Comparisons and Associations between Hip-Joint Position Sense and Glycosylated Hemoglobin in Elderly Subjects with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus—A Cross-Sectional Study
Abstract
:1. Introduction
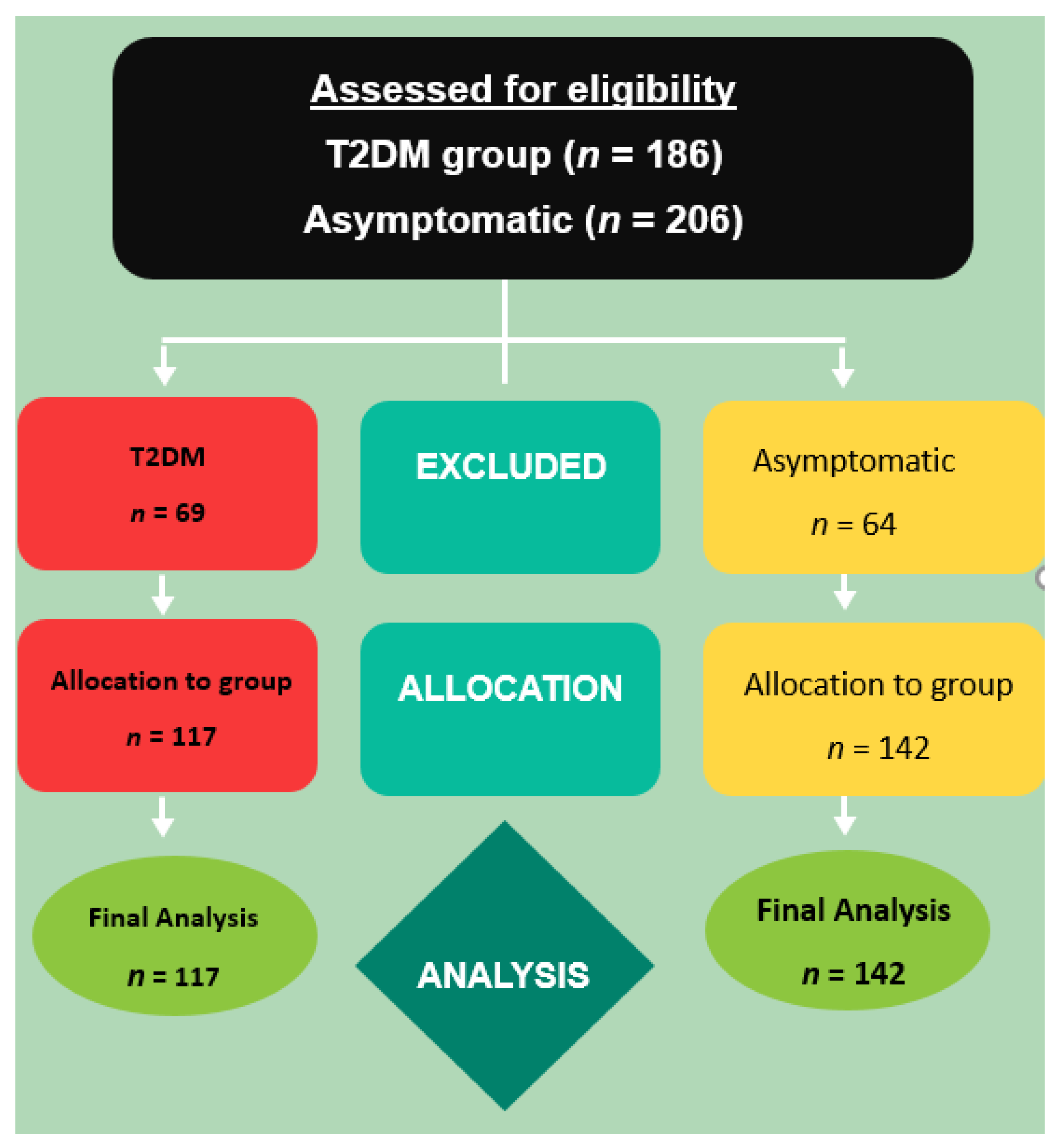
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Subjects
2.2. Semmes Weinstein Monofilament Examination (SWME)
2.3. Laboratory Testing for HbA1c
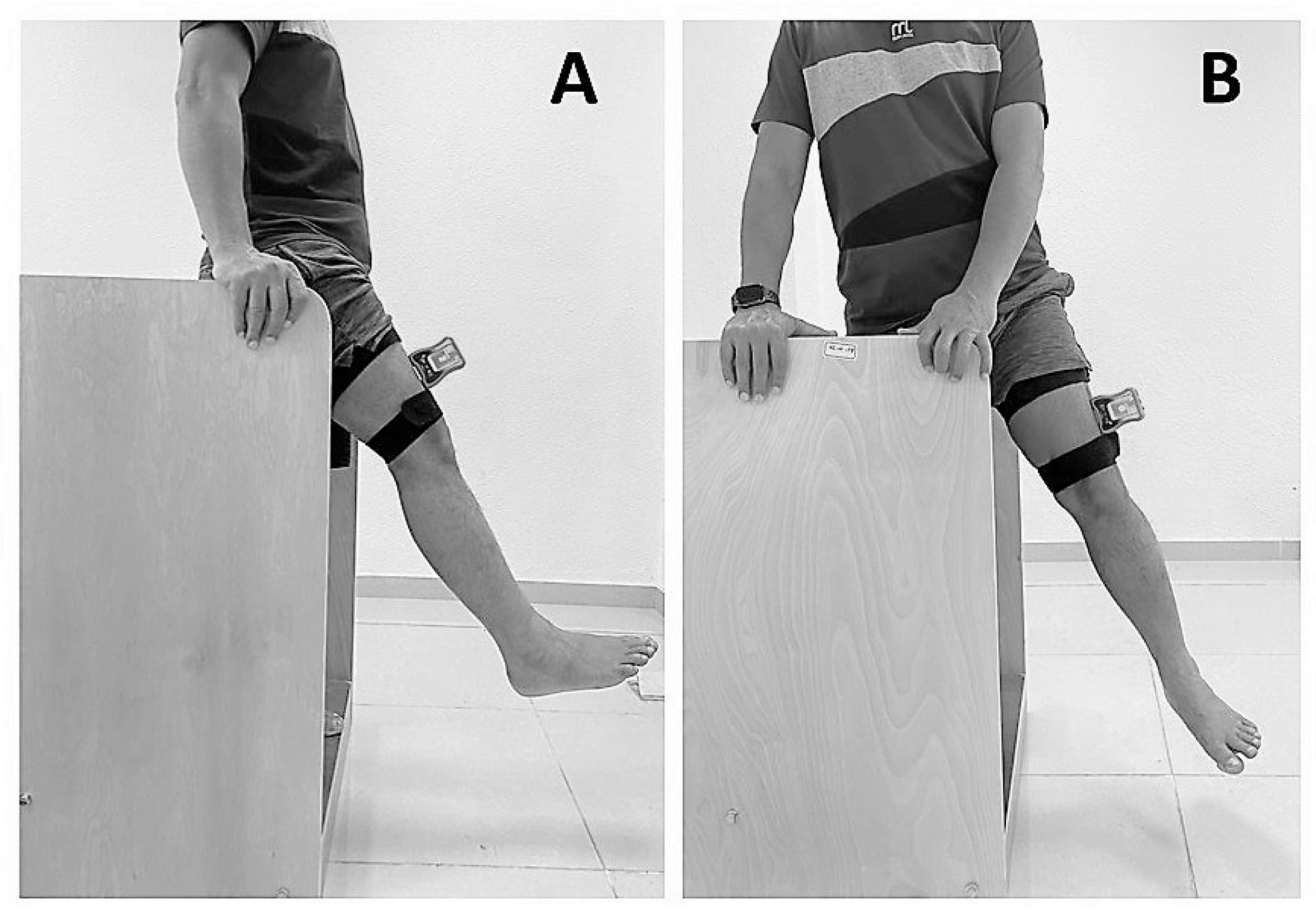
2.4. Assessment of Hip-Joint Position Sense
2.5. Sample-Size Estimation
2.6. Statistical Analysis
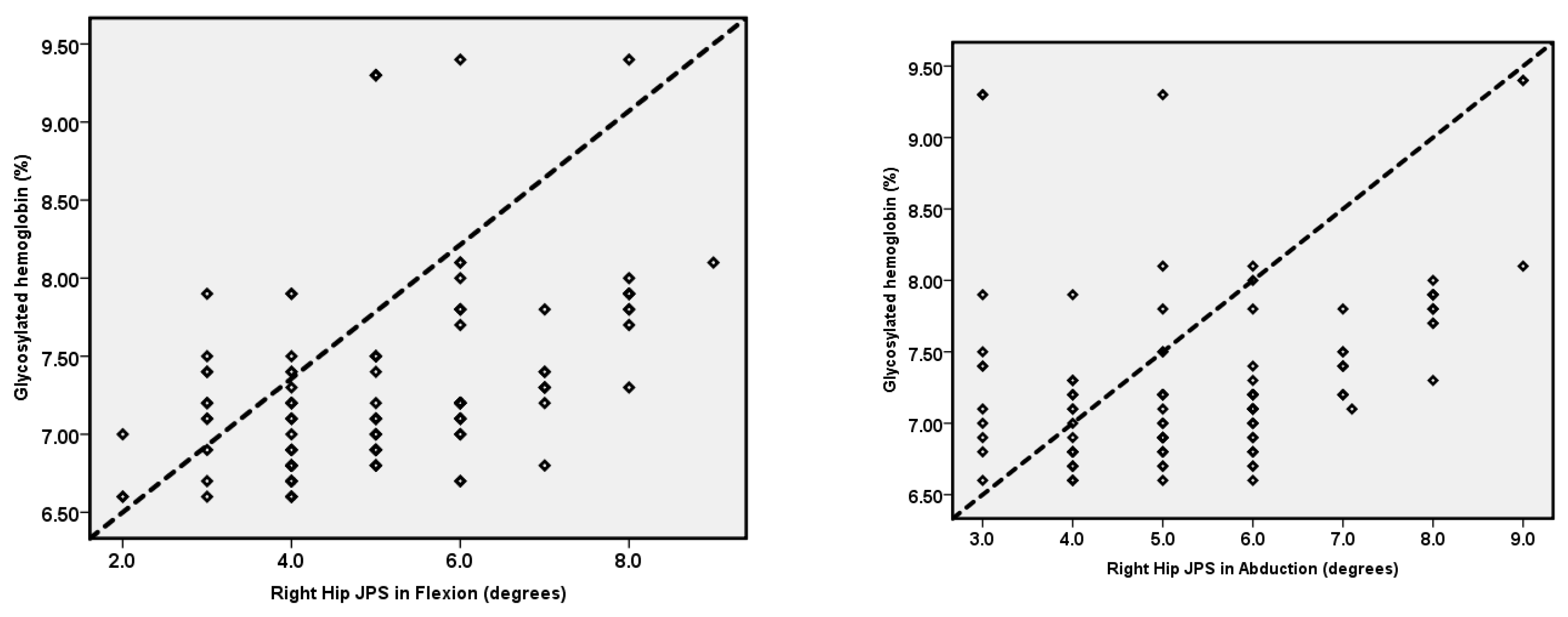
3. Results
4. Discussion
Limitations of the Study
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Gelener, P.; İyigün, G.; Özmanevra, R. Proprioception and Clinical Correlation. In Proprioception; IntechOpen: London, UK, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Ager, A.L.; Borms, D.; Deschepper, L.; Dhooghe, R.; Dijkhuis, J.; Roy, J.-S.; Cools, A. Proprioception: How is it affected by shoulder pain? A systematic review. J. Hand Ther. 2020, 33, 507–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Qu, X. Age-related differences in the relationships between lower-limb joint proprioception and postural balance. Hum. Factors 2019, 61, 702–711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- David, E.; Amasay, T.; Ludwig, K.; Shapiro, S. The effect of foam rolling of the hamstrings on proprioception at the knee and hip joints. Int. J. Exerc. Sci. 2019, 12, 343–349. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Mendelsohn, M.E.; Overend, T.J.; Petrella, R.J. Effect of rehabilitation on hip and knee proprioception in older adults after hip fracture: A pilot study. Am. J. Phys. Med. Rehabil. 2004, 83, 624–632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alshahrani, M.S.; Reddy, R.S.; Tedla, J.S.; Asiri, F.; Alshahrani, A. Association between Kinesiophobia and Knee Pain Intensity, Joint Position Sense, and Functional Performance in Individuals with Bilateral Knee Osteoarthritis. Healthcare 2022, 10, 120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wingert, J.R.; Welder, C.; Foo, P. Age-related hip proprioception declines: Effects on postural sway and dynamic balance. Arch. Phys. Med. Rehabil. 2014, 95, 253–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saeed Alshahrani, M.; Reddy, R.S.; Asiri, F.; Tedla, J.S.; Alshahrani, A.; Kandakurti, P.K.; Kakaraparthi, V.N. Correlation and comparison of quadriceps endurance and knee joint position sense in individuals with and without unilateral knee osteoarthritis. BMC Musculoskelet. Disord. 2022, 23, 444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alshahrani, M.S.; Reddy, R.S. Relationship between Kinesiophobia and Ankle Joint Position Sense and Postural Control in Individuals with Chronic Ankle Instability—A Cross-Sectional Study. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 2792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moulton, C.D.; Costafreda, S.G.; Horton, P.; Ismail, K.; Fu, C.H. Meta-analyses of structural regional cerebral effects in type 1 and type 2 diabetes. Brain Imaging Behav. 2015, 9, 651–662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, J.H.; Yu, K.P.; Yoon, Y.-S.; Kim, E.S.; Jeon, J.H. Relationship between HbA1c and complex regional pain syndrome in stroke patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus. Ann. Rehabil. Med. 2016, 40, 779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abaraogu, U.O.; Ochi, C.; Umahi, E.; Ogbonnaya, C.; Onah, I. Individuals with type 2 diabetes are at higher risk of chronic musculoskeletal pain: A study with diabetes cohort. Int. J. Diabetes Dev. Ctries. 2017, 37, 267–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdulameer, S.A.; Sulaiman, S.A.S.; Hassali, M.A.A.; Subramaniam, K.; Sahib, M.N. Osteoporosis and type 2 diabetes mellitus: What do we know, and what we can do? Patient Prefer. Adherence 2012, 6, 435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Almurdhi, M.M.; Reeves, N.D.; Bowling, F.L.; Boulton, A.J.; Jeziorska, M.; Malik, R.A. Reduced lower-limb muscle strength and volume in patients with type 2 diabetes in relation to neuropathy, intramuscular fat, and vitamin D levels. Diabetes Care 2016, 39, 441–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Holte, K.B.; Juel, N.G.; Brox, J.I.; Hanssen, K.F.; Fosmark, D.S.; Sell, D.R.; Monnier, V.M.; Berg, T.J. Hand, shoulder and back stiffness in long-term type 1 diabetes; cross-sectional association with skin collagen advanced glycation end-products. The Dialong study. J. Diabetes Its Complicat. 2017, 31, 1408–1414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Deursen, R.W.M.; Simoneau, G.G. Foot and ankle sensory neuropathy, proprioception, and postural stability. J. Orthop. Sport. Phys. Ther. 1999, 29, 718–726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vinik, A.I.; Casellini, C.; Neumann, S. Diabetes and the nervous system. In Diabetes Complications, Comorbidities and Related Disorders; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2020; pp. 275–353. [Google Scholar]
- Wallace, C.; Reiber, G.E.; LeMaster, J.; Smith, D.G.; Sullivan, K.; Hayes, S.; Vath, C. Incidence of falls, risk factors for falls, and fall-related fractures in individuals with diabetes and a prior foot ulcer. Diabetes Care 2002, 25, 1983–1986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gilman, S. Joint position sense and vibration sense: Anatomical organisation and assessment. J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatry 2002, 73, 473–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Qu, X.; Hu, X.; Zhao, J.; Zhao, Z. The roles of lower-limb joint proprioception in postural control during gait. Appl. Ergon. 2022, 99, 103635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsu, W.-C.; Lu, T.-W.; Liu, M.-W. Lower limb joint position sense in patients with type II diabetes mellitus. Biomed. Eng. Appl. Basis Commun. 2009, 21, 271–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reddy, R.S.; Alshahrani, M.S.; Tedla, J.S.; Asiri, F.; Nambi, G.; Kakaraparthi, V.N. Cervical Joint Position Sense in Individuals With Type 2 Diabetes and Its Correlations With Glycated Hemoglobin Levels: A Cross-Sectional Study. J. Manip. Physiol. Ther. 2022, 45, 273–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, I.; Noohu, M.M.; Verma, S.; Singla, D.; Hussain, M.E. Effect of sensorimotor training on balance measures and proprioception among middle and older age adults with diabetic peripheral neuropathy. Gait Posture 2019, 74, 114–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feng, Y.; Schlösser, F.J.; Sumpio, B.E. The Semmes Weinstein monofilament examination as a screening tool for diabetic peripheral neuropathy. J. Vasc. Surg. 2009, 50, 675–682.e1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kim, Y.; Kim, H.; Choi, S.; Park, Y.; Lee, S.; Cho, B. Clinical usefulness of the two-site Semmes-Weinstein monofilament test for detecting diabetic peripheral neuropathy. J. Korean Med. Sci. 2003, 18, 103–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Little, R.R. Glycated hemoglobin standardization–National glycohemoglobin standardization program (NGSP) perspective. Clin. Chem. Lab. Med. 2003, 41, 1191–1198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sherwani, S.I.; Khan, H.A.; Ekhzaimy, A.; Masood, A.; Sakharkar, M.K. Significance of HbA1c test in diagnosis and prognosis of diabetic patients. Biomark. Insights 2016, 11, 95–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herman, W.H.; Fajans, S.S. Hemoglobin A1c for the diagnosis of diabetes: Practical considerations. Pol. Arch. Med. Wewn. 2010, 120, 37–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reddy, R.S.; Tedla, J.S.; Alshahrani, M.S.; Asiri, F.; Kakaraparthi, V.N.; Samuel, P.S.; Kandakurti, P.K. Reliability of hip joint position sense tests using a clinically applicable measurement tool in elderly participants with unilateral hip osteoarthritis. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romero-Franco, N.; Montaño-Munuera, J.A.; Fernández-Domínguez, J.C.; Jiménez-Reyes, P. Validity and reliability of a digital inclinometer to assess knee joint position sense in an open kinetic chain. J. Sport Rehabil. 2019, 28, 332–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, H. Sample size determination and power analysis using the G* Power software. J. Educ. Eval. Health Prof. 2021, 18, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goulet-Pelletier, J.-C.; Cousineau, D. A review of effect sizes and their confidence intervals, Part I: The Cohen’sd family. Quant. Methods Psychol. 2018, 14, 242–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gibbons, C.H. Diabetes and metabolic disorders and the peripheral nervous system. Continuum Lifelong Learn. Neurol. 2020, 26, 1161–1183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chandrasekharan, B.; Srinivasan, S. Diabetes and the enteric nervous system. Neurogastroenterol. Motil. 2007, 19, 951–960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ettinger, L.R.; Boucher, A.; Simonovich, E. Patients with type 2 diabetes demonstrate proprioceptive deficit in the knee. World J. Diabetes 2018, 9, 59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moslemi Haghighi, F.; Ghafarinejad, F.; Hemmati, L.; Saadat, Z.; Oorangi, Z.; Torabi, S.; Mohammadzadeh, M.A. Evaluation of ankle joint proprioception and balance in patients with type 2 diabetes and healthy subjects. J. Rehabil. Sci. Res. 2015, 2, 17–19. [Google Scholar]
- Haghighi, F.M. Evaluation of knee proprioception and kinesthesia in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus. Niger. J. Med. Rehabil. 2014, 17, 23–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maras, O.; Dulgeroglu, D.; Cakci, A. Ankle Proprioception in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus. J. Am. Podiatr. Med. Assoc. 2021, 111, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferlinc, A.; Fabiani, E.; Velnar, T.; Gradisnik, L. The importance and role of proprioception in the elderly: A short review. Mater. Socio-Med. 2019, 31, 219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nardone, A.; Schieppati, M. Group II spindle fibres and afferent control of stance. Clues from diabetic neuropathy. Clin. Neurophysiol. 2004, 115, 779–789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Usgu, S.; Ramazanoğlu, E.; Yakut, Y. The Relation of Body Mass Index to Muscular Viscoelastic Properties in Normal and Overweight Individuals. Medicina 2021, 57, 1022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Unver, B.; Selici, K.; Akbas, E.; Erdem, E.U. Foot posture, muscle strength, range of motion, and plantar sensation in overweight and obese. J. Appl. Biomech. 2020, 37, 87–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yümin, E.T.; Şimşek, T.T.; Sertel, M.; Ankaralı, H. The effect of age and body mass index on plantar cutaneous sensation in healthy women. J. Phys. Ther. Sci. 2016, 28, 2587–2595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grewal, G.; Sayeed, R.; Yeschek, S.; Menzies, R.A.; Talal, T.K.; Lavery, L.A.; Armstrong, D.G.; Najafi, B. Virtualizing the assessment: A novel pragmatic paradigm to evaluate lower extremity joint perception in diabetes. Gerontology 2012, 58, 463–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wagman, I.H.; Pierce, D.S.; Burger, R.E. Proprioceptive influence in volitional control of individual motor units. Nature 1965, 207, 957–958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gidu, D.V.; Badau, D.; Stoica, M.; Aron, A.; Focan, G.; Monea, D.; Stoica, A.M.; Calota, N.D. The Effects of Proprioceptive Training on Balance, Strength, Agility and Dribbling in Adolescent Male Soccer Players. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 2028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swash, M.; Fox, K.P. The effect of age on human skeletal muscle studies of the morphology and innervation of muscle spindles. J. Neurol. Sci. 1972, 16, 417–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skelton, D.A. Effects of physical activity on postural stability. Age Ageing 2001, 30, 33–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.M.; Oh, S.; Kwon, J.W. Effect of plyometric versus ankle stability exercises on lower limb biomechanics in taekwondo demonstration athletes with functional ankle instability. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 3665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nielsen, S.G.; Danielsen, J.H.; Grønbæk, H.N.; Molsted, S.; Jacobsen, S.S.; Vilsbøll, T.; Varming, A.R. Transforming Motivation for Exercise in a Safe and Kind Environment—A Qualitative Study of Experiences among Individuals with Type 2 Diabetes. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 6091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khah, J.; Kumar, T.; Sharan, A.; Kumar, A. Relation of glycated hemoglobin with nerve conduction study and proprioception in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus. J. Indira Gandhi Inst. Med. Sci. 2021, 7, 39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tiwari, P.; Siddiqui, Z.A. Effect of blood sugar level on lower limb proprioception in diabetes. Int. J. Phys. Educ. Sport. Health 2018, 5, 214–216. [Google Scholar]

| Variables | T2DM Group (n = 117) | Asymptomatic Group (142) | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Age (years) | 59.82 ± 6.80 | 57.52 ± 6.90 | 0.065 |
| Gender (M:F) | 73:44 | 86:56 | |
| Height (cm) | 167.81 ± 11.69 | 162.03 ± 7.48 | <0.001 |
| Weight (kg) | 75.95 ± 9.83 | 64.40 ± 6.14 | <0.001 |
| BMI (kg/m2) | 27.24 ± 4.63 | 24.58 ± 2.31 | <0.001 |
| Duration of diabetes (years) | 6.73 ± 2.33 | - | - |
Monofilament test (%)
| 73.2 26.8 0 | - | - |
| Glycosylated hemoglobin (HbA1c) | 7.29 ± 0.58 | - | - |
| Variables | T2DM Group (n = 117) (Mean ± SD) | Asymptomatic Group (n = 142) (Mean ± SD) | 95% CI of the Difference | Cohen’s d | SEM | MDC | p-Value | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Lower | Upper | |||||||
| Right-hip JPS in 25° flexion (°) | 5.10 ± 1.52 | 3.35 ± 1.27 | 1.41 | 2.09 | 1.24 | 0.67 | 1.85 | <0.001 |
| Right-hip JPS in 25° abduction (°) | 5.48 ± 1.54 | 3.01 ± 1.44 | 2.10 | 2.83 | 1.65 | 0.68 | 1.87 | <0.001 |
| Left-hip JPS in 25° flexion (°) | 5.21 ± 1.51 | 3.08 ± 1.23 | 1.79 | 2.46 | 1.54 | 0.66 | 1.82 | <0.001 |
| Left-hip JPS in 25° abduction (°) | 5.71 ± 1.47 | 2.35 ± 1.06 | 3.05 | 3.67 | 2.62 | 0.64 | 1.76 | <0.001 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Asiri, F.; Reddy, R.S.; Narapureddy, B.R.; Raizah, A. Comparisons and Associations between Hip-Joint Position Sense and Glycosylated Hemoglobin in Elderly Subjects with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus—A Cross-Sectional Study. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 15514. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph192315514
Asiri F, Reddy RS, Narapureddy BR, Raizah A. Comparisons and Associations between Hip-Joint Position Sense and Glycosylated Hemoglobin in Elderly Subjects with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus—A Cross-Sectional Study. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health. 2022; 19(23):15514. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph192315514
Chicago/Turabian StyleAsiri, Faisal, Ravi Shankar Reddy, Bayapa Reddy Narapureddy, and Abdullah Raizah. 2022. "Comparisons and Associations between Hip-Joint Position Sense and Glycosylated Hemoglobin in Elderly Subjects with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus—A Cross-Sectional Study" International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health 19, no. 23: 15514. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph192315514
APA StyleAsiri, F., Reddy, R. S., Narapureddy, B. R., & Raizah, A. (2022). Comparisons and Associations between Hip-Joint Position Sense and Glycosylated Hemoglobin in Elderly Subjects with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus—A Cross-Sectional Study. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 19(23), 15514. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph192315514







