1. Introduction
The increasing prevalence of nephrolithiasis in the last decade has become a global problem [
1,
2,
3,
4,
5,
6,
7]. The financial burden associated with urolithiasis has been estimated to be as high as EUR 54.38 million in Germany and up to USD 2 billion to 5.3 billion per year in the United States [
8,
9,
10]. Nephrolithiasis not only increases the economic costs but also impairs the patients’ quality of life [
11]. Nephrolithiasis is related to many factors, such as age, gender, water intake, hot climate, humidity, metabolic syndromes, and the heat environment [
12,
13,
14,
15,
16,
17,
18].
Water intake is inversely related to the risk of kidney stones, and a large intake of water is essential for the therapy and prevention of stone recurrences [
19,
20]. In both men and women, an inverse association between fluid intake and urolithiasis risk in patients without a history of urolithiasis has been confirmed [
21].
In addition, many studies have reported that metabolic syndrome, including obesity, hypertension, dyslipidemia, and hyperglycemia, increases the risk of nephrolithiasis [
22,
23,
24,
25]. Not only is body size positively associated with daily oxalate excretion [
26], but obesity is also related to low urinary pH (potential of hydrogen), which may increase the risk of uric acid stone formation [
27]. On the other hand, insulin resistance is noted to decrease urinary citrate excretion in patients with calcium stones [
28]. The increased prevalence of metabolic syndrome over the past half century may partly explain the elevated prevalence of nephrolithiasis during that period [
2,
3,
4].
Kidney stones can either be radiolucent or radiopaque [
29]. Radiolucent stones include pure uric acid stones and indinavir-related stones [
30]. Uric acid stones are the main radiolucent stones in the general population. Pure uric acid stones, which are characterized by their radiolucency on plain radiographs [
31], can best be detected by computed tomography [
32]. However, a combination of abdominal ultrasound and plain radiographs is a common cost-effective diagnostic alternative for radiolucent stones [
31,
32,
33,
34].
A Brazilian study reported a nine-fold increase in the risk of lithiasis among workers in high-temperature workplaces [
35]. A case study from the southern Indian steel industry also showed an elevated risk of kidney stones among workers exposed to high occupational heat stress [
17]. Taiwan is located in a subtropical (northern) to tropical (southern) area. We also have a high prevalence of nephrolithiasis of up to 9.6% [
36]. In addition to the hot temperature in Southern Taiwan throughout the year (28 to 35 degrees Celsius), there is a high density of steel-related factories in which many workers need to be exposed to high-temperature environments. However, there are no related data about the prevalence of radiolucent stones among workers in high-temperature workplaces. The aim of this study was to investigate the risk of radiolucent stone formation among workers in high-temperature workplaces and the related risk factors associated with the condition.
2. Materials and Methods
The study protocols were reviewed and approved by the Institutional Review Board of Kaohsiung Medical University Hospital (KMUHIRB-E(II)-20210116, date of approval: 24 May 2021). We used the data of workers’ health examinations by the Taiwan Occupational Safety and Health Administration (TOHSA). Because the individual information was scrambled, written informed consent was waived by the institutional review board.
For the current study, the diagnosis of radiolucent nephrolithiasis was made according to a method described in the literature [
34,
37]. In brief, the plain abdominal radiographs of workers who were diagnosed with nephrolithiasis based on abdominal sonography were scrutinized to identify those with radiolucent stones to be included in the present investigation. On the other hand, workers with the findings of nephrolithiasis from plain radiographs were grouped under the category “other stones”.
The participants who fulfilled three or more of the following five criteria, published by the Bureau of Health Promotion, Department of Health, Executive Yuan in Taiwan, were diagnosed as having metabolic syndrome: (1) a waist circumference larger than or equal to 90 cm in men or 80 cm in women; (2) a medical history of hypertension, a systolic blood pressure higher than or equal to 130 mmHg, or a diastolic blood pressure higher than or equal to 85 mmHg; (3) a medical history of diabetes mellitus or a fasting serum glucose higher than or equal to 100 mg/dL; (4) a circulating high-density lipoprotein cholesterol (HDL) concentration lower than 40 mg/dL in men or 50 mg/dL in women; and (5) a serum triglyceride level higher than or equal to 150 mg/dL.
Six departments of the steel industry were grouped into hot-temperature workplaces, including the departments of the electric furnace, the converter, vacuum oxidization decarbonization, preparation, the continuous slab caster, and the continuous billet caster. The workers in these six departments were categorized as the group of “heat exposure”. The other workers were grouped as “non-heat exposure”.
All serum and urine samples were analyzed by a hospital with a central laboratory that was certified by an international certificate system performed by the Taiwan Accreditation Foundation (TAF). Serum creatinine and uric acid were measured with commercial kits using an automatic biochemical analyzer (SPOTCHEM EZ SP-4430) in accordance with the manufacturer’s instructions (Arkary, Inc., Kyoto, Japan). Midstream urine specimens were collected in a urine collection kit (Becton, Dickinson and Company, East Rutherford, NJ, USA) with a volume of 5–10 mL from all participants in the morning, considering the circadian rhymes of urine pH values under physiological conditions. Urinalysis was performed by an automatic urine analyzer system (Cobas® 6500 urine analyzer, F. Hoffmann-La Roche Ltd., Basel, Switzerland).
We compared the three groups (radiolucent stones, other stones, and a non-stone group), using a descriptive analysis, an ANOVA (analysis of variance), and a chi-square test cross table. Then, we used logistic regressions to analyze the ORs (odds ratios) with 95% confident intervals to elucidate the relative risks of potential factors that may influence the incidence of radiolucent stone formation, including age, urine pH and gravity, and serum creatinine and uric acid concentrations as well as heat exposure. A linear regression analysis was conducted to determine the significance of the correlations between the factor(s) identified by the logistic regression and the probability of radiolucent stone formation. We performed the analyses using SPSS (IBM SPSS Statistics, IBM, Armonk, NY, USA) version 20 with a two-tailed α-level of 0.05.
3. Results
Of the 1681 steel workers enrolled in this study, 1480 (88%) showed no evidence of nephrolithiasis after abdominal sonographic and plain abdominal radiographic examinations. On the other hand, 116 workers (6.9%) exhibited nephrolithiasis on both examinations (i.e., the “other stone” group), and 85 (5.1%) workers were diagnosed as having radiolucent nephrolithiasis by demonstrating positive findings on abdominal sonographic examinations without supporting evidence from plain radiographs (
Table 1). The average age of the radiolucent stone group was 37.9 years, and this group was significantly older than the non-stone group by 2.3 years. The group of other stones had the longest working duration among the three groups. Other factors such as urine pH, urine gravity, the serum uric acid level, and serum creatinine did not show significant differences among the three groups in the ANOVA tests. In addition, the workers with renal stones, including radiolucent stones, had a significantly higher prevalence of abnormal urinary RBC and WBC counts, according to the chi-square test.
The group with radiolucent stones was significantly older and had more heat exposure than the non-stone group.
Table 2 shows that workers exposed to heat environments had a higher prevalence of radiolucent stones (18/206 vs. 67/1359,
p = 0.025). The group with radiolucent stones had 61.2% of workers older than 35 years, while this number was 46.1% in the non-stone group (
p = 0.007). Most of the workers in this study were males, but no significant difference in gender distribution was noted between the two groups.
Table 3 shows the results of a logistic regression of radiolucent stones predicted by age, working duration, metabolic syndrome, gender, heat exposure, urine pH, urine gravity, serum uric acid level, and creatinine. Although our results identified age, heat exposure, and hyperuricemia as risk factors for nephrolithiasis, only age demonstrated statistical significance, with an odds ratio of 1.052 (
p = 0.008). On the other hand, despite the apparently higher odds ratio for heat exposure (OR = 1.728), it missed statistical significance by a narrow margin (
p = 0.052). Because this was a cross-section study, the abnormal urinary RBC and WBC counts may have been induced by renal stones. As a result, we only included urine pH, urine gravity, serum uric acid, and serum creatinine in our logistic regression analysis.
To elucidate the association between age and heat exposure, we regrouped our subjects by age with 35 years being adopted as the cut-off point, taking into consideration their mean age of 35.73 years and median age of 35 years before investigating the effect of heat exposure. Four subgroups were obtained after regrouping by age and heat exposure, namely those with an age ≤35 years without heat exposure (group 1, n = 726); those with an age >35 years without heat exposure (group 2, n = 633); those with an age ≤35 years with heat exposure (group 3, n = 105); and those with an age >35 years with heat exposure (group 4, n = 101). The p-value of the chi-square test was 0.516, indicating no difference in the age distribution between the groups with and without heat exposure.
Through grouping by age and heat exposure, a logistic regression of the significance of potential predictors of radiolucent stones, including working duration, metabolic syndrome, gender, urine pH, urine gravity, serum uric acid level, and serum creatinine demonstrated the statistical significance of all three groups, with odds ratios of 2.126, 2.695, and 2.899 for groups 2, 3, and 4, respectively, when compared with group 1 (
Table 4).
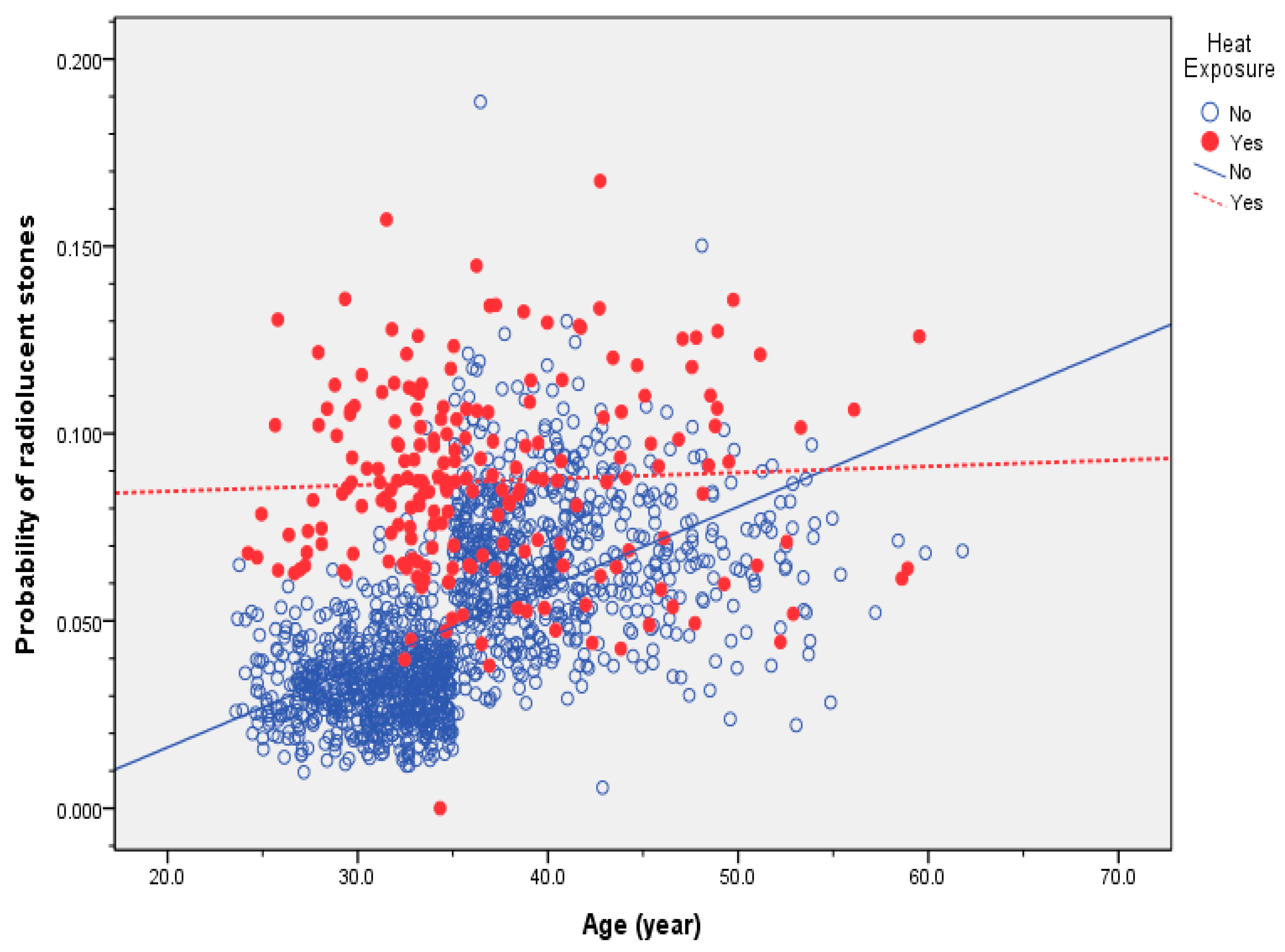
We used the probability of radiolucent nephrolithiasis calculated from the last model to evaluate the impacts of age and heat exposure, as shown in
Figure 1. We found a lack of association between the probability of nephrolithiasis and age among workers with heat exposure (r
2 = 0.002,
p = 0.504), while the probability of radiolucent was nephrolithiasis significantly correlated with age in workers without heat exposure (r
2 = 0.323,
p < 0.001).
4. Discussion
Our research found an increased prevalence of radiolucent stones among workers exposed to high temperatures, regardless of their age, while those without heat exposure showed an increased prevalence with age. Our findings were consistent with those of previous studies [
37,
38,
39]. The prevalences of nephrolithiasis and radiolucent stones in this study were 12.0% and 5.1%, respectively. The overall prevalence of nephrolithiasis in Taiwan is 9.6%, with an age-adjusted prevalence of 9.01% in males [
36,
40]. The prevalence of nephrolithiasis was higher in steel workers than the general population. The possible mechanism of heat-exposure-induced radiolucent nephrolithiasis may be related to chronic dehydration due too much sweating in a high-temperature workplace [
38,
41]. Thus, reminding workers under heat exposure to increase water and electrolyte intake can not only avoid heat injuries such as heat stroke and heat exhaustion but can also improve dehydration and decrease the risk of nephrolithiasis.
Although the serum uric acid level in the group with radiolucent nephrolithiasis was higher than that in the non-stone group, with the odds ratio of serum uric acid being 1.184-1.185, despite the absence of statistical significance (p-values were 0.054 on first logistic regression and 0.055 on second logistic regression). In addition, urine pH and serum creatinine were not significantly different between the two groups, suggesting relative minor impacts of urological factors on radiolucent nephrolithiasis compared to heat exposure and age.
Although heat exposure, age, and gender are well-known risk factors for nephrolithiasis [
35,
37,
39,
42], the results of the current study suggest an interaction among these factors by identifying age as a risk factor for radiolucent nephrolithiasis without heat exposure. The odds ratio of age was 1.052 in the first logistic regression model, while it was 2.126 for group 2 versus group 1 in the second logistic regression model. The findings implied that the risk of radiolucent nephrolithiasis among workers aged >35 years was more than double compared to that in their younger counterparts in the absence heat exposure, suggesting that age was not only a risk factor for general nephrolithiasis but also a risk factor for radiolucent stone disease. Interestingly, while we found an increased probability of radiolucent stone formation with age among workers without heat exposure, the probability remained high in workers with heat exposure regardless of their age. Despite the previous finding that uric acid stone and atypical stones were associated with the older population, the current study showed that younger individuals may also be at risk of radiolucent stone formation (e.g., uric acid stone) if their occupation involves heat exposure. In this study, the lack of a significant association between gender and the prevalence of radiolucent stones may partly be attributed to the notably lower proportion of females compared to males, which may obscure the significance of this finding.
Although a number of previous studies showed a correlation between metabolic syndrome and uric acid nephrolithiasis, we did not observe a significant association in our study. The average age of the workers in the factory was 35.7 years, which may explain the low prevalence of metabolic syndrome that usually develops in individuals with advanced age. Such a low prevalence of metabolic syndrome in our study population (i.e., 18.1%) may have contributed to the lack of a significant correlation with radiolucent nephrolithiasis.
Moreover, urine pH has been found to affect the risk of urolithiasis; while a pH below 5.5 is known to increase the risk of uric acid stone formation, a pH over 6.0 favors the development of calcium stones. In view of such an impact, we included urine pH in our logistic regression analysis, which demonstrated no significant impact of pH on the incidence of radiolucent nephrolithiasis in our participants.
We defined radiolucent stones as positive abdominal ultrasound findings without radiopacities on plain radiography. A prior study suggested the effectiveness of sonography as a diagnostic tool for detecting kidney stones in patients with suspected nephrolithiasis [
33]. Consistently, a previous clinical study on 62 patients showed that both computed tomography and ultrasound were excellent for diagnosing ureteral stones [
34]. Considering the cost-effectiveness and radiation exposure, sonography appeared to be a reasonable first choice in the diagnosis of urolithiasis. Due to the radiolucent characteristic of pure uric acid stones, ultrasound examination of the kidneys should always be considered if uric acid stones are suspected [
31]. Despite the common acceptance of dual-energy computed tomography as the gold standard for the direct visualization of uric acid stones [
32], the associated cost remains an important concern. Therefore, we suggest the combined use of plain abdominal radiography with sonography for the diagnosis of radiolucent stones, taking into consideration the cost of radiation exposure and the risk of allergy to the contrast medium pertinent to computed tomography.
Because we did not have information about the volume of water drank and the diet content of the participants in this study, the potential contributions of hydration and diet-related factors to urolithiasis remain unclear. Nevertheless, given that the company did not have any policy to restrict its workers’ water intake or their use of the toilet, the study subjects were supposed to be well hydrated. In addition, the provision of similar food for lunch by the company for its workers, regardless of the departments in which they worked (i.e., with or without heat exposure), may also preclude a significant influence of food on nephrolithiasis. On the other hand, although meat consumption is a main risk factor for uric acid stone formation, we did not include relevant items in the questionnaire to acquire such information. Finally, heterogeneity in examination results may bias our findings because the abdominal sonographic studies were not conducted by a single gastroenterologist, and the reports of plain abdominal radiographs were produced by multiple radiologists due to the large number of participants in the current study. However, provided that all gastroenterologists and radiologists involved in the present investigation were board-certified and well qualified for their assignments, it was a rational assumption that the impact of inter-rater variation on the interpretation of examination findings was minimal.
5. Conclusions
The current study involving over a thousand steel workers demonstrated a significant positive association between heat exposure and radiolucent nephrolithiasis without notable impacts from gender, urine pH and specific gravity, and serum creatinine and uric acid concentrations. In contrast to an increased incidence of nephrolithiasis with age among those without heat exposure, an elevated incidence was noted in heat-exposed individuals regardless of their age. The finding underscored a potential increase in the risk of radiolucent nephrolithiasis in the relatively young population who work in an environment involving constant heat exposure.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, I.-C.L. and H.-Y.C.; methodology, I.-C.L. and H.-Y.C.; software, I.-C.L. and C.-C.Y.; validation, C.-H.H., S.-Y.C., and H.-Y.C.; formal analysis, I.-C.L.; investigation, C.-W.L. and C.-H.L.; resources, I.-C.L. and H.-Y.C.; data curation, I.-C.L. and C.-H.L.; writing—original draft preparation, I.-C.L. and H.-Y.C.; writing—review and editing, H.-Y.C.; visualization, I.-C.L.; supervision, H.-Y.C.; project administration, I.-C.L. and H.-Y.C.; funding acquisition, I.-C.L. and H.-Y.C. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This work was supported by the National Science Council (grant No. MOST111-2314-B-037-038-MY2) and grants from the Kaohsiung Medical University Hospital (KMUH110-0T01). This study was also supported by the E-DA Hospital (EDAHP102039).
Institutional Review Board Statement
The study was conducted in accordance with the Declaration of Helsinki and was approved by the Institutional Review Board of Kaohsiung Medical University Hospital (KMUHIRB-E(II)-20210116, date of approval: 24 May 2021).
Informed Consent Statement
Patient consent was waived because the data from the worker health examination obtained by the Taiwan Occupational Safety and Health Administration (TOHSA) and the individual information were scrambled.
Acknowledgments
We would like to express our sincere appreciation to the workers and employers for their cooperation. The authors declare no competing financial interest. This work was partially supported by the Research Center for Precision Environmental Medicine, Kaohsiung Medical University, Kaohsiung, Taiwan, from The Featured Areas Research Center Program within the framework of the Higher Education Sprout Project by the Ministry of Education (MOE) in Taiwan and by Kaohsiung Medical University Research Center grants (KMU-TC111A01 and KMUTC111IFSP01).
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Brikowski, T.H.; Lotan, Y.; Pearle, M.S. Climate-related increase in the prevalence of urolithiasis in the United States. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2008, 105, 9841–9846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hesse, A.; Brandle, E.; Wilbert, D.; Kohrmann, K.U.; Alken, P. Study on the prevalence and incidence of urolithiasis in Germany comparing the years 1979 vs. 2000. Eur. Urol. 2003, 44, 709–713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trinchieri, A.; Coppi, F.; Montanari, E.; Del Nero, A.; Zanetti, G.; Pisani, E. Increase in the prevalence of symptomatic upper urinary tract stones during the last ten years. Eur. Urol. 2000, 37, 23–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshida, O.; Okada, Y. Epidemiology of urolithiasis in Japan: A chronological and geographical study. Urol. Int. 1990, 45, 104–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Johnson, R.J.; Sánchez-Lozada, L.G.; Newman, L.S.; Lanaspa, M.A.; Diaz, H.F.; Lemery, J.; Rodriguez-Iturbe, B.; Tolan, D.R.; Butler-Dawson, J.; Sato, Y.; et al. Climate Change and the Kidney. Ann. Nutr. Metab. 2019, 74 (Suppl. 3), 38–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, W.S.; Kim, W.S.; Lim, Y.H.; Hong, Y.C. High Temperatures and Kidney Disease Morbidity: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis. J. Prev. Med. Public Health Yebang Uihakhoe Chi 2019, 52, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ross, M.E.; Vicedo-Cabrera, A.M.; Kopp, R.E.; Song, L.; Goldfarb, D.S.; Pulido, J.; Warner, S.; Furth, S.L.; Tasian, G.E. Assessment of the combination of temperature and relative humidity on kidney stone presentations. Environ. Res. 2018, 162, 97–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pearle, M.S. When is medical prophylaxis cost-effective for recurrent calcium stones? Int. Braz. J. Urol. 2002, 28, 365. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Saigal, C.S.; Joyce, G.; Timilsina, A.R. Direct and indirect costs of nephrolithiasis in an employed population: Opportunity for disease management? Kidney Int. 2005, 68, 1808–1814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knoll, T.; Wendt-Nordahl, G.; Trojan, L.; Wenke, A.; Roeder, N.; Alken, P. Current aspects of stone therapy. Aktuelle Urol. 2005, 36, 47–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bensalah, K.; Tuncel, A.; Gupta, A.; Raman, J.D.; Pearle, M.S.; Lotan, Y. Determinants of quality of life for patients with kidney stones. J. Urol. 2008, 179, 2238–2243, discussion 2243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferrari, P.; Piazza, R.; Ghidini, N.; Bisi, M.; Galizia, G.; Ferrari, G. Lithiasis and risk factors. Urol. Int. 2007, 79 (Suppl. 1), 8–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dallas, K.B.; Conti, S.; Liao, J.C.; Sofer, M.; Pao, A.C.; Leppert, J.T.; Elliott, C.S. Redefining the Stone Belt: Precipitation Is Associated with Increased Risk of Urinary Stone Disease. J. Endourol. 2017, 31, 1203–1210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fram, E.B.; Sorensen, M.D.; Bird, V.G.; Stern, J.M. Geographic location is an important determinant of risk factors for stone disease. Urolithiasis 2017, 45, 429–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boonruksa, P.; Maturachon, T.; Kongtip, P.; Woskie, S. Heat Stress, Physiological Response, and Heat-Related Symptoms among Thai Sugarcane Workers. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 6363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Malig, B.J.; Wu, X.M.; Guirguis, K.; Gershunov, A.; Basu, R. Associations between ambient temperature and hepatobiliary and renal hospitalizations in California, 1999 to 2009. Environ. Res. 2019, 177, 108566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Venugopal, V.; Latha, P.K.; Shanmugam, R.; Krishnamoorthy, M.; Srinivasan, K.; Perumal, K.; Chinnadurai, J.S. Risk of kidney stone among workers exposed to high occupational heat stress—A case study from southern Indian steel industry. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 722, 137619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vicedo-Cabrera, A.M.; Goldfarb, D.S.; Kopp, R.E.; Song, L.; Tasian, G.E. Sex differences in the temperature dependence of kidney stone presentations: A population-based aggregated case-crossover study. Urolithiasis 2020, 48, 37–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Curhan, G.C.; Willett, W.C.; Rimm, E.B.; Stampfer, M.J. A prospective study of dietary calcium and other nutrients and the risk of symptomatic kidney stones. N. Engl. J. Med. 1993, 328, 833–838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borghi, L.; Meschi, T.; Amato, F.; Briganti, A.; Novarini, A.; Giannini, A. Urinary volume, water and recurrences in idiopathic calcium nephrolithiasis: A 5-year randomized prospective study. J. Urol. 1996, 155, 839–843. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, C.; Zhang, C.; Wang, X.L.; Liu, T.Z.; Zeng, X.T.; Li, S.; Duan, X.W. Self-Fluid Management in Prevention of Kidney Stones: A PRISMA-Compliant Systematic Review and Dose-Response Meta-Analysis of Observational Studies. Medicine 2015, 94, e1042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duffey, B.G.; Pedro, R.N.; Kriedberg, C.; Weiland, D.; Melquist, J.; Ikramuddin, S.; Kellogg, T.; Makhlouf, A.A.; Monga, M. Lithogenic risk factors in the morbidly obese population. J. Urol. 2008, 179, 1401–1406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lieske, J.C.; de la Vega, L.S.; Gettman, M.T.; Slezak, J.M.; Bergstralh, E.J.; Melton, L.J., 3rd; Leibson, C.L. Diabetes mellitus and the risk of urinary tract stones: A population-based case-control study. Am. J. Kidney Dis. 2006, 48, 897–904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Obligado, S.H.; Goldfarb, D.S. The association of nephrolithiasis with hypertension and obesity: A review. Am. J. Hypertens. 2008, 21, 257–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- West, B.; Luke, A.; Durazo-Arvizu, R.A.; Cao, G.; Shoham, D.; Kramer, H. Metabolic syndrome and self-reported history of kidney stones: The National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (NHANES III) 1988–1994. Am. J. Kidney Dis. 2008, 51, 741–747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lemann, J., Jr.; Pleuss, J.A.; Worcester, E.M.; Hornick, L.; Schrab, D.; Hoffmann, R.G. Urinary oxalate excretion increases with body size and decreases with increasing dietary calcium intake among healthy adults. Kidney Int. 1996, 49, 200–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maalouf, N.M.; Sakhaee, K.; Parks, J.H.; Coe, F.L.; Adams-Huet, B.; Pak, C.Y. Association of urinary pH with body weight in nephrolithiasis. Kidney Int. 2004, 65, 1422–1425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cupisti, A.; Meola, M.; D’Alessandro, C.; Bernabini, G.; Pasquali, E.; Carpi, A.; Barsotti, G. Insulin resistance and low urinary citrate excretion in calcium stone formers. Biomed. Pharm. 2007, 61, 86–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moe, O.W. Kidney stones: Pathophysiology and medical management. Lancet 2006, 367, 333–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parmar, M.S. Kidney stones. BMJ 2004, 328, 1420–1424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allison, D.J.; Dixon, A.K. The Genitourinary Tract Calculus Disease and Urothelial Lesions, 4th ed.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2001; Volume 2. [Google Scholar]
- Primak, A.N.; Fletcher, J.G.; Vrtiska, T.J.; Dzyubak, O.P.; Lieske, J.C.; Jackson, M.E.; Williams, J.C., Jr.; McCollough, C.H. Noninvasive differentiation of uric acid versus non-uric acid kidney stones using dual-energy CT. Acad. Radiol. 2007, 14, 1441–1447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Middleton, W.D.; Dodds, W.J.; Lawson, T.L.; Foley, W.D. Renal calculi: Sensitivity for detection with US. Radiology 1988, 167, 239–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patlas, M.; Farkas, A.; Fisher, D.; Zaghal, I.; Hadas-Halpern, I. Ultrasound vs CT for the detection of ureteric stones in patients with renal colic. Br. J. Radiol. 2001, 74, 901–904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atan, L.; Andreoni, C.; Ortiz, V.; Silva, E.K.; Pitta, R.; Atan, F.; Srougi, M. High kidney stone risk in men working in steel industry at hot temperatures. Urology 2005, 65, 858–861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, Y.H.; Huang, W.C.; Tsai, J.Y.; Lu, C.M.; Chen, W.C.; Lee, M.H.; Hsu, H.S.; Huang, J.K.; Chang, L.S. Epidemiological studies on the prevalence of upper urinary calculi in Taiwan. Urol. Int. 2002, 68, 172–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Negri, A.L.; Spivacow, R.; Del Valle, E.; Pinduli, I.; Marino, A.; Fradinger, E.; Zanchetta, J.R. Clinical and biochemical profile of patients with “pure” uric acid nephrolithiasis compared with “pure” calcium oxalate stone formers. Urol. Res. 2007, 35, 247–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walsh, P.C.; Retik, A.B.; Vaughan, E.D., Jr. Urinary Lithiasis: Etiology, Diagnosis, and Medical management. In Campbell’s Urology, 8th ed.; Menon, M., Resnick, M.I., Eds.; WB Saunders: Philadelphia, PA, USA, 2002; pp. 3229–3234. [Google Scholar]
- Amato, M.; Lusini, M.L.; Nelli, F. Epidemiology of nephrolithiasis today. Urol. Int. 2004, 72 (Suppl. 1), 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, W.Y.; Chen, Y.F.; Carter, S.; Chang, H.C.; Lan, C.F.; Huang, K.H. Epidemiology of upper urinary tract stone disease in a Taiwanese population: A nationwide, population based study. J. Urol. 2013, 189, 2158–2163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prince, C.L.; Scardino, P.L.; Wolan, C.T. The effect of temperature, humidity and dehydration on the formation of renal calculi. J. Urol. 1956, 75, 209–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carson, C.C. Renal calculus disease. Clin. Geriatr. Med. 1990, 6, 115–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).