Research on the Relationship between Physical Literacy, Physical Activity and Sedentary Behavior
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Design and Participants
2.2. Physical Literacy
2.3. Physical Activity
2.4. Mediating Effect
2.5. Data Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Characteristics of Students
3.2. Gender Difference
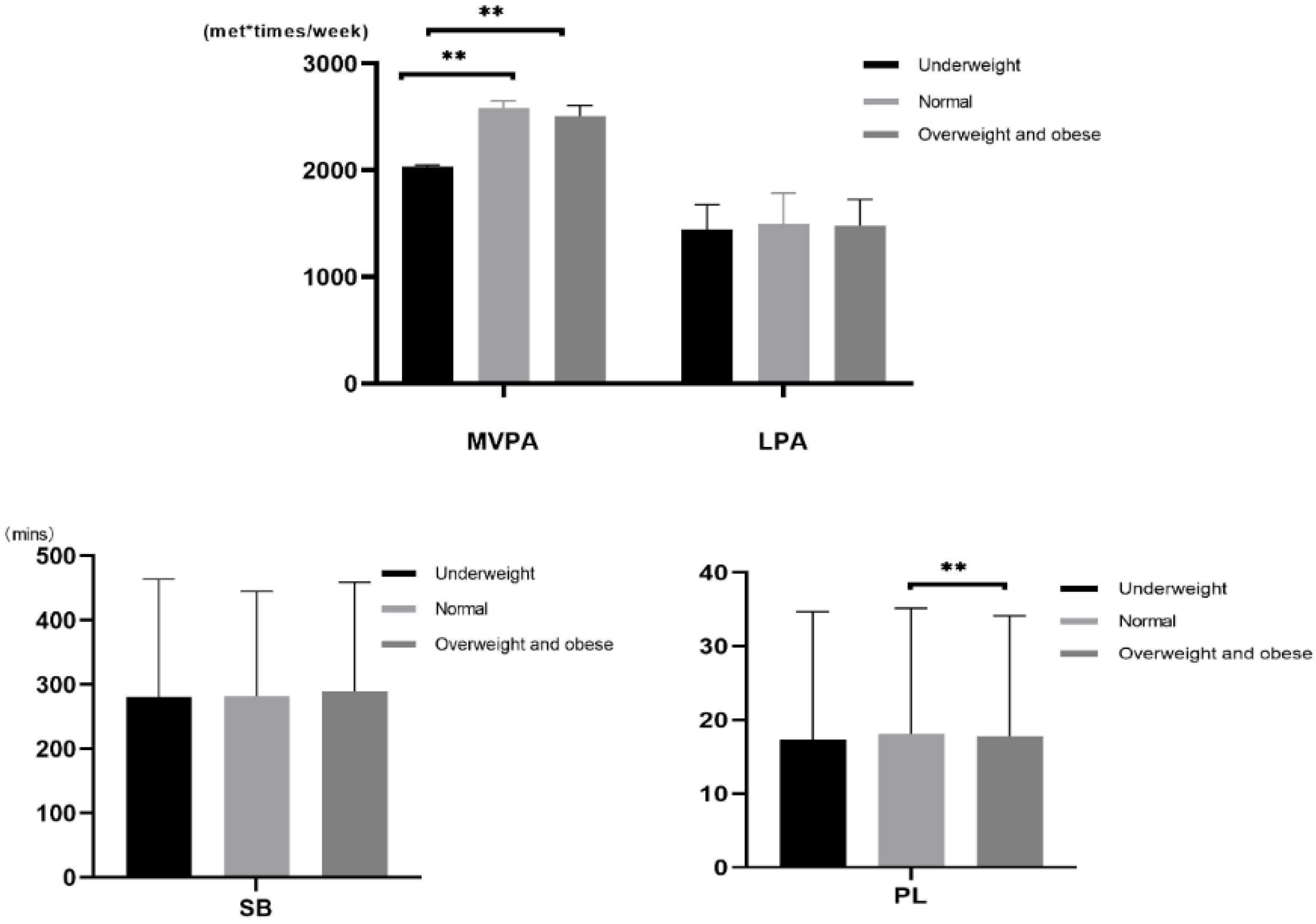
3.3. Variable Differences of Different Weight Status Categories
3.4. Correlation Analysis of Variables
3.5. Regression Analysis and Intermediary Effect Test
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Warburton, D.E.R.; Bredin, S.S.D. Health benefits of physical activity: A systematic review of current systematic reviews. Curr. Opin. Cardiol. 2017, 32, 541–556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Biddle, S. Physical activity and mental health: Evidence is growing. World Psychiatry 2016, 15, 176–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bull, F.C.; Al-Ansari, S.S.; Biddle, S.; Borodulin, K.; Buman, M.P.; Cardon, G.; Carty, C.; Chaput, J.P.; Chastin, S.; Chou, R.; et al. World Health Organization 2020 guidelines on physical activity and sedentary behaviour. Br. J. Sports Med. 2020, 54, 1451–1462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Loprinzi, P.D. Frequency of moderate-to-vigorous physical activity (MVPA) is a greater predictor of systemic inflammation than total weekly volume of MVPA: Implications for physical activity promotion. Physiol. Behav. 2015, 141, 46–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reyes-Molina, D.; Alonso-Cabrera, J.; Nazar, G.; Parra-Rizo, M.A.; Zapata-Lamana, R.; Sanhueza-Campos, C.; Cigarroa, I. Association between the Physical Activity Behavioral Profile and Sedentary Time with Subjective Well-Being and Mental Health in Chilean University Students during the COVID-19 Pandemic. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 2107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, E.; Kim, Y. Effect of university students’ sedentary behavior on stress, anxiety, and depression. Perspect. Psychiatr. Care 2019, 55, 164–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Talapko, J.; Perić, I.; Vulić, P.; Pustijanac, E.; Jukić, M.; Bekić, S.; Meštrović, T.; Škrlec, I. Mental Health and Physical Activity in Health-Related University Students during the COVID-19 Pandemic. Healthcare 2021, 9, 801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andrea, R.P.; Luc, N.B.; Fabián, F. Impact of COVID-19 induced lockdown on physical activity and sedentary behavior among university students: A systematic review. Medwave 2021, 21, e8456. [Google Scholar]
- Bertrand, L.; Shaw, K.A.; Ko, J.; Deprez, D.; Chilibeck, P.D.; Zello, G.A. The impact of the coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) pandemic on university students’ dietary intake, physical activity, and sedentary behaviour. Appl. Physiol. Nutr. Metab. 2021, 46, 265–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, X.F.; Wang, L.; Pan, A. Epidemiology and determinants of obesity in China. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 2021, 9, 373–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Telleria-Aramburu, N.; Arroyo-Izaga, M. Risk factors of overweight/obesity-related lifestyles in university students: Results from the EHU12/24 study. Br. J. Nutr. 2022, 127, 914–926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xue, B.; Zhang, X.; Li, T.; Gu, Y.; Wang, R.; Chen, W.; Ren, X.; Liu, X.; Chen, G.; Lin, Y.; et al. Knowledge, attitude, and practice of obesity among university students. Ann. Palliat. Med. 2021, 10, 4539–4546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Winpenny, E.M.; Smith, M.; Penney, T.; Foubister, C.; Guagliano, J.M.; Love, R.; Clifford Astbury, C.; van Sluijs, E.M.F.; Corder, K. Changes in physical activity, diet, and body weight across the education and employment transitions of early adulthood: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Obes. Rev. 2020, 21, e12962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Pfledderer, C.D.; Bai, Y.; Brusseau, T.A.; Burns, R.D.; King Jensen, J.L. Changes in college students’ health behaviors and substance use after a brief wellness intervention during COVID-19. Prev. Med. Rep. 2022, 26, 101743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cairney, J.; Dudley, D.; Kwan, M.; Bulten, R.; Kriellaars, D. Physical Literacy, Physical Activity and Health: Toward an Evidence-InforMed. Conceptual Model. Sports Med. 2019, 49, 371–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edwards, L.C.; Bryant, A.S.; Keegan, R.J.; Morgan, K.; Jones, A.M. Definitions, Foundations and Associations of Physical Literacy: A Systematic Review. Sports Med. 2017, 47, 113–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hannah, G. Physical Literacy across the World. Sport Educ. Soc. 2021, 26, 692–695. [Google Scholar]
- Davids, K.; Araújo, D.; Brymer, E. Designing Affordances for Health-Enhancing Physical Activity and Exercise in Sedentary Individuals. Sports Med. 2016, 46, 933–938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, R.S.; Sum, R.K.; Li, M.H.; Huang, Y.; Niu, X.L. Association between Physical Literacy and Physical Activity: A Multilevel Analysis Study among Chinese Undergraduates. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 7874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elsborg, P.; Heinze, C.; Melby, P.S.; Nielsen, G.; Bentsen, P.; Ryom, K. Associations between previous sport and exercise experience and physical literacy elements among physically inactive Danes. BMC Public Health 2021, 21, 1248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, R.S.; Sum, R.K.W.; Hu, Y.N.; Gao, T.Y. Assessing factor structure of the simplified Chinese version of Perceived Physical Literacy Instrument for undergraduates in Mainland China. J. Exerc. Sci. Fit. 2020, 18, 68–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Craig, C.L.; Marshall, A.L.; Sjöström, M.; Bauman, A.E.; Booth, M.L.; Ainsworth, B.E.; Pratt, M.; Ekelund, U.; Yngve, A.; Sallis, J.F.; et al. International physical activity questionnaire: 12-country reliability and validity. Med. Sci. Sports Exerc. 2003, 35, 1381–1395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kwan, M.Y.W.; Graham, J.D.; Healey, C.; Paolucci, N.; Brown, D.M. Stopping the Drop: Examining the Impact of a Pilot Physical Literacy-Based Intervention Program on Physical Activity Behaviours and Fitness during the Transition into University. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 5832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cairney, J. Towards a Physical Literacy Framework to Guide the Design, Implementation and Evaluation of Early Childhood Movement Based Interventions Targeting Cognitive Development. Ann. Sports Med. Res. 2016, 3. [Google Scholar]
- Li, M.H.; Sit, C.H.P.; Wong, S.H.S.; Wing, Y.K.; Ng, C.K.; Sum, R.K.W. Promoting physical activity and health in Hong Kong primary school children through a blended physical literacy intervention: Protocol and baseline characteristics of the “Stand+Move” randomized controlled trial. Trials 2021, 22, 944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petrusevski, C.; Morgan, A.; MacDermid, J.; Wilson, M.; Richardson, J. Framing physical literacy for aging adults: An integrative review. Disabil. Rehabil. 2021, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karp, G.G.; Brown, H.; Scruggs, P.W.; Berei, C. Cultivating Leadership, Pedagogy and Programming for CSPAP and Healthy, Active Lifestyles at the University of Idaho. J. Phys. Educ. Recreat. Dance 2017, 88, 29–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mendoza-Muñoz, M.; Barrios-Fernández, S.; Adsuar, J.C.; Pastor-Cisneros, R.; Risco-Gil, M.; García-Gordillo, M.; Carlos-Vivas, J. Influence of Body Composition on Physical Literacy in Spanish Children. Biology 2021, 10, 482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delisle Nyström, C.; Traversy, G.; Barnes, J.D.; Chaput, J.P.; Longmuir, P.E.; Tremblay, M.S. Associations between domains of physical literacy by weight status in 8- to 12-year-old Canadian children. BMC Public Health 2018, 18, 1043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Elmesmari, R.; Martin, A.; Reilly, J.J.; Paton, J.Y. Comparison of accelerometer measured levels of physical activity and sedentary time between obese and non-obese children and adolescents: A systematic review. BMC Pediatr. 2018, 18, 106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hamer, O.; Larkin, D.; Relph, N.; Dey, P. Fear-related barriers to physical activity among adults with overweight and obesity: A narrative synthesis scoping review. Obes. Rev. 2021, 22, e13307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Denise, R.; Joseph, S.D.; Adilson, M.; Miguel, P.; Stevo, P.; Jovan, G.; Bojan, M.; Yolanda, D. Physical Activity and Body-Mass-Index: Do Family, Friends and Teachers Restrain the Risk for Physical Inactivity in Adolescents? Sustainability 2021, 13, 6992. [Google Scholar]
- Ajibewa, T.A.; Beemer, L.R.; Sonneville, K.R.; Miller, A.L.; Toledo-Corral, C.; Robinson, L.E.; Hasson, R.E. Psychological Stress and Lowered Physical Activity Enjoyment in Adolescents With Overweight/Obesity. Am. J. Health Promot. 2021, 35, 766–774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caldwell, H.A.T.; Di Cristofaro, N.A.; Cairney, J.; Bray, S.R.; MacDonald, M.J.; Timmons, B.W. Physical Literacy, Physical Activity, and Health Indicators in School-Age Children. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 5367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cowley, J.G.; McIntosh, I.; Kiely, J.; Collins, D.J. The post 16 gap: How do young people conceptualise PE? An exploration of the barriers to participation in physical education, physical activity and sport in senior school pupils. Int. J. Adolesc. Med. Health 2021, 33, 313–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levine, J.A.; Lanningham-Foster, L.M.; McCrady, S.K.; Krizan, A.C.; Olson, L.R.; Kane, P.H.; Jensen, M.D.; Clark, M.M. Interindividual variation in posture allocation: Possible role in human obesity. Science 2005, 307, 584–586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hu, S.; Zhang, X.; Stamatiou, M.; Hambly, C.; Huang, Y.; Ma, J.; Li, Y.; Speakman, J.R. Higher than predicted resting energy expenditure and lower physical activity in healthy underweight Chinese adults. Cell Metab. 2022, 34, 1413–1415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, J.; Pereira, M.; Wolfson, J.; Laska, M.; Nelson, T.; Neumark-Sztainer, D. Developmental Trends and Determinants of Physical Activity From Adolescence to Adulthood Differ by Ethnicity/Race and Sex. J. Phys. Act. Health 2018, 15, 345–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kristen, M.; Kaigang, L.; Manfred, D.; Katherine, T.; Abigail, N.-B. The Association of Light Physical Activity With Health Indicators Among Middle-Aged and Older Adults. Innovation in Aging 2020, 4. [Google Scholar]
- Al-Rashed, F.; Alghaith, A.; Azim, R.; AlMekhled, D.; Thomas, R.; Sindhu, S.; Ahmad, R. Increasing the Duration of Light Physical Activity Ameliorates Insulin Resistance Syndrome in Metabolically Healthy Obese Adults. Cells 2020, 9, 1189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suzuki, K.; Niimura, H.; Kida, H.; Eguchi, Y.; Kitashima, C.; Takayama, M.; Mimura, M. Increasing light physical activity helps to maintain cognitive function among the community-dwelling oldest old population: A cross-sectional study using actigraph from the Arakawa 85+ study. Geriatr. Gerontol. Int. 2020, 20, 773–778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moura, B.P.; Rufino, R.L.; Faria, R.C.; Amorim, P.R.S. Effects of isotemporal substitution of sedentary behavior with light-intensity or moderate-to-vigorous physical activity on cardiometabolic markers in male adolescents. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0225856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Emily, E.; Edward, M.; Neha, G. Can Light Physical Activity Improve Cognition Among Older Adults? A Scoping Review. Innov. Aging 2020, 4, 891–892. [Google Scholar]

| Boy N = 829 (27.7%) | Girl N = 2167 (72.3%) | All (2996) | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Age (years) | 20.33 ± 1.22 | 20.09 ± 1.20 | 20.16 ± 1.21 |
| High (cm) | 177.64 ± 6.07 | 163.24 ± 5.20 | 167.23 ± 8.44 |
| Weigh (kg) | 71.48 ± 12.77 | 54.67 ± 7.98 | 59.32 ± 12.16 |
| Bmi (kg/m2) | 22.61 ± 3.57 | 20.50 ± 2.72 | 21.08 ± 3.13 |
| Grade | |||
| 1 | 1425 | 47.50% | |
| 2 | 725 | 24.19% | |
| 3 | 846 | 28.23% | |
| Major | |||
| PE | 458 | 15.30% | |
| Non-PE | 2538 | 84.70% | |
| Weight status categories | |||
| Underweight | 585 | 19.50% | |
| Normal | 1973 | 65.90% | |
| Overweight and obese | 438 | 14.60% |
| Boy N = 829 | CV | Girl N = 2167 | CV | t | p | 95% CI | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MVPA | 3846.52 ± 2989.42 | 0.777 | 1960.02 ± 1998.65 | 1.020 | 16.791 | 0.000 | 1666.053 | 2106.948 |
| LPA | 1879.14 ± 1310.79 | 0.698 | 1597.71 ± 1269.61 | 0.795 | 5.303 | 0.000 | 177.335 | 385.538 |
| SB | 365.82 ± 174.96 | 0.478 | 415.00 ± 157.68 | 0.380 | −7.071 | 0.000 | −62.835 | −35.541 |
| PL | 31.72 ± 6.79 | 0.214 | 29.22 ± 5.36 | 0.184 | 9.523 | 0.000 | 1.986 | 3.016 |
| Underweight N = 585 | Normal N = 1973 | Overweight and Obese N = 438 | F | p | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MVPA | 2022.09 ± 2044.64 | 2628.55 ± 2535.4 | 2436.21 ± 2576.44 | 13.87 | 0.00 |
| LPA | 1609.63 ± 1276.23 | 1699.9 ± 1285.87 | 1654.1 ± 1306.39 | 1.18 | 0.31 |
| SB | 409.83 ± 151.35 | 397.16 ± 166.4 | 409.19 ± 169.58 | 1.92 | 0.15 |
| PL | 29.61 ± 5.12 | 30.14 ± 6.02 | 29.33 ± 6.29 | 4.37 | 0.01 |
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1. MVPA | / | |||
| 2. LPA | 0.299 ** | / | ||
| 3. SB | 0.192 ** | 0.001 | / | |
| 4. PL | 0.316 ** | 0.141 ** | −0.124 ** | / |
| Effect | F | p | β | t | p | 95% CI | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Model 1 | ||||||||
| MVPA = cPL + e1 | c | 331.195 | 0.000 | 0.316 | 18.199 | 0.000 | 117.583 | 145.980 |
| SB = a1PL + e2 | a1 | 47.128 | 0.000 | −0.124 | −6.865 | 0.000 | −4.450 | −2.473 |
| LPA = a2PL + e2 | a2 | 60.456 | 0.000 | 0.141 | 7.775 | 0.000 | 22.946 | 38.422 |
| MVPA = c’PL + b1SB + b2LPA + e3 | c’ | 235.269 | 0.000 | 0.259 | 15.452 | 0.000 | 94.323 | 121.740 |
| b1 | −0.160 | −9.661 | 0.000 | −2.893 | −1.917 | |||
| b2 | 0.263 | 15.805 | 0.000 | 0.440 | 0.565 | |||
| Model 2 | ||||||||
| MVPA = cPL + e1 | c | 294.687 | 0.000 | 0.200 | 12.453 | 0.000 | 70.384 | 96.692 |
| SB = a1PL + e2 | a1 | 28.232 | 0.000 | −0.085 | −4.561 | 0.000 | −3.377 | −1.346 |
| LPA = a2PL + e2 | a2 | 39.531 | 0.000 | 0.097 | 5.257 | 0.000 | 13.291 | 29.103 |
| MVPA = c’PL + b1SB + b2LPA + e3 | c’ | 243.725 | 0.000 | 0.172 | 10.971 | 0.000 | 58.993 | 84.669 |
| b1 | −0.104 | −6.808 | 0.000 | −2.012 | −1.112 | |||
| b2 | 0.198 | 12.834 | 0.000 | 0.320 | 0.436 | |||
| Effect | Boot SE | t | p | LLCI | ULCI | c’ cs | Percent Effect | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Total effect of X on Y | 83.538 | 6.709 | 12.453 | 0.000 | 70.384 | 96.692 | 0.200 | |
| Direct effect of X on Y | 71.831 | 6.548 | 10.971 | 0.000 | 58.993 | 84.669 | 0.172 | 85.986% |
| Indirect effect(s) of X on Y | Effect | Boot SE | Boot LLCI | Boot ULCI | ||||
| TOTAL | 11.707 | 1.926 | 8.174 | 15.644 | 14.014% | |||
| SB | 3.690 | 1.046 | 1.843 | 5.941 | 4.417% | |||
| LPA | 8.017 | 1.672 | 4.879 | 11.380 | 9.597% |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yan, W.; Meng, Y.; Wang, L.; Zhang, T.; Chen, L.; Li, H. Research on the Relationship between Physical Literacy, Physical Activity and Sedentary Behavior. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 16455. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph192416455
Yan W, Meng Y, Wang L, Zhang T, Chen L, Li H. Research on the Relationship between Physical Literacy, Physical Activity and Sedentary Behavior. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health. 2022; 19(24):16455. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph192416455
Chicago/Turabian StyleYan, Wenjing, Yihan Meng, Lina Wang, Ting Zhang, Leqin Chen, and Hongjuan Li. 2022. "Research on the Relationship between Physical Literacy, Physical Activity and Sedentary Behavior" International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health 19, no. 24: 16455. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph192416455
APA StyleYan, W., Meng, Y., Wang, L., Zhang, T., Chen, L., & Li, H. (2022). Research on the Relationship between Physical Literacy, Physical Activity and Sedentary Behavior. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 19(24), 16455. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph192416455





