Characteristics, Possible Origins, and Health Risk Assessment of Trace Elements in Surface Waters of the Han River Watershed, South Korea
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
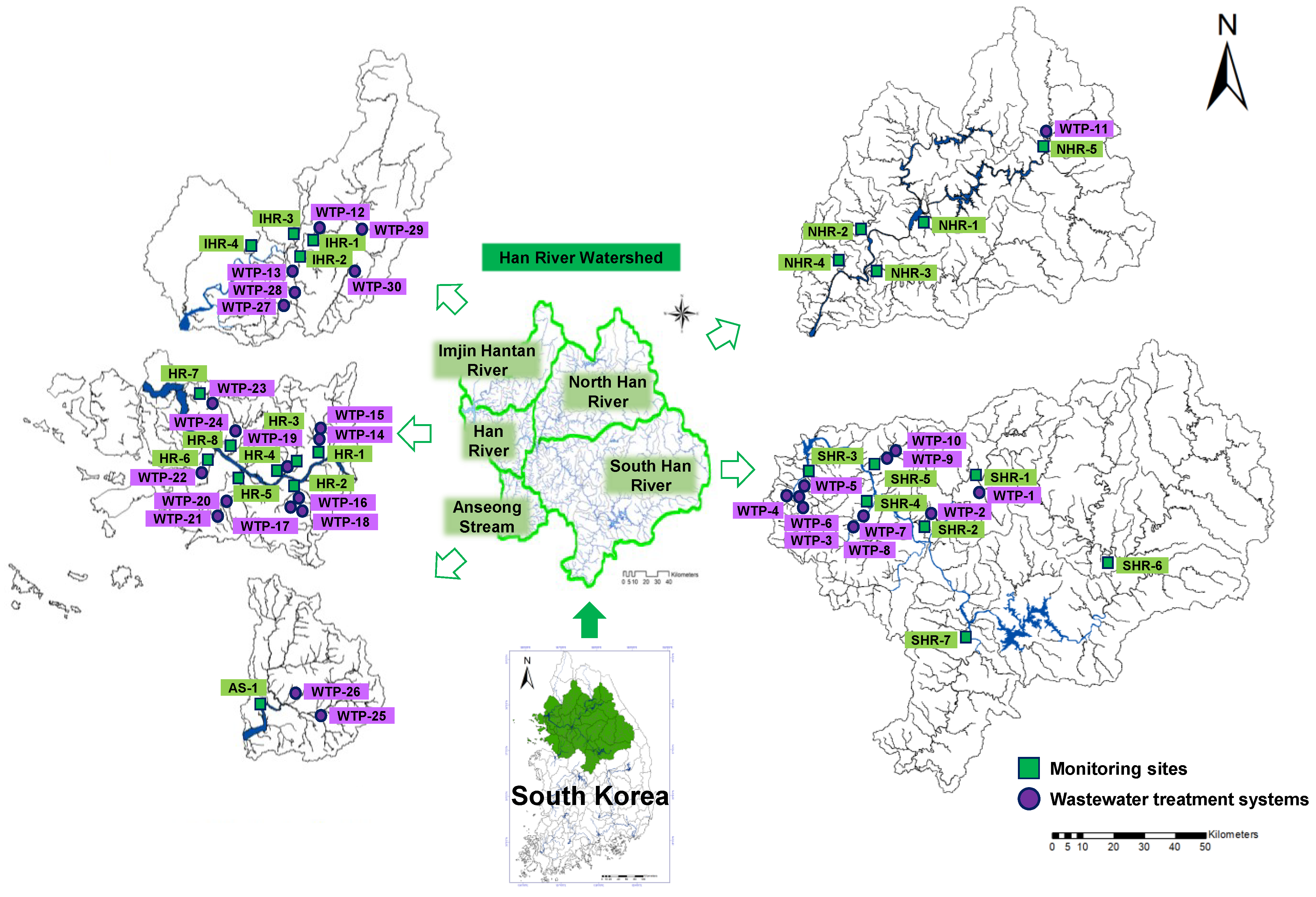
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Sampling Collection and Analysis
2.3. Statistical Analysis Methods
2.4. Health Risk Assessment
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Distribution of Trace Elements along the River
3.2. Correlation Matrix
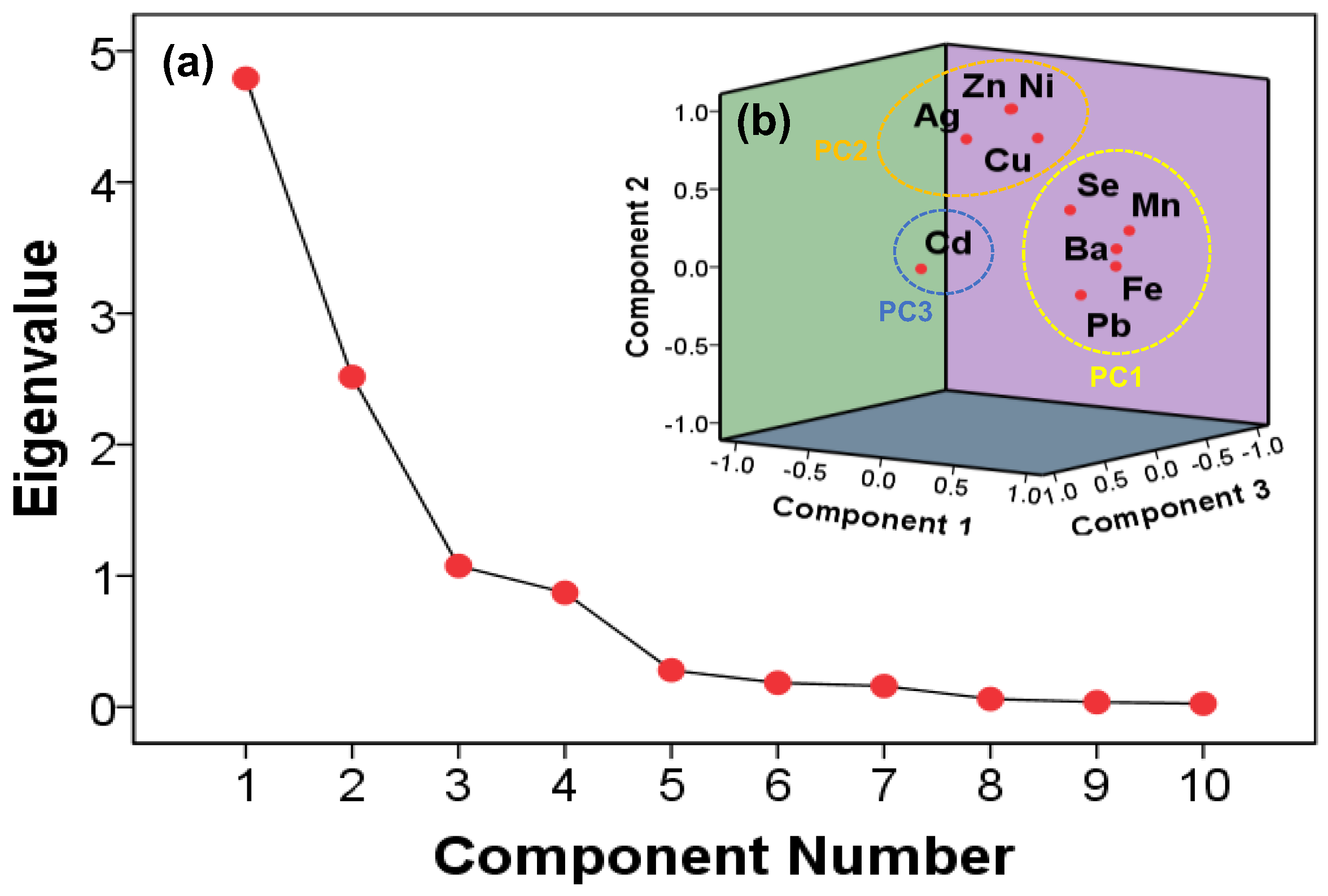
3.3. Factor and Principal Component Analysis
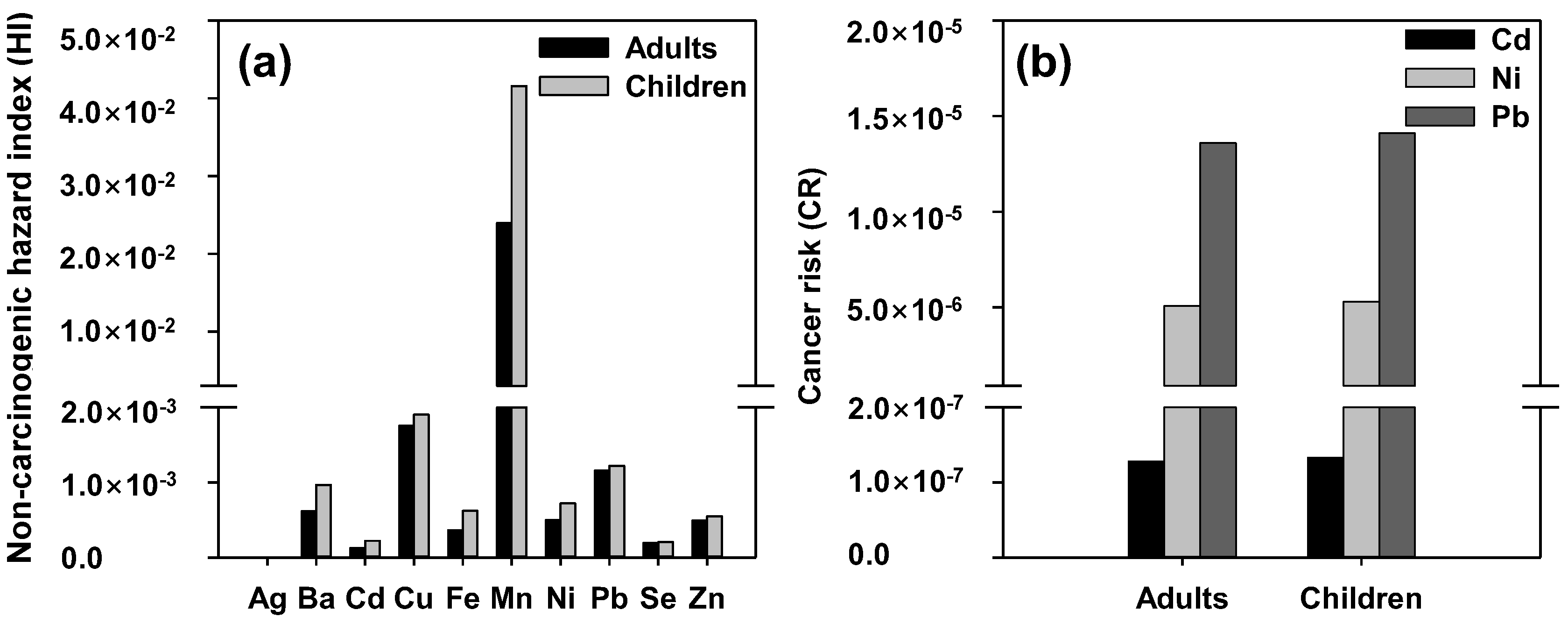
3.4. Risk Assessment on Human Health
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Goel, P. Water Pollution: Causes, Effects and Control; New Age International: Hong Kong, China, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Shiklomanov, I.A.; Rodda, J.C. World Water Resources at the Beginning of the Twenty-First Century; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Helmer, R.; Hespanhol, I. Water Pollution Control: A Guide to the Use of Water Quality Management Principles; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 1997. [Google Scholar]
- Hong, N.; Zhu, P.; Liu, A.; Zhao, X.; Guan, Y. Using an innovative flag element ratio approach to tracking potential sources of heavy metals on urban road surfaces. Environ. Pollut. 2018, 243, 410–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, J.; Guo, S.; Zeng, G.-m.; Li, F.; Gu, Y.; Shi, Y.; Shi, L.; Liu, W.; Peng, S. A new exploration of health risk assessment quantification from sources of soil heavy metals under different land use. Environ. Pollut. 2018, 243, 49–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, C.; Yang, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Cai, Z. PAHs and heavy metals in the surrounding soil of a cement plant Co-Processing hazardous waste. Chemosphere 2018, 210, 247–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, B.; Shao, S.; Fu, Z.; Li, Y.; Ni, H.; Chen, S.; Zhou, Y.; Jin, B.; Shi, Z. Identifying heavy metal pollution hot spots in soil-rice systems: A case study in South of Yangtze River Delta, China. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 658, 614–625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, F.; Sun, Y.; Tao, Y.; Guo, Y.; Li, Z.; Zhao, X.; Zhou, S. Pollution characteristics in a dusty season based on highly time-resolved online measurements in northwest China. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 650, 2545–2558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Islam, M.S.; Han, S.; AHMED, M.K.; Masunaga, S. Assessment of trace metal contamination in water and sediment of some rivers in Bangladesh. J. Water Environ. Technol. 2014, 12, 109–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Xiao, J.; Jin, Z.; Wang, J. Geochemistry of trace elements and water quality assessment of natural water within the Tarim River Basin in the extreme arid region, NW China. J. Geochem. Explor. 2014, 136, 118–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhuang, P.; Huiling, Z.; Wensheng, S. Biotransfer of heavy metals along a soil-plant-insect-chicken food chain: Field study. J. Environ. Sci. 2009, 21, 849–853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuen, J.; Olin, P.H.; Lim, H.; Benner, S.G.; Sutherland, R.; Ziegler, A. Accumulation of potentially toxic elements in road deposited sediments in residential and light industrial neighborhoods of Singapore. J. Environ. Manag. 2012, 101, 151–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davis, A.P.; Shokouhian, M.; Ni, S. Loading estimates of lead, copper, cadmium, and zinc in urban runoff from specific sources. Chemosphere 2001, 44, 997–1009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McKenzie, E.R.; Wong, C.M.; Green, P.G.; Kayhanian, M.; Young, T.M. Size dependent elemental composition of road-associated particles. Sci. Total Environ. 2008, 398, 145–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- McKenzie, E.R.; Money, J.E.; Green, P.G.; Young, T.M. Metals associated with stormwater-relevant brake and tire samples. Sci. Total Environ. 2009, 407, 5855–5860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mummullage, S.; Egodawatta, P.; Ayoko, G.A.; Goonetilleke, A. Use of physicochemical signatures to assess the sources of metals in urban road dust. Sci. Total Environ. 2016, 541, 1303–1309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jalali, M.; Hemati, N. Chemical fractionation of seven heavy metals (Cd, Cu, Fe, Mn, Ni, Pb, and Zn) in selected paddy soils of Iran. Paddy Water Environ. 2013, 11, 299–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nkinahamira, F.; Suanon, F.; Chi, Q.; Li, Y.; Feng, M.; Huang, X.; Yu, C.-P.; Sun, Q. Occurrence, geochemical fractionation, and environmental risk assessment of major and trace elements in sewage sludge. J. Environ. Manag. 2019, 249, 109427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, Y.; Liu, X.; Bai, J.; Shih, K.; Zeng, E.Y.; Cheng, H. Assessing heavy metal pollution in the surface soils of a region that had undergone three decades of intense industrialization and urbanization. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2013, 20, 6150–6159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, M.M.; Ali, M.L.; Islam, M.S.; Rahman, M.Z. Preliminary assessment of heavy metals in water and sediment of Karnaphuli River, Bangladesh. Environ. Nanotechnol. Monit. Manag. 2016, 5, 27–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Khound, N.J.; Bhattacharyya, K.G. Multivariate statistical evaluation of heavy metals in the surface water sources of Jia Bharali river basin, North Brahmaputra plain, India. Appl. Water Sci. 2017, 7, 2577–2586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhaoyong, Z.; Abuduwaili, J.; Fengqing, J. Heavy metal contamination, sources, and pollution assessment of surface water in the Tianshan Mountains of China. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2015, 187, 33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chao, S.; Liu, J.; Chen, Y.; Cao, H.; Zhang, A. Implications of seasonal control of PM2.5-bound PAHs: An integrated approach for source apportionment, source region identification and health risk assessment. Environ. Pollut. 2019, 247, 685–695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cramer, M.; Rinas, M.; Kotzbauer, U.; Tränckner, J. Surface contamination of impervious areas on biogas plants and conclusions for an improved stormwater management. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 217, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chowdhury, S.; Mazumder, M.J.; Al-Attas, O.; Husain, T. Heavy metals in drinking water: Occurrences, implications, and future needs in developing countries. Sci. Total Environ. 2016, 569, 476–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tchounwou, P.B.; Yedjou, C.G.; Patlolla, A.K.; Sutton, D.J. Heavy metal toxicity and the environment. Mol. Clin. Environ. Toxicol. 2012, 101, 133–164. [Google Scholar]
- Fazio, F.; Piccione, G.; Tribulato, K.; Ferrantelli, V.; Giangrosso, G.; Arfuso, F.; Faggio, C. Bioaccumulation of heavy metals in blood and tissue of striped mullet in two Italian lakes. J. Aquat. Anim. Health 2014, 26, 278–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, H.; Qin, D.; Chen, Z.; Tang, S.; Bai, S.; Mou, Z. Heavy metal levels in fish from Heilongjiang River and potential health risk assessment. Bull. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2016, 97, 536–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Antoniadis, V.; Levizou, E.; Shaheen, S.M.; Ok, Y.S.; Sebastian, A.; Baum, C.; Prasad, M.N.; Wenzel, W.W.; Rinklebe, J. Trace elements in the soil-plant interface: Phytoavailability, translocation, and phytoremediation–A review. Earth-Sci. Rev. 2017, 171, 621–645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, G.; Xu, L.; Song, S.; Zhu, C.; Wu, Q.; Zhang, L.; Wu, L. Effects of long-term low-dose cadmium exposure on genomic DNA methylation in human embryo lung fibroblast cells. Toxicology 2008, 244, 49–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giri, S.; Singh, A.K. Risk assessment, statistical source identification and seasonal fluctuation of dissolved metals in the Subarnarekha River, India. J. Hazard. Mater. 2014, 265, 305–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smith, A.H.; Hopenhayn-Rich, C.; Bates, M.N.; Goeden, H.M.; Hertz-Picciotto, I.; Duggan, H.M.; Wood, R.; Kosnett, M.J.; Smith, M.T. Cancer risks from arsenic in drinking water. Environ. Health Perspect. 1992, 97, 259–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ministry of Environment. Korea Water Pollution Standard Method; Ministry of Environment: Sejong City, Republic of Korea, 2022.
- Dimri, D.; Daverey, A.; Kumar, A.; Sharma, A. Monitoring water quality of River Ganga using multivariate techniques and WQI (Water Quality Index) in Western Himalayan region of Uttarakhand, India. Environ. Nanotechnol. Monit. Manag. 2021, 15, 100375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- López-Alonso, M.; Rey-Crespo, F.; Herrero-Latorre, C.; Miranda, M. Identifying sources of metal exposure in organic and conventional dairy farming. Chemosphere 2017, 185, 1048–1055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dominick, D.; Juahir, H.; Latif, M.T.; Zain, S.M.; Aris, A.Z. Spatial assessment of air quality patterns in Malaysia using multivariate analysis. Atmos. Environ. 2012, 60, 172–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaiser, H.F. An index of factorial simplicity. Psychometrika 1974, 39, 31–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zanotti, C.; Rotiroti, M.; Fumagalli, L.; Stefania, G.; Canonaco, F.; Stefenelli, G.; Prévôt, A.; Leoni, B.; Bonomi, T. Groundwater and surface water quality characterization through positive matrix factorization combined with GIS approach. Water Res. 2019, 159, 122–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jia, Z.; Li, S.; Wang, L. Assessment of soil heavy metals for eco-environment and human health in a rapidly urbanization area of the upper Yangtze Basin. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 3256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Liu, N.; Ni, T.; Xia, J.; Dai, M.; He, C.; Lu, G. Non-carcinogenic risks induced by metals in drinking source water of Jiangsu Province, China. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2011, 177, 449–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- US EPA. Risk Assessment Guidance for Superfund Volume 1: Human Health Evaluation Manual (Part E, Supplemental Guidance for Dermal Risk Assessment) Final; EPA: Washington, DC, USA, 2004.
- Wang, J.; Liu, G.; Liu, H.; Lam, P.K. Multivariate statistical evaluation of dissolved trace elements and a water quality assessment in the middle reaches of Huaihe River, Anhui, China. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 583, 421–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Islam, A.R.M.T.; Islam, H.T.; Mia, M.U.; Khan, R.; Habib, M.A.; Bodrud-Doza, M.; Siddique, M.A.B.; Chu, R. Co-distribution, possible origins, status and potential health risk of trace elements in surface water sources from six major river basins, Bangladesh. Chemosphere 2020, 249, 126180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mohammadi, A.A.; Zarei, A.; Majidi, S.; Ghaderpoury, A.; Hashempour, Y.; Saghi, M.H.; Alinejad, A.; Yousefi, M.; Hosseingholizadeh, N.; Ghaderpoori, M. Carcinogenic and non-carcinogenic health risk assessment of heavy metals in drinking water of Khorramabad, Iran. MethodsX 2019, 6, 1642–1651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prasad, S.; Saluja, R.; Joshi, V.; Garg, J. Heavy metal pollution in surface water of the Upper Ganga River, India: Human health risk assessment. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2020, 192, 742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zeng, X.; Liu, Y.; You, S.; Zeng, G.; Tan, X.; Hu, X.; Hu, X.; Huang, L.; Li, F. Spatial distribution, health risk assessment and statistical source identification of the trace elements in surface water from the Xiangjiang River, China. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2015, 22, 9400–9412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ustaoğlu, F.; Taş, B.; Tepe, Y.; Topaldemir, H. Comprehensive assessment of water quality and associated health risk by using physicochemical quality indices and multivariate analysis in Terme River, Turkey. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2021, 28, 62736–62754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, K.; Jiao, J.J.; Huang, J.; Huang, R. Multivariate statistical evaluation of trace elements in groundwater in a coastal area in Shenzhen, China. Environ. Pollut. 2007, 147, 771–780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Helena, B.; Pardo, R.; Vega, M.; Barrado, E.; Fernandez, J.M.; Fernandez, L. Temporal evolution of groundwater composition in an alluvial aquifer (Pisuerga River, Spain) by principal component analysis. Water Res. 2000, 34, 807–816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, M.; Ramanathan, A.; Tripathi, R.; Farswan, S.; Kumar, D.; Bhattacharya, P. A study of trace element contamination using multivariate statistical techniques and health risk assessment in groundwater of Chhaprola Industrial Area, Gautam Buddha Nagar, Uttar Pradesh, India. Chemosphere 2017, 166, 135–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tou, F.; Yang, Y.; Feng, J.; Niu, Z.; Pan, H.; Qin, Y.; Guo, X.; Meng, X.; Liu, M.; Hochella, M.F. Environmental risk implications of metals in sludges from waste water treatment plants: The discovery of vast stores of metal-containing nanoparticles. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2017, 51, 4831–4840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, C.-W.; Lin, K.-H.; Kuo, Y.-M. Application of factor analysis in the assessment of groundwater quality in a blackfoot disease area in Taiwan. Sci. Total Environ. 2003, 313, 77–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, L.; Wang, Z.; Shan, J.; Chen, J.; Tang, C.; Yi, M.; Zhao, X. Distribution characteristics and sources of trace metals in sediment cores from a trans-boundary watercourse: An example from the Shima River, Pearl River Delta. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2016, 134, 186–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Men, C.; Liu, R.; Xu, L.; Wang, Q.; Guo, L.; Miao, Y.; Shen, Z. Source-specific ecological risk analysis and critical source identification of heavy metals in road dust in Beijing, China. J. Hazard. Mater. 2020, 388, 121763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adachi, K.; Tainosho, Y. Characterization of heavy metal particles embedded in tire dust. Environ. Int. 2004, 30, 1009–1017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, K.-H.; Kim, D.-S.; Lee, T.-J. The temporal variabilities in the concentrations of airborne lead and its relationship to aerosol behavior. Atmos. Environ. 1997, 31, 3449–3458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.; Wu, E.; Zhang, B.; Bai, X.; Lei, P.; Qiao, X.; Li, Y.-F.; Li, B.; Wu, G.; Gao, Y. Pollution characteristics and ecological risks associated with heavy metals in the Fuyang river system in North China. Environ. Pollut. 2021, 281, 116994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reddy, M.V.; Babu, K.S.; Balaram, V.; Satyanarayanan, M. Assessment of the effects of municipal sewage, immersed idols and boating on the heavy metal and other elemental pollution of surface water of the eutrophic Hussainsagar Lake (Hyderabad, India). Environ. Monit. Assess. 2012, 184, 1991–2000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuusisto-Hjort, P.; Hjort, J. Land use impacts on trace metal concentrations of suburban stream sediments in the Helsinki region, Finland. Sci. Total Environ. 2013, 456, 222–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dietrich, M.; Huling, J.; Krekeler, M.P. Metal pollution investigation of Goldman Park, Middletown Ohio: Evidence for steel and coal pollution in a high child use setting. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 618, 1350–1362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ayrault, S.; Priadi, C.R.; Pape, P.L.; Bonté, P. Occurrence, sources and pathways of antimony and silver in an urban catchment. In Urban Environment; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2013; pp. 425–435. [Google Scholar]
- Birmili, W.; Allen, A.G.; Bary, F.; Harrison, R.M. Trace metal concentrations and water solubility in size-fractionated atmospheric particles and influence of road traffic. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2006, 40, 1144–1153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alves, R.I.; Sampaio, C.F.; Nadal, M.; Schuhmacher, M.; Domingo, J.L.; Segura-Muñoz, S.I. Metal concentrations in surface water and sediments from Pardo River, Brazil: Human health risks. Environ. Res. 2014, 133, 149–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitra, S.; Sarkar, S.K.; Raja, P.; Biswas, J.K.; Murugan, K. Dissolved trace elements in Hooghly (Ganges) River Estuary, India: Risk assessment and implications for management. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2018, 133, 402–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saha, N.; Rahman, M.S.; Ahmed, M.B.; Zhou, J.L.; Ngo, H.H.; Guo, W. Industrial metal pollution in water and probabilistic assessment of human health risk. J. Environ. Manag. 2017, 185, 70–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horton, L.M.; Mortensen, M.E.; Iossifova, Y.; Wald, M.M.; Burgess, P. What do we know of childhood exposures to metals (arsenic, cadmium, lead, and mercury) in emerging market countries? Int. J. Pediatr. 2013, 2013, 872596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, L.; Gong, D.; Zhao, W.; Lin, L.; Yang, W.; Guo, W.; Tang, X.; Li, Q. Spatial-temporal distribution characteristics and health risk assessment of heavy metals in surface water of the Three Gorges Reservoir, China. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 704, 134883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, X.; Zhang, Y.; Ding, Z.; Wang, T.; Lian, H.; Sun, Y.; Wu, J. Bioaccessibility and health risk of arsenic and heavy metals (Cd, Co, Cr, Cu, Ni, Pb, Zn and Mn) in TSP and PM2.5 in Nanjing, China. Atmos. Environ. 2012, 57, 146–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akoto, O.; Gyimah, E.; Zhan, Z.; Xu, H.; Nimako, C. Evaluation of health risks associated with trace metal exposure in water from the Barekese reservoir in Kumasi, Ghana. Hum. Ecol. Risk Assess. Int. J. 2019, 26, 1134–1148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, H.; Xu, C.; Wang, J.; Xiang, Y.; Ren, M.; Qie, H.; Zhang, Y.; Yao, R.; Li, L.; Lin, A. Health risk assessment based on source identification of heavy metals: A case study of Beiyun River, China. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2021, 213, 112046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahmed, A.S.; Hossain, M.B.; Babu, S.O.F.; Rahman, M.M.; Sarker, M.S.I. Human health risk assessment of heavy metals in water from the subtropical river, Gomti, Bangladesh. Environ. Nanotechnol. Monit. Manag. 2021, 15, 100416. [Google Scholar]
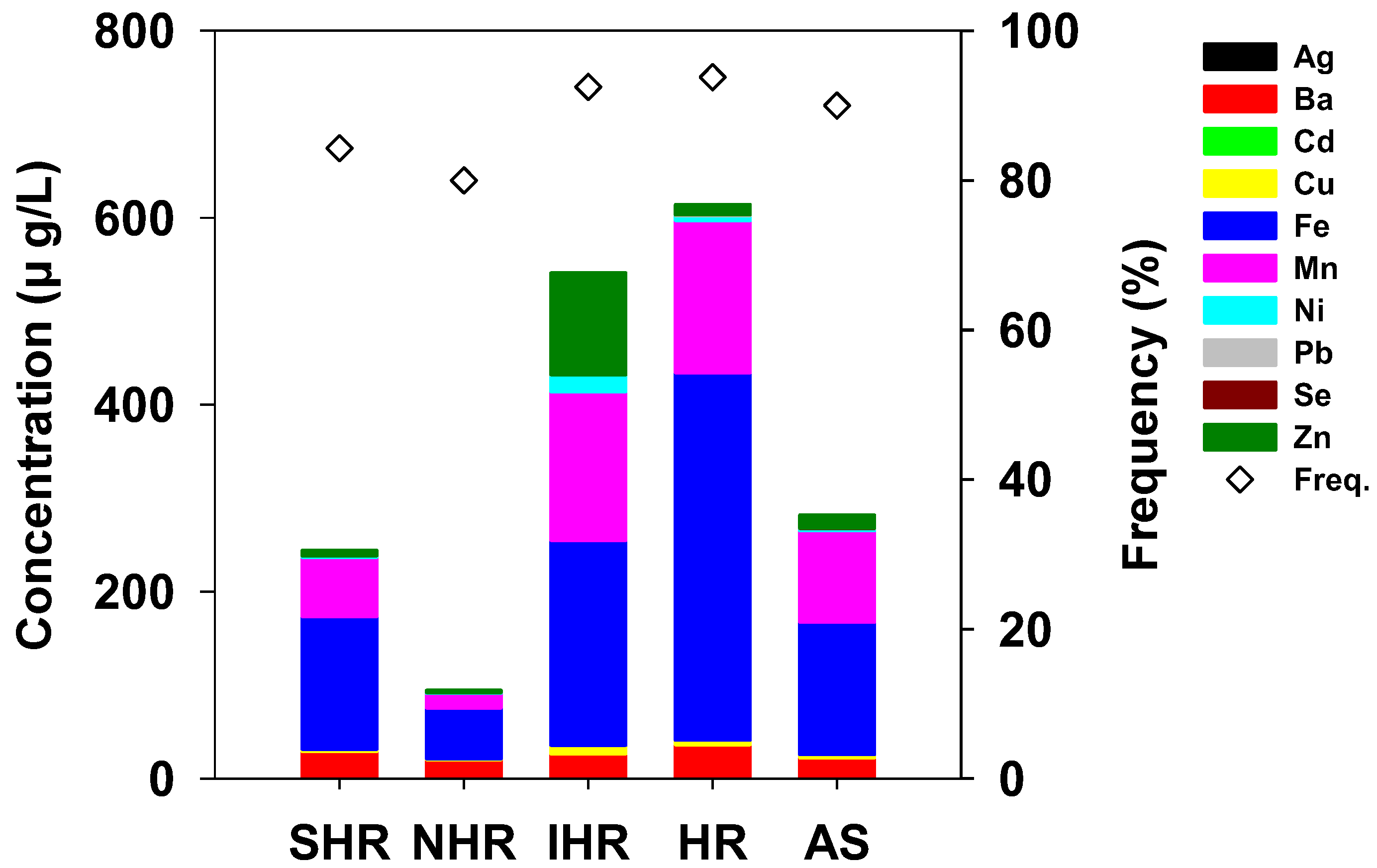


| Compounds | Min Conc. (µg/L) | Max Conc. (µg/L) | Mean Conc. (µg/L) | Standard Deviation (µg/L) | Frequency Detected (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ag | 0.002 | 0.036 | 0.004 | 0.013 | 24 |
| Ba | 8.150 | 65.430 | 29.048 | 12.365 | 100 |
| Cd | 0.003 | 0.035 | 0.014 | 0.008 | 100 |
| Cu | 0.290 | 16.120 | 3.800 | 3.563 | 96 |
| Fe | 30.430 | 1453.090 | 217.128 | 301.030 | 100 |
| Mn | 8.670 | 729.970 | 102.364 | 153.044 | 100 |
| Ni | 0.380 | 57.730 | 5.139 | 11.567 | 100 |
| Pb | 0.050 | 2.510 | 0.463 | 0.524 | 100 |
| Se | 0.060 | 0.190 | 0.059 | 0.042 | 56 |
| Zn | 0.500 | 404.420 | 23.334 | 79.630 | 100 |
| Compounds | South Korea | WHO | US EPA | EU | BIS | Canada | Japan | China |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ag | 100 * | 100 | 50 | |||||
| Ba | 1300 | 2000 | 700 | 2000 | 700 * | |||
| Cd | 5 | 3 | 5 | 5 | 3 | 7 | 3 | 5 |
| Cu | 1000 * | 2000 | 1300 | 2000 | 1500 * | 2000 | 1000 | 1000 |
| Fe | 300 * | 300 * | 300 * | 200 * | 300 | 300 * | 300 | 300 |
| Mn | 50 * | 100 * | 50 * | 50 * | 100 | 120 | 50 | 100 |
| Ni | 70 | 20 | 20 | 10 * | 20 * | |||
| Pb | 10 | 10 * | 15 | 10 | 10 | 5 | 10 | 10 |
| Se | 10 | 40 * | 50 | 10 | 10 | 50 | 10 | 10 |
| Zn | 3000 * | 4000 * | 5000 * | 5000 | 5000 * | 1000 | 1000 |
| Cd | Cu | Zn | Mn | Pb | Ni | Ag | Ba | Se | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cd | 1 | ||||||||
| Cu | 0.293 | 1 | |||||||
| Zn | 0.598 ** | 0.806 ** | 1 | ||||||
| Mn | 0.29 | 0.788 ** | 0.653 ** | 1 | |||||
| Pb | 0.588 ** | 0.578 ** | 0.528 ** | 0.732 ** | 1 | ||||
| Ni | 0.385 | 0.846 ** | 0.771 ** | 0.812 ** | 0.542 ** | 1 | |||
| Ag | 0.386 | 0.365 | 0.346 | 0.409* | 0.537 ** | 0.362 | 1 | ||
| Ba | 0.271 | 0.675 ** | 0.429 * | 0.622 ** | 0.615 ** | 0.615 ** | 0.319 | 1 | |
| Se | 0.194 | 0.54 ** | 0.473 | 0.635 ** | 0.393 | 0.676 ** | 0.233 | 0.452 * | 1 |
| Fe | 0.466 * | 0.692 ** | 0.588 ** | 0.828 ** | 0.840 ** | 0.619 ** | 0.568 ** | 0.625 ** | 0.373 |
| Variable | Components | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Factor 1 | Factor 2 | Factor 3 | |
| Fe | 0.945 | 0.074 | 0.152 |
| Mn | 0.920 | 0.276 | −0.016 |
| Ba | 0.874 | 0.164 | 0.045 |
| Pb | 0.871 | −0.083 | 0.393 |
| Se | 0.424 | 0.341 | −0.141 |
| Ni | 0.087 | 0.970 | −0.034 |
| Zn | 0.058 | 0.961 | −0.094 |
| Ag | 0.079 | 0.838 | 0.387 |
| Cu | 0.385 | 0.837 | 0.122 |
| Cd | 0.151 | 0.091 | 0.934 |
| Eigenvalues | 3.630 | 3.506 | 1.247 |
| % of Variance | 36.295 | 35.055 | 12.471 |
| Cumulative % | 36.295 | 71.350 | 83.822 |
| KMO and Bartlett’s Test | |||
| Kaiser-Meyer-Olkin Measure of Sampling Adequacy | 0.756 | ||
| Bartlett’s Test of Sphericity | Approx. Chi-Square | 241.074 | |
| df | 45 | ||
| Sig. | 0.000 | ||
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Im, J.K.; Cho, Y.C.; Kim, Y.S.; Lee, S.; Kang, T.; Kim, S.H. Characteristics, Possible Origins, and Health Risk Assessment of Trace Elements in Surface Waters of the Han River Watershed, South Korea. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 15822. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph192315822
Im JK, Cho YC, Kim YS, Lee S, Kang T, Kim SH. Characteristics, Possible Origins, and Health Risk Assessment of Trace Elements in Surface Waters of the Han River Watershed, South Korea. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health. 2022; 19(23):15822. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph192315822
Chicago/Turabian StyleIm, Jong Kwon, Yong Chul Cho, Young Seuk Kim, Soyoung Lee, Taegu Kang, and Sang Hun Kim. 2022. "Characteristics, Possible Origins, and Health Risk Assessment of Trace Elements in Surface Waters of the Han River Watershed, South Korea" International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health 19, no. 23: 15822. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph192315822
APA StyleIm, J. K., Cho, Y. C., Kim, Y. S., Lee, S., Kang, T., & Kim, S. H. (2022). Characteristics, Possible Origins, and Health Risk Assessment of Trace Elements in Surface Waters of the Han River Watershed, South Korea. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 19(23), 15822. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph192315822








