Eight Good Reasons for Careful Monitoring and Evaluation of the Vaccine Campaign against COVID-19: Lessons Learned through the Lombardy Experience for Dealing with Next Challenges
Abstract
:1. The Ongoing Vaccine Campaign Is a Remarkable ‘Natural’ Experiment
2. Developing a Vaccine Integrated Platform
3. Generating Evidence from the Vaccine Integrated Platform
4. Summarizing Evidence and Expanding the Platform Use
5. Strengths, Pitfalls, Methodologic Challenges
6. Future Challenges
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Cioffi, A.; Cioffi, F. COVID-19 vaccine: Risk of inequality and failure of public health strategies. Ethics Med. Public Health 2021, 17, 100653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, I.; Essue, B.; Nouvet, E.; Sandman, L.; Razavi, S.D.; Noorulhuda, M.; Goold, S.; Danis, M.; Biemba, G.; Abelson, J.; et al. Priority setting during the COVID-19 pandemic: Going beyond vaccines. BMJ Glob. Health 2021, 6, e004686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Darby, A.C.; A Hiscox, J. Covid-19: Variants and vaccination. BMJ 2021, 372, n771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Petousis-Harris, H. Assessing the Safety of COVID-19 Vaccines: A Primer. Drug Saf. 2020, 43, 1205–1210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stephan, D.; Cordeanu, E.M.; Gaertner, S. Real life studies and good clinical practice. Lancet Haematol. 2016, 3, e160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Berger, M.L.; Mamdani, M.; Atkins, D.; Johnson, M.L. Good research practices for comparative effectiveness research: Defining, reporting and interpreting nonrandomized studies of treatment effects using secondary data sources: The ISPOR Good Research Practices for Retrospective Database Analysis Task Force Report—Part I. Value Health 2002, 12, 1044–1052. [Google Scholar]
- Corrao, G.; Mancia, G. Generating Evidence From Computerized Healthcare Utilization Databases. Hypertension 2015, 65, 490–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Corrao, G.; Cantarutti, A. Building reliable evidence from real-world data: Needs, methods, cautiousness and recommendations. Pulm. Pharmacol. Ther. 2018, 53, 61–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmidt, H. Vaccine Rationing and the Urgency of Social Justice in the Covid-19 Response. Hastings Cent. Rep. 2020, 50, 46–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corrao, G.; Rea, F.; Carle, F.; Scondotto, S.; Allotta, A.; Lepore, V.; D’Ettorre, A.; Tanzarella, C.; Vittori, P.; Abena, S.; et al. Stratification of the risk of developing severe or lethal Covid-19 using a new score from a large Italian population: A population-based cohort study. BMJ Open 2021, 11, e053281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Available online: https://www.regione.lombardia.it/wps/portal/istituzionale/HP/istituzione/Giunta/sedute-delibere-giunta-regionale/DettaglioDelibere/delibera-4353-legislatura-11 (accessed on 14 January 2022).
- Polack, F.P.; Thomas, S.J.; Kitchin, N.; Absalon, J.; Gurtman, A.; Lockhart, S.; Perez, J.L.; Marc, G.P.; Moreira, E.D.; Zerbini, C.; et al. Safety and Efficacy of the BNT162b2 mRNA Covid-19 Vaccine. N. Engl. J. Med. 2021, 383, 2603–2615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baden, L.R.; El Sahly, H.M.; Essink, B.; Kotloff, K.; Frey, S.; Novak, R.; Diemert, D.; Spector, S.A.; Rouphael, N.; Creech, C.B.; et al. Efficacy and safety of the mRNA-1273 SARS-CoV-2 vaccine. N. Engl. J. Med. 2021, 384, 403–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramasamy, M.N.; Minassian, A.M.; Ewer, K.J.; Flaxman, A.L.; Folegatti, P.M.; Owens, D.R.; Voysey, M.; Aley, P.K.; Angus, B.; Babbage, G.; et al. Safety and immunogenicity of ChAdOx1 nCoV-19 vaccine administered in a prime-boost regimen in young and old adults (COV002): A single-blind, randomised, controlled, phase 2/3 trial. Lancet 2021, 396, 1979–1993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sadoff, J.; Gray, G.; Vandebosch, A.; Cárdenas, V.; Shukarev, G.; Grinsztejn, B.; Goepfert, P.A.; Truyers, C.; Fennema, H.; Spiessens, B.; et al. Safety and Efficacy of Single-Dose Ad26.COV2.S Vaccine against Covid-19. N. Engl. J. Med. 2021, 384, 2187–2201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Voysey, M.; Clemens, S.A.C.; Madhi, S.A.; Weckx, L.Y.; Folegatti, P.M.; Aley, P.K.; Angus, B.; Baillie, V.L.; Barnabas, S.L.; Bhorat, Q.E.; et al. Safety and efficacy of the ChAdOx1 nCoV-19 vaccine (AZD1222) against SARS-CoV-2: An interim analysis of four randomised controlled trials in Brazil, South Africa, and the UK. Lancet 2021, 397, 99–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Voysey, M.; Clemens, S.A.C.; Madhi, S.A.; Weckx, L.Y.; Folegatti, P.M.; Aley, P.K.; Angus, B.; Baillie, V.L.; Barnabas, S.L.; Bhorat, Q.E.; et al. Single-dose administration and the influence of the timing of the booster dose on immunogenicity and efficacy of ChAdOx1 nCoV-19 (AZD1222) vaccine: A pooled analysis of four randomised trials. Lancet 2021, 397, 881–891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dagan, N.; Barda, N.; Kepten, E.; Miron, O.; Perchik, S.; Katz, M.A.; Hernán, M.A.; Lipsitch, M.; Reis, B.; Balicer, R.D. BNT162b2 mRNA Covid-19 Vaccine in a Nationwide Mass Vaccination Setting. N. Engl. J. Med. 2021, 384, 1412–1423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suter, K.; Briel, M.; Günther, J. Number needed to treat (NNT) und Number needed to harm (NNH). Weitere Abkömmlinge der Vier-Felder-Tafel [The number needed to treat (NNT) and the number needed to harm (NNH)]. Med. Monatsschr. Pharm. 2015, 38, 103–106. [Google Scholar]
- Strain, T.; Brage, S.; Sharp, S.J.; Richards, J.; Tainio, M.; Ding, D.; Benichou, J.; Kelly, P. Use of the prevented fraction for the population to determine deaths averted by existing prevalence of physical activity: A descriptive study. Lancet Glob. Health 2020, 8, e920–e930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wise, J. Covid-19: European countries suspend use of Oxford-AstraZeneca vaccine after reports of blood clots. Br. Med. J. 2021, 372, n699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- European Medicines Agency. COVID-19 Vaccine AstraZeneca: PRAC Investigating Cases of Thromboembolic Events-Vaccine’s Benefits Currently Still Outweigh Risks-Update. 11 March 2021. Available online: https://www.ema.europa.eu/en/news/covid-19-vaccineastrazeneca-prac-investigating-casesthromboembolic-events-vaccines-benefits (accessed on 14 June 2021).
- European Medicines Agency. Annex to Vaxzevria Art.5.3-Visual Risk Contextualization. Available online: https://www.ema.europa.eu/en/documents/chmp-annex/annex-vaxzevria-art53-visual-risk-contextualisation_en.pdf (accessed on 23 April 2021).
- Pottegård, A.; Lund, L.C.; Karlstad, Ø.; Dahl, J.; Andersen, M.; Hallas, J.; Lidegaard, Ø.; Tapia, G.; Gulseth, H.L.; Ruiz, P.L.D.; et al. Arterial events, venous thromboembolism, thrombocytopenia, and bleeding after vaccination with Oxford-AstraZeneca ChAdOx1-S in Denmark and Norway: Population based cohort study. Br. Med. J. 2021, 373, n1114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- WHO. COVID-19 Weekly Epidemiological Update, 25 February 2021. Special Edition: Proposed Working Definitions of SARS-CoV-2 Variants of Interest and Variants of Concern; WHO: Geneva, Switzerland, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Aleem, A.; Akbar Samad, A.B.; Slenker, A.K. Emerging Variants of SARS-CoV-2 and Novel Therapeutics against Coronavirus (COVID-19); StatPearls Publishing: Treasure Island, FL, USA, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Graham, F. Daily briefing: Why the Delta variant spreads so fast. Nature 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- European Centre for Disease Prevention and Control. ECDC Statement on the SARS-CoV-2 Delta Variant in the EU/EEA, 23 June 2021. Available online: https://www.ecdc.europa.eu/en/news-events/ecdc-statement-sars-cov-2-delta-variant-eueea (accessed on 30 November 2021).
- Supasa, P.; Zhou, D.; Dejnirattisai, W.; Liu, C.; Mentzer, A.J.; Ginn, H.M.E.; Zhao, Y.; Duyvesteyn, H.M.; Nutalai, R.; Tuekprakhon, A.; et al. Reduced neutralization of SARS-CoV-2 B.1.1.7 variant by convalescent and vaccine sera. Cell 2021, 184, 2201–2211.e7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, X.; Tang, H.; McDanal, C.; Wagh, K.; Fischer, W.; Theiler, J.; Yoon, H.; Li, D.; Haynes, B.F.; Sanders, K.O.; et al. SARS-CoV-2 variant B.1.1.7 is susceptible to neutralizing antibodies elicited by ancestral spike vaccines. Cell Host Microbe 2021, 29, 529–539.e3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tartof, S.Y.; Slezak, J.M.; Fischer, H.; Hong, V.; Ackerson, B.K.; Ranasinghe, O.N.; Frankland, T.B.; Ogun, O.A.; Zamparo, J.M.; Gray, S.; et al. Effectiveness of mRNA BNT162b2 COVID-19 vaccine up to 6 months in a large integrated health system in the USA: A retrospective cohort study. Lancet 2021, 398, 1407–1416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El Sahly, H.M.; Baden, L.R.; Essink, B.; Doblecki-Lewis, S.; Martin, J.M.; Anderson, E.J.; Campbell, T.B.; Clark, J.; Jackson, L.A.; Fichtenbaum, C.J.; et al. Efficacy of the mRNA-1273 SARS-CoV-2 Vaccine at Completion of Blinded Phase. N. Engl. J. Med. 2021, 385, 1774–1785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doria-Rose, N.; Suthar, M.S.; Makowski, M.; O’Connell, S.; McDermott, A.B.; Flach, B.; Ledgerwood, J.E.; Mascola, J.R.; Graham, B.S.; Lin, B.C.; et al. Antibody Persistence through 6 Months after the Second Dose of mRNA-1273 Vaccine for Covid-19. N. Engl. J. Med. 2021, 384, 2259–2261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baraniuk, C. How long does covid-19 immunity last? BMJ 2021, 373, n1605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corrao, G.; Franchi, M.; Cereda, D.; Bortolan, F.; Zoli, A.; Borriello, C.R.; Della Valle, G.P.; Tirani, M.; Pavesi, G.; Barone, A.; et al. Persistence of protective action against SARS-CoV-2 clinical outcomes up to 9 months since vaccine completion. Retrospective observational analysis of the mass vaccination of Lombardy, Italy. Lancet Inf. Dis. 2021, in press. [Google Scholar]
- Carstensen, B. Age-period-cohort models for the Lexis diagram. Stat. Med. 2007, 26, 3018–3045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Overbaugh, J. Understanding protection from SARS-CoV-2 by studying reinfection. Nat. Med. 2020, 26, 1680–1681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corrao, G.; Franchi, M.; Rea, F.; Cereda, D.; Barone, A.; Borriello, C.R.; Della Valle, G.P.; Ercolanoni, M.; Fortino, I.; Jara, J.; et al. Protective action of natural and induced immunization against the occurrence of delta or alpha variants of SARS-CoV-2 infection: A test-negative case-control study. BMC Med. 2021, in press. [Google Scholar]
- Mancia, G.; Rea, F.; Ludergnani, M.; Apolone, G.; Corrao, G. Renin-Angiotensin-Aldosterone System Blockers and the Risk of Covid-19. N. Engl. J. Med. 2020, 382, 2431–2440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Corrao, G.; Cantarutti, A.; Monzio Compagnoni, M.; Franchi, M.; Rea, F. Change in healthcare during Covid-19 pandemic was assessed through observational designs. J. Clin. Epidemiol. 2021, 142, 45–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Au, W.Y.; Cheung, P.P.H. Diagnostic performances of common nucleic acid tests for SARS-CoV-2 in hospitals and clinics: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Lancet Microbe 2021, 2, e704–e714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suissa, S. Immortal time bias in pharmaco-epidemiology. Am. J. Epidemiol. 2008, 167, 492–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Austin, P.C. An introduction to propensity score methods for reducing the effects of confounding in observational studies. Multivar. Behav. Res. 2011, 46, 399–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Corrao, G.; Ghirardi, A.; Di Bari, M.; Zambon, A.; Della Vedova, G.; Lapi, F.; Cipriani, F.; Caputi, A.; Vaccheri, A.; Gregori, D.; et al. User-only design for assessing drug effectiveness in clinical practice. Pharmacoepidemiol. Drug Saf. 2014, 23, 859–867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lopez Bernal, J.; Andrews, N.; Gower, C.; Gallagher, E.; Simmons, R.; Thelwall, S.; Stowe, J.; Tessier, E.; Groves, N.; Dabrera, G.; et al. Effectiveness of COVID-19 Vaccines against the B.1.617.2 (Delta) Variant. N. Engl. J. Med. 2021, 385, 585–594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schultze, A.; Walker, A.J.; MacKenna, B.; Morton, C.E.; Bhaskaran, K.; Brown, J.P.; Rentsch, C.T.; Williamson, E.; Drysdale, H.; Croker, R.; et al. Risk of COVID-19-related death among patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease or asthma prescribed inhaled corticosteroids: An observational cohort study using the OpenSAFELY platform. Lancet Respir. Med. 2020, 8, 1106–1120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Devine, E.B.; Van Eaton, E.; Zadworny, M.E.; Symons, R.; Devlin, A.; Yanez, D.; Yetisgen, M.; Keyloun, K.R.; Capurro, D.; Alfonso-Cristancho, R.; et al. Automating Electronic Clinical Data Capture for Quality Improvement and Research: The CERTAIN Validation Project of Real World Evidence. EGEMS 2018, 6, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- European Translational Information and Knowledge Management Services (eTRIKS). Proposal for a Data Sharing Federation Model for Secure Sharing of Biomedical Data for Secondary Research Purposes. Available online: https://www.etriks.org/wp-content/uploads/115446-eTRIKS-D7.9-Data-sharing-federation-model.pdf (accessed on 14 January 2022).



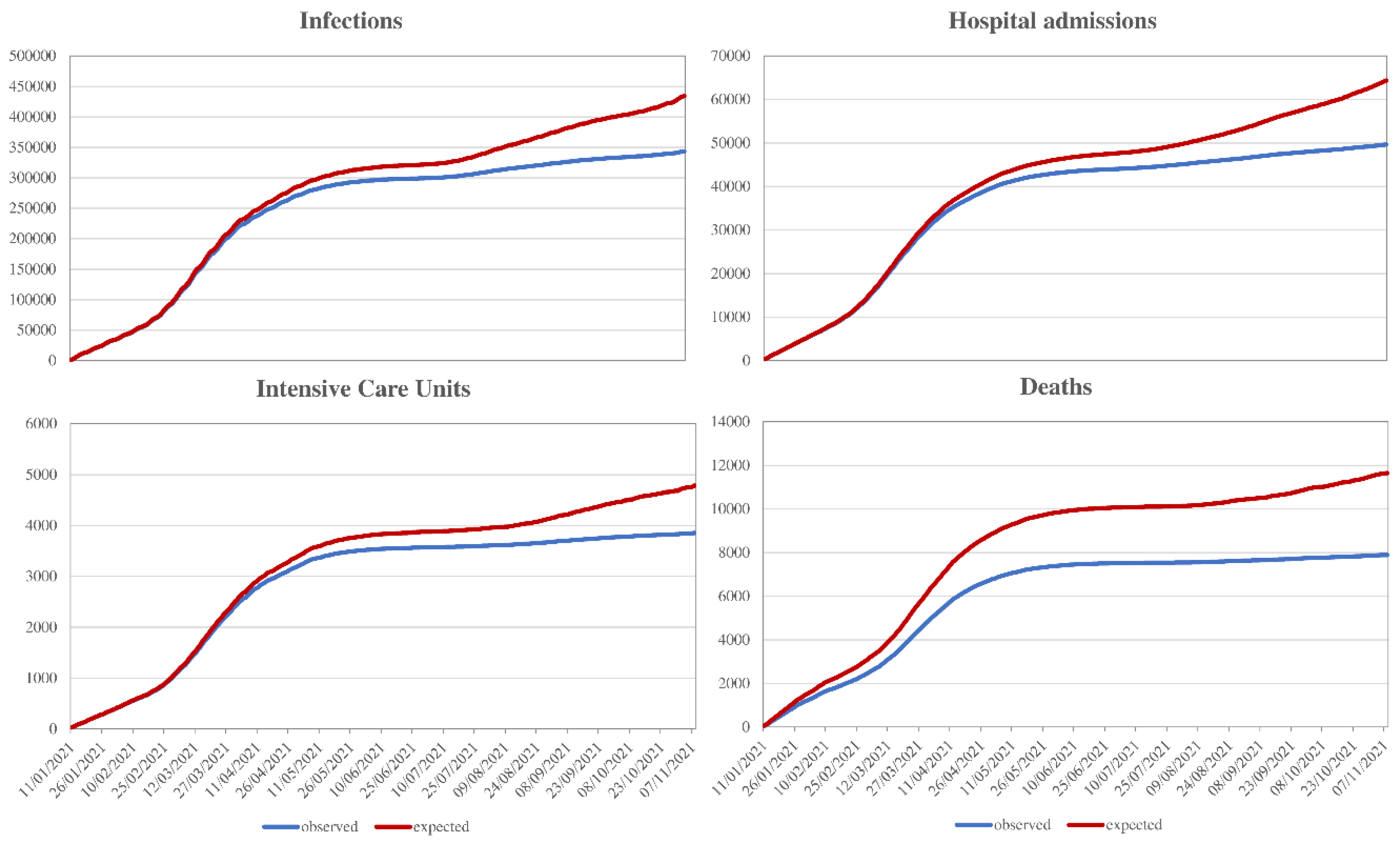

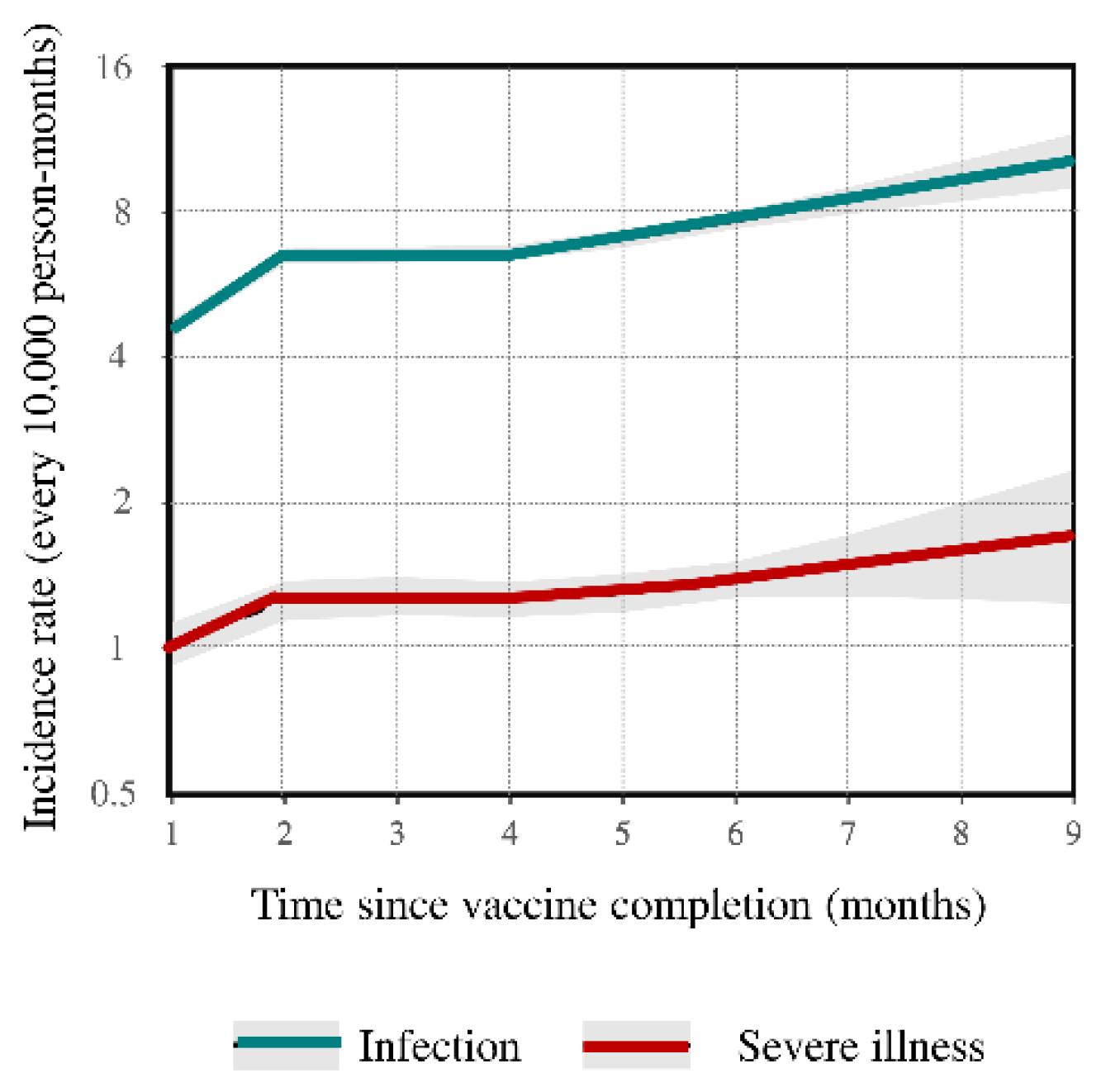
| # Events | Vaccine Status | HR | (95% CI) | Vaccine Effectiveness | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Positivity to nasopharyngeal swap | 291,128 | Partial | 0.161 | (0.159 to 0.164) | 84% |
| Full | 0.100 | (0.098 to 0.103) | 90% | ||
| Admission to ordinary hospital ward | 35,736 | Partial | 0.100 | (0.096 to 0.104) | 90% |
| Full | 0.031 | (0.029 to 0.033) | 97% | ||
| Admission to intensive care unit | 3450 | Partial | 0.033 | (0.027 to 0.040) | 97% |
| Full | 0.008 | (0.005 to 0.013) | 99% | ||
| Death | 6956 | Partial | 0.073 | (0.067 to 0.081) | 93% |
| Full | 0.009 | (0.007 to 0.011) | 99% |
| Controls (N = 4960) | Delta Cases (N = 496) | Alpha Cases (N = 496) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| N (%) | N (%) | RRR (95% CI) † | N (%) | RRR (95% CI) † | p-Value ‡ | |
| Previous infection | ||||||
| Unlike | 4411 (88.9) | 490 (98.8) | 0% (reference) | 487 (98.2) | 0% (reference) | |
| Ascertained | 549 (11.1) | 6 (1.2) | 90% (76% to 95%) | 9 (1.8) | 85% (70% to 92%) | 0.547 |
| Vaccination | ||||||
| No | 2650 (53.4) | 349 (70.4) | 0% (reference) | 402 (81.1) | 0% (reference) | |
| Partial | 876 (17.7) | 93 (18.8) | 29% (7% to 45%) | 65 (13.1) | 62% (48% to 71%) | 0.001 |
| Complete | 1434 (28.9) | 54 (10.9) | 75% (66% to 82%) | 29 (5.8) | 90% (85% to 94%) | 0.003 |
| Post-Vaccine SARS-CoV-2 Infection | Post-Vaccine Severe COVID-19 Illness | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cases | Controls | OR | (95% CI) | Cases | Controls | OR | (95% CI) | |
| Age category | ||||||||
| <40 yrs | 3083 (21.2%) | 2805 (15.6%) | 1.00 | (ref.) | 84 (2.8%) | 2581 (8.5%) | 1.00 | (ref.) |
| 40 to 59 yrs | 7247 (40.3%) | 6903 (38.4%) | 0.76 | (0.70 to 0.83) | 384 (12.7%) | 6204 (20.5%) | 1.60 | (1.14 to 2.25) |
| 60 to 79 yrs | 3892 (21.7%) | 4926 (27.4%) | 0.46 | (0.42 to 0.51) | 660 (21.8%) | 6416 (21.2%) | 2.48 | (1.76 to 3.50) |
| ≥80 yrs | 3024 (16.8%) | 3332 (18.5%) | 0.51 | (0.44 to 0.59) | 1895 (62.7%) | 15,029 (49.7%) | 6.99 | (4.89 to 9.99) |
| Sex | ||||||||
| Female | 10,023 (55.7%) | 10,164 (56.5%) | 1.00 | (ref.) | 1505 (49.8%) | 17,299 (57.2%) | 1.00 | (ref.) |
| Male | 7973 (44.3%) | 7832 (43.5%) | 1.03 | (0.99 to 1.08) | 1518 (50.2%) | 12,931 (42.8%) | 1.41 | (1.31 to 1.52) |
| Contact with RHS | ||||||||
| <5 | 7430 (41.3%) | 7258 (40.6%) | 1.00 | (ref.) | 402 (13.3%) | 7674 (25.4%) | 1.00 | (ref.) |
| 6 to 100 | 8392 (46.6%) | 8815 (49.0%) | 1.06 | (1.01 to 1.12) | 1445 (47.8%) | 16,240 (53.7%) | 1.60 | (1.41 to 1.82) |
| ≥100 | 2174 (12.1%) | 1923 (10.7%) | 1.43 | (1.31 to 1.56) | 1.176 (38.9%) | 6316 (20.9%) | 3.19 | (2.76 to 3.69) |
| Vaccine type | ||||||||
| mRNA-based | 14,432 (80.2%) | 14,571 (81.0%) | 1.00 | (ref.) | 2657 (87.9%) | 26,617 (88.0%) | 1.00 | (ref.) |
| Adenovirus-vectored | 3564 (19.8%) | 3425 (19.0%) | 1.33 | (1.24 to 1.44) | 366 (12.1%) | 3613 (12.0%) | 0.97 | (0.83 to 1.15) |
| Previous SARS-CoV-2 infection | ||||||||
| No | 17,824 (99.0%) | 16,957 (99.0%) | 1.00 | (ref.) | 2922 (96.7%) | 28,799 (95.3%) | 1.00 | (ref.) |
| Yes | 172 (1.0%) | 1039 (5.8%) | 0.15 | (0.13 to 0.88) | 101 (3.3%) | 1431 (4.7%) | 0.67 | (0.54 to 0.84) |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Corrao, G.; Bertolaso, G.; Pavesi, G.; Moratti, L. Eight Good Reasons for Careful Monitoring and Evaluation of the Vaccine Campaign against COVID-19: Lessons Learned through the Lombardy Experience for Dealing with Next Challenges. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 1073. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph19031073
Corrao G, Bertolaso G, Pavesi G, Moratti L. Eight Good Reasons for Careful Monitoring and Evaluation of the Vaccine Campaign against COVID-19: Lessons Learned through the Lombardy Experience for Dealing with Next Challenges. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health. 2022; 19(3):1073. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph19031073
Chicago/Turabian StyleCorrao, Giovanni, Guido Bertolaso, Giovanni Pavesi, and Letizia Moratti. 2022. "Eight Good Reasons for Careful Monitoring and Evaluation of the Vaccine Campaign against COVID-19: Lessons Learned through the Lombardy Experience for Dealing with Next Challenges" International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health 19, no. 3: 1073. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph19031073
APA StyleCorrao, G., Bertolaso, G., Pavesi, G., & Moratti, L. (2022). Eight Good Reasons for Careful Monitoring and Evaluation of the Vaccine Campaign against COVID-19: Lessons Learned through the Lombardy Experience for Dealing with Next Challenges. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 19(3), 1073. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph19031073






