|---|---|
| SS | 10000 ± 5 | NH4+-N | 0.4 ± 0.1 |
| VSS | 6100 ± 2 | TN | 6.86 ± 0.5 |
| COD | 62 ± 1 | PO43−-P | 21.54 ± 0.5 |
| TOC | 16.51 ± 0.5 | TP | 21.94 ± 1 |
| Samples | S1 | S2 | S3 | S4 | S5 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NH4+-N | 2 ± 0.5 | 2 ± 0.5 | 10 ± 1 | 32 ± 1 | 45 ± 1 |
| TN | 21 ± 0.5 | 19 ± 0.5 | 41 ± 0.5 | 61 ± 1 | 82 ± 2 |
| PO43−-P | 12 ± 0.5 | 14 ± 0.5 | 24 ± 0.5 | 64 ± 1 | 84 ± 2 |
| TP | 14 ± 0.5 | 18 ± 0.5 | 30 ± 1 | 84 ± 1 | 104 ± 2 |
| COD | 62 ± 2 | 71 ± 1 | 500 ± 4 | 1450 ± 5 | 2700 ± 5 |
| Parameters | S1 | S2 | S3 | S4 | S5 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| VSS (g/L) | 6.10 ± 0.5 | 5.89 ± 0.5 | 5.65 ± 0.5 | 5.02 ± 0.5 | 4.38 ± 0.5 |
| Dx (50) (μm) | 1749 ± 5 | 1674 ± 2 | 1605 ± 2 | 69.03 ± 1 | 46.87 ± 1 |
| SV30 ratio (%) | 51 ± 1 | 48 ± 1 | 44 ± 1 | 34 ± 1 | 29 ± 1 |
| SVI (mL/g) | 83.60 ± 1 | 81.49 ± 1 | 77.87 ± 1 | 79.43 ± 1 | 78.80 ± 1 |
| Parameters | S1′ | S2′ | S3′ | S4′ | S5′ |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| VSS (g/L) | 5.17 ± 0.2 | 4.96 ± 0.2 | 4.54 ± 0.2 | 3.67 ± 0.2 | 3.09 ± 0.2 |
| Dx (50) (μm) | 1497 ± 5 | 1596 ± 5 | 1578 ± 4 | 1674 ± 5 | 1421 ± 5 |
| SV30 ratio (%) | 72 ± 1 | 71 ± 1 | 75 ± 1 | 57 ± 1 | 54 ± 1 |
| SVI (mL/g) | 139.3 ± 1 | 143.1 ± 1 | 165.2 ± 2 | 155. 3 ± 1 | 168.3 ± 1 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tian, M.; Liu, F.; Guo, J.; Li, W.; Zhang, M.; Li, X. Effect of Different Acid and Base Potassium Ferrate Pretreatment on Organic Acid Recovery by Anaerobic Digestion of Sludge. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 15093. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph192215093
Tian M, Liu F, Guo J, Li W, Zhang M, Li X. Effect of Different Acid and Base Potassium Ferrate Pretreatment on Organic Acid Recovery by Anaerobic Digestion of Sludge. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health. 2022; 19(22):15093. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph192215093
Chicago/Turabian StyleTian, Mengjia, Feng Liu, Jiawen Guo, Wei Li, Mao Zhang, and Xiang Li. 2022. "Effect of Different Acid and Base Potassium Ferrate Pretreatment on Organic Acid Recovery by Anaerobic Digestion of Sludge" International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health 19, no. 22: 15093. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph192215093
APA StyleTian, M., Liu, F., Guo, J., Li, W., Zhang, M., & Li, X. (2022). Effect of Different Acid and Base Potassium Ferrate Pretreatment on Organic Acid Recovery by Anaerobic Digestion of Sludge. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 19(22), 15093. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph192215093