Electromyographic Analysis of Paraspinal Muscles of Scoliosis Patients Using Machine Learning Approaches
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Participants
2.2. Experimental Design
2.3. Machine Learning Approaches
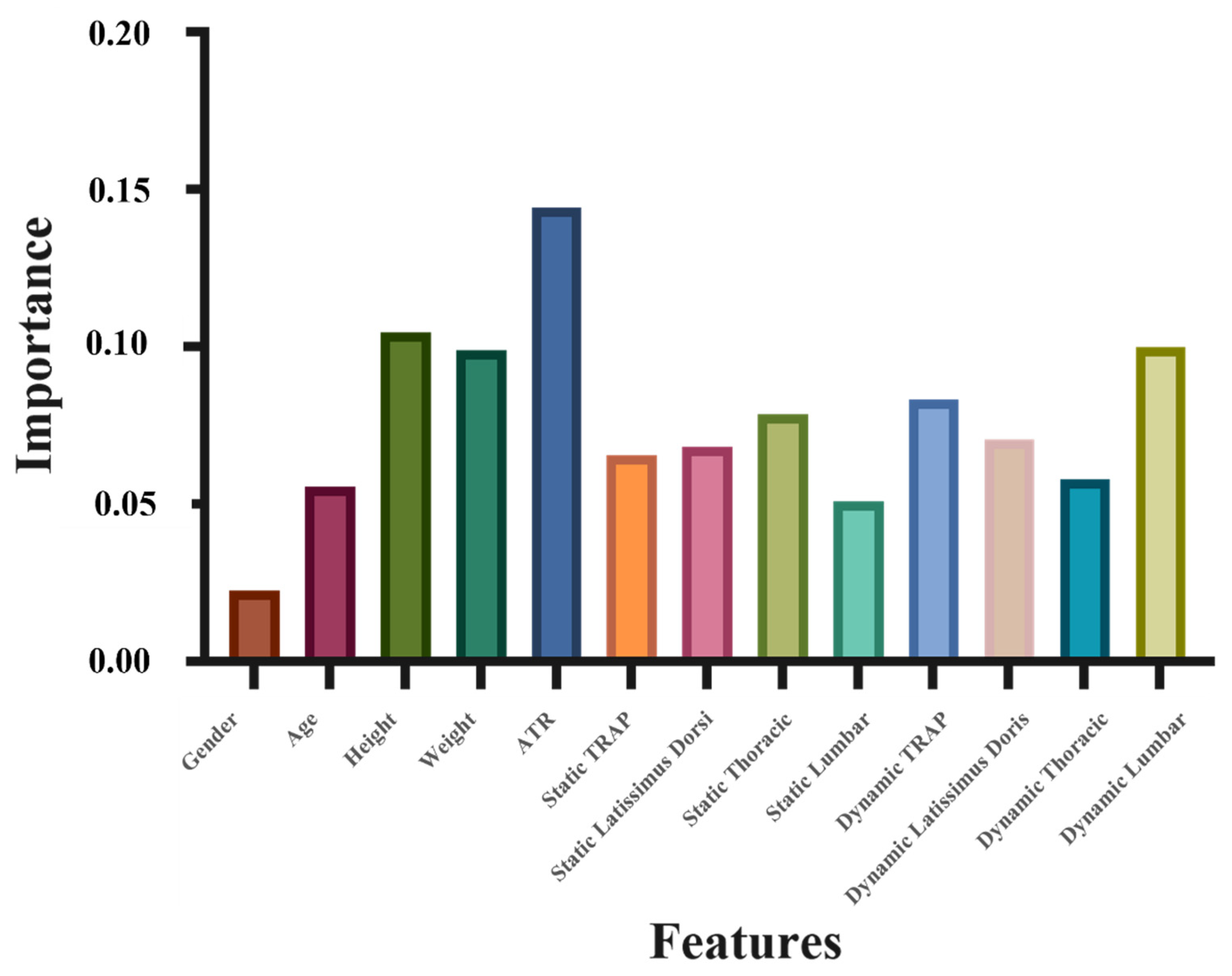
2.4. Importance Analysis
- There are about 1/3 data left after the training of each decision tree in the random forest method, called out-of-bag (OOB) data (Breiman, 1996). The OOB data are used to estimate the trained trees and calculate the data error, which is marked as errOOB1 for each decision tree.
- Noise is added randomly to interfere with the features of all of the OOB samples. This OOB data error is calculated and marked as errOOB2.
- We assume that there are N trees in total, and the importance of a feature is determined by sum(errOOB2-errOOB1)/N.
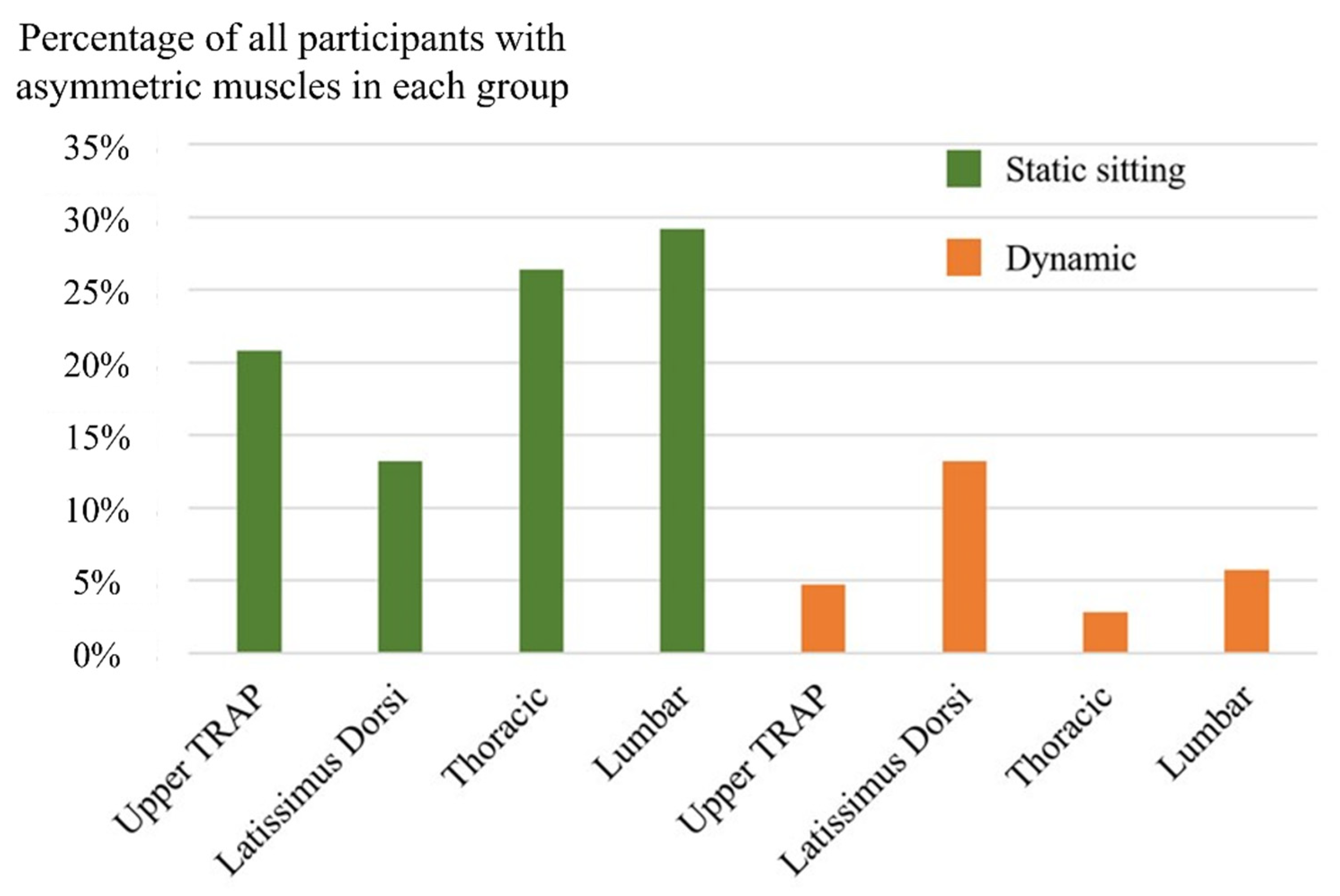
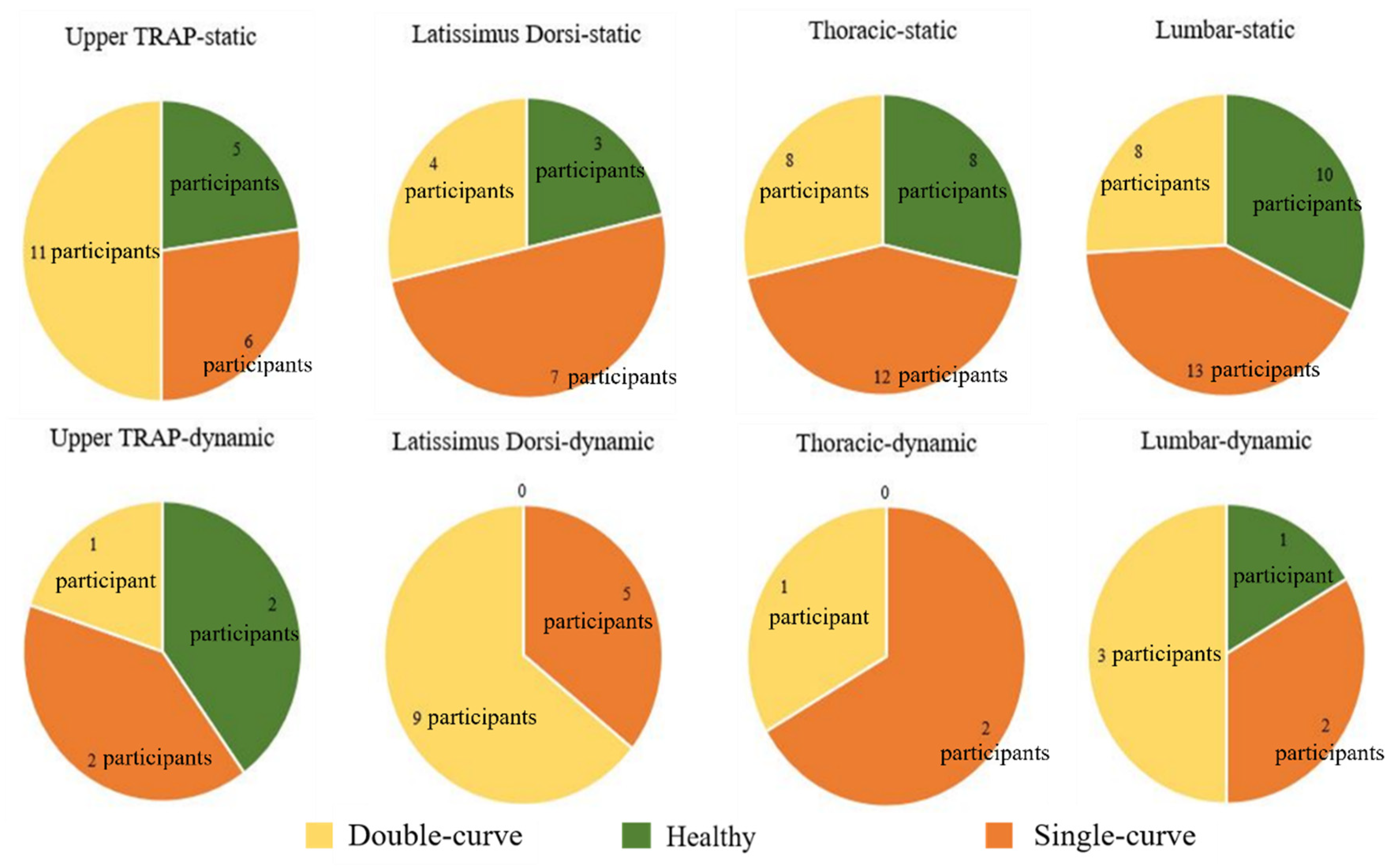
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Meier, M.P.; Klein, M.P.; Krebs, D.; Grob, D.; Müntener, M. Fiber Transformations in Multifidus Muscle of Young Patients with Idiopathic Scoliosis. Spine 1997, 22, 2357–2364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tambe, A.D.; Panikkar, S.J.; Millner, P.A.; Tsirikos, A.I. Current concepts in the surgical management of adolescent idiopathic scoliosis. Bone Jt. J. 2018, 100-B, 415–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Li, T.; Yuan, W.; Zhang, Z.; Wei, J.; Qiu, G.; Shen, J. Mental health of patients with adolescent idiopathic scoliosis and their parents in China: A cross-sectional survey. BMC Psychiatry 2019, 19, 147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rainoldi, L.; Zaina, F.; Villafañe, J.H.; Donzelli, S.; Negrini, S. Quality of life in normal and idiopathic scoliosis adolescents before diagnosis: Reference values and discriminative validity of the SRS-22. A cross-sectional study of 1205 pupils. Spine J. 2015, 15, 662–667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davies, G.; Reid, L. Effect of scoliosis on growth of alveoli and pulmonary arteries and on right ventricle. Arch. Dis. Child. 1971, 46, 623–632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tahirbegolli, B.; Obertinca, R.; Bytyqi, A.; Kryeziu, B.; Hyseni, B.; Taganoviq, B.; Shabani, B. Factors affecting the prevalence of idiopathic scoliosis among children aged 8–15 years in Prishtina, Kosovo. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 16786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Y.; Dang, Y.; Wu, X.; Yang, Y.; Reinhardt, J.; He, C.; Wong, M. Epidemiological study of adolescent idiopathic scoliosis in Eastern China. J. Rehabil. Med. 2017, 49, 512–519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Horne, J.P.; Flannery, R.; Usman, S. Adolescent idiopathic scoliosis: Diagnosis and management. Am. Fam. Physician 2014, 89, 193–198. [Google Scholar]
- Ratahi, E.D.; Crawford, H.A.; Thompson, J.M.; Barnes, M.J. Ethnic Variance in the Epidemiology of Scoliosis in New Zealand. J. Pediatr. Orthop. 2002, 22, 784–787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanders, J.O.; Browne, R.H.; McConnell, S.J.; Margraf, S.A.; Cooney, T.E.; Finegold, D.N. Maturity assessment and curve progression in girls with idiopathic scoliosis. J. Bone Jt. Surg. 2007, 89, 64–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ylikoski, M. Height of girls with adolescent idiopathic scoliosis. Eur. Spine J. 2003, 12, 288–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Konieczny, M.R.; Senyurt, H.; Krauspe, R. Epidemiology of adolescent idiopathic scoliosis. J. Child. Orthop. 2013, 7, 3–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chen, B.; Tan, Q.; Chen, H.; Luo, F.; Xu, M.; Zhao, J.; Liu, P.; Sun, X.; Su, N.; Zhang, D.; et al. Imbalanced development of anterior and posterior thorax is a causative factor triggering scoliosis. J. Orthop. Transl. 2019, 17, 103–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, K.; Zhai, X.; Sun, K.; Wang, H.; Yang, C.; Li, M. A narrative review of machine learning as promising revolution in clinical practice of scoliosis. Ann. Transl. Med. 2021, 9, 67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lotan, S.; Kalichman, L. Manual therapy treatment for adolescent idiopathic scoliosis. J. Bodyw. Mov. Ther. 2019, 23, 189–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Weinstein, S.L.; Dolan, L.A.; Cheng, J.C.; Danielsson, A.; Morcuende, J.A. Adolescent idiopathic scoliosis. Lancet 2008, 371, 1527–1537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Weinstein, S.L.; Ponseti, I.V. Curve progression in idiopathic scoliosis. J. Bone Jt. Surg. 1983, 65, 447–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamen, G. Electromyographic Kinesiology. In Research Methods in Biomechanics; Human Kinetics Publisher: Champaign, IL, USA, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Cheung, J.; Halbertsma, J.P.K.; Veldhuizen, A.G.; Sluiter, W.J.; Maurits, N.M.; Cool, J.C.; Van Horn, J.R. A preliminary study on electromyographic analysis of the paraspinal musculature in idiopathic scoliosis. Eur. Spine J. 2004, 14, 130–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- de Oliveira, A.S.; Gianini, P.E.S.; Camarini, P.M.F.; Bevilaqua-Grossi, D. Electromyographic Analysis of Paravertebral Muscles in Patients with Idiopathic Scoliosis. Spine 2011, 36, E334–E339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reaz, M.B.I.; Hussain, M.S.; Mohd-Yasin, F. Techniques of EMG signal analysis: Detection, processing, classification and applications. Biol. Proced. Online 2006, 8, 11–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Avikainen, V.J.; Rezasoltani, A.; Kauhanen, H.A. Asymmetry of Paraspinal EMG-Time Characteristics in Idiopathic Scoliosis. J. Spinal Disord. 1999, 12, 61–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chwala, W.; Koziana, A.; Kasperczyk, T.; Walaszek, R.; Płaszewski, M. Electromyographic Assessment of Functional Symmetry of Paraspinal Muscles during Static Exercises in Adolescents with Idiopathic Scoliosis. BioMed Res. Int. 2014, 2014, 573276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stetkarova, I.; Zamecnik, J.; Bocek, V.; Vasko, P.; Brabec, K.; Krbec, M. Electrophysiological and histological changes of paraspinal muscles in adolescent idiopathic scoliosis. Eur. Spine J. 2016, 25, 3146–3153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Pessin, J.E. Mechanisms for fiber-type specificity of skeletal muscle atrophy. Curr. Opin. Clin. Nutr. Metab. Care 2013, 16, 243–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Acaroglu, E.; Akel, I.; Alanay, A.; Yazici, M.; Marcucio, R. Comparison of the Melatonin and Calmodulin in Paravertebral Muscle and Platelets of Patients with or without Adolescent Idiopathic Scoliosis. Spine 2009, 34, E659–E663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vergari, C.; Skalli, W.; Gajny, L. A convolutional neural network to detect scoliosis treatment in radiographs. Int. J. Comput. Assist. Radiol. Surg. 2020, 15, 1069–1074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Zhang, K.; Fan, H.; Huang, Z.; Xiang, Y.; Yang, J.; He, L.; Zhang, L.; Yang, Y.; Li, R.; et al. Development and validation of deep learning algorithms for scoliosis screening using back images. Commun. Biol. 2019, 2, 390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, P.; Lu, Z.; Song, J. Variable importance analysis: A comprehensive review. Reliab. Eng. Syst. Saf. 2015, 142, 399–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horng, M.-H.; Kuok, C.-P.; Fu, M.-J.; Lin, C.-J.; Sun, Y.-N. Cobb Angle Measurement of Spine from X-Ray Images Using Convolutional Neural Network. Comput. Math. Methods Med. 2019, 2019, 6357171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Greiner, K.A. Adolescent idiopathic scoliosis: Radiologic decision-making. Am. Fam. Physician 2002, 65, 1817–1822. [Google Scholar]
- NORAXON EMG Meeting. Available online: https://edisciplinas.usp.br/pluginfile.php/5050267/mod_resource/content/1/EMG-Meeting%202006%20Abstracts.pdf (accessed on 15 November 2021).
- Faul, F.; Erdfelder, E.; Lang, A.-G.; Buchner, A. G*Power 3: A flexible statistical power analysis program for the social, behavioral, and biomedical sciences. Behav. Res. Methods 2007, 39, 175–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cortes, C.; Vapnik, V. Support-vector networks. Mach. Learn. 1995, 20, 273–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Breiman, L. Random forests. Mach. Learn. 2001, 45, 5–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Biau, G.; Scornet, E. A random forest guided tour. TEST 2016, 25, 197–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ramirez, L.; Durdle, N.; Raso, V.; Hill, D. A Support Vector Machines Classifier to Assess the Severity of Idiopathic Scoliosis from Surface Topography. IEEE Trans. Inf. Technol. Biomed. 2006, 10, 84–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, J.-S.; Cho, Y.-S.; Moon, S.-B.; Kim, M.-J.; Lee, H.D.; Lee, S.Y.; Ji, Y.-H.; Park, Y.-S.; Han, C.-S.; Jang, S.-H. Scoliosis Screening through a Machine Learning Based Gait Analysis Test. Int. J. Precis. Eng. Manuf. 2018, 19, 1861–1872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- The ABC of EMG: A Practical Introduction to Kinesiological Electromyography. Available online: http://www.noraxon.com/wp-content/uploads/2014/12/ABC-EMG-ISBN.pdf (accessed on 15 November 2021).
- Singh, R.; Iqbal, K.; White, G.; Holtz, J.K. A Review of EMG Techniques for Detection of Gait Disorders. Artif. Intell.-Appl. Med. Biol. 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kwok, G.; Yip, J.; Cheung, M.C.; Yick, K.L. Evaluation of Myoelectric Activity of Paraspinal Muscles in Adolescents with Idiopathic Scoliosis during Habitual Standing and Sitting. BioMed Res. Int. 2015, 2015, 958450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Vabalas, A.; Gowen, E.; Poliakoff, E.; Casson, A.J. Machine learning algorithm validation with a limited sample size. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0224365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bunnell, W.P. An objective criterion for scoliosis screening. J. Bone Jt. Surg. 1984, 66, 1381–1387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larson, J.E.; Meyer, M.A.; Boody, B.; Sarwark, J.F. Evaluation of angle trunk rotation measurements to improve quality and safety in the management of adolescent idiopathic scoliosis. J. Orthop. 2018, 15, 563–565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanner, J.M.; Whitehouse, R.H. Clinical longitudinal standards for height, weight, height velocity, weight velocity, and stages of puberty. Arch. Dis. Child. 1976, 51, 170–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hoppenfeld, S. Histochemical findings in paraspinal muscles of patients with idiopathic scoliosis. In Scoliosis and Muscle; Zorab, P.A., Ed.; Heinemann Medical Books: London, UK, 1974; pp. 113–114. [Google Scholar]
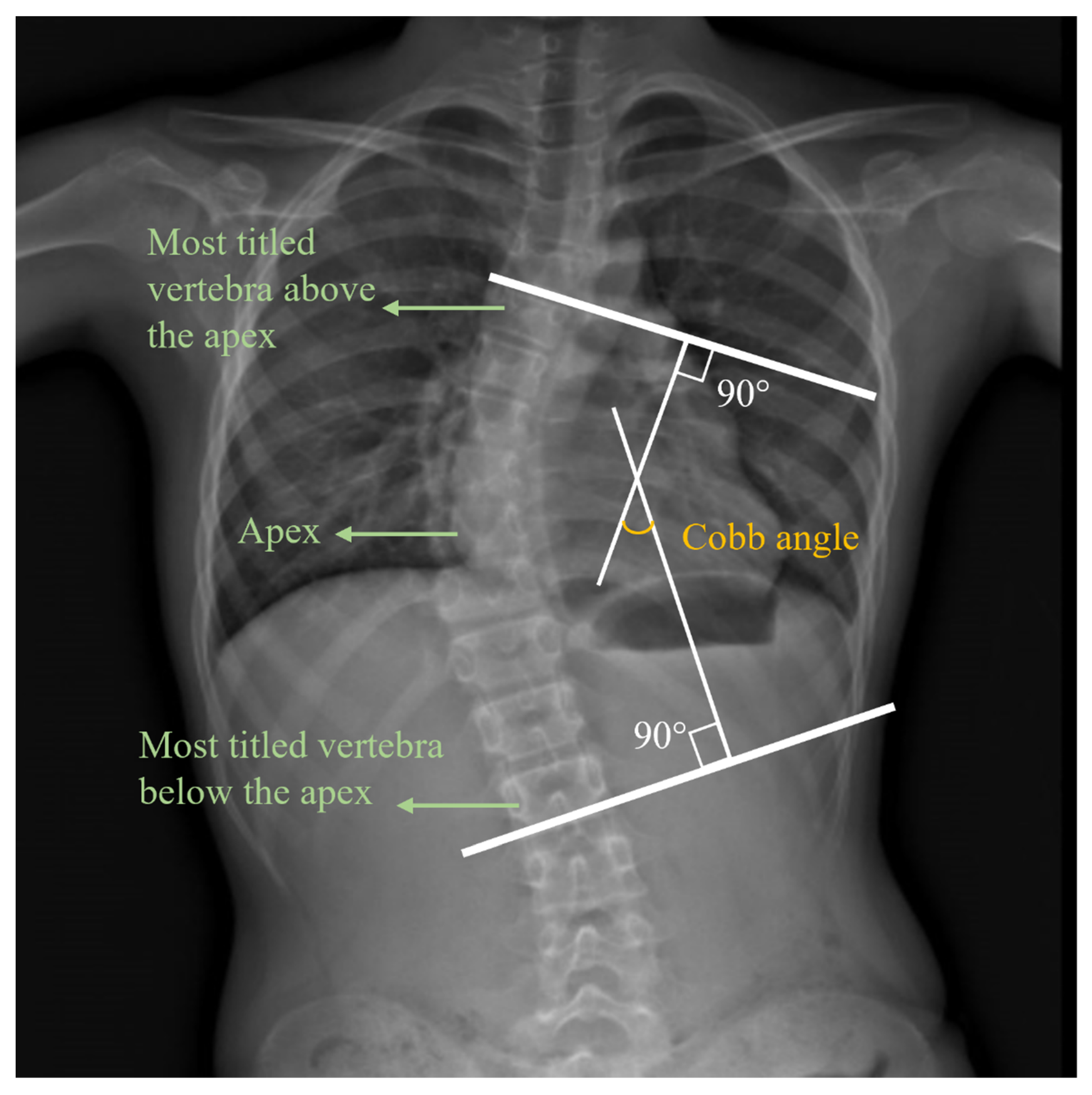
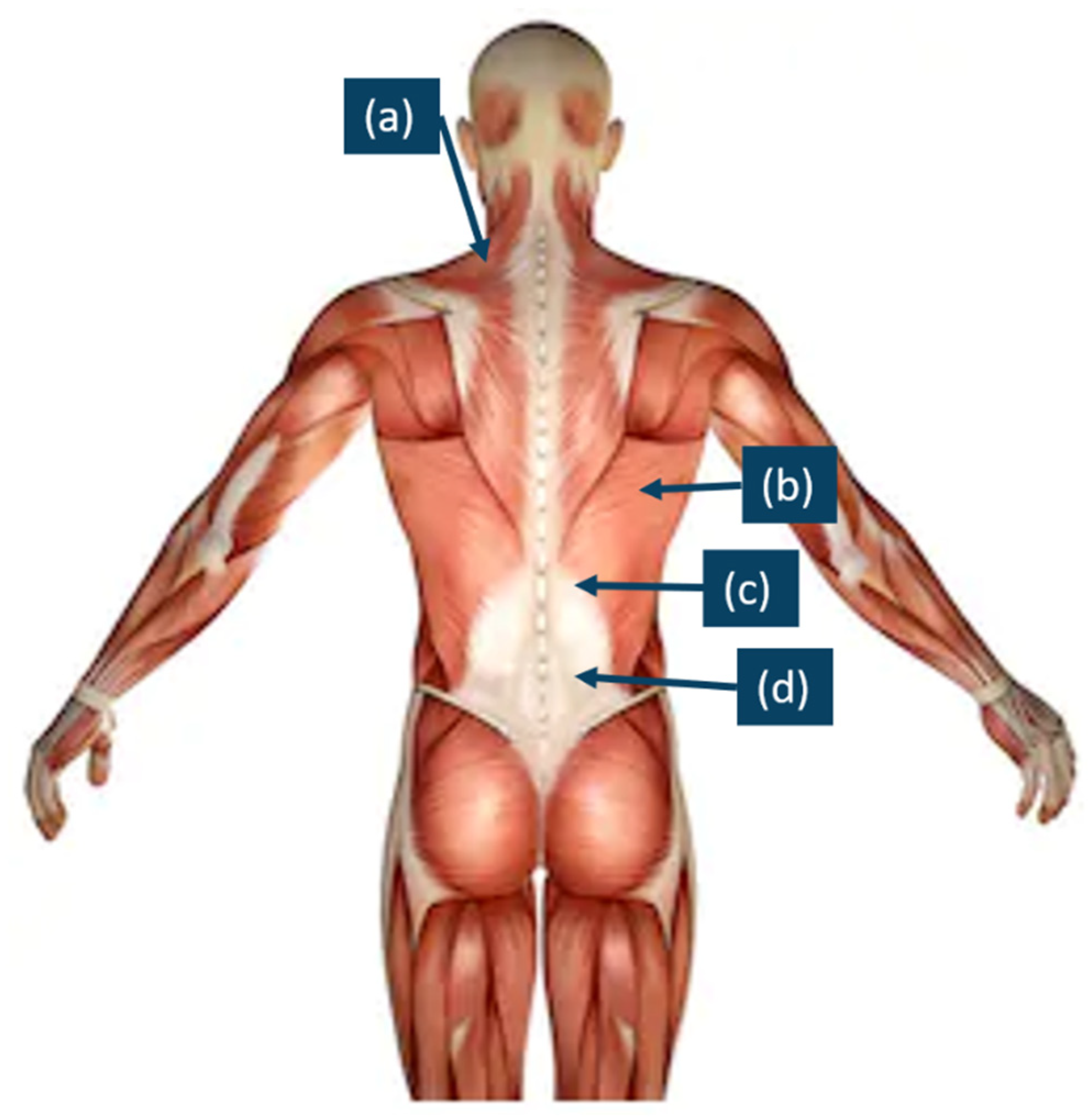
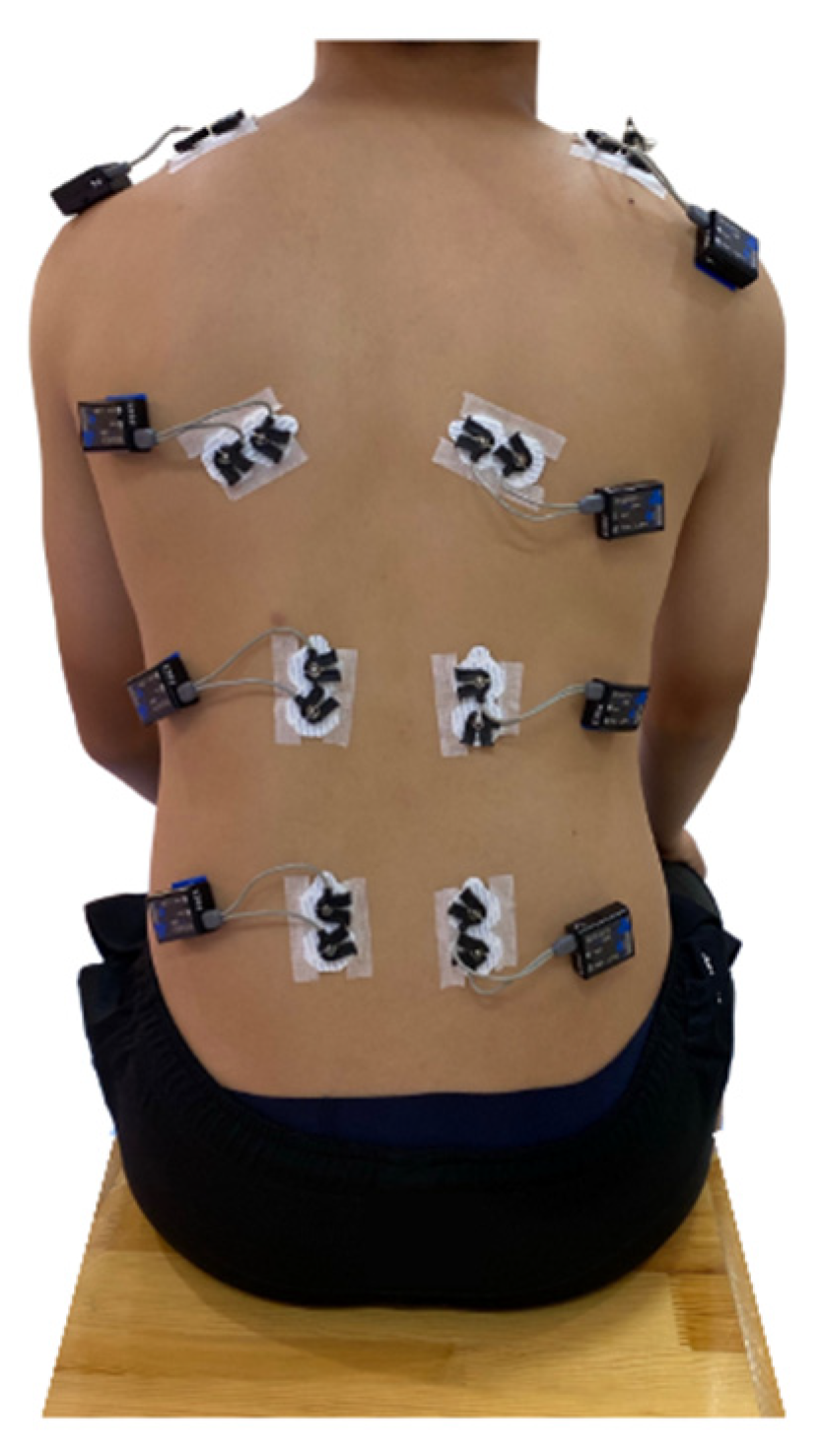

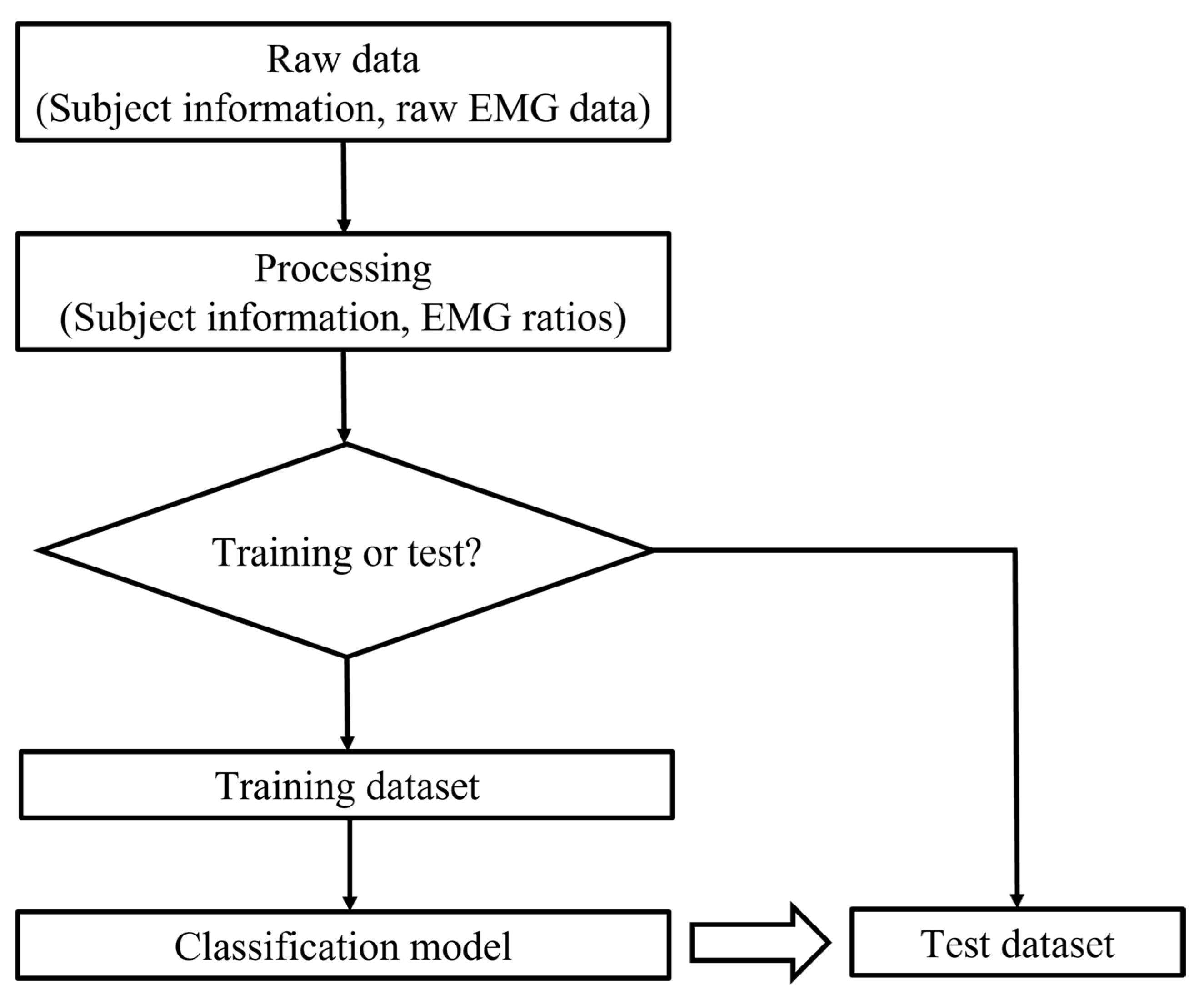
| No. of Participants | No. of Male Participants | No. of Female Participants | Age/Years Old | Height/m | Weight/kg | ATR/° | Cobb Angle/° | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Participants with scoliosis | Single-curve scoliosis | 39 | 12 | 27 | 14.51 ± 3.34 | 1.62 ± 0.09 | 46.68 ± 11.39 | 6.74 ± 4.35 | 21.97 ± 10.11 |
| Double-curve scoliosis | 34 | 2 | 32 | 15.00 ± 4.51 | 1.62 ± 0.07 | 47.04 ± 9.27 | 8.50 ± 3.61 | 27.59 ± 9.94 | |
| All | 73 | 14 | 59 | 14.63 ± 3.82 | 1.61 ± 0.09 | 46.55 ± 10.46 | 7.35 ± 4.12 | 23.72 ± 10.65 | |
| Participants without scoliosis | 33 | 10 | 23 | 14.36 ± 4.78 | 1.57 ± 0.12 | 44.85 ± 10.14 | 2.79 ± 3.23 | 1.03 ± 2.03 | |
| All | 106 | 24 | 82 | 14.44 ± 4.11 | 1.60 ± 1.01 | 45.68 ± 10.45 | 6.12 ± 4.38 | 17.48 ± 13.61 | |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liang, R.; Yip, J.; Fan, Y.; Cheung, J.P.Y.; To, K.-T.M. Electromyographic Analysis of Paraspinal Muscles of Scoliosis Patients Using Machine Learning Approaches. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 1177. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph19031177
Liang R, Yip J, Fan Y, Cheung JPY, To K-TM. Electromyographic Analysis of Paraspinal Muscles of Scoliosis Patients Using Machine Learning Approaches. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health. 2022; 19(3):1177. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph19031177
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiang, Ruixin, Joanne Yip, Yunli Fan, Jason P. Y. Cheung, and Kai-Tsun Michael To. 2022. "Electromyographic Analysis of Paraspinal Muscles of Scoliosis Patients Using Machine Learning Approaches" International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health 19, no. 3: 1177. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph19031177
APA StyleLiang, R., Yip, J., Fan, Y., Cheung, J. P. Y., & To, K.-T. M. (2022). Electromyographic Analysis of Paraspinal Muscles of Scoliosis Patients Using Machine Learning Approaches. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 19(3), 1177. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph19031177








