Status and Prospect of Ecological Environment in the Belt and Road Initiative Regions
Abstract
:1. The Development of Belt and Road Initiative
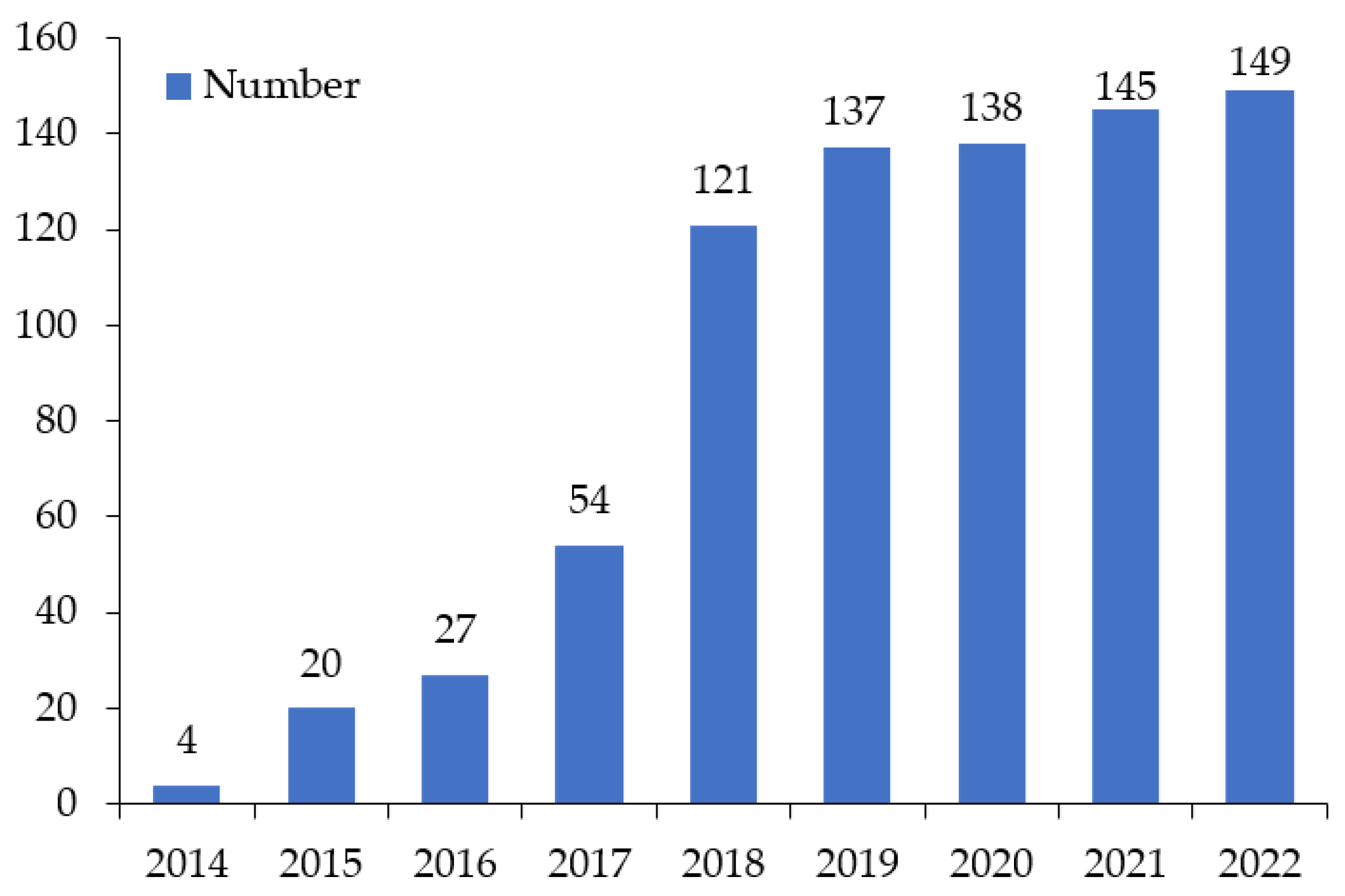
2. Temporal Variation of BRI-Involved Countries
3. Classification of the BRI-Involved Countries
4. Ecological Environment Status in Belt and Road Initiative Regions
4.1. Overall Ecological Environmental Patterns
4.2. Vegetation Coverage Conditions
4.3. Climate Change Effects
4.4. Natural Resources Conditions
4.5. The Role of BRI in the Context of the Ecological Environment
5. Prospects for Future Studies Related to Ecological Environment in the BRI Regions
5.1. Comparative Study before and after the Implementation of the BRI
5.2. Research on Ecological Environmental Laws and Policies
5.2.1. Research on Ecological Environmental Laws of BRI-Related Countries
5.2.2. Ecological Environmental Policies Evaluation
5.3. Research on Natural Resources Complementary among BRI Participating Countries
5.4. Research on the Expansion Area
5.5. Study on the Impact of International Emergencies
5.6. Interdisciplinary Research
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Xu, X.; Yeats, R.S.; Yu, G. Five Short Historical Earthquake Surface Ruptures near the Silk Road, Gansu Province, China. Bull. Seismol. Soc. Am. 2010, 100, 541–561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Chen, Y.N.; Wang, Y.; Li, W.H. Drought promoted the disappearance of civilizations along the ancient Silk Road. Environ. Earth Sci. 2016, 75, 1116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, C.B.; Qin, Y.; Du, X.X.; He, J.W.; Fan, X. Ecosystem Health and Environmental Geography in the Belt and Road Regions. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 5843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belt and Road Portal. Xi Jinping Delivered an Important Speech Calling for the Joint Construction of the Silk Road Economic Belt. 2013. Available online: https://www.yidaiyilu.gov.cn/xwzx/xgcdt/1875.htm (accessed on 19 July 2022).
- Belt and Road Portal. Xi Jinping Delivered a Speech in the Indonesian Parliament: Jointly Building a China-ASEAN Community of Common Destiny. 2013. Available online: https://www.yidaiyilu.gov.cn/xwzx/xgcdt/62334.htm (accessed on 19 July 2022).
- Huang, Y. Understanding China’s Belt & Road Initiative: Motivation, framework and assessment. China Econ. Rev. 2016, 40, 314–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koboevic, Z.; Kurtela, Z.; Vujicic, S. The Maritime Silk Road and China’s Belt and Road Initiative. Nase More 2018, 65, 113–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Szadziewski, H. Converging anticipatory geographies in Oceania: The Belt and Road Initiative and Look North in Fiji. Political Geogr. 2020, 77, 102119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- IISS. China’s Belt and Road Initiative in Latin America and the Caribbean. 2018. Available online: https://www.iiss.org/publications/strategic-comments/2018/chinas-bri-in-latin-america (accessed on 20 July 2022).
- Belt and Road Forum for International Cooperation. Joint Communique of the Leaders Roundtable of the Belt and Road Forum for International Cooperation. 2017. Available online: http://2017.beltandroadforum.org/english/n100/2017/0516/c22-423.html (accessed on 20 July 2022).
- Qian, X.Y.; Liang, Q.M.; Liu, L.J.; Zhang, K.; Liu, Y. Key points for green management of water-energy-food in the Belt and Road Initiative: Resource utilization efficiency, final demand behaviors and trade inequalities. J. Clean. Prod. 2022, 362, 132386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, H.M.; Du, W.P.; Feng, Z.M.; Yang, Y.Z.; Xue, Z.C. Exploring adaptive approaches for social-ecological sustainability in the Belt and Road countries: From the perspective of ecological resource flow. J. Environ. Manag. 2022, 311, 114898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhai, F. China’s belt and road initiative: A preliminary quantitative assessment. JAFEB 2018, 55, 84–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, X.; Si, Y.W. China’s Belt and Road Initiative and Corporate Innovation. Finance Res. Lett. 2022, 48, 103052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, X.; Hu, Y.Y.; Yin, H.T.; Geng, Y.; Bleischwitz, R. Trade impacts of China’s Belt and Road Initiative: From resource and environmental perspectives. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2019, 150, 104430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.F.; Bennett, M.M. The geopolitics of knowledge communities: Situating Chinese and foreign studies of the Green Belt and Road Initiative. Geoforum 2022, 128, 168–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dunford, M.; Liu, W.D. Chinese perspectives on the Belt and Road Initiative. Camb. J. Reg. Econ. Soc. 2019, 12, 145–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ministry of Commerce People’s Republic of China. China’s Investment Cooperation with BRI Participating Countries in 2021. 2022. Available online: http://english.mofcom.gov.cn/article/statistic/foreigntradecooperation/202203/20220303285883.shtml (accessed on 20 July 2022).
- Belt and Road Portal. A List of Countries That Have Signed BRI Cooperation Documents with China. 2022. Available online: https://www.yidaiyilu.gov.cn/xwzx/roll/77298.htm (accessed on 20 July 2022).
- Oliveira, G.D.T.; Murton, G.; Rippa, A.; Harlan, T.; Yang, Y. China’s Belt and Road Initiative: Views from the ground. Political Geogr. 2020, 82, 102225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Belt and Road Forum for International Cooperation. Full Text: Vision and Actions on Jointly Building Belt and Road. 2017. Available online: http://beltandroadforum.org/english/n100/2017/0410/c22-45.html (accessed on 21 July 2022).
- Szadziewski, H. Everyday geoeconomics: The belt and road initiative in Oceania. Geogr. Res. 2021, 59, 483–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- OBOReurope. New Zealand for a Partnership with China on the BRI. 2019. Available online: https://www.oboreurope.com/en/new-zealand-partnership-bri/ (accessed on 22 July 2022).
- Li, Y.B.; Zhu, X.F. The 2030 Agenda for Sustainable Development and China’s Belt and Road Initiative in Latin America and the Caribbean. Sustainability 2019, 11, 2297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chen, Z.H.; Wang, H. Research on the impact of the Belt and Road Initiative on the sustainability of the resource-based economy of participating countries. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2022, 29, 91139–91154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muhammad, S.; Long, X.; Salman, M.; Dauda, L. Effect of urbanization and international trade on CO2 emissions across 65 belt and road initiative countries. Energy 2020, 196, 117102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Li, Z.; Chen, M.; Song, X.; Kang, P. Spatial Variability of Water Resources State of Regions around the Belt and Road. Water 2021, 13, 2102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, X.C.; Zhu, K.W.; Sun, Y.L.; Zhao, W.Y.; Chen, F. Bibliometric research on the development of climate change in the BRI regions. Adv. Clim. Change Res. 2021, 12, 254–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tracy, E.F.; Shvarts, E.; Simonov, E.; Babenko, M. China’s new Eurasian ambitions: The environmental risks of the Silk Road Economic Belt. Eurasian Geogr. Econ. 2017, 58, 56–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- de Bruyn, M.; Stelbrink, B.; Morley, R.J.; Hall, R.; Carvalho, G.R.; Cannon, C.H.; van den Bergh, G.; Meijaard, E.; Metcalfe, I.; Boitani, L.; et al. Borneo and Indochina are Major Evolutionary Hotspots for Southeast Asian Biodiversity. Syst. Biol. 2014, 63, 879–901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ng, L.; Campos-Arceiz, A.; Sloan, S.; Hughes, A.C.; Tiang, D.C.F.; Li, B.V.; Lechner, A.M. The scale of biodiversity impacts of the Belt and Road Initiative in Southeast Asia. Biol. Conserv. 2020, 248, 108691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, T.T.; Chen, H.P.; Hao, X.; Wang, H.J. Projected changes in temperature and precipitation extremes over the Silk Road Economic Belt regions by the Coupled Model Intercomparison Project Phase 5 multi-model ensembles. Int. J. Clim. 2018, 38, 4077–4091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, D.; Ni, L.; Jiang, X.G.; Fang, S.F.; Wu, H.; Zhang, X.P. Spatiotemporal Analysis of Vegetation Changes Along the Belt and Road Initiative Region From 1982 to 2015. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 122579–122588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, P.P.; Xu, M.; Li, R.Q. Impacts of climate change on water resources in the major countries along the Belt and Road. Peerj 2021, 9, e12201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zuo, Q.T.; Song, Y.X.; Wang, H.J.; Li, J.L.; Han, C.H. Spatial variations of extreme precipitation events and attribution analysis in the main water resource area of the Belt and Road Initiative. Theor. Appl. Climatol. 2021, 144, 535–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, C.D.; Wu, H.; Jiang, X.G. Temporal and Spatial Change Monitoring of Drought Grade Based on ERA5 Analysis Data and BFAST Method in the Belt and Road Area during 1989–2017. Adv. Meteorol. 2019, 2019, 4053718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, J.M.; Li, X.J.; Wang, P.T.; Wang, J.C.; Ren, Z.Y. Hazard analysis of tsunami disaster on the Maritime Silk Road. Acta Oceanol. Sin. 2020, 39, 74–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, X.B.; Chen, H.; Li, C.L. Evaluate Typhoon Disasters in 21st Century Maritime Silk Road by Super-Efficiency DEA. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2019, 16, 1614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, X.B.; Yu, X.R.; Li, C.L.; Ji, Z.H. Information diffusion-based risk assessment of natural disasters along the Silk Road Economic Belt in China. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 244, 118744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.; Zhang, J.T.; Ge, Q.S.; Hao, Z.X. Projected changes in risk of heat waves throughout Belt and Road Region in the 21st century. Chin. Sci. Bull.-Chin. 2021, 66, 3045–3058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.Z.; Liu, K.; Wang, M.; Koks, E.E. A River Flood and Earthquake Risk Assessment of Railway Assets along the Belt and Road. IJDRR 2021, 12, 553–567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Liu, N.; Zhang, Y.F.; Zhang, T.Y.; Ren, X.X. Risk prevention of marine and meteorological disasters along the 21st Century Maritime Silk Road. Chin. Sci. Bull.-Chin. 2020, 65, 453–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chai, D.L.; Wang, M.; Liu, K. Driving factors of natural disasters in belt and road countries. IJDRR 2020, 51, 101774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhuang, Y.H.; Zhang, J.Y. Diurnal asymmetry in future temperature changes over the main Belt and Road regions. Ecosyst. Health Sust. 2020, 6, 1749530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- An, Y.; Tan, X.C.; Gu, B.H.; Zhu, K.W. Flood risk assessment using the CV-TOPSIS method for the Belt and Road Initiative: An empirical study of Southeast Asia. Ecosyst. Health Sust. 2020, 6, 1765703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, Y.; Cui, P.; Regmi, A.D.; Murray, V.; Pasuto, A.; Titti, G.; Shafique, M.; Priyadarshana, D.G.T. An international program on Silk Road Disaster Risk Reduction-a Belt and Road initiative (2016–2020). J. Mt. Sci. 2018, 15, 1383–1396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yan, M.; Fan, S.X.; Zhang, L.; Mahmood, R.; Chen, B.W.; Dong, Y.Q. Vegetation Dynamics Due to Urbanization in the Coastal Cities along the Maritime Silk Road. Land 2022, 11, 164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, S.; Liu, L.; Liu, Y.; Gao, J.; Dai, E.; Feng, A.; Wang, W. The Belt and Road: Geographical pattern and regional risks. J. Geogr. Sci. 2019, 29, 483–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.Y.; Li, Y.; Chen, A.P.; Gao, M.D.; Slette, I.J.; Piao, S.L. The impact of the 2009/2010 drought on vegetation growth and terrestrial carbon balance in Southwest China. Agric. For Meteorol. 2019, 269, 239–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, J.; Fu, B.J.; Gao, G.Y.; Lu, Y.H.; Liu, Y.; Lu, N.; Wang, S. Effects of precipitation and restoration vegetation on soil erosion in a semi-arid environment in the Loess Plateau, China. Catena 2016, 137, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.X.; Zhao, W.W.; Hua, T.; Wang, S.; Fu, B.J. Slower vegetation greening faced faster social development on the landscape of the Belt and Road region. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 697, 134103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, X.; Liu, H.; Jiao, F.; Gong, H.; Lin, Z. Time-varying trends of vegetation change and their driving forces during 1981–2016 along the silk road economic belt. Catena 2020, 195, 104796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.; Liu, H.; Jiao, F.; Gong, H.; Lin, Z. Nonlinear relationship of greening and shifts from greening to browning in vegetation with nature and human factors along the Silk Road Economic Belt. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 766, 142553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Ren, M.X.; Lu, X.; Li, Y.; Cao, J.J. Effect of the Belt and Road Initiatives on Trade and Its Related LUCC and Ecosystem Services of Central Asian Nations. Land 2022, 11, 828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Y.J.; Shi, F.Z.; Hu, X.; Li, X.Y. Threshold Vegetation Greenness under Water Balance in Different Desert Areas over the Silk Road Economic Belt. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 2452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Chen, Y.; Li, W.; Deng, H.; Fang, G. Potential impacts of climate change on vegetation dynamics in Central Asia. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2015, 120, 12345–12356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, X.Z.; Jia, J.H.; Liu, H.Y.; Lin, Z.S. Relative importance of climate change and human activities for vegetation changes on China’s silk road economic belt over multiple timescales. Catena 2019, 180, 224–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, D.W.; Wu, L.L.; Huang, S.Q.; Zhang, Z.Y.; Ahmad, F.; Zhang, G.L.; Shi, N.U.; Xu, H. Ecology and environment of the Belt and Road under global climate change: A systematic review of spatial patterns, cost efficiency, and ecological footprints. Ecol. Indic. 2021, 131, 108327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, J.; Jiang, T.; Wang, Y.; Su, B.; Tao, H.; Qin, J.; Zhai, J. Spatiotemporal variations of aridity index over the Belt and Road region under the 1.5 °C and 2.0 °C warming scenarios. J. Geogr. Sci. 2020, 30, 37–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ma, Y.-J.; Shi, F.-Z.; Hu, X.; Li, X.-Y. Climatic Constraints to Monthly Vegetation Dynamics in Desert Areas Over the Silk Road Economic Belt. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, X.; Jiang, L.B.; Shi, F.Z.; Li, X.Y.; Zhang, S.L.; Zhao, Y.D.; Ma, Y.J.; Gao, Z.; Bai, Y. Intensified Drought Enhances Coupling Between Vegetation Growth and Pregrowing Season Precipitation in the Drylands of the Silk Road Economic Belt. J. Geophys. Res. 2021, 126, e2020JG005914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schlaepfer, D.R.; Bradford, J.B.; Lauenroth, W.K.; Munson, S.M.; Tietjen, B.; Hall, S.A.; Wilson, S.D.; Duniway, M.C.; Jia, G.; Pyke, D.A.; et al. Climate change reduces extent of temperate drylands and intensifies drought in deep soils. Nat. Commun. 2017, 8, 14196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chai, Q.M.; Fu, S.; Wen, X.Y. Modeling the implementation of NDCs and the scenarios below 2 degrees C for the Belt and Road countries. Ecosyst. Health Sust. 2020, 6, 1766998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Li, Z.; Li, W.; Deng, H.; Shen, Y. Water and ecological security: Dealing with hydroclimatic challenges at the heart of China’s Silk Road. Environ. Earth Sci. 2016, 75, 881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, K.F.; Yu, B.L.; Huang, C.; Wu, J.P.; Sun, X.F. Exploring spatiotemporal patterns of electric power consumption in countries along the Belt and Road. Energy 2018, 150, 847–859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sattar, A.; Hussain, M.N.; Ilyas, M. An Impact Evaluation of Belt and Road Initiative (BRI) on Environmental Degradation. Sage Open 2022, 12, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salam, M.; Xu, Y.Z. Trade openness and environment: A panel data analysis for 88 selected BRI countries. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2022, 29, 23249–23263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, Y.; Zhou, J.H.; Zhou, S.Q.; Rao, D.K.; Zhou, J.; Fareed, Z. Investigating the Role of Education, Foreign Investment, and Economic Development for Sustainable Environment in BRI Countries: Application of Method of Movements Quantile Regression. Front. Environ. Sci. 2022, 10, 332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hussain, J.; Khan, A.; Zhou, K. The impact of natural resource depletion on energy use and CO2 emission in Belt & Road Initiative countries: A cross-country analysis. Energy 2020, 199, 117409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Shi, X.P.; Hu, C. Per capita CO2 emissions divergence influenced by bilateral trade with china under the belt and road initiative. Sustain. Prod. Consum. 2021, 27, 1589–1601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abernethy, V.D. Nature’s services: Societal dependence on natural ecosystems. Popul. Environ. 1999, 20, 277–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, T.T.; Gong, X.L.; Guo, Y.H.; Yang, Y.S.; Pan, B.B.; Li, S.P.; Dong, J. Electricity cooperation strategy between China and ASEAN countries under ‘The Belt and road’. Energy Strategy Rev. 2020, 30, 100512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y. Environmental risks and opportunities for countries along the Belt and Road: Location choice of China’s investment. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 211, 14–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suocheng, D.; Zehong, L.; Yu, L.; Guangyi, S.; Huilu, Y.; Juanle, W.; Jun, L.; Qiliang, M.; Yongbin, H. Resources, Environment and Economic Patterns and Sustainable Development Modes of the Silk Road Economic Belt. J. Resour. Ecol. 2015, 6, 65–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, L.J.; Li, D.Q.; Guo, X.P.; Xue, J.; Wang, C.C.; Sun, W.J. Cooperation risk of oil and gas resources between China and the countries along the Belt and Road. Energy 2021, 227, 120445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.X.; Yang, Y.J.; Zhou, L.; Hou, H.P.; Zhang, Y.Z.; Liang, J.; Zhang, S.L. Ecological restoration in mining areas in the context of the Belt and Road initiative: Capability and challenges. Environ. Impact Assess. Rev. 2022, 95, 106767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiang, Y.J.; Zhang, Q.L.; Wang, D.L.; Wu, S.A. Mining Investment Risk Assessment for Nations along the Belt and Road Initiative. Land 2022, 11, 1287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zuo, Q.T.; Diao, Y.X.; Hao, L.G.; Han, C.H. Comprehensive Evaluation of the Human-Water Harmony Relationship in Countries Along the Belt and Road. Water Resour. Manag. 2020, 34, 4019–4035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zoogah, D.B. Natural resource endowment and firm performance: The moderating role of institutional endowment. Glob. Strategy J. 2018, 8, 578–611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, K.; Wang, S.Q.; He, J.J.; Song, J.N.; Fang, C.L.; Jia, X.P. Mapping the environmental footprints of nations partnering the Belt and Road Initiative. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2021, 164, 105068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.Z.; Feng, Z.M.; Sun, T.; Tang, F. Water resources endowment and exploitation and utilization of countries along the Belt and Road. J. Nat. Resour. Policy Res. 2019, 34, 1146–1156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, Y.Y.; Tian, X.; Geng, Y.; Zhong, S.Z.; Cui, X.W.; Zhang, X.; Moss, D.A.; Bleischwitz, R. Driving Factors of Agricultural Virtual Water Trade between China and the Belt and Road Countries. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2019, 53, 5877–5886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, L.; Zou, Z.; Liang, S.; Xu, M. Virtual scarce water flows and economic benefits of the Belt and Road Initiative. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 253, 119936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Howard, K.W.F.; Howard, K.K. The new Silk Road Economic Belt as a threat to the sustainable management of Central Asia’s transboundary water resources. Environ. Earth Sci. 2016, 75, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, P.Y.; Qian, H.; Howard, K.W.F.; Wu, J.H. Building a new and sustainable Silk Road economic belt. Environ. Earth Sci. 2015, 74, 7267–7270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Y.; Lin, W.P.; Wu, M.Q.; Liu, K.; Yu, X.M.; Gao, J. Remote Sensing Monitoring of Ecological-Economic Impacts in the Belt and Road Initiatives Mining Project: A Case Study in Sino Iron and Taldybulak Levoberezhny. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 3308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, C.; Zhang, H.; Zeng, Y.; Li, F.; Liu, Y.; Qin, C.; Yuan, J. Total-Factor Energy Efficiency in BRI Countries: An Estimation Based on Three-Stage DEA Model. Sustainability 2018, 10, 278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Khan, A.; Yang, C.G.; Hussain, J.; Bano, S.; Nawaz, A. Natural resources, tourism development, and energy-growth-CO2 emission nexus: A simultaneity modeling analysis of BRI countries. Resour. Policy 2020, 68, 101751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chin, M.Y.; Ong, S.L.; Ooi, D.B.Y.; Puah, C.H. The impact of green finance on environmental degradation in BRI region. Environ. Dev. Sustain. 2022, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coenen, J.; Bager, S.; Meyfroidt, P.; Newig, J.; Challies, E. Environmental Governance of China’s Belt and Road Initiative. Environ. Policy Gov. 2021, 31, 3–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rauf, A.; Liu, X.; Amin, W.; Ozturk, I.; Rehman, O.U.; Sarwar, S. Energy and Ecological Sustainability: Challenges and Panoramas in Belt and Road Initiative Countries. Sustainability 2018, 10, 2743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hughes, A.C.; Lechner, A.M.; Chitov, A.; Horstmann, A.; Hinsley, A.; Tritto, A.; Chariton, A.; Li, B.V.; Ganapin, D.; Simonov, E.; et al. Horizon Scan of the Belt and Road Initiative. Trends Ecol. Evol. 2020, 35, 583–593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lechner, A.M.; Chan, F.K.S.; Campos-Arceiz, A. Biodiversity conservation should be a core value of China’s Belt and Road Initiative. Nat. Ecol. Evol. 2018, 2, 408–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ascensão, F.; Fahrig, L.; Clevenger, A.; Corlett, R.; Jaeger, J.; Laurance, W.; Pereira, H. Environmental challenges for the Belt and Road Initiative. Nat. Sustain. 2018, 1, 206–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, B.X.; Hu, J.M.; Chen, G.; Xiao, D.; Cheng, S.X. The environmental effects of regional economic cooperation: Evidence from the Belt and Road Initiative. Front. Environ. Sci. 2022, 10, 1731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hughes, A.C. Understanding and minimizing environmental impacts of the Belt and Road Initiative. Conserv. Biol. 2019, 33, 883–894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Huang, M.X.; Li, S.Y. The analysis of the impact of the Belt and Road initiative on the green development of participating countries. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 722, 137869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheshmehzangi, A.; Xie, L.; Tan-Mullins, M. Pioneering a Green Belt and Road Initiative (BRI) Alignment between China and other members: Mapping BRI’s Sustainability Plan. Blue-Green Syst. 2021, 3, 49–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, X.; Teng, C.B.; Zhang, J.J. Impact of the Belt and Road Initiative on environmental quality in countries along the routes. Chin. J. Popul. Resour. Environ. 2021, 19, 344–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Chen, C.L.; Hu, C. Does the Belt and Road Initiative Increase the Carbon Emission Intensity of Participating Countries. China World Econ. 2021, 29, 1–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Wang, R. Research on the Environmental Effects of China’s Outward Foreign Direct Investment (OFDI): Empirical Evidence Based on the Implementation of the Belt and Road Initiative (BRI). Sustainability 2022, 14, 12868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xin, L.; Wang, Y.M. Towards a green world: The impact of the Belt and Road Initiative on the carbon intensity reduction of countries along the route. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2022, 29, 28510–28526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]



| Proposal | Time (Location) | Specific Routes |
|---|---|---|
| Silk Road Economic Belt | September 7, 2013 (in Kazakhstan, Central Asia) | (1) Connecting China to Europe and the Baltic Sea (via Central Asia and Russia). (2) Connecting China to the Persian Gulf, and the Mediterranean (through Central Asia and West Asia). (3) Connecting China to the Indian Ocean (via the Indo-China Peninsula). |
| 21st Century Maritime Silk Road | October 3, 2013 (in Indonesia, Southeast Asia) | (1) From Chinese coastal ports to Europe (via the South China Sea and the Malacca Strait to the Indian Ocean). (2) From Chinese coastal ports to the South Pacific (via the South China Sea). |
| Region | Time | Country |
|---|---|---|
| Asia | 2014 | Qatar, Sri Lanka, Kazakhstan |
| 2015 | Korea, Turkey, Iraq, Azerbaijan, Georgia, Armenia, Tajikistan, Uzbekistan | |
| 2016 | Cambodia, Laos, Bangladesh, Iran, Afghanistan | |
| 2017 | Mongolia, Singapore, Timor-Leste, Malaysia, Myanmar, Vietnam, Brunei, Pakistan, Nepal, Maldives, Lebanon, Thailand | |
| 2018 | United Arab Emirates, Kuwait, Oman, Saudi Arabia, Bahrain, Kyrgyzstan, Indonesia, Philippines | |
| 2019 | Yemen | |
| 2022 | Syria | |
| Africa | 2016 | Egypt |
| 2017 | Morocco, Madagascar | |
| 2018 | Sudan, South Africa, Senegal, Sierra Leone, Côte d’Ivoire, Somalia, Cameroon, South Sudan, Seychelles, Guinea, Ghana, Zambia, Mozambique, Gabon, Namibia, Mauritania, Angola, Djibouti, Ethiopia, Kenya, Nigeria, Chad, Congo, Zimbabwe, Algeria, Tanzania, Burundi, Cabo Verde, Uganda, Gambia, Togo, Rwanda, Tunisia, Libya | |
| 2019 | Equatorial Guinea, Liberia, Lesotho, Comorin, Benin, Mali, Niger | |
| 2021 | The Democratic Republic of the Congo, Botswana, Central Africa, Guinea-Bissau, Eritrea, Burkina Faso, Sao Tome and Principe | |
| 2022 | Malawi | |
| Europe | 2014 | Belarus |
| 2015 | Russia, Poland, Serbia, Czech Republic, Bulgaria, Slovakia, Hungary, North Macedonia | |
| 2017 | Albania, Croatia, Bosnia and Herzegovina, Montenegro, Estonia, Lithuania, Slovenia, Romania, Latvia, Ukraine, Moldova | |
| 2018 | Austria, Greece, Malta, Portugal | |
| 2019 | Italy, Luxembourg, Cyprus | |
| Oceania | 2017 | New Zealand |
| 2018 | Papua New Guinea, Samoa, Niue, Fiji, The Federated States of Micronesia, Cook Islands, Tonga, Vanuatu | |
| 2019 | Solomon Islands | |
| 2020 | Kiribati | |
| South America | 2018 | Chile, Guyana, Bolivia, Uruguay, Venezuela, Surinam, Ecuador |
| 2019 | Peru | |
| 2022 | Argentina | |
| North America and the Caribbean | 2017 | Panama |
| 2018 | Costa Rica, El Salvador, Dominica, Trinidad and Tobago, Antigua and Barbuda, Dominica, Grenada | |
| 2019 | Barbados, Cuba, Jamaica | |
| 2022 | Nicaragua |
| Category | Income Group | Country |
|---|---|---|
| The Silk Road Economic Belt region | High income (17) | Austria, Cyprus, Czech Republic, Croatia, Estonia, Greece, Poland, Slovakia, Slovenia, Lithuania, Hungary, Romania, Latvia, Malta, Portugal, Italy, Luxembourg |
| Upper middle income (15) | Turkey, Iraq, Armenia, Azerbaijan, Albania, Bulgaria, Bosnia and Herzegovina, Belarus, Georgia, Kazakhstan, Russia, Serbia, Montenegro, North Macedonia, Moldova | |
| Lower middle income (6) | Mongolia, Iran, Kyrgyzstan, Tajikistan, Uzbekistan, Ukraine | |
| Low income (2) | Afghanistan, Syria | |
| The 21st Century Maritime Silk Road region | High income (10) | Korea, Singapore, Brunei, United Arab Emirates, Kuwait, Qatar, Oman, Saudi Arabia, Bahrain, Seychelles |
| Upper middle income (9) | Malaysia, Maldives, Thailand, South Africa, Gabon, Namibia, Libya, Equatorial Guinea, Botswana | |
| Lower middle income (33) | Timor-Leste, Myanmar, Cambodia, Vietnam, Laos, Pakistan, Sri Lanka, Bangladesh, Nepal, Lebanon, Indonesia, Philippines, Senegal, Côte d’Ivoire, Cameroon, Ghana, Mauritania, Angola, Djibouti, Kenya, Nigeria, Congo, Zimbabwe, Algeria, Tanzania, Cabo Verde, Morocco, Tunisia, Egypt, Lesotho, Comoros, Benin, Sao Tome and Principe | |
| Low income (25) | Yemen, Sudan, Sierra Leone, Somalia, South Sudan, Guinea, Zambia, Mozambique, Ethiopia, Chad, The Democratic Republic of the Congo, Burundi, Uganda, Gambia, Togo, Rwanda, Madagascar, Liberia, Mali, Niger, Central Africa, Guinea-Bissau, Eritrea, Burkina Faso, Malawi | |
| The natural extension region of the Maritime Silk Road | High income (7) | New Zealand, Chile, Uruguay, Panama, Trinidad and Tobago, Antigua and Barbuda, Barbados |
| Upper middle income (16) | Fiji, Niue, Cook Islands, Tonga, Guyana, Venezuela, Surinam, Ecuador, Peru, Argentina, Costa Rica, Dominica, Dominican, Grenada, Cuba, Jamaica | |
| Lower middle income (9) | Papua New Guinea, Samoa, The Federated States of Micronesia, Vanuatu, Solomon Islands, Kiribati, Bolivia, El Salvador, Nicaragua |
| Precipitation Level | Belt and Road Region |
|---|---|
| The highest level (Annual precipitation: 1867 mm) | South-Eastern Asia |
| The moderate level | Mongolia-Russia; Central Asia; Central and Eastern Europe |
| The lowest level (Annual precipitation: 142 mm) | Western Asia; Northern Africa |
| Region | Natural Disaster Type |
|---|---|
| Southeast Asia | Floods; landslides; winter drought |
| South Asia | Floods; landslides; drought; earthquakes |
| West Asia | Floods; landslides; winter drought; earthquakes |
| Central Asia | Floods; earthquakes; landslides; summer drought |
| Central and Eastern Europe | Floods; landslides |
| The Middle East | Earthquakes; floods; droughts |
| North Africa | Floods; landslides; summer drought |
| The Mean Annual NDVI | Region |
|---|---|
| Above 0.7 | South Asia |
| 0.4–0.7 | East Europe; Russia; South China |
| Below 0.2 | Central Asia; West Asia |
| Changing Situation | Region and Countries |
|---|---|
| Decreasing water resources | Central and West Asia, South Africa, South China, Chile, Bolivia and Venezuela |
| Increasing water resources | North Africa, Russia, Mongolia Plateau, West China, Southeast Asia, Peru and Uruguay |
| Resources Type | Content (Proportion) |
|---|---|
| The total recoverable oil | 203.64 Gt (Accounting for 66% of the global total) |
| The total recoverable natural gas | 204.2 × 1012 m3 (Accounting for 65.5% of the global total) |
| The total mining areas | 24,234 km2 (Accounting for 42.31% of the global mining areas) |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Du, X.; Qin, Y.; Huang, C. Status and Prospect of Ecological Environment in the Belt and Road Initiative Regions. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 17091. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph192417091
Du X, Qin Y, Huang C. Status and Prospect of Ecological Environment in the Belt and Road Initiative Regions. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health. 2022; 19(24):17091. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph192417091
Chicago/Turabian StyleDu, Xixi, Yi Qin, and Chunbo Huang. 2022. "Status and Prospect of Ecological Environment in the Belt and Road Initiative Regions" International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health 19, no. 24: 17091. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph192417091
APA StyleDu, X., Qin, Y., & Huang, C. (2022). Status and Prospect of Ecological Environment in the Belt and Road Initiative Regions. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 19(24), 17091. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph192417091







