Extraction, Purification, Characterization and Application in Livestock Wastewater of S Sulfur Convertase
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Enrichment and Isolation of Sulfur-Transforming Bacteria
2.2. Morphology and Identification of the Strain L1
2.3. Location and Validation of S2− Transformation Active Components in the Strain L1
2.3.1. Location of S2− Transformation Active Components in Strain L1
2.3.2. Effects of Heat, SDS, and Proteinase K Treatments on S2− Conversion Activity by the Culture Supernatant of Strain L1
2.4. Optimization of Enzyme Conversion Ability
2.5. Extraction and Purification of the Sulfur Convertase
2.5.1. Extraction and Purification of Sulfur Convertase
2.5.2. Determination of Protein Concentration and Molecular Weight
2.6. Effect of Physiochemical Factors on Sulfur Convertase Activity
2.6.1. Optimum Reaction Temperature and Thermal Stability of Enzymes
2.6.2. Stability of Sulfur Convertase over Storage Time
2.6.3. Effect of Inhibitors and Organic Solvents on Enzyme Activity
2.6.4. Effect of Redox on Enzyme Activity
2.6.5. Zymolyte Competition Experiments
2.7. Sulfur Conversion Capacity of Enzymes under Livestock Wastewater
2.8. Detection and Analysis Methods
3. Results and Discussion
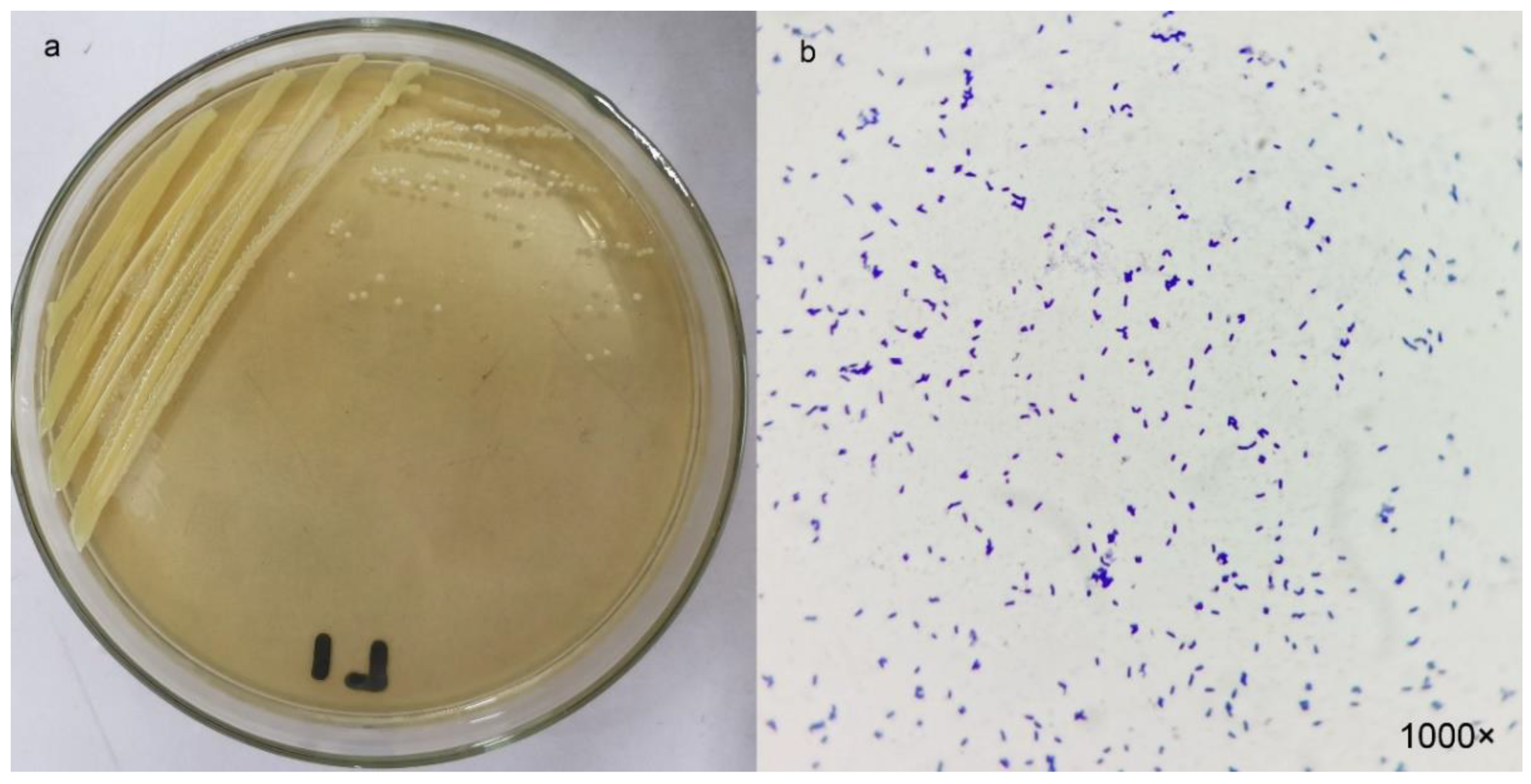
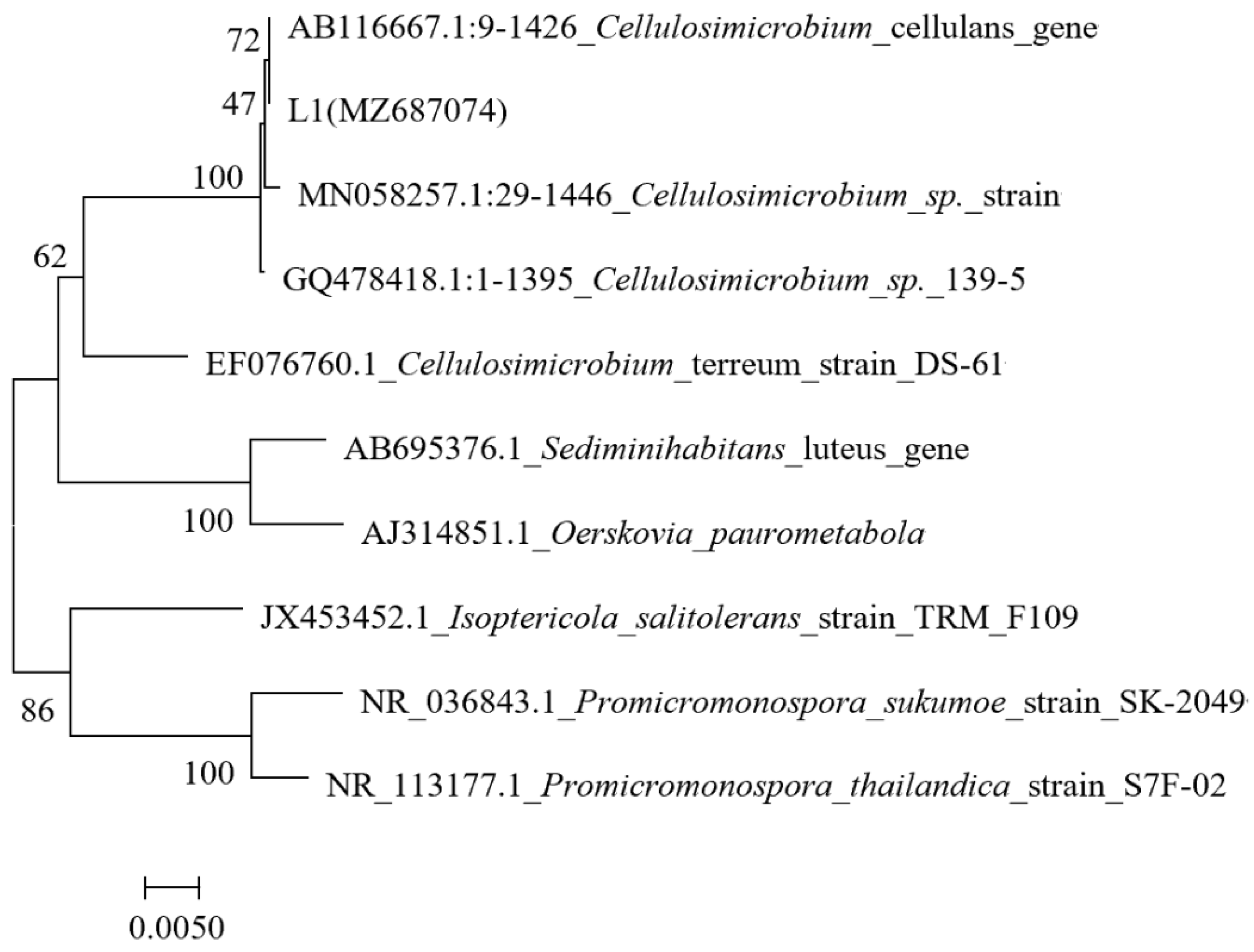
3.1. Isolation and Identification of Sulfur-Transforming Strain L1
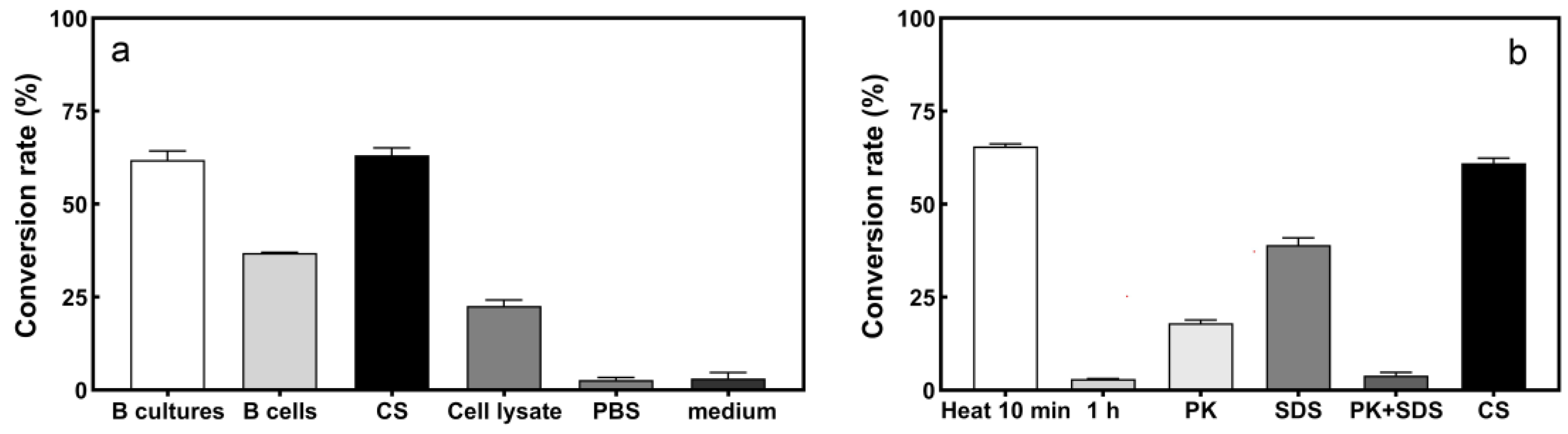
3.2. Location of Active Component of S2− Conversion by Strain Cellulosimicrobium sp. L1
3.3. Optimization of Enzyme Conversion Activity
3.4. Extraction and Purification of Sulfur Convertase
3.4.1. Extraction and Purification of Sulfur Convertase
3.4.2. Protein Molecular Weight of Sulfur Convertase
3.5. Property Studies of the Purified Sulfur Convertase
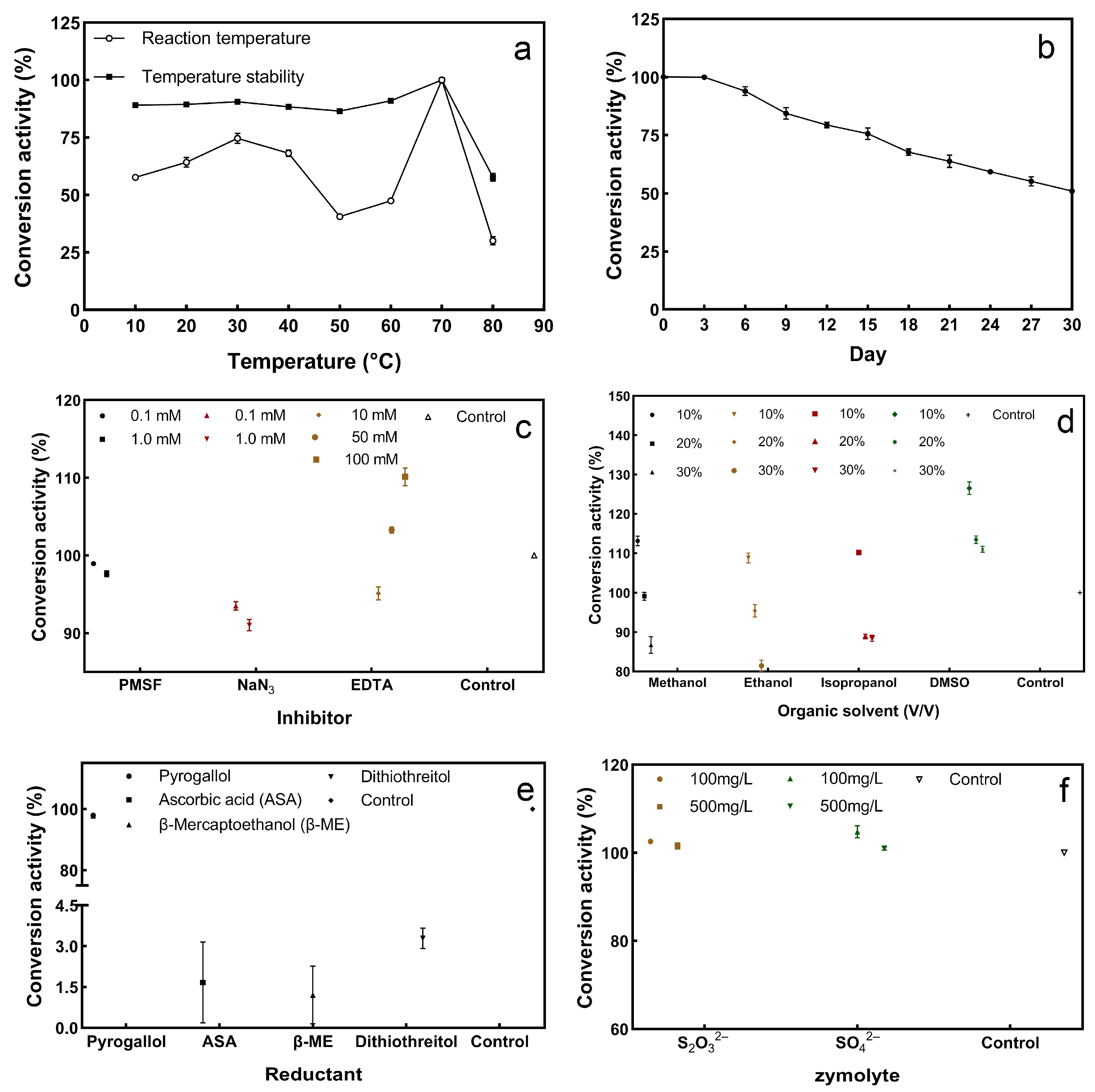
3.5.1. Activity and Stability of Sulfur Convertase at Different Temperatures
3.5.2. Sulfur Convertase Stability over Storage Time
3.5.3. Effect of Inhibitors and Organic Solvents on Sulfur Convertase Activity
3.5.4. Effect of Redox on Sulfur Convertase Activity
3.5.5. Effect of Zymolyte Competition on Sulfur Convertase Activity
3.6. Sulfur Conversion of Enzymes under Livestock Wastewater Conditions
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Gruzdev, E.V.; Latygolets, E.A.; Beletsky, A.V.; Grigoriev, M.A.; Mardanov, A.V.; Kadyrbaev, M.K.; Ikkert, O.P.; Karnachuk, O.V.; Ravin, N.V. The Microbial Community of Poultry Farm Waste and Its Role in Hydrogen Sulfide Production. Microbiology 2021, 90, 507–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pham, C.H.; Saggar, S.; Berben, P.; Palmada, T.; Ross, C. Removing Hydrogen Sulfide Contamination in Biogas Produced from Animal Wastes. J. Environ. Qual. 2019, 48, 32–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kim, D.-H.; Yun, H.-S.; Kim, Y.-S.; Kim, J.-G. Pollutant-Removing Biofilter Strains Associated with High Ammonia and Hydrogen Sulfide Removal Rate in a Livestock Wastewater Treatment Facility. Sustainability 2021, 13, 7358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, X.; Chi, Q.; Wang, D.; Chi, X.; Teng, X.; Li, S. Hydrogen sulfide inhalation-induced immune damage is involved in oxidative stress, inflammation, apoptosis and the Th1/Th2 imbalance in broiler bursa of Fabricius. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2018, 164, 201–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saksrithai, K.; King, A.J.J.A.R.N. Controlling hydrogen sulfide emissions during poultry productions. J. Anim. Res. Nutr. 2018, 3, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, J.J.; Chang, Y.C.; Chen, Y.J.; Chang, K.C.; Lee, S.Y. Hydrogen sulfide removal from livestock biogas by a farm-scale bio-filter desulfurization system. Water Sci. Technol. 2013, 67, 1288–1293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Da Silva, M.L.B.; Mezzari, M.P.; Ibelli, A.M.G.; Gregory, K.B. Sulfide removal from livestock biogas by Azospirillum-like anaerobic phototrophic bacteria consortium. Int. Biodeterior. Biodegrad. 2014, 86, 248–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pokorna, D.; Zabranska, J. Sulfur-oxidizing bacteria in environmental technology. Biotechnol. Adv. 2015, 33, 1246–1259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Watsuntorn, W.; Ruangchainikom, C.; Rene, E.; Lens, P.; Chulalaksananukul, W.J.B.T. Comparison of sulphide and nitrate removal from synthetic wastewater by pure and mixed cultures of nitrate-reducing, sulphide-oxidizing bacteria. Bioresour. Technol. 2019, 272, 40–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watsuntorn, W.; Ruangchainikom, C.; Rene, E.R.; Lens, P.N.L.; Chulalaksananukul, W. Hydrogen sulfide oxidation under anoxic conditions by a nitrate-reducing, sulfide-oxidizing bacterium isolated from the Mae Um Long Luang hot spring, Thailand. Int. Biodeterior. Biodegrad. 2017, 124, 196–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hansen, M.J.; Pedersen, C.L.; Søgaard Jensen, L.H.; Guldberg, L.B.; Feilberg, A.; Nielsen, L.P. Removal of hydrogen sulphide from pig house using biofilter with fungi. Biosyst. Eng. 2018, 167, 32–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Servos, M.R.; Bennie, D.T.; Burnison, B.K.; Jurkovic, A.; McInnis, R.; Neheli, T.; Schnell, A.; Seto, P.; Smyth, S.A.; Ternes, T.A. Distribution of estrogens, 17β-estradiol and estrone, in Canadian municipal wastewater treatment plants. Sci. Total Environ. 2005, 336, 155–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pudi, A.; Rezaei, M.; Signorini, V.; Andersson, M.P.; Baschetti, M.G.; Mansouri, S.S. Hydrogen sulfide capture and removal technologies: A comprehensive review of recent developments and emerging trends. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2022, 298, 121448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodríguez Couto, S.; Toca Herrera, J.L. Industrial and biotechnological applications of laccases: A review. Biotechnol. Adv. 2006, 24, 500–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, L.; Lu, M.; Li, Q.; Zhang, J.; Zong, Y.; She, Z. Three-dimensional fluorescence excitation–emission matrix (EEM) spectroscopy with regional integration analysis for assessing waste sludge hydrolysis treated with multi-enzyme and thermophilic bacteria. Bioresour. Technol. 2014, 171, 22–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arun, C.; Sivashanmugam, P. Identification and optimization of parameters for the semi-continuous production of garbage enzyme from pre-consumer organic waste by green RP-HPLC method. Waste Manag. 2015, 44, 28–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mahesh, M.; Swarnalatha, S.; Gnanamani, A.; Sekaran, G. Preparation and characterization of sulfide: Quinone oxidoreductase immobilized carbon matrix for the treatment of sulphide rich post-tanning wastewater. Biocatal. Agric. Biotechnol. 2020, 23, 101457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raksha Rao, K.; Vipin, A.V.; Hariprasad, P.; Anu Appaiah, K.A.; Venkateswaran, G. Biological detoxification of Aflatoxin B1 by Bacillus licheniformis CFR1. Food Control 2017, 71, 234–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Qin, X.; Guo, Y.; Zhang, Q.; Ma, Q.; Ji, C.; Zhao, L. Enzymatic degradation of deoxynivalenol by a novel bacterium, Pelagibacterium halotolerans ANSP101. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2020, 140, 111276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verma, J.; Pandey, S. Characterization of partially purified alkaline protease secreted by halophilic bacterium Citricoccus sp. isolated from agricultural soil of northern India. Biocatal. Agric. Biotechnol. 2019, 17, 605–612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, M.; Gao, Z.; Xing, S.; Long, J.; Li, C.; He, L.; Wang, X. Purification, characterization, and chemical modification of Bacillus velezensis SN-14 fibrinolytic enzyme. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2021, 177, 601–609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kilroy, W.P. The iodometric determination of dithionite, thiosulphate and sulphite in the presence of alkali and/or cyanide. Talanta 1980, 27, 343–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, C.; An, D.; Xiao, Q.; Chen, F.; Zhang, Y.; Weng, H.; Xiao, A.J.M.D. Convenient Agarose Preparation with Hydrogen Peroxide and Desulfation Process Analysis. Mar. Drugs 2021, 19, 297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dedkov, Y.M.; Elizarova, O.V.; Kel’ina, S.Y. Dichromate method for the determination of chemical oxygen demand. J. Anal. Chem. 2000, 55, 777–781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, K.; Zhu, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Lin, H. Determination of ammonia nitrogen in natural waters: Recent advances and applications. Trends Environ. Anal. Chem. 2019, 24, e00073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, C.-X.; Sun, X.-Y.; Liu, B.; Lian, H.-T. Determination of Total Phosphorus in Water Sample by Digital Imaging Colorimetry. Chin. J. Anal. Chem. 2007, 35, 850–853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cline, J.D. Spectrophotometric determination of hydrogen sulfide in natural waters 1. Limnol. Oceanogr. 1969, 14, 454–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korobov, V.V.; Zhurenko, E.Y.; Galkin, E.G.; Zharikova, N.V.; Iasakov, T.R.; Starikov, S.N.; Sagitova, A.I.; Markusheva, T.V. Cellulosimicrobium sp. strain NPZ-121, a degrader of 2,4,5-trichlorophenoxyacetic acid. Microbiology 2018, 87, 147–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bertel-Sevilla, A.; Cervantes-Ceballos, L.; Tirado-Ballestas, I.; Maldonado-Rojas, W.; Alzate-Restrepo, J.; Olivero-Verbel, J.J.E.t. Biodegradation of biodiesel-oil by Cellulosimicrobium sp. Isolated from Colombian Caribbean soils. Environ. Technol. 2020, 41, 2337–2349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bharagava, R.N.; Mishra, S. Hexavalent chromium reduction potential of Cellulosimicrobium sp. isolated from common effluent treatment plant of tannery industries. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2018, 147, 102–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liang, X.; Mohamed, E.A.; Lancine, S.; Yueju, Z.; Jonathan, S.; Fuguo, X.; Yan, W.; Hongping, Y.; Yang, L.J.T. Novel Aflatoxin-Degrading Enzyme from Bacillus shackletonii L7. Toxins 2017, 9, 36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sigman, D.S.; Mooser, G. Chemical Studies of Enzyme Active Sites. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 1975, 44, 889–931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Larsen, A.; Moe, E.; Helland, R.; Gjellesvik, D.; Willassen, N.J.T.F.j. Characterization of a recombinantly expressed proteinase K-like enzyme from a psychrotrophic Serratia sp. FEBS J. 2006, 273, 47–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, R.; Liu, H.; Xun, L. Cytoplasmic Localization of Sulfide:Quinone Oxidoreductase and Persulfide Dioxygenase of Cupriavidus pinatubonensis JMP134. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2017, 83, e01820-17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sousa, F.; Pereira, J.; Marreiros, B.; Pereira, M.J.B.e.b.a.B. Taxonomic distribution, structure/function relationship and metabolic context of the two families of sulfide dehydrogenases: SQR and FCSD. BBA Bioenerg. 2018, 1859, 742–753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bagchi, A.; Roy, D.; Roy, P.J.J.o.B.S.; Dynamics. Homology modeling of a transcriptional regulator SoxR of the Lithotrophic sulfur oxidation (Sox) operon in alpha-proteobacteria. J. Biomol. Struct. Dyn. 2005, 22, 571–577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aliabadi, N.; Aminzadeh, S.; Karkhane, A.A.; Haghbeen, K. Thermostable chitinase from Cohnella sp. A01: Isolation and product optimization. Braz. J. Microbiol. 2016, 47, 931–940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chen, L.; Li, W.; Zhao, Y.; Zhang, S.; Meng, L.; Zhou, Y. Characterization of sulfide oxidation and optimization of sulfate production by a thermophilic Paenibacillus naphthalenovorans LYH-3 isolated from sewage sludge composting. J. Environ. Sci. 2023, 125, 712–722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Liu, S.; Liu, X.; Li, X.; Wen, Q.; Lin, J.J. Identification and characterization of an ETHE1-like sulfur dioxygenase in extremely acidophilic Acidithiobacillus spp. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2014, 98, 7511–7522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Y.-B.; Zhang, Z.-F.; Shao, M.-Y.; Kang, K.-H.; Tan, Z.; Li, J.-L.J.M.B. Sulfide: Quinone oxidoreductase from echiuran worm Urechis unicinctus. Mar. Biotechnol. 2011, 13, 93–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Luo, X.; Dong, Y.; Hui, M.; Xu, L.; Li, H.; Lv, J.; Yang, L.; Cui, Y. Uric acid and creatinine biosensors with enhanced room-temperature storage stability by a multilayer enzyme matrix. Anal. Chim. Acta 2022, 1227, 340264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iyer, P.V.; Ananthanarayan, L. Enzyme stability and stabilization—Aqueous and non-aqueous environment. Process Biochem. 2008, 43, 1019–1032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaikh, I.K.; Dixit, P.P.; Shaikh, T.M. Purification and characterization of alkaline soda-bleach stable protease from Bacillus sp. APP-07 isolated from Laundromat soil. J. Genet. Eng. Biotechnol. 2018, 16, 273–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nazari, L.; Mehrabi, M. Purification and characterization of an extracellular thermotolerant alkaliphilic serine protease secreted from newly isolated Bacillus sp. DEM07 from a hot spring in Dehloran, Iran. Biocatal. Agric. Biotechnol. 2019, 18, 101053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suzuki, Y.; Taguchi, K.; Hanyu, S.; Kure, T.; Enoki, Y.; Otagiri, M.; Sakai, H.; Matsumoto, K. Oxidized liposomal artificial red blood cells rescue azide-poisoned mice from lethal toxidrome by recovering cytochrome c oxidase activity. J. Drug Deliv. Sci. Technol. 2022, 71, 103282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, L.; Yu, X.; Wei, C.; Qiu, L.; Yu, C.; Xing, Q.; Fan, Y.; Deng, Z. Production and characterization of a novel alkaline protease from a newly isolated Neurospora crassa through solid-state fermentation. LWT 2020, 122, 108990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guven, R.G.; Kaplan, A.; Guven, K.; Matpan, F.; Dogru, M. Effects of various inhibitors on β-galactosidase purified from the thermoacidophilic Alicyclobacillus acidocaldarius subsp. Rittmannii isolated from Antarctica. Biotechnol. Bioprocess Eng. 2011, 16, 114–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Y.; Yin, H.; Peng, H.; Lu, G.; Dang, Z.J.J.O.H.M. Proteomic mechanism of decabromodiphenyl ether (BDE-209) biodegradation by Microbacterium Y2 and its potential in remediation of BDE-209 contaminated water-sediment system. J. Hazard. Mater. 2020, 387, 121708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adou, K.E.; Kouakou, A.R.; Ehouman, A.D.; Tyagi, R.D.; Drogui, P.; Adouby, K. Coupling anaerobic digestion process and electrocoagulation using iron and aluminium electrodes for slaughterhouse wastewater treatment. Sci. Afr. 2022, 16, e01238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Zhang, H.; Chen, Z.; Wei, D.; Song, Y.; Ma, Y.; Zhang, H. Achieving biogas production and efficient pollutants removal from nitrogenous fertilizer wastewater using combined anaerobic digestion and autotrophic nitrogen removal process. Bioresour. Technol. 2021, 339, 125659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miri, S.; Davoodi, S.; Brar, S.; Rouissi, T.; Sheng, Y.; Martel, R.J.B.t. Psychrozymes as novel tools to biodegrade p-xylene and potential use for contaminated groundwater in the cold climate. Bioresour. Technol. 2021, 321, 124464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elmawgoud, H.A.; Elshiekh, T.M.; Abdelkreem, M.; Khalil, S.A.; Alsabagh, A.M. Optimization of petroleum crude oil treatment using hydrogen sulfide scavenger. Egypt. J. Pet. 2019, 28, 161–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Strain | S2− Conversion Rate (%) | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| 24 h | 48 h | 72 h | |
| L1 | 26.48 | 47.57 | 71.87 |
| L2 | 19.45 | 38.42 | 47.03 |
| L3 | 22.23 | 42.15 | 51.94 |
| L4 | 20.06 | 31.39 | 37.51 |
| L5 | 14.62 | 27.42 | 34.57 |
| L6 | 15.74 | 24.46 | 29.14 |
| S1 | 20.46 | 36.18 | 41.25 |
| S2 | 7.46 | 19.53 | 23.67 |
| S3 | 10.59 | 24.06 | 36.01 |
| S4 | 5.09 | 13.46 | 14.92 |
| S5 | 7.86 | 21.24 | 30.31 |
| S6 | 30.28 | 43.51 | 62.40 |
| CK | 3.80 | 11.65 | 14.50 |
| Purification Steps | Total Activity (mg) | Total Protein (mg) | Specific Activity (mg/mg) | Purification (Fold) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Crude sulfur convertase | 0.342 | 0.132 | 2.59 | 1.00 |
| (NH4)2SO4 precipitation (60~80%) | 0.240 | 0.028 | 8.57 | 3.31 |
| Sephadex G-75 | 0.5 | 0.035 | 14.29 | 5.52 |
| Group | Ammonia Nitrogen (mg/L) | Total Phosphorus (mg/L) | COD (mg/L) | S2− (mg/L) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| L1 | 1747.0 ± 54.6 | 196.1 ± 3.8 | 35002.0 ± 352.0 | 0.0 ± 0.0 |
| Sulfur convertase | 1565.2 ± 45.8 | 167.7 ± 14.9 | 32478.0 ± 0.0 | 0.0 ± 0.0 |
| Control | 1729.8 ± 3.2 | 296.5 ± 0.7 | 37196.0 ± 248.0 | 75.7 ± 3.1 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, X.; Zhai, W.; Duan, X.; Gou, C.; Li, M.; Wang, L.; Basang, W.; Zhu, Y.; Gao, Y. Extraction, Purification, Characterization and Application in Livestock Wastewater of S Sulfur Convertase. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 16368. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph192316368
Li X, Zhai W, Duan X, Gou C, Li M, Wang L, Basang W, Zhu Y, Gao Y. Extraction, Purification, Characterization and Application in Livestock Wastewater of S Sulfur Convertase. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health. 2022; 19(23):16368. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph192316368
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Xintian, Wei Zhai, Xinran Duan, Changlong Gou, Min Li, Lixia Wang, Wangdui Basang, Yanbin Zhu, and Yunhang Gao. 2022. "Extraction, Purification, Characterization and Application in Livestock Wastewater of S Sulfur Convertase" International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health 19, no. 23: 16368. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph192316368
APA StyleLi, X., Zhai, W., Duan, X., Gou, C., Li, M., Wang, L., Basang, W., Zhu, Y., & Gao, Y. (2022). Extraction, Purification, Characterization and Application in Livestock Wastewater of S Sulfur Convertase. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 19(23), 16368. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph192316368





