Word2vec Word Embedding-Based Artificial Intelligence Model in the Triage of Patients with Suspected Diagnosis of Major Ischemic Stroke: A Feasibility Study
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Methods
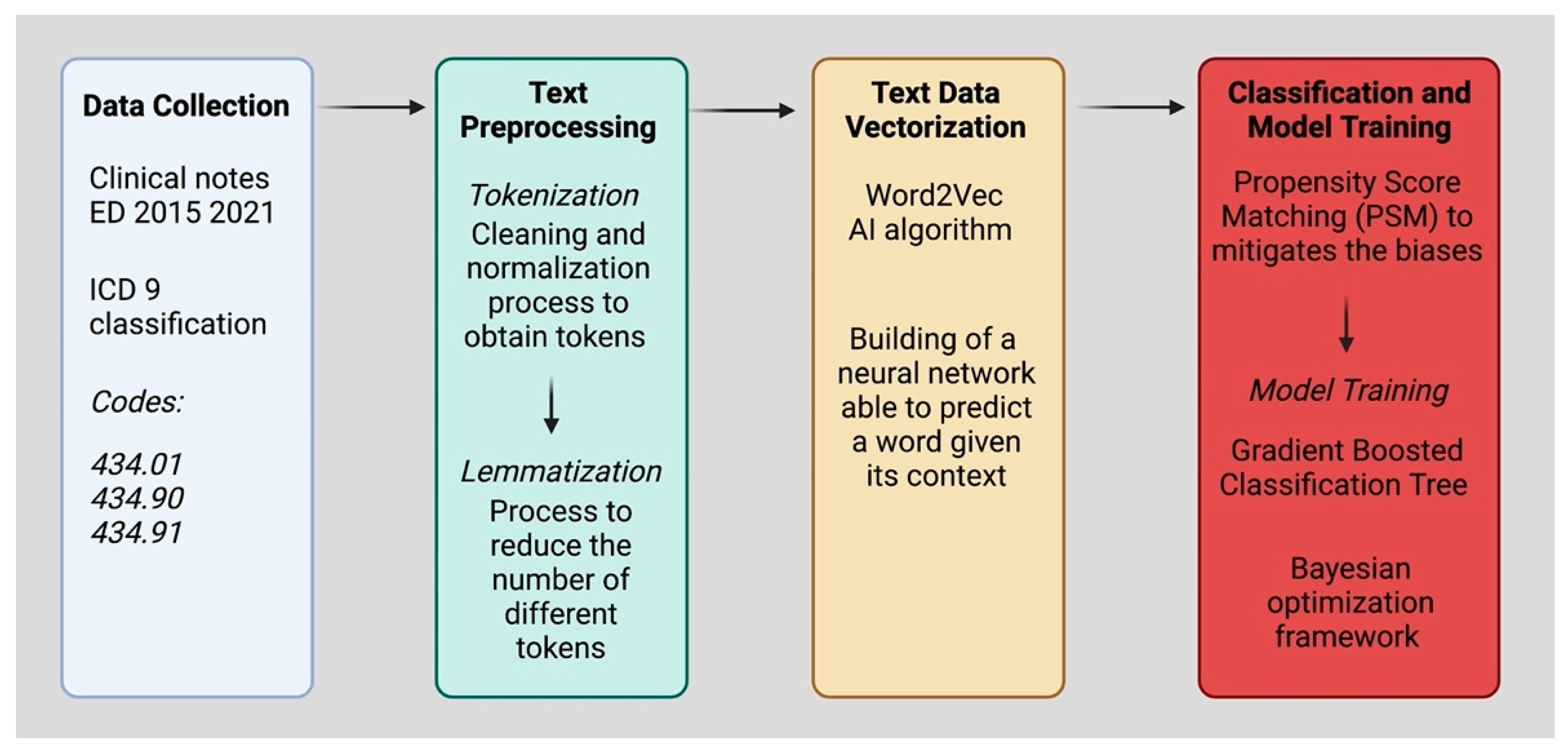
2.1. Data Collection
2.2. Text Preprocessing
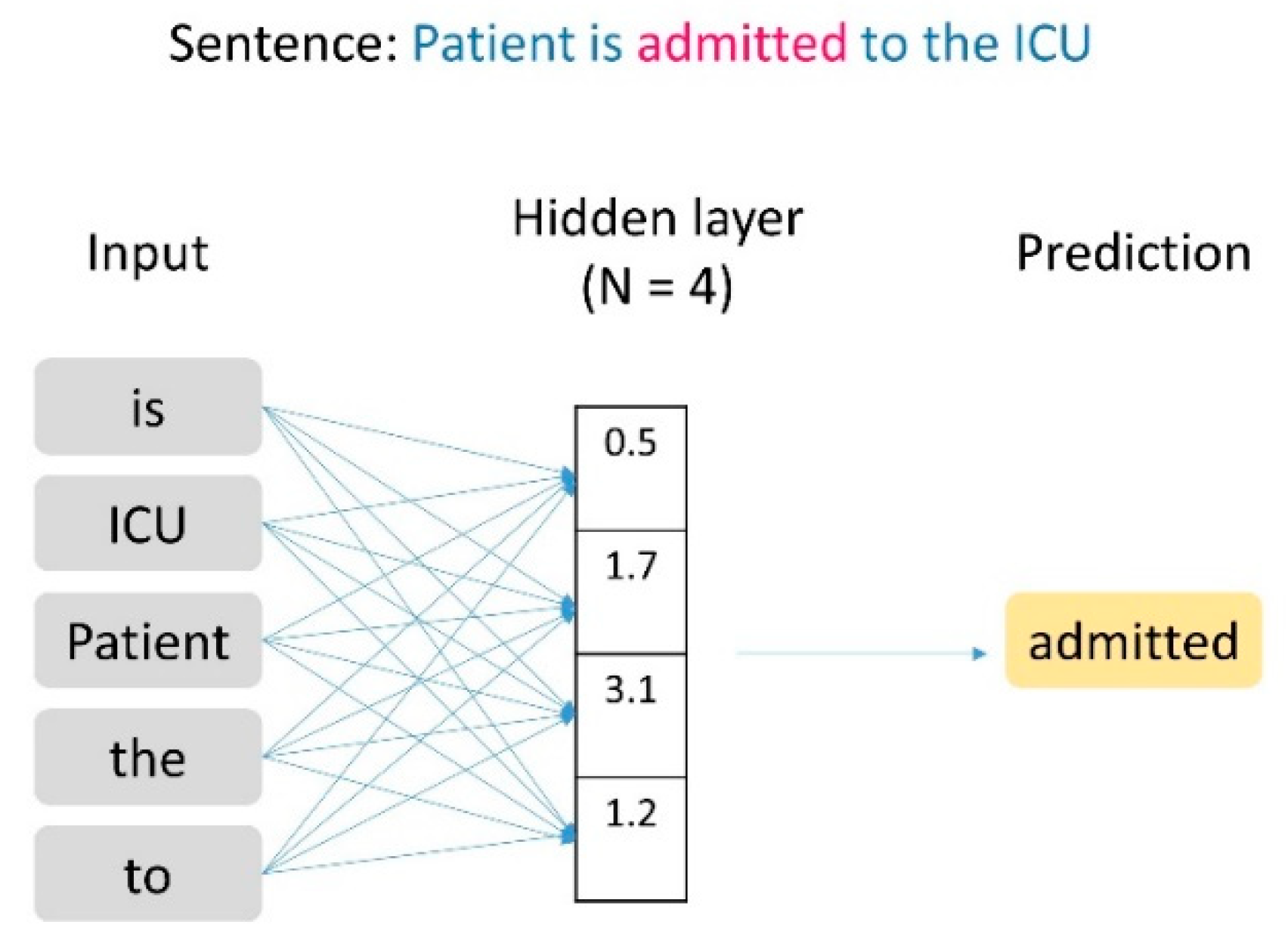
2.3. Text Data Vectorization
2.4. Classification and Model Training
3. Results
3.1. Dataset
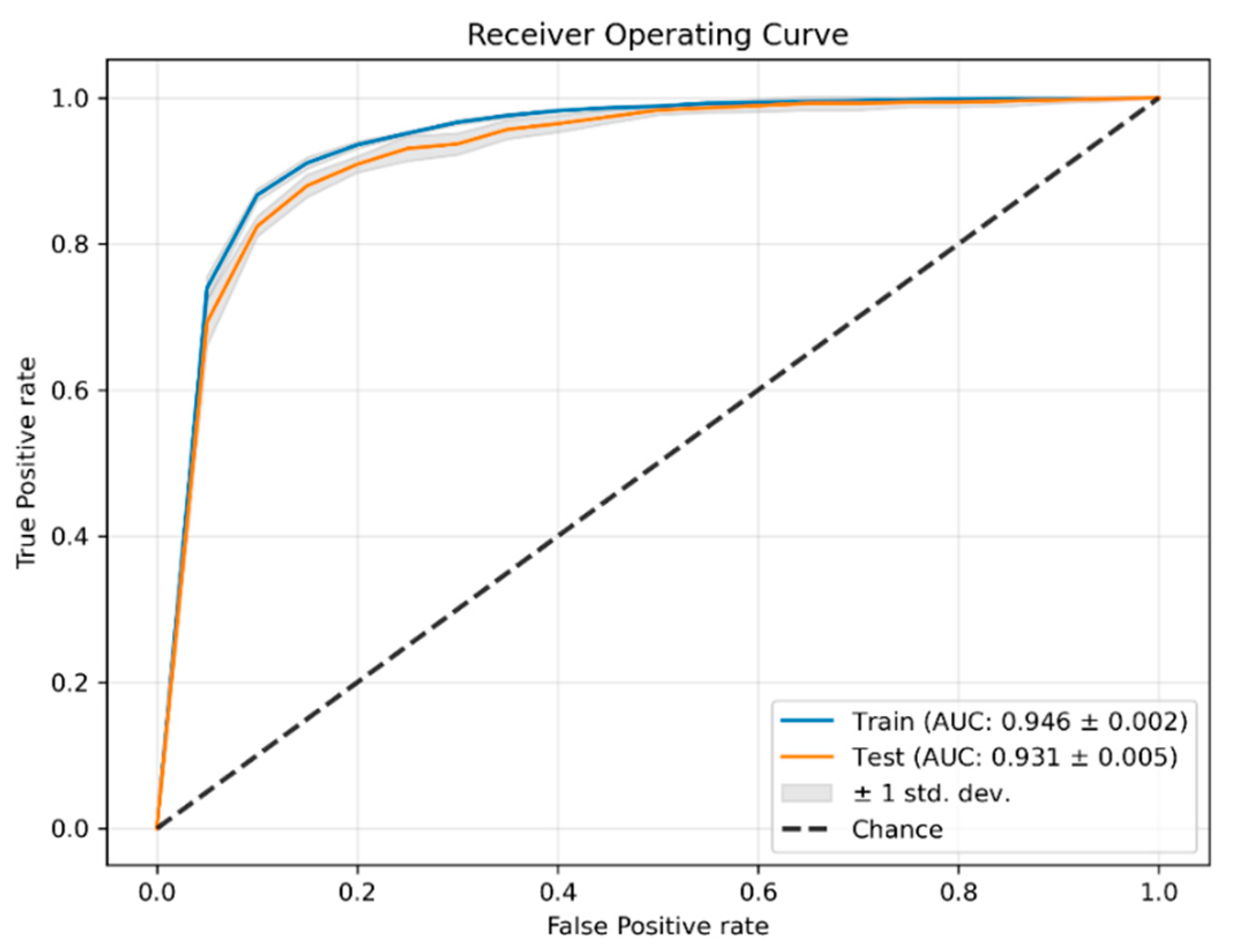
3.2. Classification
4. Discussion
4.1. Diagnosis of Major Ischemic Stroke
4.2. Word2vec Word Embedding-Based Artificial Intelligence Model
Limitations of the Study
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
| Train | Test | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Control | MIS | Control | MIS | |
| F1 | 0.959 (±0.005) | 0.187 (±0.018) | 0.957 (±0.007) | 0.175 (±0.018) |
| Precision | 0.999 (±0.001) | 0.109 (±0.011) | 0.998 (±0.001) | 0.098(±0.011) |
| Recall | 0.921 (±0.010) | 0.959 (±0.011) | 0.920 (±0.013) | 0.847 (±0.029) |
| Support | 243,663 | 519 | 60,916 | 129 |
| Train | Test | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Control | MIS | Control | MIS | |
| F1 | 0.955 (±0.004) | 0.177 (±0.011) | 0.954 (±0.004) | 0.169 (±0.011) |
| Precision | 0.999 (±0.001) | 0.098 (±0.007) | 0.998 (±0.001) | 0.094(±0.007) |
| Recall | 0.914 (±0.008) | 0.923 (±0.006) | 0.914 (±0.009) | 0.879 (±0.019) |
| Support | 243,663 | 519 | 60,916 | 129 |
| Color Code | Precision | Recall | F1 | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Control | MIS | Control | MIS | Control | MIS | |
| Red | 0.990 | 0.163 | 0.762 | 0.869 | 0.861 | 0.275 |
| Yellow | 0.996 | 0.134 | 0.861 | 0.871 | 0.923 | 0.233 |
| Green | 0.999 | 0.013 | 0.953 | 0.568 | 0.976 | 0.026 |
| Color Code | Precision | Recall | F1 | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Control | MIS | Control | MIS | Control | MIS | |
| Red | 0.995 | 0.163 | 0.743 | 0.939 | 0.851 | 0.279 |
| Yellow | 0.997 | 0.126 | 0.846 | 0.897 | 0.915 | 0.221 |
| Green | 0.999 | 0.013 | 0.952 | 0.568 | 0.975 | 0.026 |
References
- Go, A.S.; Mozaffarian, D.; Roger, V.L.; Benjamin, E.J.; Berry, J.D.; Blaha, M.J.; Dai, S.; Ford, E.S.; Fox, C.S.; Franco, S.; et al. Heart disease and stroke statistics--2014 update: A report from the American Heart Association. Circulation 2014, 129, e28–e292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Saver, J.L. Time is brain—Quantified. Stroke 2006, 37, 263–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Liberman, A.L.; Prabhakaran, S. Stroke Chameleons and Stroke Mimics in the Emergency Department. Curr. Neurol. Neurosci. Rep. 2017, 17, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Levine, D.A.; Wadley, V.G.; Langa, K.M.; Unverzagt, F.W.; Kabeto, M.U.; Giordani, B.; Howard, G.; Howard, V.J.; Cushman, M.; Judd, S.E.; et al. Risk Factors for Poststroke Cognitive Decline: The REGARDS Study (Reasons for Geographic and Racial Differences in Stroke). Stroke 2018, 49, 987–994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saver, J.L.; Fonarow, G.C.; Smith, E.E.; Reeves, M.J.; Grau-Sepulveda, M.V.; Pan, W.; Olson, D.M.; Hernandez, A.F.; Peterson, E.D.; Schwamm, L.H. Time to Treatment With Intravenous Tissue Plasminogen Activator and Outcome From Acute Ischemic Stroke. JAMA 2013, 309, 2480–2488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Emberson, J.; Lees, K.R.; Lyden, P.; Blackwell, L.; Albers, G.; Bluhmki, E.; Brott, T.; Cohen, G.; Davis, S.; Donnan, G.; et al. Effect of treatment delay, age, and stroke severity on the effects of intravenous thrombolysis with alteplase for acute ischaemic stroke: A meta-analysis of individual patient data from randomised trials. Lancet 2014, 384, 1929–1935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tawil, S.E.; Muir, K.W. Thrombolysis and thrombectomy for acute ischaemic stroke. Clin. Med. 2017, 17, 161–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Albers, G.W.; Marks, M.P.; Kemp, S.; Christensen, S.; Tsai, J.P.; Ortega-Gutierrez, S.; McTaggart, R.A.; Torbey, M.T.; Kim-Tenser, M.; Leslie-Mazwi, T.; et al. Thrombectomy for Stroke at 6 to 16 Hours with Selection by Perfusion Imaging. N. Engl. J. Med. 2018, 378, 708–718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fugate, J.E.; Rabinstein, A.A. Absolute and Relative Contraindications to IV rt-PA for Acute Ischemic Stroke. Neurohospitalist 2015, 5, 110–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ekundayo, O.J.; Saver, J.L.; Fonarow, G.C.; Schwamm, L.H.; Xian, Y.; Zhao, X.; Hernandez, A.F.; Peterson, E.D.; Cheng, E.M. Patterns of emergency medical services use and its association with timely stroke treatment: Findings from Get With the Guidelines-Stroke. Circ. Cardiovasc. Qual. Outcomes 2013, 6, 262–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, J.; Band, R.; Abboud, M.E.; Pajerowski, W.; Guo, M.; David, G.; Mechem, C.C.; Messé, S.R.; Carr, B.G.; Mullen, M.T. Accuracy of Emergency Medical Services Dispatcher and Crew Diagnosis of Stroke in Clinical Practice. Front. Neurol. 2017, 8, 466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Schwamm, L.H.; Wu, O.; Song, S.S.; Latour, L.L.; Ford, A.L.; Hsia, A.W.; Muzikansky, A.; Betensky, R.A.; Yoo, A.J.; Lev, M.H.; et al. Intravenous thrombolysis in unwitnessed stroke onset: MR WITNESS trial results. Ann. Neurol. 2018, 83, 980–993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murray, N.M.; Unberath, M.; Hager, G.D.; Hui, F.K. Artificial intelligence to diagnose ischemic stroke and identify large vessel occlusions: A systematic review. J. Neurointerv. Surg. 2020, 12, 156–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Soun, J.E.; Chow, D.S.; Nagamine, M.; Takhtawala, R.S.; Filippi, C.G.; Yu, W.; Chang, P.D. Artificial Intelligence and Acute Stroke Imaging. AJNR Am. J. Neuroradiol. 2021, 42, 2–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schmidt, H. Probabilistic part-of-speech tagging using decision trees. In New Methods in Language Processing; Routledge: London, UK, 2013; p. 154. [Google Scholar]
- Rehurek, R.; Sojka, P. Gensim–python framework for vector space modelling. NLP Cent. Fac. Inform. Masaryk. Univ. Brno Czech Repub. 2011, 3, 2. [Google Scholar]
- Kline, A.; Luo, Y. PsmPy: A Package for Retrospective Cohort Matching in Python. Annu. Int. Conf. IEEE Eng. Med. Biol. Soc. 2022, 2022, 1354–1357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pedregosa, F.; Varoquaux, G.; Gramfort, A.; Michel, V.; Thirion, B.; Grisel, O.; Blondel, M.; Louppe, G.; Prettenhofer, P.; Weiss, R.; et al. Scikit-learn: Machine Learning in Python. J. Mach. Learn. Res. 2011, 12, 2825–2830. [Google Scholar]
- Ke, G.; Meng, Q.; Finley, T.; Wang, T.; Chen, W.; Ma, W.; Ye, Q.; Liu, T.-Y. LightGBM: A Highly Efficient Gradient Boosting Decision Tree. In Proceedings of the 31st International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems (NIPS), Long Beach, CA, USA, 4–9 December 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Tim Head; MechCoder; Gilles Louppe; Iaroslav Shcherbatyi; fcharras; Zé Vinícius; cmmalone; Christopher Schröder; nel215; Nuno Campos. Scikit-optimize/scikit-optimize: v0.5.2. Available online: https://zenodo.org/record/1207017#.Y3eIH3bMJPY. (accessed on 14 November 2022).
- Prabhakaran, S.; Ruff, I.; Bernstein, R.A. Acute stroke intervention: A systematic review. JAMA 2015, 313, 1451–1462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arenillas, J.F.; Cortijo, E.; García-Bermejo, P.; Levy, E.I.; Jahan, R.; Liebeskind, D.; Goyal, M.; Saver, J.L.; Albers, G.W. Relative cerebral blood volume is associated with collateral status and infarct growth in stroke patients in SWIFT PRIME. J. Cereb. Blood Flow Metab. 2018, 38, 1839–1847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oostema, J.A.; Chassee, T.; Baer, W.; Edberg, A.; Reeves, M.J. Brief Educational Intervention Improves Emergency Medical Services Stroke Recognition. Stroke 2019, 50, 1193–1200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gorchs-Molist, M.; Solà-Muñoz, S.; Enjo-Perez, I.; Querol-Gil, M.; Carrera-Giraldo, D.; Nicolàs-Arfelis, J.M.; Jiménez-Fàbrega, F.X.; Pérez de la Ossa, N. An Online Training Intervention on Prehospital Stroke Codes in Catalonia to Improve the Knowledge, Pre-Notification Compliance and Time Performance of Emergency Medical Services Professionals. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 6183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oostema, J.A.; Nasiri, M.; Chassee, T.; Reeves, M.J. The quality of prehospital ischemic stroke care: Compliance with guidelines and impact on in-hospital stroke response. J. Stroke Cerebrovasc. Dis. 2014, 23, 2773–2779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, C.B.; Peterson, E.D.; Smith, E.E.; Saver, J.L.; Liang, L.; Xian, Y.; Olson, D.M.; Shah, B.R.; Hernandez, A.F.; Schwamm, L.H.; et al. Emergency medical service hospital prenotification is associated with improved evaluation and treatment of acute ischemic stroke. Circ. Cardiovasc. Qual. Outcomes 2012, 5, 514–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Yperzeele, L.; Van Hooff, R.J.; De Smedt, A.; Valenzuela Espinoza, A.; Van de Casseye, R.; Hubloue, I.; De Keyser, J.; Brouns, R. Prehospital stroke care: Limitations of current interventions and focus on new developments. Cerebrovasc. Dis. 2014, 38, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brice, J.H.; Griswell, J.K.; Delbridge, T.R.; Key, C.B. Stroke: From recognition by the public to management by emergency medical services. Prehosp. Emerg. Care 2002, 6, 99–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bellantoni, G.; Guerrini, F.; Del Maestro, M.; Galzio, R.; Luzzi, S. Simple schwannomatosis or an incomplete Coffin-Siris? Report of a particular case. eNeurologicalSci 2019, 14, 31–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luzzi, S.; Del Maestro, M.; Elbabaa, S.K.; Galzio, R. Letter to the Editor Regarding “One and Done: Multimodal Treatment of Pediatric Cerebral Arteriovenous Malformations in a Single Anesthesia Event”. World Neurosurg. 2020, 134, 660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luzzi, S.; Del Maestro, M.; Galzio, R. Letter to the Editor. Preoperative embolization of brain arteriovenous malformations. J. Neurosurg. 2019, 132, 2014–2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campanella, R.; Guarnaccia, L.; Cordiglieri, C.; Trombetta, E.; Caroli, M.; Carrabba, G.; La Verde, N.; Rampini, P.; Gaudino, C.; Costa, A.; et al. Tumor-Educated Platelets and Angiogenesis in Glioblastoma: Another Brick in the Wall for Novel Prognostic and Targetable Biomarkers, Changing the Vision from a Localized Tumor to a Systemic Pathology. Cells 2020, 9, 294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Luzzi, S.; Crovace, A.M.; Lacitignola, L.; Valentini, V.; Francioso, E.; Rossi, G.; Invernici, G.; Galzio, R.J.; Crovace, A. Engraftment, neuroglial transdifferentiation and behavioral recovery after complete spinal cord transection in rats. Surg. Neurol. Int. 2018, 9, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mikolov, T.; Chen, K.; Corrado, G.s.; Dean, J. Efficient Estimation of Word Representations in Vector Space. In Proceedings of the Workshop at ICLR, Scottsdale, AZ, USA, 2–4 May 2013; Volume 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Powers, W.J.; Rabinstein, A.A.; Ackerson, T.; Adeoye, O.M.; Bambakidis, N.C.; Becker, K.; Biller, J.; Brown, M.; Demaerschalk, B.M.; Hoh, B.; et al. 2018 Guidelines for the Early Management of Patients With Acute Ischemic Stroke: A Guideline for Healthcare Professionals From the American Heart Association/American Stroke Association. Stroke 2018, 49, e46–e110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, F.; Jiang, Y.; Zhi, H.; Dong, Y.; Li, H.; Ma, S.; Wang, Y.; Dong, Q.; Shen, H.; Wang, Y. Artificial intelligence in healthcare: Past, present and future. Stroke Vasc. Neurol. 2017, 2, 230–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.; Zhao, C.; He, S.; Gu, Y.; Alfarraj, O.; Abugabah, A. LogUAD: Log Unsupervised Anomaly Detection Based on Word2Vec. Comput. Syst. Sci. Eng. 2022, 41, 1207–1222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pu, B.; Li, K.; Li, S.; Zhu, N. Automatic Fetal Ultrasound Standard Plane Recognition Based on Deep Learning and IIoT. IEEE Trans. Ind. Inform. 2021, 17, 7771–7780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Yang, Y.; Wang, T.; Sherratt, R.S.; Zhang, J. Big Data Service Architecture: A Survey. J. Internet Technol. 2020, 21, 13. [Google Scholar]
- Duan, M.; Li, K.; Liao, X.; Li, K. A Parallel Multiclassification Algorithm for Big Data Using an Extreme Learning Machine. IEEE Trans. Neural Netw. Learn. Syst. 2018, 29, 2337–2351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Control | MIS | Measure | p-Value | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Female | 148,464 (48.7%) | 305 (47.1%) | # | 0.13 |
| Age | 55 (Q1 = 38.1, Q3 = 73.8) | 75 (Q1 = 67.9, Q3 = 83.9) | Years | <<0.001 |
| Admissions | 304,579 | 648 | # |
| Control | MIS | Measure | p-Value | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Female | 30,163 (46.5%) | 305 (47.1%) | # | 0.13 |
| Age | 75 (Q1 = 68.3, Q3 = 83.9) | 75 (Q1 = 67.9, Q3 = 83.9) | Years | 0.86 |
| Admissions | 64,800 | 648 | # |
| Train | Test | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Control | MIS | Control | MIS | |
| F1 | 0.941 (±0.001) | 0.137 (±0.002) | 0.941 (±0.002) | 0.132 (±0.005) |
| Precision | 0.998 (±0.001) | 0.074 (±0.001) | 0.998 (±0.001) | 0.072 (±0.003) |
| Recall | 0.891 (±0.002) | 0.878 (±0.005) | 0.891 (±0.005) | 0.839 (±0.021) |
| Support | 243,663 | 519 | 60,916 | 129 |
| Color Code | Precision | Recall | F1 | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Control | MIS | Control | MIS | Control | MIS | |
| Red | 0.987 | 0.138 | 0.721 | 0.834 | 0.833 | 0.237 |
| Yellow | 0.995 | 0.110 | 0.827 | 0.864 | 0.903 | 0.195 |
| Green | 0.999 | 0.009 | 0.927 | 0.613 | 0.961 | 0.018 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Desai, A.; Zumbo, A.; Giordano, M.; Morandini, P.; Laino, M.E.; Azzolini, E.; Fabbri, A.; Marcheselli, S.; Giotta Lucifero, A.; Luzzi, S.; et al. Word2vec Word Embedding-Based Artificial Intelligence Model in the Triage of Patients with Suspected Diagnosis of Major Ischemic Stroke: A Feasibility Study. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 15295. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph192215295
Desai A, Zumbo A, Giordano M, Morandini P, Laino ME, Azzolini E, Fabbri A, Marcheselli S, Giotta Lucifero A, Luzzi S, et al. Word2vec Word Embedding-Based Artificial Intelligence Model in the Triage of Patients with Suspected Diagnosis of Major Ischemic Stroke: A Feasibility Study. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health. 2022; 19(22):15295. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph192215295
Chicago/Turabian StyleDesai, Antonio, Aurora Zumbo, Mauro Giordano, Pierandrea Morandini, Maria Elena Laino, Elena Azzolini, Andrea Fabbri, Simona Marcheselli, Alice Giotta Lucifero, Sabino Luzzi, and et al. 2022. "Word2vec Word Embedding-Based Artificial Intelligence Model in the Triage of Patients with Suspected Diagnosis of Major Ischemic Stroke: A Feasibility Study" International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health 19, no. 22: 15295. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph192215295
APA StyleDesai, A., Zumbo, A., Giordano, M., Morandini, P., Laino, M. E., Azzolini, E., Fabbri, A., Marcheselli, S., Giotta Lucifero, A., Luzzi, S., & Voza, A. (2022). Word2vec Word Embedding-Based Artificial Intelligence Model in the Triage of Patients with Suspected Diagnosis of Major Ischemic Stroke: A Feasibility Study. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 19(22), 15295. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph192215295