Toxic Metals in Particulate Matter and Health Risks in an E-Waste Dismantling Park and Its Surrounding Areas: Analysis of Three PM Size Groups
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
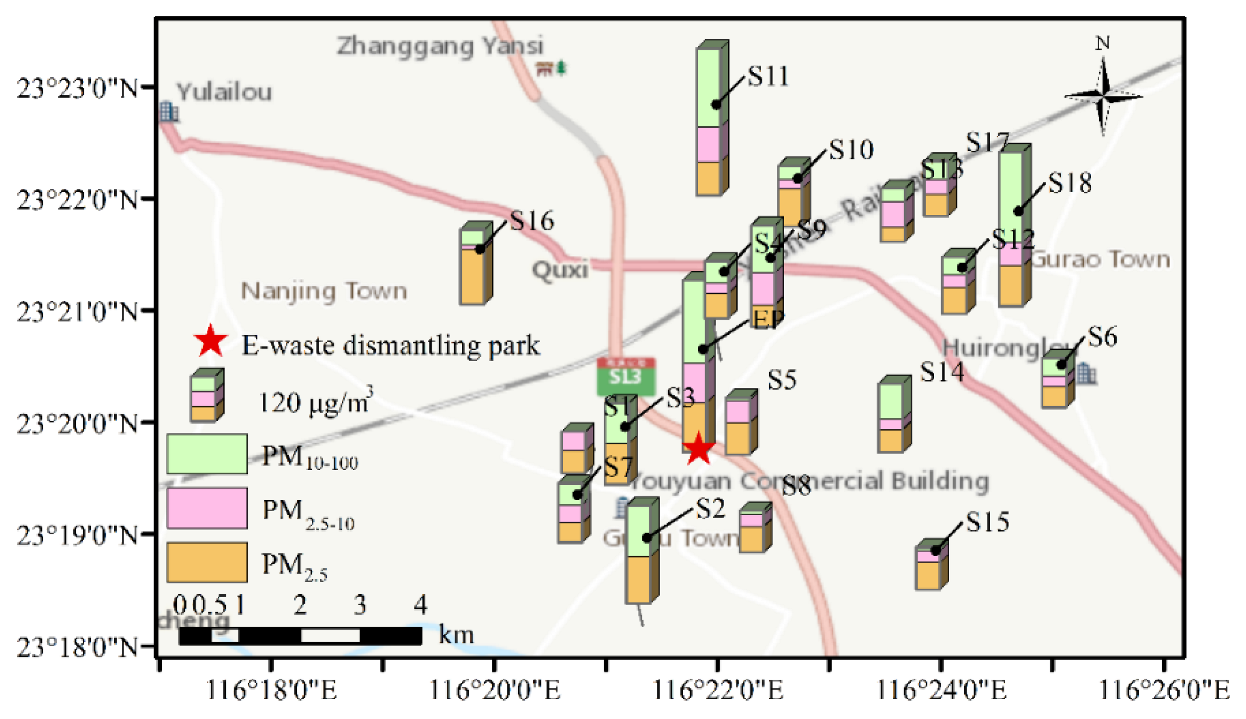
2.1. Study Site and Sample Collection
2.2. Sample Pretreatments and Instrumental Analysis
2.3. Source Apportionment Analysis
2.4. Human Health Risk Assessment via Inhalation
2.5. Statistical Analysis
2.6. Quality Assurance and Quality Control
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. PM2.5, PM10, and TSP Pollution in E-Waste Area
3.2. Metal Pollution Profile in PM2.5, PM10, and TSP
3.3. Size Fraction of the Toxic Metals in PM2.5, PM2.5–10, and PM10–100
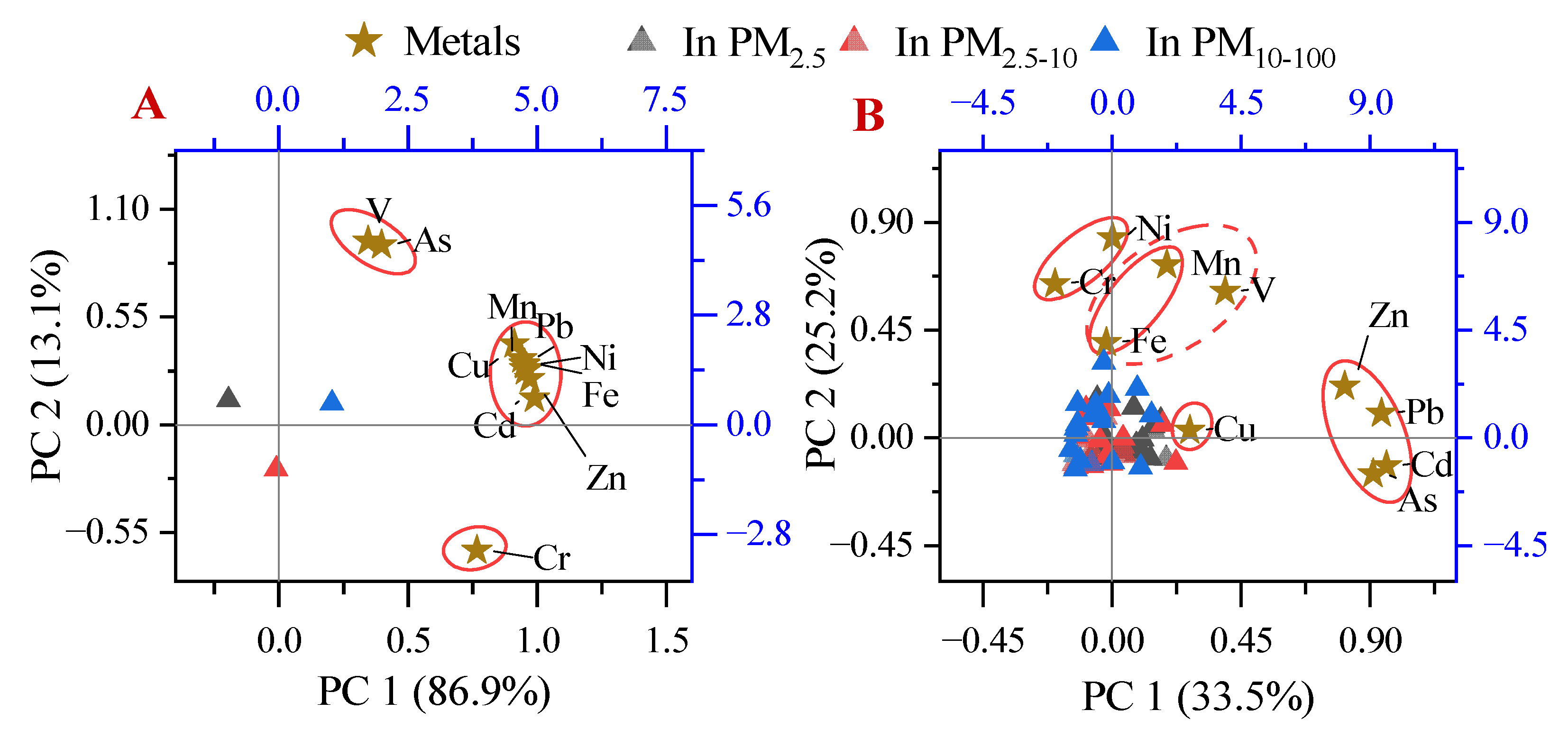
3.4. Source Analysis
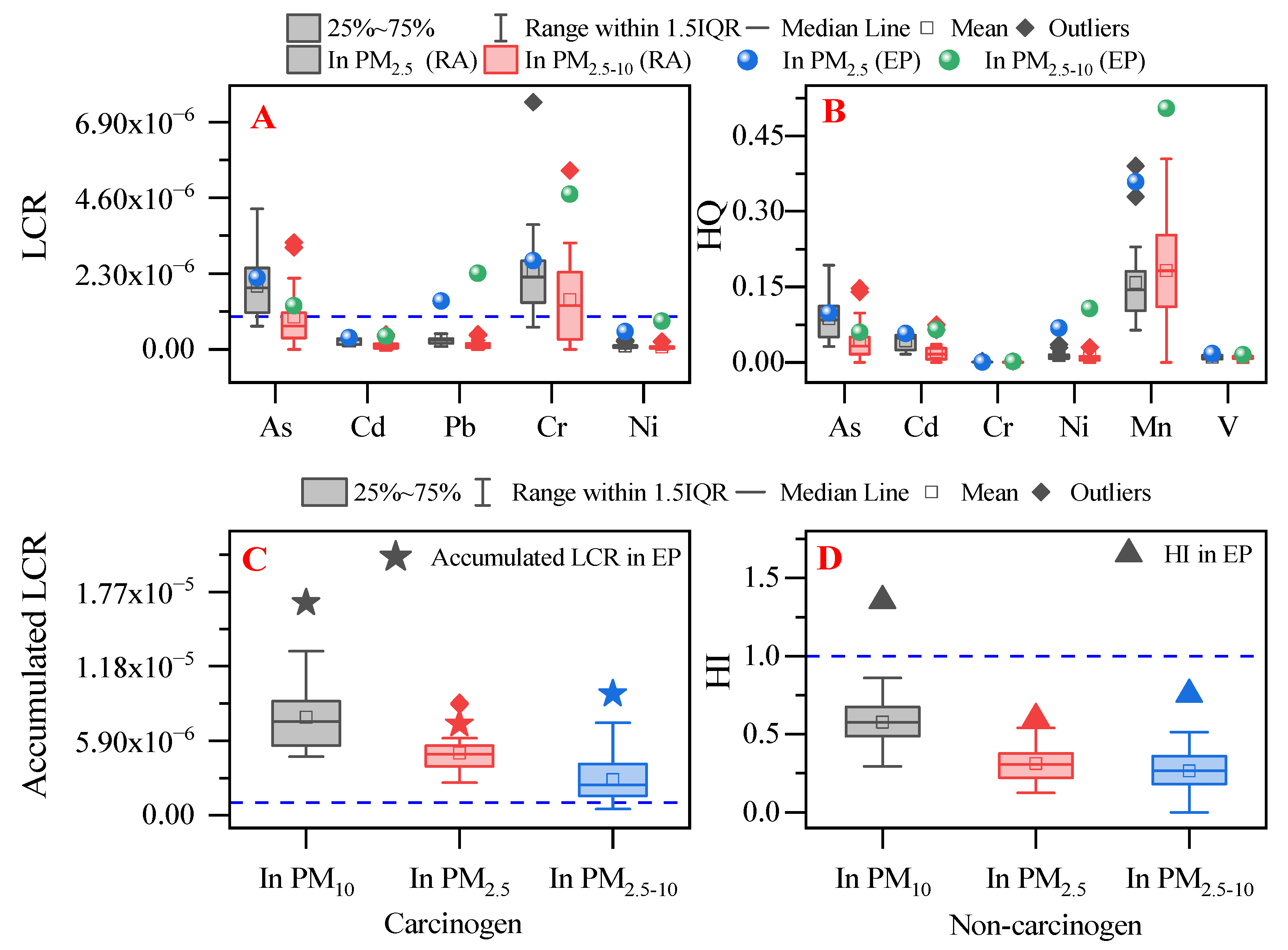
3.5. Inhalation Health Risk Assessment
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Straif, K.; Benbrahim-Tallaa, L.; Baan, R.; Grosse, Y.; Secretan, B.; El Ghissassi, F.; Bouvard, V.; Guha, N.; Freeman, C.; Galichet, L.; et al. A review of human carcinogens—Part C: Metals, arsenic, dusts, and fibres. Lancet. Oncol. 2009, 10, 453–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, M.; Wang, W.; Li, J.; Wang, T.; Xu, Z.; Song, Y.; Zhang, W.; Zhou, L.; Lian, C.; Yang, J.; et al. High fraction of soluble trace metals in fine particles under heavy haze in central China. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 841, 156771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, X.; Shao, L.; Jones, T.; Li, Y.; Cao, Y.; Zhang, M.; Ge, S.; Yang, C.X.; Lu, J.; BeruBe, K. Oxidative potential and water-soluble heavy metals of size-segregated airborne particles in haze and non-haze episodes: Impact of the “Comprehensive Action Plan” in China. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 814, 152774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Y.; Zhang, M.; Chen, H.; Qi, Z.; Liu, C.; Chen, Q.; Long, T. Estimation of Children’s Soil and Dust Ingestion Rates and Health Risk at E-Waste Dismantling Area. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 7332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jomova, K.; Valko, M. Advances in metal-induced oxidative stress and human disease. Toxicology 2011, 283, 65–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kastury, F.; Smith, E.; Doelsch, E.; Lombi, E.; Donnelley, M.; Cmielewski, P.L.; Parsons, D.W.; Scheckel, K.G.; Paterson, D.; de Jonge, M.D.; et al. In Vitro, in Vivo, and Spectroscopic Assessment of Lead Exposure Reduction via Ingestion and Inhalation Pathways Using Phosphate and Iron Amendments. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2019, 53, 10329–10341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kastury, F.; Smith, E.; Lombi, E.; Donnelley, M.W.; Cmielewski, P.L.; Parsons, D.W.; Noerpel, M.; Scheckel, K.G.; Kingston, A.M.; Myers, G.R.; et al. Dynamics of Lead Bioavailability and Speciation in Indoor Dust and X-ray Spectroscopic Investigation of the Link between Ingestion and Inhalation Pathways. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2019, 53, 11486–11495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ibanez, C.; Suhard, D.; Elie, C.; Ebrahimian, T.; Lestaevel, P.; Roynette, A.; Dhieux-Lestaevel, B.; Gensdarmes, F.; Tack, K.; Tessier, C. Evaluation of the Nose-to-Brain Transport of Different Physicochemical Forms of Uranium after Exposure via Inhalation of a UO4 Aerosol in the Rat. Environ. Health Perspect. 2019, 127, 97010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Eriksen Hammer, S.; Dorn, S.L.; Dartey, E.; Berlinger, B.; Thomassen, Y.; Ellingsen, D.G. Occupational Exposure among Electronic Repair Workers in Ghana. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 8477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Yang, X.; Wang, H.; Jia, G.; Wang, T. Relationship between ambient PM2.5 exposure and blood cadmium level in children under 14 years in Beijing, China. J. Hazard. Mater. 2021, 403, 123871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, X.; Xu, X.; Boezen, H.M.; Huo, X. Children with health impairments by heavy metals in an e-waste recycling area. Chemosphere 2016, 148, 408–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Farzan, S.F.; Howe, C.G.; Chen, Y.; Gilbert-Diamond, D.; Cottingham, K.L.; Jackson, B.P.; Weinstein, A.R.; Karagas, M.R. Prenatal lead exposure and elevated blood pressure in children. Environ. Int. 2018, 121, 1289–1296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, F.; Yi, X.; Guo, J.; Xu, S.; Xiao, Y.; Huang, X.; Duan, Y.; Luo, D.; Xiao, S.; Huang, Z.; et al. Association of plasma and urine metals levels with kidney function: A population-based cross-sectional study in China. Chemosphere 2019, 226, 321–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, M.; Li, Y.; Zhang, B.; Zhou, A.; Zheng, T.; Qian, Z.; Du, X.; Zhou, Y.; Pan, X.; Hu, J. A nested case-control study of prenatal vanadium exposure and low birthweight. Human Reprod. 2016, 31, 2135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liu, J.; Cao, H.; Zhang, Y.; Chen, H. Potential years of life lost due to PM2.5-bound toxic metal exposure: Spatial patterns across 60 cities in China. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 812, 152593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Wang, T.; Zhou, S.; Lee, S.; Huang, Y.; Gao, Y.; Wang, W. Microscopic observation of metal-containing particles from Chinese continental outflow observed from a non-industrial site. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2013, 47, 9124–9131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, K.; Huang, L.; Yan, B.; Li, H.; Sun, H.; Bi, J. Effect of lead pollution control on environmental and childhood blood lead level in Nantong, China: An interventional study. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2014, 48, 12930–12936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, L.L.; Gong, W.; Shen, S.P.; Wang, Z.H.; Yao, J.X.; Wang, J.; Yu, J.; Gao, R.; Wu, G. Multiple metal exposures and their correlation with monoamine neurotransmitter metabolism in Chinese electroplating workers. Chemosphere 2017, 182, 745–752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, L.; Wu, K.; Li, Y.; Qi, Z.; Han, D.; Zhang, B.; Gu, C.; Chen, G.; Liu, J.; Chen, S.; et al. Blood lead and cadmium levels and relevant factors among children from an e-waste recycling town in China. Environ. Res. 2008, 108, 15–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, X.; Gong, R.; Chen, W.Q.; Li, J. Uncovering the Recycling Potential of “New” WEEE in China. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2016, 50, 1347–1358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Awasthi, A.K.; Zeng, X.; Li, J. Environmental pollution of electronic waste recycling in India: A critical review. Environ. Pollut. 2016, 211, 259–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bi, X.H.; Simoneit, B.R.T.; Wang, Z.Z.; Wang, X.M.; Sheng, G.Y.; Fu, J.M. The major components of particles emitted during recycling of waste printed circuit boards in a typical e-waste workshop of South China. Atmos. Environ. 2010, 44, 4440–4445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leung, A.O.; Duzgoren-Aydin, N.S.; Cheung, K.C.; Wong, M.H. Heavy metals concentrations of surface dust from e-waste recycling and its human health implications in southeast China. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2008, 42, 2674–2680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bo, Z.; Xia, H.; Long, X.; Cheng, Z.; Cong, X.; Lu, X.; Xu, X. Elevated lead levels from e-waste exposure are linked to decreased olfactory memory in children. Environ. Pollut. 2017, 231, 1112–1121. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, C.L.; Bao, L.J.; Luo, P.; Wang, Z.Y.; Li, S.M.; Zeng, E.Y. Potential health risk for residents around a typical e-waste recycling zone via inhalation of size-fractionated particle-bound heavy metals. J. Hazard. Mater. 2016, 317, 449–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, X.; Xu, X.; Zheng, X.; Reponen, T.; Chen, A.; Huo, X. Heavy metals in PM2.5 and in blood, and children’s respiratory symptoms and asthma from an e-waste recycling area. Environ. Pollut. 2016, 210, 346–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rautela, R.; Arya, S.; Vishwakarma, S.; Lee, J.; Kim, K.H.; Kumar, S. E-waste management and its effects on the environment and human health. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 773, 145623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, Y. Pollution: Centralized pilot for e-waste processing. Nature 2016, 538, 41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, W.; Yang, Y.; Xu, Z. PM10 and PM2.5 and health risk assessment for heavy metals in a typical factory for cathode ray tube television recycling. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2013, 47, 12469–12476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, X.; Ma, S.; Zhang, X.; Yang, Y.; Li, G.; Yu, Y. Halogenated and organophosphorous flame retardants in surface soils from an e-waste dismantling park and its surrounding area: Distributions, sources, and human health risks. Environ. Int. 2020, 139, 105741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yue, C.; Ma, S.; Liu, R.; Yang, Y.; Li, G.; Yu, Y.; An, T. Pollution profiles and human health risk assessment of atmospheric organophosphorus esters in an e-waste dismantling park and its surrounding area. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 806, 151206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, W.; Lin, Y.; Yang, H.; Ling, W.; Liu, L.; Zhang, W.; Lu, D.; Liu, Q.; Jiang, G. Internal Exposure and Distribution of Airborne Fine Particles in the Human Body: Methodology, Current Understandings, and Research Needs. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2022, 56, 6857–6869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- HJ-657-2013; Ambient Air and Stationary Source Emission—Determination of Metals in Ambient Particulate Matter—Inductively Coupled Plasma/Mass Spectrometry (ICP-MS). Ministry of Ecology and Environment of the People’s Republic of China: Beijing, China, 2013.
- Lu, X.; Wang, L.; Li, L.Y.; Lei, K.; Huang, L.; Kang, D. Multivariate statistical analysis of heavy metals in street dust of Baoji, NW China. J. Hazard. Mater. 2010, 173, 744–749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anaman, R.; Peng, C.; Jiang, Z.C.; Liu, X.; Zhou, Z.R.; Guo, Z.H.; Xiao, X.Y. Identifying sources and transport routes of heavy metals in soil with different land uses around a smelting site by GIS based PCA and PMF. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 823, 153759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taner, S.; Pekey, B.; Pekey, H. Fine particulate matter in the indoor air of barbeque restaurants: Elemental compositions, sources and health risks. Sci. Total Environ. 2013, 454–455, 79–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhai, Y.; Liu, X.; Chen, H.; Xu, B.; Zhu, L.; Li, C.; Zeng, G. Source identification and potential ecological risk assessment of heavy metals in PM2.5 from Changsha. Sci. Total Environ. 2014, 493, 109–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Li, S.; Chen, Z.; Wang, F.; Chen, J.; Wang, L. A systemic ecological risk assessment based on spatial distribution and source apportionment in the abandoned lead acid battery plant zone, China. J. Hazard. Mater. 2018, 354, 170–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, P.; Fulekar, M.H. Multivariate and statistical approaches for the evaluation of heavy metals pollution at e-waste dumping sites. SN Appl. Sci. 2019, 1, 1506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Li, G.; Yang, Y.; An, T. Pollution evaluation and health risk assessment of airborne toxic metals in both indoors and outdoors of the Pearl River Delta, China. Environ. Res. 2019, 179, 108793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, C.H.; Huang, L.; Shin, J.Y.; Artigas, F.; Fan, Z.H. Characterization of concentration, particle size distribution, and contributing factors to ambient hexavalent chromium in an area with multiple emission sources. Atmos. Environ. 2014, 94, 701–708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- An, T.; Huang, Y.; Li, G.; He, Z.; Chen, J.; Zhang, C. Pollution profiles and health risk assessment of VOCs emitted during e-waste dismantling processes associated with different dismantling methods. Environ. Int. 2014, 73, 186–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- EPA. Risk Assessmen Guidance for Superfund; U.S. Environmental Protection Agency: Washington, DC, USA, 1989; Volume I.
- Hu, X.; Zhang, Y.; Ding, Z.; Wang, T.; Lian, H.; Sun, Y.; Wu, J. Bioaccessibility and health risk of arsenic and heavy metals (Cd, Co, Cr, Cu, Ni, Pb, Zn and Mn) in TSP and PM2.5 in Nanjing, China. Atmos. Environ. 2012, 57, 146–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- GB 3095-2012; Ambient Air Quality Standards. MEP: Beijing, China, 2012.
- Duan, J.; Tan, J. Atmospheric heavy metals and Arsenic in China: Situation, sources and control policies. Atmos. Environ. 2013, 74, 93–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- WHO, Regional Office for Europe. Air Quality Guidelines for Europe, 2nd ed.; World Health Organization, Regional Office for Europe: København, Denmark, 2000; Available online: https://apps.who.int/iris/handle/10665/107335 (accessed on 30 June 2022).
- Deng, W.J.; Louie, P.K.K.; Liu, W.K.; Bi, X.H.; Fu, J.M.; Wong, M.H. Atmospheric levels and cytotoxicity of PAHs and heavy metals in TSP and PM2.5 at an electronic waste recycling site in southeast China. Atmos. Environ. 2006, 40, 6945–6955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, X.B.; Xu, X.J.; Yekeen, T.A.; Zhang, Y.L.; Chen, A.M.; Kim, S.S.; Dietrich, K.N.; Ho, S.M.; Lee, S.A.; Reponen, T.; et al. Ambient Air Heavy Metals in PM2.5 and Potential Human Health Risk Assessment in an Informal Electronic-Waste Recycling Site of China. Aerosol Air. Qual. Res. 2016, 16, 388–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wong, M.H.; Wu, S.C.; Deng, W.J.; Yu, X.Z.; Luo, Q.; Leung, A.O.; Wong, C.S.; Luksemburg, W.J.; Wong, A.S. Export of toxic chemicals—A review of the case of uncontrolled electronic-waste recycling. Environ. Pollut. 2007, 149, 131–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- IARC. Arsenic, Metals, Fibres, and Dusts. A Review of Human Carcinogens; WHO Press: Lyon, France, 2012; Volume 100C. [Google Scholar]
- Priya, A.; Hait, S. Toxicity characterization of metals from various waste printed circuit boards. Process Saf. Environ. 2018, 116, 74–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, H.; Peters, T.M.; Casuccio, G.S.; Lersch, T.L.; West, R.R.; Kumar, A.; Kumar, N.; Ault, A.P. Elevated Concentrations of Lead in Particulate Matter on the Neighborhood-Scale in Delhi, India As Determined by Single Particle Analysis. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2016, 50, 4961–4970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heyder, J.; Gebhart, J.; Rudolf, G.; Schiller, C.F.; Stahlhofen, W. Deposition of particles in the human respiratory tract in the size range 0.005–15 μm. J. Aerosol Sci. 1986, 17, 811–825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, J.Z.; Wu, S.M.; Pan, Y.; Zhang, L.G.; Cao, Z.B.; Zhang, X.Q.; Yonemochi, S.; Hosono, S.; Wang, Y.; Oh, K.; et al. Enrichment of heavy metals in fine particles of municipal solid waste incinerator (MSWI) fly ash and associated health risk. Waste Manag. 2015, 43, 239–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, P.; Guo, H.; Zhang, Z.; Ou, C.; Hang, J.; Fan, Q.; He, C.; Wu, B.; Feng, Y.; Xing, B. Bioaccessibility and exposure assessment of trace metals from urban airborne particulate matter (PM10 and PM2.5) in simulated digestive fluid. Environ. Pollut. 2018, 242, 1669–1677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seinfeld, J.H.; Pandis, S.N. Atmospheric Chemistry and Physics: From Air Pollution to Climate Change, 3rd ed.; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, S.P.; Li, X.; Cai, M.J.; Gao, Y.; Xu, C.; Schwab, J.J.; Yuan, C.S. Size distributions and health risks of particle-bound toxic elements in the southeast coastland of China. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. Int. 2021, 28, 44565–44579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hetland, R.B.; Myhre, O.; Lag, M.; Hongve, D.; Schwarze, P.E.; Refsnes, M. Importance of soluble metals and reactive oxygen species for cytokine release induced by mineral particles. Toxicology 2001, 165, 133–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Li, Y.; Kang, D.; Wang, J.; Zhang, Y.; Du, D.; Pan, B.; Lin, Z.; Huang, C.; Dong, Q. Tetrabromobisphenol A and heavy metal exposure via dust ingestion in an e-waste recycling region in Southeast China. Sci. Total Environ. 2016, 541, 356–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flint, L.C.; Arias-Paic, M.S.; Korak, J.A. Removal of hexavalent chromium by anion exchange: Non-target anion behavior and practical implications. Environ. Sci.-Water Res. Technol. 2021, 7, 2397–2413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomann, O.; Pihlatie, M.; Schuler, J.A.; Himanen, O.; Kiviaho, J. Method for Measuring Chromium Evaporation from SOFC Balance-of-Plant Components. Electrochem. Solid State Lett. 2012, 15, B35–B37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, S.N.; Zheng, N.; Tang, L.; Ji, X.F.; Li, Y.Y.; Hua, X.Y. Pollution characteristics, sources, and health risk assessment of human exposure to Cu, Zn, Cd and Pb pollution in urban street dust across China between 2009 and 2018. Environ. Int. 2019, 128, 430–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, K.; Wang, Y.; Tian, H.; Gao, X.; Zhang, Y.; Wu, X.; Zhu, C.; Gao, J. Atmospheric emission characteristics and control policies of five precedent-controlled toxic heavy metals from anthropogenic sources in China. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2015, 49, 1206–1214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agrawal, H.; Eden, R.; Zhang, X.; Fine, P.M.; Katzenstein, A.; Miller, J.W.; Ospital, J.; Teffera, S.; Cocker, D.R., III. Primary particulate matter from ocean-going engines in the Southern California Air Basin. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2009, 43, 5398–5402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tao, J.; Zhang, L.; Cao, J.; Zhong, L.; Chen, D.; Yang, Y.; Chen, D.; Chen, L.; Zhang, Z.; Wu, Y.; et al. Source apportionment of PM2.5 at urban and suburban areas of the Pearl River Delta region, south China—With emphasis on ship emissions. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 574, 1559–1570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Element | EP Site | Surrounding Residential Area | Urban Site | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mean | Geomean (±SD *) | Median (Range) | Mean | |
| PM2.5 (μg/m3) | 131.75 | 77.08 (±30.31) | 70.01 (39.12–147.92) | 89.30 |
| As (ng/m3) | 4.48 | 3.51 (±1.99) | 3.85 (1.46–8.80) | 3.25 |
| Cd (ng/m3) | 1.75 | 1.19 (±0.5) | 1.47 (0.49–2.08) | 0.56 |
| Pb (ng/m3) | 162.90 | 27.93 (±12.02) | 31.28 (10.09–53.24) | 18.52 |
| Cr (ng/m3) | 8.36 | 6.36 (±4.68) | 6.84 (2.11–23.28) | 9.35 |
| Mn (ng/m3) | 54.54 | 21.53 (±12.96) | 21.90 (9.74–59.33) | 33.75 |
| V (ng/m3) | 5.33 | 2.82 (±1.33) | 2.77 (1.04–5.35) | 18.71 |
| Ni (ng/m3) | 18.59 | 3.01 (±2.3) | 2.69 (1.29–9.73) | 9.66 |
| Zn (ng/m3) | 308.25 | 95.61 (±60) | 101.96 (15.14–242.26) | 156.75 |
| Cu (ng/m3) | 122.11 | 36.76 (±62.64) | 35.85 (3.09–195.76) | 71.56 |
| Fe (ng/m3) | 1607.38 | 1016.07 (±1.99) | 552.92 (244.72–1425.39) | 375.89 |
| PM10 (μg/m3) | 235.28 | 116.67 (±40.68) | 103.08 (83.27–182.30) | 111.93 |
| As (ng/m3) | 7.21 | 5.24 (±2.85) | 4.93 (1.85–10.92) | 4.60 |
| Cd (ng/m3) | 3.74 | 1.72 (±0.76) | 1.76 (0.56–3.45) | 0.82 |
| Pb (ng/m3) | 419.38 | 44.32 (±16.16) | 41.95 (19.03–90.86) | 48.51 |
| Cr (ng/m3) | 23.00 | 10.41 (±3.78) | 9.73 (6.85–21.01) | 13.17 |
| Mn (ng/m3) | 131.33 | 48.89 (±15.62) | 47.30 (29.87–85.38) | 51.57 |
| V (ng/m3) | 9.95 | 5.6 (±1.93) | 5.60 (3.06–11.50) | 23.36 |
| Ni (ng/m3) | 47.87 | 5.27 (±2.12 | 4.90 (3.54–10.26) | 15.27 |
| Zn (ng/m3) | 758.01 | 170. (±41) | 163.18 (43.51–357.35) | 214.39 |
| Cu (ng/m3) | 287.99 | 66.81 (±101.45) | 68.61 (8.17–368.75) | 59.43 |
| Fe (ng/m3) | 4771.38 | 1763.88 (±2.85) | 1503.17 (986.84–4010.48) | 1136.26 |
| TSP (μg/m3) | 457.42 | 183.78 (±104.83) | 155.42 (106.71–411.34) | 128.47 |
| As (ng/m3) | 12.67 | 6.39 (±2.64) | 7.33 (2.88–11.43) | 5.07 |
| Cd (ng/m3) | 6.19 | 2.04 (±0.67) | 2.24 (0.88–3.37) | 0.84 |
| Pb (ng/m3) | 1224.95 | 54.28 (±17.59) | 56.18 (24.55–92.29) | 67.78 |
| Cr (ng/m3) | 36.77 | 17.81 (±5.63) | 18.42 (11.51–36.01) | 19.73 |
| Mn (ng/m3) | 295.21 | 86.06 (±44.43) | 77.89 (45.88–196.36) | 61.25 |
| V (ng/m3) | 15.60 | 7.66 (±4.46) | 6.72 (4.33–23.26) | 21.74 |
| Ni (ng/m3) | 126.30 | 8.72 (±3.7) | 9.04 (4.46–18.09) | 18.10 |
| Zn (ng/m3) | 1636.70 | 250.29 (±104.12) | 248.36 (113.33–505.69) | 266.25 |
| Cu (ng/m3) | 1126.66 | 70.11 (±77.67) | 75.95 (11.45–315.66) | 75.75 |
| Fe (ng/m3) | 15,309.03 | 1507.04 (±2.64) | 2623.64 (1470.36–11,297.02) | 1727.61 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wu, Y.; Li, G.; An, T. Toxic Metals in Particulate Matter and Health Risks in an E-Waste Dismantling Park and Its Surrounding Areas: Analysis of Three PM Size Groups. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 15383. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph192215383
Wu Y, Li G, An T. Toxic Metals in Particulate Matter and Health Risks in an E-Waste Dismantling Park and Its Surrounding Areas: Analysis of Three PM Size Groups. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health. 2022; 19(22):15383. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph192215383
Chicago/Turabian StyleWu, Yingjun, Guiying Li, and Taicheng An. 2022. "Toxic Metals in Particulate Matter and Health Risks in an E-Waste Dismantling Park and Its Surrounding Areas: Analysis of Three PM Size Groups" International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health 19, no. 22: 15383. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph192215383
APA StyleWu, Y., Li, G., & An, T. (2022). Toxic Metals in Particulate Matter and Health Risks in an E-Waste Dismantling Park and Its Surrounding Areas: Analysis of Three PM Size Groups. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 19(22), 15383. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph192215383








