Deep Learning for the Automatic Quantification of Pleural Plaques in Asbestos-Exposed Subjects
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Material and Methods
2.1. Study Design
2.2. Settings
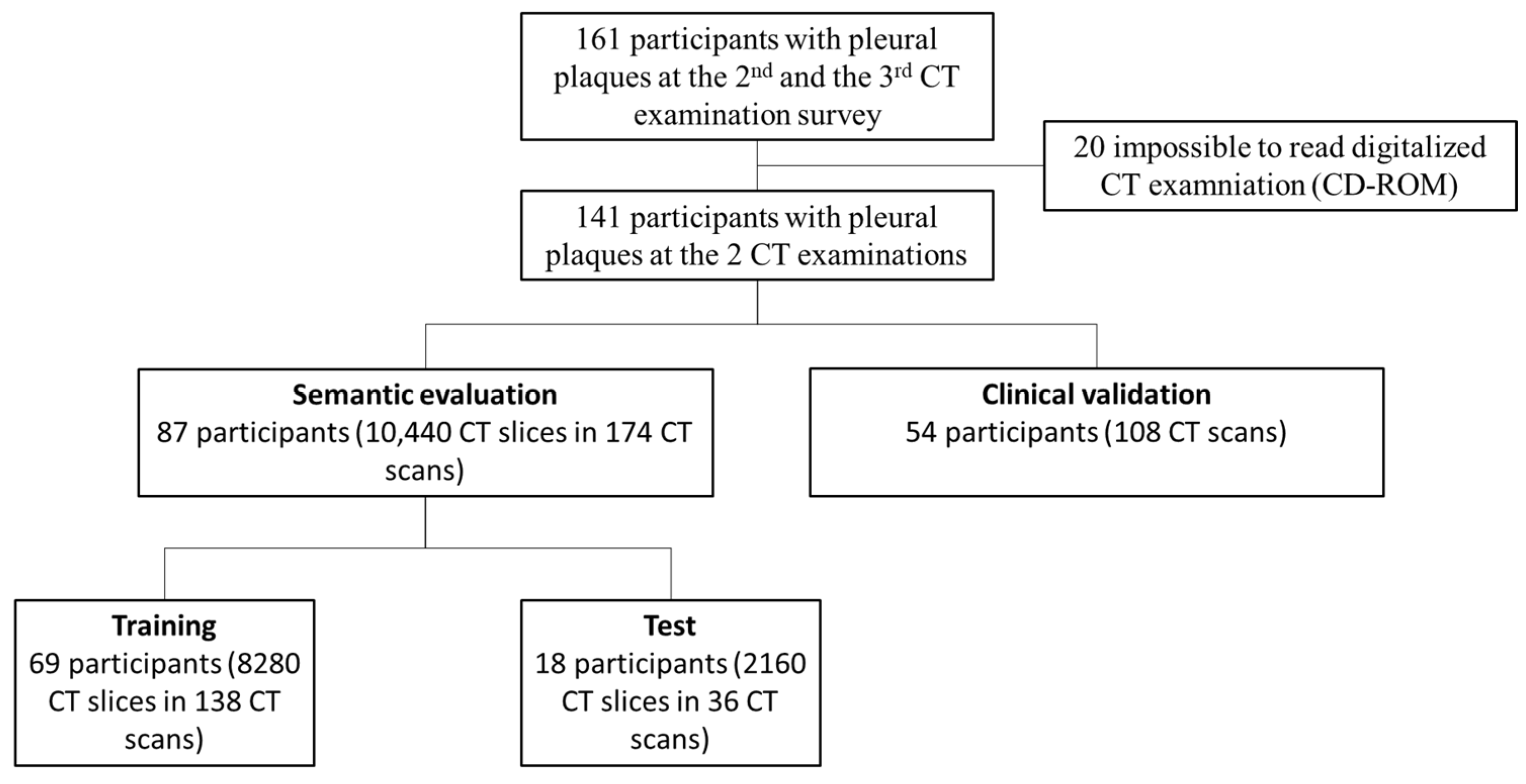
2.3. Participants
2.4. Data
2.5. Chest CT Scans Visual Analysis
2.6. AI Training Framework
2.7. Test Cohort
2.8. Clinical Validation Cohort
2.9. Reproducibility Assessment
2.10. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Participants
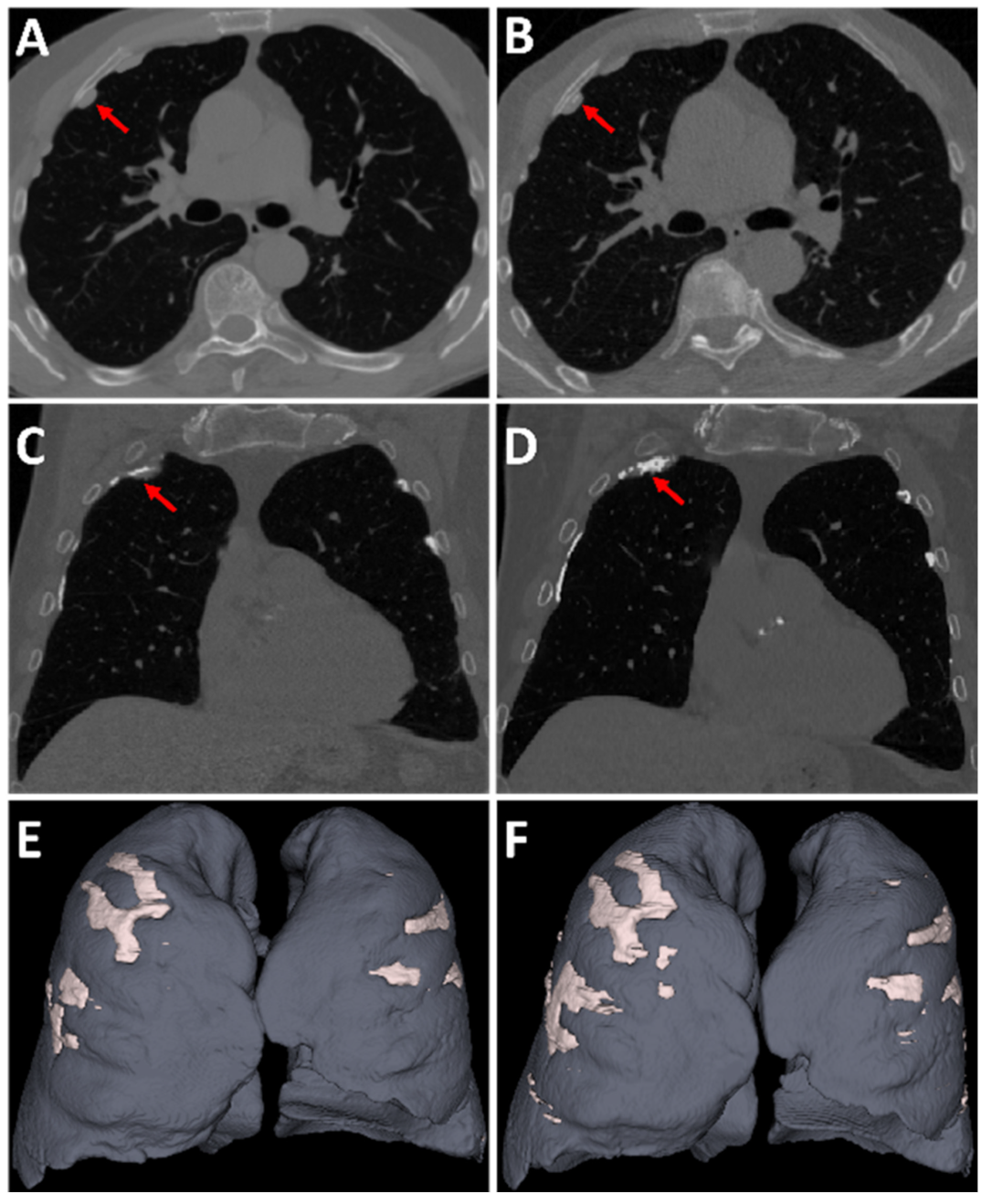
3.2. Similarity and Concordance of Test Cohort
3.3. Correlations with Visual Pleural Plaques Extent Score
3.4. Longitudinal Comparison of Pleural Plaques Volume Progression
3.5. Reproducibility of Evaluation
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Guidotti, T.L.; Miller, A.; Christiani, D.; Wagner, G.; Balmes, J.; Harber, P.; Brodkin, C.A.; Rom, W.; Hillerdal, G.; Harbut, M.; et al. Diagnosis and Initial Management of Nonmalignant Diseases Related to Asbestos. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2004, 170, 691–715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Remy-Jardin, M.; Sobaszek, A.; Duhamel, A.; Mastora, I.; Zanetti, C.; Remy, J. Asbestos-related Pleuropulmonary Diseases: Evaluation with Low-Dose Four–Detector Row Spiral CT. Radiology 2004, 233, 182–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laurent, F.; Tunon de Lara, M. Exposure to asbestos. Role of thoracic imagery in screening and follow-up. Rev. Mal. Respir. 1999, 16, 1193–1202. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Beigelman-Aubry, C.; Ferretti, G.; Mompoint, D.; Ameille, J.; Letourneux, M.; Laurent, F. Computed tomographic atlas of benign asbestos related pathology. Rev. Mal. Respir. 2007, 24, 759–781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Staples, C.A.; Gamsu, G.; Ray, C.S.; Webb, W.R. High resolution computed tomography and lung function in asbestos-exposed workers with normal chest radiographs. Am. Rev. Respir. Dis. 1989, 139, 1502–1508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Norbet, C.; Joseph, A.; Rossi, S.S.; Bhalla, S.; Gutierrez, F.R. Asbestos-related lung disease: A pictorial review. Curr. Probl. Diagn. Radiol. 2015, 44, 371–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gevenois, P.A.; de Maertelaer, V.; Madani, A.; Winant, C.; Sergent, G.; De Vuyst, P. Asbestosis, pleural plaques and diffuse pleural thickening: Three distinct benign responses to asbestos exposure. Eur. Respir. J. 1998, 11, 1021–1027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paris, C.; Thierry, S.; Brochard, P.; Letourneux, M.; Schorle, E.; Stoufflet, A.; Ameille, J.; Conso, F.; Pairon, J.C.; National APEXS Members. Pleural plaques and asbestosis: Dose– and time–response relationships based on HRCT data. Eur. Respir. J. 2009, 34, 72–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Clin, B.; Paris, C.; Ameille, J.; Brochard, P.; Conso, F.; Gislard, A.; Laurent, F.; Letourneux, M.; Luc, A.; Schorle, E.; et al. Do asbestos-related pleural plaques on HRCT scans cause restrictive impairment in the absence of pulmonary fibrosis? Thorax 2011, 66, 985–991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Moolgavkar, S.H.; Anderson, E.L.; Chang, E.T.; Lau, E.C.; Turnham, P.; Hoel, D.G. A review and critique of U.S. EPA’s risk assessments for asbestos. Crit. Rev. Toxicol. 2014, 44, 499–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kopylev, L.; Christensen, K.Y.; Brown, J.S.; Cooper, G.S. A systematic review of the association between pleural plaques and changes in lung function. Occup. Environ. Med. 2015, 72, 606–614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pairon, J.-C.; Laurent, F.; Rinaldo, M.; Clin, B.; Andujar, P.; Ameille, J.; Brochard, P.; Chammings, S.; Ferretti, G.; Galateau-Sallé, F.; et al. Pleural Plaques and the Risk of Pleural Mesothelioma. JNCI J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 2013, 105, 293–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pairon, J.-C.; Andujar, P.; Rinaldo, M.; Ameille, J.; Brochard, P.; Chamming’S, S.; Clin, B.; Ferretti, G.; Gislard, A.; Laurent, F.; et al. Asbestos Exposure, Pleural Plaques, and the Risk of Death from Lung Cancer. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2014, 190, 1413–1420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Laurent, F.; Paris, C.; Ferretti, G.R.; Beigelman, C.; Montaudon, M.; Latrabe, V.; Jankowski, A.; Badachi, Y.; Clin, B.; Gislard, A.; et al. Inter-reader agreement in HRCT detection of pleural plaques and asbestosis in participants with previous occupational exposure to asbestos. Occup. Environ. Med. 2014, 71, 865–870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Cleemput, J.; De Raeve, H.; Verschakelen, J.A.; Rombouts, J.; Lacquet, L.M.; Nemery, B. Surface of Localized Pleural Plaques Quantitated by Computed Tomography Scanning. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2001, 163, 705–710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cha, Y.K.; Kim, J.S.; Kwon, J.H. Quantification of pleural plaques by computed tomography and correlations with pulmonary function: Preliminary study. J. Thorac. Dis. 2018, 10, 2118–2124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Dournes, G.; Dubois, A.; Benlala, I.; Lacourt, A.; Paris, C.; Gislard, A.; Clin, B.; Pairon, J.-C.; Baldacci, F.; Laurent, F. 3-Dimensional Quantification of Composite Pleural Plaque Volume in Patients Exposed to Asbestos Using High-resolution Computed Tomography: A Validation Study. J. Thorac. Imaging 2019, 34, 320–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hesamian, M.H.; Jia, W.; He, X.; Kennedy, P. Deep Learning Techniques for Medical Image Segmentation: Achievements and Challenges. J. Digit. Imaging 2019, 32, 582–596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hansell, D.M.; Bankier, A.A.; MacMahon, H.; McLoud, T.C.; Müller, N.L.; Remy, J. Fleischner Society: Glossary of Terms for Thoracic Imaging. Radiology 2008, 246, 697–722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ronneberger, O.; Fischer, P.; Brox, T. U-Net: Convolutional Networks for Biomedical Image Segmentation. In Proceedings of the Medical Image Computing and Computer-Assisted Intervention—MICCAI 2015; Navab, N., Hornegger, J., Wells, W.M., Frangi, A.F., Eds.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2015; pp. 234–241. [Google Scholar]
- De Brébisson, A.; Montana, G. Deep neural networks for anatomical brain segmentation. In Proceedings of the 2015 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition Workshops (CVPRW), Boston, MA, USA, 7–12 June 2015; pp. 20–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Huo, Y.; Xu, Z.; Xiong, Y.; Aboud, K.; Parvathaneni, P.; Bao, S.; Bermudez, C.; Resnick, S.M.; Cutting, L.E.; Landman, B.A. 3D Whole Brain Segmentation using Spatially Localized Atlas Network Tiles. NeuroImage 2019, 194, 105–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Coupé, P.; Mansencal, B.; Clément, M.; Giraud, R.; Denis de Senneville, B.; Ta, V.-T.; Lepetit, V.; Manjon, J.V. AssemblyNet: A large ensemble of CNNs for 3D whole brain MRI segmentation. NeuroImage 2020, 219, 117026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, Y.-D.; Liu, Q.; Quan, Z.-B. Automated image segmentation using improved PCNN model based on cross-entropy. In Proceedings of the 2004 International Symposium on Intelligent Multimedia, Video and Speech Processing, Hong Kong, China, 20–22 October 2004; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2005; pp. 743–746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sudre, C.H.; Li, W.; Vercauteren, T.; Ourselin, S.; Cardoso, M.J. Generalised Dice overlap as a deep learning loss function for highly unbalanced segmentations. arXiv 2017, arXiv:1707.03237, 240–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sugino, T.; Kawase, T.; Onogi, S.; Kin, T.; Saito, N.; Nakajima, Y. Loss Weightings for Improving Imbalanced Brain Structure Segmentation Using Fully Convolutional Networks. Healthcare 2021, 9, 938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kingma, D.P.; Ba, J. Adam: A Method for Stochastic Optimization. Comput. Sci. 2017, arXiv:1412.6980v9. [Google Scholar]
- Taha, A.A.; Hanbury, A. Metrics for evaluating 3D medical image segmentation: Analysis, selection, and tool. BMC Med. Imaging 2015, 15, 29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bland, J.M.; Altman, D.G. Measuring agreement in method comparison studies. Stat. Methods Med. Res. 1999, 8, 135–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Landis, J.R.; Koch, G.G. The measurement of observer agreement for categorical data. Biometrics 1977, 33, 159–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dournes, G.; Hall, C.S.; Willmering, M.M.; Brody, A.S.; Macey, J.; Bui, S.; Denis-De-Senneville, B.; Berger, P.; Laurent, F.; Benlala, I.; et al. Artificial intelligence in CT for quantifying lung changes in the era of CFTR modulators. Eur. Respir. J. 2021, 2100844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zha, W.; Fain, S.B.; Schiebler, M.L.; Evans, M.D.; Nagle, S.K.; Liu, F. Deep convolutional neural networks with multiplane consensus labeling for lung function quantification using UTE proton MRI. J. Magn. Reson. Imaging JMRI 2019, 50, 1169–1181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- LeCun, Y.; Bengio, Y.; Hinton, G. Deep learning. Nature 2015, 521, 436–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, J.; Lee, K.; Shin, E.; Choy, G.; Do, S. How much data is needed to train a medical image deep learning system to achieve necessary high accuracy? arXiv 2015, arXiv:1511.06348. [Google Scholar]
- Sousa, A.M.; Castelo-Fernández, C.; Osaku, D.; Bagatin, E.; Reis, F.; Falcão, A.X. An Approach for Asbestos-related Pleural Plaque Detection. In Proceedings of the 2020 42nd Annual International Conference of the IEEE Engineering in Medicine & Biology Society (EMBC), Montréal, QC, Canada, 20–24 July 2020; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2020; pp. 1343–1346. [Google Scholar]
- Alfudhili, K.M.; Lynch, D.A.; Laurent, F.; Ferretti, G.R.; Dunet, V.; Beigelman-Aubry, C. Focal pleural thickening mimicking pleural plaques on chest computed tomography: Tips and tricks. Br. J. Radiol. 2016, 89, 20150792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kim, Y.; Myong, J.-P.; Lee, J.K.; Kim, J.S.; Kim, Y.K.; Jung, S.-H. CT Characteristics of Pleural Plaques Related to Occupational or Environmental Asbestos Exposure from South Korean Asbestos Mines. Korean J. Radiol. 2015, 16, 1142–1152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maxim, L.D.; Niebo, R.; Utell, M.J. Are pleural plaques an appropriate endpoint for risk analyses? Inhal. Toxicol. 2015, 27, 321–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]

| Training Cohort | Test Cohort | Clinical Validation Cohort | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| (n = 69) | (n = 18) | (n = 54) | ||
| Age | Years | 71 ± 4 | 71 ± 5 | 70 ± 4 |
| Gender | Male/Female | 68/1 | 18/0 | 54/0 |
| Smoking status | Never smoker | 14 | 5 | 18 |
| Ex smoker | 51 | 11 | 32 | |
| Current Smoker | 4 | 2 | 4 | |
| Asbestos exposure | ||||
| Total duration (y) | 36 (34–38) | 38 (35–39) | 35 (33–37) | |
| Time since first exposure (y) | 52 ± 5 | 53 ± 6 | 52 ± 4 | |
| Related conditions | ||||
| Lung nodule (yes/no) | 15/54 | 9/9 | 29/25 | |
| Asbestosis (yes/no) | 4/65 | 1/17 | 3/51 | |
| Lung cancer (yes/no) | 3/66 | 0/18 | 4/50 |
| 2D Pixel Similarity | Pleural Plaques | Calcified Pleural Plaques |
| N = 2160 axial CT slices | ||
| Balanced Accuracy | 0.78 | 0.90 |
| DICE | 0.63 | 0.82 |
| Recall | 0.56 | 0.80 |
| Precision | 0.71 | 0.84 |
| 3D Volume Extent (mL) | Pleural Plaques | Calcified Pleural Plaques |
| N = 36 CT scans | ||
| Concordance: CCC (95% CI) | 0.98 (0.96; 0.99) | 0.99 (0.99; 0.99) |
| Bland–Altman (mL): Mean difference (LOA) | 2.3 (−17.4; 22) | −0.3 (−2.2; 1.6) |
| CT2nd | CT3rd | p-Value | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| AI-driven quantification | ||||
| Pleural Plaques (mL) | Median | 7.1 | 12.1 | <0.001 |
| 95%CI | (4.4–11.5) | (9.8–16.9) | ||
| Calcified Pleural Plaques (mL) | ||||
| Median | 1.3 | 3.5 | <0.001 | |
| 95%CI | (0.6–2.6) | (2.2–5.3) |
| Pleural Plaques | Calcified Pleural Plaques | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Comparisons | 2D 1 | 3D 2 | 2D 1 | 3D 2 |
| AI vs. AI (n = 2160 CT slices in 36 CT) | >0.99 | >0.99 [0.99–1] | >0.99 | >0.99 [0.99–1] |
| Manual1 vs. Manual2 (n = 1200 CT slices in 20 CT) | 0.72 | 0.98 [0.95–0.99] | 0.75 | 0.98 [0.95–0.99] |
| Manual1 vs. Manual1 (n = 1200 CT slices in 20 CT) | 0.87 | 0.98 [0.97–0.99] | 0.89 | 0.99 [0.97–0.99] |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Benlala, I.; De Senneville, B.D.; Dournes, G.; Menant, M.; Gramond, C.; Thaon, I.; Clin, B.; Brochard, P.; Gislard, A.; Andujar, P.; et al. Deep Learning for the Automatic Quantification of Pleural Plaques in Asbestos-Exposed Subjects. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 1417. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph19031417
Benlala I, De Senneville BD, Dournes G, Menant M, Gramond C, Thaon I, Clin B, Brochard P, Gislard A, Andujar P, et al. Deep Learning for the Automatic Quantification of Pleural Plaques in Asbestos-Exposed Subjects. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health. 2022; 19(3):1417. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph19031417
Chicago/Turabian StyleBenlala, Ilyes, Baudouin Denis De Senneville, Gael Dournes, Morgane Menant, Celine Gramond, Isabelle Thaon, Bénédicte Clin, Patrick Brochard, Antoine Gislard, Pascal Andujar, and et al. 2022. "Deep Learning for the Automatic Quantification of Pleural Plaques in Asbestos-Exposed Subjects" International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health 19, no. 3: 1417. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph19031417
APA StyleBenlala, I., De Senneville, B. D., Dournes, G., Menant, M., Gramond, C., Thaon, I., Clin, B., Brochard, P., Gislard, A., Andujar, P., Chammings, S., Gallet, J., Lacourt, A., Delva, F., Paris, C., Ferretti, G., Pairon, J.-C., & Laurent, F. (2022). Deep Learning for the Automatic Quantification of Pleural Plaques in Asbestos-Exposed Subjects. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 19(3), 1417. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph19031417







